Vg1-Nodal heterodimers are the endogenous inducers of mesendoderm
Figures
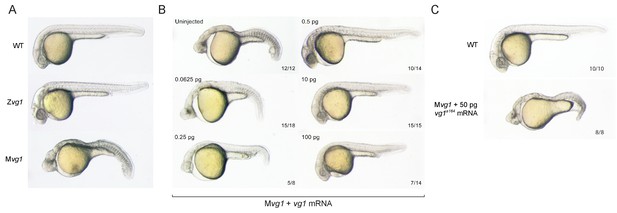
Maternal vg1 is required for mesendoderm formation.
(A) Zygotic and maternal vg1 (Zvg1 and Mvg1) mutants and wild-type (WT) embryo at 28 hours post-fertilization (hpf). See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for information about the vg1 mutant alleles, and Figure 1—figure supplement 2 for analysis of left-right asymmetry in WT and Zvg1 embryos. (B) Mvg1 embryos injected with 0.0625–100 pg of vg1 mRNA. (C) Mvg1 embryo injected with 50 pg of vg1 mRNA containing the 8 bp deletion found in the genetic mutants (vg1a164).
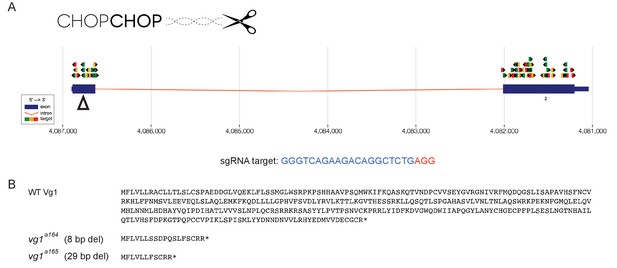
vg1 mutant alleles.
(A) Single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) targeting the vg1/dvr1/gdf3 gene were designed using CHOPCHOP (Labun et al., 2016; Montague et al., 2014). Colored arrows indicate possible sgRNA targets, color-coded according to predicted efficiency (green: good to red: bad). Open arrowhead indicates the location of the sgRNA used in this study. The sgRNA sequence is provided in blue, with the PAM motif in red. (B) 8 bp (vg1a164) and 29 bp (vg1a165) deletion alleles cause frameshifts in Vg1, truncating it from a 355 amino acid protein to predicted 18 and 11 amino acid peptides, respectively.
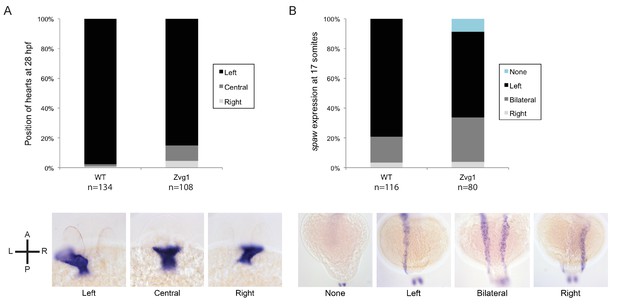
Left-right asymmetry in Zvg1 mutants.
(A) Heart positioning at 28 hpf in WT and Zvg1 embryos, detected by expression of cmlc2 by in situ hybridization. (B) Expression of southpaw (spaw), a Nodal ligand involved in left-right asymmetry, at the 17-somite stage in WT and Zvg1 embryos. spaw is expressed in the lateral plate mesoderm.
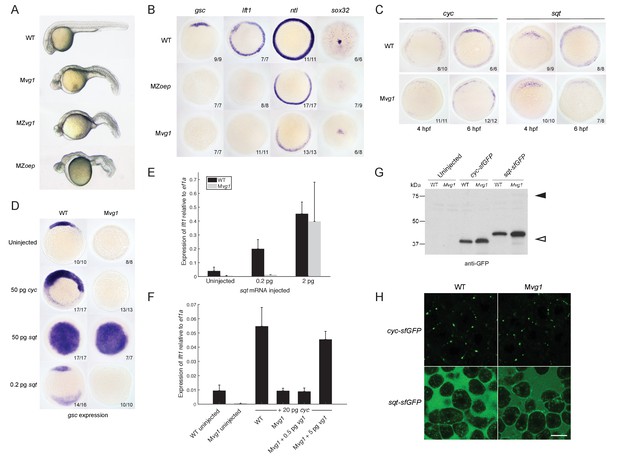
Endogenous Nodal signaling requires Vg1.
(A) Mvg1, maternal-zygotic vg1 (MZvg1) and maternal-zygotic oep (MZoep) mutants at 28 hpf. (B) Expression of Nodal target genes gsc, lft1 and ntl at 50% epiboly and sox32 at 90% epiboly in WT, Mvg1 and MZoep embryos. (C) cyc and sqt expression at 4 and 6 hpf in WT and Mvg1 embryos. (D) gsc expression at 50% epiboly in WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of cyc mRNA, 50 pg or 0.2 pg of sqt mRNA. (E) qPCR of lft1 expression at 50% epiboly relative to ef1a in WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 0.2 pg or 2 pg of sqt mRNA. The mean and standard error of the mean (SEM) was plotted. (F) qPCR of lft1 expression at 50% epiboly relative to ef1a in embryos injected with 20 pg of cyc mRNA in combination with 0.5 pg or 5 pg of vg1 mRNA. The mean and SEM was plotted. (G) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of cyc-sfGFP or sqt-sfGFP mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates the position of full-length protein, open arrowhead indicates processed protein. 8 embryos at 50% epiboly were loaded per well. (H) Live imaging of the animal cap of sphere-stage WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of cyc-sfGFP or sqt-sfGFP mRNA. Scale bar, 17 um.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw qPCR data for Figure 2E and F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28183.007
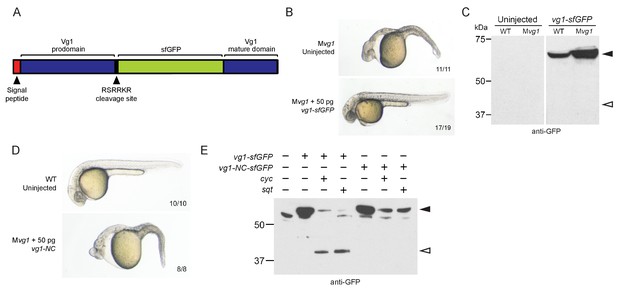
Vg1 processing requires Nodal.
(A) superfolderGFP (sfGFP) was inserted into vg1 downstream of the predicted basic cleavage site. (B) Mvg1 embryo injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA, shown at 28 hpf. (C) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-sfGFP; open arrowhead indicates the predicted size of cleaved Vg1-sfGFP. 8 embryos at 50% epiboly were loaded per well. (D) Mvg1 embryo injected with 50 pg of non-cleavable vg1 mRNA (vg1-NC, RSRRKR->SQNTSN), shown at 28 hpf. Embryos were injected with up to 200 pg of vg1-NC mRNA with no rescue. (E) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of Mvg1 embryos injected with 10 pg of vg1-sfGFP or vg1-NC-sfGFP mRNA and 10 pg of cyc or sqt mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-sfGFP, open arrowhead indicates cleaved Vg1-sfGFP. Molecular weights in kDa. 8 embryos at 50% epiboly were loaded per well. See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
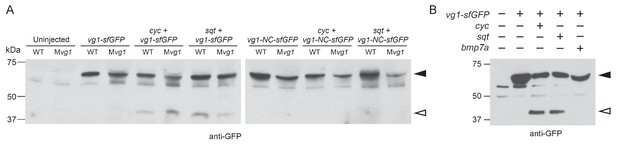
Vg1 processing requires Nodal.
(A) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP or vg1-NC-sfGFP mRNA and 50 pg of cyc or sqt mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-sfGFP, open arrowhead indicates cleaved Vg1-sfGFP. 8 embryos at 50% epiboly were loaded per well. (B) Anti-GFP reducing immunoblot of Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and 50 pg of cyc, sqt or bmp7a mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-sfGFP, open arrowhead indicates processed Vg1-sfGFP. Molecular weights in kDa. 8 embryos at 50% epiboly were loaded per well.
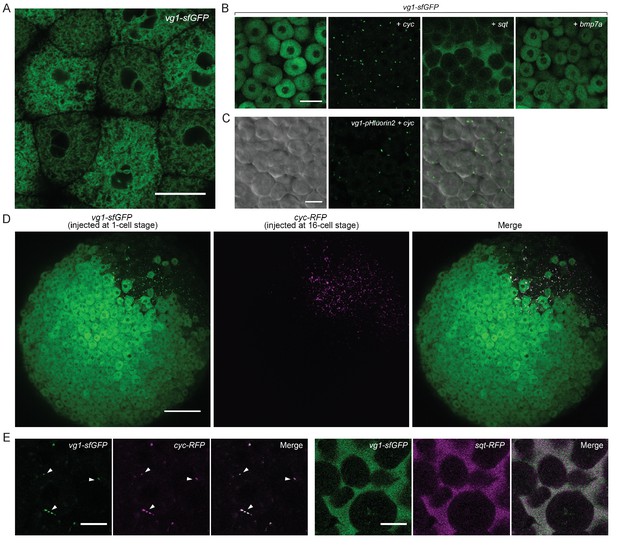
Vg1 secretion requires Nodal.
(A) Live imaging of Mvg1 embryo injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA. Scale bar, 17 um. (B) Mvg1 embryos co-injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and 50 pg of cyc, sqt or bmp7a mRNA. Scale bar, 17 um. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1A. (C) Mvg1 embryo co-injected with 50 pg of pH-sensitive fluorescent vg1 (vg1-pHluorin2) and 50 pg of cyc mRNA. Scale bar, 17 um. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1B. (D) Mvg1 embryo co-injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA at the 1-cell stage and 10 pg of cyc-RFP mRNA into 1 cell at the 16-cell stage. Scale bar, 100 um. (E) Mvg1 embryos co-injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and 50 pg of cyc- or sqt-RFP mRNA. Arrowheads indicate examples of co-localization. Scale bar, 17 um. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1C.
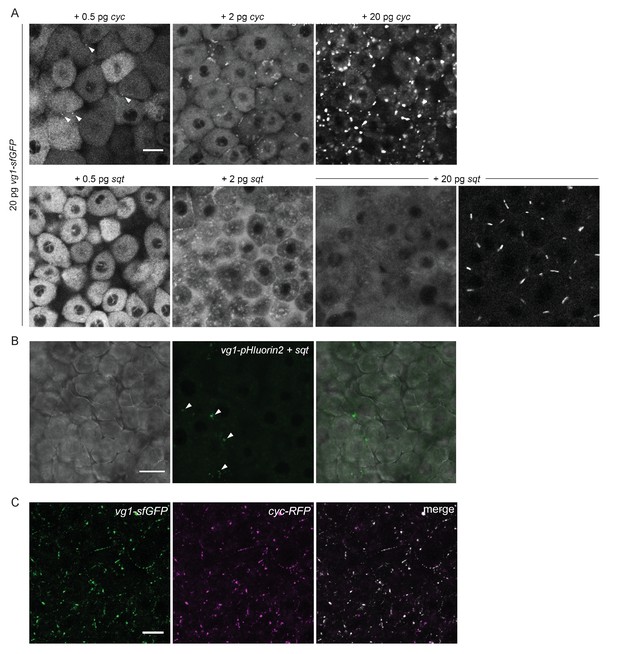
Vg1 secretion requires Nodal.
(A) Mvg1 embryos co-injected with 20 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and 0.5 pg, 2 pg or 20 pg of cyc or sqt mRNA. These images were all captured under the same microscope settings. Arrowheads indicate small extracellular puncta. Note that the puncta increase in size with increasing concentrations of cyc mRNA. Co-expression of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and sqt mRNA can result in extracellular diffuse signal and/or extracellular puncta. Scale bar, 17 um. See Table 1 for quantification. (B) Mvg1 embryo co-injected with pH-sensitive fluorescent vg1 (vg1-pHluorin2) and sqt. Arrowheads indicate fluorescent puncta. Scale bar, 17 um. (C) Z-stack of Mvg1 embryo co-injected with 50 pg of vg1-sfGFP and 50 pg of cyc-sfGFP. Scale bar, 17 um.
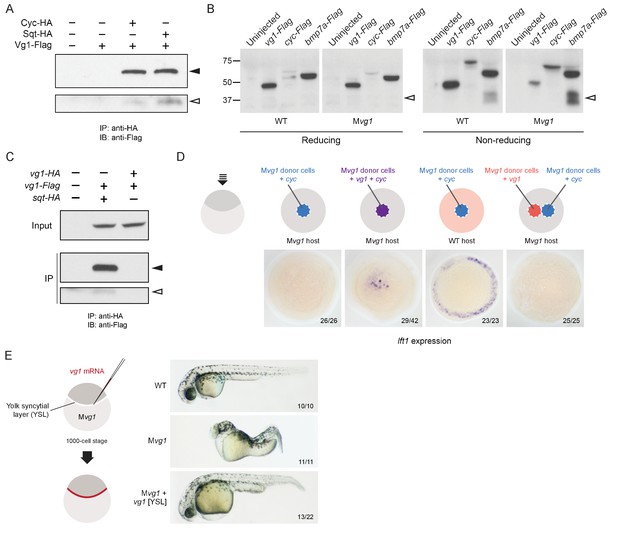
Vg1 and Nodal form heterodimers, and are only active when co-expressed.
(A) Anti-Flag reducing immunoblot (IB) of anti-HA immunoprecipitates (IP) from lysates of Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of cyc-HA, sqt-HA and/or 50 pg of vg1-Flag mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-Flag; open arrowhead indicates cleaved Vg1-Flag. See also Figure 5—figure supplements 1A and B. (B) Anti-Flag reducing and non-reducing immunoblots of WT and Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of vg1-Flag, cyc-Flag or bmp7a-Flag, collected at 50% epiboly. Under reducing conditions the proteins migrated at sizes consistent with the theoretical molecular weights for full-length monomers: Vg1-Flag – 42 kDa; Cyc-Flag – 58 kDa; Bmp7a-Flag – 50 kDa. Open arrowhead indicates where mature Bmp7a-Flag homodimers are expected to migrate as two species under non-reducing conditions (Little and Mullins, 2009). For an annotated gel, see Figure 5—figure supplement 1C. (C) Anti-Flag reducing immunoblot of anti-HA IP from lysates of Mvg1 embryos injected with 50 pg of sqt-HA and vg1-Flag mRNAs or vg1-HA and vg1-Flag mRNAs. Black arrowhead indicates full-length Vg1-Flag; open arrowhead indicates cleaved Vg1-Flag. (D) Transplantation of cells from donor embryos injected with cyc, vg1 or cyc and vg1 mRNAs into host embryos for analysis of Nodal target gene lft1 expression at 50% epiboly. mRNAs were co-injected with sfGFP mRNA to verify successful transplantation using DAB staining (Figure 5—figure supplement 2A). (E) Injection of vg1 mRNA into the yolk syncytial layer (YSL) of Mvg1 mutants, shown at 32 hpf. For Nodal target gene expression in vg1 mRNA YSL-injected embryos see Figure 5—figure supplement 2B. vg1 was co-injected with a fluorescent dextran to verify YSL localization (Figure 5—figure supplement 2C).
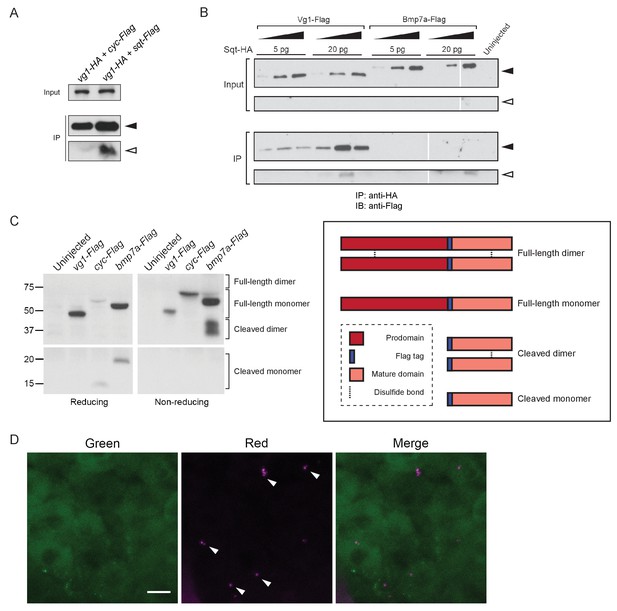
Vg1 and Nodal form heterodimers.
(A) Anti-Flag reducing immunoblot of anti-HA IP from lysates of WT embryos injected with 50 pg of vg1-HA mRNA and 50 pg of cyc-Flag or sqt-Flag mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length protein; open arrowhead indicates cleaved protein. (B) Anti-Flag reducing immunoblot of anti-HA IP from lysates of Mvg1 embryos injected with either 5 pg or 20 pg of sqt-HA mRNA combined with increasing concentrations (5 pg, 20 pg or 50 pg) of vg1-Flag or bmp7a-Flag mRNA. Black arrowhead indicates full-length protein; open arrowhead indicates cleaved protein. In contrast to Vg1-Flag, the mature domain of Bmp7a-Flag is more readily detected than the full-length protein (Little and Mullins, 2009). The samples were loaded onto three gels run under the same conditions at the same time (gel boundaries are marked by white vertical lines). (C) Anti-Flag reducing and non-reducing immunoblots of Mvg1 embryos injected with vg1-Flag, cyc-Flag or bmp7a-Flag mRNA (from Figure 5B). Approximate locations of expected monomers and dimers are indicated. TGF-beta family protein dimers are connected by disulfide bonds, which are broken under reducing conditions. (D) Z-stack of ~256-cell stage Mvg1 embryo co-injected with 100 pg of vg1-Dendra2 mRNA at the 1-cell stage and 5 pg of cyc mRNA at the 64-cell stage immediately followed by photoconversion. The red puncta represent Vg1-Dendra2 protein synthesized before the 64-cell stage that has heterodimerized and been secreted with Cyc protein.
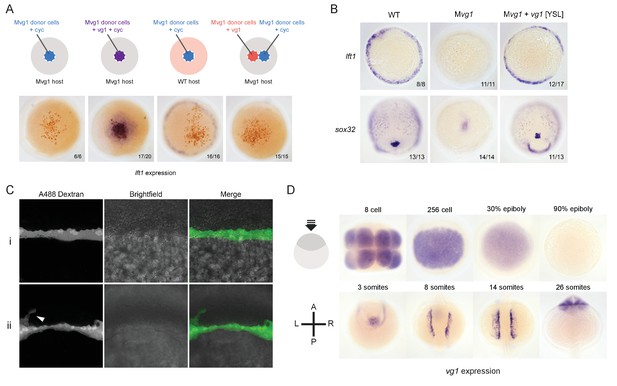
Vg1 and Nodal are only active when co-expressed.
(A) Transplantation experiments with DAB staining to show the location of the transplanted cells (orange) and lft1 expression (purple). (B) in situ hybridizations for a mesoderm marker (lft1) and an endoderm marker (sox32) in vg1 mRNA YSL-injected embryos. (C) Confocal imaging of Mvg1 embryos injected with 100 pg of vg1 and 500 pg of Alexa 488 dextran into the embryonic YSL at the 1000-cell stage. The majority of fluorescent dextran localized to the YSL (i), but in some cases dextran was detectable in a few margin cells (ii, white arrowhead). (D) Endogenous vg1 expression in WT embryos.
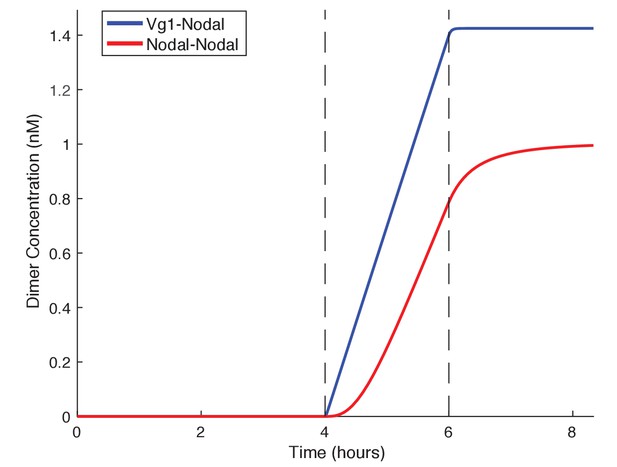
Vg1 can enable rapid response to low concentrations of Nodal.
Kinetic model comparing Nodal homodimer formation in the absence of Vg1 (red line) and Vg1-Nodal heterodimer formation in the presence of a maternal Vg1 pool (blue line). For both conditions Nodal monomer production begins at 4 hpf (the onset of zygotic transcription and translation, first dotted line) and concludes after mesendodermal patterning (6 hpf, second dotted line). For the heterodimer simulation an excess of Vg1 is provided in the initial conditions.
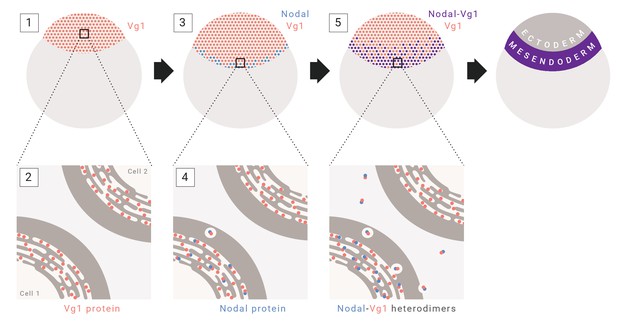
Model for mesendoderm induction in zebrafish.
As described in the main text: (1) vg1 mRNA is inherited from the mother, and is ubiquitous in the early embryo; (2) Vg1 protein is synthesized ubiquitously and retained predominantly in the ER; (3) cyc and sqt are transcribed and translated in the YSL; (4) Cyc and Sqt form heterodimers with Vg1, resulting in Vg1 secretion and cleavage; (5) Cyc-Vg1 and Sqt-Vg1 heterodimers activate the Nodal signaling pathway to induce mesendoderm.
Tables
Quantification of Vg1-sfGFP localization in Mvg1 embryos co-injected with 20 pg of vg1-sfGFP mRNA and 0.5–20 pg of cyc or sqt mRNA.
See Figure 4—figure supplement 1A for examples of Vg1-sfGFP extracellular localization.
| mRNA co-injected with 20 pg vg1-sfGFP | Intracellular | Extracellular puncta | Extracellular diffuse | Extracellular puncta + diffuse | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyc (pg) | 0.5 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| 20 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | |
| sqt (pg) | 0.5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 4 | |
| 5 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | |
| 20 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 3 | |
Additional files
-
Source code 1
Nodal homodimerization versus Vg1-Nodal heterodimerization simulation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28183.018
-
Source code 2
Ordinary differential equations for Nodal homodimer simulation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28183.019
-
Source code 3
Ordinary differential equations for Vg1-Nodal heterodimer simulation.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28183.020
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28183.021





