Unexpected arousal modulates the influence of sensory noise on confidence
Figures
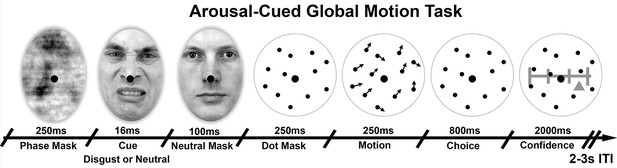
Arousal-Cued global motion task.
Trial schematic illustrating our arousal-cued global motion task, in which an unexpected, masked disgusted face increased arousal just prior to a motion judgement and confidence rating. On each trial motion stimulus of variable precision (15 or 25 degrees standard deviation, σ) were preceded by either a masked disgust or neutral face, followed by the perceived neutral mask. Participants then made a forced-choice motion discrimination and subjective confidence rating. Histogram and average luminance-matching was applied between conditions and frames to eliminate pupillary artefacts, see Materials and methods for more details.
© 1998, Karolinska Institutet, Psychology section, All Rights Reserved. Face stimuli images taken from the Karolinska Directed Emotional Faces database and adapted with permission (ID AM25DIS).
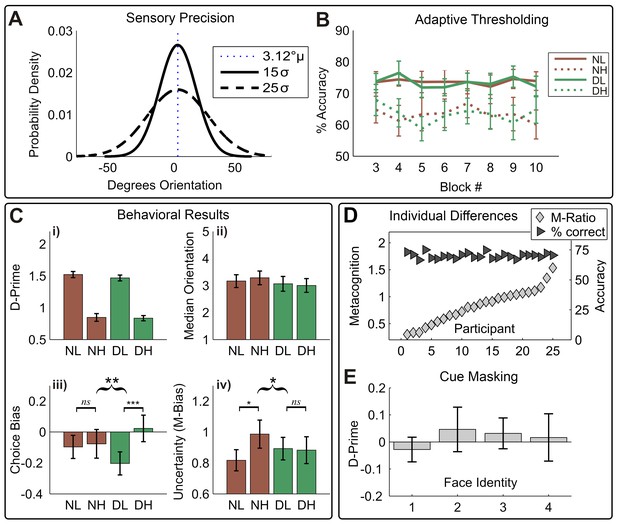
Overview of behavioral results.
(A) Manipulation of sensory precision; stimulus probability density functions show our low (15 σ) and high (25 σ) variance conditions; stimulus mean and variance were orthogonally manipulated using a global-motion stimulus. (B) The performance was held constant using adaptive thresholding separately for disgust vs. neutral trials; conditions labels are neutral low variance (NL), neutral high variance (NH), disgust low variance (DL), disgust high variance (DH). (C) Degraded sensory precision reduces perceptual sensitivity; cues had no impact on either motion detection (i) or threshold (ii). Instead, disgust cues selectively increased rightward bias for low-variance stimuli (iii), suggesting arousal altered stimulus expectations. As predicted by interoceptive inference, arousing cues significantly decrease the impact of noise on uncertainty (M-bias) (iv). Curly brackets indicate F-test of 2-way interaction, square brackets indicate post-hoc t-tests (*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05). All error bars +/- SEM. (D) Although performance was held constant (dark triangles, % correct), participants show considerable variability in metacognitive sensitivity (light diamonds, M-Ratio), reproducing previous results using the signal-theoretic confidence model. (E) Participants had no awareness of cue valence in a post-task forced choice test using identical trial parameters; 95% confidence intervals for d-prime on all four face pairs overlap zero (see Materials and methods, Valence Detection Task).
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Table with variable codes used in Figure 2—source data 1.
Please see Materials and methods for full descriptions of all variables.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18103.005
-
Figure 2—source data 1
This csv table contains the data for Figure 2.
All data are split by condition, NL = “neutral cue low variance”, NH = “Neutral cue high variance”, DL = “disgust cue low variance, DH = “disgust cue high variance”.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18103.006
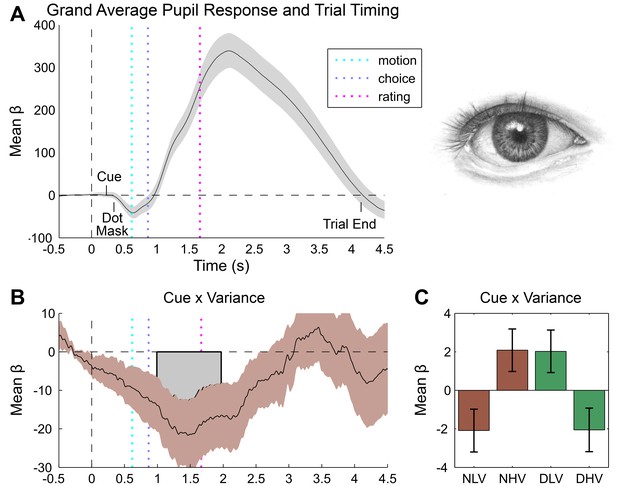
Pupillometry results.
(A) Results of general linear modelling (GLM) of pupil responses; the pupil grand mean response function shows a canonical orientation response, peaking during confidence rating before returning to baseline in the 2–3 s jittered inter-trial interval. (B) As predicted, pupillary fluctuations encode the interaction of exteroceptive noise and unexpected internal arousal, time locked to the response interval and onset of confidence rating. (C) For illustration, mean response for each condition, extracted from significant time-window controlling for all explanatory and nuisance variables. GLMs were fit across all trials to each time point of the pupil series. Explanatory variables encoded main effects of stimulus noise, variance, confidence, and interactions thereof, revealing the amplitude and timing of each effect. The effects are independent from task-difficulty; trial-wise mean signal and RT were controlled in all analyses. Significance assessed using a cluster-based permutation t-test, cluster alpha = 0.05; cluster shown by shaded grey patch. See Materials and methods for more details.
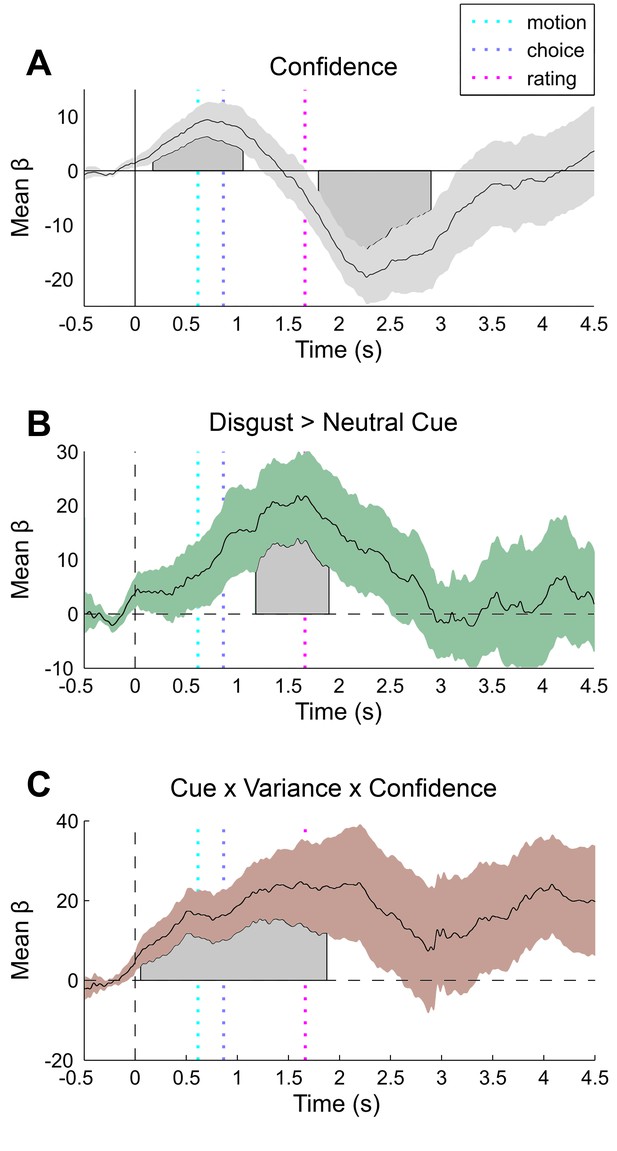
Additional pupil effects of interest.
(A) Confidence is biphasically encoded in pupil responses, with a stimulus-locked dilatory effect and a rating-locked constriction effect. Cues (B, disgust > neutral) increased dilation from response to rating. (C) Three-way interaction of cue valence, variance, and confidence showing that magnitude of cue-related pupil reversal correlates with trialwise confidence. Results of general linear modelling of the pupil, with explanatory variables encoding the main effects of stimulus noise, variance, confidence, and interactions thereof, revealing the amplitude and timing of each effect. The effects are independent from task-difficulty; trialwise mean signal and RT were controlled in all analyses. Significance assessed using a cluster-based permutation t-test, cluster alpha = 0.05; cluster shown by shaded grey patch. See Materials and methods for more details.
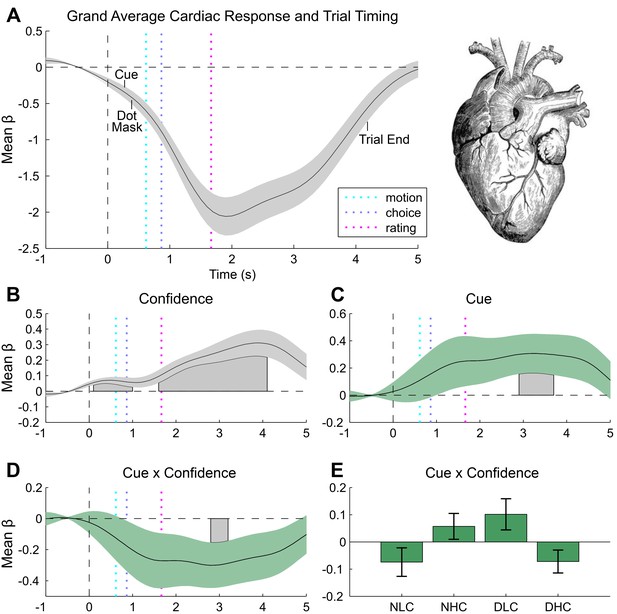
Cardiac results.
(A) Grand mean cardiac response function showing canonical heart rate deceleration orientation response, and trial timings. (B) Subjective confidence ratings encoded by greater heart rate acceleration, beginning with stimulus onset and peaking during ratings. (C) Unseen disgust cues increase heart rate during confidence rating. (D) This effect interacts with confidence, effectively reversing the mapping of cardiac acceleration and subjective uncertainty. (E) To illustrate this effect, trials were median split into high and low confidence for each disgust condition (e.g., neutral low confidence, NLC), and mean response was extracted from within the significant cue by confidence window. Results of general linear modelling of instantaneous heart rate, with explanatory variables encoding the main effects of stimulus noise, variance, confidence, and interactions thereof, revealing the amplitude and timing of each effect. Effects are independent from task-difficulty; trial-wise mean signal and RT were controlled in all analyses. Significance assessed using a cluster-based permutation t-test, cluster alpha = 0.05; cluster shown by shaded grey patch. See Materials and methods for more details.





