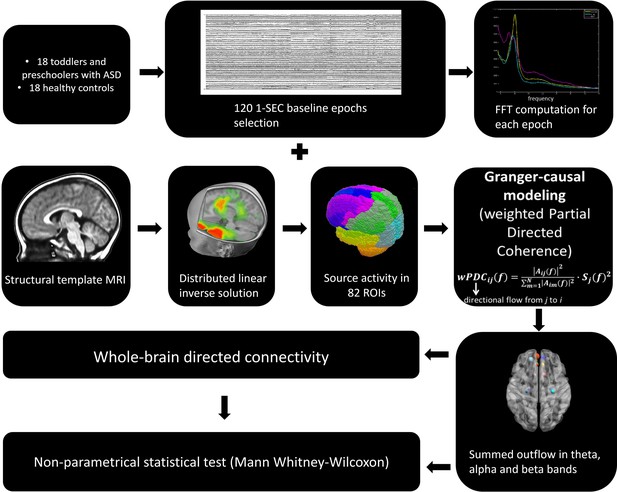
Early alterations of social brain networks in young children with autism
Figures
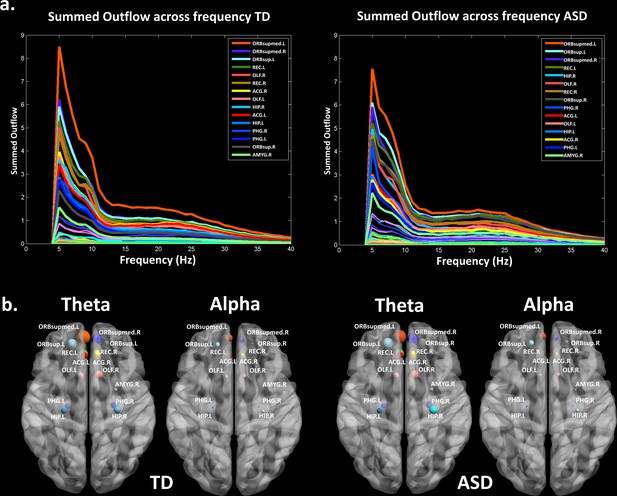
Summed outflow of the largest drivers across frequencies.
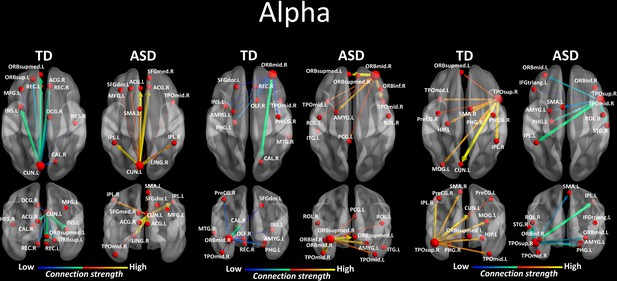
(a) The summed outflow of the largest drivers across frequencies is illustrated for each group (TD, Left; ASD, Right). (b) Regions consistently showing large driving in both groups for theta and alpha. Summed outflows are represented as spheres: the larger the sphere, the higher the summed outflow. ROIs are displayed on an ICBM Average Brain, axial top view. See acronyms list in Table 2.
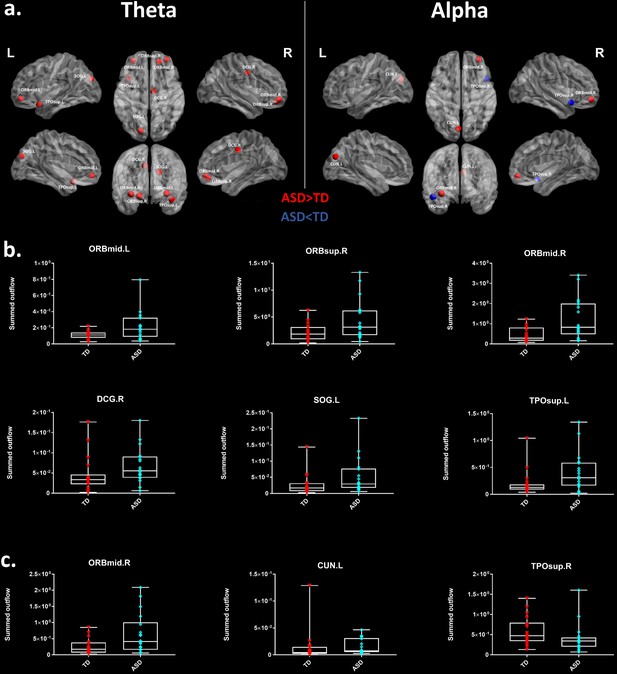
Summed outflow differences in the ASD group compared to their typically developing peers.
(a) On the left, the 6 ROIs with a statistically significant different summed outflow in the ASD group compared to their TD peers for the theta band. On the right, the 3 ROIs with a statistically significant different summed outflow in the ASD group compared to their TD peers for the alpha band. A red nod indicates increased driving, a blue nod indicates decreased driving. Corresponding ROIs are displayed on an ICBM Average Brain, with sagital, axial and corronal views. (b) Boxplots with the summed outflow values comparing each group for each significant ROI in the theta band. (c) Boxplots with the summed outflow values comparing each group for each significant ROI in the alpha band. The boxplots display the full range of variation of the summed outflows (from min to max), rectangles span the interquartile range and the median. See acronyms list in Table 2.
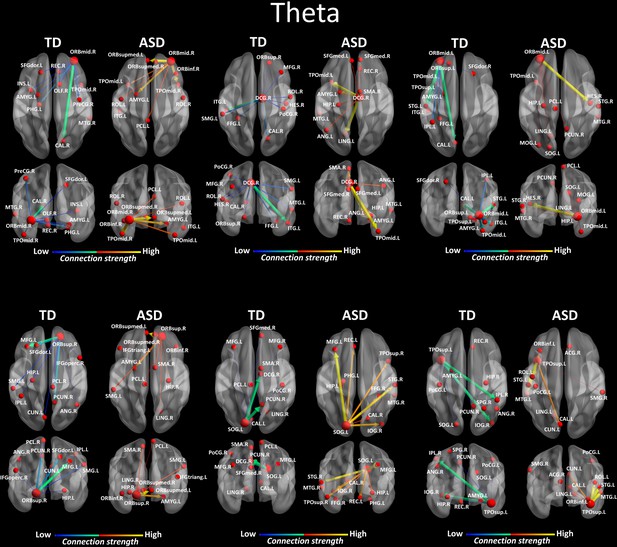
Region-to-region directed functional connectivity for the theta band (4–7 Hz) from each of the six significant ROIs represented as large red spheres.
Outflows are represented as arrows: the larger the arrow, the stronger the outflow. ROIs and connections are displayed on an ICBM Average Brain, axial and coronal views. See acronyms list in Table 2.
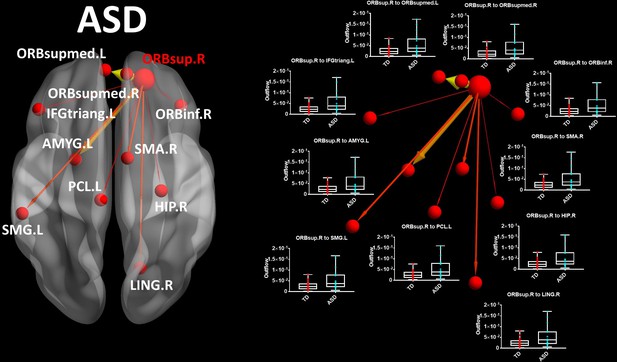
ORBsup.R seed (large red sphere) for the ASD group in theta band.
Boxplots with the outflow values comparing each group for each connection. Outflows are represented as arrows: the larger the arrow, the stronger the outflow. The boxplots display the full range of variation (from min to max) of the outflow values, rectangles span the interquartile range and the median. See acronyms list in Table 2.
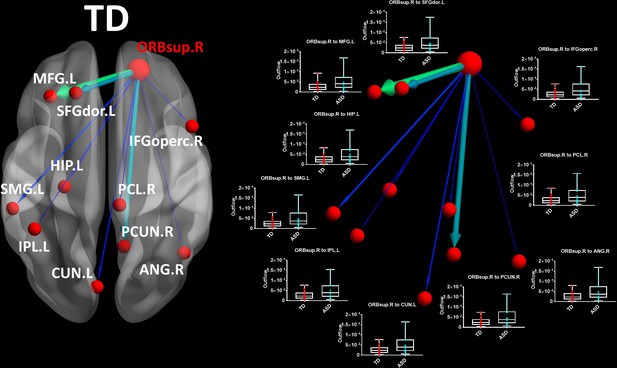
ORBsup.R seed for the (large red sphere) for the TD group in theta band.
Boxplots with the outflow values comparing each group for each connection. Outflows are represented as arrows: the larger the arrow, the stronger the outflow. The boxplots display the full range of variation (from min to max) of the outflow values, rectangles span the interquartile range and the median. See acronyms list in Table 2.
Region-to-region directed functional connectivity for the alpha band (8–12 Hz) from each of the three significant ROIs, represented as large red spheres.
Outflows are represented as arrows: the larger the arrow, the stronger the outflow. ROIs and connections are displayed on an ICBM Average Brain, axial and coronal views. See acronyms list in Table 2.
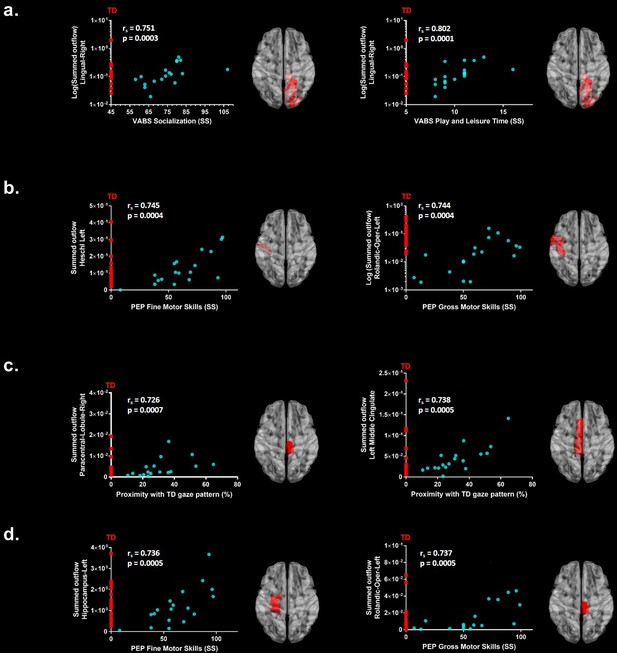
Significant correlations after FDR correction between the summed outflow in theta for the ASD participants (represented as blue dots) and (a) standardized VABS-II scores, (b) PEP-3 standardized scores and (c) Proximity Index.
(d) Significant correlations after FDR correction between the summed outflow in alpha and PEP-3 standardized scores. TD summed outflow values are plotted on the Y axis in red. Corresponding ROI are displayed on an ICBM Average Brain, axial top view.

Exemplar single time frame of the normative gaze pattern for each group on one random time frame.
Each dot represents the gaze position for an individual participant. The face has been blurred on purpose to preserve anonymity but was fully visible for the participants during the experiment.
Tables
Characteristics of Study Participants.
| Characteristic | Autism spectrum disorder | Typically developing | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender ratio (M/F) | 16/2 | 13/5 | |||
| Mean, SD, N | Mean, SD, N | T value | df | P value | |
| Age in years | 3.1, 0.8, 18 | 3.1, 0.9, 18 | 0.165 | 34 | 0.87 |
| ADOS CSS | 7.9, 1.6, 18 | 1.1, 0.47, 18 | 17.87 | 34 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Cognitive verbal/pre-verbal | 67.78, 18.85, 18 | 95.81, 7, 16 | −5.87 | 32 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Expressive language | 50.28, 27.49, 18 | 92.94, 8.61, 16 | −6.24 | 32 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Receptive language | 60.06, 23.93, 18 | 96.19, 6.17, 16 | −6.17 | 32 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Fine motor | 61.83, 23.59, 18 | 88.81, 16.01, 16 | −3.85 | 32 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Gross motor | 59.33, 27.86, 18 | 90.56, 7.66, 16 | −4.56 | 32 | 0.000 |
| PEP-Visual Motor Imitation | 56.11, 25.29, 18 | 93.69, 6.93, 16 | −6.05 | 32 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-Adaptive Behaviour Composite | 75.5, 10.73, 18 | 105.28, 10.19, 18 | −8.53 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-Communication | 76.5, 12.59, 18 | 107.28, 8.16, 18 | −8.7 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-Daily living skills | 79.94, 11.28, 18 | 103.56, 9.28, 18 | −6.85 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-Socialization | 74.67, 11.26, 18 | 102.89, 6.98, 18 | −9.03 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-Motor Skills | 83.56, 10.8, 18 | 101.44, 12.15, 18 | −4.66 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-receptive language | 10, 2.45, 18 | 16.89, 2.32, 18 | −8.65 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-expressive language | 10.11, 2.4, 18 | 16.56, 1.5, 18 | −9.65 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-gross motor skills | 13.83, 5.53, 18 | 14.89, 1.78, 18 | −0.77 | 34 | 0.449 |
| VABS-II-fine motor skills | 12.06, 2.58, 18 | 15.61, 2.45, 18 | −4.23 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-interpersonal relationships | 10.06, 2.6, 18 | 15.83, 2.26, 18 | −7.12 | 34 | 0.000 |
| VABS-II-play and leisure time | 10.33, 2.03, 18 | 17, 1.68, 18 | −10.73 | 34 | 0.000 |
Acronyms Table
| 1 | PreCG.L | Precentral Gyrus Left |
| 2 | PreCG.R | Precentral Gyrus Right |
| 3 | SFGdor.L | Frontal Superior Left |
| 4 | SFGdor.R | Frontal Superior Right |
| 5 | ORBsup.L | Frontal Superior Orbital Left |
| 6 | ORBsup.R | Frontal Superior Orbital Right |
| 7 | MFG.L | Frontal Middle Left |
| 8 | MFG.R | Frontal Middle Right |
| 9 | ORBmid.L | Frontal Middle Orbital Left |
| 10 | ORBmid.R | Frontal Middle Orbital Right |
| 11 | IFGoperc.L | Frontal Inferior Operculum Left |
| 12 | IFGoperc.R | Frontal Inferior Operculum Right |
| 13 | IFGtriang.L | Frontal Inferior Triangularis Left |
| 14 | IFGtriang.R | Frontal Inferior Triangularis Right |
| 15 | ORBinf.L | Frontal Inferior Orbital Left |
| 16 | ORBinf.R | Frontal Inferior Orbital Right |
| 17 | ROL.L | Rolandic Operculum Left |
| 18 | ROL.R | Rolandic Operculum Right |
| 19 | SMA.L | Supplementary Motor Area Left |
| 20 | SMA.R | Supplementary Motor Area Left |
| 21 | OLF.L | Olfactory Left |
| 22 | OLF.R | Olfactory Right |
| 23 | SFGmed.L | Frontal Superior Medial Left |
| 24 | SFGmed.R | Frontal Superior Medial Right |
| 25 | ORBsupmed.L | Frontal Medial Orbital Left |
| 26 | ORBsupmed.R | Frontal Medial Orbital Right |
| 27 | REC.L | Rectus Left |
| 28 | REC.R | Rectus Right |
| 29 | INS.L | Insula Left |
| 30 | INS.R | Insula Right |
| 31 | ACG.L | Cingulum Anterior Left |
| 32 | ACG.R | Cingulum Anterior Right |
| 33 | DCG.L | Cingulum Middle Left |
| 34 | DCG.R | Cingulum Middle Right |
| 35 | PCG.L | Cingulum Posterior Left |
| 36 | PCG.R | Cingulum Posterior Right |
| 37 | HIP.L | Hippocampus Left |
| 38 | HIP.R | Hippocampus Right |
| 39 | PHG.L | ParaHippocampal Left |
| 40 | PHG.R | ParaHippocampal Right |
| 41 | AMYG.L | Amygdala Left |
| 42 | AMYG.R | Amygdala Right |
| 43 | CAL.L | Calcarine Left |
| 44 | CAL.R | Calcarine Right |
| 45 | CUN.L | Cuneus Left |
| 46 | CUN.R | Cuneus Right |
| 47 | LING.L | Lingual Left |
| 48 | LING.R | Lingual Right |
| 49 | SOG.L | Occipital Superior Left |
| 50 | SOG.R | Occipital Superior Right |
| 51 | MOG.L | Occipital Middle Left |
| 52 | MOG.R | Occipital Middle Right |
| 53 | IOG.L | Occipital Inferior Left |
| 54 | IOG.R | Occipital Inferior Right |
| 55 | FFG.L | Fusiform Left |
| 56 | FFG.R | Fusiform Right |
| 57 | PoCG.L | Postcentral Left |
| 58 | PoCG.R | Postcentral Right |
| 59 | SPG.L | Parietal Superior Left |
| 60 | SPG.R | Parietal Superior Right |
| 61 | IPL.L | Parietal Inferior Left |
| 62 | IPL.R | Parietal Inferior Right |
| 63 | SMG.L | SupraMarginal Left |
| 64 | SMG.R | SupraMarginal Right |
| 65 | ANG.L | Angular Left |
| 66 | ANG.R | Angular Right |
| 67 | PCUN.L | Precuneus Left |
| 68 | PCUN.R | Precuneus Right |
| 69 | PCL.L | Paracentral Lobule Left |
| 70 | PCL.R | Paracentral Lobule Right |
| 71 | HES.L | Heschl Left |
| 72 | HES.R | Heschl Right |
| 73 | STG.L | Temporal Superior Left |
| 74 | STG.R | Temporal Superior Right |
| 75 | TPOsup.L | Temporal Pole Superior Left |
| 76 | TPOsup.R | Temporal Pole Superior Right |
| 77 | MTG.L | Temporal Middle Left |
| 78 | MTG.R | Temporal Middle Right |
| 79 | TPOmid.L | Temporal Pole Middle Left |
| 80 | TPOmid.R | Temporal Pole Middle Right |
| 81 | ITG.L | Temporal Inferior Left |
| 82 | ITG.R | Temporal Inferior Right |