Dopamine signaling tunes spatial pattern selectivity in C. elegans
Figures
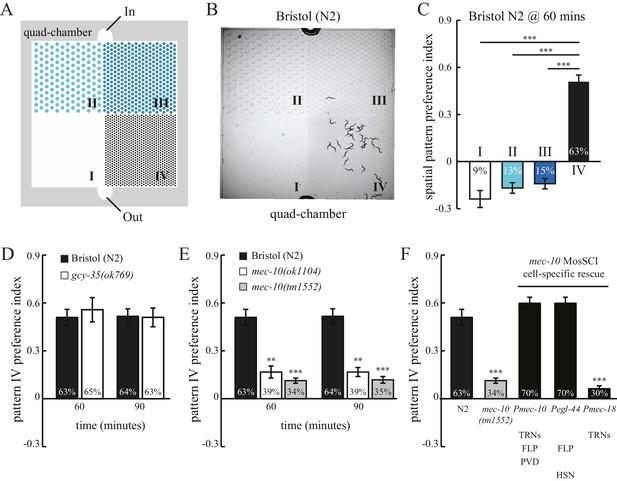
C. elegans exhibits spatial pattern selectivity.
(A) A schematic drawing of the polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) chamber used in the spatial pattern preference assay. Each chamber is divided into four sections (I–IV). The PDMS chamber (designated quad-chamber) is filled with M9 buffer. Worms are loaded with M9 buffer into the chamber through the ‘In’ port. Detailed information about the chamber dimensions is shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1A. (B) C. elegans N2 strain prefers to remain in pattern IV that has the highest density of PDMS pillars. The image was taken 60 min after the worms were loaded into the chamber. (C) The degree of pattern preference was quantified at 60 min in two ways. First, the percentage of worms within each pattern was calculated (shown inside the bars). Second, spatial pattern preference index values for each section were obtained using the following formula: [# of worms in that section – (# of worms in the other three sections/3)] ÷ total # of worms. If worms are equally distributed among the different patterns, then all the index values are zero. If no worm is found in a given pattern, then the index value of that pattern is −0.33. If all worms are found within a single pattern, then the index value of that pattern is 1. n = 12; ***p<0.001 when compared to the index value of pattern IV; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. (D) N2 worms and gcy-35(ok769) mutants show a similar preference for pattern IV. n = 6 for gcy-35 mutants, and n = 10 for N2. (E) Pattern selectivity was significantly impaired in mec-10(ok1104) and mec-10(tm1552) mutant worms; n = 5 for each mec-10 mutant, and n = 10 for N2. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 when compared with N2; Student’s t test. (F) Cell-specific rescue of mec-10(tm1552) mutant worms. Transgenic worms that carry single-copy transgenes (MosSCI; Pmec-10::mec-10cDNA, Pegl-44::mec-10cDNA, or Pmec-18::mec-10cDNA) were examined for their pattern IV selectivity. n = 5 for each transgenic worm strain. ***p<0.001 when compared with N2; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. Error bars denote s.e.m.
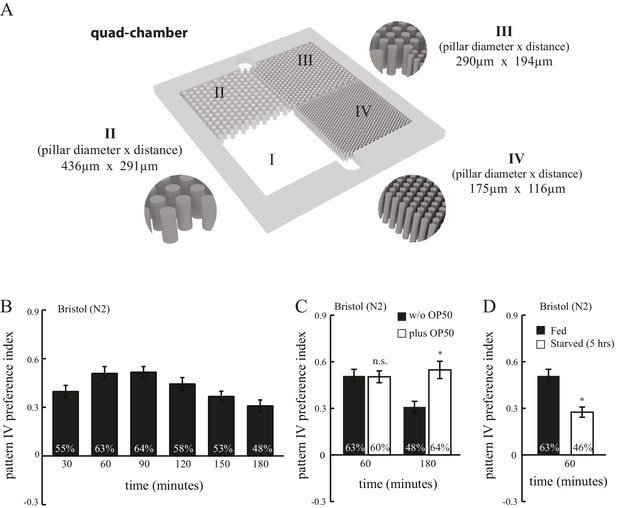
Spatial pattern selectivity is modulated by feeding state.
(A) An illustration showing the dimensions of the quad-chamber. (B) The time course of spatial pattern selection. Spatial pattern preference index values and % of worms in pattern IV were measured at indicated time points, n = 10. (C) The presence of food (E. coli OP50) in the chamber prolonged the selection of pattern IV. n = 10. (D) Starvation (5 hr prior to loading) diminished pattern selectivity of N2 worms. n = 10 for fed worms, and n = 4 for starved worms. *p<0.05; n.s. not significant; Student’s t test. Error bars denote s.e.m.

Spatial pattern selectivity is an individual behavior that relies on mechanosensation and spatial context.
(A) Spatial pattern selectivity is not a social behavior. ‘Single’ – A single N2 worm was loaded into the quad-chamber, and its location was recorded at 60 min. Twenty chambers with single worms were analyzed each time, and experiments were repeated four times. ‘Group’ – A group of twenty N2 worms was loaded into a quad-chamber each time, and experiments were repeated four times. Percentage of worms in pattern IV at 60 min was plotted, and error bars indicate s.e.m. (B) A representative image showing N2 worms in a chamber containing only two patterns; one with no pillars (same as pattern I in the quad-chamber), and the other with the same design as pattern III. (C) N2 worms show preference for pattern III at 60 min after loading, indicating that pattern preference depends on relative rather than absolute pillar density. n = 5; **p<0.01; Student’s t test. error bars denote s.e.m.
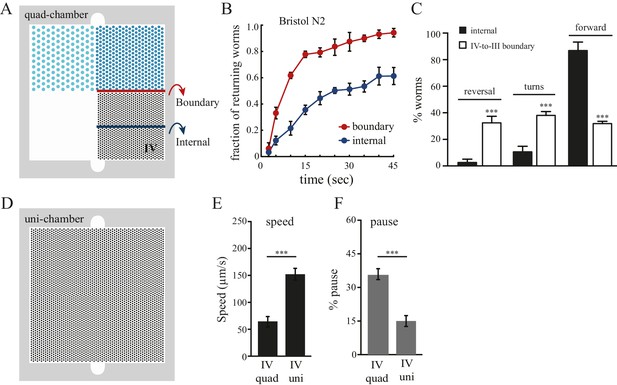
Boundary experience impacts C. elegans spatial pattern selectivity.
Crossing the boundary from pattern IV to pattern III stimulates worms to return to pattern IV. (A) The red line indicates the boundary between patterns IV and III, and the blue line serves as a reference line in the middle of pattern IV. (B) The fraction of worms returning to pattern IV at indicated time points. Time zero indicates the moment that worms cross the red line (from pattern IV to III) or the blue line. Data were collected between 55–65 min after the worms were loaded into the chambers. n = 6. (C) Worms exhibit increased reversal and turning rates when they cross the pattern IV-to-III boundary. n = 6. (D) The design of the uniform chamber (uni-chamber). This chamber has only one pillar array pattern, which is identical to pattern IV in the quad-chamber. (E–F) Worms show different locomotion properties within pattern IV depending on the presence of absence of alternative surrounding patterns. The speed of moving (µm/sec) and the pause rates (%) were quantified from worms within pattern IV in either the quad-chamber or the uni-chamber. The number of independent repeats, n = 6; ***p<0.001; Student’s t test. Error bars denote s.e.m.
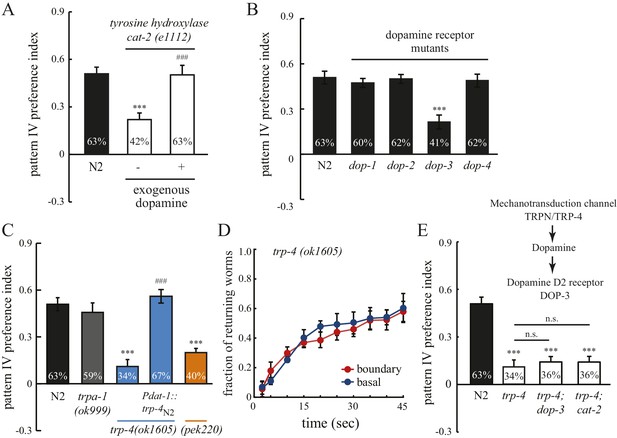
Spatial pattern selectivity of C. elegans requires dopamine signaling.
(A) The requirement for dopamine biosynthesis. Mutant cat-2 worms (e1112) that lack CAT-2 tyrosine hydroxylase show impaired preference for pattern IV, which is rescued by the addition of dopamine (2 mM). The number of independent repeats, n = 10; ***p<0.001 when compared with N2; ###p<0.001 when compared with cat-2(e1112) mutants; Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison tests. (B) The D2 dopamine receptor DOP-3 is required for spatial pattern selectivity. n = 12; ***p<0.001 when compared with N2; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. (C) Preference for pattern IV requires the mechanotransduction TRP-4 channel in dopamine neurons. trpa-1(ok999) mutants were used as controls. Pdat-1 was placed before the trp-4 cDNA to drive specific expression in dopamine neurons. n = 12, ***p<0.001 when compared with N2, ***p<0.001 when compared with N2, ###p<0.001 when compared with trp-4(ok1605) mutants, Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison tests. (D) Mutant worms that lack TRP-4 do not show the enhanced returning behavior at boundaries. n = 6. (E) Double mutant worms (trp-4; dop-3 and trp-4; cat-2) exhibited identical defects as the trp-4 single mutant, suggesting that TRP-4, dopamine, and DOP-3 function in the same pathway. n = 12; ***p<0.001 when compared with N2; n.s.: not significant compared with trp-4(ok1605); Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison tests. All data were collected 60 min after the worms were loaded into the chambers. Error bars denote s.e.m.

The design strategy for a trp-4 allele (pek220).
A disruption cassette that contains gfp::tbb-2utr and Prps-0::hygR::unc-54utr was inserted into trp-4 exon 2, which results in a deletion and an early stop codon that put trp-4 out-of-frame after the amino acid residue 53.
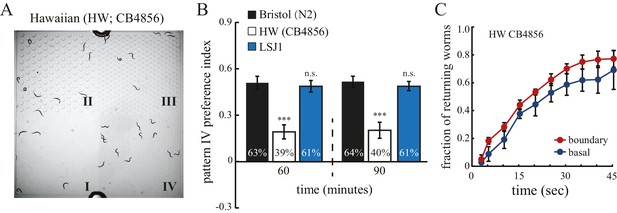
Hawaiian strain does not select pattern IV.
(A) The Hawaiian CB4856 strain (HW) does not show significant preference for pattern IV of the quad-chamber. The representative image was taken at 60 min after the worms were loaded into the chamber. (B) Quantification of the preference for pattern IV of N2, HW, and LSJ1 (a sibling of the N2 strain) worms in the quad-chamber at 60 and 90 min. n = 12. (C) HW CB4856 worms do not show enhanced returning at boundaries. n = 6. Data were collected as described in Figure 2B.
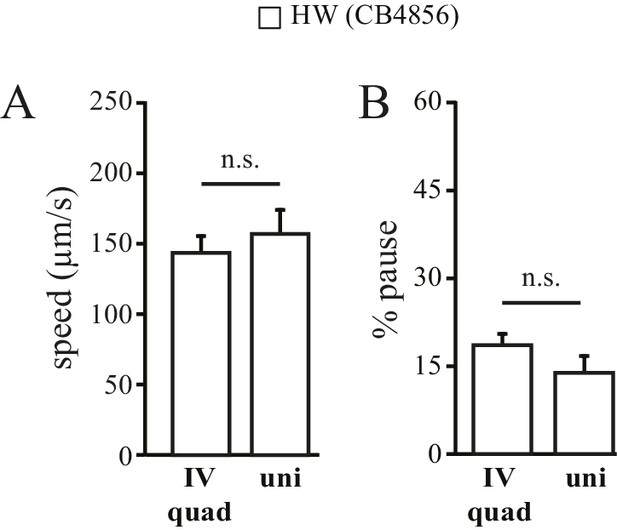
HW worms show identical locomotory behavior in quad- and uni- chambers.
Traveling speed (A) and % pause (B) were quantified as described in Figure 1. n = 5; n.s.: not significant.
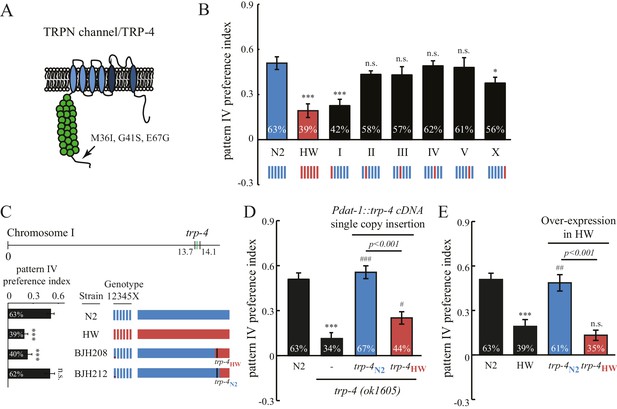
Polymorphisms in the mechanotransduction TRP-4 channel contribute to the variation of spatial pattern selectivity.
(A) A cartoon illustrating the amino acid substitutions (M36I, G41S, and E67G) in HW TRP-4. (B) Chromosomes I and X were linked to altered spatial pattern selectivity between N2 and HW strains. Hybrid N2/HW strains carrying one HW chromosome (red) and five N2 chromosomes (blue) were quantified for spatial preference at 60 min. n = 12 for N2 and HW worms; n = 10 for worms with chromosome substitutions. (C) Recombinant inbred strains harboring N2 and HW trp-4 genes showed distinct behavior in the spatial pattern preference test at 60 min. n = 12. Estimated regions of recombination (around 13.7 Mb in BJH208 and 14.1 Mb in BJH212) are indicated in the upper panel. The BJH208 strain that carries the N2 trp-4 gene shows enrichment, but the BJH212 strain with HW trp-4 does not (lower panel). (D) Transgenic trp-4(ok1605) worms expressing single-copy N2 or HW TRP-4 in dopaminergic neurons (Pdat-1::trp-4 cDNA) were tested in the spatial pattern preference assay. n = 12 for N2 and trp-4(ok1605) worms, n = 10 for worms with the transgenes. ***p<0.001, when compared to N2; ###p<0.001 and #p<0.05 when compared to trp-4(ok1605) mutants. Error bars denote s.e.m. (E) Transgenic HW worms carrying extrachromosomal arrays with either N2 or HW trp-4 cDNA driven by Pdat-1 were examined in the spatial pattern preference assay. n = 12. Data were collected 60 min after worm loading (unless specified otherwise). One-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple comparison tests were used for statistic analyses in Figure 5. ***p<0.001 when compared to N2; ##p<0.01 when compared to HW worms. Error bars denote s.e.m.
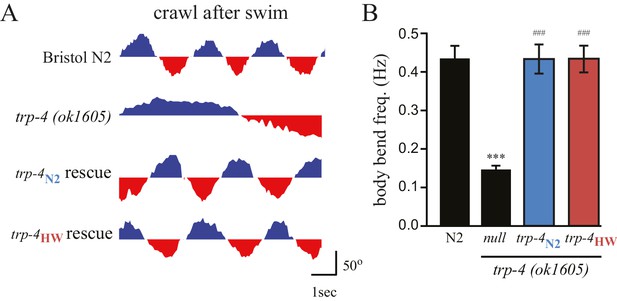
Both N2 and HW trp-4 cDNAs rescue defects in the swim-to-crawl transition of trp-4(ok1605) mutant worms.
(A) The swim-to-crawl transition was analyzed as described in previous studies (Vidal-Gadea et al., 2011). Blue: dorsal body bend. Red: ventral body bend. (B) Transgenic trp-4(ok1605) worms carrying either N2 or HW TRP-4 show normal body bend frequency at the swim-to-crawl transition. n = 16 for each strain, ***p<0.001 when compared to N2; ###p<0.001 when compared with trp-4(ok1605) mutants, Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison tests. Error bars denote s.e.m.
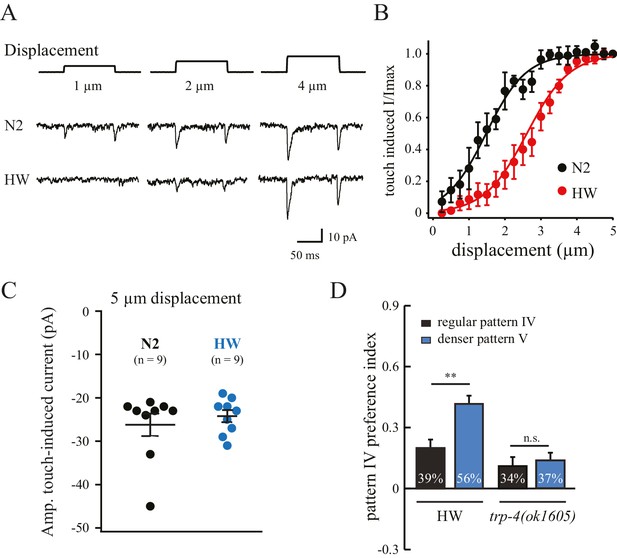
Polymorphisms in TRP-4 alter mechanosensitivity of dopaminergic neurons.
(A) Representative traces of mechanoreceptor currents in wild type N2 and HW dopaminergic CEP neurons in response to small mechanical displacements (1 μm, 2 μm and 4 μm). Whole-cell patch clamp recordings (holding potential at −75 mV) were carried out at 20°C. (B) Stimulus-current curves of TRP-4 mechanogated on-currents in response to mechanical displacement. Data were fitted with a Boltzmann function. For N2 worms, the half-maximal displacement is 1.48 ± 0.04 µm and the slope factor is 0.56 ± 0.04 µm. For HW worms, the half-maximal displacement is 2.71 ± 0.03 µm, the slope factor is 0.58 ± 0.03 µm. n = 8 for N2 and n = 6 for HW; **p<0.01 and *p<0.05 when compared with HW worms. (C) A comparison of absolute current amplitudes in N2 and HW worms (at 5 µm displacements, n = 9 for N2 and n = 9 for HW). (D) Increases in pillar density in pattern IV enhanced HW aggregation but had little impact on trp-4(ok1605) mutant worms. Denser pattern V consisted of a pillar layout of 194 µm (pillar diameter) x 95 µm (distance between pillars). **p<0.01. Error bars denote s.e.m.
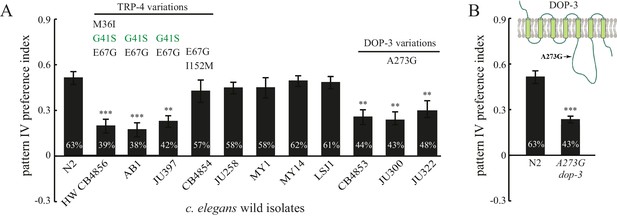
Natural variations in either TRP-4 or DOP-3 tune spatial pattern selectivity in C. elegans.
(A) Spatial preference of C. elegans natural isolates was quantified using regular quad-chambers. n = 12 for each strain, ***p<0.001 and **p<0.01 when compared to N2; Dunnett's multiple comparison tests. (B) CRISPR/Cas9 edited N2 worms carrying the A273G substitution and wild type N2 worms were compared using the spatial pattern preference assay. n = 12; ***p<0.001, Student’s t test. Data from the spatial pattern preference assay were collected at 60 min. Error bars denote s.e.m.





