Variant proteins stimulate more IgM+ GC B-cells revealing a mechanism of cross-reactive recognition by antibody memory
Figures
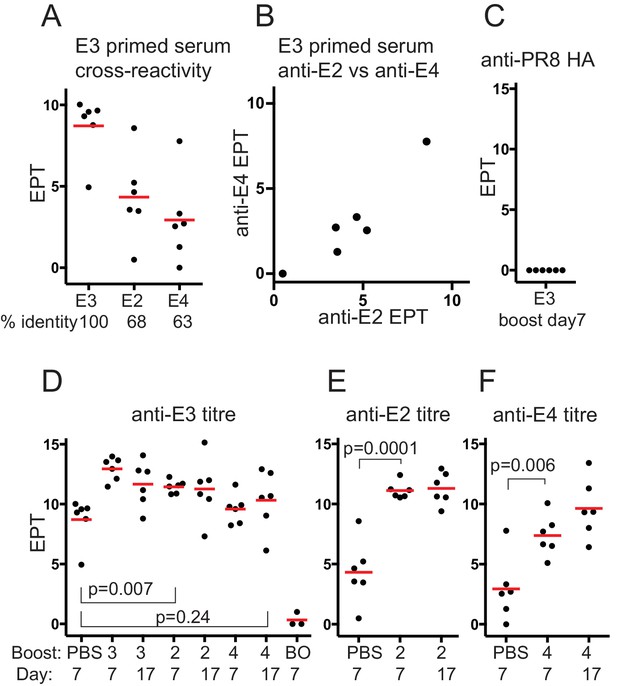
Serum antibody responses after boosting with Dengue envelope protein variants.
(A) Cross-reactivity of E3 primed serum IgG with E-protein variants. Red bar shows mean value. Serum used was from mice mock-boosted with PBS 37 days after E3 priming and obtained 7 days later; E3, Dengue-3 envelope protein; E2, Dengue-2 envelope protein; E4, Dengue-4 envelope protein; % identity, sequence identity between E3 envelope protein and respective protein; end-point titre (EPT) values plotted are log2 of 1/(end point dilution x 100), each unit increase represents a doubling of titre. (B) E3 primed mouse serum cross-reactivity with E2 versus E4. (C) Control. Anti-PR8 HA serum IgG titre of E3 day 7boost serum. (D) Anti-E3 serum IgG titre after boosting with respective proteins. Red bar shows mean value. n = 6 from two independent experiments for each group except boost only, n = 3; first set of data points reproduced from panel A for comparison; numbers 3, 2 and 4 refer to serotype of Dengue-envelope protein used for boost; BO, adjuvant primed, E3 boosted, analysed 7 days later; Day, days after boosting. p-values calculated using two-tailed Students t-test after testing for equality of variance. (E) Anti-E2 serum IgG titre after E2 boost. Red bar shows mean value. n = 6 from two independent experiments for each group; labeling and statistics as for panel D. (F) Anti-E4 serum IgG titre after E4 boost. Red bar shows mean value. n = 6 from two independent experiments for each group; labeling and statistics as for panel D.
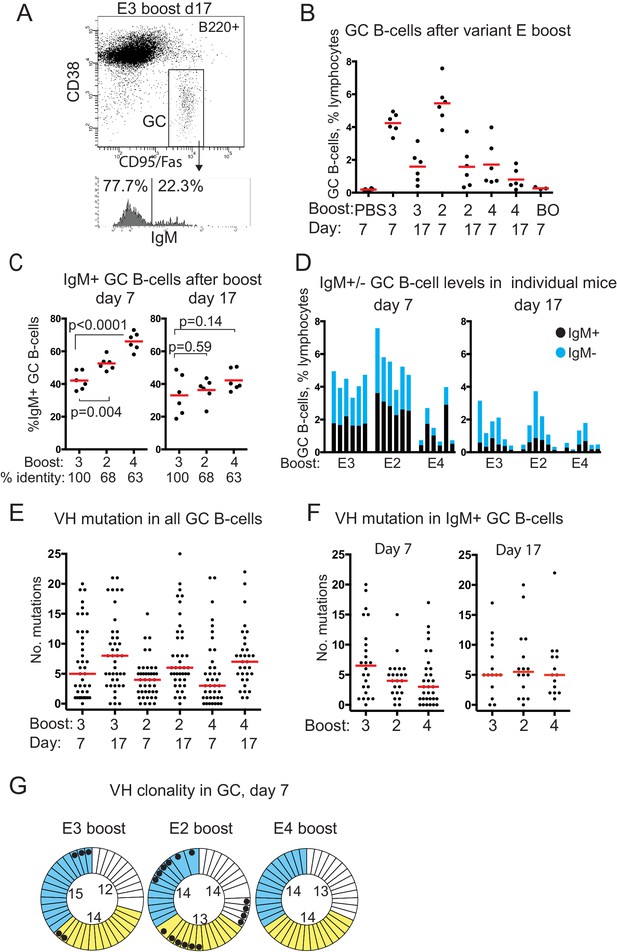
GC B-cell levels, isotypes, VH mutation and clonality after boosting with E-protein variants.
(A) FACS gating strategy used to identify and sort GC B-cells and determine isotype. (B) GC B-cell levels after E-variant boosting, expressed as % total lymphocytes; Red bar shows mean value; numbers 3,2 and 4 refer to serotype of Dengue-envelope protein used for boost; BO, boost only, adjuvant primed, E3 boosted day 37, analysed 7 days later; Day, days after boosting. (C) % IgM+ GC B-cells, of total GC B-cells, after boosting. Red bar shows mean value. n = 6 from two independent experiments for each group; labels as for panel B except % identity which refers to sequence identity between E3 and other variants; p-values calculated using two-tailed Students t-test after testing for equality of variance. (D) Levels of IgM+ and IgM- GC B-cells in individual boosted mice. (E) Number of mutations detected in VH of all isotypes of GC B-cells, from n = 3 mice except E4 boost day 17, n = 2. Red bar is median value. VH region sequenced is CDR1 to FR3; labeling as panel B. (F) Number of mutations detected in VH of IgM+ GC B-cells, from n = 3 mice except E4 boost day 17, n = 2. Red bar is median value. (G) Clonality of sequences from single GC B-cells 7 days after boosting; colours indicate different mice in each group; thin sectors, unique sequences; thicker sectors two or three clonal sequences according to sector size; black dots, VH 14–3 or VH14-4 sequences; numbers in circles, number of sequences from that mouse; Identical VH clones had the same: V-gene, CDR3 length, J-gene, D-gene if assigned, D-reading frame, three or fewer differences in CDR3 amino acid sequence.
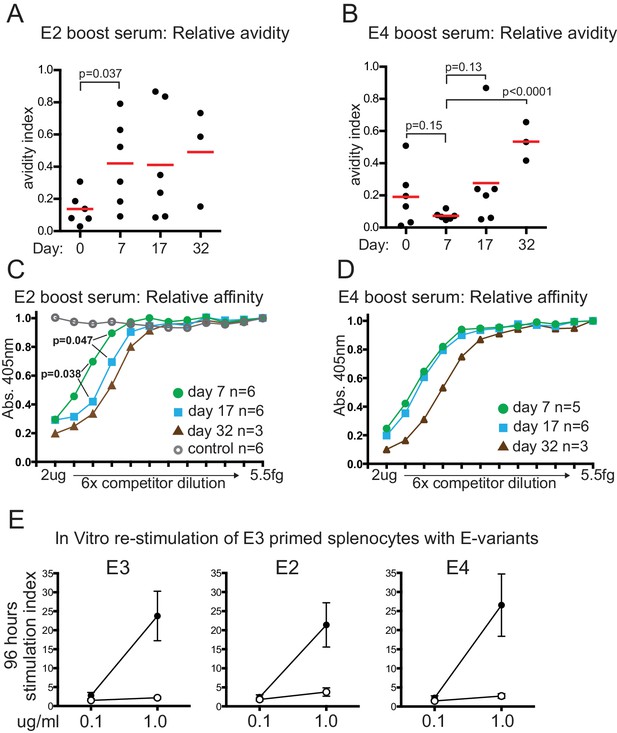
Relative serum affinity and avidity after boosting with E-protein variants, and T-cell re-stimulation.
(A) Relative avidity of E2 boost serum for E2, measured by resistance to 7M Urea. Red bar shows mean value; Day, days after E2 boosting; Day 0 sample was from mice mock-boosted with PBS 37 days after priming with E3 and obtained 7 days later. (B) Relative avidity of E4 boost serum for E4, measured by resistance to 7M Urea. Labeling as for panel A; Day 0 sample was from mice mock-boosted with PBS 37 days after priming with E3 and obtained 7 days later (C) Relative affinity of E2 boosted serum for E2. Inhibition by lower concentration of competitor implies higher affinity of serum for competitor. Maximum competitor amount 2 μg in 50 μl followed by six-fold dilutions of competitor; timepoint of samples and numbers of individuals in group indicated. Open circles, E2 boost day 17 serum competed with irrelevant His-tagged protein measured on E2 target (D) Relative affinity of E4 boosted serum for E4. Labeling as for panel A. (E) T-cell proliferation measured by 3H incorporation 96 hr after re-stimulation in vitro with indicated amounts of E-protein variants; error bars indicate standard error of the mean; n = 4 or five from two independent experiments (see source data). Closed symbols, E3 primed mouse splenocytes re-stimulated with indicated E-protein variant. Open symbols, adjuvant primed mouse splenocytes re-stimulated with indicated E-protein variant.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3 panels C, D and E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26832.006
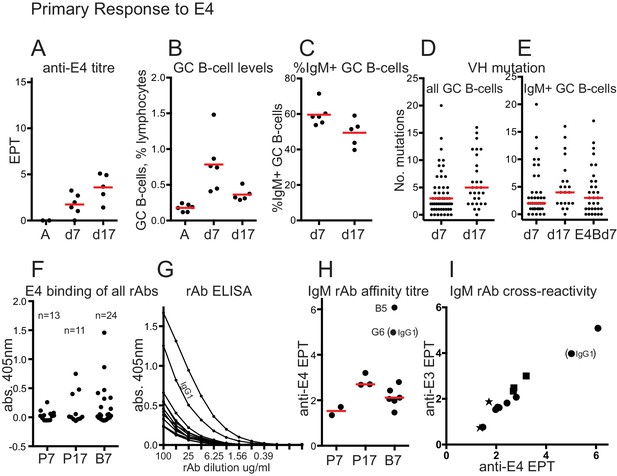
Primary response to E4 and rAb binding.
(A) anti-E4 IgG titre after E4 priming; Red bars show mean titres; A, serum from adjuvant-only primed mice at day 45; d7, 7 days after E4 priming; d17, 17 days after E4 priming; EPT, end-point titre calculated as for Figure 1. (B) GC B-cell levels after E4 priming; Red bars indicate mean levels; A, cells from adjuvant-only primed mice 7 days after priming; other x-axis labels as for panel A. (C) %IgM + GC B-cells after E4 priming; Red bars show mean values; x-axis labels as for panel A. (D) Numbers of VH mutations in all isotypes of GC B-cells after E4 priming; Red bars show median values, from n = 3 mice (d7) and n = 2 mice (d17); x-axis labels as for panel A. (E) Numbers of VH mutations in IgM+ GC B-cells after E4 priming and boosting; Red bars show median values, from n = 3 mice (d7), n = 2 mice (d17) and n = 3 mice E4Bd7; x-axis labels as for panel A except E4Bd7, 7 days after E4 boosting which was 38 days after E3 priming. (F) ELISA screen of binding of all 48 rAbs. rAbs incubated at 100μgml−1. Number of rAbs in each group indicated. P7, 7 days after E4 prime; P17, 17 days after E4 prime; B7, 7 days after E4 boost. As the antibodies were cloned as chimeric human IgG1 antibodies the background from non-specific human polyclonal IgG binding has been subtracted from O.D. readings. Values in supplementary file 2. (G) ELISA titration of rAbs that showed binding O.D. > 0.1 in panel F. All but one were IgM. IgG1 rAb indicated. Background subtraction as for panel F, using appropriate dilution of polyclonal IgG. (H) Anti-E4 end point titre of positive-binding rAbs, used as a proxy of rAB affinity. X-axis labels as for panel F. End-point titre values plotted are log2 of 1/end point dilution (undiluted = 100μgml−1). Red bars show median values (excluding any IgG1 data). Stronger binding IgM rAb ‘B5’, and IgG1 rAb ‘G6’ EPT readings indicated. (I) anti-E3 versus anti-E4 endpoint titres. Star, E4 prime day 7 rAbs; Square, E4 prime day 17 rAbs; circle, E4 boost day 7 rAbs. IgG1 EPT reading indicated. End-point titre values plotted are log2 of 1/end point dilution (undiluted = 100μgml−1).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
GC B-cell VH Sequences.
VH sequences from single sorted GC B-cells. Sequences are grouped into treatment groups, and within this, arranged in blocks for sequences from individual mice. Raw sequences were analysed by IMGT V-Quest. Due to cloning and sequencing primers being at start of FR1 region, this region not included in mutation analysis. CDR1T, total mutations in CDR1; CDR1S, silent mutations in CDR1; CDR1R, replacement mutations in CDR1; likewise for FR2, CDR2 and FR3 regions; Tot Mut, total mutations in CDR1 to FR3 regions.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26832.008
-
Supplementary file 2
Data on recombinant antibodies
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26832.009
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26832.010





