Striatal cholinergic interneuron pause response requires Kv1 channels, is absent in dyskinetic mice, and is restored by dopamine D5 receptor inverse agonism
Figures
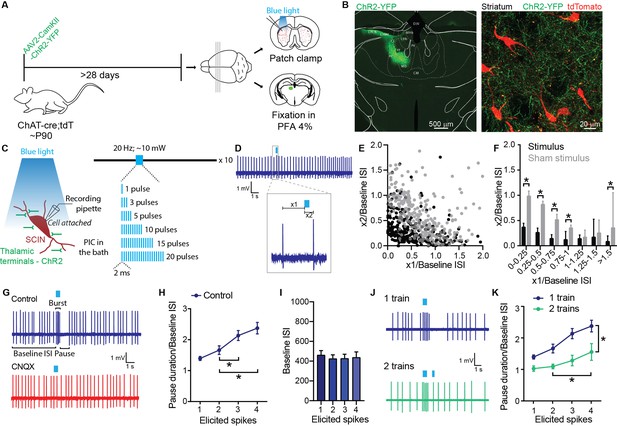
Striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCIN) burst-pause response to activation of thalamic terminals.
(A) Experimental design. (B) Micrograph showing the thalamic region transfected with ChR2-YFP (left) and a striatal region (z-stack maximal projection) showing tdTomato-reported SCINs and thalamic terminals expressing ChR2-YFP (right). (C) Schematic representation of optogenetic stimulation of thalamic inputs to a SCIN recorded in cell-attached configuration. Picrotoxin (PIC, 100 µM; GABA-A antagonist) was present in the bath in all experiments. (D) Representative recording of a SCIN that responded to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals with 1 spike. Inset: Details of the measurements of x1 and x2 values. x1: time from the last spike before the optogenetic stimulation and the start of the stimulation; x2: time from the initiation of stimulation to the following spike. (E) x2/baseline ISI vs x1/baseline ISI for single spike responses to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (black dots) and for sham stimulation (gray dots). (F) Data shown in E were binned and expressed as median and 95% confidence interval. *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. (G) Representative recordings of the pause response of a SCIN to optogenetic stimulation of thalamic terminals in cell-attached configuration before and after bath application of CNQX (20 µM; AMPA receptor antagonist). (H) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (one-way RM ANOVA, treatment 2 vs 3 spikes: *p=0.0032; 2 vs 4 spikes: *p=0.0017). (I) Baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (one-way RM ANOVA, ns). (J) Representative recordings of SCIN stimulated with one train of optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (top) or with two trains (bottom). (K) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with one or two trains of stimulation pulses. The second train occurs 350 ms after the first train (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns; treatment *p<0.0001; elicited spikes *p<0.0001; 2 vs 4 spikes *p=0.0042). Mean ± SEM; n=11–18 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCIN) burst-pause response to activation of thalamic terminals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
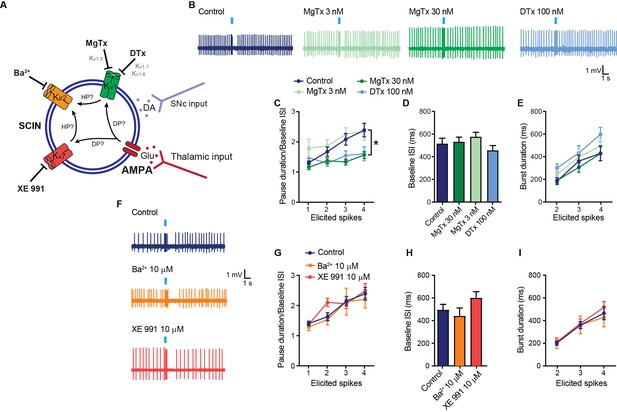
Contribution of the Kv1 current to the pause response.
(A) Schematic representation of the tested hypotheses. DP: depolarization; HP: hyperpolarization; Glu: glutamate; DA: dopamine. (B) Representative recordings of striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) in response to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without margatoxin (MgTx; Kv1.3 channel blocker) or dendrotoxin (DTx; Kv1.1 and Kv1.6 channels blocker) in the bath. (C) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without MgTx 3 nM, 30 nM, or DTx 100 nM, in the bath (two-way RM ANOVA interaction ns, treatment *p=0.0051; control-MgTx 30 nM: *p=0.0005; control-MgTx 3 nM: ns; control-DTX: *p=0.0462; MgTx 30 nM-MgTx 3 nM: *p<0.0001; MgTx 30 nM-DTX: ns; MgTx 3 nM-DTX: *p=0.0027). (D) Baseline ISI of SCINs recorded with or without MgTx 3 nM, 30 nM, or DTx (one-way ANOVA, ns). (E) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without MgTx 3 nM, 30 nM, or DTx 100 nM, in the bath (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). (F) Representative recordings of SCINs in response to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without Ba2+ (10 µM; Kir2.2 channel blocker at this concentration) or XE 991 (10 µM; Kv7 channel blocker) in the bath. (G) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without 10 µM XE 991 or 10 µM Ba2+ (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). (H) Baseline ISI of SCINs recorded with or without Ba2+ or XE 991 (one-way ANOVA, ns). (I) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, for the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). Mean ± SEM; n=7–16 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Contribution of the Kv1 current to the pause response.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
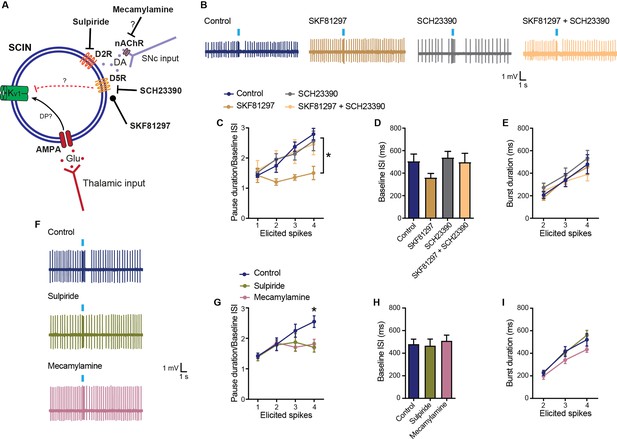
Modulation of the pause response by dopamine receptors.
(A) Schematic representation of the tested hypotheses. DP: depolarization. (B) Representative responses of striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with SKF81297 (2 µM; D1/D5 selective agonist), SCH23390 (10 µM; D1/D5 selective antagonist), or SKF81297+SCH23390 in the bath. (C) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction p=0.0381, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: control vs SKF81297: 3 spikes *p=0.0001; 4 spikes *p=0.0010.). (D) Baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, *p=0.0906). (E) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). (F) Representative responses of SCINs to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with sulpiride (10 µM; D2-type receptor selective antagonist) or mecamylamine (10 µM; nicotinic receptor antagonist) in the bath. (G) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction p=0.0369, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: control vs sulpiride: 4 spikes *p=0.0056; control vs mecamylamine: 4 spikes *p=0.0167.). (H) Baseline ISI of SCIN that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, ns). (I) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). Mean ± SEM; n=7–15 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Modulation of the pause response by dopamine receptors.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
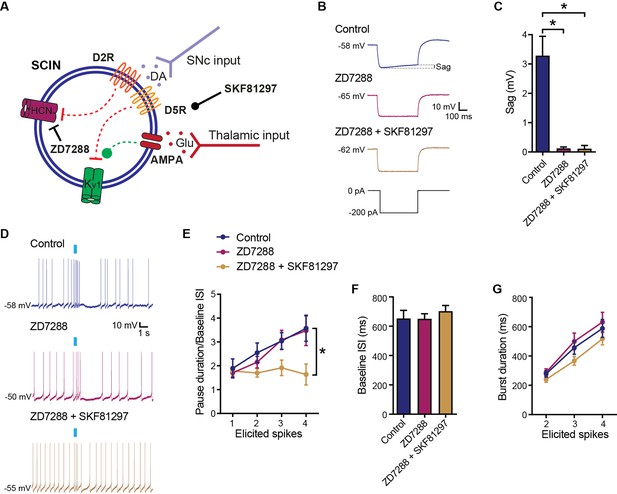
D5 receptor (D5R) modulation independent of Ih current.
(A) Schematic representation of the tested hypotheses. (B) Time matched representative responses of striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) to hyperpolarizing current steps with or without ZD7288 (30 µM; HCN channel blocker) in the recording pipette, and with or without SKF81297 (2 µM; D1/D5 selective agonist) in the bath. (C) Sag evaluated in the hyperpolarizing step, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA), p<0.0001; Tukey’s multiple comparisons test: control vs ZD7288 *p<0.0001; control vs ZD7288+SKF81297 *p<0.0001. (D) Representative responses in whole-cell configuration to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions. (E) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns, treatment p=0.0373; control vs ZD7288+SKF81297: *p=0.0005; ZD7288 vs ZD7288+SKF81297: *p=0.0067). (F) Baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, ns). (G) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). Mean ± SEM; n=13/14 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
D5 receptor (D5R) modulation independent of Ih current.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
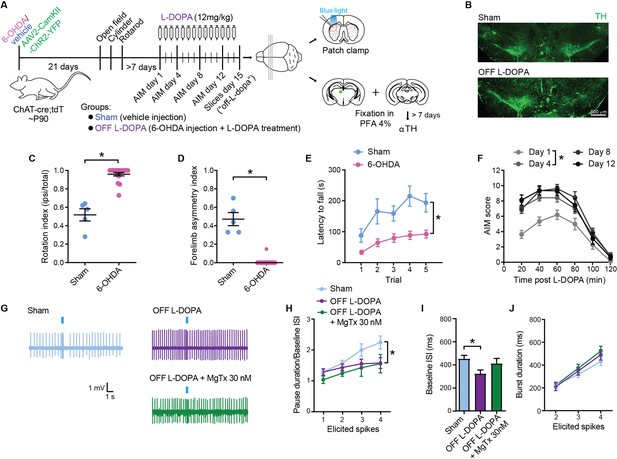
Striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from L-DOPA-treated parkinsonian mice show a reduced pause response.
(A) Experimental design. (B) Micrographs showing TH immunostaining at the level of the substantia nigra. (C–E) Rotation index (C), forelimb asymmetry (D), and latency to fall from the rotarod (E) for sham and 6-OHDA mice (C–D: unpaired t test, **p<0.0001; E two-way RM ANOVA, interaction: *p=0.0284, n=5 sham and 22 6-OHDA mice). (F) Abnormal involuntary movement (AIM) score of chronically L-DOPA-treated 6-OHDA mice (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction: p=0.0081; post hoc: day 1 vs day 4 *p<0.03). (G) Representative cell-attached recordings of the pause response of SCINs to optogenetic stimulation of thalamic terminals, in a sham and a dyskinetic mouse in the OFF L-DOPA condition, with or without margatoxin (MgTx) 30 nM in the bath. (H) Pause duration/baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns, treatment *p=0.0227; Sham vs OFF L-DOPA: *p=0.0301; OFF L-DOPA vs OFF L-DOPA+MgTx: ns; Sham vs OFF L-DOPA+MgTx: *p=0.0032). (I) Baseline ISI of SCIN that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, *p=0.0254; Sham vs OFF L-DOPA: *p=0.0201; OFF L-DOPA vs OFF L-DOPA+MgTx: ns; Sham vs OFF L-DOPA+MgTx: ns). (J) Burst duration of SCINs that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, ns). Mean ± SEM; n=14–27 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from L-DOPA-treated parkinsonian mice show a reduced pause response.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
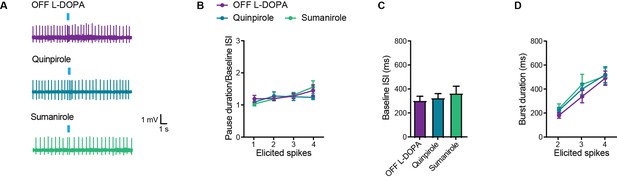
D2-type receptor agonists do not restore the pause response in striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from OFF L-DOPA parkinsonian mice.
(A) Representative cell-attached recordings of the pause response of SCINs to optogenetic stimulation of thalamic terminals, in a dyskinetic mouse in the OFF L-DOPA condition, with or without quinpirole 1 µM or sumanirole 10 µM in the bath. (B) Pause duration/baseline interspike interval (ISI) of SCINs from OFF L-DOPA dyskinetic mice that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns, treatment ns). (C) Baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, ns). (D) Burst duration of SCINs from dyskinetic mice OFF L-DOPA that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns, treatment ns). Mean ± SEM; n=10–14 cells per group, from >5 mice.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
D2-type receptor agonists do not restore the pause response in striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from OFF L-DOPA parkinsonian mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
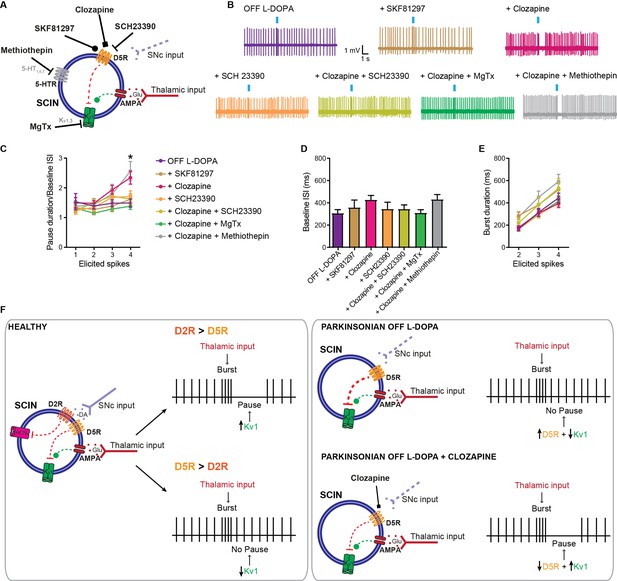
The D1/D5 receptor inverse agonist clozapine restores the pause response in striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from OFF L-DOPA parkinsonian mice.
(A) Schematic representation of the tested hypothesis. (B) Representative responses of SCINs from OFF L-DOPA dyskinetic mice to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, with or without SKF81297, clozapine (10 µM; D1/D5 receptor inverse agonist), SCH23390 (10 µM; D1/D5 selective antagonist), clozapine+SCH23390, clozapine+methiothepin (10 μM; 5-HT receptor agonist) or clozapine+MgTx, in the bath. (C) Pause duration/baseline interspike interval (ISI) of SCINs from OFF L-DOPA dyskinetic mice that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction *p=0.0083, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: 4 elicited spikes: OFF L-DOPA vs clozapine: *p=0.0193; OFF L-DOPA vs clozapine+methiothepin: *p=0.0434). (D) Baseline ISI of SCINs that responded with 1, 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (one-way ANOVA, ns). (E) Burst duration of SCINs from dyskinetic mice OFF L-DOPA that responded with 2, 3, or 4 spikes to optogenetic activation of thalamic terminals, under the above conditions (two-way RM ANOVA, interaction ns, treatment ns). Mean ± SEM; n=6–17 cells per group, from >5 mice. (F) Schematic representation of conclusion. Left, in physiologic conditions, the balance of D2 vs D5 activation emerges as a determinant of the Kv1-dependent pause expression; right, in parkinsonian mice, an imbalance toward D5 signaling abolishes the pause (top), which can be reset with D5 inverse agonism (bottom).
-
Figure 7—source data 1
The D1/D5 receptor inverse agonist clozapine restores the pause response in striatal cholinergic interneurons (SCINs) from OFF L-DOPA parkinsonian mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102184/elife-102184-fig7-data1-v1.xlsx





