A comprehensive analysis of coregulator recruitment, androgen receptor function and gene expression in prostate cancer
Figures
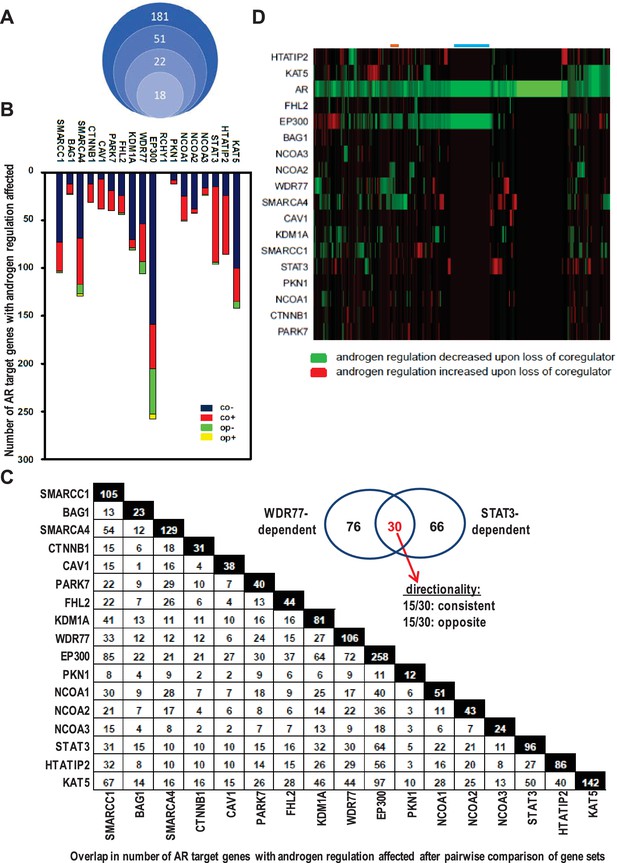
Contribution of 18 clinically relevant coregulators to androgen regulation of AR target gene expression.
(A) 181 coregulators that interact physically and functionally with AR were considered for inclusion. 51 of the 181 coregulators demonstrate deregulated protein expression between CaP and benign prostate and these coregulators were withheld for further study. Differential expression of 22 of these 51 coregulators correlated with more aggressive CaP behavior. For these 22 coregulators, which likely represent critical contributors to AR activity in CaP progression, a siRNA screen was done in LNCaP cells to evaluate effects on AR expression, CaP cell morphology and CaP cell death. Silencing of 4 of the 22 coregulators decreased markedly AR protein expression. The latter 4 coregulators were excluded from subsequent experiments and the remaining 18 coregulators were withheld for subsequent studies on AR target gene expression. (B) Gene specificity and context-dependency of coregulator contribution to androgen regulation of AR target gene expression. co+, androgen regulation is increased (+) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation remains consistent (co); co-, androgen regulation is decreased (-) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation remains consistent (co); op+, androgen regulation is increased (+) after loss of coregulator but direction of regulation is opposite (op); op-, androgen regulation is decreased (-) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation is opposite (op). Y-axis and bar lengths indicate the number of AR target genes for which androgen regulation is altered after silencing of each coregulator that is listed on the X-axis. Results reflect the effect of 48 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881. R1881 or vehicle treatment was administered 42 hr after siRNA transfection. Figure 1—source data 1 provides numerical information for data shown here. (C) Pairwise comparison between all coregulator-dependent AR target gene sets to determine overlap in number of genes. The X- and Y-axes mark the AR target gene sets for which androgen regulation is altered after knock-down of the individual coregulators that are listed on the axes. Black square indicates number of genes in the corresponding coregulator-dependent gene set. White square indicates the number of genes that overlap between 2 gene sets that intersect (left panel). Figure 1—source data 2 provide the p-values for the significance of the overlap for the 136 pairwise comparisons. The Venn diagram shows the number of genes that are unique to or are shared by the WDR77- and STAT3-dependent AR target gene sets. Of the 30 genes that overlap between the 2 AR gene sets, 15 show consistent directionality of androgen regulation in both gene sets. The other 15 genes display opposite directionality of androgen regulation (right panel). (D) Unsupervised clustering of AR target genes (columns) based on coregulator dependence of affected AR target gene sets (rows). Green, gene for which androgen regulation decreases upon loss of coregulator (-); red, gene for which androgen regulation increases upon loss of coregulator (+); blue line, mutual exclusivity in coregulator dependence (EP300); orange line, cooperativity in coregulator dependence (EP300 and SMARCA4). AR silencing served as the control condition.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Gene specificity and context-dependency of coregulator contribution to androgen regulation of AR target gene expression.
co+, androgen regulation is increased (+) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation remains consistent (co); co-, androgen regulation is decreased (-) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation remains consistent (co); op+, androgen regulation is increased (+) after loss of coregulator but direction of regulation is opposite (op); op-, androgen regulation is decreased (-) after loss of coregulator and direction of regulation is opposite (op). Results reflect the effect of 48 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881. R1881 or vehicle treatment was administered 42 hr after siRNA transfection. Treatment groups contained 3 biological replicates.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.006
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Summary of p-values for data presented in Figure 1C.
Hypergeometric test was used to derive the statistical significance of the overlap between lists of genes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.007
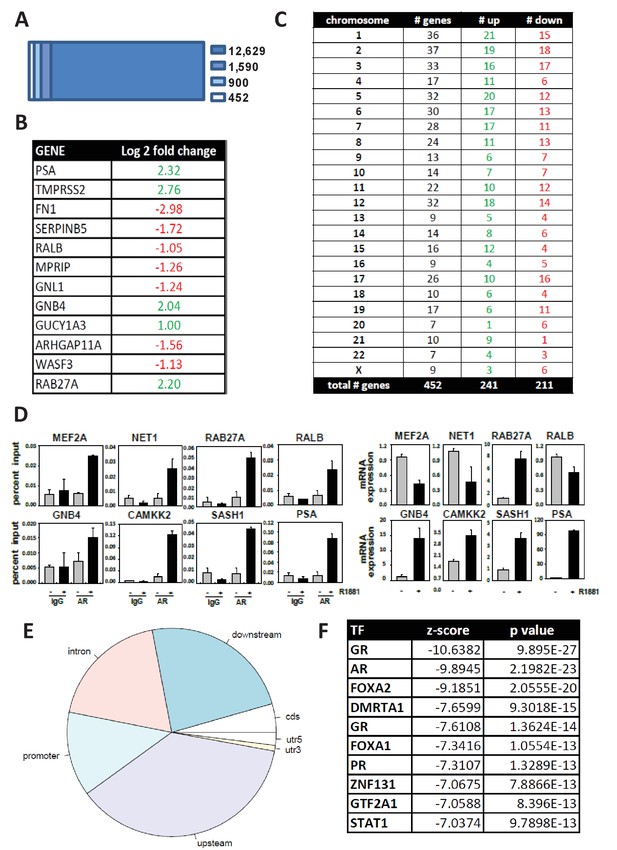
Isolation and validation of a 452 AR target gene signature.
(A) 1590 of 12,629 genome-wide ARBS sites in LNCaP cells are present within 300 Kb of the TSSs of 900 androgen-responsive genes. Of these 900 genes, 452 had at least a 2-fold change in expression upon exposure of LNCaP cells to 5 nM of the synthetic androgen R1881 for 48 hr, as determined using a custom Agilent gene expression oligoarray. (B) Representative sample of 452 AR target genes. Log fold change indicates the level of androgen regulation. Fold change represent mean value obtained from biological triplicates. Green, androgen-induced gene; red, androgen-repressed gene. (C) Overview of chromosomal distribution of 452 AR target genes. Green, number of androgen-induced genes; red, number of androgen-repressed genes. (D) ChIP validation of androgen-dependent recruitment of AR to the predicted AREs within AR target genes (left panel). Real-time RT-PCR validation of androgen dependent changes in corresponding gene expression (right panel). Results reflect the effect of 16 hr treatment with 5nM R1881. (E) Genomic location of ARBSs within the 452 AR target genes. (F) Cistrome identification of 10 most significantly enriched TF binding sites in ARBSs of the 452 AR target genes, with corresponding z-scores and p values. The 2 GR entries reflect different consensus binding motifs.
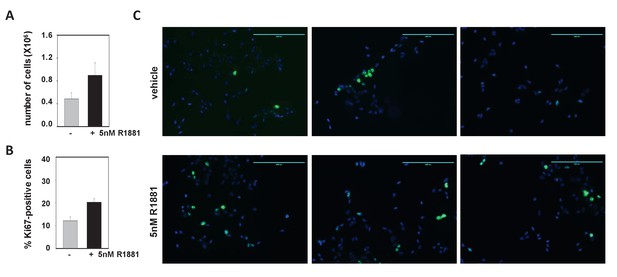
The effect of 5nM R1881 on proliferation of LNCaP cells.
(A) LNCaP cells were treated with 5nM R1881 or ethanol vehicle for 48 hr. After 48 hr, the cells were detached and the cell number was counted using the trypan blue exclusion method as described. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and represent 4 biological replicates per treatment group. (B) LNCaP cells were treated with 5nM R1881 or ethanol vehicle for 48 hr. After 48 hr, cells were analyzed via immunofluorescence staining for proliferation marker Ki-67 (green). Cells were DAPI-stained to visualize cell nuclei (blue). Images were taken at 10x magnification using an EVOS FL system and semi-quantified using ImageJ software version 1.43. The percentage of Ki67-positive nuclei were determined. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and represent counts from 1,800 cells per treatment condition, which were derived from 22 different slide areas each. (C) Three representative images of Ki-67-and DAPI-stained cells after 48 hr treatment with ethanol (top panel) or 5nM R1881 (bottom panel).
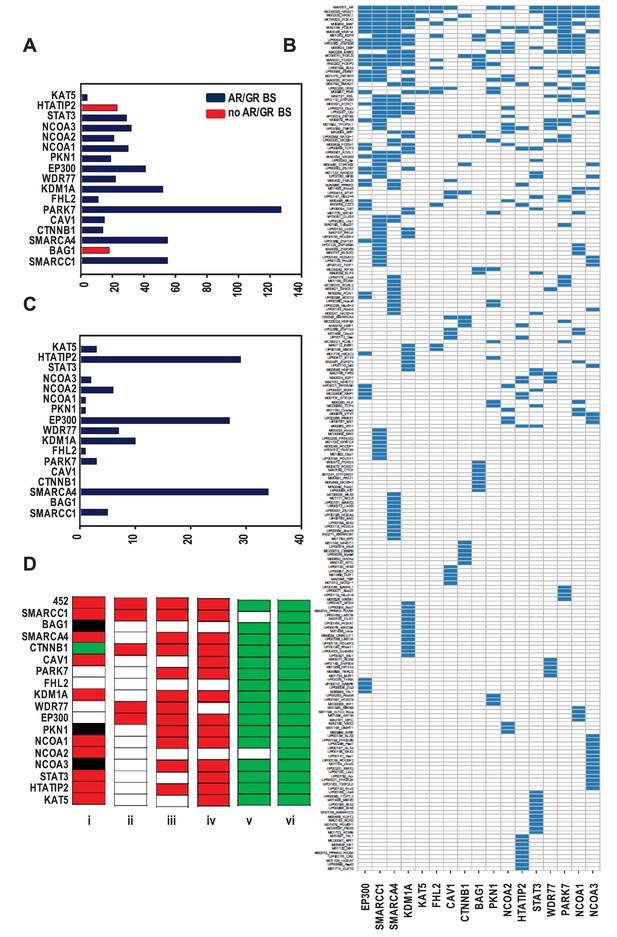
Organization of ARBSs, cell biology and clinical relevance associated with the coregulator-dependent AR target gene signatures.
(A) Number of overrepresented TF binding sites (TFBSs), and AR or GR binding sites (BSs) that are identified in ARBSs of coregulator-dependent AR target gene sets using Cistrome project tools. Figure 2—source data 1 provides numerical information for data shown here. (B) Heatmap summarizing clustering of overrepresented TFBSs within and among ARBSs in the AR target gene sets. Blue bar, one overrepresented TFBS. (C) Number of IPA categories that associate with individual coregulator-dependent AR target gene signatures. Figure 2—source data 2 provides numerical information for data shown here. (D) GSEA analyses of coregulator-dependent AR target gene sets between normal prostate from patients treated with dutasteride versus vehicle treatment (GSE9972) (i), between localized CaP versus normal prostate (GSE21034) (ii), between localized CaP that recurs biochemically versus localized CaP that does not recur biochemically (GSE21034) (iii), between localized versus metastatic CaP (GSE32269) (iv), between CaP versus normal bone marrow (GSE32269) (v) and between luminal versus basal epithelial prostate cells (GSE67070) (vi). Red, significant negative enrichment; green, significant positive enrichment; white, no enrichment; black, NES could not be determined. False discovery rate <0.25 was considered significant enrichment.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Overview of number of TF binding sites (TFBSs), and AR or GR binding sites (BSs) that are identified in ARBSs of coregulator-dependent AR target gene sets using Cistrome project tools.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.010
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Overview of the number of Ingenuity Pathway Analysis categories that associate with individual coregulator-dependent AR target gene signatures.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.011
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Overview of transcription factor (TF) binding sites identified in ARBSs present in 452 AR target genes.
Overview of transcription factor (TF) binding sites identified in ARBSs present in 452 AR target genes. Left to right: Column 1: TF binding sites identified in ARBSs in the overarching 452 AR target gene signature. Columns 2–18: TF binding sites identified in ARBSs in AR target gene sets that depend on the 17 coregulators shown. Blue, statistically significantly enrichment of the TF binding sites and corresponding p-value; none, no statistically significant TF binding site enrichment.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.012
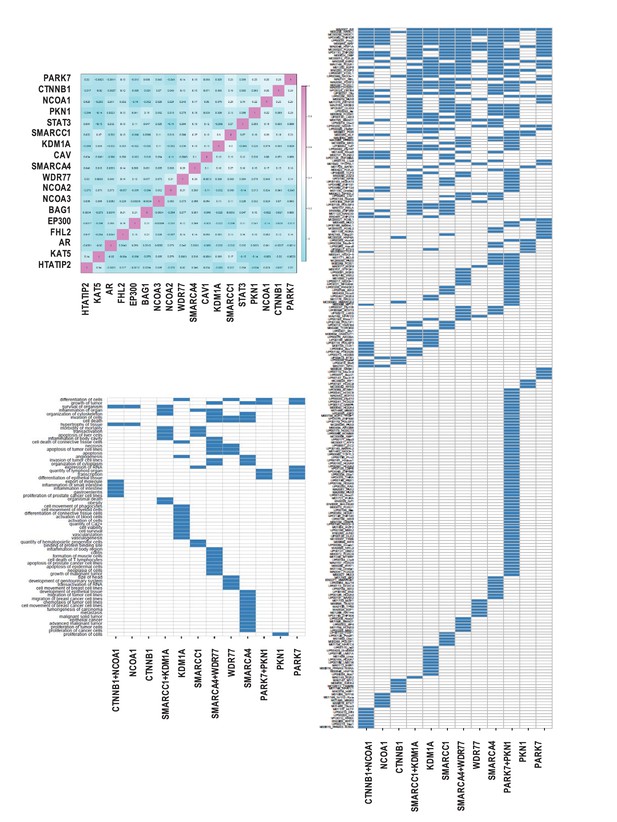
Correlation of coregulator-dependent androgen-responsiveness of AR target genes.
(A) Pair-wise pearson correlation of coregulator-dependent androgen-responsiveness of AR target genes. For each pair of coregulators, the correlation was calculated based on the effect of loss of coregulator on androgen-regulation of AR target gene expression, as described in Supplementary file 5, panel A. (B) Cistrome analysis on ARBSs found in 4 pairs of AR target gene sets with the strongest Pearson correlation. AR target gene set pairs CTNNB1 +NCOA1, PARK7 +PKN1, SMARCA4 +WDR77 and SMARCC1 +KDM1A showed the strongest Pearson correlation of coregulator-dependent androgen-responsiveness, as shown in panel A. For each paired gene set, cistrome analysis was done on ARBSs from the individual AR target gene sets and on combined ARBSs found in both gene sets. The heatmap summarized the clustering of overrepresented TFBSs within and among ARBSs in the AR target gene sets. Blue bar, one overrepresented TFBS. (C) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis on gene signatures that are make up 4 pairs of AR target gene sets with the strongest Pearson correlation. AR target gene set pairs CTNNB1 +NCOA1, PARK7 +PKN1, SMARCA4 +WDR77 and SMARCC1 +KDM1A showed the strongest Pearson correlation of coregulator-dependent androgen-responsiveness, as shown in panel A. For each paired gene set, IPA identified the enriched functions annotations that are associated the individual AR target gene sets and the combined gene set. The heatmap summarizes the clustering of enriched functions within and among AR target gene sets. Blue bar, one enriched function term.
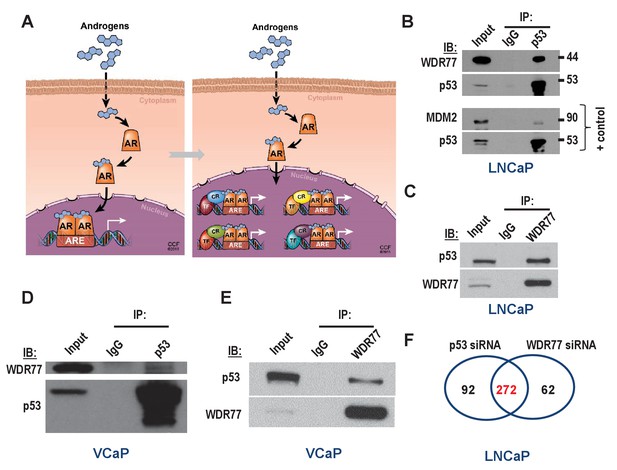
Isolation of coregulator-dependent AR transcriptional codes.
(A) Global AR action in CaP cells partitions into discrete transcriptional mechanisms in which ARE-bound AR interacts with select coregulators (CRs) and transcription factors (TFs) to control distinct biological processes and CaP aggressiveness. (B, C) Co-immunoprecipitation assays in which order of antibody used for co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting is switched show interaction between WDR77 and p53. Co-IP is done in LNCaP cells that express wild-type p53. Interaction between p53 and MDM2 is shown as a positive control. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting. (D, E) Co-immunoprecipitation assays in which order of antibody used for co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting are switched show interaction between WDR77 and p53 in VCaP cells that express p53 R248Q. (F) Overlap in genome-wide p53- and WDR77-dependent androgen-responsive gene expression. Results reflect the effect of 48 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881. R1881 or vehicle treatment was administered 42 hr after siRNA transfection. Numbers, number of genes.
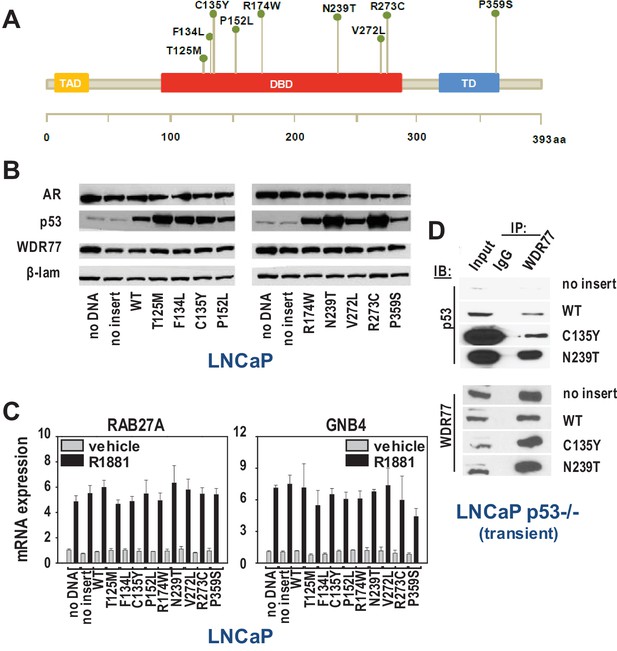
WDR77-p53 interaction is maintained in CaP cells that express gain of function p53 mutants.
(A) Overview of p53 somatic mutations that are present at the subclonal level in localized CaP and are enriched in metastatic CR-CaP. Mutations studied were reported in (Hong et al., 2015). (B) Western blotting on nuclear fractions of LNCaP cells that were transfected with empty vector, vector expressing wild-type p53, or vectors that individually express each of the 9 clinically relevant p53 mutants. To control for loading differences, blots were reprobed for laminin. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of the effect of transfections using empty vector, vector expressing wild-type p53, or vectors that individually express each of the 9 clinically relevant p53 mutants. 16 hr after electroporation (Schmidt et al., 2012), LNCaP cells were seeded in medium supplemented with charcoal-stripped FBS. 1 day later, medium was changed and cells were treated with 5nM R1881 or vehicle for 48 hr. RAB27A and GNB4 expression was evaluated using real-time RT-PCR. Target gene mRNA levels were normalized with the values obtained from GAPDH expression and are expressed as relative expression values, taking the value obtained from one of the vehicle-treated samples as 1. Columns, means of values obtained from 3 independent biological replicates; bars, sem. Grey bars, treatment with vehicle; black bars, treatment with R1881. (D) Co-IP studies in LNCaP cells in which p53 expression had been silenced (Guseva et al., 2012), and subsequently transfected using empty vector, vector encoding wild-type p53 or p53 mutants C135Y or N239T. Cells were harvested 72 hr after transfection. Transient, LNCaP cells in which endogenous expression of p53 had been silenced (Guseva et al., 2012) were transiently transfected with empty vector, or expression vectors for wild-type p53, p53 C135Y or p53 N239T. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting
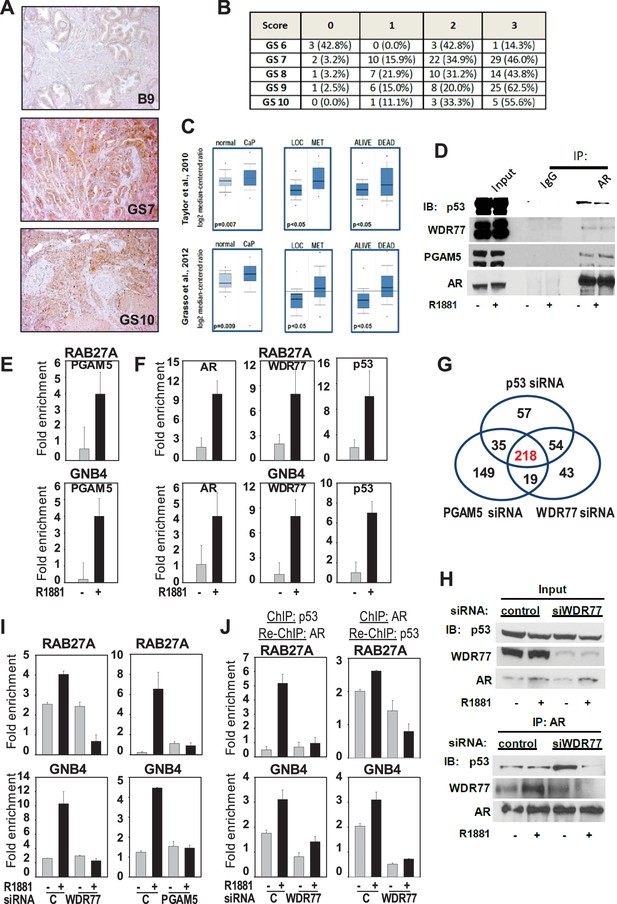
Mechanism underlying WDR77-dependent AR and p53 interaction.
(A) Representative images of prostate and CaP TMA cores that were subjected to immunohistochemistry using an antibody directed against PGAM5. B9, benign prostate; GS, Gleason score. 10x magnification. (B) Overview of quantitation of PGAM5 immunohistochemistry on CaP cores. Columns represent different scores. Rows represent CaP cores that are grouped according to Gleason scores. GS, Gleason score. Number, number of TMA cores; %, percentage of cores per GS group. (C) Oncomine analyses done on 2 CaP gene expression profiling studies. PGAM5 mRNA expression was determined in normal prostate versus CaP (left panels), in localized (LOC) CaP versus metastatic (MET) CaP (middle panels), and taken into consideration follow-up information on 5 year survival status of patients (alive or dead). Figure 5—source data 1 provides more information on PGAM5 peptides identified using IP-mass spectrometry. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation assay shows interaction between AR, WDR77, PGAM5 and p53. Co-IP is done in LNCaP cells after 16 hr treatment with R1881 or vehicle. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting. (E) ChIP validation of androgen-dependent recruitment of PGAM5 to AREs within WDR77-responsive AR target genes RAB27A and GNB4. Results reflect the effect of 16 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881 or vehicle. (F) ChIP validation of androgen-dependent recruitment of AR, PGAM5 and p53 to the same AREs within WDR77-responsive AR target genes RAB27A and GNB4. Culture conditions are as under E. (G) Overlap in genome-wide p53-, WDR77-, and pGAM5-dependent androgen-responsive gene expression. Results reflect the effect of 48 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881. R1881 or vehicle treatment was administered 42 hr after siRNA transfection. Numbers, number of genes. (H) Co-immunoprecipitation assay demonstrates WDR77-dependence of AR and p53 interaction. Co-IP is done in LNCaP cells after 16 hr treatment with R1881 or vehicle. Treatment was given 72 hr after transfection using siRNAs targeting WDR77 or control siRNAs. (I) ChIP validation of reliance of androgen-dependent recruitment of p53 to WDR77-responsive AREs on WDR77 and PGAM5. Culture conditions are as under E. (J) ChIP-re-ChIP experiments validate androgen- and WDR77-dependent co-recruitment of p53 and AR to the same GNB4 and RAB27A gene regions. Culture conditions and data representation is as under H. Data shown in panels D-I are derived from LNCaP cells.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
PGAM5 peptides identified after IP-mass spectrometry.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.016
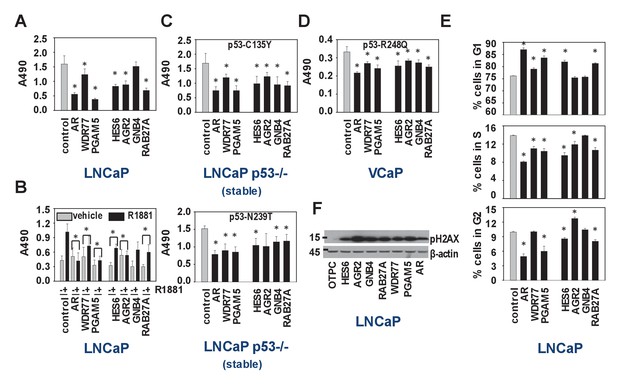
Biological consequences of WDR77-dependent AR and p53 interaction.
(A) Silencing of regulators and effectors of the AR-WDR77-p53 transcriptional code decreases CaP cell viability. LNCaP cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting AR, WDR77, PGAM5, HES6, AGR2, GNB4 or RAB27A, or control siRNAs. Medium was changed 16 hr later, and an MTS assay reading absorbance at 490 nm was performed 96 hr after transfection. Columns, Mean values from five individual measurements; bars, SEM. (B) Viability experiment as under (A) except that cells were treated for 96 hr with vehicle (grey bars) or 5nM R1881 (black bars) at medium change after 16 hr. (C) Viability experiment described under (A) in p53-null LNCaP cells that stably express p53 C135Y (top panel) or N239T (bottom panel). (D) Viability experiment described under (A) in VCaP cells that endogenously express p53 R248Q. (E) Silencing of regulators and effectors of the AR-WDR77-p53 transcriptional code delays cell cycle progression. LNCaP cells were transfected and harvested as above. Cells were stained using propidium iodide and flow cytometry was performed. Columns, Mean values from three individual biological replicates; bars, SEM. (F) Silencing of regulators and effectors of the AR-WDR77-p53 transcriptional code alters phospho-H2AX expression. LNCaP cells were transfected as above. Cells were harvested and total protein extracts were subjected to western blot analysis using an antibody directed against phospho-H2AX. To control for potential loading differences, blots were stripped and reprobed with an antibody targeted at β-actin. Figure 6—source data 1 provides p-values for the data shown in panels A, B, C, D and E. *, significance with p<0.05 compared to control siRNA condition; stable, LNCaP cells in which endogenous expression of p53 had been silenced were stably transfected with expression vectors for p53 C135Y or p53 N239T.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Summary of p-values for data presented in Figure 6.
For panels A, C, D, and E, p-values were derived using welch two sample t-test. Values are compared to those obtained from the control siRNA group with changes considered significant at p<0.05. For panel B, p-values are derived using paired t-test. The fold change in values obtained after R1881 treatment is calculated for each siRNA group and values for specific siRNA groups are compared to those derived from the control siRNA group. Changes are considered significant at p<0.05.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.018
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Design of oligoarray, overview of AR target genes studied, and overview of coregulators considered for analysis.
(A) Overview of genes included in custom Agilent oligoarray Rows, categories of genes included on 8 × 15K custom Agilent oligoarray. Columns, Number of genes identified for inclusion on the array, and number of genes for which Agilent catalogue probes were available for inclusion. (B) Overview of 452 AR target gene signature Gene name, HUGO gene symbol; FC, fold change (C) Overview of coregulators considered, prioritized and withheld for analysis A PudMed search for papers that contain the terms ‘AR’ and ‘CaP’ in their title and/or abstract was performed. Abstracts fulfilling these criteria were screened for reference to coregulator function, and if so, full-length papers were reviewed individually to verify description of a bona fide AR-associated coregulator. Left to right: Column 1: 181 coregulators for which literature search was done. Column 2: 51 coregulators for which differential protein expression has been reported in CaP when compared to benign prostate (yes entries). Column 3: 22 coregulators for which differential expression in CaP correlated with aggressive disease, and were analyzed in Figures 4–6 (yes entries). Column 4: 18 coregulators for which siRNA-mediated silencing did not affect AR expression, CaP cell morphology or CaP cell survival and were included in final analyses (yes entries).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.019
-
Supplementary file 2
Characterization of 452 AR target gene signature
(A) Androgen regulation of AR target gene expression in VCaP cells VCaP cells were seeded in medium supplemented with charcoal-stripped FBS (CSS). 2 days later, medium was changed and cells were treated with 5 nm R1881 or ethanol vehicle for 48 hr. Cells were harvested and AR target gene expression was evaluated using real-time RT-PCR. Target gene mRNA levels were normalized with the values obtained from GAPDH expression and are expressed as relative expression values, taking the value obtained from one of the vehicle-treated samples as 1. Columns, means of values obtained from three independent biological replicates; bars, sem. Note the consistency of androgen regulation of majority (7/8) of AR target genes obtained from LNCaP cells also in VCaP cells. (B) Kinetics of androgen regulation of AR target gene expression LNCaP cells were seeded in medium supplemented with charcoal-stripped FBS (CSS). 2 days later, medium was changed and cells were with 5 nm R1881 or ethanol for 4 or 8 hr. Timepoints were chosen as androgen regulation of androgen-induced AR target genes is detectable at 4 hr, and androgen regulation of androgen-repressed AR target genes becomes apparent at 8 hr. Target gene mRNA levels were normalized with the values obtained from GAPDH expression and are expressed as relative expression values, taking the value obtained from one of the vehicle-treated samples at the 4 hr time point as 1. Columns, means of values obtained from three independent biological replicates; bars, sem values. Note the consistency in kinetics of androgen regulation of newly recognized AR target genes (bottom 2 rows) with that of the well-known ARE-driven genes PSA, SCAP, FN1 and SERPINB5 (top row). (C) Representative real-time RT-PCR validation of Agilent oligoarray data Side-by-side comparison of Agilent oligoarray data and real-time RT-PCR data using same RNA samples. Expression data shown are derived from genes for which Agilent oligoarray expression was low (Y axis values, top row), and thus likely less reliable.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.020
-
Supplementary file 3
Ingenuity pathway analyses on AR target gene signatures
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.021
-
Supplementary file 4
Impact of silencing of 22 clinically relevant coregulators on prostate cancer cells and AR expression
(A) Real-time RT-PCR validation of siRNA-mediated coregulator knock-out efficiency LNCaP cells were transfected with On Target siRNA SmartPools directed against 22 coregulators, against AR, or with non-targeting On Target Plus control SmartPool. At 96 hr after transfection, cells were harvested and RNA was extracted for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Target gene mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are expressed as relative expression, taking the value obtained from one of the control siRNA-transfected conditions as 1. Columns, means of values obtained from three independent biological replicates; bars, sem. Gray bars, control siRNA-transfected cells; Black bars, specific siRNA-transfected cells (B) Morphology of LNCaP cells following coregulator silencing LNCaP cells were transfected with individual On Target siRNA SmartPools directed against each of the 22 coregulators, against AR, or a non-targeting On Target Plus control SmartPool. At 96 hr after transfection, cells were imaged using Infinity Analyze software. (C) Effects of coregulator silencing on AR protein expression levels LNCaP cells were transfected with individual On Target siRNA SmartPools directed against each of the 22 coregulators or against AR, or with non-targeting On Target Plus control SmartPools (c). At 96 hr after transfection, cells were harvested and total protein extracts were subjected to western blot analysis using an antibody directed against AR. To control for potential loading differences, blots were stripped and reprobed with an antibody targeted at β-actin.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.022
-
Supplementary file 5
Impact of coregulator silencing on androgen regulation of AR target genes
(A) Nomenclature used to describe the effect of loss of coregulator on androgen regulation of AR target gene expression co+, androgen regulation is more pronounced (+) after loss of coregulator expression and the direction of androgen regulation remains consistent (co); co-, androgen regulation is less pronounced (-) after loss of coregulator expression and the direction of androgen regulation remains consistent (co); op+, androgen regulation is more pronounced (+) after loss of coregulator expression and the direction of androgen regulation is opposite (op); op-, as androgen regulation is less pronounced (-) after loss of coregulator expression and direction of androgen regulation is opposite (op). Androgen-induced, gene which expression is increased in control siRNA (c)-transfected cells after androgen stimulation; androgen-repressed gene which expression is decreased in control siRNA (c)-transfected cells after androgen stimulation. Spec, specific for one coregulator (B) Overview of coregulators that affect androgen regulation of the genes encoding RAB27A and GNB4 (C) Experimental validation of recruitment of 6 representative coregulators to the genes encoding RAB27A and GNB4 ChIP studies verifying recruitment of 6 coregulators at AREs within the genes encoding RAB27A and GNB4. ChIP was done on LNCaP cells that had been treated with 5nM R1881 or vehicle for 16 hr. Coregulators analyzed via ChIP were chosen based on availability of suitable antibodies. (D) Time course of androgen-dependent recruitment of AR (left), NCOA3 (middle) and WDR77 (right) to AREs in the genes encoding RAB27A and GNB4 ChIP was done on LNCaP cells that had been treated with 5nM R1881 or vehicle for 1, 4, 16 or 48 hr. (E) Impact of knock-down of WDR77 or NCOA3 on kinetics of androgen-regulation of RAB27A and GNB4 LNCaP cells were transfected with On Target siRNA SmartPools directed against WDR77 or NCOA3, or with non-targeting On Target Plus control SmartPool (c). At 42 hr after transfection, cells were treated with 5nM R1881 (+) or vehicle (-). After 1, 4, 16 or 48 hr, cells were harvested and RNA was extracted for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Target gene mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH expression and are expressed as relative expression, taking the value obtained from one of the control siRNA-transfected conditions for each siRNA group at each time point as 1. Columns, means of values obtained from three independent biological replicates; bars, sem. Gray bars, control siRNA-transfected cells; Black bars, specific siRNA-transfected cells. (Top left) Effects of WDR77 (top) and NCOA3 (bottom) silencing on GNB4 mRNA expression; (Top right) Effects of WDR77 (top) and NCOA3 (bottom) silencing on RAB27A mRNA expression: (Bottom panels) verification of WDR77 siRNA-mediated silencing (left), verification of NCOA3 siRNA-mediated silencing (right).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.023
-
Supplementary file 6
Isolation of a STAT3-dependent AR-IRF1 transcriptional code.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation assay shows interaction between IRF1 and STAT3 in LNCaP cells. (B) Overlap in genome-wide IRF1- and STAT3-dependent androgen-responsive gene expression. Results reflect the effect of 48 hr treatment of LNCaP cells with 5nM R1881. R1881 or vehicle treatment was administered 42 hr after siRNA transfection. Numbers, number of genes. (C) Overlap in IPA functional annotation between the androgen-responsive genes that depend on WDR77 and p53 (from Figure 3, panel F) and the androgen-responsive genes that depend on IRF1 and STAT3 (from panel B of this figure) (p<2.2.E-16). Genes subjected to IPA are those listed in the center of Venn diagrams shown in panel F of Figure 3 and panel B of this figure. Numbers, number of functional annotations.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.024
-
Supplementary file 7
cBio Portal analysis of copy number variation and somatic mutations that affect the 18 identified coregulators in patients prostate cancer specimens.
n = number of CaP clinical specimens for which DNA sequencing or copy number variation data is available. Numbers in columns indicate the percentage of CaP cases in each study for which somatic mutations and/or copy number variations that affect corresponding coregulator have been reported.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.025
-
Supplementaty file 8
TP53 binding motif identified from the promoters of WDR77- and p53- dependent androgen-responsive genes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.026
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.28482.027





