IGF2 mRNA binding protein-2 is a tumor promoter that drives cancer proliferation through its client mRNAs IGF2 and HMGA1
Figures
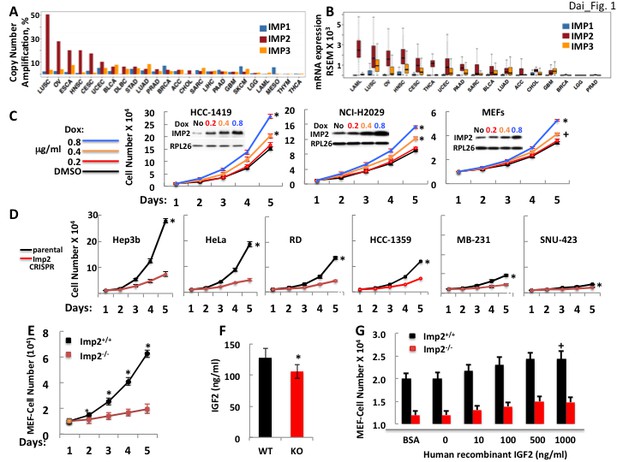
The IMP2 gene is amplified and overexpressed in many cancers and drives proliferation.
(A) The frequency of IMP1,2,3 gene copy number amplification in various cancers. Data from TCGA. (B) IMP1, 2 and 3 mRNA levels in various cancers. Data from TCGA. (C) IMP2 overexpression enhances proliferative rate. A vector encoding an IMP2 cDNA downstream of a doxycycline sensitive promoter was stably expressed in HCC-1419, NCI-H2029 and MEFs. Cells were treated with Doxycycline at the doses indicated and cell number was determined daily. +p<0.05, *p<0.01 vs DMSO. (D) CRISPR-mediated inactivation of the IMP2 genes slows proliferation. The Hep3b, HeLa, RD, HCC-1359, MB-231 and SNU-423 cell lines were transfected with Cas9/CRISPR and a guide RNA directed at either GFP (black) or IMP2 (red) sequences. Unselected polyclonal cell mixtures were plated in replicate and cell number was determined daily. *p<0.01 vs Imp2 CRISPR. (E) Imp2−/− MEFs proliferate more slowly than Imp2+/+ MEFs. Littermate embryos from Imp2+/− ± were harvested at e12.5–13.5 to derive Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Polyclonal mixtures were plated in replicate at passage 4 and cell number was determined daily. *p<0.01 vs Imp2−/−. (F) Imp2−/− MEFs produce less medium IGF2 than Imp2+/+ MEFs. Aliquots of the medium were taken at day 3 from the MEF cultures in Figure 1E and assayed for IGF2 polypeptide. *p<0.01 vs Imp2+/+. (G) Supramaximal IGF2 does not restore the slower proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs to that of Imp2+/+ MEFs. Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs were plated in replicate in standard culture medium with the addition of BSA (1 ug/ml) or various amounts of human recombinant IGF2 and cell number was determined 48 hr later. +p<0.05 vs BSA.
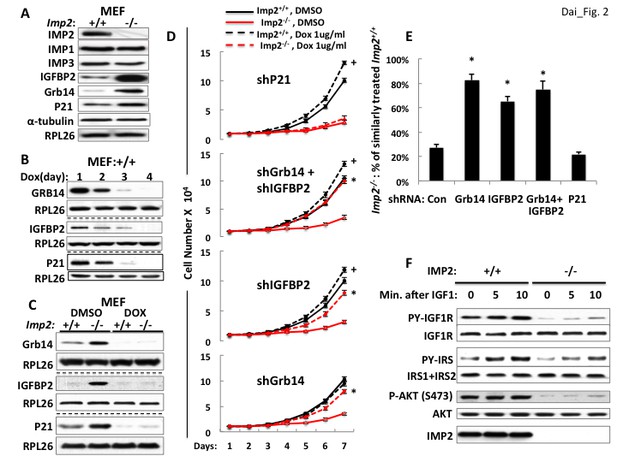
Overexpression of the Grb14 and IGFBP2 polypeptides is mostly responsible for the slowed proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs.
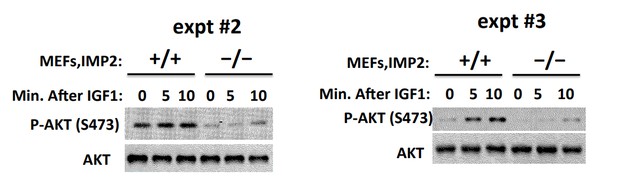
(A) Imp2−/− MEFs exhibit increased abundance of the IGFBP2, Grb14 and P21Cip1 polypeptides as compared with Imp2+/+ MEFs but unaltered levels of IMP1 and IMP3. (B) Time course of shRNA-mediated depletion of Grb14, Igfbp2 and P21Cip1 from Imp2+/+ MEF. (C) The effect of shRNA expression on the Grb14, IGFBP2 and P21Cip1 polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Polyclonal populations of Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs stably expressing shRNAs directed at Grb14, Igfbp2 or P21Cip1 were extracted 72 hr after addition of doxycycline. (D) Depletion of the Grb14 and IGFBP2 increases proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs preferentially as compared with Imp2+/+ MEFs. Polyclonal populations of Imp2+/+ (black) and Imp2−/− (red) MEFs stably expressing shRNAs directed at Grb14, Igfbp2, Grb14 and Igfbp2 or P21Cip1 were plated in replicate and DMSO (solid) or doxycycline (dashed) was added eight hours thereafter. The cell number was determined following day (=day 1) and daily thereafter. + = p < 0.05, Dox vs DMSO, Imp2+/+; *=p < 0.01 Dox vs DMSO, Imp2−/−. (E) The shRNAs against Grb14, Igfbp2 or both restore the proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs close to that of the correspondingly treated Imp2+/+ MEFs, but p21Cip1 shRNA does not. The increase in cell number at day 7 as shown in Figure 2D for Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs was recalculated as follows: the bar labeled ‘Con’ represents the increase in cell number at day 7 of Imp2−/− MEFs treated with DMSO divided by the increase in cell number at day 7 of DMSO-treated Imp2+/+ MEFs, multiplied by 100. The other bars represent the same calculation for the doxycycline-treated Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs stably expressing shRNAs directed at Grb14, Igfbp2, Grb14 and Igfbp2 or P21Cip1. *=p < 0.01 vs Con. (F) IGF1R signaling is impaired in Imp2−/− MEFs. Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs, serum starved overnight were rinsed in serum-free DMEM and stimulated immediately thereafter by addition of human recombinant IGF1 (30 nM). Extracts were prepared before and at the times shown thereafter; the extracts and IPs of IGF1R and IRS1 +IRS2 therefrom were subjected to immunoblots as indicated.
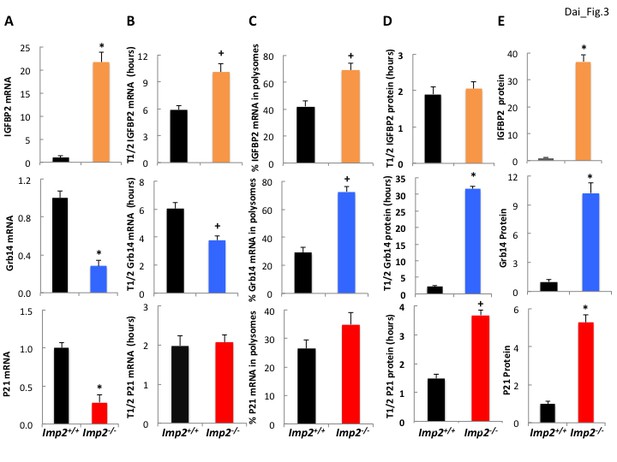
IGFBP2 polypeptide overabundance in Imp2−/− MEFs is due to increased gene transcription whereas Grb14 polypeptide overabundance is due to markedly slower polypeptide degradation.
(A) Igfbp2, Grb14 and P21 mRNA abundance in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. RNA was extracted from Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs and the abundance of Grb14, Igfbp2, P21, Gapdh and Actb mRNA was determined by QPCR. The difference in Ct value between the Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs was converted to a numerical fraction; the value for the abundance of the Imp2+/+ MEFs was set to 1.0 (black bars) and the relative abundance of the Imp2−/− MEFs is shown in colored bars. Values determined by genome-wide RNAseq are found in Supplementary file 2. (B) The turnover of Igfbp2, Grb14 and P21 mRNAs in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Actinomycin 1 uM was added to rapidly growing Imp2+/+ (black) and Imp2−/− (colored) MEFs; RNA was extracted at 0,2,4,6,8,10, 12 hr thereafter and the abundance of Grb14, Igfbp2, P21, Gapdh and Actb was determined by QPCR. The rate of decline was determined by least squares and the time representing a 50% decrease of the initial value is shown. (C) The percentage of Igfbp2, Grb14 and P21 mRNAs residing in polysomes in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Total RNA and post-mitochondrial extracts were prepared from equal numbers of rapidly growing Imp2+/+ (black) and Imp2−/− (colored) MEFs; the post-mitochondrial extracts were subjected to sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Total RNA and RNA extracted from the pooled polysomal fractions was quantified by QPCR and the ratio of polysomal/total RNA X 100 was determined for Grb14, Igfbp2 and P21. (D) The turnover of the IGFBP2, Grb14 and P21 polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Cycloheximide 250 μM, was added to rapidly growing Imp2+/+ (black) and Imp2−/− (colored) MEFs; extracts prepared at t = 0 and every hour for 12 hr were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot for Grb14, IGFBP2 and P21. Relative abundance was determined by densitometry; the rate of decline was calculated as in 3B. (E) The abundance of the IGFBP2, Grb14 and P21 polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Extracts prepared from rapidly growing Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs were subjected to SDS-PAGE and the relative abundance of Grb14, IGFBP2 and P21 was determined by immunoblot; the values for Imp2+/+ were set to 1.0 (black) and the relative value for Imp2−/− is shown in the colored bars. Values determined by MS are found in Supplementary file 2. For all sections, +p<0.05, *=p < 0.01 vs Imp2+/+.
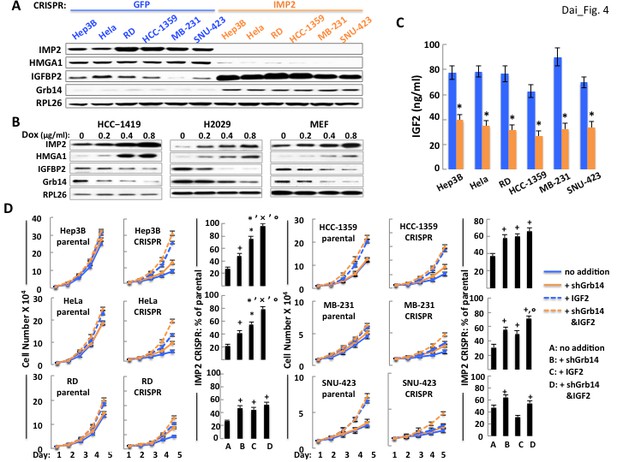
The ability of IMP2 to drive the proliferation of human cancer cells is mostly due to IMP2 regulation of IGF2, Grb14 and IGFBP2 abundance.
(A) CRISPR mediated deletion of IMP2 from human cancer cell lines causes markedly increased abundance of IGFBP2 and Grb14. Extracts prepared from the six cell lines shown in Figure 1D were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot as indicated. (B) Overexpression of IMP2 in human cancer cell lines and MEFs reduces the abundance of IGFBP2 and Grb14. Extracts prepared from the HCC-1419, NCI-H2029 and MEFs stably overexpressing doxycycline-sensitive cDNAs for IMP2, as shown in Figure 1C were immunoblotted for IGFBP2 and Grb14. (C) CRISPR mediated deletion of IMP2 from human cancer cell lines reduces production of IGF2. Aliquots of the medium from the cells depicted in Figure 1D were taken at day five and assayed for IGF2; the level in the cell-free medium (approximately 7 ng/ml) has been subtracted. *=p < 0.01 vs parental. (D) Exogenous IGF2 and depletion of Grb14 increases proliferation of IMP2-deficient cancer cells in a preferential and often additive manner as compared with the parental cells. The variants of the Hep3b, HeLa, RD, HCC-1359, MB-231 and SNU-423 cell lines shown in Figure 1D, which had been transfected with Cas9/CRISPR and a guide RNA directed at either GFP (parental) or IMP2 (CRISPR) sequences, were infected with Lentiviral vectors encoding a Doxycycline responsive shRNA against Grb14. The cells were grown in the presence of DMSO (blue solid line, ‘no addition’), DMSO and IGF2 (500 ng/ml, blue dashed line, ‘+IGF2’), Doxycycline (orange solid line, ‘+shGrb14’), or Doxycycline and IGF2 (orange dashed line, ‘+shGrb14 and IGF2’). Cell number was determined daily. The bar graphs show the increase in cell number at day 5 of the cells designated ‘CRISPR’ divided by the increase in cell number at day 5 of the comparably treated ‘parental’ cells, multiplied by 100. + = p < 0.05, *=p < 0.01 vs A; x =<0.01 vs B; °=p < 0.05 vs C.
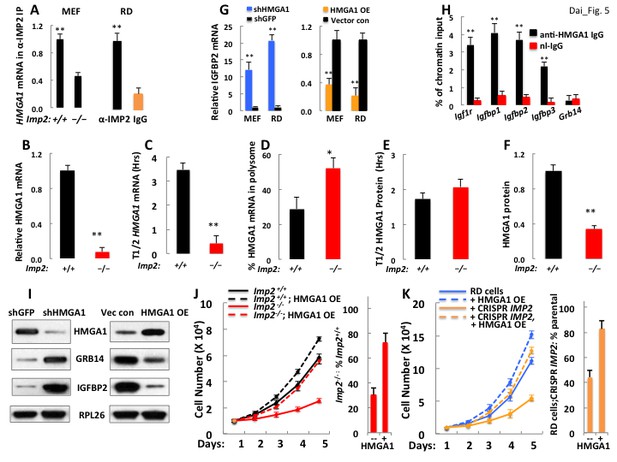
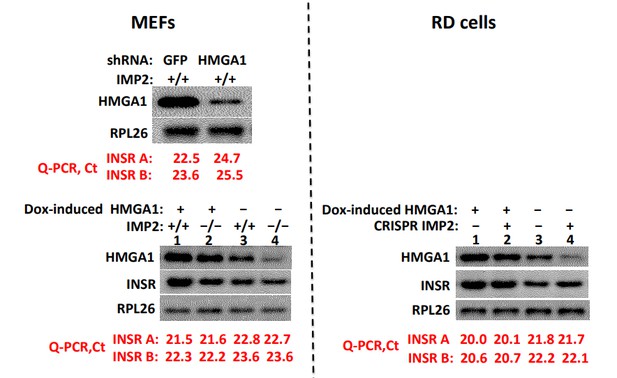
A decreased level of Hmga1, an IMP2 client mRNA, causes the upregulation of IGFBP2 and Grb14 abundance and the slowed proliferation of IMP2 deficient MEFs and RD cells.
(A) IMP2 binds Hmga1 mRNA. IPs were prepared from extracts of Imp2+⁄+ and Imp−⁄− MEFs (left pair) and from RD cells (right pair) with anti-IMP2 antibody (black) or nonimmune IgG (orange). The relative enrichment of HMGA1 mRNA in each IP is quantified by real time RT-PCR. (B) Hmga1 mRNA abundance in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. RNA was extracted from Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs and the abundance of HMGA1 mRNA was determined by QPCR. The abundance in Imp2−/− MEFs relative to Imp2+/+ MEFs (set to 1.0, black bars) is shown in the red bar. (C) The turnover of Hmga1 mRNAs in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The t1/2 of Hmga1 mRNA turnover was determined as in Figure 3B. (D) The percentage of Hmga1mRNAs residing in polysomes in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. Determined as in Figure 3C. (E) The turnover of the HMGA1 polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The t1/2 of HMGA1 polypeptide turnover determined as in Figure 3D. (F) The abundance of the HMGA1polypeptides in Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs. The relative abundance of HMGA1was determined by quantitation of extract immunoblots. Values determined by MS are found in Supplementary file 2. For Figure 5B–F, +p<0.05, *p<0.01 vs Imp2+/+. (G) IGFBP2 mRNA is regulated by the abundance of HMGA1 polypeptide. IGFBP2 mRNA in RD cells and Imp2+/+ MEFs stably expressing doxycycline-inducible shRNAs against HMGA1 (left set) or doxycycline-inducible HMGA1 cDNAs (right set). Doxycycline = colored bars; DMSO = black bars. (H) HMGA1 binds the Igfbp2 but not the Grb14 promoter. MEFs (~10 million) were washed and protein was cross-linked to DNA using formaldehyde. ChIP was performed as described in Methods using antibodies to HMGA1 (black) or nonimmune IgG (red). (I) Both IGFBP2 and Grb14 protein levels are regulated by HMGA1 polypeptide abundance. Immunoblots were performed using MEFs extracted 72 hr after doxycycline induction of Hmga1 shRNA (left) or induction of HMGA1 cDNA expression (right). (J) HMGA1 overexpression restores the proliferation of Imp2−/− MEFs close to that of the similarly treated Imp2+/+ MEFs. Parental MEFs or MEFs stably expressing a doxycycline-inducible HMGA1 overexpressing MEF cells were treated with doxycycline and cell number was measured daily. The bar graphs were calculated as in Figure 2E. (K) The HMGA1 overexpression restores the proliferation of IMP2 CRISPR RD cells nearly identical to similarly treated parental RD cells. As in Figure 5J.

RNAseq indicates that IMP2 binds HMGA1 mRNA predominantly at the 3’UTR.
. The read density track over the Hmga1 transcript is shown; the input RNA is below, and the IMP2-IP is the upper track, showing significant enrichment across the 3’UTR. The sequence of murine Let7a and a potential Hmga1 3’UTR target site are shown.
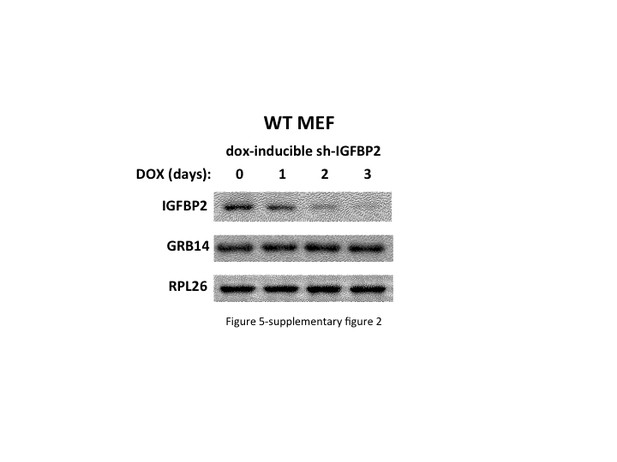
Depletion of IGFBP2 does not affect the abundance of Grb14.
. Doxycycline-inducible shRNA directed at Igfbp2 was stably expressed in MEFs. Extracts were prepared before and 1, 2 and 3 days after addition of doxycycline (100 ng/ml) and immunoblotted for the IGFBP2, Grb14 and rpL26 polypeptides.
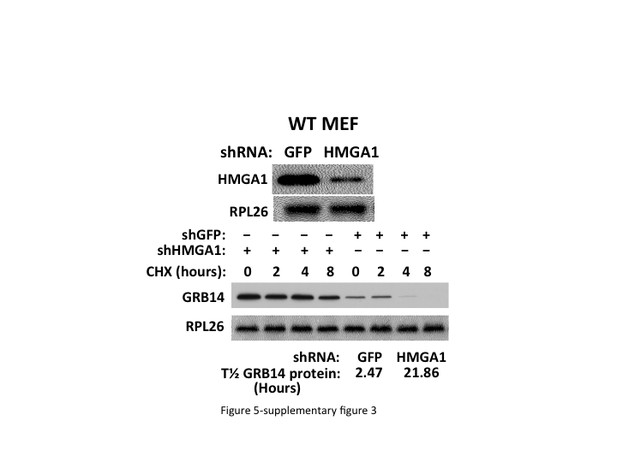
Depletion of HMGA1 prolongs the half-life of the Grb14 polypeptide.
. Doxycycline-inducible shRNAs directed against Hmga1 or GFP were stably expressed in MEFs. Forty eight hours after addition of doxycycline (100 ng/ml), cycloheximide (250 μM) was added and extracts were prepared before and at 2, 4 and 8 hr thereafter. The pre-CHX extracts were immunoblotted for HMGA1 and all samples were immunobloted for Grb14 and rpL26; a representative immunoblot is shown. The relative abundance of Grb14 at 2, 4 and 8 hr, estimated by densitometry, was divided into the preCHX value and the time to a 50% reduction was calculated as 2.47 hr for shRNA-GFP and 21.86 hr for shRNA-Hmga1.
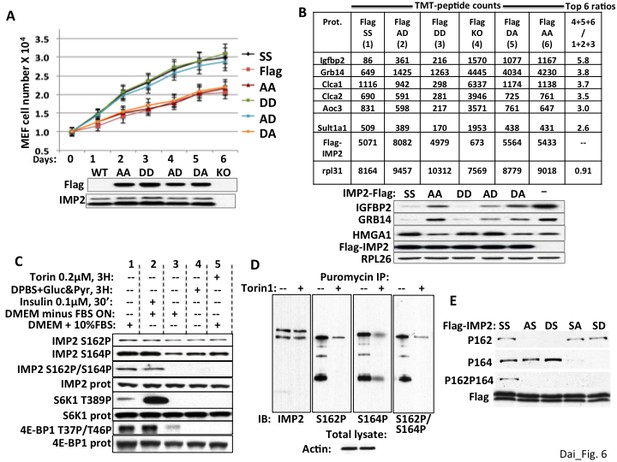
The ability of IMP2 to stimulate MEF proliferation and reduce IGFBP2 and Grb14 abundance requires an acidic charge at IMP2 residue 164.
(A) The ability of IMP2 to drive MEF proliferation requires an acidic charge at IMP2 residue 164. Imp2−/− MEFs were engineered to express doxycycline-inducible cDNAs encoding Flag tagged IMP2 wildtype (SS), Ser162Ala/Ser164Ala (AA), Ser162Ala/Ser164Asp (AD), Ser162Asp/Ser164Asp (DD), Ser162Asp/Ser164Ala (DA) or empty flag vector (Flag). Doxycycline was adjusted to achieve Flag-IMP2 variant expression approximating the level of IMP2 found in wildtype Imp2+/+ MEFs, indicated as WT in the immunoblot. The MEFs expressing the six Flag tagged IMP2 variants were plated in replicate and grown in the presence of the adjusted level of doxycycline. Cell number was determined daily. Each point on the curves for SS, AD and DD do not differ from each other but differ from those for Flag, AA and DA starting at day 2, p<0.01. (B) Genome-wide proteomics reveals that the abundance of the IGFBP2 and Grb14 polypeptides in Imp2−/− MEFs expressing Flag-IMP2 with an Ala at residue 164 is similar to that in MEFs lacking IMP2. Whole cell extracts prepared from the six doxycycline-treated MEFs expressing Flag-IMP2 variants or empty Flag vector shown Figure 6A were analyzed by genome wide TMT proteomics. The values for each of the 7964 polypeptides (detected in all six lines) in the (slower growing) Imp2−/− MEFs expressing Flag-IMP2-AA, Flag-IMP2-DA and Flag-vector (KO) were summed and divided by the sum of that polypeptide in MEFs expressing Flag-IMP2 wildtype (SS), Flag-IMP2-AD and Flag-IMP2-DD. This ratio was then sorted from highest to lowest value and the values are shown for the polypeptides showing 6 highest ratios. The abundance of the Flag-IMP2 polypeptide variants and the endogenous rpL31 polypeptide, the latter meant to reflect overall polypeptide abundance, are also shown. The entire data set is in Supplementary file 3. Extracts of the MEFs described in Figure 6A,B were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted as indicated. (C) The phosphorylation of IMP2(Ser164) and concurrent dual phosphorylation of IMP2(Ser162/Ser164) are post-translationally regulated by mTOR. 293E cells were grown continuously in DMEM with 10% FCS (columns 1, 4, 5) were treated with torin1, 200 nM (column 5) or switched to DPBS containing glucose, 25 mM and pyruvate,1mM (column 4) 3 hr prior to extraction some cells. Other 293 cells were subjected to overnight serum withdrawal (columns 2,3) followed by addition of insulin 100 nM for 30 min. (column 2) prior to extraction. The extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot as indicated. (D) Nascent IMP2 polypeptides bound to puromycin are co-translationally phosphorylated at Ser162 and Ser164 by mTOR. Twenty min. after addition of torin1 (200 nM) to rapidly growing RD cells, puromycin was added at 10 ug/ml, and the cells were extracted 10 min. later. The extracts were blotted for IMP2 and puromycin immunoprecipitates were blotted for IMP2 and IMP2(Ser162P) and IMP2(Ser164P). (E) The modification of Ser162 does not affect the phosphorylation of Ser164 and vice versa. 293 cells were transiently transfected with vectors encoding Flag-tagged wildtype IMP2 (SS) or the Flag-IMP2 mutants Ser162Ala (AS), Ser162Asp (DS), Ser164Ala (SA) or Ser164Asp (SD). Flag immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunobloted as indicated.
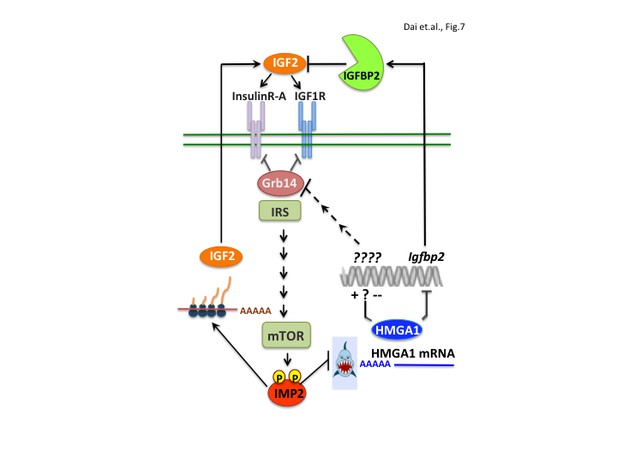
IMP2 promotes proliferation by increasing IGF2 polypeptide and by stabilizing HMGA1 mRNA, whose polypeptide product suppresses the abundance of IGFBP2 and Grb14, inhibitors of IGF2 action.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27155.012Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
RNA seq of total RNA and of IMP2 immunoprecipitates from Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27155.013
-
Supplementary file 2
Proteomic analysis of Imp2+/+ and Imp2−/− MEFs left tab = summary middle tab = all data right tab = polypeptide ratios: Imp2−/−/Imp2+/+.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27155.014
-
Supplementary file 3
Proteomic analysis of Imp2−/− MEFs stably expressing empty Flag vector (designated C) or Flag-IMP2, wildtype (Ser162/Ser164) or with Ser162 and Ser164 substituted with either Ala or Asp: WT/AD/DD/DA/AA/.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27155.015