CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis invalidates a putative cancer dependency targeted in on-going clinical trials
Figures
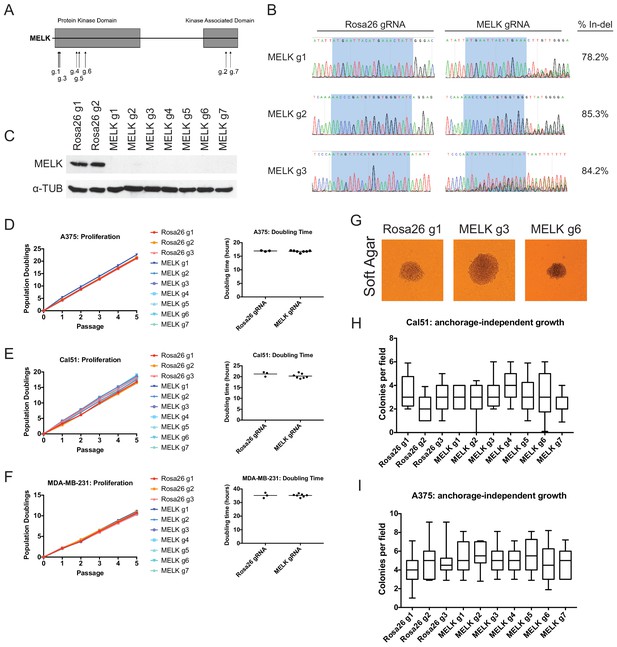
Mutation of the MELK kinase domain does not affect cancer cell proliferation or anchorage-independent growth.
(A) Domain structure of MELK and locations of the sequences targeted by 7 MELK gRNAs. (B) Genomic DNA was purified from the indicated population of MDA-MB-231 cells and the targeted loci were amplified by PCR. Percent indel formation was estimated using TIDE analysis. The highlighted region indicates 20 nucleotides or 15 nucleotides of the sequence recognized by the guide RNA. Other sequence traces are presented in Figure 1—figure supplements 1–3. (C) Western blot analysis of GFP+ MDA-MB-231 cells using the Abcam ab108529 MELK antibody. Alpha-tubulin levels were analyzed as a loading control. (D–F) Proliferation and doubling time analysis of A375, Cal51, and MDA-MB-231 cell lines transduced with 3 Rosa26 gRNAs or with 7 MELK gRNAs. (G) Images of colonies from the indicated Cal51 strains grown in soft agar. (H–I) Quantification of anchorage-independent growth in Cal51 or A375 cells transduced with the indicated gRNA. For each assay, colonies were counted in at least 15 fields under a 10x objective. Boxes represent the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles of colonies per field, while the whiskers represent the 10th and 90th percentiles.
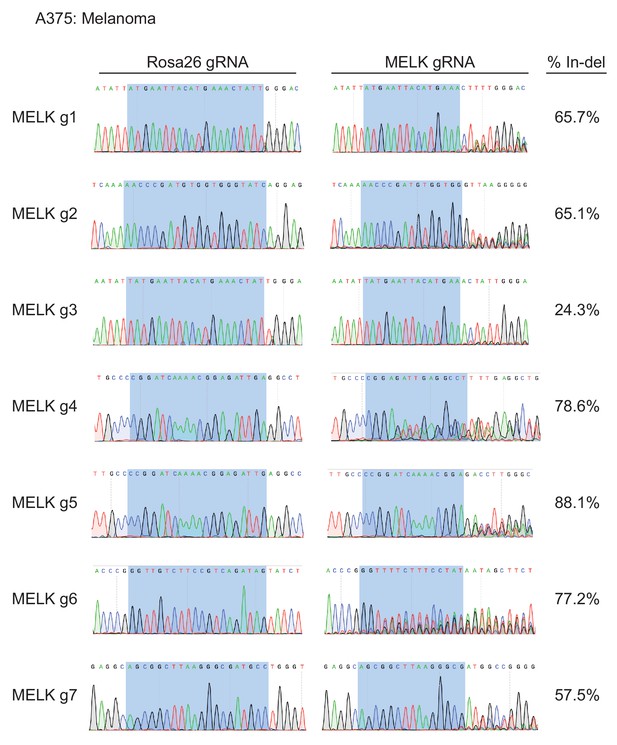
Mutation of MELK using seven different guide RNAs in the A375 melanoma cell line.
Following sorting of GFP+ populations, genomic DNA was purified from each cell line and the targeted loci were amplified by PCR. The amplified fragments were sequenced using the forward and reverse PCR primers (Supplementary file 2), and indel formation was estimated using TIDE analysis. The highlighted region indicates 20 nucleotides or 15 nucleotides of the sequence recognized by the guide RNA.
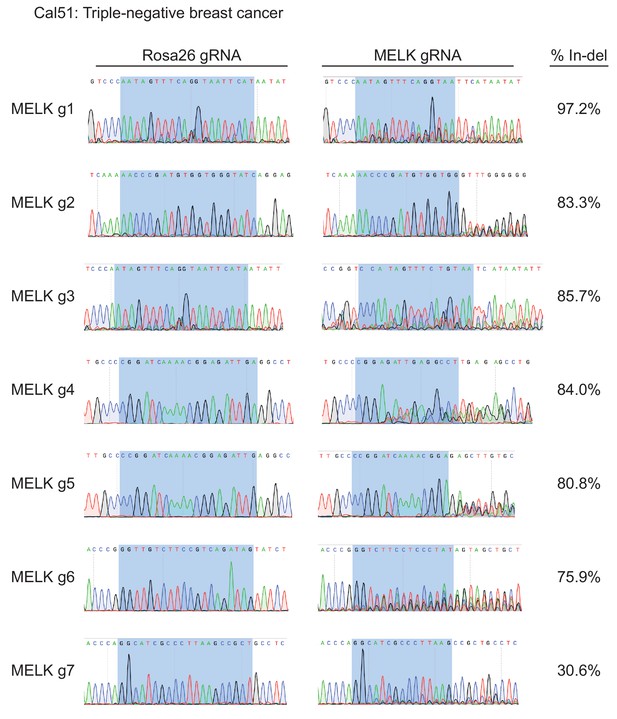
Mutation of MELK using seven different guide RNAs in the Cal51 triple-negative breast cancer cell line.
Following sorting of GFP+ populations, genomic DNA was purified from each cell line and the targeted loci were amplified by PCR. The amplified fragments were sequenced using the forward and reverse PCR primers (Supplementary file 2), and indel formation was estimated using TIDE analysis. The highlighted region indicates 20 nucleotides or 15 nucleotides of the sequence recognized by the guide RNA. The heterogeneity in sequence reads at MELK g1 and MELK g3 in the Rosa26 gRNA line was observed in multiple samples, and likely represent polymorphisms present in the Cal51 population.
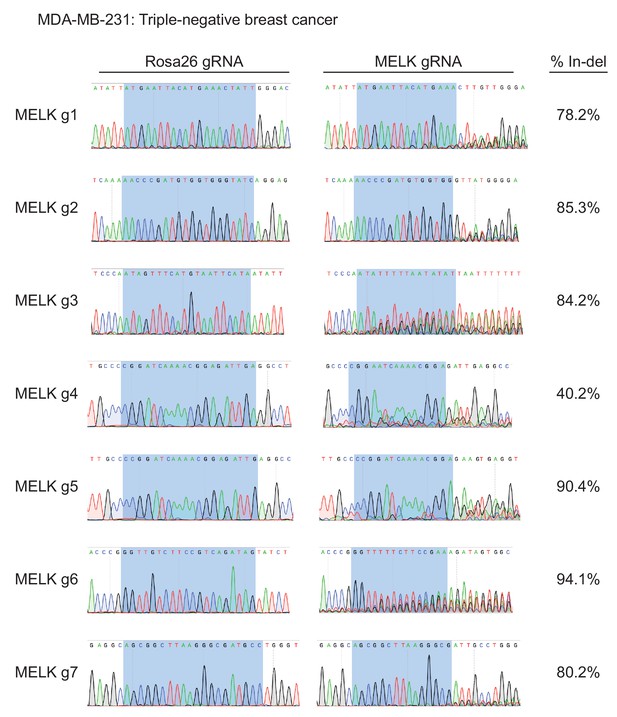
Mutation of MELK using seven different guide RNAs in the MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell line.
Following sorting of GFP+ populations, genomic DNA was purified from each cell line and the targeted loci were amplified by PCR. The amplified fragments were sequenced using the forward and reverse PCR primers (Supplementary file 2), and indel formation was estimated using TIDE analysis. The highlighted region indicates 20 nucleotides or 15 nucleotides of the sequence recognized by the guide RNA.
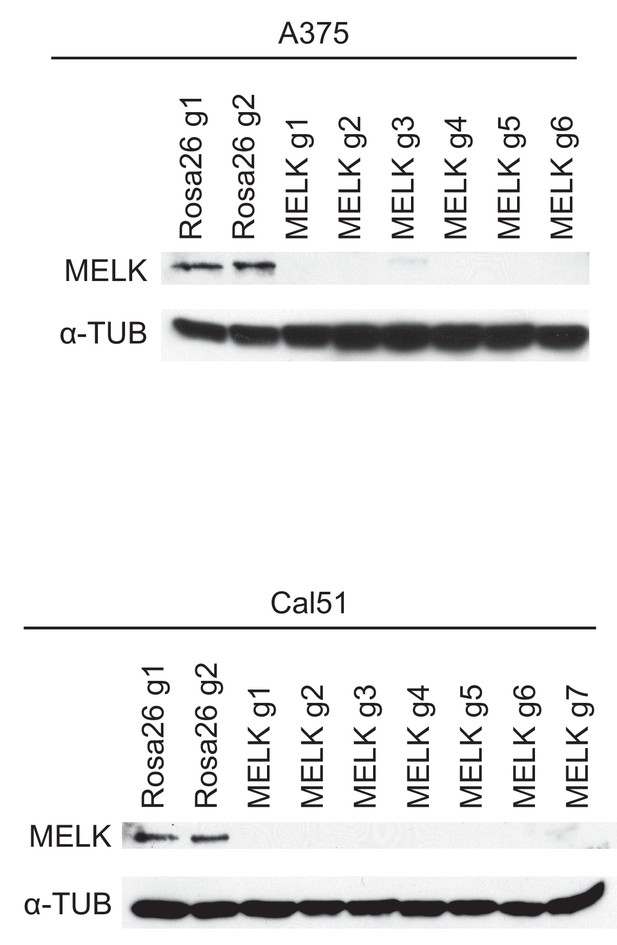
Western blot analysis of MELK-disrupted cell populations.
Following sorting of GFP+ populations, whole-cell lysate was collected and analyzed for MELK expression using the Abcam ab108529 antibody. Alpha-tubulin was analyzed as a loading control.
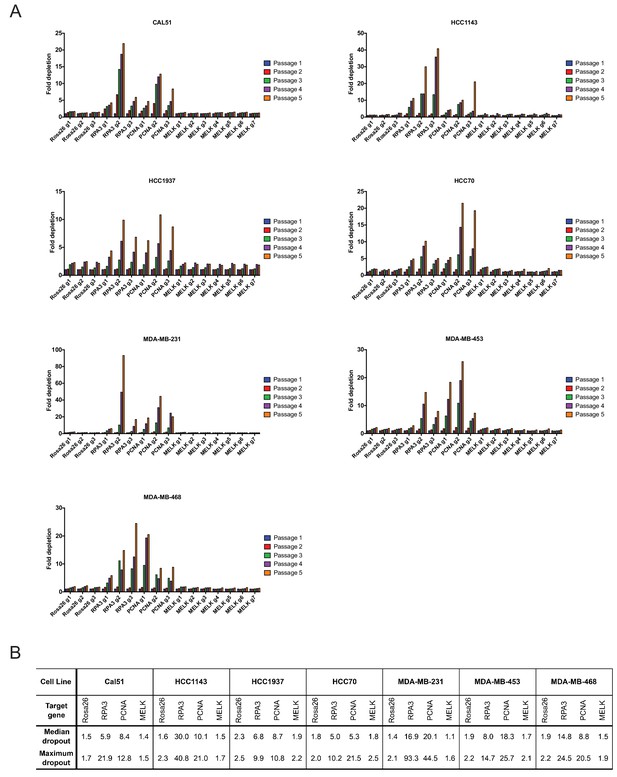
Guide RNAs targeting MELK fail to drop out in triple-negative breast cancer cell line competition experiments.
(A) The fold change in the percentage of GFP+ cells, relative to the percentage of GFP+ cells at passage 1, is displayed for seven triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. (B) A table summarizing the results presented in (A) is displayed.
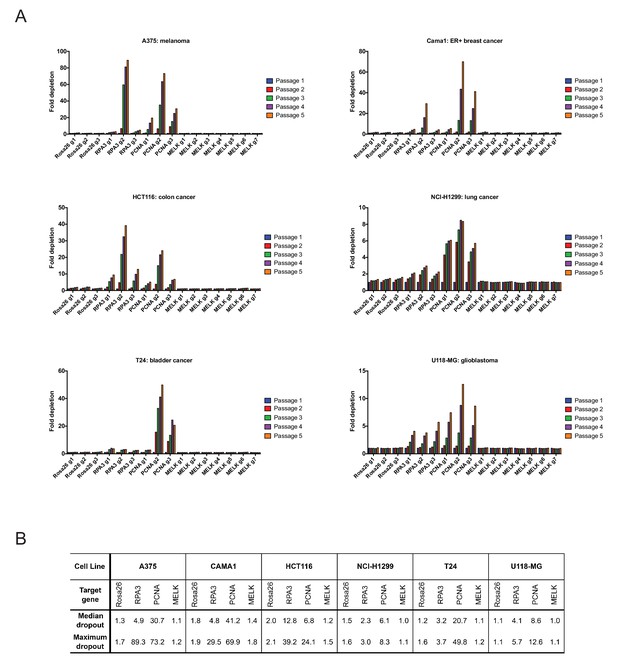
Guide RNAs targeting MELK fail to drop out in several cancer cell lines.
(A) The fold change in the percentage of GFP+ cells, relative to the percentage of GFP+ cells at passage 1, is displayed for six additional cancer cell lines. (B) A table summarizing the results presented in (A) is displayed.
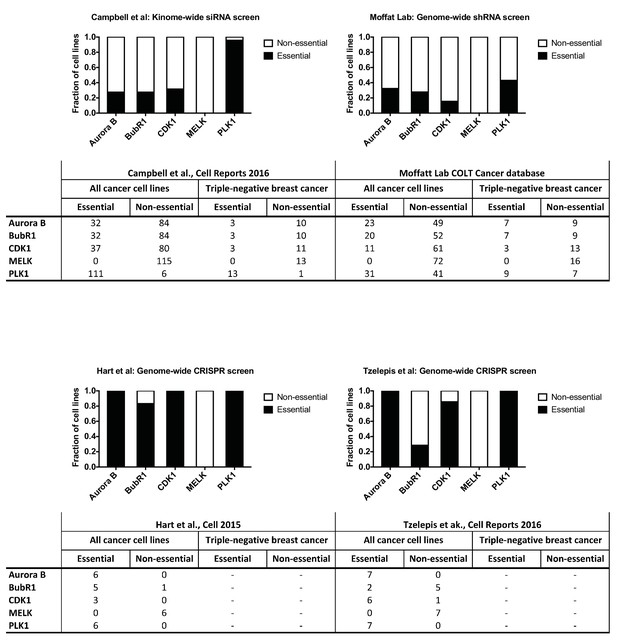
Unbiased screens do not identify MELK as a cancer dependency.
Gene essentiality data were examined from a kinome-wide siRNA screen (Campbell et al., 2016), a genome-wide shRNA screen (Marcotte et al., 2012; Hart et al., 2014), and two genome-wide CRISPR screens (Hart et al., 2015; Tzelepis et al., 2016). In the kinome-wide screen, a gene with a Z score < −2 was considered essential. In the Hart et al. genome-wide CRISPR screen, a gene with a Bayes Factor >5 was considered essential. In the genome-wide shRNA screen and the Tzelepis et al. CRISPR screen, a threshold of p<0.01 was used to identify essential genes.
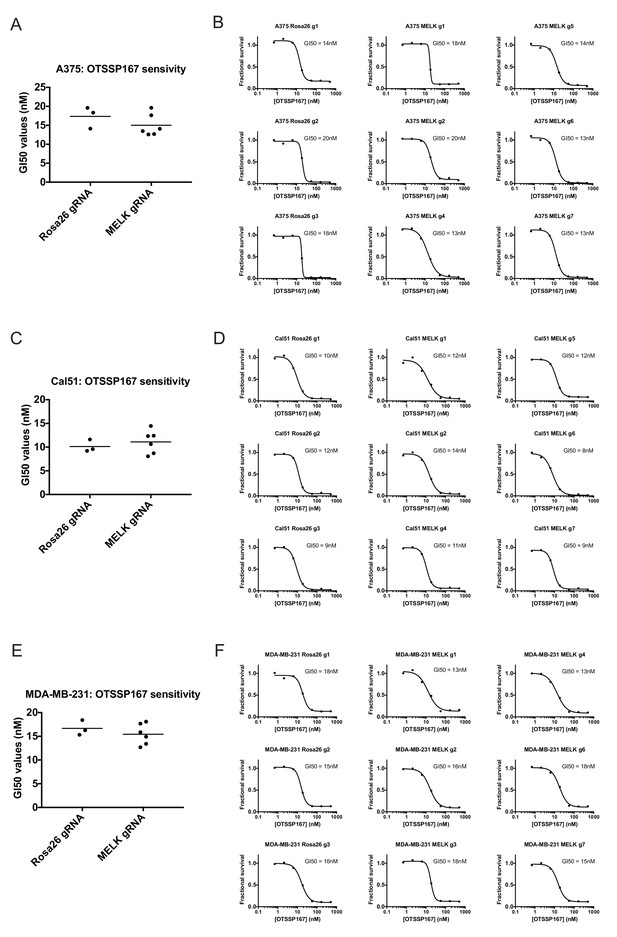
Mutating MELK does not affect OTS167 sensitivity.
(A) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of A375 cells harboring guide RNAs targeting Rosa26 or MELK. (B) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated A375 cell lines. (C) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of Cal51 cells harboring guide RNAs targeting Rosa26 or MELK. (D) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated Cal51 cell lines. (E) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of MDA-MB-231 cells harboring guide RNAs targeting Rosa26 or MELK. (F) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated MDA-MB-231 cell lines.
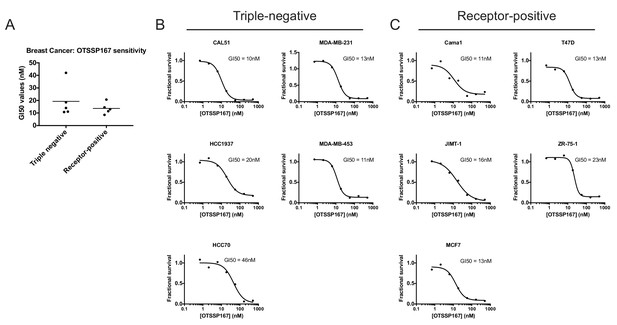
Receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines are sensitive to OTS167.
(A) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of various breast cancer cell lines. (B and C) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated cell lines. Note that the summary values in (A) represent averages from 2 or three replicate experiments per cell line, while individual replicate experiments are displayed in (B) and (C).
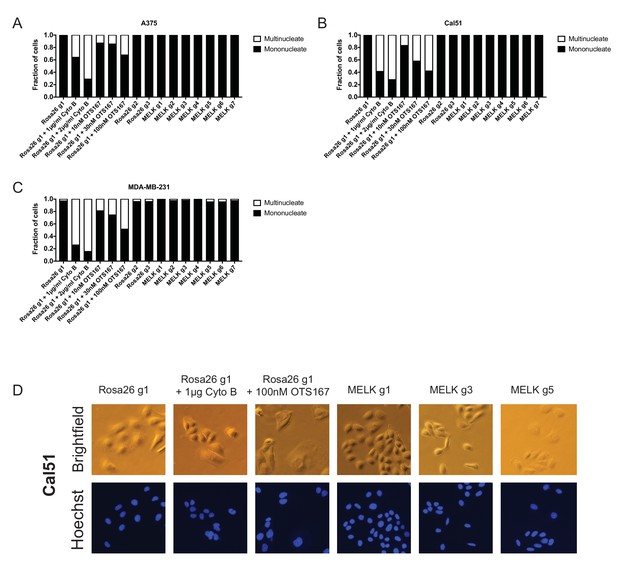
OTS167 treatment, but not MELK mutation, causes the accumulation of multinucleate cells.
(A–C) Cells were either untreated or treated with the indicated drug for 24 hr. Subsequently, cells were stained with Hoechst dye and at least 200 cells for each condition were examined. (D) Representative images of Cal51 cells stained with Hoechst.
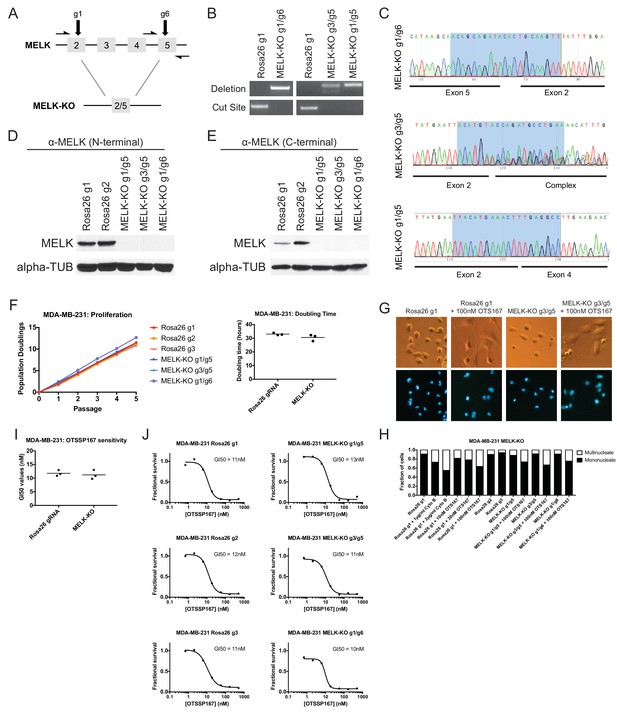
MELK-knockout cell lines proliferate at normal rates and remain sensitive to OTS167.
(A) Schematic of exons in the MDA-MB-231 MELK-KO g1/g6 knockout line. Half-arrows indicate positions of either cut-site or deletion-spanning primers used to screen these colonies. Primer sequences are presented in Supplementary file 2. (B) PCR validation of 3 independent MELK-KO clones. Note that amplification of the MELK-KO g3/g5 DNA with deletion-spanning primers yielded deletion products of at least two distinct sizes. (C) Sanger sequence validation of 3 independent MELK-KO clones. While MELK-KO g1/g6 and g1/g5 harbor a single homozygous deletion, MELK-KO g3/g5 harbors at least two distinct deletions. (D) Western blot analysis of MELK-KO clones using an antibody that recognizes a region in the N-terminal kinase domain (Abcam ab108529). (E) Western blot analysis of MELK-KO clones using an antibody that recognizes a region in the C-terminal domain (Cell Signal 2274S). (F) Proliferation analysis and doubling time measurements of MELK-KO cell lines. (G) Representative images of Rosa26 gRNA or MELK-KO clones either untreated or treated with 100 nM OTS167 and then stained with Hoechst dye. (H) The indicated cell lines were either left untreated or were treated with the cytokinesis inhibitor cytochalasin B or with OTS167. Cells were then stained with Hoechst dye. For each experiment, at least 200 cells were counted. (I) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of either MDA-MB-231 Rosa26 gRNA or MELK-KO clones. (J) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated cell lines.
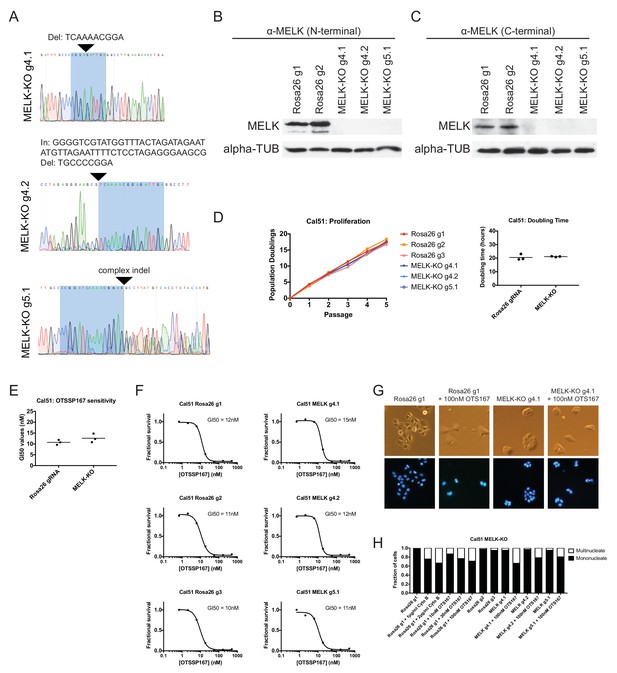
Generation and analysis of Cal51 MELK-KO cell lines.
(A) Sanger sequencing of 3 independent Cal51 MELK-KO clones transduced with single gRNAs targeting the MELK kinase domain. The highlighted regions indicate bases recognized by the gRNA. (B) Western blot analysis of MELK-KO clones using an antibody that recognizes a region in the N-terminal kinase domain (Abcam ab108529). (C) Western blot analysis of MELK-KO clones using an antibody that recognizes a region in the C-terminal domain (Cell Signal 2274S). (D) Proliferation analysis and doubling time measurements of MELK-KO cell lines. (E) Summary of GI50 values from OTS167 treatment of either Cal51 Rosa26 gRNA or MELK-KO clones. (F) 7 point dose-response curves of OTS167 in the indicated cell lines. (G) Representative images of Rosa26 gRNA or MELK-KO clones either untreated or treated with 100 nM OTS167 and then stained with Hoechst dye. (H) The indicated cell lines were either left untreated or were treated with the cytokinesis inhibitor cytochalasin B or with OTS167. Cells were then stained with Hoechst dye. For each experiment, at least 200 cells were counted.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Guide RNA sequences.
The sequences of every guide RNA and the protein domain targeted by the guide RNAs are displayed.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24179.016
-
Supplementary file 2
PCR primers to amplify MELK gRNA cut sites and deletions.
The sequences of PCR primers used in this manuscript are displayed.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24179.017





