Effects of myosin variants on interacting-heads motif explain distinct hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy phenotypes
Figures
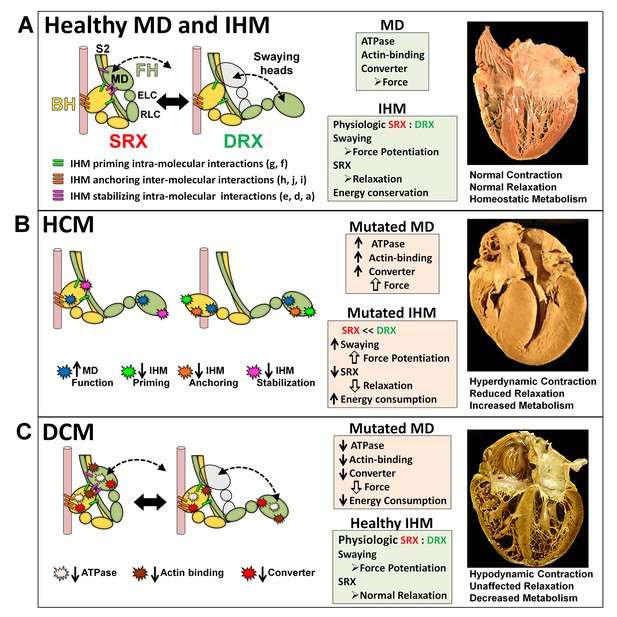
The molecular pathogenesis of hypertrophic (HCM) and dilated (DCM) cardiomyopathy assessed in the context of the myosin interacting-heads motif (IHM) paradigm.
Myosin interactions involved in IHM assembly and myosin motor domain (MD) functions that are altered by PVs and LPVs are depicted. (A) Relaxed healthy cardiac muscle contains myosin heads populations in the super-relaxed (SRX) state (left) with lowest ATP consumption and a disordered relaxed (DRX) state (right) with swaying free heads that generate force with higher ATP consumption. The population of cardiac myosins in SRX is more stable than in skeletal muscle (Hooijman et al., 2011 and see Material and methods) which supports physiologic contraction and relaxation, energy conservation, and normal cardiac morphology. (B) HCM myosin variants both alter residues involved in MD functions (causing increased biophysical power [Tyska et al., 2000]), and destabilize IHM interactions (particularly those with altered electrostatic charge). Reduced populations of myosins in the SRX state and increased populations of myosins in DRX as well as enhanced MD properties will result in increased contractility, decreased relaxation, and increased ATP consumption, the three major phenotypes observed in HCM hearts. Compensatory signals may promote ventricular hypertrophy. (C) MYH7 DCM variants have modest effects on IHM interactions but substantially reduce MD functions, particularly nucleotide binding, resulting in reduced ATP consumption and sarcomere power (Schmitt et al., 2006), with minimal impact on relaxation and overall diminished contractility. Compensatory signals result in ventricular dilatation to maintain circulatory demands in DCM hearts.
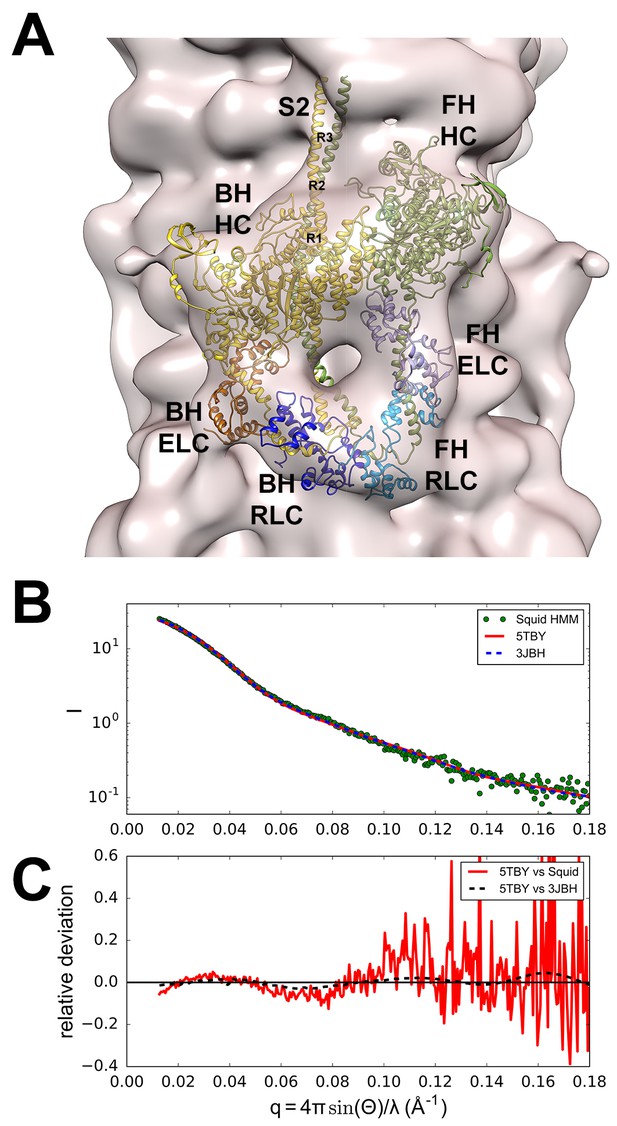
Structure of the human β-cardiac myosin interacting-heads motif.
(A) Quasi-atomic homologous model of human β-cardiac myosin interacting-heads motif (IHM) PDB 5TBY composed of blocked (BH) and free (FH) heads, fitted to the human cardiac thick filament 3D-map EMD-2240 (Al-Khayat et al., 2013). (Also see Video 1.) Domains and residue equivalence are provided in Supplementary file 1. Sarcomere proteins depicted are MHC (BH: gold, FH: olive), essential light chain (ELC associated with BH: brown, FH: purple), and regulatory light chain (RLC associated with BH: dark blue, FH: blue). The three negatively-charged rings in the S2 are labeled R1, R2 and R3. (B) Calculated small angle X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) profile of PDB 5TBY (red line) matches the experimental squid heavy meromyosin SAXS profile (green dots) (Gillilan et al., 2013). Integrated scattering intensity (I in arbitrary units) is given as a function of momentum transfer, q = 4π sin(θ)/λ, with a scattering angle of 2θ and a wavelength of λ. (C) Relative deviation between PDB 5TBY scattering and squid HMM (red line) is calculated as (Imodel-Iexp)/Iexp. The corresponding difference in scattering between PDB 5TBY and PDB 3JBH models is also shown on the same scale (black dashed line). Comparison shows that the models cannot be distinguished based on currently available scattering data (See Supplementary Figures).
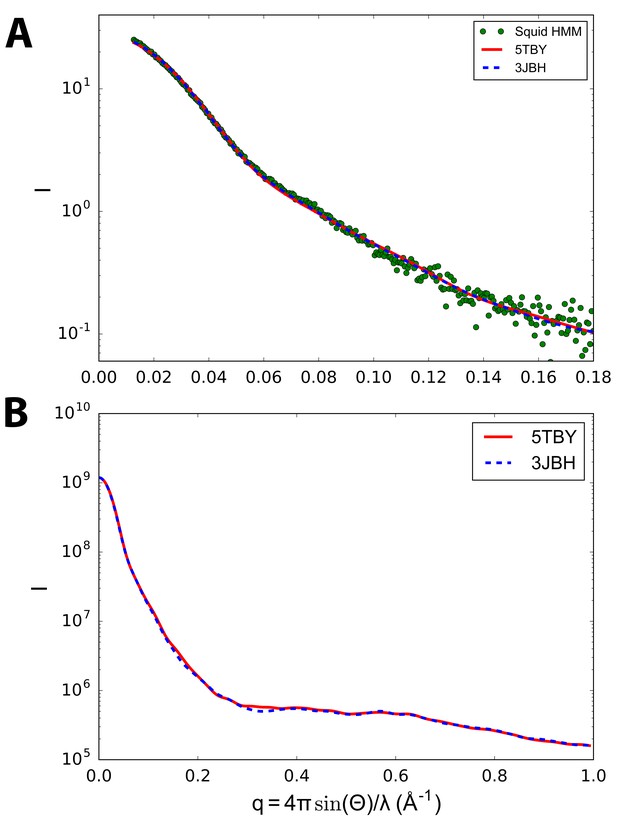
Calculated small angle X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) profile of PDB 5TBY (red line) matches experimental squid heavy meromyosin (HMM) SAXS profile (green dots) (Gillilan et al., 2013).
The comparison of model-based tarantula PDB 3JBH (blue dashed line) vs. human cardiac ventricular IHM PDB 5TBY (red line) scattering with measured squid HMM scattering profiles (green dots) in (A) shows that the models cannot be distinguished based on the scattering data that is currently available. Computations are performed using the FoXS algorithm (Schneidman-Duhovny et al., 2013) using the default parameters of hydration layer, excluded volume, and background adjustment (Gillilan et al., 2013). In the case of (A) the ‘profile offset’ optimization was performed to obtain best fit with the data at widest angles. The predicted scattering profiles are based on electron microscopy-derived striated tarantula muscle PDB 3JBH (Alamo et al., 2016) (blue dashed line) IHM models. Calculated wide-angle scattering data (B), computed without reference to the squid HMM profile, confirms that the models do not significantly differ in the wide angle X-ray solution scattering (WAXS) region.
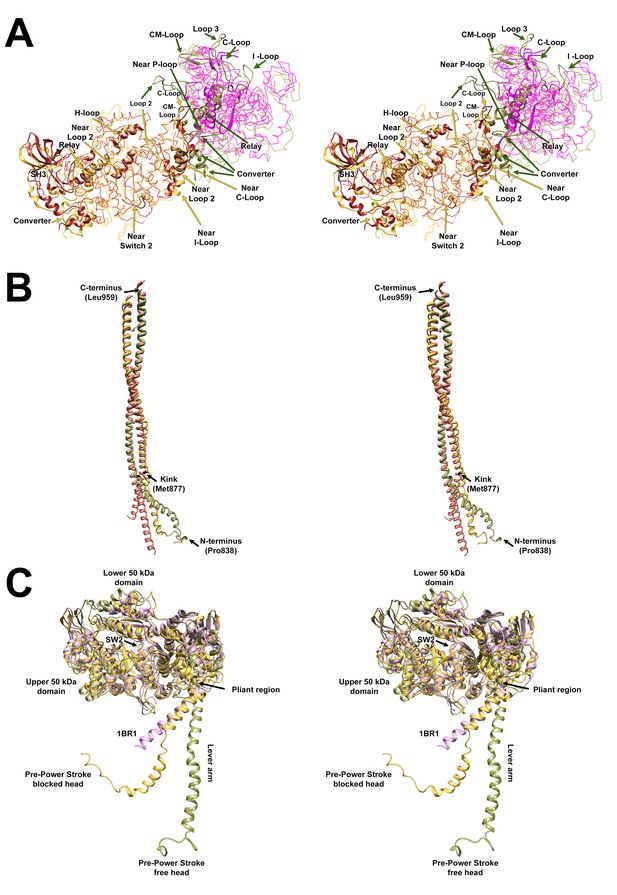
Wide-eye stereo pairs that compare the PDB 5TBY model with crystal structures of fragments for human β-cardiac S1 MD fragment (PDB 4DB1) and S2.
(A) Superimposed MDs of S1 from the PDB 5TBY antavd a S1 fragment of human β-cardiac myosin S1 crystal structure PDB 4DB1 (AMPPNP rigor-like structure) See Video 2. Color code: PDB 5TBY: Blocked head (gold), free head (FH) (olive); PDB 4DB1: blocked head (brown), free head (magenta). All chains are shown as wires with the interacting loops highlighted as ribbons. (B) Superimposed S2 from the PDB 5TBY (same color code as A) and the S2 of the human β-cardiac myosin S2 (pink) crystal structure PDB 2FXM (Blankenfeldt et al., 2006) See Video 3. (C) Free and blocked head structures of PDB 5TBY vs. PDB 1BR1 structures (See Video 4). The free and blocked head MDs of PDB 5TBY (same color code as A) fits well the pre-powerstroke PDB 1BR1 crystal structure (magenta). The ELC and RLC were removed to highlight their lever arms, which are in the same plane but have different angles.
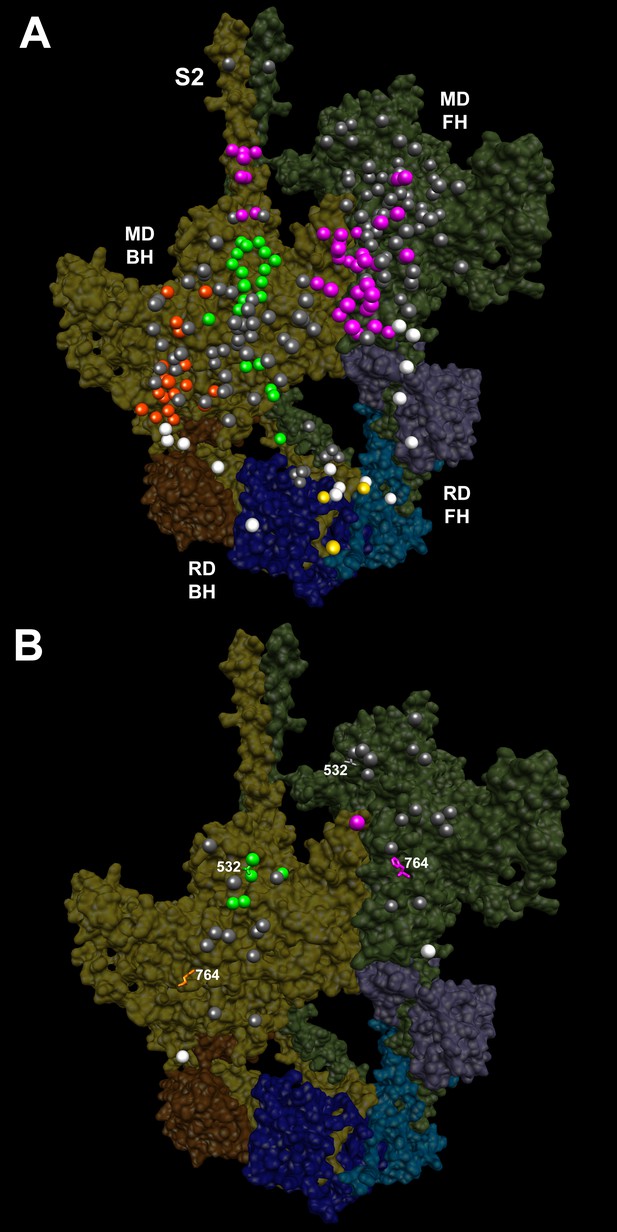
IHM PDB 5TBY models depicting pathogenic (PVs) and likely pathogenic variants (LPVs), in HCM and DCM (listed in Tables 1–3).
Each variant appears as a pair, one located on or associated with the blocked head (BH, olive) and one on the free head (FH, green). Associated proteins are the essential light chain (ELC interacting with BH, brown; FH, purple) and regulatory light chain (RLC interacting with BH, dark blue; FH, light blue). (A) HCM PVs and LPVs that alter residues involved in IHM interactions (73/135 variants, 54%) are represented by colored balls: priming, green (‘f’ and ‘g’, Figure 3—figure supplement 2); anchoring, orange (‘i’ and ‘j’, Figure 3—figure supplement 3); stabilizing, pink (‘a’, ‘d’, and ‘e’, Figure 3—figure supplement 4); scaffolding, white (ELC-MHC and RLC-MHC); RLC-RLC interface, yellow (Figure 3—figure supplement 5). For variants with multiple IHM interactions, only one is depicted. PVs and LPVs that do not alter residues involved in IHM interactions are grey. (B) DCM PV and LPV (7/27; 26%) defined here are colored as described above, along with two prior PVs (S532P and F764L, denoted by side chains) that alter IHM interacting residues. Detailed IHM PDB 5TBY models of variants involved in specific interactions are provided in Supplemental Files and Videos 5 and 6).
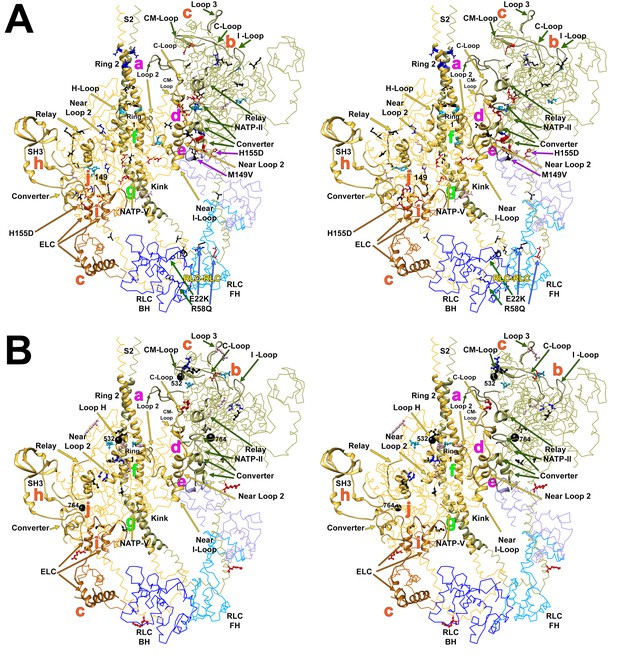
Wide-eye stereo pairs of the IHM PDB 5TBY model showing HCM pathogenic variants (A) and DCM pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants (B).
(A) IHM PDB 5TBY model mapping 40 HCM pathogenic variants (that produced 39 distinct substitutions in MHC and four substitutions in the regulatory and essential light chains; Table 1, in the main text) depicted as balls and sticks, with all chains are shown as wires, and the interaction loops highlighted as ribbons. 22/31 PVs (observed 71%, expected 49%, p=0.019) involved on interactions are charge-changing, according to this color code for their Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue). (B) IHM PDB 5TBY model mapping 27 DCM-causing variants, showing 26 residues substituted by 27 variants on each head (Table 3, in the main text) depicted as balls and sticks, with all chains are shown as wires, and the interaction loops highlighted as ribbons. Five of seven (71%) DCM PVs and LPVs involved on interactions are charge-changing, according to this color code for their Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue).
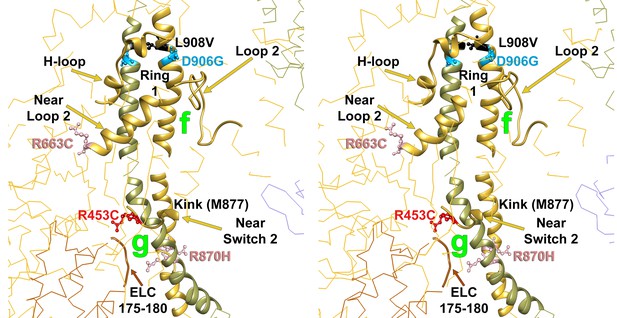
Wide-eye stereo pair of the IHM PDB 5TBY model showing the five HCM variants that alter residues involved in IHM priming (intra-molecular interactions ‘g’ and ‘f’).
Three variants alter resides that participate in ‘f’ sub-interactions (‘f.1’: D906G, L908V; ‘f.2’: R663H) and two alter residues that participate in ‘g’ interactions (R453C and R870H). All chains are shown as wires, with the interacting loops highlighted as ribbons. Only amino acid substitutions (caused by cardiomyopathy variants) within these interacting loops are highlighted as balls and sticks. The color code reflects the variant’s Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue).
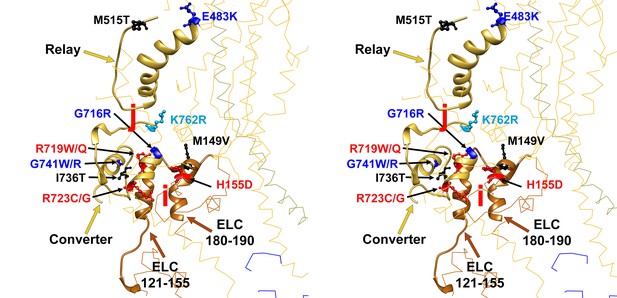
Wide-eye stereo pair of the IHM PDB 5TBY model showing 13 HCM pathogenic variants involved in anchoring the IHM.
Intermolecular interactions between (‘j’, ‘i’) myosin and the essential light chain anchor the blocked head anchoring on the neighboring S2. Five substitutions are involved on interaction ‘j’ between blocked head relay (G483K, M515T) and converter (I736T and G741W/R) with the neighbor S2. Six MHC (G716R, R719W/Q, R723G/C and K762R) variants interact (‘i’) with the same loop of the blocked head ELC with the neighboring MHC S2. Two substitutions are located on the ELC. All chains are shown as wires, with the interacting loops highlighted as ribbons. Only amino acid substitutions (caused by cardiomyopathy variants) within these interacting loops are highlighted as balls and sticks. The color code reflects the variant’s Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue).
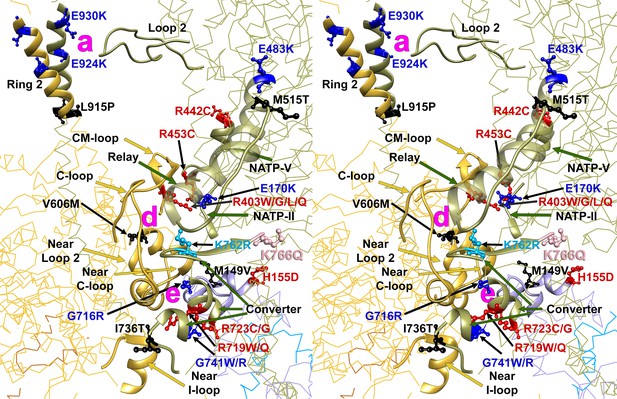
Wide-eye stereo pair of the IHM PDB 5TBY model showing sites of 25 HCM variants that alter IHM stabilizing residues.
Twenty-three MHC variants and two ELC variants alter IHM residues that dock the free head onto the blocked head (‘e’, ‘d’ and ‘a’ interactions). Nineteen MYH7 substitutions are at residues participating in two ‘d’ sub-interactions (‘d.1’: E170K, R403W/G/L/Q, R453C, R442C; ‘d.2’: G716R, R719W/Q, R723G/C, I736T, G741W/R, E483K, M515T, K762R, K766Q), three substitutions are at ‘e’ interactions (MYH7 V606M; MYL3 M149V and H155D), and three at ‘a’ interactions (MYH7 L915P, E924K and E930K). Notably, nine of twelve substitutions involved in sub-interaction “d.2 “alter the charge. All chains are shown as wires, with the interacting loops highlighted as ribbons. Only amino acid substitutions (caused by cardiomyopathy variants) within these interacting loops are highlighted as balls and sticks. The color code reflects the variant’s Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue).
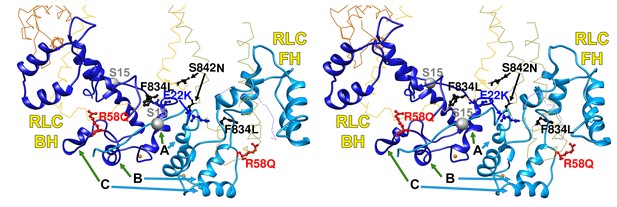
Wide-eye stereo pair of the IHM PDB 5TBY model showing four variants located in the RLC-RLC interface region.
Variants in MHC (S842N and F834L) and RLC (E22K and R58Q) alter residues that allow proper docking of the two opposite surfaces of the RLC-RLC interface when the IHM is initially assembled. The large gray ball denotes phosphorylated Ser15. The small grey yellow denotes the RLC Ca2+ pocket. All chains are shown as wires, with the interacting loops highlighted as ribbons. Only amino acid substitutions (caused by cardiomyopathy variants) within these interacting loops are highlighted as balls and sticks. The color code reflects the variant’s Δq: −2 (dark red), −1 (pink), 0 (black),+1 (light blue) and +2 (dark blue).

Sequence alignment of human cardiac, chicken skeletal and tarantula striated MHC with the locations of HCM variants.
Variant positions (arrowheads) are color-coded according their charge-change, as in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.

Sequence alignment of human cardiac, chicken skeletal and tarantula striated MHC with the locations of DCM variants.
Variant positions (arrowheads) are color-coded as in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.

Sequence alignment of human cardiac, chicken skeletal and tarantula striated ELC with the locations of HCM variants.
HCM variant positions are (arrowheads) color-coded as in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.

Sequence alignment of human cardiac, chicken skeletal and tarantula striated RLC with the location of HCM variants.
HCM variant positions are (arrowheads) color-coded as in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
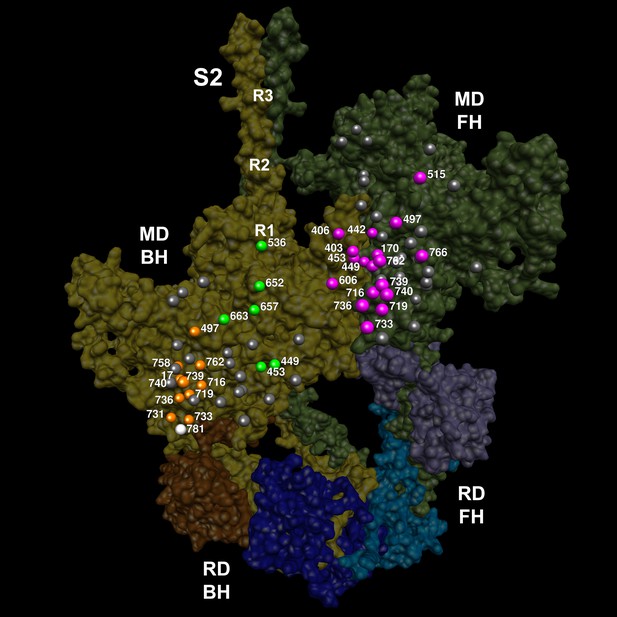
The location of 14 variants located on the mesa (Spudich, 2015; Homburger et al., 2016) of the blocked head (BH, olive) and free head (FH, green).
The three negatively-charged rings in the blocked head S2 are labeled R1, R2 and R3. The associated sarcomere proteins are depicted as in Figure 3. The myosin mesas are roughly orthogonal (blocked head mesa, parallel to the page; free head mesa, perpendicular to the page; see Video 7). HCM PVs are enriched on the mesa and in IHM interactions when located either on the blocked or free head, suggesting that these disrupt crucial determinants of cardiac relaxation, accounting for diastolic dysfunction in HCM.
Videos
A homologous human β-cardiac myosin IHM structure.
The PDB 5TBY IHM model is initially depicted as a ribbon structure that includes paired myosin heads (blocked head (BH), gold, free head (FH), olive), essential light chain (ELC associated with BH: brown, FH: purple), and regulatory light chain (RLC associated with BH: dark blue, FH: blue). The PDB 5TBY IHM model is then fitted into the human cardiac thick filament (3D-map EMD-2240; A(Al-Khayat et al., 2013) as detailed in Materials and methods. See legend of Figure 2A.
The motor domain (MD) of the PDB 5TBY model closely matches the crystal structure of a fragment for human β-cardiac S1 MD (PDB 4DB1).
The movie shows superimposed MDs of S1s from the PDB 5TBY model and a S1 fragment of PDB 4DB1 (S1 bound to adenylylimidodiphosphate (AMPPNP), a nonhydrolysable analogue of ATP to induce a rigor-like structure, open conformation) as ribbons. The MDs of PDB 5TBY blocked and free heads are in gold and olive respectively while the corresponding fragments from PDB 4DB1 are in brown and magenta. See legend of Figure 2—figure supplement 2A.
The sub-fragment 2 (S2) of the PDB 5TBY IHM model closely matches the crystal structures of S2 for human β-cardiac (PDB 2FXM)(Blankenfeldt et al., 2006).
The movie shows the two S2 strands as ribbons of PDB 5TBY in gold and olive (blocked and free heads, respectively) and 2FXM in pink. See legend of Figure 2—figure supplement 2B.
The PDB 5TBY IHM model shows that the blocked and free myosin heads are in the pre-powerstroke state (Zoghbi et al., 2004; Xu et al., 2003; Llinas et al., 2015) and bent at the ‘pliant region’ as defined by Houdusse et al. (2000).
The movie shows the free and blocked head structures of PDB 5TBY IHM model as ribbons in gold and olive respectively, versus the pre-powerstroke state PDB 1BR1 crystal structure (magenta). The ELC and RLC were removed to highlight their lever arms, which are in the same plane but have different angles. See legend of Figure 2—figure supplement 2C.
Semi-transparent, space-filled PDB 5TBY IHM structure depicting the impact of HCM variants, when exposed to different IHM environments.
HCM variants reside on the myosin blocked head (gold), myosin free head (olive), essential light chain (associated with blocked head (brown) or free head, (purple)), and regulatory light chain (associated with blocked head (dark blue) or free head (blue)). Variants are depicted as balls, colored according to the IHM interactions that are disrupted in each environment: priming, green; anchoring, orange; stabilizing, pink, scaffolding, white and regulatory, yellow. Grey variants alter residues that are not involved in IHM interactions. See legend of Figure 3A.
Semi-transparent, space-filled PDB 5TBY IHM structure depicting the impact of DCM variants when residing on the myosin blocked head (gold) and myosin free head (olive).
Variants are depicted as balls, colored according to the interactions that that disrupt: priming, green; anchoring, orange; stabilizing, pink, and scaffolding, white. Grey variants alter residues that are not involved in IHM interactions. The side chains of two previously reported DCM variants (Schmitt et al., 2006), S532P and F764L are also colored according to the IHM interaction that these disrupt. See legend of Figure 3B
Semi-transparent, space-filled 5TBY IHM structure depicting only HCM variants that reside on the blocked head and free head mesas.
The myosin blocked head (gold), myosin free head (olive), essential light chain (associated with blocked head (brown) or free head (purple)), and regulatory light chain (associated with blocked head (dark blue), or free head (blue)) are shown. Mesa variants (numbered according to the amino acid that is altered) are depicted as balls, colored according to the IHM interactions that is disrupted in each environment: priming, green; anchoring, orange; stabilizing, pink, and scaffolding, white. Grey variants alter residues that are not involved in IHM interactions. See legend of Figure 4.
Tables
HCM pathogenic variants (PVs) causing 39 MYH7, 2 MYL2, and 2 MYL3 amino acid substitutions.
| Substitution | Location* | BH interaction* | Type* | FH interaction* | Type* | Δq† | Motor Domain Function‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH7 | Motor Domain | ||||||
| Y115H | Near ATP Binding I | +1 | |||||
| E170K | Near ATP-binding II | d.1 | Stabilizing | +2 | |||
| R249Q | Near ATP Binding III | -2 | |||||
| I263T | Near ATP Binding IV | 0 | |||||
| P307H | Near ATP Binding IV | +1 | |||||
| R403W/G/L/Q | CM-Loop | d.1 | Stabilizing | -2 | Actin interface 1 | ||
| R442C | Near ATP Binding V | d.1 | Stabilizing | -2 | |||
| R453C | Near ATP Binding V | g | Priming | d.1 | Stabilizing | -2 | |
| E483K | Near Relay | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | +2 | |
| M515T | Relay | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | 0 | Relay |
| V606M | Helix-loop-helix | e | Stabilizing | 0 | Actin interface | ||
| R663H | Near Loop 2 | f.2 | Priming | -1 | |||
| M690T | SH2 helix | 0 | |||||
| I702N | SH1 helix | 0 | |||||
| G708A | SH1 helix | 0 | |||||
| G716R | Converter | i | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | +2 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| R719W/Q | Converter | i, | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | -2 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| R723G/C | Converter | i | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | -2 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| I736T | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | 0 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| G741W / R | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | 0 / + 2 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| K762R | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | +1 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | Converter | |||||
| K766Q | Converter | d.2 | Stabilizing | -1 | Converter | ||
| Regulatory Domain | |||||||
| A797T | Neck-ELC interface | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | |
| F834L | Head-tail junction | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | |
| S2 | |||||||
| S842N | Head-tail junction | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | |
| R870H | Kink | g | Priming | g | Priming | -1 | |
| D906G | Ring1 | f.2 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | +1 | |
| L908V | Ring1 | f.2 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | 0 | |
| L915P | Ring2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | 0 | |
| E924K | Ring2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | +2 | |
| E930K | Ring2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | +2 | |
| Light Meromyosin | |||||||
| A1379T | Near skip 2 residue | 0 | |||||
| R1781C | Near skip 4 residue | -2 | |||||
| MYL3 | Essential Light Chain | ||||||
| M149V | Chain F | i | Anchoring | e | Stabilizing | 0 | |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| H155D | Chain F | i | Anchoring | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | -2 | |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | e | Stabilizing | ||||
| MYL2 | Regulatory Light Chain | ||||||
| E22K | Near S15 | RLC-RLC | Regulating | RLC-RLC | Regulating | +2 | |
| RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||
| R58Q | Chains B-C loop | RLC-RLC | Regulating | -2 | |||
| RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding |
-
All PVs identified in 6112 HCM patients (Walsh et al., 2017) are shown. In MYH7 there are 40 PVs, leading to 39 distinct substitutions at 33 positions while in MYL2 and MYL3 there are four more pathogenic variants. HCM PVs located on the mesa are bolded.
-
*Supplementary file 1 defines domain locations and Supplementary file 2 defines IHM interactions, refined using the PISA analysis (Krissinel and Henrick, 2007) that are highlighted as in Figure 3, excluding the two LMM substitutions. RLC–RLC denotes interface region between regulatory light chains.
-
†Δq: variant induced electrical charge change. Δq defines whether the substituted amino acid changes the charge (bolded) or not (Δq = 0).
-
‡Motor domain functions are ascribed only to variants within involved residues. RLC–RLC denotes interface region between regulatory light chains. Variants at IHM interactions sites are colored according to the interaction affected: priming = green, anchoring = orange, stabilizing = pink, scaffolding = white, regulating = yellow.
HCM likely pathogenic variants (LPVs) causing 95 MYH7 amino acid substitutions.
| Substitution | Location* | BH interaction* | Type* | FH interaction* | Type* | Δq‡ | Motor Domain Function§ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH7 | Motor Domain | ||||||
| R17C | SH3 | h | Anchoring | -2 | |||
| R143Q | -2 | ||||||
| K146N | -1 | ||||||
| R169G/K/S | Near P-loop | d.1 | Stabilizing | −2/–1/−2 | |||
| Q193R | Near P-loop | +2 | |||||
| A199V | Near Loop 1 | 0 | |||||
| R204C | Loop 1 | -2 | Actin interface | ||||
| G214D | Loop 1 | -1 | Actin interface | ||||
| N232H | Near Switch 2 | +1 | |||||
| D239N | Switch 1 | +1 | ATP-Binding III | ||||
| R243H† | Switch 1 | -1 | ATP-Binding III | ||||
| F244C | Switch 1 | 0 | ATP-Binding III | ||||
| K246I | Near Switch 1 | -1 | |||||
| F247L | Near Switch 1 | 0 | |||||
| I248T | Near Switch 1 | 0 | |||||
| G256E | Near Switch 1 | -1 | |||||
| I263M | Near ATP-Binding IV | 0 | |||||
| L267V | Near ATP-Binding IV | 0 | |||||
| Y283C | 0 | ||||||
| S291F | Near I-loop | 0 | |||||
| D309N | I-loop | +1 | MD-RLC interface | ||||
| I323N | I-loop | 0 | MD-RLC interface | ||||
| E328G | Near I-loop | +1 | |||||
| V338M | 0 | ||||||
| K351E | Near C-loop | -2 | |||||
| G354S | Near C-loop | 0 | |||||
| E374V | C-Loop | d.2 | Stabilizing | +1 | Actin interface | ||
| A381D | C-Loop | d.2 | Stabilizing | -1 | Actin interface | ||
| Y386C | Near C-loop | e | Stabilizing | 0 | |||
| V406M | CM-loop | d.1 | Stabilizing | 0 | Actin Interface I | ||
| Y410D | CM-loop | d.1 | Stabilizing | -1 | Actin Interface I | ||
| V411I | CM-loop | d.1 | Stabilizing | 0 | Actin Interface I | ||
| L427M | 0 | ||||||
| T449S | Near Switch 2 | g | Priming | d.1 | Stabilizing | 0 | |
| R453S/H | Near Switch 2 | g | Priming | d.1 | Stabilizing | 0/–1 | |
| I457T | Near Switch 2 | 0 | |||||
| I478N | Near Switch 2 | 0 | |||||
| N479S | Near Switch 2 | 0 | |||||
| M493V/L/I | Relay | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | 0 | Relay |
| E497G/D | Relay | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | +1/0 | Relay |
| 1521T | Near Relay | 0 | |||||
| E536D | H-loop | f.2 | Priming | 0 | Actin Interface II | ||
| H576R | Loop 3 | +1 | Actin Interface III | ||||
| G584R | Near Loop 3 | +2 | |||||
| V586A | Near Loop 3 | 0 | |||||
| R652G | Near Loop 2 | f.2 | Priming | -2 | |||
| K657Q | Near Loop 2 | f.2 | Priming | -1 | |||
| R663C | Near Loop 2 | f.2 | Priming | -2 | |||
| R671C | Near SH2 helix | -2 | |||||
| R694C/H | SH2 helix | −2/–1 | |||||
| P710H/L | Converter | +1/0 | Converter | ||||
| P731A | Converter | j | Anchoring | 0 | Converter | ||
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| G733E | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | -1 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| R739S | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | -2 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| K740N | Converter | j | Anchoring | d.2 | Stabilizing | -1 | Converter |
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| L749Q | Converter | j | Anchoring | 0 | Converter | ||
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| F758C | Converter | j | Anchoring | 0 | Converter | ||
| ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ||||||
| V763M | Converter | d.2 | Stabilizing | 0 | Converter | ||
| G768R | Converter | +2 | Converter | ||||
| L781P | Pliant | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | Pivot |
| R783H | Pliant | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | -1 | Pivot |
| Regulatory Domain | |||||||
| R787C | Neck-ELC interface | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | -2 | |
| A797P | Neck-ELC interface | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | |
| L811P | Neck-ELC-RLC interface | ELC-MHC RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | RLC-MHC | Scaffolding | 0 | |
| S2 | |||||||
| K847E | Head-tail junction | -2 | |||||
| E848G | Head-tail junction | +1 | |||||
| M849T | Head-tail junction | ||||||
| A850D | Head-tail junction | -1 | |||||
| R858H | g | Priming | g | Priming | -1 | ||
| E894G | Ring 1 | f.1 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | +1 | |
| L898V | Ring 1 | f.1 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | 0 | |
| A901P | Ring 1 | f.1 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | 0 | |
| E903G | Ring 1 | f.1 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | +1 | |
| Q914H | +1 | ||||||
| D928N | Ring 2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | +1 | |
| E929K | Ring 2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | +2 | |
| E930Q | Ring 2 | a | Stabilizing | a | Stabilizing | +1 | |
| E949K | Ring 3 | +2 | |||||
| E967K | +2 | ||||||
| R1053Q | -2 | ||||||
| Light Meromyosin | |||||||
| E1356K | +2 | ||||||
| R1382Q | Near skip 2 residue | -2 | |||||
| L1428S | 0 | ||||||
| R1606C | Near skip 3 residue | -2 | |||||
| A1763T | 0 | ||||||
| R1781H | Near skip 4 residue | -1 | |||||
| M1782V | Near skip 4 residue |
-
All LPVs identified in 6112 HCM patients (Walsh et al., 2017) are shown. In MYH7 there 95 LPVs, leading to 95 distinct amino acid substitutions at 87 positions.
-
*Supplementary file 1 defines domain locations and Supplementary file 2 defines IHM interactions, refined using the PISA analysis (Krissinel and Henrick, 2007) that are highlighted as in Figure 3, excluding the LMM variants. HCM LPVs located on the mesa are bolded.
-
†R243H was identified in both HCM and DCM cohorts. RLC–RLC denotes interface region between regulatory light chains.
-
‡Δq: variant induced electrical charge change. Δq defines whether the substituted amino acid changes the charge (bolded) or not (Δq = 0).
-
§Motor domain functions are ascribed only to variants within involved residues. Variants at IHM interactions sites are colored according to the interaction affected: priming = green, anchoring = orange, stabilizing = pink, scaffolding = white.
DCM pathogenic variants (PVs) and likely pathogenic variants (LPVs) causing 27 MYH7 amino acid substitutions.
| Substitution | Location‡ | BH interaction‡ | Type‡ | FH interaction‡ | Type‡ | Δq§ | Motor Domain Function¶ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH7 | Motor Domain | ||||||
| G144V | Near ATP Binding I | 0 | |||||
| G178R | ATP-binding II (P-loop) | +2 | ATP Binding II | ||||
| G181R | ATP-binding II (P-loop) | +2 | ATP Binding II | ||||
| I201T | Near 25/50 junction (Loop 1) | 0 | |||||
| R243H† | ATP-binding III (Switch 1) | -1 | ATP Binding III | ||||
| G245E | ATP-binding III (Switch 1) | -1 | ATP Binding III | ||||
| I248F | Near ATP-binding III | 0 | |||||
| R369Q | C-Loop (Loop 4) | d.2 | Stabilizing | -2 | Actin interface | ||
| D469Y | ATP-binding V (Switch 2) | +1 | ATP Binding V | ||||
| I524V | Near H-Loop | f.2 | Priming | 0 | |||
| E525K | Near H-Loop | f.2 | Priming | +2 | |||
| I533V | H-Loop | f.2 | Priming | 0 | Actin interface II | ||
| R567H | Actin-interface III (Loop 3) | -1 | Actin interface III | ||||
| N597K | Helix-loop-helix | +1 | Actin interface | ||||
| C672F | Near SH2 Helix | 0 | |||||
| R783P | Pliant | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | ELC-MHC | Scaffolding | -2 | Pivot |
| S2 | |||||||
| R904C*/H | Ring1 | f.2 | Priming | f.2 | Priming | −2/–1 | |
| E1152V | +1 | ||||||
| Light Meromyosin | |||||||
| R1193H | Near skip 1 residue | -1 | |||||
| E1286K | +2 | ||||||
| R1434C | -2 | ||||||
| D1450N | +1 | ||||||
| R1574W | -2 | ||||||
| Q1794E | -1 | ||||||
| E1801K | Near skip 4 residue | +2 | |||||
| E1914K | +2 | . |
-
All PVs and LPVs identified in 1315 DCM patients (Walsh et al., 2017) are shown. In MYH7 there are 27 DCM pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants, leading to 27 distinct substitutions at 26 residues. DCM LPVs located on the mesa are bolded.
-
*R904C is the only DCM PV.
-
†R243H was identified in both HCM and DCM cohorts. In this cohort, no variants in MYL2 or MYL3 caused DCM.
-
‡Supplementary file 1 defines domain locations and Supplementary file 2 defines IHM interactions, refined using the PISA analysis (Krissinel and Henrick, 2007) that are highlighted as in Figure 3, excluding the LMM variants.
-
§Δq: variant induced electrical charge change. Δq defines whether the substituted amino acid changes the charge (bolded) or not (Δq = 0).
-
¶Motor domain functions are ascribed only to variants within involved residues. Variants at IHM interactions sites are colored according to the interaction affected: priming = green, stabilizing = pink, scaffolding = white.
The distribution of HCM variants across IHM and MD functional residues.
| Specified site | Variants within site | Rate | Amino acids within site | Expected rate | Rate ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHM Interactions (All) | 73 | 0.541 | 447 | 0.2310 | 2.34 | 7.95e-15 |
| Priming | 17 | 0.126 | 113 | 0.0584 | 2.16 | 2.64e-03 |
| Anchoring | 24 | 0.178 | 156 | 0.0806 | 2.21 | 2.11e-04 |
| Stabilizing | 48 | 0.356 | 189 | 0.0977 | 3.64 | 5.37e-16 |
| Scaffolding | 24 | 0.178 | 120 | 0.0620 | 2.87 | 2.97e-06 |
| MD Functional | 39 | 0.289 | 194 | 0.1000 | 2.89 | 7.87e-10 |
-
The numbers of distinct pathogenic and likely pathogenic HCM variants (n = 135) affecting IHM interaction sites and motor domain (MD) functional residues are shown. Variant numbers are also tabulated separately for the four major IHM interactions: priming, anchoring, stabilizing and scaffolding. Note that a single variant may impact more than one interaction. The number of myosin amino acid residues (total protein length = 1935 residues) that compromise the IHM interaction sites or MD functions was used to determine the proportion of variants that would be expected to lie in the region of interest under the null (a uniform distribution), and the rates are compared with a binomial test. Full details of all variants are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
The distribution of DCM variants across IHM and MD functional residues.
| Specified site | Variants within site | Rate | Amino acids within site | Expected rate | Rate ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHM Interactions (All) | 7 | 0.259 | 447 | 0.2310 | 1.120 | 0.6550 |
| Priming | 5 | 0.185 | 113 | 0.0584 | 3.170 | 0.0186 |
| Anchoring | 0 | 0.000 | 156 | 0.0806 | 0.000 | 0.1650 |
| Stabilizing | 1 | 0.037 | 189 | 0.0977 | 0.379 | 0.5120 |
| Scaffolding | 1 | 0.037 | 120 | 0.0620 | 0.597 | 1.0000 |
| MD Functional | 7 | 0.259 | 210 | 0.1090 | 2.380 | 0.0222 |
-
The numbers of distinct pathogenic and likely pathogenic DCM variants (n = 27) affecting IHM interactions and motor domain (MD) functional residues are shown. Variant numbers are also tabulated separately for the four major IHM interactions: priming, anchoring, stabilizing and scaffolding. Note that a single variant may impact more than one interaction. The number of myosin amino acid residues (total protein length = 1935 residues) that compromise the IHM interaction sites or MD functions was used to determine the proportion of variants that would be expected to lie in the region of interest under the null (a uniform distribution), and the rates are compared with a binomial test. Full details of all variants are shown in Table 3.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Domains of human β-cardiac myosin.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.029
-
Supplementary file 2
Intra- and inter-molecular interactions sequences involved in human β-cardiac myosin interacting-heads motif (IHM) PDB 5TBY.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.030
-
Supplementary file 3
HCM variants cluster on residues involved in IHM-related inter- and intra-molecular interactions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.031
-
Supplementary file 4
DCM-causing variants cluster in distinct regions of MYH7 from HCM-causing variants.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.032
-
Supplementary file 5
Variants Clustered on the Myosin Mesa.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.033
-
Supplementary file 6
Comparison of prevalence of rare (ExAC global AF <1×10−4) missense variants in MYH7 in 6112 HCM cases and ExAC controls.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.034
-
Supplementary file 7
Leveraging regional distribution for the clinical interpretation of DCM-causing variants.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24634.035





