Evidence from a natural experiment that malaria parasitemia is pathogenic in retinopathy-negative cerebral malaria
Figures
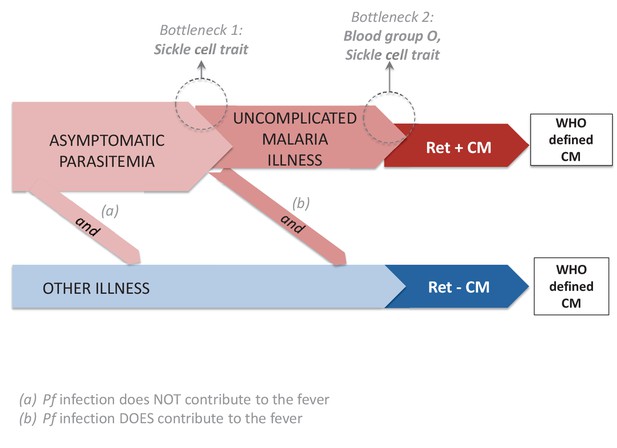
Potential pathways to clinically-defined cerebral malaria and genetic bottle necks.
There are three potential pathogenetic routes to WHO-defined cerebral malaria (CM). The first, shown in red, is the classical pathway: a malaria infection evolves into retinopathy-positive (Ret+) CM. The second and third possibilities produce retinopathy-negative (Ret-) CM. In (a) the coma is entirely the result of another etiology and the malaria parasitemia is incidental. In (b), the coma is a product of the interaction between the malaria parasitemia and an additional cause (or causes) of coma. Sickle cell trait is underrepresented in patients with Ret+ and Ret- cerebral malaria (CM) because of the bottleneck at the transition between 'malaria infection' (asymptomatic malaria) and 'malaria disease' (uncomplicated malaria). Blood group O is underrepresented in patients with Ret+ CM, but not in those with Ret- CM. Taken together, the results for sickle cell trait and blood group O suggest that some Ret- CM cases occur through pathway (b) (because sickle cell trait is underrepresented in Ret- CM) and that malaria parasites contribute to the pathogenesis of these cases, and that sickle cell trait reduces the pathogenetic potential of malaria infection for Ret- CM but do not provide evidence that blood group O reduces the pathogenetic potential of malaria infection for Ret- CM.
Tables
Characteristics of study participants at admission, Means ± SD for continuous variables. The proportions of missing data are shown in Appendix 1. There are 3704 community controls, but their characteristics are not shown because only their genotypes and not their clinical characteristics were collected. Bold denotes p-value less than 0.05.
| Retinopathy Positive CM | Retinopathy Negative CM | Non-Malaria Hospital Controls | p-value, Ret + vs. Ret - | p-value, Ret + vs. Controls | p-value, Ret – vs. Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 438 | 288 | 204 | |||
| Female | 50% | 52% | 43% | 0.54 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| Age (months) | 40 ± 26 | 44 ± 30 | 46 ± 30 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.53 |
| Mid-upper arm circumference (cm) | 14.9 ± 1.6 | 15.0 ± 1.7 | 14.8 ± 1.8 | 0.72 | 0.53 | 0.39 |
| Weight (kg) | 12 ± 4 | 13 ± 5 | 13 ± 6 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.74 |
| Height (cm) | 90 ± 16 | 91 ± 17 | 91 ± 20 | 0.30 | 0.40 | 1.00 |
| Temperature (°C) | 38.6 ± 1.2 | 38.4 ± 1.4 | 37.7 ± 1.5 | 0.03 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Febrile (Temperature≥ 37.5°C) | 81% | 77% | 56% | 0.23 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Pulse rate – beats/minute | 152 ± 26 | 148 ± 24 | 139 ± 28 | 0.06 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Respiratory rate – breaths/minute | 47 ± 15 | 45 ± 13 | 45 ± 15 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.93 |
| Liver size – cm below costal margin | 2.0 ± 1.9 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 1.1 ± 1.7 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.04 |
| Spleen size – cm below costal margin | 1.7 ± 2.1 | 1.6 ± 2.1 | 0.9 ± 1.6 | 0.56 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Deep breathing | 33% | 25% | 30% | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.18 |
| Blantyre Coma Score: 0 1 2 3 4 5 | 14% 35% 49% 1% 0% 0% | 19% 38% 43% 0% 0% 0% | 28% 40% 23% 3% 0% 5% | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.90 |
| CSF opening pressure – mm of water | 176 ± 75 | 152 ± 82 | 176 ± 99 | 0.001 | 0.96 | 0.07 |
| Hematocrit -- % | 19.8 ± 6.9 | 28.2 ± 7.5 | 28.1 ± 9.6 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.86 |
| Platelets | 81,220± 67,219 | 161,600± 124,747 | 248,400± 162,287 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.86 |
| Malaria parasitemia – parasites/mm3 | 230,500± 321,924 | 180,500± 280,676 | 3,619± 28,917 | 0.03 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| White blood cells | 13,040± 9163 | 13,020± 8923 | 13,930± 9544 | 0.97 | 0.29 | 0.31 |
| Lactate – mmol/liter | 8.6 ± 5.0 | 7.3 ± 4.4 | 5.5 ± 3.9 | 0.05 | <0.001 | 0.007 |
| Blood glucose – mmol/liter | 6.1 ± 3.9 | 6.8 ± 4.4 | 7.6 ± 5.3 | 0.03 | <0.001 | 0.05 |
| CSF white cell count – % ≥ 5 | 16% | 20% | 24% | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.37 |
| Blood culture positive for pathogen | 4% | 2% | 14% | 0.51 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| HIV positive | 18% | 17% | 15% | 0.91 | 0.59 | 0.66 |
| Outcomes | ||||||
| Discharge outcome: Full recovery Neurological Sequalae Died | 69% 10% 21% | 78% 10% 12% | 57% 15% 28% | 0.003 | 0.01 | <0.001 |
The top panel displays sickle cell trait (HbAS) proportions in retinopathy-positive (Ret+) cerebral malaria (CM), retinopathy-negative (Ret-) CM and control groups. The bottom panel displays ABO blood group gene proportions in Ret+ CM, Ret- CM and control groups. The last two rows of each panel display the odds ratios comparing controls to true Ret+ and true Ret- CM groups, which account for the fact that there is measurement error in observed retinopathy status (false discovery rate = 0.07 and false omission rate = 0.05).
| Ret+ CM | Ret- CM | Non-malaria hospital controls | Community controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 438 | 287 | 192 | 3657 |
| HbAS* | 0 | 1 | 8 | 175 |
| HbAA | 437 | 286 | 184 | 3482 |
| Proportion of HbAS | 0 | .003 | .042 | .048 |
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-malaria hospital controls vs. community controls | 0.87 (0.36, 1.78) | |||
| Controls vs. true Ret- CM | 14.33 (3.21, 257.24) | |||
| Controls vs. true Ret+ CM | 1223.22 (9.87, ) | |||
| Ret+ CM | Ret- CM | Non-malaria hospital controls | Community controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 433 | 286 | 199 | 3543 |
| Blood Group O | 175 | 135 | 96 | 1739 |
| Blood Group A, B or AB | 258 | 151 | 103 | 1804 |
| Proportion of Blood Group O | .404 | .472 | .482 | .491 |
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-malaria hospital controls vs. community controls | 0.97 (0.72, 1.30) | |||
| Controls vs. true Ret- CM | 1.03 (0.83, 1.29) | |||
| Controls vs. true Ret+ CM | 1.23 (1.01, 1.50) | |||
-
* HbAS (sickle cell trait) means that that the person has one normal and one abnormal copy of the hemoglobin beta gene. HbAA means the person has two normal copies of the hemoglobin beta gene.
Inferences for lower bound on malaria parasitemia attributable fraction of Ret- CM (fraction of Ret- CM cases that would be prevented if malaria parasitemia were to be eliminated) under the sufficient-component cause model based on Figure 1 presented in Materials and methods. Inferences under the main model and sensitivity analyses that vary the effect of HbAS on malaria parasitemia incidence rate, the false discovery rate () and the false omission rate () for malarial retionopathy.
| Effect of HbAS on malaria parasitemia incidence rate | Lower bound on malaria parasitemia attributable fraction of Ret- CM Estimate (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Model | |||
| No Effect | .07 | .05 | .93 (.68, 1) |
| Sensitivity Analyses | |||
| Reduce 10% | .07 | .05 | .92 (.64, 1) |
| Reduce 41% | .07 | .05 | .88 (.46, 1) |
| No Effect | .30 | .11 | .94 (.75, 1) |
| Reduce 10% | .30 | .11 | .94 (.72, 1) |
| Reduce 41% | .30 | .11 | .91 (.58, 1) |
| No Effect | 0 | .11 | .92 (.62, 1) |
| Reduce 10% | 0 | .11 | .91 (.58, 1) |
| Reduce 41% | 0 | .11 | .86 (.37, 1) |
| No Effect | .30 | 0 | .95 (.77, 1) |
| Reduce 10% | .30 | 0 | .94 (.74, 1) |
| Reduce 41% | .30 | 0 | .91 (.61, 1) |
| No Effect | 0 | 0 | .92 (.66, 1) |
| Reduce 10% | 0 | 0 | .92 (.63, 1) |
| Reduce 41% | 0 | 0 | .87 (.44, 1) |
Sample sizes.
| Retinopathy-positive CM | Retinopathy-negative CM | Non-malaria hospital controls | Community controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | 438 | 288 | 204 | 3704 |
Missing data proportions for genetic traits.
| Retinopathy-positive CM | Retinopathy-negative CM | Non-malaria hospital controls | Community controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sickle Cell Trait | .002 | 0 | .054 | .010 |
| Blood Group | .011 | .003 | .025 | .043 |
Missing data proportions for demographic and clinical variables.
| Retinopathy-positive CM | Retinopathy-negative CM | Non-malaria hospital controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | .018 | .021 | .005 |
| Age (months) | 0 | 0 | .005 |
| Mid-upper arm circumference (cm) | .016 | .014 | .054 |
| Weight (kg) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Height (cm) | .009 | .024 | .034 |
| Temperature (°C) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pulse rate – beats/minute | .002 | 0 | .010 |
| Respiratory rate – breaths/minute | 0 | 0 | .005 |
| Liver size – cm below costal margin | .009 | .024 | .010 |
| Spleen size – cm below costal margin | .005 | .014 | .010 |
| Deep breathing | .007 | .021 | 0 |
| Blantyre Coma Score: | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CSF opening pressure – mm of water | .420 | .330 | .623 |
| Hematocrit -- % | .009 | .024 | .034 |
| Platelets | .153 | .160 | .132 |
| Malaria parasitemia – parasites/mm3 | .039 | .042 | .025 |
| White blood cells | .082 | .097 | .118 |
| Lactate – mmol/liter | .653 | .753 | .564 |
| Blood glucose – mmol/liter | .014 | .003 | 0 |
| CSF white cell count – % ≥ 5 | .277 | .170 | .275 |
| Blood culture positive for pathogen | .039 | .024 | .059 |
| HIV positive | .144 | .153 | .353 |
| Discharge outcome | 0 | .007 | 0 |
Odds ratio comparing community controls to true Ret+ CM and Ret- CM groups, which account for the fact that there is measurement error in observed retinopathy status (false discovery rate = 0.07 and false omission rate = 0.05). The p-values are two-sided p-values for testing that the odds ratio equals 1.
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| HbAS | ||
| Controls vs. true Ret- CM | 14.43 (3.23, 258.94) | <0.0001 |
| Controls vs. true Ret+ CM | 1234.96 (9.93,) | <0.0001 |
| BGO | ||
| Controls vs. true Ret- CM | 1.03 (0.83, 1.29) | 0.79 |
| Controls vs. true Ret+ CM | 1.23 (1.01, 1.51) | 0.04 |





