A viral protein promotes host SAMS1 activity and ethylene production for the benefit of virus infection
Figures
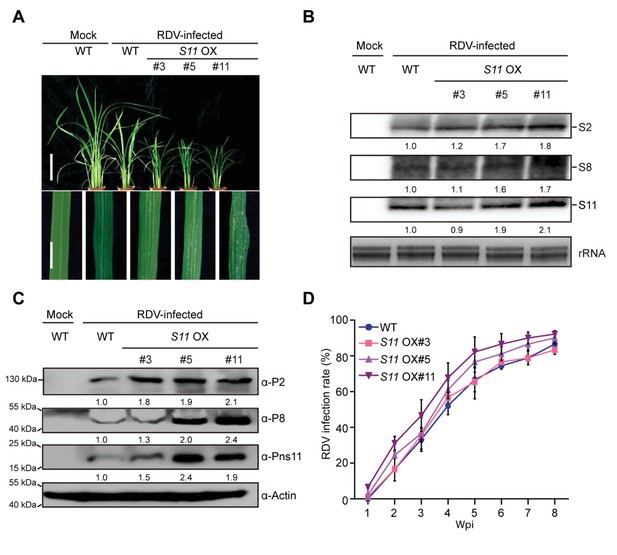
Pns11 overexpression lines are more susceptible to RDV infection than WT plants.
(A) Symptoms of the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and S11 OX transgenic plants; images were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars = 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (B) Detection of RDV S2, S8, and S11 genomic segments in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and in S11 OX transgenic plants by northern blot. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (C) Detection of RDV P2, P8, and Pns11 protein in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and S11 OX transgenic plants by western blot. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (D) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms of 30 individual plants for each case at 0–8 wpi. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
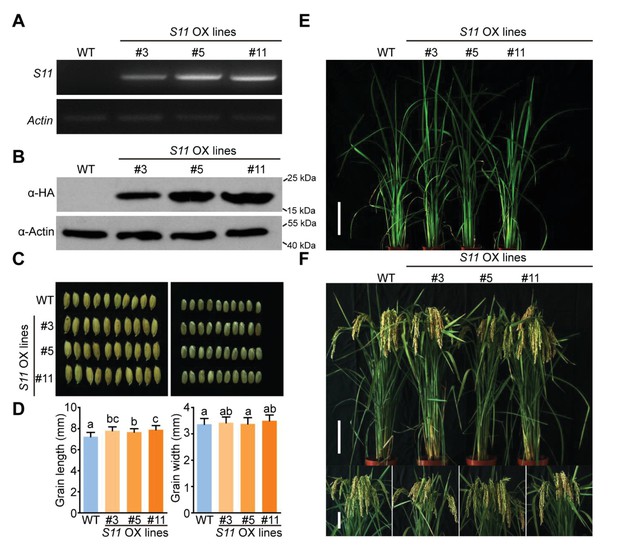
Phenotype and identification of S11-overexpressing lines.
(A) Expression levels of S11 driven by the Ubiquitin promoter in transgenic rice lines (#3, #5, and #11). Actin was used as an internal control. (B) Western blot analysis of Pns11 protein expression level in transgenic lines. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. (C) Comparison of seed size with (left panel) or without the hull (right panel) from WT and three S11-overexpressing lines. (D) Statistical analysis of the seed length and width of well-filled grains. Each value is average of 8 plants and each plant has 100 grains. Bars indicate SD. Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc test was performed for multiple comparisons, different letters indicate significant difference between the compared pairs (p<0.05). (E) Phenotypic comparison of field-grown plants at vegetative growth status. Bar = 10 cm. (F) Phenotypic comparison of field-grown plants at grain-filling period. Bar = 15 cm (upper panel) and 10 cm (lower panel).
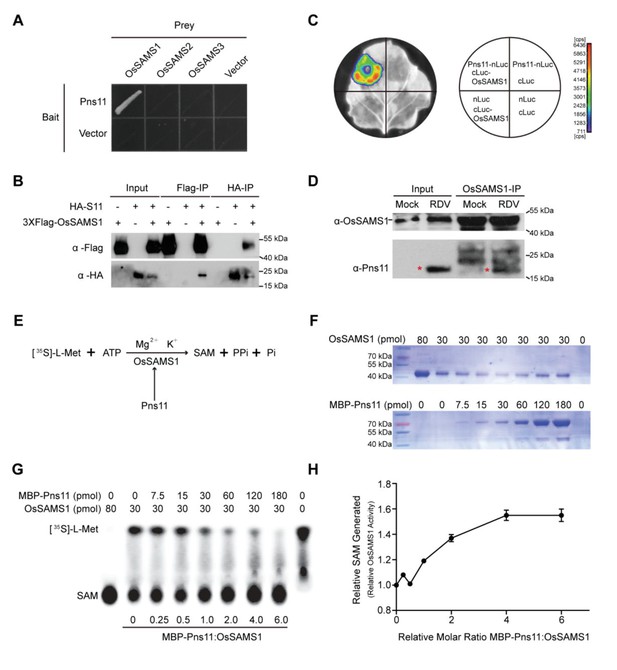
Pns11 interacts with OsSAMS1 and enhances its activity.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assay for the interaction of Pns11 with OsSAMS1. The bait vector contained full-length Pns11; the prey vector contained OsSAMS1, OsSAMS2, or OsSAMS3. Yeast strains were cultured on the Trp –Leu –His –Ade selection medium. (B) Co-IP assay for the interaction of Pns11 with OsSAMS1. Pns11 and OsSAMS1 proteins were transiently expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves for 3 days. Plant extracts were then immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies, separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, and blotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies. (C) Luciferase complementation imaging assay for the interaction of Pns11 and OsSAMS1. Agrobacterium strain EHA105 harboring different construct combinations was infiltrated into different N. benthamiana leaf regions. After 3 days of infiltration, luciferase activities were recorded in these regions. Cps, signal counts per second. (D) In vivo pull-down assay confirmed the interaction between Pns11 and OsSAMS1 during RDV infection in rice using α-OsSAMS1 antibody. The red asterisks indicate the location of Pns11. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (E) Diagram of the assay. In the reaction, OsSAMS1 catalyzes a two-step reaction in the presence of Mg2+ and K+ that involves the transfer of the adenosyl moiety of ATP to methionine to form SAM and tripolyphosphate, which is subsequently cleaved to PPi and Pi. Conversion of L-[35S]-Met to SAM is activated by Pns11. (F) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of OsSAMS1 and Pns11 at the varying amounts of used in this assay. (G) Autoradiograph of a representative chromatogram showing SAM generated by OsSAMS1 in reactions containing varying molar ratios of maltose-binding protein (MBP)-Pns11 to OsSAMS1. The positions of labeled L-[35S]-Met substrate and SAM product are indicated. L-[35S]-Met and SAM in each reaction was calculated after phosphorimager quantitation of radioactivity in individual spots. (H) Stoichiometry of activation. The graph illustrates relative OsSAMS1 activity with increasing molar ratios of MBP-Pns11:OsSAMS1. Data were obtained from three independent experiments.
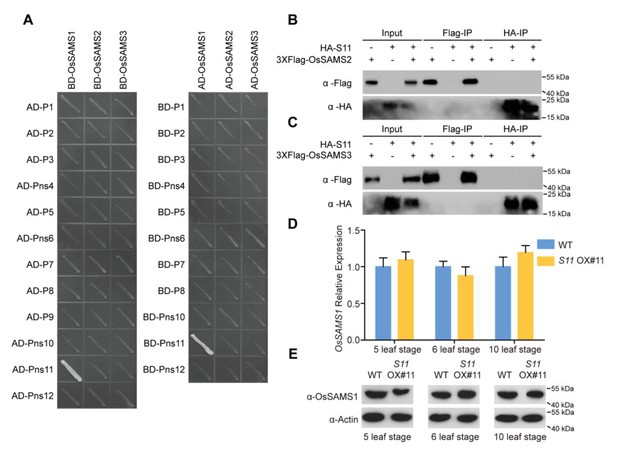
RDV Pns11 specifically interacts with OsSAMS1 and does not affect OsSAMS1 expression.
(A) Pns11 and OsSAMS1 specifically interact with each other in a yeast two-hybrid assay. (B) Co-IP assay for the interaction of Pns11 with OsSAMS2. Pns11 and OsSAMS2 proteins were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves for 3 days, plant extracts were then immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody, separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, and blotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody. (C) Co-IP assay for the interaction of Pns11 with OsSAMS3. Pns11 and OsSAMS3 proteins were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves for 3 days, plant extracts were then immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody, separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel, and blotted with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibody. (D) Real-time PCR of OsSAMS1 relative expression in S11 OX#11 and WT rice from 5, 6 and 10 leaf stages. The average (±standard deviation) values from three biological repeats are shown. The expression levels of the assayed genes were normalized to the expression level of OsEF-1α. (E) Western blot of OsSMS1 expression in S11 OX#11 and WT rice from 5, 6 and 10 leaf stages. Actin was probed and served as a loading control.
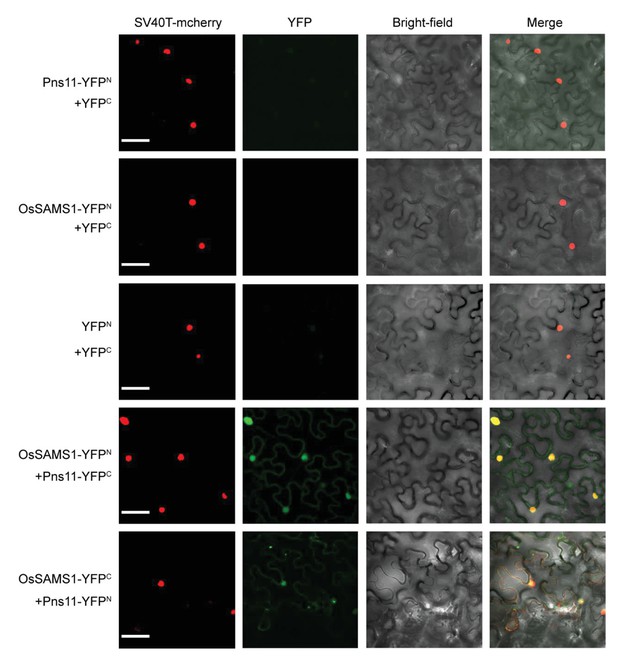
Pns11 and OsSAMS1 are co-localized in both nucleus and cytoplasm.
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) interaction. Constructs expressing Pns11 and OsSAMS1 fused to the N- or C-terminal portions of yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) were delivered to N. benthamiana leaf cells by agroinfiltration. Cells were photographed 3 days post-infiltration at 40X magnification using a confocal laser scanning microscope. SV40T-mCherry was used as a marker for the nucleus. The co-expressed proteins are indicated above the photographs, which are representative of results with all possible combinations of fusion proteins. Bar = 20 μm.
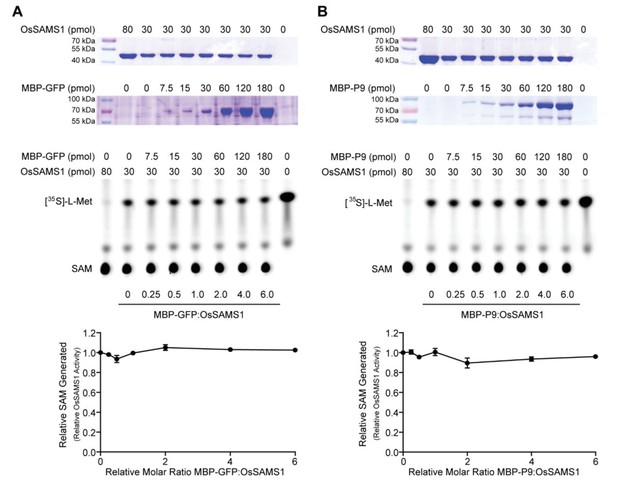
Neither GFP nor P9 affects OsSAMS1 activity in vitro.
(A) The upper graph represents the coomassie brilliant blue staining of varying amounts of OsSAMS1 and GFP, respectively. The middle graph is an autoradiograph of a representative chromatogram showing SAM generated by OsSAMS1 in reactions containing varying molar ratios of MBP-GFP to OsSAMS1. The positions of labeled L-[35S]-Met substrate and SAM product are indicated. L-[35S]-Met and SAM in each reaction was calculated after phosphorimager quantitation of radioactivity in individual spots. The lower graph is the stoichiometry of activation, which illustrates relative OsSAMS1 activity, with increasing molar ratio of MBP-GFP to OsSAMS1. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. (B) The upper graph represents the coomassie brilliant blue staining of varying amounts of OsSAMS1 and P9, respectively. The middle graph is an autoradiograph of a representative chromatogram showing SAM generated by OsSAMS1 in reactions containing varying molar ratios of MBP-P9 to OsSAMS1. The positions of labeled L-[35S]-Met substrate and SAM product are indicated. L-[35S]-Met and SAM in each reaction was calculated after phosphorimager quantitation of radioactivity in individual spots. The lower graph is the stoichiometry of activation, which illustrates relative OsSAMS1 activity, with increasing molar ratio of MBP-P9 to OsSAMS1. Data were obtained from three independent experiments.
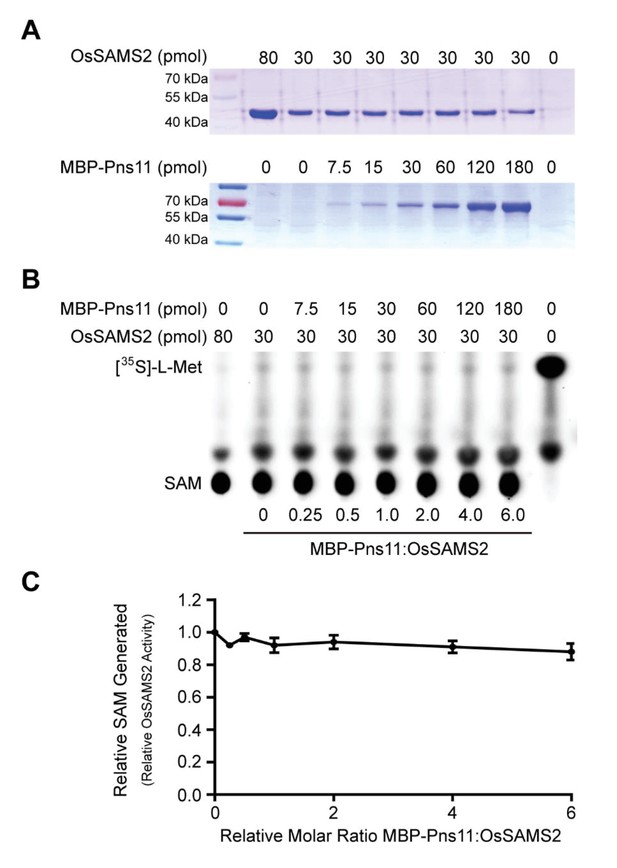
Pns11 does not affect OsSAMS2 activity in vitro.
(A) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of varying amounts of OsSAMS2 and Pns11, respectively. (B) Autoradiograph of a representative chromatogram showing SAM generated by OsSAMS2 in reactions containing varying molar ratios of MBP-Pns11 to OsSAMS2. The positions of labeled L-[35S]-Met substrate and SAM product are indicated. L-[35S]-Met and SAM in each reaction was calculated after phosphorimager quantitation of radioactivity in individual spots. (C) Stoichiometry of activation. The graph illustrates relative OsSAMS2 activity, with increasing molar ratio of MBP-Pns11 to OsSAMS2. Data were obtained from three independent experiments.
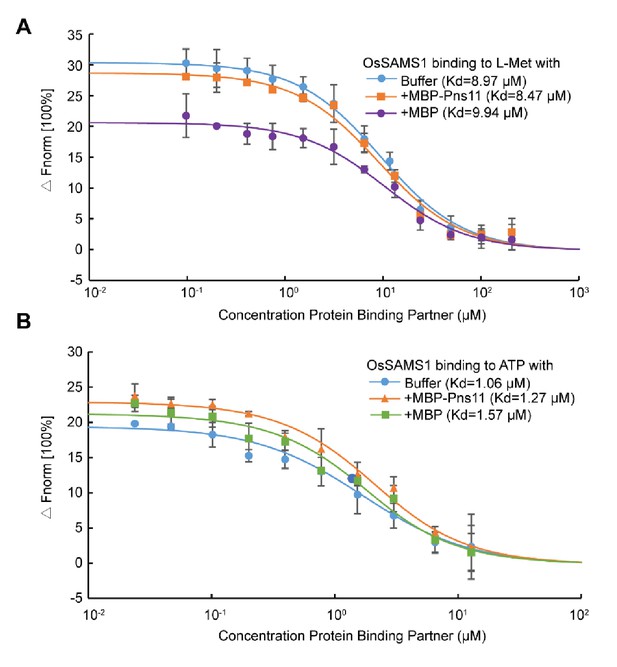
Pns11 does not affect the affinity of OsSAMS1 to the substrates L-Met or ATP.
(A) Pns11 does not affect dynamic association between OsSAMS1 and L-Met. Data were collected from microscale thermophoresis (MST) assays as described in the 'Materials and methods'. Experiments were repeated three times and error bars indicate SD. Fnorm, normalized fluorescence. (B) Pns11 does not affect dynamic association between OsSAMS1 and ATP. Data were collected from MST assays as described in the 'Materials and methods'. Experiments were repeated three times and error bars indicate SD. Fnorm, normalized fluorescence.
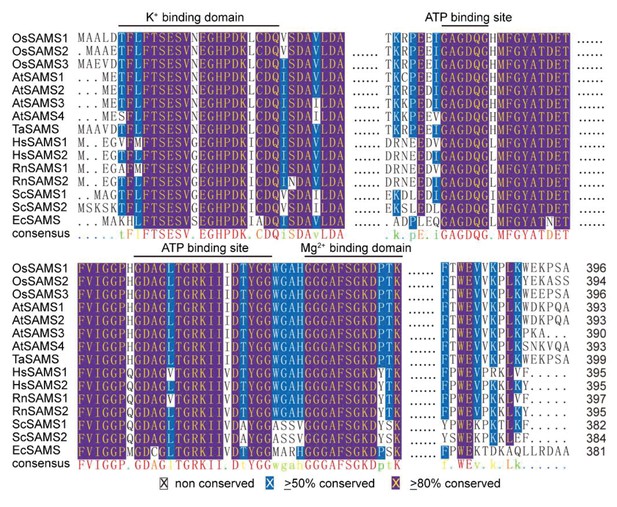
Multiple alignments of SAM synthetase proteins.
Multiple alignments of SAM synthetase proteins. The amino acid secquence of OsSASM1 synthetase protein (Q0DKY4.1) were aligned with Oryza sativa SAM synthetase 2 (OsSAMS2, P93438.1), O. sativa SAM synthetase 3 (OsSAMS3, Q9LGU6.1), Arabidopsis thaliana SAM synthetase 1 (AtSAMS1, P23686.2), A. thaliana SAM synthetase 2 (AtSAMS2, P17562.1), A. thaliana SAM synthetase 3 (AtSAMS3, Q9SJL8.1), A. thaliana SAM synthetase 4 (AtSAMS4, Q9LUT2.1), Triticum aestivum SAM synthetase (TaSAMS, B0LXM0.1), Homo sapiens SAM synthetase 1 (HsSAMS1, Q00266.2), H. sapiens SAM synthetase 2 (HsSAMS2, P31153.1), Rattus norvegicus SAM synthetase 1 (RnSAMS1, P13444.2), R. norvegicus SAM synthetase 2 (RnSAMS2, P18298.1), Saccharomyces cerevisiae SAM synthetase 1 (ScSAMS1, P10659.2), S. cerevisiae SAM synthetase 1 (ScSAMS1, P19358.3), and Escherichia coli SAM synthetase (EcSAMS, P0A817.2). ≥50% conserved and ≥80% conserved amino acids were in blue and purple, respectively. Four SAM synthetase signature motifs were indicated. SAM code numbers are from UniProt.
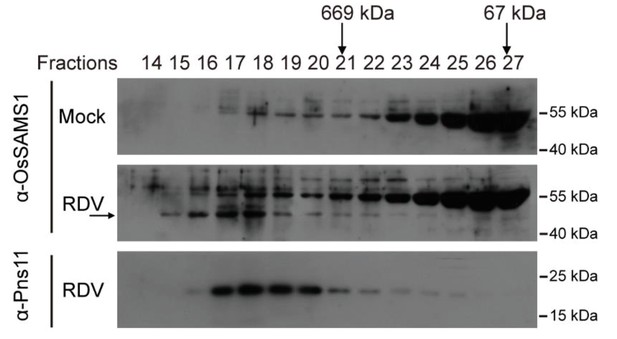
Gel-filtration analysis of Pns11 and OsSAMS1.
Gel filtration analysis of Pns11 and OsSAMS1. The high-molecular-weight fraction peak of Pns11 and OsSAMS1 is indicated. The two vertical black arrows indicate fractions in which the 669-kDa and 67-kDa protein standards eluted. The horizontal black arrows indicate the location of OsSAMS1. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi.
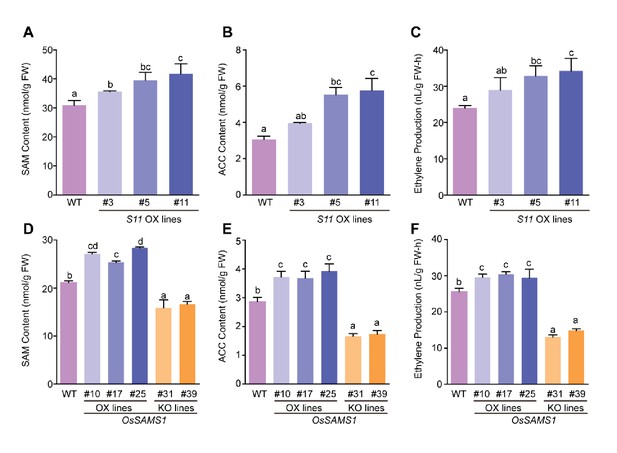
SAM, ACC, and ethylene contents in OsSAMS1 and S11 transgenic lines.
(A) SAM contents in the S11-overexpression lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (B) ACC contents in the S11-overexpression lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (C) Ethylene contents in the S11-overexpression lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (D) SAM contents in the OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (E) ACC contents in the OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (F) Ethylene contents in the OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc test was performed for multiple comparisons. Letters indicate significant differences, p<0.05. Data are from three replicates. FW, fresh weight.
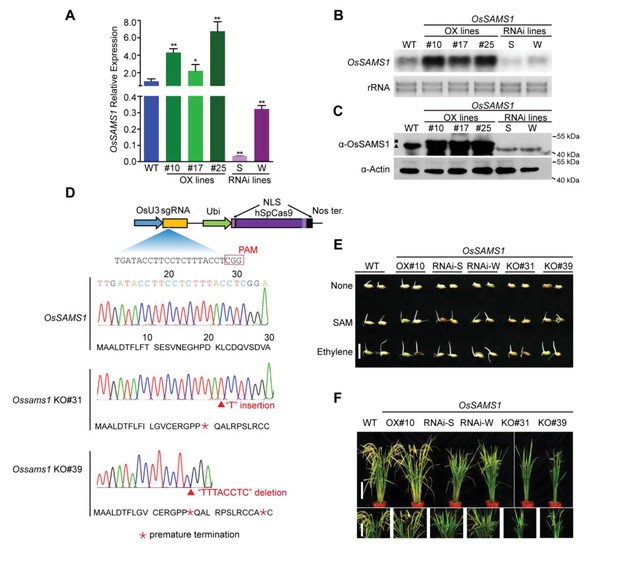
Phenotype and identification of OsSAMS1 transgenic lines.
(A) Expression levels of OsSAMS1 in WT, OX and RNAi transgenic lines. (14-d-old seedlings). The average (± standard deviation) values from three biological replicates are shown. Significant differences are indicated (*p<0.05, **p<0.01) based on Student’s t-test. (B) Northern blot analysis of OsSAMS1 mRNA expression level in WT, OX and RNAi transgenic lines. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. (C) Western blot analysis of OsSAMS1 protein expression level in transgenic lines. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. The black square indicates protein OsSAMS1 with flag tag, the black triangle indicates endogenous OsSAMS1 protein in rice. (D) Schematic of the OsSAMS1Cas9 construct. Key elements and the sgRNA sequence for specifically targeting OsSAMS1 are indicated. DNA sequencing chromatograms of two Ossams1 KO lines. The mutations, ‘T’ insertion in line Ossams1 KO#31 and ‘TTTACCTC’ deletion in line Ossams1 KO#39, which lead to premature termination in the amino acid sequence of OsSAMS1 are indicated. (E) Effect of SAM and ethylene on seed germination in the OsSAMS1 transgenic lines. SAM concentration was 1 mM, ethylene concentration was 10 ppm. Bar = 1 cm. (F) Phenotypic comparison of field-grown plants at the grain-filling stage. Bar = 15 cm (upper panel) and 10 cm (lower panel).
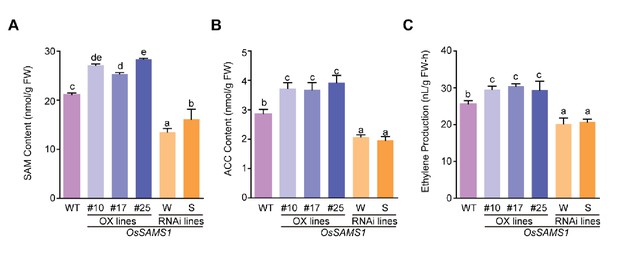
SAM, ACC and ethylene contents in OsSAMS1 transgenic lines.
(A) SAM content in OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (B) ACC content in OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). (C) Ethylene content in OsSAMS1 transgenic lines and WT plants (using 40-d-old seedlings). Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc tests were performed for multiple comparisons. Letters indicate significantly different results, p<0.05. Data are from three replicates. FW, fresh weight.
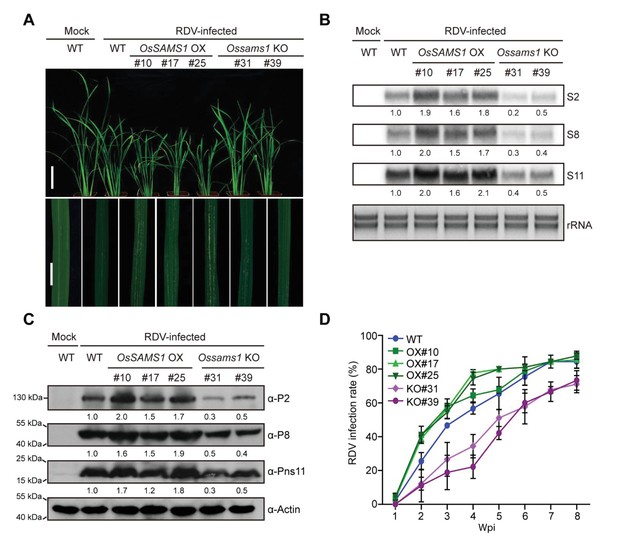
Overexpression of OsSAMS1 enhances RDV infection whereas knockout of OsSAMS1 reduces RDV infection.
(A) Symptoms of the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and OsSAMS1 OX/KO transgenic plants; images were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars = 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (B) Detection of RDV S2, S8, and S11 genomic segments in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and in OsSAMS1 OX/KO transgenic plants by northern blot. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (C) Detection of RDV P2, P8, and Pns11 proteins in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants and in OsSAMS1 OX/KO transgenic plants by western blot. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (D) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms at 0–8 wpi of 30 individual plants for each case. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
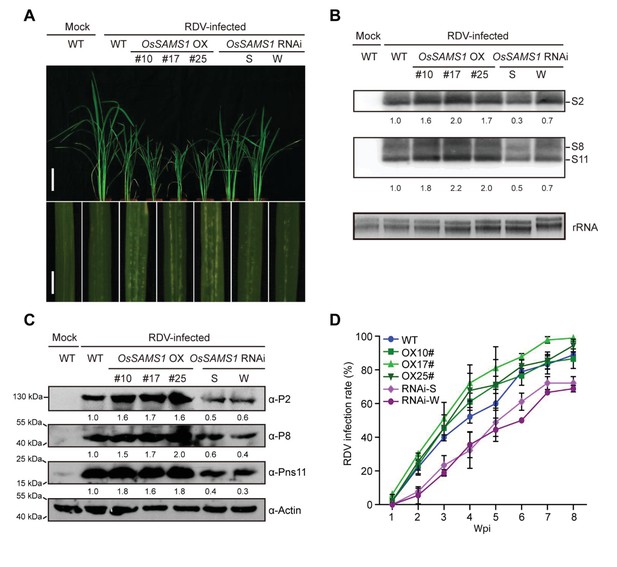
Overexpression of OsSAMS1 enhances RDV infection while downregulation of OsSAMS1 reduces RDV infection.
(A) Symptoms of mock or RDV-infected WT plants as well as OsSAMS1 OX/RNAi transgenic plants, pictures were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars, 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (B) Detection of RDV genomic S2, S8, S11 in mock or RDV-infected WT plants as well as in OsSAMS1 OX/RNAi transgenic plants by northern blot. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (C) Detection of RDV protein P2, P8, Pns11 in mock or RDV-infected WT plants as well as in OsSAMS1 OX/RNAi transgenic plants by western blot. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (D) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms at 0–8 wpi of 30 individual plants for each case. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
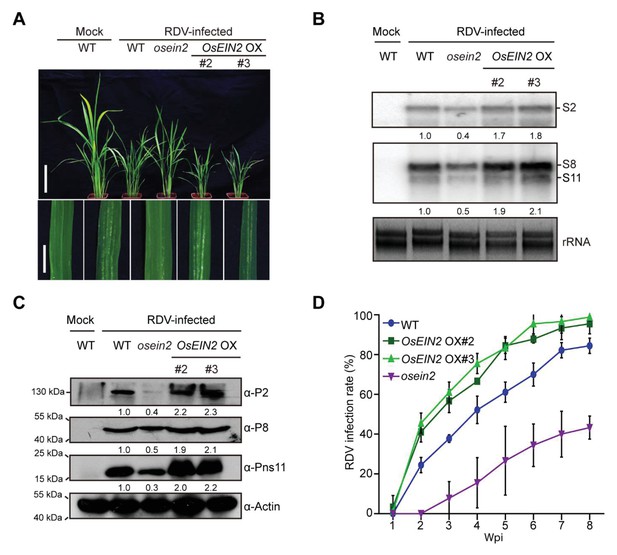
The ethylene-response mutant (osein2) shows increased tolerance of RDV infection whereas overexpression (OX) of OsEIN2 results in enhanced susceptibility.
(A) Symptoms of the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants, osein2, and OsEIN2-overexpression (OX) plants; images were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars = 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (B) Detection of RDV S2, S8, and S11 genomic segments in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants, osein2, and OsEIN2 OX plants by northern blot. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (C) Detection of RDV P2, P8, and Pns11 proteins in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic) plants, osein2, and OsEIN2 OX plants by western blot. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (D) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms at 0–8 wpi of 30 individual plants for each case. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
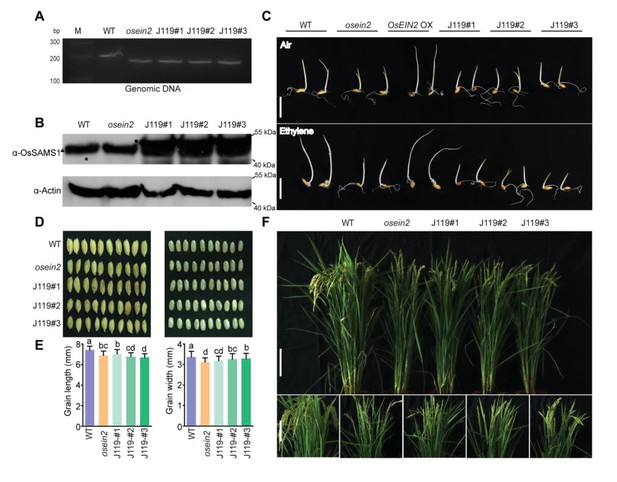
Phenotype and identification of OsSAMS1 OE/osein2 (J119) transgenic lines.
(A) Confirmation of osein2 and J119 lines by PCR-based analysis. (B) Western blot analysis of OsSAMS1 protein expression level in transgenic lines. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. The black square indicates protein OsSAMS1 with Flag tag, the black triangle indicates endogenous OsSAMS1 protein in rice. (C) Effect of air and ethylene on seed germination in the transgenic lines. Ethylene concentration was 10 ppm. Bar = 1 cm. (D) Comparison of seed size with (left panel) or without the hull (right panel) from WT, osein2 and J119 lines. (E) Statistical analysis of seed length and width of well-filled grains. Each value is an average for 8 plants and each plant has 100 grains. Bars indicate SD. Different letters indicate a significant difference between the compared pairs (p<0.05). (F) Phenotypic comparison of field-grown plants at the grain-filling stage. Bar = 15 cm.
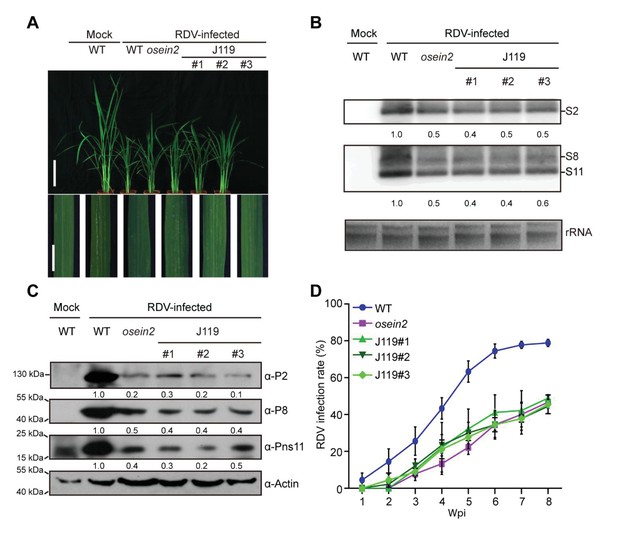
Overexpressed OsSAMS1 in osein2 (J119) results in increased tolerance of RDV infection.
(A) Symptoms of the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic), osein2 and J119 plants; images were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars = 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (B) Detection of RDV S2, S8, and S11 genomic segments in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic), osein2 and J119 plants by northern blot. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. (C) Detection of RDV P2, P8, and Pns11 proteins in the mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected WT (non-transgenic), osein2 and J119 plants by northern blot. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. (D) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms at 0–8 wpi of 30 individual plants for each case. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
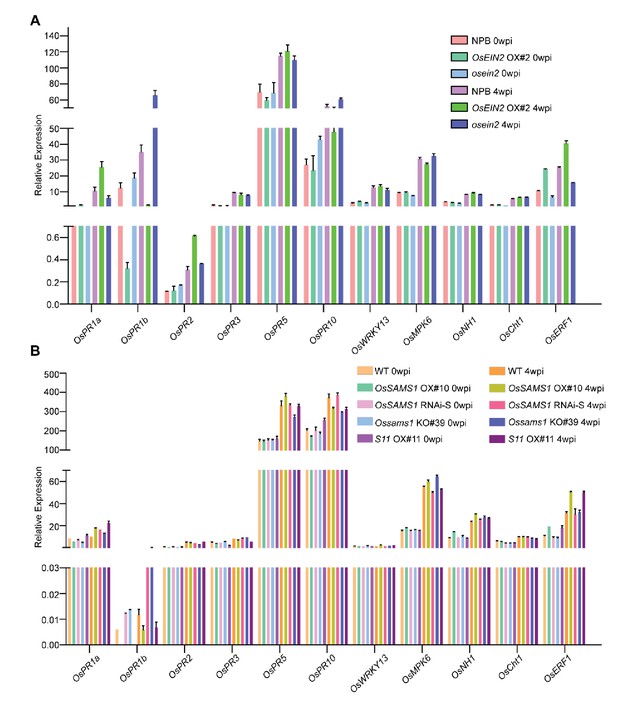
Detection of salicylic acid (SA)-, jasmonic acid (JA)- and ethylene-responsive genes.
(A) Expression of SA-, JA- and ethylene-responsive genes over time after RDV infection in NPB, OSEIN2 OX#2 and osein2 rice lines. (B) Expression of SA-, JA- and ethylene-responsive genes over time after RDV infection in WT, OsSAMS1 OX#10, OsSAMS1 RNAi-S, Ossams1 KO#39 and S11 OX #11 rice lines.
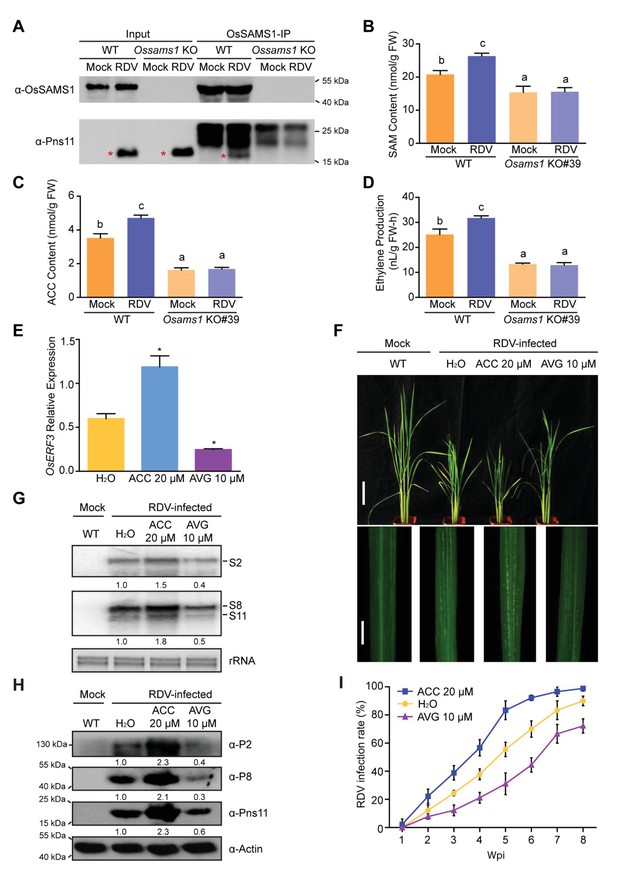
Ethylene is induced by RDV infection, which enhances the susceptibility of rice to RDV infection.
(A) In vivo pull-down in WT and Ossams1 KO lines, with or without RDV infection (40-d-old seedlings, 4 wpi), using anti-OsSAMS1 antibody. The red asterisk indicates the location of Pns11. (B) SAM content in WT and Ossams1 KO lines, with or without RDV infection (40-d-old seedlings, 4 wpi). (C) ACC content in WT and Ossams1 KO lines, with or without RDV infection (40-d-old seedlings, 4 wpi). (D) Ethylene content in WT and Ossams1 KO lines, with or without RDV infection (40-d-old seedlings, 4 wpi). Tukey’s honestly significant difference post hoc tests were performed for multiple comparisons. Letters indicate significantly different results, p<0.05. Data are from three replicates. FW, fresh weight. (E) Expression of OsERF3 after 24 hr treatment with H2O, 20 μM ACC, or 10 μM AVG. OsERF3 was chosen as the positive control for ethylene responsiveness. The average (± standard deviation) values from three biological replicates are shown. Significant differences (*p<0.05) are based on Student’s t-test. (F) Phenotypic comparison of mock-inoculated WT or RDV-infected rice plants pre-treated with H2O, 20 μM ACC, or 10 μM AVG; images were taken at 4 wpi. Scale bars = 10 cm (upper panel) and 5 cm (lower panel). (G) Northern blot analysis of RDV S2, S8, and S11 genomic segments. The blots were hybridized with radiolabeled riboprobes specific for each RNA segment. rRNAs were stained with ethidium bromide and served as loading controls. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (H) Western blot analysis of RDV P2, P8, and Pns11 proteins. Actin was probed and served as a loading control. Tissues were collected at 4 wpi. (I) The incidences of infection, which were determined by visual assessment of disease symptoms at 0–8 wpi of 30 individual plants for each case. Means and standard deviations were obtained from three independent experiments.
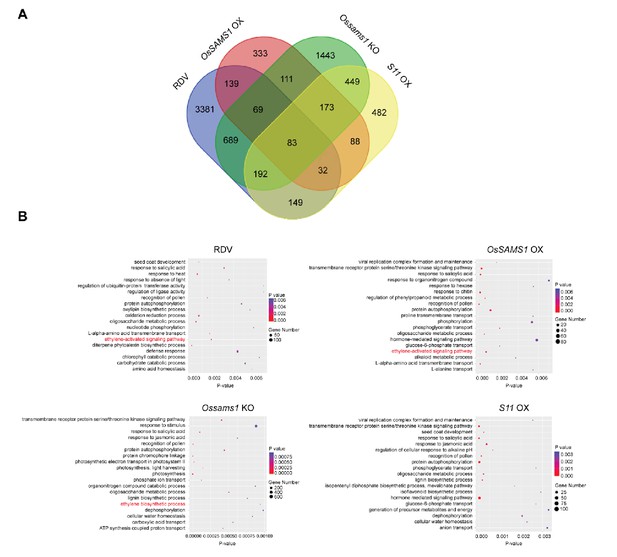
GO biological process over-representation in differentially expressed genes after RDV infection and in transgenic rice plants.
(A) Venn diagrams showing the overlaps among differentially expressed genes after RDV infection and in OsSAMS1 (OsSAMS1 OX#25, Ossams1 KO#39) and S11 (S11 OX#11) transgenic rice plants. For RDV-infected rice samples, 14-d-old seedlings of WT were inoculated with RDV and the RNA of the aboveground partsof the plants was isolated for analysis. For the transgenic plants, 42-d-old seedlings were used for RNA extraction. The responsive genes were identified by reads per kilobase per million reads (RPKM) requiring more than two-fold change between the experimental and control samples (FDR < 0.05). Each experiment was performed with three biological replicates. (B) Gene Ontology (GO) biological process over-representation for genes that are differentially expressed in RDV-infected and OsSAMS1 and S11 transgenic rice. A homology-based annotation was performed by Blast2Go software. Briefly, all the gene sequences of the differentially expressed genes were blasted against the Swiss-Prot database with high E-value (1 × 10−5) and GO annotation was performed against the Gene Ontology Database. Fisher’s Exact Test was used to detect GO biological process over-representation in the differentially expressed genes groups by using all identified genes as the background set. p<0.05.
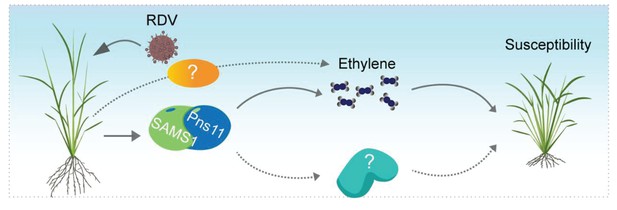
Possible model for Pns11 enhancement of OsSAMS1 enzymatic activity to increase ethylene levels and enhance host susceptibility to viral infection.
The model proposes that the RDV-encoded protein Pns11 specifically interacts with OsSAMS1 to enhance its enzymatic activity, resulting in a corresponding increase in ethylene, and thus enhancing rice susceptibility to RDV infection. However, RDV infection may affect other pathways and SAM is also the precursor of polyamine and a methyl donor for methylation, therefore, other pathways may be involved in RDV pathogenesis and need further study.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Non-preference test.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.025
-
Supplementary file 2
Record of the number of rice plants showing RDV symptoms at time course and infection rates statistical analysis.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.026
-
Supplementary file 3
Differentially expressed genes of RDV-infected and OsSAMS1 and S11 transgenic rice RNA-seq analysis.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.027
-
Supplementary file 4
Responses of genes related to polyamine by RDV infection.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.028
-
Supplementary file 5
(A) Constructs in this study. (B) Primers for plasmids constructions in this study. (C) LC-MS/MS conditions. (D) Primers for RNA gel blot probes, real-time PCR, and semi-quantitative RT-PCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.029
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.27529.030





