Site-specific glycosylation regulates the form and function of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton
Figures
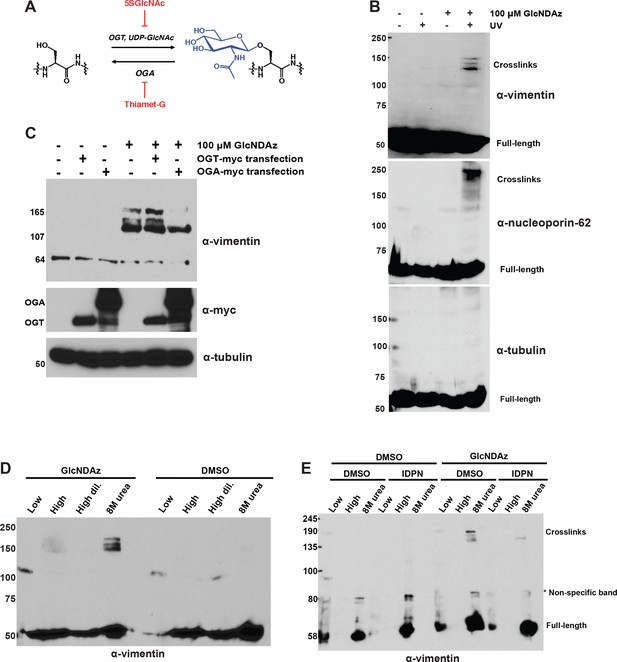
Vimentin engages in O-GlcNAc-mediated protein-protein interactions within assembled IFs.
(A) O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) uses the nucleotide-sugar donor UDP-GlcNAc to add O-GlcNAc to protein substrates. O-GlcNAcase (OGA) removes O-GlcNAc moieties. 5SGlcNAc and Thiamet-G are specific small molecule inhibitors of OGT and OGA, respectively. (B) 293T cells were treated with DMSO vehicle or GlcNDAz (48 hr) and UV light (or not) as indicated, and lysates were prepared in denaturing buffer and analyzed by IB. O-GlcNAc-mediated protein-protein interactions manifest as high molecular weight GlcNDAz-crosslinked complexes (labeled). Heavily glycosylated nucleoporin-62 is a positive control, whereas unglycosylated tubulin is a negative control. Vimentin IB was performed with the D21H3 antibody. (C) 293T cells were transfected with OGT-myc or OGA-myc constructs, as indicated, and subjected to GlcNDAz crosslinking as above. Crosslinked and uncrosslinked endogenous vimentin species were detected in lysates made in denaturing buffer by IB (D21H3 antibody). (D) 293T cells were subjected to GlcNDAz crosslinking as above. Then, soluble (disassembled) and insoluble (assembled) vimentin populations were separated by differential extraction, as described (Herrmann et al., 2004). Low, low ionic strength buffer. High, high dil., high ionic strength buffer (loaded both as-is and diluted, as recommended (Herrmann et al., 2004)). 8M urea extracts fully assembled IFs. Crosslinked and uncrosslinked vimentin species were detected by IB (D21H3 antibody). (E) 293T cells were treated with GlcNDAz for 48 hr, treated with 1% IDPN or DMSO vehicle for 30 min, and exposed to UV. Then, cells were subjected to differential extraction, as above, and analyzed by IB (D21H3 antibody). Note that the uncrosslinked vimentin band appears in the 8M urea fraction of IDPN-treated cells because IDPN treatment collapses vimentin IFs into insoluble aggregates (see Figure 1—figure supplement 1G) (Durham, 1986).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Proteomic analysis of vimentin GlcNDAz crosslinks.
Full proteomics results are available for download as a Scaffold (.sf3) file on the eLife web site. Free software to view Scaffold files is available at http://www.proteomesoftware.com/products/scaffold/download/.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31807.006
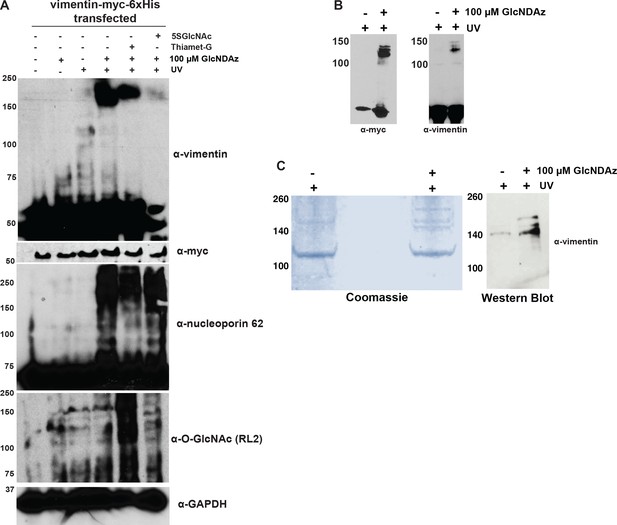
Analysis of vimentin GlcNDAz crosslinks.
(A) 293T cells transfected with vimentin-myc-6xHis were treated with DMSO vehicle or GlcNDAz for 24 hr, treated with vehicle, 100 µM 5SGlcNAc, or 50 µM Thiamet-G for an additional 24 hr, and then UV-crosslinked. Lysates were analyzed by fluorescent IB (V9 antibody). Nucleoporin-62 is a positive control for GlcNDAz crosslinking. GAPDH is a loading control. (B) 293T cells transfected with vimentin-myc-6xHis were treated with DMSO vehicle or GlcNDAz (48 hr) and UV light (or not) as indicated. Lysates were analyzed by IB (D21H3 antibody). Vimentin-myc-6xHis and endogenous vimentin crosslink similarly. (C) 293T cells were transfected with vimentin-myc-6xHis for 48 hr, treated with DMSO vehicle or GlcNDAz as in Figure 1, and UV-crosslinked. Crosslinked and uncrosslinked vimentin populations were purified from lysates by tandem anti-myc IP and nickel affinity chromatography. Crosslinks were visualized by colloidal Coomassie stain (left) and IB (D21H3 antibody) (right). (D) Peptide coverage map from GlcNDAz-crosslinked complexes of vimentin purified in (C). Found peptides are highlighted in yellow. (E) Top protein IDs from vimentin crosslinks. Full proteomics results are available for download as a Scaffold (.sf3) file on the eLife web site (Figure 1—source data 1). Free software to view Scaffold files is available at http://www.proteomesoftware.com/products/scaffold/download/. (F) 293T cells were GlcNDAz-crosslinked as in (A) and subjected to differential extraction as in Figure 1D (left). Then, the 8M urea fractions from DMSO or GlcNDAz samples were divided, half of each sample was exchanged into non-denaturing IP buffer, and samples were analyzed by vimentin IB (V9 antibody) (right). (G) HeLa cells were treated with DMSO vehicle or 1% IDPN for 1 hr, fixed, stained for vimentin (D21H3 antibody), and analyzed by confocal microscopy. (H) 293T cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle) or GlcNDAz for 48 hr and UV light as indicated. Lysates were normalized for protein amount and analyzed by fluorescent IB (V9 antibody). n = 4.
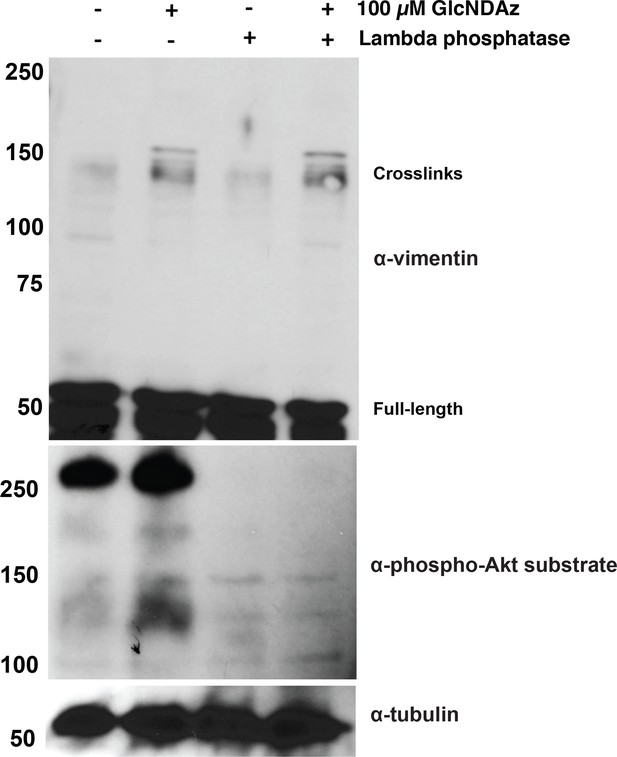
Vimentin GlcNDAz crosslinks are not affected by phosphatase treatment.
293T cells were GlcNDAz-crosslinked as in Figure 1 and extracted in non-denaturing buffer. Cell lysates were normalized to 1 mg/ml, mock-treated or treated with lambda phosphatase for 1 hr at 30°C, and analyzed by IB (D21H3 antibody). An anti-phospho-Akt substrate IB serves as a control for successful dephosphorylation.
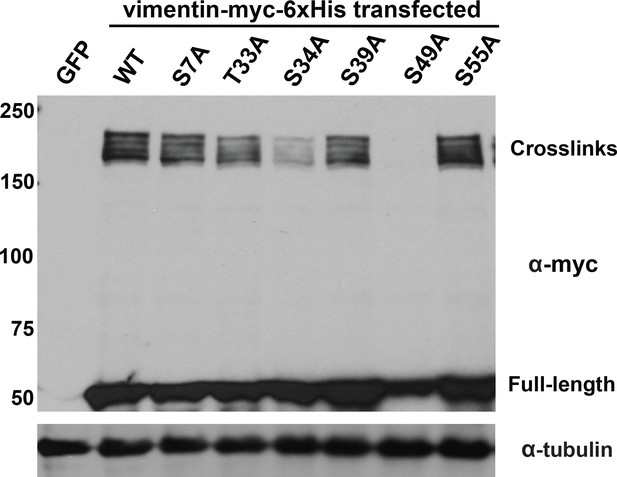
Specific glycosylation sites in the vimentin head domain are required for homotypic, O-GlcNAc-mediated interactions.
293T cells were transfected with GFP only (control) or WT or mutant vimentin-myc-6xHis constructs as indicated for 24 hr, subjected to GlcNDAz crosslinking, and analyzed by IB. Tubulin is a loading control.
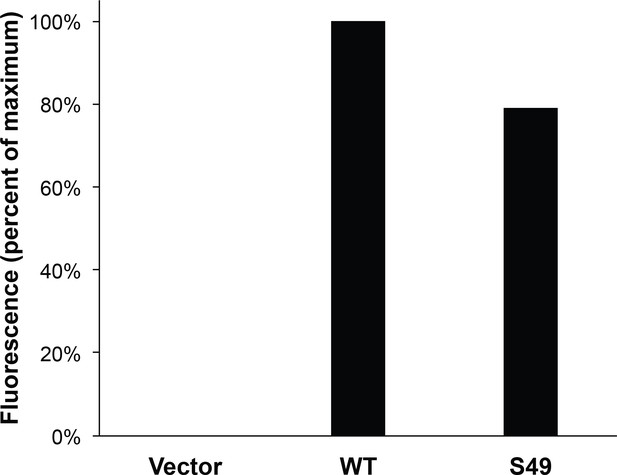
Quantitative examination of S49 glycosylation.
293T cells were transfected with vimentin-myc-6xHis constructs as indicated for 24 hr and then treated with vehicle only or 100 µM GalNAz for an additional 24 hr. Lysates were subjected to click reactions with an alkyne-Cy5 probe followed by anti-myc IP, and were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorescence scanning.
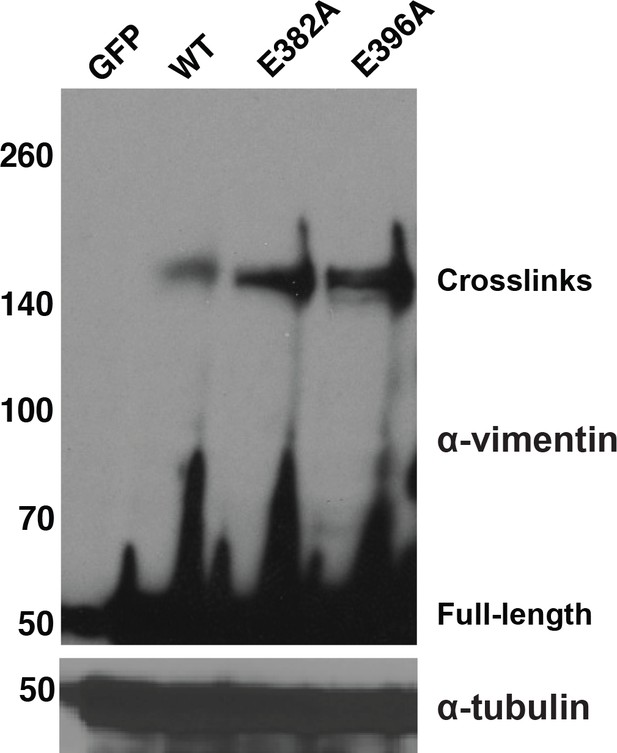
Mutations in putative extracellular GlcNAc-binding sites of vimentin do not reduce intracellular GlcNDAz crosslinking.
293T cells were transfected with vector or WT or mutant vimentin-myc-6xHis constructs as indicated for 24 hr, subjected to GlcNDAz crosslinking, and analyzed by IB (D21H3 antibody). Tubulin is a loading control.
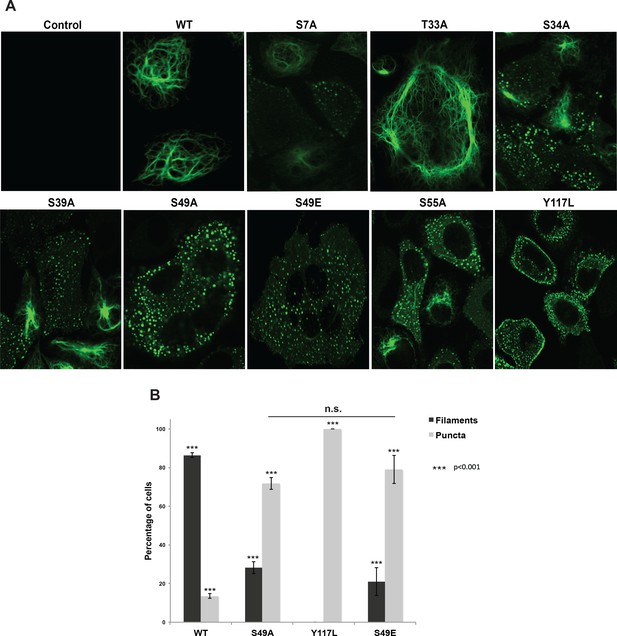
Head domain glycosylation sites are required for vimentin IF assembly and morphology in vivo.
(A) A vimentin−/− HeLa clone was stably transduced with empty vector (control) or expression constructs encoding WT or mutant vimentin-mEmerald and then imaged by laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy. (B) Vimentin-reconstituted HeLa cells were imaged as in (A) and cells were scored for filaments or puncta (≥400 cells per genotype). Differences in both filament and puncta measurements are significant across all genotype comparisons (***p<0.001, Student’s t-test) except for S49A and S49E, which are indistinguishable from each other.
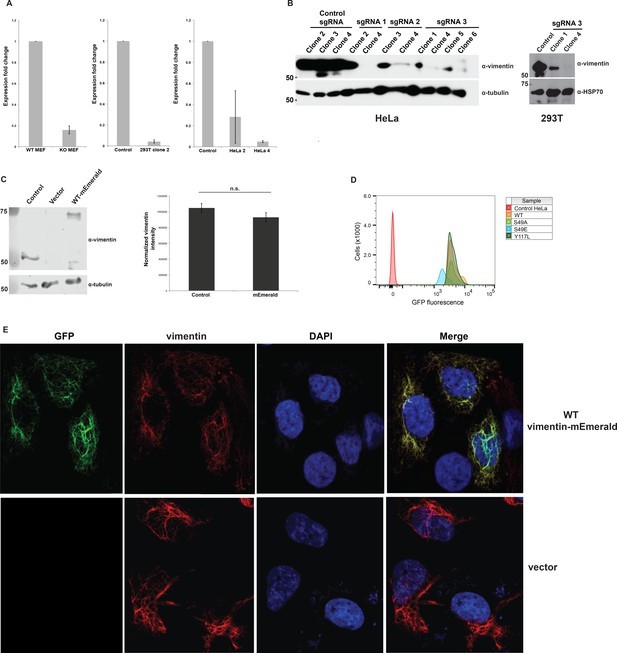
Construction and validation of vimentin-reconstituted cells.
Successful CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of vimentin was verified by actin-normalized qPCR (A) and IB (D21H3 antibody) (B). mRNA from WT and vimentin knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) serve as positive and negative controls for the qPCR assay in (A). Single vimentin−/− clones (HeLa, sgRNA 1 clone 4; 293T, sgRNA 3 clone 4) were used to construct vimentin-reconstituted cell lines. (C) Parental (i.e., un-manipulated) HeLa cells (control) and vimentin−/− HeLa cells reconstituted with either empty vector or WT vimentin-mEmerald were lysed and analyzed by fluorescent anti-vimentin IB (V9 antibody) (left). Quantification of the fluorescence intensities (right) demonstrates that vimentin-mEmerald expression level is indistinguishable from that of endogenous vimentin. n = 2. n.s., not significant, Student’s t-test. (D) Vimentin−/− HeLa cells reconstituted with empty vector (control) or WT or mutant vimentin-mEmerald constructs were sorted by flow cytometry to obtain the top one-third of mEmerald-expressing cells and then used in all subsequent experiments. (E) Parental HeLa cells were transfected with empty vector or WT vimentin-mEmerald for 24 hr, fixed, permeabilized, and imaged for total vimentin (D21H3 antibody immunofluorescence) and vimentin-mEmerald (mEmerald tag fluorescence).
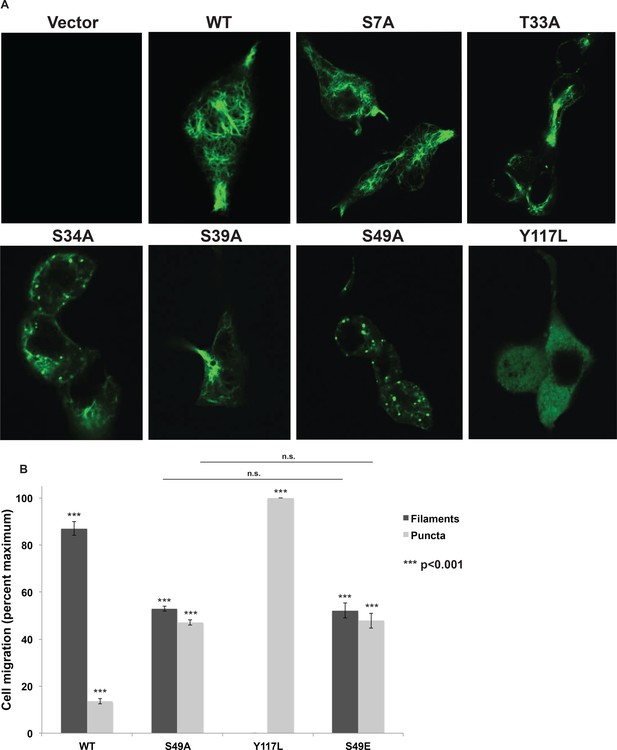
Head domain glycosylation sites are required for vimentin IF assembly and morphology in vivo.
(A) A vimentin−/−293T clone was stably transduced with empty vector (control) or expression constructs encoding WT or mutant vimentin-mEmerald and was imaged by laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy. (B) Vimentin IF assembly state was quantified by imaging as in (A) and scoring assembled and disassembled vimentin in each cell (≥400 cells per genotype). Differences in both filament and puncta measurements are significant across all genotype comparisons (***p<0.001, Student’s t-test) except for S49A and S49E, which are indistinguishable from each other.
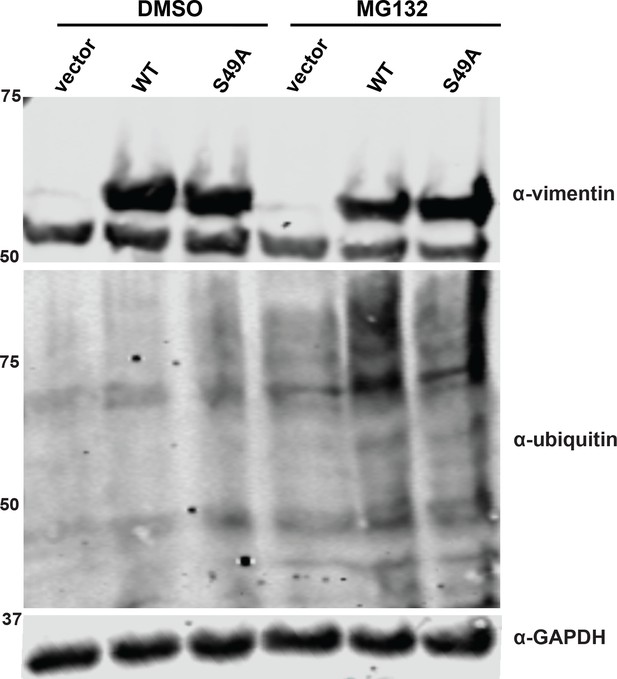
S49A mutation does not affect vimentin stability.
293T cells were transfected with vimentin-myc-6xHis constructs as indicated and treated with either vehicle (DMSO) or 12 µM MG132 for 13 hr. Lysates were analyzed by fluorescent IB (V9 antibody for vimentin).
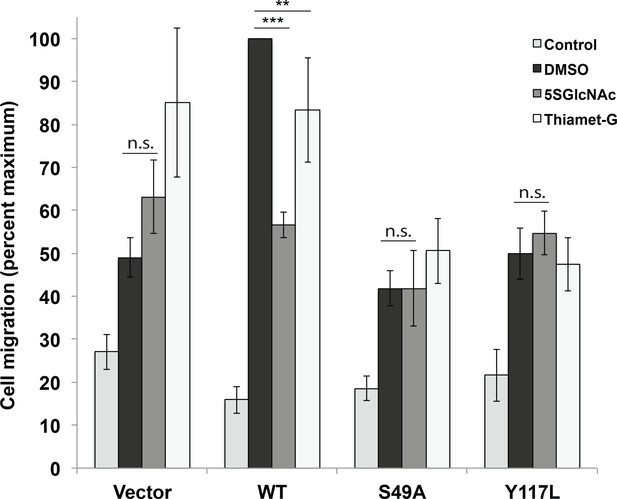
Vimentin O-GlcNAcylation is required for cell migration.
Vimentin−/− HeLa cells reconstituted with empty vector or WT, S49A or Y117L vimentin-mEmerald expression constructs were serum-starved for 72 hr, treated with either vehicle control (DMSO), 100 µM 5SGlcNAc or 50 µM Thiamet-G for 6 hr, and then assayed by Transwell migration using 10% fetal bovine serum as a chemoattractant (or no serum, ‘Control’). Migrated cells were stained with crystal violet and four fields of view were imaged and counted for each of four biological replicates. The WT DMSO serum-stimulated sample was defined as maximum migration and used to normalize all data. Serum-stimulated migration is impaired in cells lacking vimentin or expressing mutant vimentin. 5SGlcNAc and Thiamet-G each inhibit migration in cells expressing WT vimentin, but have no effect on cells lacking vimentin or expressing mutant vimentin. n = 4, ***p<0.001, **p=0.006, n.s. not significant, ANOVA followed by Student’s t-test. For simplicity, only selected statistical comparisons are indicated on the graph. Please see Figure 4—source data 1 for comprehensive statistical comparisons.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Full statistical analyses of cell migration data.
(A) Migration data were first compared by analysis of variance (ANOVA) using JMP software. The results of the ANOVA, as well as the effect test, are displayed. (B) Pairwise t-tests for all combinations of data points were performed. Level and –Level indicate the sample and the sample it is being compared to, respectively. The calculated difference, standard error, and upper and lower confidence levels (CL) are shown, as well as the p value for each t-test. (C) Comprehensive comparison of all samples and conditions. Any two samples that do not share a letter in column two are statistically significantly different from each other.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31807.015
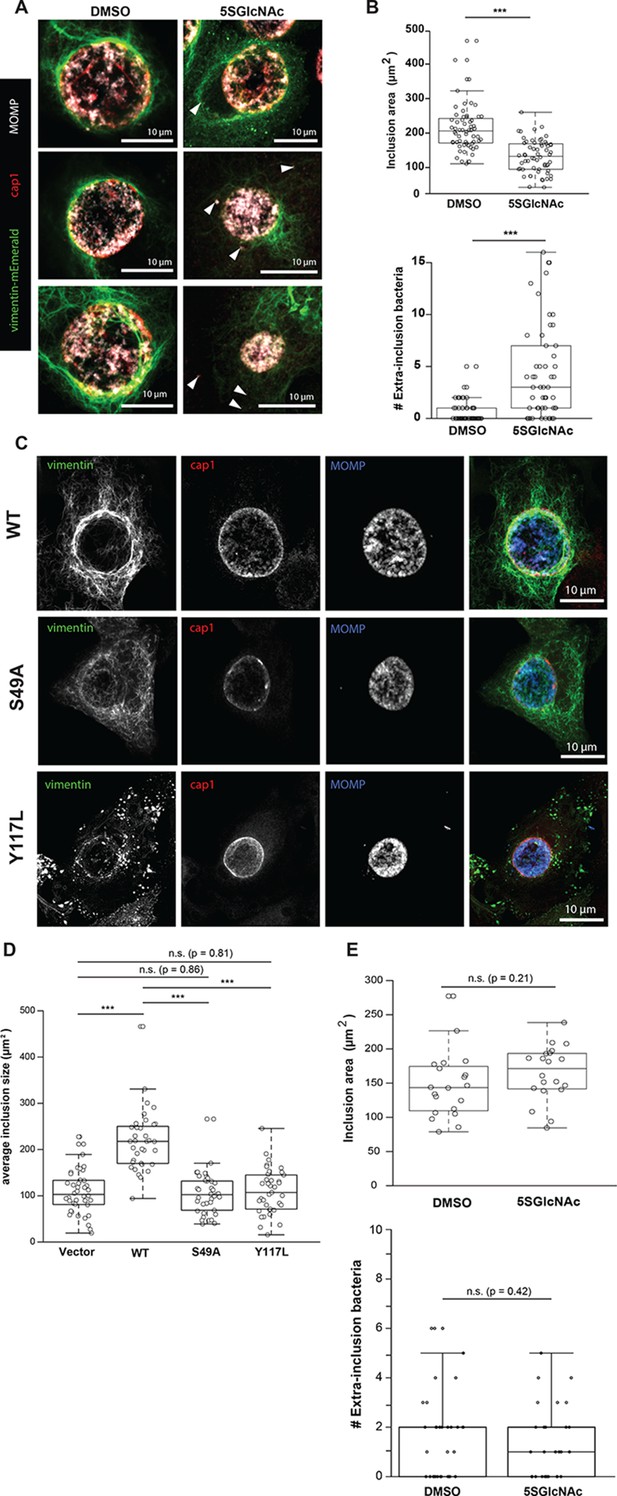
Chlamydia trachomatis requires OGT activity and vimentin glycosylation sites to maintain inclusion integrity during infection.
(A) HeLa cells reconstituted with WT vimentin-mEmerald were infected with Chlamydia for ten hours and treated with DMSO vehicle or 50 µM 5SGlcNAc for an additional 20 hr. Cells were fixed and immunostained for MOMP (to mark individual bacteria) and cap1 (to mark the inclusion membrane), along with vimentin-mEmerald imaging. Representative images are shown. Arrows indicate extra-inclusion bacteria. (B) Quantification of inclusion area and number of extra-inclusion bacteria from images in (A). n = 60, ***p<0.001, Welch’s t-test. (C) Reconstituted HeLa cell lines were infected with Chlamydia for 30 hr and then fixed, stained, and imaged as in (A). Representative images are shown. (D) Quantification of inclusion area from images in (C). n ≥ 54, ***p<0.001, Welch’s t-test. n.s., not significant. (E) HeLa cells reconstituted with empty vector were infected with Chlamydia, treated with DMSO vehicle or 50 µM 5SGlcNAc, and fixed and stained as in (A). Inclusion size (top; n = 20, p=0.21, Student’s t-test) and extra-inclusional bacteria (bottom; n = 28, p=0.42, Student’s t-test) were quantified. n.s., not significant.
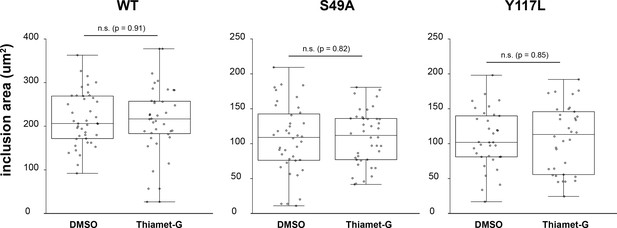
No effect of Thiamet-G treatment on Chlamydia inclusion size.
HeLa cells reconstituted with WT (n = 36), S49A (n = 40) or Y117L (n = 34) vimentin-mEmerald were infected with Chlamydia for 10 hr and treated with DMSO vehicle or 50 µM Thiamet-G for an additional 20 hr. Cells were fixed and stained for cap1 and MOMP. Inclusion area was quantified and plotted as in Figure 5.
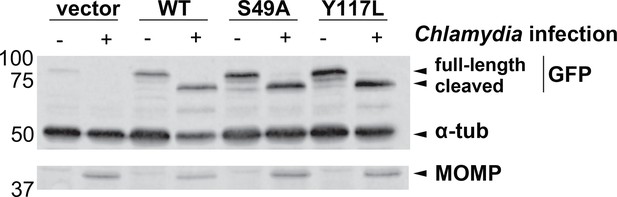
The S49A mutation does not prevent Chlamydia-induced vimentin cleavage.
HeLa cells reconstituted with WT, S49A or Y117L vimentin-mEmerald were infected with Chlamydia (MOI = 0.5) for 30 hr, lysed, and analyzed by anti-GFP (mEmerald tag), tubulin, and MOMP IB, as indicated.
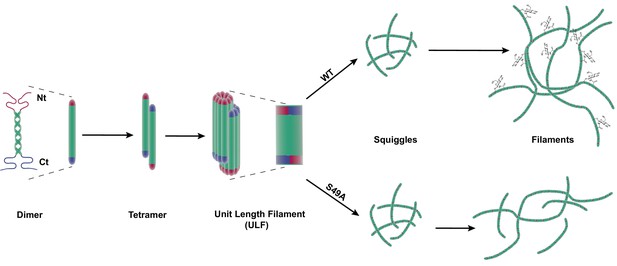
Site-specific glycosylation regulates the form and function of vimentin IFs.
Our data suggest a model wherein glycosylation of the N-terminal vimentin head domain (red), particularly on S49, promotes homotypic vimentin-vimentin interactions, and assembly and/or maintenance of mature IFs under both homeostatic and Chlamydia infection conditions.

Partial conservation of S49 among vimentin orthologs and human type III IF proteins.
(A) Human vimentin S49 is conserved across several vertebrate vimentin orthologs. (B) S49 is conserved in human desmin but not peripherin or glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), the other type III IF proteins.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (HeLa) | vimentin -/- | this paper | ||
| Cell line (293T/17) | 293T vimentin -/- | this paper | ||
| Cell line (HeLa) | HeLa | |||
| Cell line (293T/17) | 293T/UAP1 | PMCID: PMC3323966 | Stably expressing AGX1(F383G) | |
| Antibody | Anti-O-GlcNAc RL2 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz: sc-59624 | 1:300 |
| Antibody | anti-myc 9E10 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Santa Cruz: sc-40 | 1:300 |
| Antibody | anti-tubulin | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma: T6074 | 1:10,000 |
| Antibody | anti-nucleoporin-62 | BD Biosciences | BD Biosciences: 610498 | 1:1,000 |
| Antibody | anti-vimentin D21H3 | Cell Signaling | Cell Signaling: 5741 | 1:1,000; 1:100 |
| Antibody | anti-vimentin V9 | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich: V6389 | 1:1,000 |
| Antibody | anti-GFP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | ThermoFisher: A11122 | |
| Antibody | Goat anti-rabbit IgG | Southern Biotechnology | Southern Biotech: 4030-05 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse IgG | Southern Biotechnology | Southern Biotech: 1030-05 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse k light chain | Southern Biotechnology | Southern Biotech: 1050-05 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific: A-11012 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) Alexa Fluor 594 conjugate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific: A-11005 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) IRDye 800CW conjugate | Li-Cor | Li-Cor: 925-32211 | 1:5,000 |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) IRDye 800CW conjugate | Li-Cor | Li-Cor: 925-32210 | 1:5,000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mEmerald-vimentin-N-18 | Addgene | Addgene: 54301 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLenti CMV/TO Hygro DEST | Addgene plasmid: 17291 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLenti CMV Neo DEST (705-1) | Addgene plasmid: 17392 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mEmerald-vimentin-N-18/ pLenti6 CMV Neo | this paper | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mEmerald-vimentin-N-18/ pLenti6 CMV Hygro | this paper | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Thiamet-G | Duke Small Molecule Synthesis Facility | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Ac45SGlcNAc | Benjamin Swarts, Central Michigan University | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Advansta ECL | Advansta | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | vimentin sgRNA | Duke Functional Genomics Facility | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | vimentin sgRNA | Duke Functional Genomics Facility | ||
| Sequence-based reagent | vimentin sgRNA | Duke Functional Genomics Facility | ||
| Biological sample (virus) | Cas9 Lentivirus | Duke Functional Genomics Facility | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | pENTR Directional TOPO cloning kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific: K240020 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Gateway LR Clonase II Enzyme | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Thermo Fisher Scientific:11791100 |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31807.021





