Novel class IIb microcins show activity against Gram-negative ESKAPE and plant pathogens
Figures

Novel class IIb microcins are found in numerous Enterobacteriaceae genomes.
(A) Sequence alignments of the newly identified microcin and immunity genes with the gene clusters of E. coli (Ec) CA46 and K. pneumoniae (Kp) RYC492 using Easyfig (Sullivan et al., 2011). Antimicrobial (A) and immunity (I) genes in the center are represented by darker and lighter shades, respectively. X=mchX, I=mchI, B=mchB, E=mceE, L=mceL, M=mceM. (B,C) Phylogenetic trees of antimicrobial and corresponding immunity genes using codon-aligned nucleotide sequences with general time reversible model with discrete gamma distribution (GTR+G) and the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with discrete gamma distribution (HKY+G), respectively. (D) MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004) alignment of the amino acid sequence of the signal peptide sequence as well as the C-terminus of the antimicrobial peptides.
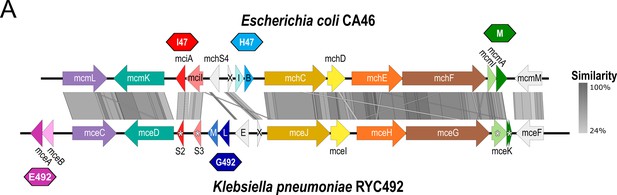
Comparison of class IIb microcin gene clusters from E. coli CA46 and K. pneumoniae RYC492.
BLAST sequence comparison of gene clusters was created using Easyfig (Sullivan et al., 2011). (A) Antimicrobial and immunity genes of each cluster are represented by darker and lighter shades, respectively. Colored polygons represent functional microcins MccE492 (pink) and MccG492 (dark blue) from K. pneumoniae as well as MccH47 (light blue), MccI47 (red), and MccM (green) from E. coli. X=mchX, I=mchI, B=mchB, E=mceE, L=mceL, M=mceM. Asterisks indicate truncated and non-functional microcin or immunity genes.
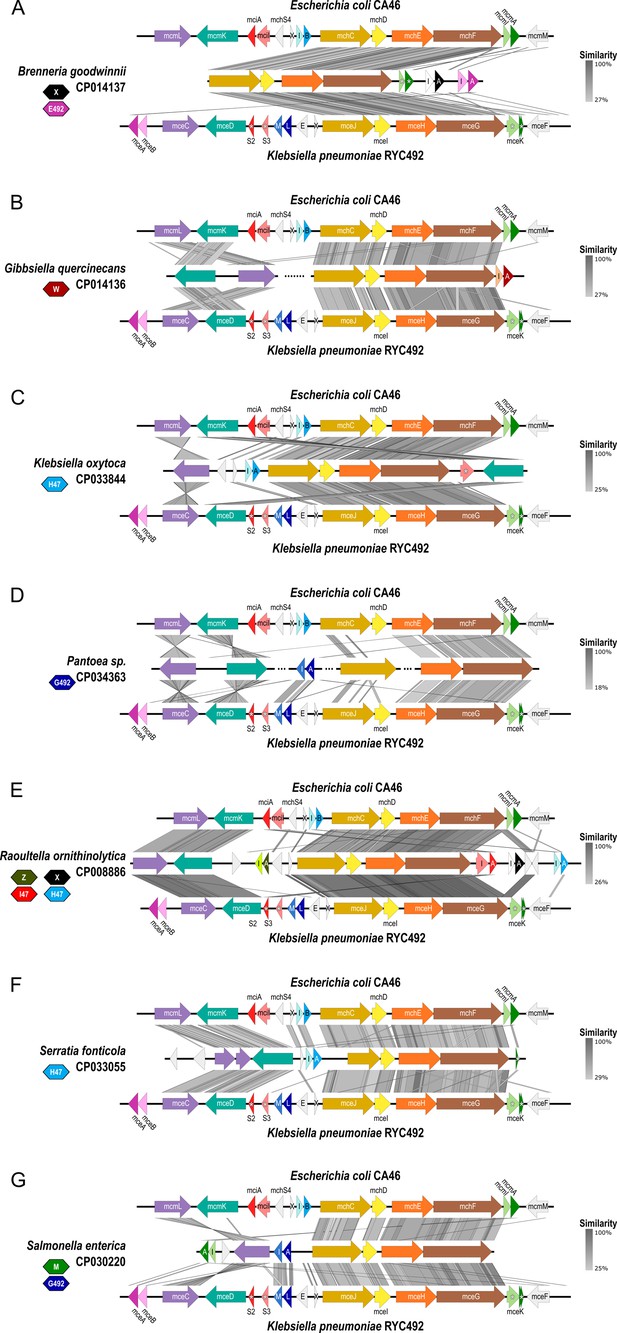
Comparison of class IIb microcin gene cluster from newly identified genomes with E. coli CA46 and K. pneumoniae RYC492.
BLAST sequence comparison of gene clusters was created using Easyfig (Sullivan et al., 2011). (A-G) Antimicrobial and immunity genes of each cluster are represented by darker and lighter shades, respectively. Colored polygons represent novel microcins from the genome indicated on the left: MccE492 (pink), MccG492 (dark blue), MccH47 (light blue), MccI47 (red), MccM (green), MccX (black), MccW (dark red), and MccZ (dark green). X=mchX, I=mchI, B=mchB, E=mceE, L=mceL, M=mceM. Asterisks indicate truncated and non-functional microcin or immunity genes.

Region and domain prediction of antimicrobial (A) and immunity peptides (B) using SMART (Letunic et al., 2021).
Previously known proteins are highlighted in bold.
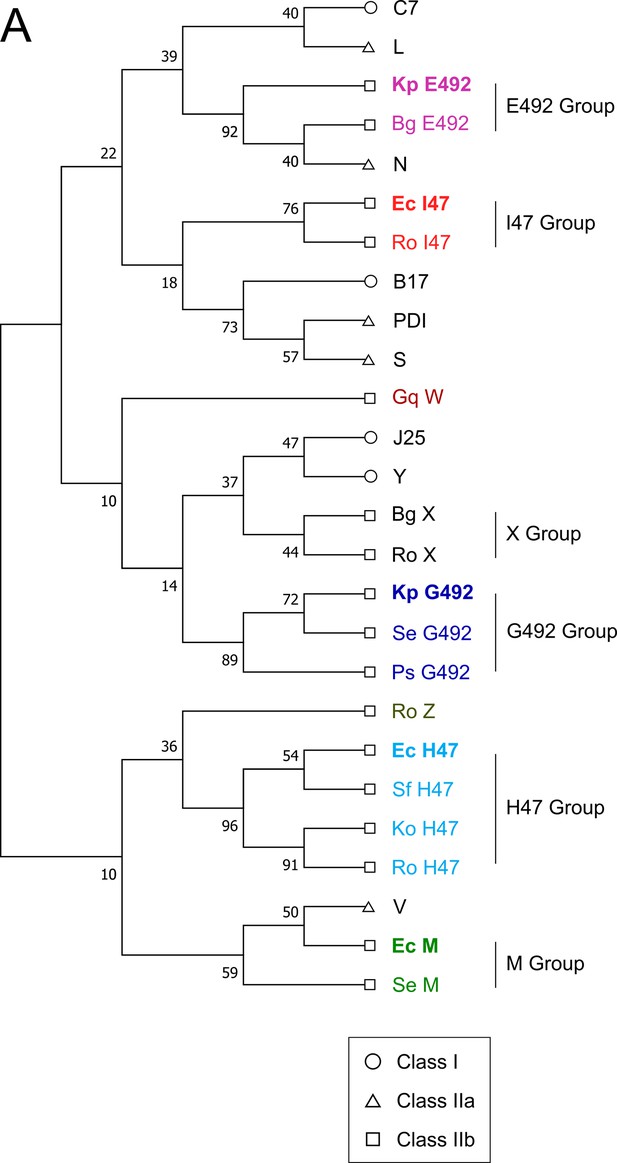
Phylogeny of all microcins from the classes I, IIa, and IIb.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of all known microcin genes using codon-aligned nucleotide sequences with general time reversible model with discrete gamma distribution (GTR+G). The respective signal peptides were removed to ensure alignment of the active regions with antimicrobial activity. Previously known class IIb microcins are highlighted in bold.

Novel class IIb microcins are effective inhibitors of Enterobacteriaceae and Gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens.
(A) Heatmap summarizing the inhibitory potential of known and novel class IIb microcins against a library of Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonadales, and Gram-positive bacteria, including multidrug-resistant isolates (red) as determined by static inhibition assays with live-producing bacteria. *=activity determined through microcin purification and minimum inhibitory concentration assays (Mortzfeld et al., 2022; Palmer et al., 2020). (B) Relative minimum inhibitory concentrations for S. enterica (Se) G492 against different bacterial species. Note that Se G492 is 256 times more potent against A. baumannii (BAA 1790) compared to K. pneumoniae (BAA 1705). (C) Static inhibition assays comparing K. pneumoniae (Kp) E492, Kp G492, Ec H47, E. coli (Ec) I47, Ec M, and Se G492 activity from single colony production against multidrug-resistant A. baumannii (BAA 1790) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA14). Note that iron-limited conditions (DP) are required for antimicrobial activity, confirming action of class IIb microcins. L-ara=L-arabinose, DP = 2,2-dipyridyl, scale bars: 1 cm.
Tables
Blastp results and closest matches to the known class IIb microcins MccE492, MccG492, MccH47, MccI47, or MccM.
Red color indicates no significant match found.
| Microcin name | Species | Accession no. | Antimicrobial gene name | Antimicrobial closest match | Identical/total length | E-value | Immunity gene name | Immunity closest match | Identical/total length | E-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bg E492 | Brenneria goodwinii | CP014137 | Bg E492A | Kp E492A (mceA) | 35/106 | 2.00E-14 | Bg E492I | Kp E492I (mceB) | 14/94 | 6.00E-04 |
| Bg X | Brenneria goodwinii | CP014137 | Bg XA | Kp E492A (mceA) | 21/98 | 6.90E-02 | Bg XI | Ec MI (mcmI) | 10/78 | 2.60E+00 |
| Gq W | Gibbsiella quercinecans | CP014136 | Gq WA | Ec I47A (mciA) | 7/103 | 8.10E+00 | Gq WI | Ec MI (mcmI) | 8/74 | 3.30E+02 |
| Ko H47 | Klebsiella oxytoxa | CP033844 | Ko H47A | Ec H47A (mchB) | 32/77 | 1.00E-07 | Ko H47I | Ec H47I (mchI) | 19/69 | 2.00E-14 |
| Ps G492 | Pantoea sp. | CP034363 | Ps G492A | Kp G492A (mceL) | 43/89 | 6.00E-09 | Ps G492I | Kp G492I (mceM) | 37/85 | 2.00E-20 |
| Ro Z | Raoultella ornithinolytica | CP008886 | Ro ZA | Ec MA (mcmA) | 21/64 | 1.00E-03 | Ro ZI | Ec MI (mcmI) | 5/74 | 2.00E+01 |
| Ro H47 | Raoultella ornithinolytica | CP008886 | Ro H47A | Ec H47A (mchB) | 31/79 | 2.00E-07 | Ro H47I | Ec H47I (mchI) | 21/69 | 4.00E-14 |
| Ro I47 | Raoultella ornithinolytica | CP008886 | Ro I47A | Ec I47A (mciA) | 37/79 | 4.00E-26 | Ro I47I | Ec I47I (mciI) | 64/135 | 1.00E-43 |
| Ro X | Raoultella ornithinolytica | CP008886 | Ro XA | Ec MA (mcmA) | 18/99 | 4.40E-01 | Ro XI | Ec MI (mcmI) | 9/61 | 1.00E-02 |
| Sf H47 | Serratia fonticola | CP033055 | Sf H47A | Ec H47A (mchB) | 38/87 | 8.00E-11 | Sf H47I | Ec H47I (mchI) | 48/68 | 4.00E-22 |
| Se G492 | Salmonella enterica | CP030220 | Se G492A | Kp G492A (mceL) | 56/85 | 1.00E-11 | Se G492I | Kp G492I (mceM) | 38/84 | 1.00E-23 |
| Se M | Salmonella enterica | CP030220 | Se MA | Ec MA (mcmA) | 34/90 | 1.00E-17 | Se MI | Ec MI (mcmI) | 38/71 | 6.00E-04 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Blastp results and closest matches to the known or novel class IIb microcins.
Red color indicates no significant match found.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102912/elife-102912-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/102912/elife-102912-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





