Mouse color and wavelength-specific luminance contrast sensitivity are non-uniform across visual space
Figures
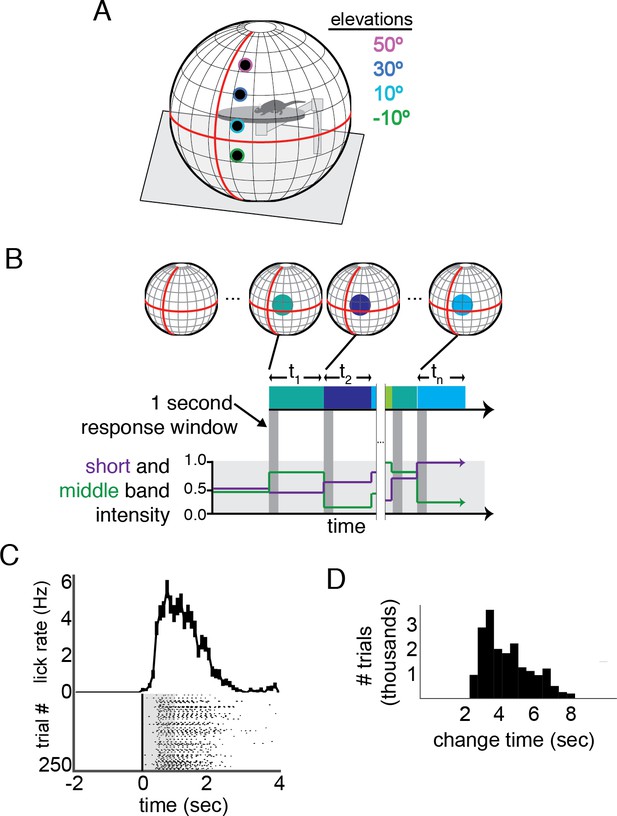
Change detection task in an immersive visual stimulation environment capable of delivering short- and middle-wavelength band stimulation.
(A) The visual stimulation environment, with the positions and size of stimuli shown; the colored edges were not a part of the presented stimulus, but indicate the color scheme used to denote elevation throughout the other figures. (B) A schematic of the task. The background was set to mean intensity for each wavelength band. At variable times, tn, the intensity of short and middle wavelength bands within a 15° diameter circle changed. If the mouse licked within 1 s of this change (indicate by the dark grey boxes), a reward was delivered. Schematic short and middle band intensities are shown on the lower plot; corresponding stimulus changes are shown both in blocks and cirlces above each epoch. The schematized circles are larger than actual stimuli, for clarity. (C) Example performance in a single session across 250 trials. Each lick is shown relative to stimulus change; the response window is overlaid in grey. A histogram of lick times is shown above. Error bars are S.E.M. (D) The distribution of change times (t in panel B) across the trials used for analysis of change detection performance. The distribution follows a log sampling distribution, enforcing roughly equal probability of a change occurring as the mouse continues to wait.
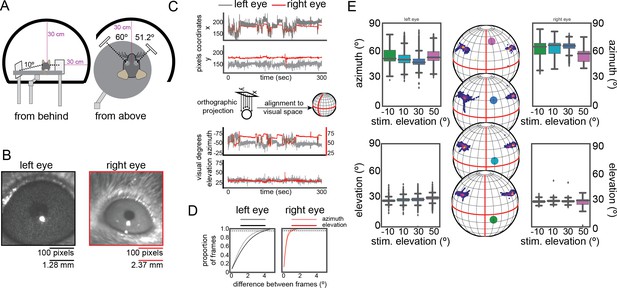
Eye position during performance of the change detection task at four elevations.
(A) Schematic depicting the geometry of the eye tracking and immersive display system. The mouse was centered in the display sphere to aid in estimation of gaze in visuotopic coordinates. Infrared dichroic mirrors were placed in front of each eye as depicted. (B) Example images from the pupil tracking of the left eye (left) and the right eye (right). For the right eye (C) Example traces depicting sensitivity of the eye tracking system and the amplitude of typical movements, in both pixels coordinates of the eye tracking images (top) and following conversion to visual coordinates (bottom). The conversion is schematized between the plots, showing an orthographic projection of the pixel coordinate system in to spherical coordinates, which are then aligned to the visual coordinate system based on the geometry depicted in panel A. (D) Estimate of the resolution of each eye tracking image, showing that 95% of frame-to-frame changes are < 1° for the right eye and < 4° for the left eye. (E) Eye position across the four elevation conditions. The elevation and azimuth are not statistically different between any pair of conditions (p>0.05, t-test, box plots). For each elevation, the center position of an ellipse fit to the pupil is shown projected into visual coordinates, with the color of each point representing the density of overlapping points.
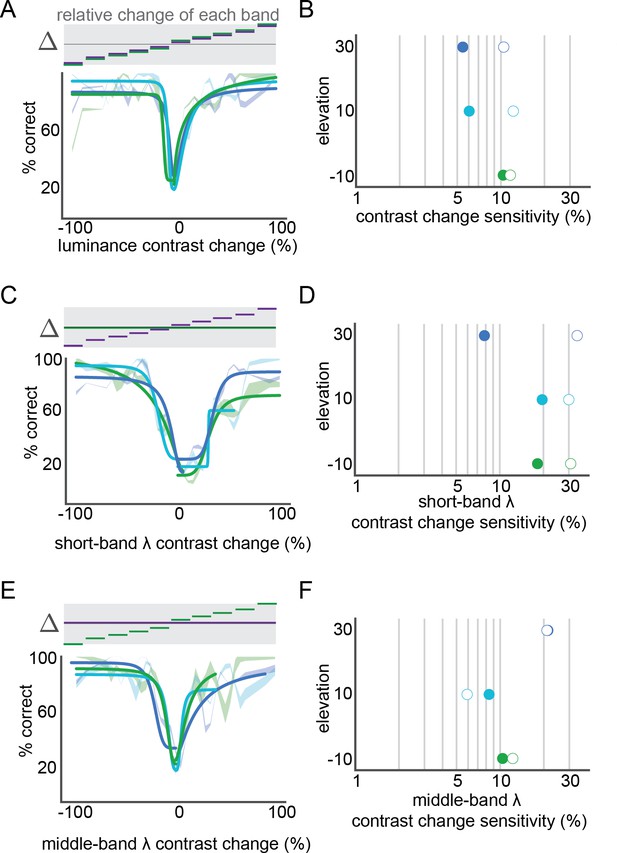
Short and middle wavelength band specific contrast sensitivity.
(A) Performance of luminance contrast change detection at three elevations (green lines: −10°, light blue lines: 10°, dark blue lines: 30°). For each elevation, a fit with hyperbolic ratio function is shown overlaid on mean performance; mean performance line thickness shows S.E.M. across mice. The stimulus is schematized above the performance, showing the corresponding relative change in each wavelength band for each condition. (B) Contrast sensitivity at each elevation, from the fits in panel A; closed circles: decrements in contrast, open circles: increments in contrast. (C,D) short-band specific luminance contrast performance across elevation, as in panels (A,B). (E,F) middle-band specific luminance contrast performance across elevation, as in panels A,B.
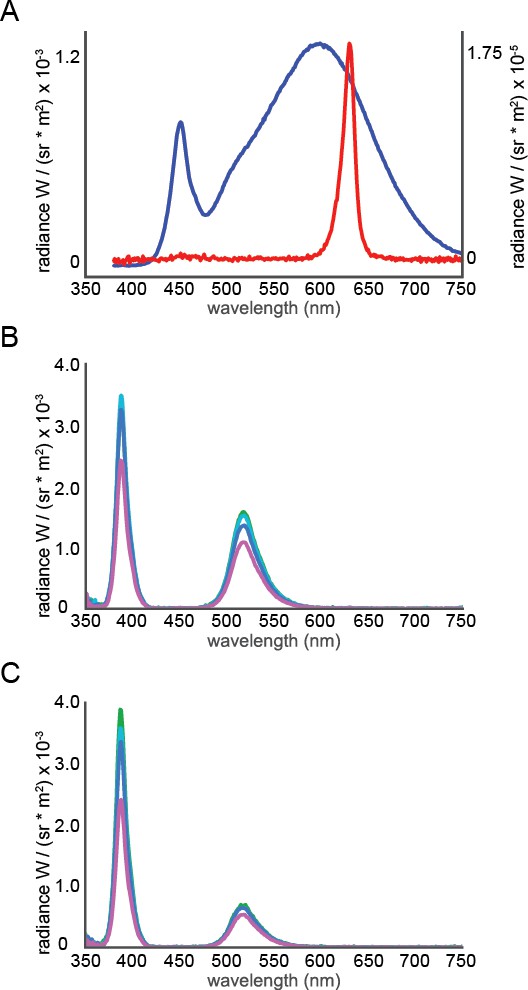
Spectral radiance of various illumination sources from 350 to 750 nm.
(A) The spectral radiance of the lighting in the Allen Institute animal housing facility, including the behavioral testing suite during lights on (blue line, left axes) and lights off (red line, right axes) conditions. Note the lack of any irradiance below 400 nm. (B) The spectral radiance off of the stimulation dome at each elevation for equal short and middle LED drive. (C) The spectral radiance off of the stimulation dome at each elevation after adjustment for wavelength-band specific non-uniformity. For panels B and C, green = −10°, light blue = 10°, dark blue = 30°, and pink = 50°.
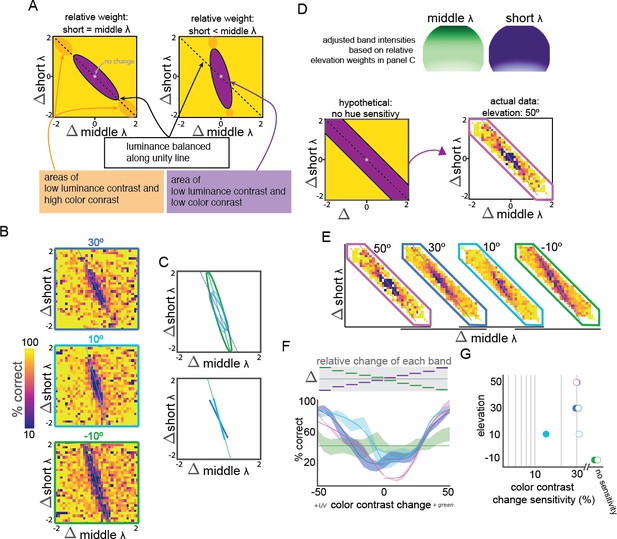
Relative short and middle-wavelength band weights and color discrimination across elevation.
(A) Schematic representation of two possible relative short and middle band weight scenarios, including some putative color contrast sensitivity. The left scenario shows equal weight of short and middle bands, leading to balanced sensitivity and chance performance in response to equal and opposite changes in short and middle band contrast, along the unity line. The right scenario shows higher middle band sensitivity, resulting in a positive shift of the slope, where the larger changes in short band contrast are required to balance changes in middle band contrast. For both scenarios, low luminance and hue contrast should yield low change detection performance (purple ellipses). Any hue discrimination occurs along the major axis of this purple ellipse, and color contrast is high near the edges (orange ellipses). Axes indicate change in each wavelength band intensity, combining the same relative changes in color and luminance across many absolute hue, chromaticity, and luminance values. (B) Observed relative weights of short and middle band weights, as in panel A., at elevations of −10° (green outline, bottom), 10° (light blue outline, middle), and 30° (dark blue outline, top). (C) Fit of the relative weights in panel B with two-dimensional Gaussians, including a plot of the major axis of the fit. These major axes are isolated in the plot below. Color corresponds to stimulus elevation (green lines: −10°, light blue lines: 10°, dark blue lines: 30°). (D) Schematic of sensitivity testing after adjusting for the wavelength band weights in panels B and C (top panels showing adjusted intensities across elevation, normalized to the non-adjusted values. Following this adjustment, the central region should be along the line of equiluminance (bottom left), so subsequent testing was focused on this spear-like region (arrow to bottom right). Actual data at elevation = 50° same as panel E. (E) Performance of change detection at four elevations (green lines: −10°, light blue lines: 10°, dark blue lines: 30°, pink lines: 50°) after short and middle weights adjustment. Because short and middle weight were not exactly balanced, performance was fit with a two-dimensional Gaussian and color sensitivity measured along the major axis (lines overlaid on each plot). (F) Hue sensitivity at each elevation. Fit with hyperbolic ratio function is shown overlaid on mean performance; mean performance line thickness shows S.E.M. across mice. The stimulus is schematized above the performance, showing the corresponding equal and opposite relative change in each wavelength band for each condition. (G) Contrast sensitivity at each elevation, from fits in panel F. Closed circles: decrements in contrast, open circles: increments in contrast.
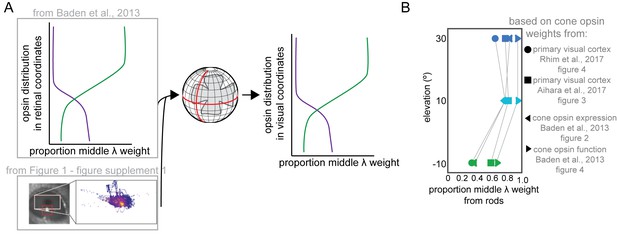
Estimating short and middle cone weights in the coordinates of our behavioral apparatus from retinal expression and functional data.
(A) To generate predictions of the relative weights of each wavelength band at each elevation tested in our paradigm, we projected retinal spatial distributions of both opsin expression and functional responses (schematized as purple and green lines, for short and middle opsins, respectively) from published reports into visual coordinates according to the eye position measured in Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (B) Normalized difference between the predicted (cone opsin expression, cone opsin functional response, V1 responses from three published reports, Baden et al., 2013, Rhim et al., 2017, and Aihara et al., 2017) and the observed behavioral weights, for −10°, 10, and 30°. The difference between our behaviorally observed middle/short ratio at each elevation and the middle/short ratios at those elevation predicted by the measures of cone opsin weight in the literature was divided by the observed ratio to estimate the proportion of the middle band weight provided by rods under our luminance conditions.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31209.009





