Noradrenaline blockade specifically enhances metacognitive performance
Figures
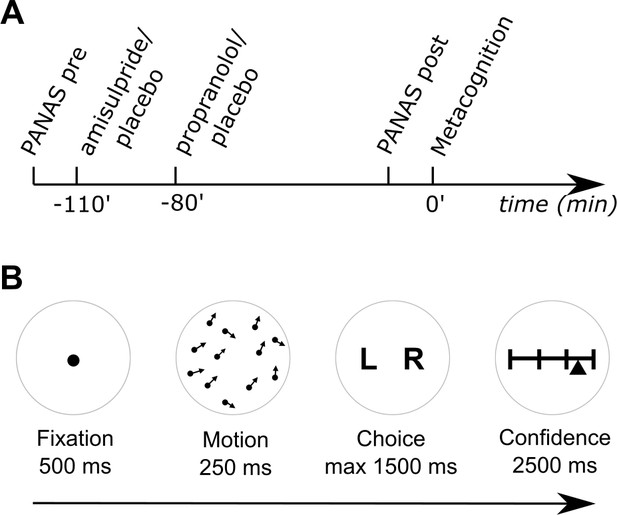
Experimental design and metacognition task.
(A) After filling out a baseline mood questionnaire (PANAS pre), subjects received two different drugs 110 and 80 min prior to the metacognition task. A dopamine subject group first received 400 mg amisulpride (dopamine D2/3 receptor antagonist) and subsequently placebo, whereas the noradrenaline group first received placebo and then 40 mg propranolol (β-adrenoceptor antagonist). Subjects of a placebo group received placebo at both times. Eighty minutes after the second drug administration, subjects filled out a second mood questionnaire (PANAS post) and then performed a metacognition task. (B) To assess subjects’ metacognitive abilities, we used a global motion discrimination task with subsequent confidence judgements. After a fixation period, subjects saw 1100 dots moving randomly with an average motion pointing either to the left or right. After 250 ms, subjects had to indicate the overall direction of the moving dots by using keyboard arrows. Subsequently, they indicated their confidence about their decision using a sliding visual analogue scale. Subjects were instructed to use the full width of the scale by indicating high confidence on the right and low confidence on the left side of the scale.
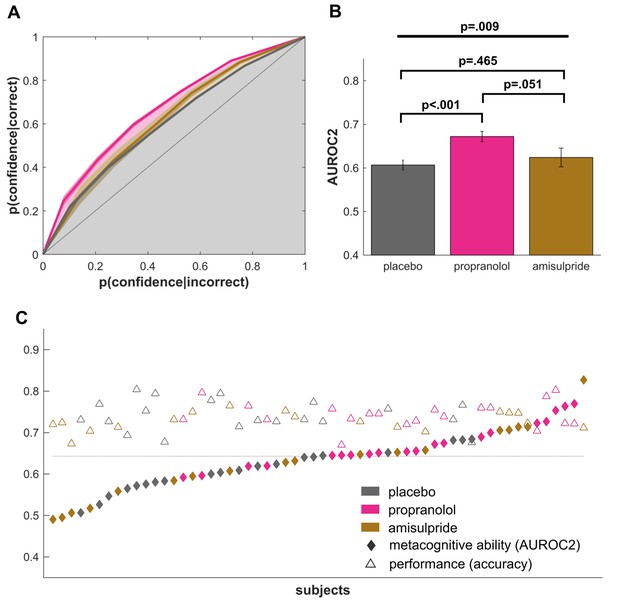
Propranolol improves metacognitive abilities.
(A) Signal detection theoretic analysis revealed a significantly increased metacognitive ability, as measured by the type-II area under the ROC curve (AUROC2). (B) A highly significant effect of propranolol compared to placebo shows that propranolol increases metacognitive abilities. The difference between propranolol and amisulpride suggests that this performance increase might be specific to an influence on noradrenaline but not dopamine function. (C) Individual AUROC2 metrics show that most subjects in the propranolol group perform above the median metacognitive performance (dotted line), while perceptual decision making performance was relatively stable across all groups. mean ±1 SEM; fat line: ANOVA; square brackets: t-tests.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figures 2 and 3.
File containing data to reproduce Figure 2 and 3 and main data analysis.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24901.005
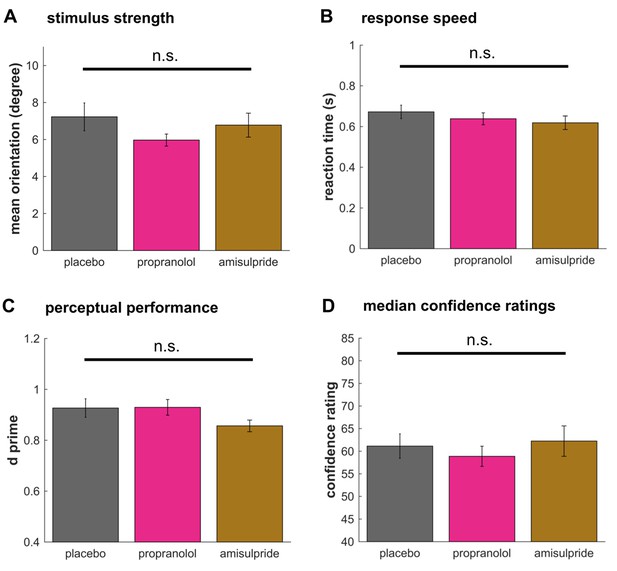
Drug effects on perceptual decision making.
No drug effects were observed on the signal strength (A, stimulus motion orientation) or the response speed (B). In line with no difference in accuracy, perceptual sensitivity d’ did not differ between groups (C). Median confidence ratings (D) showed no difference revealing that there was no bias in the average rating behaviour between groups. These findings suggest that noradrenaline blockade selectively boosts metacognitive sensitivity in the absence of any effect on perceptual decision making. mean ±1 SEM; n.s. p>0.10.
Tables
Group characteristics. The three groups did not differ in their gender, age, intellectual abilities (IQ) (Wechsler, 1999) and their positive and negative affective states before and after drug administration. PANAS: positive and negative affective schedule (Watson et al., 1988), PA: positive affect, NA: negative affect, pre: before drug administration, post: after drug administration (mean±SD).
| Placebo | Propranolol | Amisulpride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gender (f/m) | 10/10 | 10/10 | 10/10 | |
| age | 24.50 ± 4.16 | 23.15 ± 4.31 | 22.35 ± 2.21 | F(2,57)=1.74, p=0.185 |
| IQ | 112.45 ± 12.22 | 118.75 ± 8.55 | 114.60 ± 11.77 | F(2,57)=1.70, p=0.191 |
| PANAS PA pre | 31.15 ± 10.08 | 27.70 ± 8.28 | 28.90 ± 6.60 | F(2,57)=0.86, p=0.428 |
| PANAS NA pre | 11.70 ± 2.23 | 13.55 ± 5.48 | 13.10 ± 3.23 | F(2,57)=1.23, p=0.300 |
| PANAS PA post | 29.22 ± 10.47 | 27.15 ± 7.75 | 27.80 ± 8.12 | F(2,57)=0.286, p=0.752 |
| PANAS NA post | 11.45 ± 2.37 | 11.95 ± 4.87 | 11.25 ± 1.92 | F(2,57)=0.236, p=0.790 |





