Minimized human telomerase maintains telomeres and resolves endogenous roles of H/ACA proteins, TCAB1, and Cajal bodies
Figures
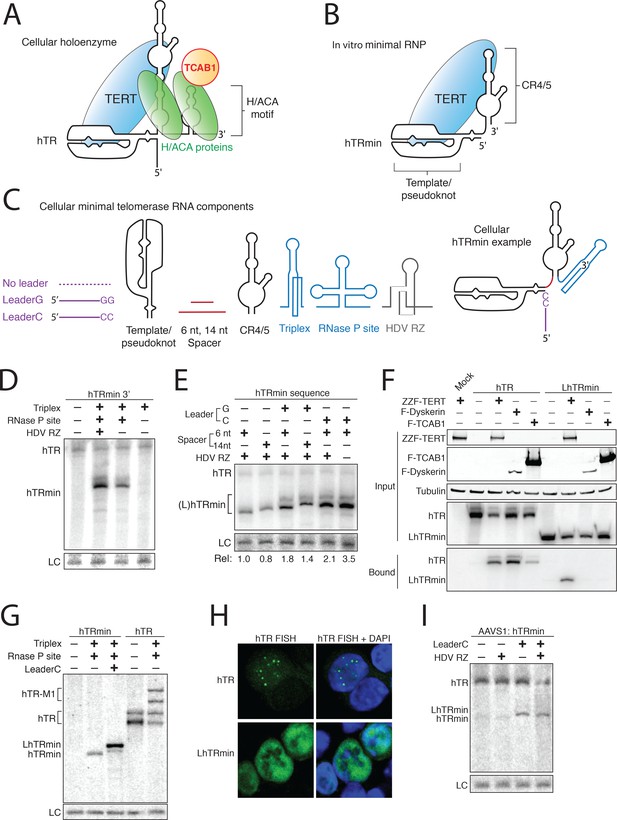
Human telomerase RNA can accumulate without H/ACA RNP biogenesis.
(A,B) Diagrams of hTR and hTRmin secondary structure and bound proteins. (C) Parts list for a cellular minimal telomerase RNA. Components are presented in 5’ to 3’ order. (D,E) Northern blot assay for RNA accumulation in transfected 293T cells. Endogenous hTR was also detected. Loading control (LC) is a cellular RNA non-specifically detected by the Northern blot probe used for normalization. In (D), all hTRmin variants are without a 5’ leader and with a 6 nt spacer. In (E), all constructs had the RNA triplex and RNase P site. hTRmin accumulation was normalized to LC to quantify relative accumulation (Rel). (F) Copurification of hTR or LhTRmin with tagged telomerase holoenzyme subunits co-overexpressed in transfected VA-13 cells. RNPs were purified from cell lysate using FLAG antibody resin and analyzed by immunoblot and Northern blot. F indicates 3xFLAG peptide, ZZ indicates tandem Protein A domains. (G) Northern blot assay for RNA accumulation in transfected VA-13 cells. RNA folding during extensive gel electrophoresis gives mature hTR two mobilities (a doublet of bands). (H) FISH detection of hTR or LhTRmin in transfected HCT116 cells. Untagged TERT was coexpressed. (I) Northern blot assay for RNA expressed from transgenes integrated at; in HCT116 cells. Endogenous hTR was also detected.
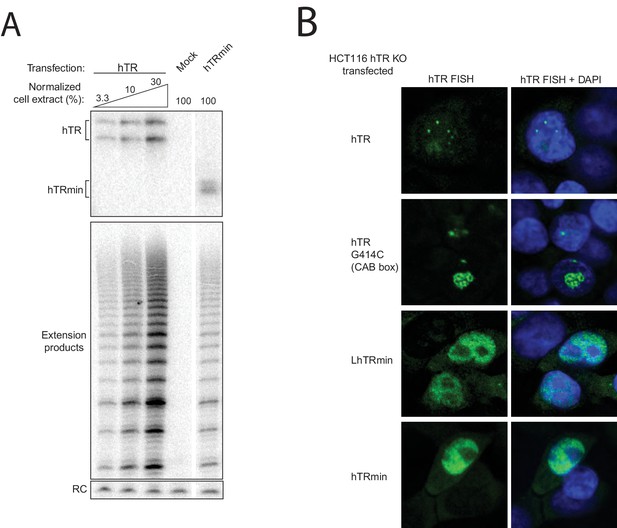
Cellular assembly of hTRmin telomerase.
(A) U2OS cells were transiently transfected with constructs encoding F-TERT and either hTRmin, hTR, or empty vector (mock). TERT was immunopurified on anti-FLAG agarose from cell extract 48 hr post-transfection. An aliquot of the bound samples were treated with TRIzol to purify RNA, which was analyzed by Northern blot. In parallel, bound samples were tested for telomerase activity by primer extension using 32P dGTP for radiolabeling. Products were precipitated and resolved by denaturing gel electrophoresis. A radioactive oligonucleotide recovery control (RC) was added prior to precipitation. For the hTR cell extract, different amounts of extract were assayed relative to the hTRmin sample set at 100%. All lanes are from the same gel. (B) HCT116 hTR KO#2 cells were transiently transfected to express hTR, CAB-box-mutant hTR (G414C), LhTRmin, or hTRmin. FISH was performed to detect the RNAs (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).
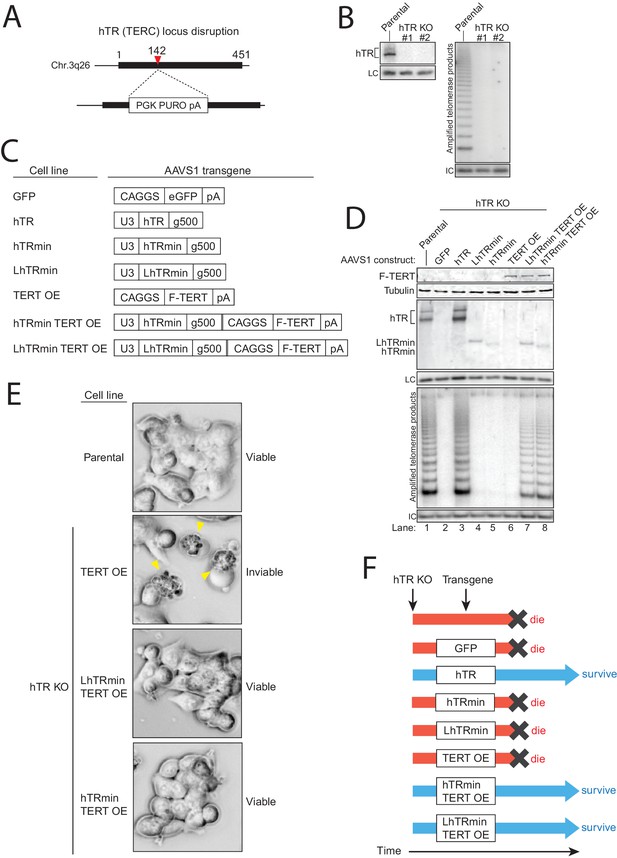
An hTRmin RNP can functionally substitute for hTR.
(A) Schematic of Cas9-mediated disruption of the hTR locus with a PURO selection cassette. (B) Northern blot and hotTRAP assays of hTR KO#1 and KO#2 clonal HCT116 cell lines. An internal control (IC) to normalize PCR amplification was always included in hotTRAP assays. (C) AAVS1 donor constructs used for transgene rescue of hTR KO HCT116 cells. RNA expression used the U3 promoter and terminated within 500 bp of transplanted genomic region from immediately downstream of endogenous hTR (g500). mRNA expression used the CAGGS promoter terminated with a polyadenylation element (pA). (D) Immunoblot, northern blot, and hotTRAP characterization of HCT116 cell lines 51 days after hTR KO targeting. (E) Brightfield microscopy images of HCT116 cell lines during the die-off interval of telomerase-negative cell cultures. Yellow arrowheads indicate membrane blebbing. (F) Chart of survival fate of HCT116 hTR KO cell lines with the indicated transgene at AAVS1.
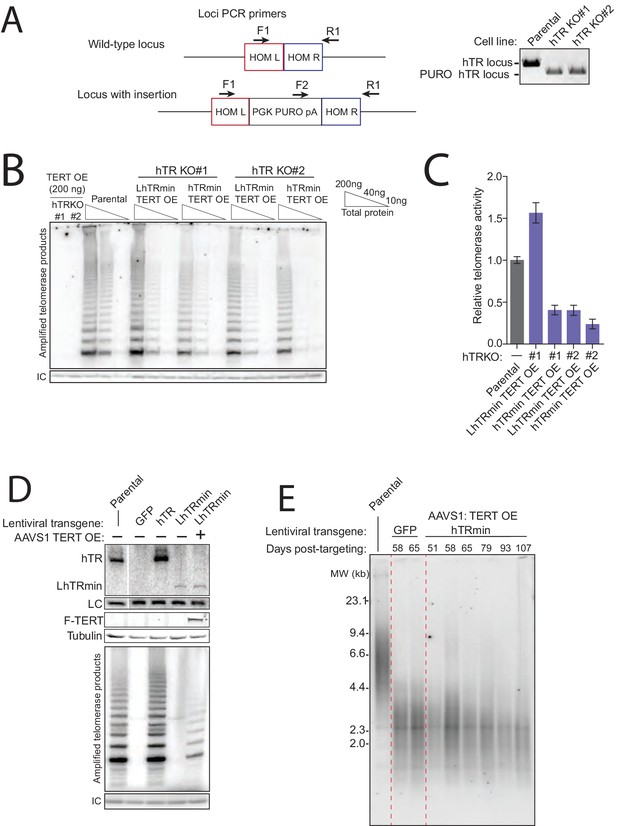
Generation of cell lines expressing hTRmin telomerase.
(A) Schematic and assay results for PCR detection of hTR locus KO. (B) Telomerase activity comparison by hotTRAP for the hTR KO cell lines with TERT OE alone or in combination with hTRmin or LhTRmin. Input total protein is whole cell lysate. Assays were from polyclonal populations following selection for transgene integration and extended post-targeting culture (114 days post-targeting for hTR KO). (C) QTRAP comparison of telomerase activity levels in the hTR KO cell lines rescued by AAVS1 hTRmin TERT OE or LhTRmin TERT OE. Values are set relative to parental HCT116 (n = 3). (D) Immunoblot, northern blot, and hotTRAP characterization of HCT116 hTR KO cells with or without TERT OE from an AAVS1 transgene and with lentiviral hTR, LhTRmin, or GFP. (E) Time course of TRF in the HCT116 hTR KO with TERT OE and lentiviral LhTRmin or negative control GFP. Days post-targeting is relative to hTR KO; 65 days post-targeting was the last time point of collection prior to die-off of the telomerase-negative cells.
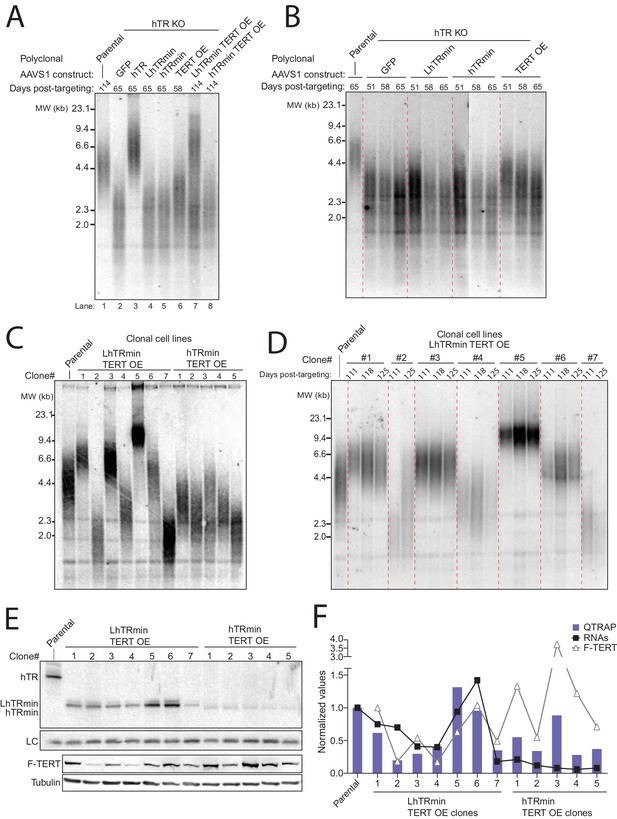
Telomerase with hTRmin supports stable telomere length maintenance.
(A) Southern blot detection of telomere restriction fragment lengths (TRF) for HCT116 cell lines after release from selection. The telomerase-negative cell line TRFs were analyzed before cultures commenced cell death. (B) Time course of TRF shortening in the telomerase-negative HCT116 cell lines. The 65 days post-targeting time point was the final cell collection before culture death. All lanes are from the same gel. Red dashed lines separate different genotypes. (C) TRF analysis for multiple clonal cell lines expressing LhTRmin with TERT OE or hTRmin with TERT OE, all cultured in parallel and assayed at the same time point 111 days post-targeting. (D) Time course of TRF in the clonal cell lines expressing LhTRmin with TERT OE or hTRmin with TERT OE. Days post-targeting refers to the hTR KO. (E) Immunoblot and Northern blot analysis of telomerase subunit expression levels across the clonal cell lines expressing LhTRmin with TERT OE or hTRmin with TERT OE, performed using cells at 111 days post-targeting. (F) Comparison of telomerase activity measured by QTRAP (purple bars) with telomerase subunit expression levels quantified from blots in (E). QTRAP (averaged, n = 5) and RNA signals were normalized to parental HCT116 cell line activity and endogenous hTR. TERT OE signals were set relative to LhTRmin TERT OE clone #1.
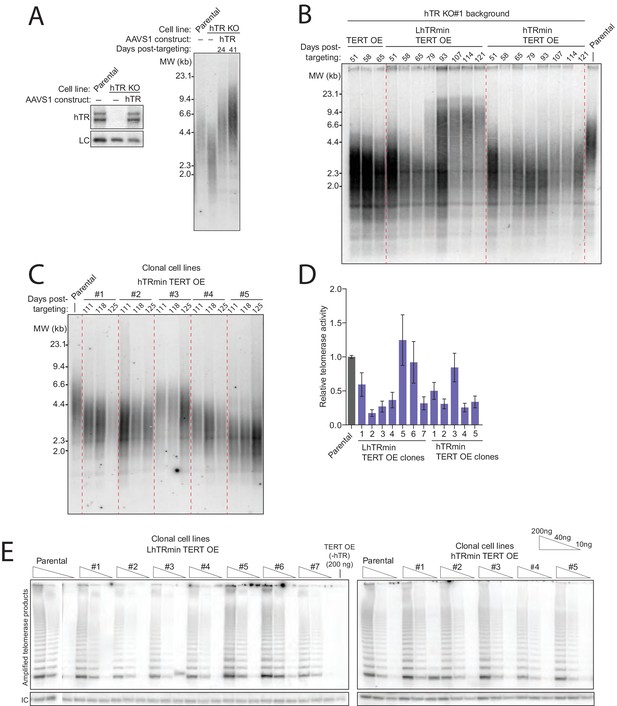
Characterization of telomere length maintenance and telomerase activity levels in hTRmin telomerase cell lines.
(A) Northern blot and TRF timecourse of HCT116 hTR KO#2 cell line rescue by transgene hTR. (B) Time course of HCT116 TRF after introduction of a transgene for TERT OE alone or with LhTRmin or hTRmin; cell cultures were polyclonal after transgene introduction. Cells with TERT OE alone died shortly after 65 days post-targeting, counted from the original hTR KO. (C) Time course of TRF in clonal cell lines of HCT116 hTR KO with AAVS1 TERT OE and hTRmin. Days post-targeting refers to the original hTR KO. (D) QTRAP data from Figure 3F with error bars from technical replicates (n = 5). (E) Telomerase activity measured by hotTRAP for the HCT116 clonal cell lines with TERT OE and LhTRmin or hTRmin. In each panel, all lanes are from the same gel.
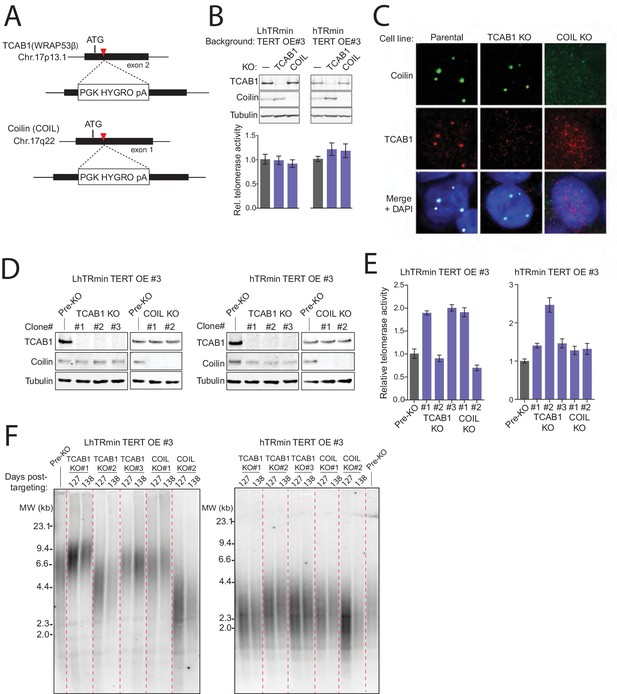
TCAB1 and Cajal bodies are not required for telomere maintenance by hTRmin telomerase.
(A) Schematic of Cas9-mediated disruption of TCAB1 and Coilin (COIL) loci with a HYGRO selection cassette. (B) Immunoblot and QTRAP analysis of the polyclonal populations of LhTRmin or hTRmin TERT OE cells selected for disruption of TCAB1 or COIL loci. QTRAP values were normalized to the cell line before TCAB1 or COIL disruption (n = 3). (C) Immunofluorescence localization of TCAB1 and Coilin in HCT116 cells. (D) Immunoblot analysis for TCAB1 and Coilin in clonal KO cell lines with LhTRmin + TERT OE or hTRmin + TERT OE. (E) QTRAP assay of the clonal cell lines in (D). QTRAP values were normalized to the cell line before TCAB1 or COIL disruption (n = 3). (F) Stable TRF lengths in clonal cell lines lacking TCAB1 or Coilin. Days post-targeting refers to the TCAB1 or COIL KO.
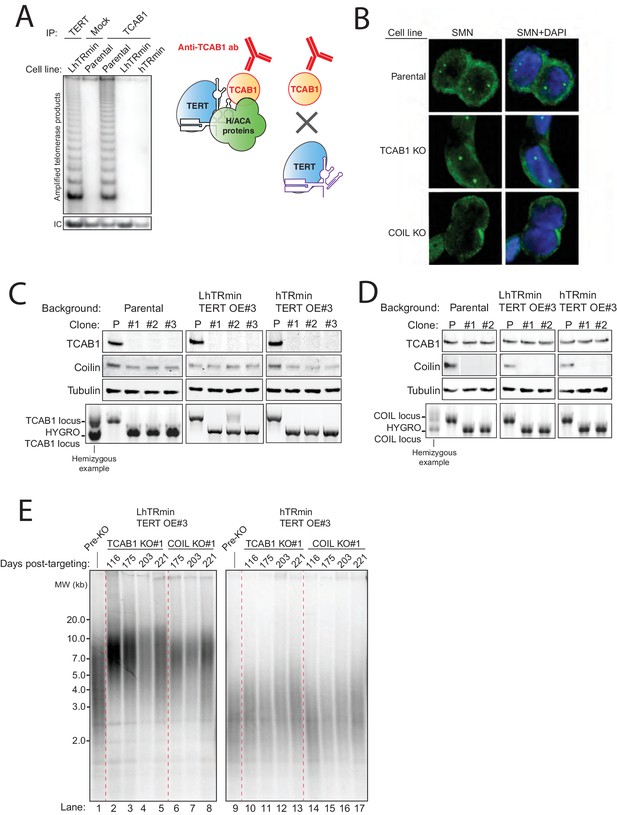
Characterization of HCT116 hTRmin with TERT OE cell lines with TCAB1 KO or Coilin KO.
(A) Immunopurification from HCT116 hTR KO cell lines expressing LhTRmin with TERT OE or hTRmin with TERT OE. Protein A/G beads were coupled with anti-TCAB1 antibody and used to immunopurify TCAB1 complexes. Rabbit IgG and anti-FLAG antibody were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Immunopurified samples were assayed by hotTRAP. (B) Immunofluorescence localization of SMN in HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO cell lines. (C,D) Immunoblot and PCR genotyping of HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO cell lines. The immunoblots are also shown in main figures. The TCAB1 KO clonal cell line #2 in the LhTRmin TERT OE#3 background had one allele with target-site mutagenesis that produced an early translation stop codon. (E) Extended culture TRF analysis of HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines from the LTRmin and hTRmin telomerase backgrounds.
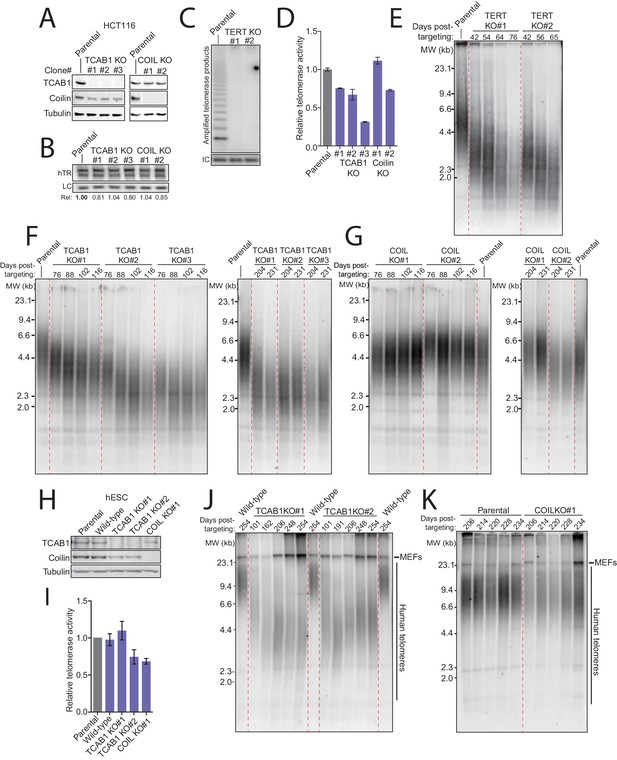
TCAB1 and Cajal bodies are not essential for telomere maintenance by endogenous telomerase.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. (B) Northern blot for hTR in HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. (C) Lack of hotTRAP telomerase activity detection in the HCT116 TERT KO clonal cell lines. (D) QTRAP analysis of telomerase activity in the HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. Values were normalized to the parental HCT116 cell line (n = 3). (E) Time course of TRF in the HCT116 TERT KO clonal cell lines. (F,G) Time course of TRF in the HCT116 TCAB1 and COIL KO clonal cell lines. (H) Immunoblot analysis of hESC TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. Wild-type refers to an hESC clonal cell line subjected to Cas9 electroporation but retaining a wild-type genotype. (I) QTRAP analysis of telomerase activity in the hESC TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. Values were normalized to the parental hESC line (n = 3). (J,K) Time course of TRF in hESC TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. Note that the long telomeres in mouse cells from the hESC feeder layer contribute some blot signal (indicated MEFs).
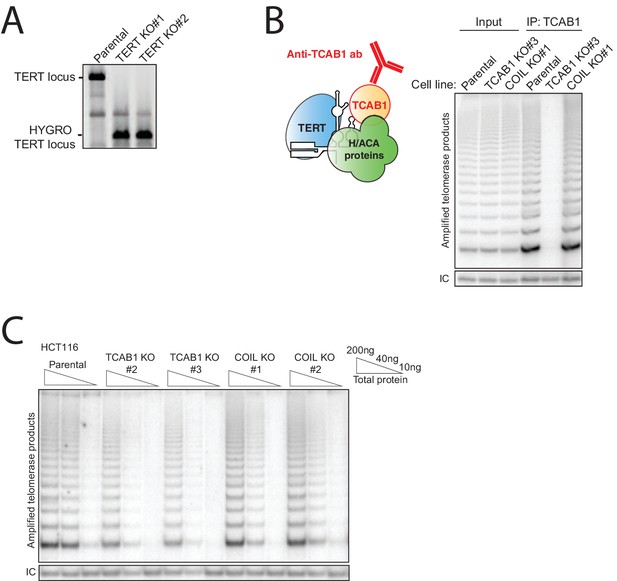
Characterization of HCT116 TERT KO, TCAB1 KO, and COIL KO cell lines with endogenous hTR.
(A) PCR genotyping of HCT116 TERT KO clonal cell lines. (B) Immunopurification of TCAB1 complexes from parental, TCAB1 KO, and COIL KO HCT116 cell lines followed by hotTRAP. (C) HotTRAP of HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO cell lines.
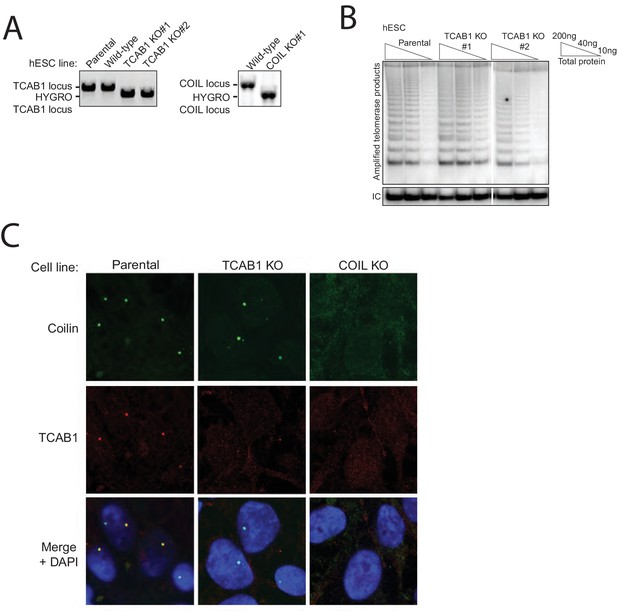
Characterization of hESC TCAB1 KO and COIL KO lines with endogenous hTR.
(A) PCR genotyping of hESC TCAB1 KO and COIL KO clonal cell lines. Wild-type refers to an hESC clonal cell line subjected to Cas9 electroporation but retaining a wild-type genotype. (B) HotTRAP of the TCAB1 KO hESC lines. (C) Immunofluorescence localization of Coilin and TCAB1 in hESC lines.
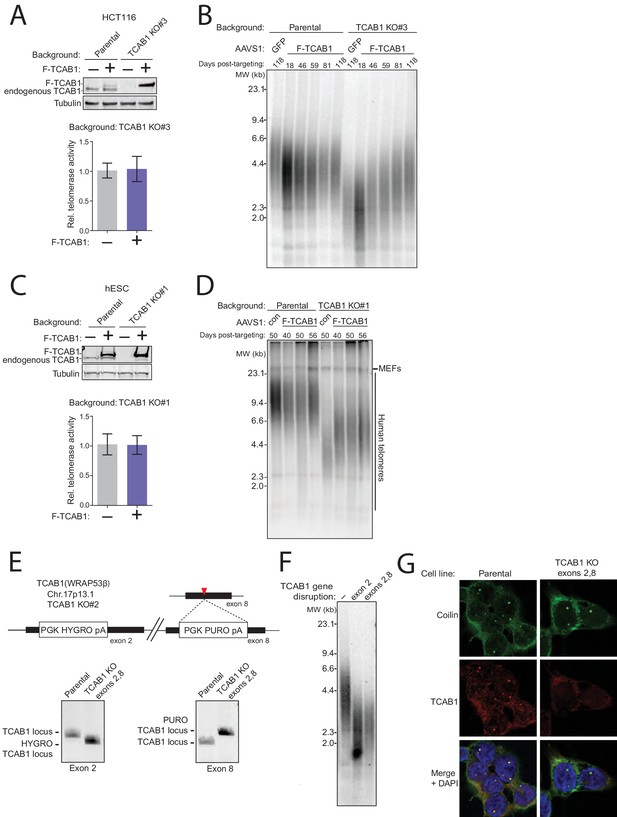
Additional controls for TCAB1 loss-of-function in TCAB1 KO cell lines.
(A) Immunoblot and QTRAP analysis of HCT116 parental and TCAB1 KO cell lines expressing F-tagged TCAB1 or GFP from transgenes at AAVS1. QTRAP values were normalized to the GFP cell line signal (n = 3). Days post-targeting refers to transgene integration. (B) Time course of TRF in cell lines from (A). (C) Immunoblot and QTRAP analysis of hESC parental and TCAB1 KO cell lines expressing F-tagged TCAB1 transgene at AAVS1. QTRAP values were normalized to the unrescued TCAB1 KO cell line signal (n = 3). Days post-targeting refers to transgene integration. (D) Time course of TRF in cell lines from (C). (E) TCAB1 double-exon-disruption schematic with TCAB1 exon 2 and exon 8 KO genotyping by PCR. TCAB1 exon 8 targeting was performed in the HCT116 TCAB1 KO#2 background, which has a hygromycin resistance cassette inserted in TCAB1 exon 2. (F) TRF of HCT116 parental, TCAB1 KO#2 background, and exon 8 disrupted TCAB1 KO#2 (double-exon-disruption) cell lines. DNA was purified from double-exon-disruption cells at 43 days post-targeting the second KO. (G) Immunofluorescence staining for Coilin (green) and TCAB1 (red) in double-exon-disruption cells.
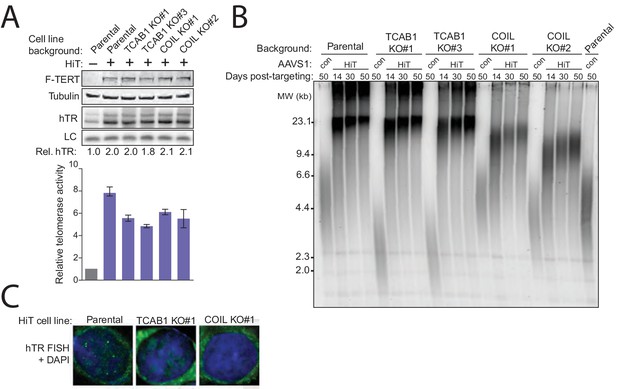
Cajal bodies promote telomere elongation upon increased telomerase expression level.
(A) Immunoblot, northern blot, and QTRAP characterization of TCAB1 KO and COIL KO HCT116 cells overexpressing hTR and TERT at AAVS1 (HiT). QTRAP values were normalized to parental HCT116 (n = 3). (B) Time course of TRF in the HiT HCT116 TCAB1 KO and COIL KO cell cultures polyclonal following HiT transgene introduction. Days post-targeting refers to HiT transgene introduction. The lanes labeled 'con' are the indicated cell line without HiT transgene introduction. (C) FISH for hTR localization in HiT HCT116 cell lines.
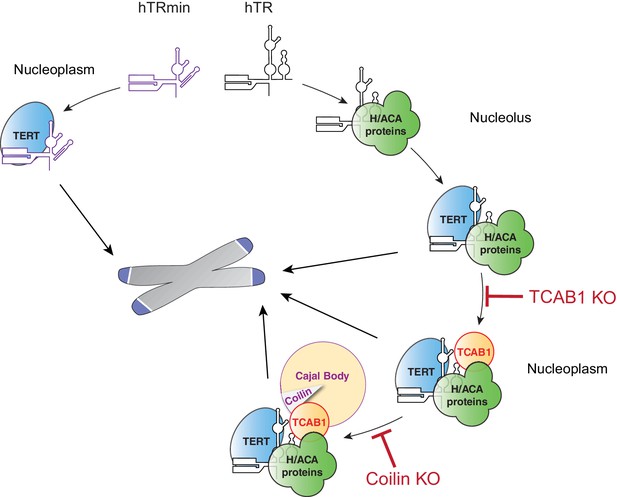
Multiple traffic pathways for human telomerase biogenesis and action at telomeres.
At left, hTRmin telomerase assembles and acts at telomeres without supplemental trafficking instructions. At right, endogenous hTR and TERT are trafficked for their assembly and for telomerase action at telomeres.





