The near-atomic cryoEM structure of a flexible filamentous plant virus shows homology of its coat protein with nucleoproteins of animal viruses
Figures
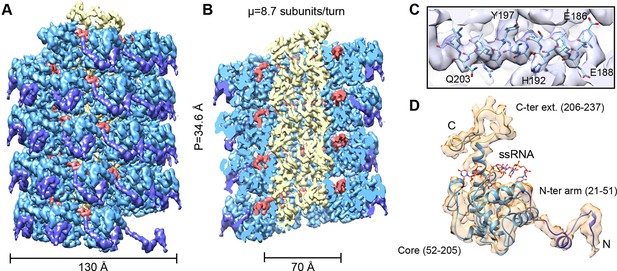
CryoEM structure of PepMV and atomic model for its CP.
(A, B) Renderings of the 3D density map for PepMV that displays a left-handed helical symmetry with 34.6 Å of helical pitch (P). The map is seen segmented domain-wise. The cut-away view (B) reveals the location of the ssRNA (red). (C) Close-up view of a region from the cryoEM map rendered in semi-transparent mode, together with the atomic model calculated for PepMV CP. (D) Isolated density for a PepMV CP subunit shown semi-transparent, and representation of the PepMVCP atomic model. Color code for PepMV CP domains: core region, blue; N-terminal arm, purple; and C-terminal extension, yellow. CP, coat protein, PepMV, Pepino mosaic virus, PepMV CP, Pepino mosaic virus coat protein.
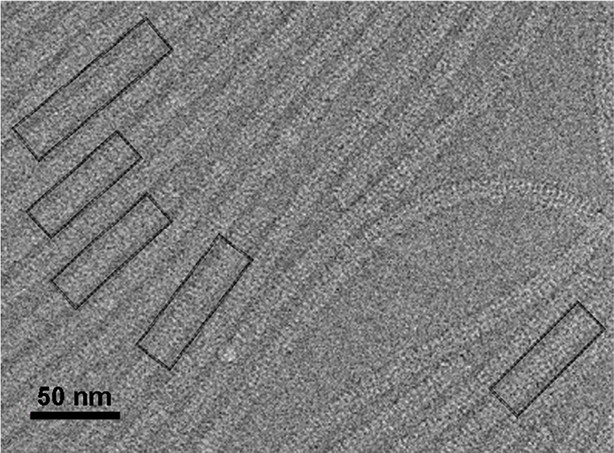
Electron micrograph of PepMV cryoEM data.
Field of an electron micrograph showing several PepMV virions. The black boxes correspond to straight segments of the helices selected for further data processing. PepMV,Pepino mosaic virus.

Helical symmetry search.
Search for helical symmetry parameters obtained in Spring package (Desfosses et al., 2014). Several 3D maps with different helical symmetry parameters are calculated starting with bi-dimensional averaged classes. Re-projections of the calculated 3D maps are then compared with the 2D averages, and their relative cross-correlation coefficients identify possible parameters. We tested a grid with variations in the helical pitch and the number of subunits per turn and calculated low resolution reconstructions using the parameters with higher correlations. The visual inspection of these initial maps lead to the selection of the helical symmetry for PepMV sample (better definition of CP subunits in the low-resolution map with 8.75 copies per turn). Further local searches were also performed to refine the symmetry. The high resolution of the final cryoEM map and its structural details confirmed the correct helical parameters. CP, coat protein.

Estimation of resolution for the cryoEM map of PepMV virions.
Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) calculated between 3D maps from two fully independently processed halves of the data set (brown line) and between the atomic model and the cryoEM map (green line). The FSC threshold at 0.14 estimates the resolution at 3.9 Å. PepMV, Pepino mosaic virus.
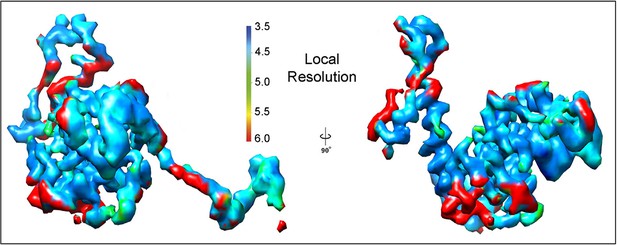
Local resolution measurement in isolated PepMV CP subunit.
Segmented density for a single PepMV CP subunit is rendered in two orientations showing the estimated local resolution. The calculations were performed with the raw cryoEM map, but only one PepMV CP subunit is shown for clarity. The color scale is also rendered. CP, coat protein; PepMV, epino mosaic virus.

Comparison between modeled PepMV CP and the atomic structure of PapMV CP.
(A) Comparison between the built atomic model for PepMV CP (colored domain wise as in Figure 1) and the reported structure for the truncated version of PapMV CP (colored grey; pdb code 1DOX (Yang et al., 2012)). The ssRNA belongs to the current model for PepMV virion. The RMSD between the structures in the core region is of 1.5 Å. (B) Comparison of the current model for PepMV CP and the atomic model for BaMV (colored brown; pdb code 5A2T (DiMaio et al., 2015). The RMSD between both structures in the core region is of 3.5 Å. The black arrow indicates a discrepancy between both atomic models in their secondary structure. A short helix in 5A2T is a loop in our model and in 1DOX. This region contributes to the RNA-binding surface.

Table of some figures of merit for the structure of the modeled PepMV CP.
Short table with figures of merit calculated in Molprobity for the validation of the atomic model of PepMV CP. PepMV CP, Pepino mosaic virus coat protein
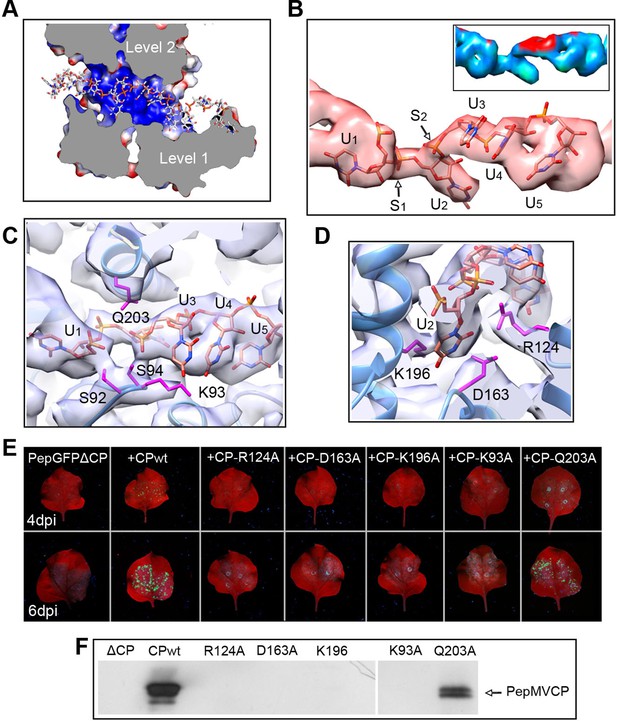
Interaction between PepMV CP and ssRNA.
(A) Cut-away rendering of four PepMV CP subunits at consecutive turns of the helix with the ssRNA between them. Molecular surfaces are colored according to their electrostatic potential using a color scale that ranges from -5KT (red) to +5KT (blue). (B) Structural detail for the density of the ssRNA associated to a single PepMV CP. ssRNA is a polyU model with five nucleotides. S1 and S2 indicate switches along the phosphate backbone. The inset renders the density region for ssRNA according to local resolution measurements (blue around 4 Å, and red at 6 Å of resolution; full color scale in Figure 1—figure supplement 4). (C, D) Focus on local protein–RNA interfaces where amino acids with possible interaction with the RNA are highlighted. (E) Trans-complementation assays between PepGFPΔCP and several CP mutants. The images show agroinfiltrated N. benthamiana leaves imaged under UV light to detect the expression of GFP. Data were recorded at 4 and 6 days post inoculation (dpi). (F) Western blot analysis of the presence of PepMV CP in preparations of fully assembled virions from trans-complementation assays. PepMV CP, Pepino mosaic virus coat protein.
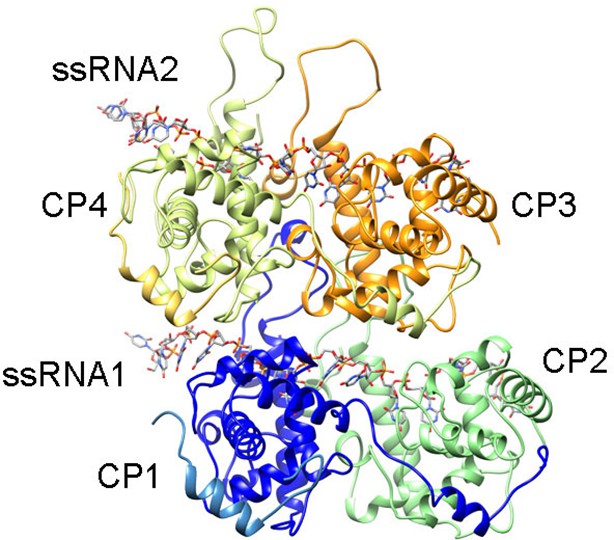
Rendering of the atomic model construction used during MDFF for the analysis of the protein-RNA interfaces.
Representation of four PepMV subunits and two molecules of ssRNA obtained after MDFF. The set was chosen to explore protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions. CP1 and CP4 also contain the N-terminal arms from adjacent subunits, whereas CP2 and CP3 lack their N-terminal arms. The set was fitted inside a region of the cryoEM map for PepMV. CP, coat protein; MDFF, molecular dynamics flexible fitting; PepMV, Pepino mosaic virus.
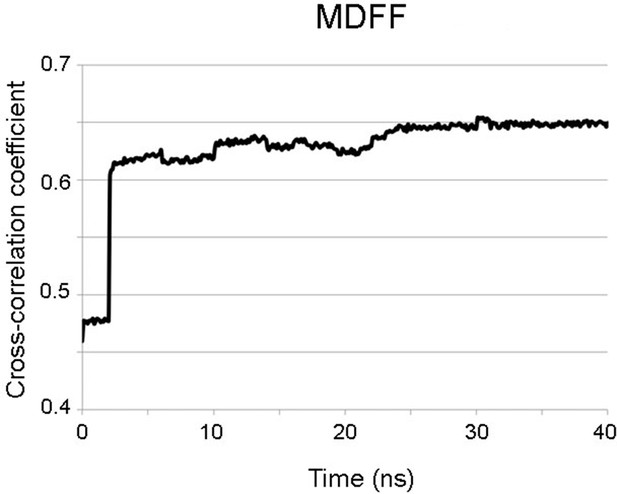
Progress during the MDFF run.
Progress of the MDFF measured as the improvement of the cross-correlation between the atomic coordinates (shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1) and the cryoEM map for PepMV along the 40 ns of the MDFF run. MDFF, molecular dynamics flexible fitting.

Sequence alignment between CP from several representatives of the genus Potexvirus.
The alignment was produced by CLC Main Workbench and indicates the degree of conservation and the consensus sequence. The alignment includes CP sequences from: Pepino mosaic virus (PepMV) (NP_663728), Papaya mosaic virus (PapMV) (P16596); Bamboo mosaic virus (BaMV) (NP_042587.1), Potato aucuba mosaic virus (PAMV) (P37993); Potato virus X (PVX) (P10468); Narcissus mosaic virus (NMV) (NP_040782); White clover mosaic virus (WClMV) (NP_620719); Lily X virus (LVX) (YP_263307); Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV) (Q00467); Plantago asiatica mosaic virus (PlAMV) (NP_620840); and Foxtail mosaic virus (FoMV) (NP_040992). The most conserved region includes D163 in PepMV CP (consensus sequence FDFFD in the alignment), one of the amino acids at the binding pocket for the ssRNA. CP, coat protein.
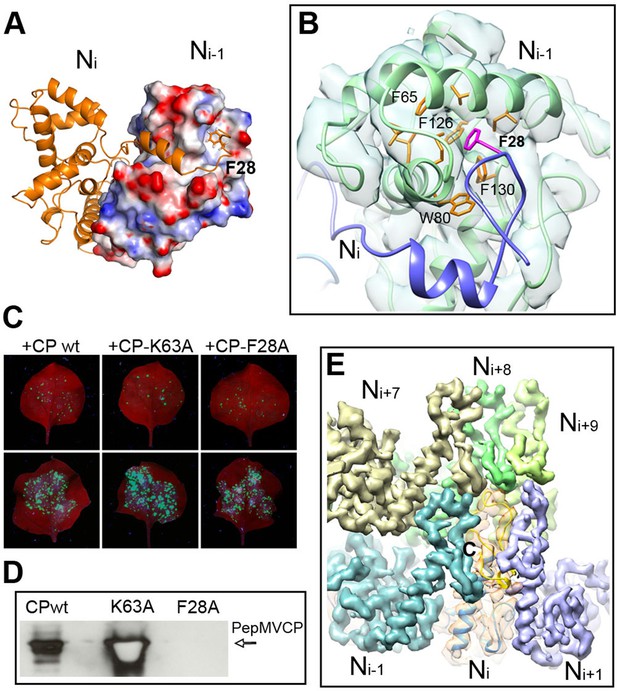
Interactions through N- and C-terminal flexible regions mediate PepMV assembly.
(A) Ni subunit links to a hydrophobic groove in the Ni-1 subunit via the N-terminal arm. (B) In the Ni-1 subunit a pocket of hydrophobic residues allocates F28 from the Ni adjacent subunit. (C) Trans-complementation assays show that F28A mutant allows for cell-to-cell movement. (D) The analysis by Western blot of virion preparations show no signal for fully assembled virions in the trans-complementation with F28A mutant. PepMVCP mutant K63A is a positive control. (E) Six segmented densities for PepMVCP are seen from the inner side of the virion. The subunit Ni is depicted semi-transparent and includes a ribbon representation for the atomic model for PepMV CP. PepMV CP, Pepino mosaic virus coat protein.
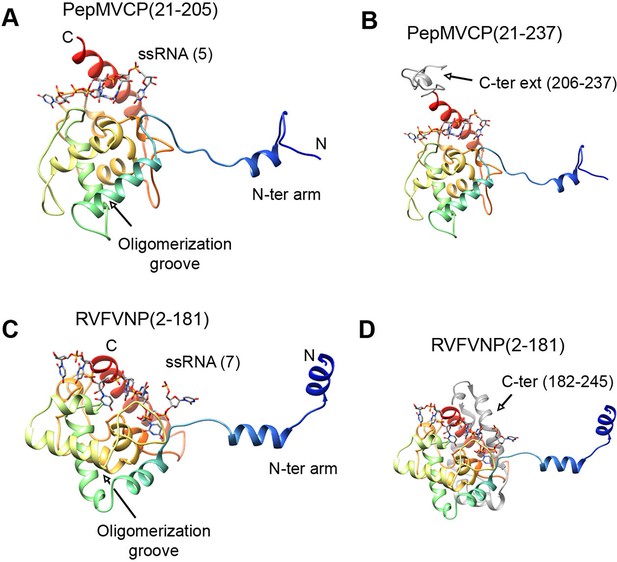
Structural homology between PepMV CP and NP from phleboviruses.
(A–D) The atomic structures for the modeled PepMV CP and for the NP from RVFV (pdb code 4H5O (Raymond et al., 2012) are depicted in similar orientations. The representations include the respective ssRNAs. Both proteins are colored in rainbow mode and their similar topology is clear when their C-terminal regions are removed (A and C). Their C-termini are seen in grey color for comparison (B and D). PepMV CP, Pepino mosaic virus coat protein; NP, nucleoprotein.





