Transgenerational dynamics of rDNA copy number in Drosophila male germline stem cells
Figures
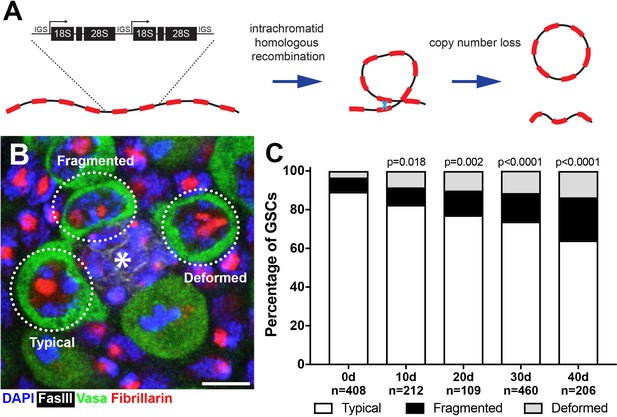
Drosophila male GSCs exhibit perturbations in nucleolar morphology with age.
(A) Illustration of rDNA destabilization through intra-chromatid recombination. (B) Apical tip of the testes stained for Fibrillarin (red, nucleolus), Vasa (green, germ cells), Fas III (white, hub) and DAPI (blue). The hub, a major component of the GSC niche, is denoted by the asterisk. GSCs with representative nucleolar morphologies are outlined. Bar: 5 μm. (C) Distribution of GSC nucleolar morphology during aging, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). P-values from chi-squared test (see methods) is shown.
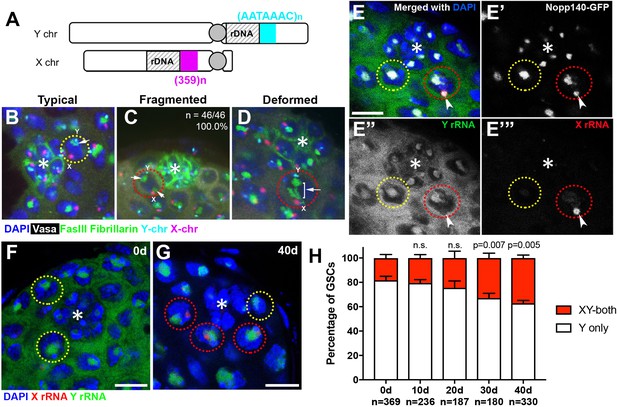
Transcriptional activation of X rDNA in GSCs with atypical nucleolar morphology.
(A) Illustration of rDNA loci on Drosophila X and Y chromosomes. Y rDNA locus is juxtaposed to (AATAAAC)n satellite repeats (cyan), whereas X rDNA locus is juxtaposed to 359 bp satellite repeats (magenta). (B–D) DNA FISH for the 359 bp satellite repeats (magenta) and (AATAAAC)n satellite repeats (cyan), combined with immunofluorescence staining for Vasa (white), FasIII/Fibrillarin (green), DAPI (blue). B: typical nucleolus, C: fragmented nucleoli, D: deformed nucleolus. The hub is denoted by (*). GSCs with typical nucleoli are indicated by yellow dotted lines, GSCs with atypical nucleoli are indicated by red dotted lines. Arrows indicate the position of nucleoli. (E) SNP in situ hybridization with Y and X chromosome-specific rRNA probes combined with Nopp140-GFP to mark nucleolar morphology. Y rRNA (green), X rRNA (red), Nopp140-GFP (white), DAPI (blue). Bar: 7.5 μm. (F, G) SNP in situ hybridization in the testes from 0 day (F) and 40 day (G) old flies. GSCs with only Y rRNA (yellow outline) and with both X and Y rRNA transcription (red outline). Y rRNA (green), X rRNA (red), DAPI (blue). (H) XY rRNA transcription during aging of GSCs, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). Mean ±SD (p-value of t-test is indicated). Note that ‘X-only’ rRNA transcription was never observed.
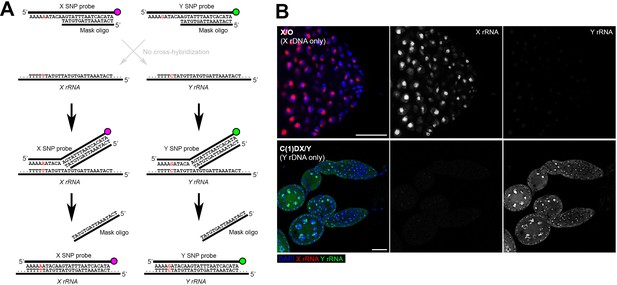
SNP-FISH is highly specific for rRNA transcribed from the Y vs X chromosomes.
(A) Schematic of the principle behind SNP-FISH for detecting rRNA transcripts. Shown is an example of a SNP in the 18S coding region of the X and Y rDNA. (B) Detection of X and Y rRNA using SNP-FISH in X/O (containing only X rDNA) and C(1)DX/Y (containing only Y rDNA) flies shows minimal cross-hybridization between probes. DAPI (blue), Y rRNA (green), X rRNA (red). Bars: 25 μm.
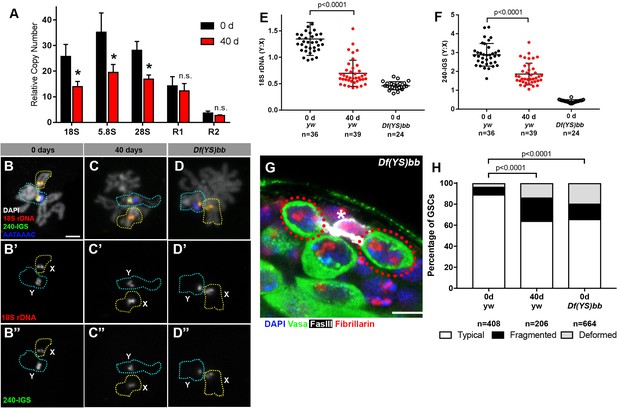
rRNA gene copy number decreases in germ cells during aging.
(A) rRNA gene copy number quantification by qPCR from 0 day and 40 day old testes. Mean ±SD (p-value *≤0.05 t-test). (B–D) FISH on testis mitotic chromosome spreads. DAPI (white), 18S rDNA (red), 240 bp IGS (green), (AATAAAC)n (blue). Bar: 2.5 μm. Y chromosome, identified by the presence of (AATAAAC)n, is indicated by cyan outline, and X chromosome is indicated by yellow outline. (E) Y:X signal intensity ratio for the 18S rDNA in mitotic germ cells in day 0, day 40 old wild type (yw) testes, and X/Df(YS)bb testes. Bracket indicates mean ±SD. p-values from Student’s t-test is shown. (F) Y:X signal intensity ratio for the IGS in mitotic germ cells in day 0, day 40 old wild type (yw) testes, and X/Df(YS)bb testes. Bracket indicates mean ±SD. p-values from Student’s t-test is shown. Note that different Y:X ratios for 18S vs. IGS probes indicates that Y rDNA locus might have higher number of IGS repeats per rDNA unit. (G) Examples of GSCs with atypical nucleolar morphology from X/Df(YS)bb flies at 0 days (red outline). Fibrillarin (red), DAPI (blue), Vasa (green), FasIII (white). The hub is denoted by (*). Bar: 5 μm. (H) Distribution of GSC nucleolar morphologies in X/Df(YS)bb flies compared to 0 and 40-day-old WT flies, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). Chi-squared test, p-values listed.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Pixel intensity measurement and its ratio from DNA FISH plotted in Figure 3E,F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.007
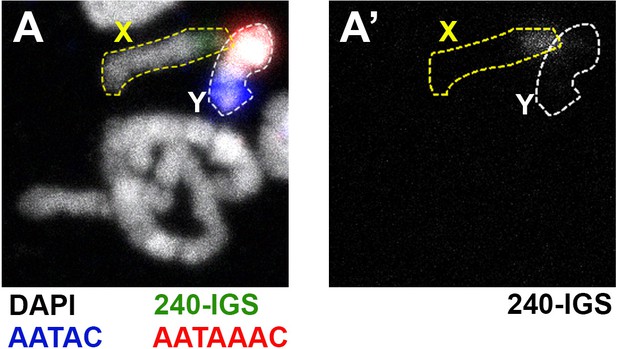
The Df(YS)bb- from Kyoto Stock Center chromosome does not have any detectable 240-IGS sequence.
(A) Chromosome spread from animals containing Df(YS)bb- chromosome shows a near complete loss of Y rDNA. The Y chromosome is marked with probes for the Y-specific AATAC (blue) and AATAAAC (red) satellite sequences. rDNA is marked by probes for the 240-IGS sequence (green). DAPI is shown in white. (A’) 240-IGS channel only.
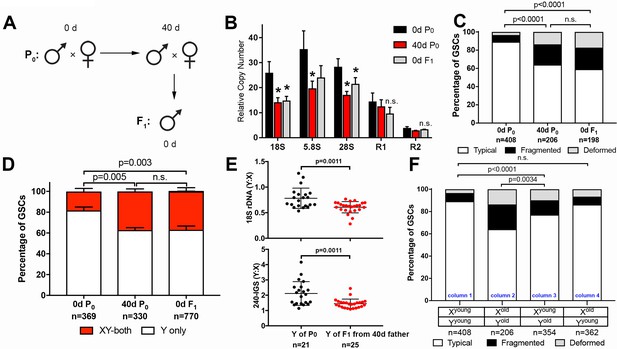
GSC nucleolar morphology and rDNA copy number decrease is heritable.
(A) Scheme for aging of flies and collection of F1 progeny from old parents. (B) rDNA quantification from testes by qPCR in P0 at 0 and 40 days, and F1 at 0 days. Mean ±SD (p-value *≤0.05, t-test). (C) GSC nucleolar morphology in young P0, old P0 and young F1, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). p-values from chi-squared test are shown. (D) Nucleolar dominance assessed by SNP in situ in GSCs from young P0, old P0 and young F1 (n, number of GSCs scored). Mean ±SD. p-value of t-test is shown. Note that ‘X-only’ rRNA transcription was never observed. (E) Y:X signal intensity ratio for the 18S rDNA and 240-IGS in mitotic germ cells comparing day 0 P0 Y and day 0 F1 Y (from day 40 father). Day 0 vs. day 40 fathers (P0) were mated to day 0 old females to yield P0 Y/X vs. F1 Y/X ratio, where X comes from the same source (day 0 yw female). Bracket indicates mean ±SD. p-values from Student’s t-test is shown. (F) Effect of X and Y chromosome inheritance from young vs. old parents on nucleolar morphology, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). P-value from chi-squared test is shown.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Pixel intensity measurement and its ratio from DNA FISH plotted in Figure 4E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.009
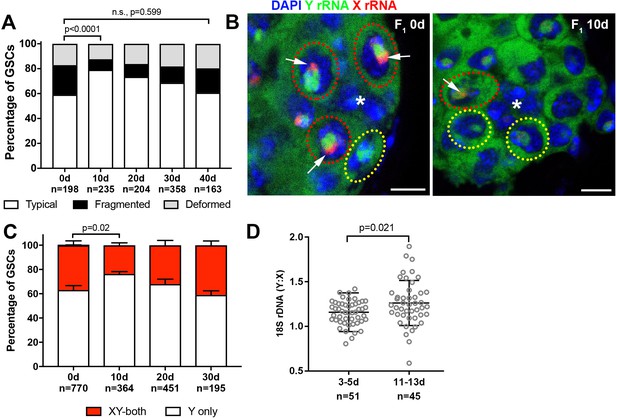
Recovery of GSC nucleolar morphology, Y rDNA dominance and Y rDNA copy number in F1 flies.
(A) Changes in GSC nucleolar morphology in F1 flies from old parents, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). p-value from chi-squared test is shown. (B) Nucleolar dominance in GSCs from day 0 and day 10 old F1 testes assessed by SNP in situ hybridization. DAPI (blue), Y rRNA (green), X rRNA (red). The hub is denoted by (*). Bars: 5 µm. Co-dominant GSCs are indicated by red dotted lines, Y-dominant GSCs are indicated by yellow dotted lines. Arrows indicate X rRNA signal, thus co-dominance. (C) Nucleolar dominance in F1 GSCs during aging, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). Mean ±SD. P-value of t-test is shown. Note that X-only rRNA transcription was never observed, except for once (out of 770 cells) at day 0, which is included in the graph. (D) Ratio of Y:X signal intensity for the 18S rDNA from mitotic chromosome spread of germ cells in F1 flies. Mean ±SD, t-test.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Pixel intensity measurement and its ratio from DNA FISH plotted in Figure 5D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.011
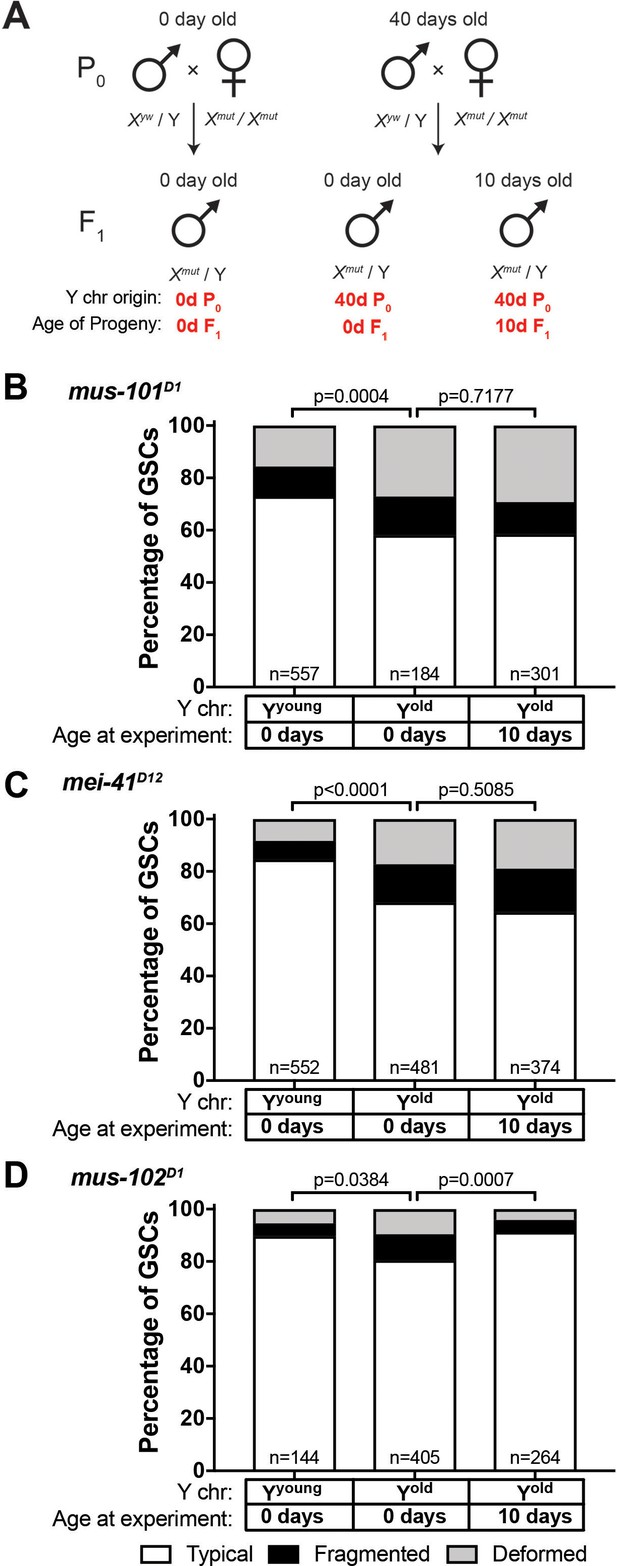
Recovery of GSC nucleolar morphology requires mus-101 and mei-41.
(A) Mating scheme to assess the ability to recover nucleolar morphology after inheriting compromised Y chromosome from old fathers. yw males (0 or 40 days old) were mated to 0 day old mus-101D1, mei-41D12, or mus-102D1 mutant females. GSC nucleolar morphology in F1 mutant males was examined by anti-Fibrillarin antibody at day 0 or 10. (B–D) GSC nucleolar morphology in 0 and 10 day-old F1 mus-101D1 (B), mei-41D12 (C), and mus-102D1 (D) mutants, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). P-values from chi-squared test between indicated conditions are shown.
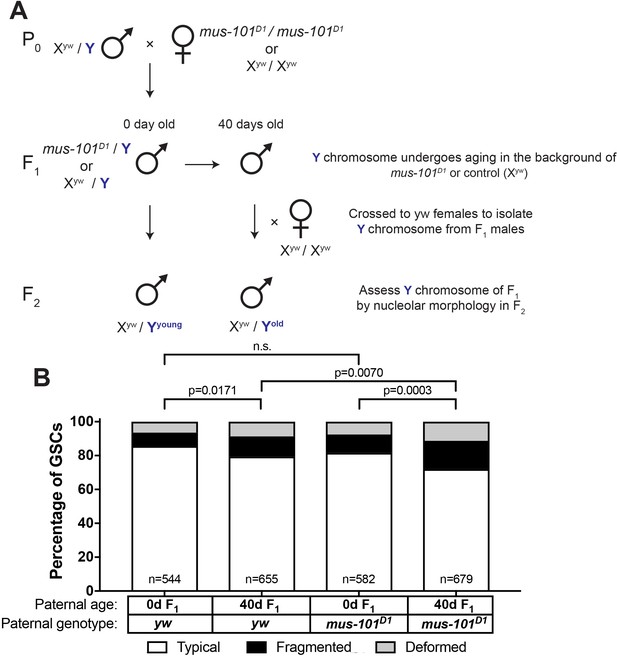
mus-101 is required for rDNA maintenance during aging.
(A) Mating scheme to compare rDNA loss during aging between yw control and mus-101D1 mutant flies. Males with the same Y chromosome are mated to either yw or mus-101D1 females. mus-101D1 and yw F1 males are mated to young females with the same X chromosome at 0 and 40 days old. All F2 males have X and Y chromosomes from the same source, independent of paternal age or genotype. (B) GSC nucleolar morphology in the sons of 0 and 40-day-old yw and mus-101D1 F1, as a percentage of total GSCs scored (n, number of GSCs scored). P-values from chi-squared test between indicated conditions are shown.

Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | yw | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 1495 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | Nopp140-GFP | PMCID: 16158326 | |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | C(1)RM/C(1;Y)6, y1 w1 f1/0 | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 9640 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | FM6/C(1)DX, y* f1 | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 784 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | Df(YS)bb/w1sn1bb*/C(1)RM, y1v1f1 | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 4491 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | y[1] eq[1]/Df(YS)bb[-] | Kyoto Stock Center | DGRC#: 101–260 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | w[1] mus-101[D1] | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 2310 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | w[1] mei-41[D12] | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 6789 |
| strain, strain background (D. melanogaster) | w[1] mus-102[D1] | Bloomington Stock Center | ID_BSC: 2317 |
| antibody | anti-Fibrillarin | Abcam | ID_abcam: ab5821 |
| antibody | anti-Fibrillarin [38F3] | Abcam | ID_abcam: ab4566 |
| antibody | anti-H3K9 dimethyl | Abcam | ID_abcam: ab32521 |
| antibody | anti-vasa | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | ID_SCB: d-26 |
| antibody | anti-Adducin-like 1B1 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | |
| antibody | anti-vasa | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | |
| antibody | anti-Fasciclin III | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Probe sequences for rRNA SNP in situ hybridization.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.014
-
Supplementary file 2
Primer sequences for genomic rDNA qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.015
-
Supplementary file 3
Probe sequences for rDNA DNA FISH.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.016
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32421.017





