Metabolic co-dependence drives the evolutionarily ancient Hydra–Chlorella symbiosis
Figures
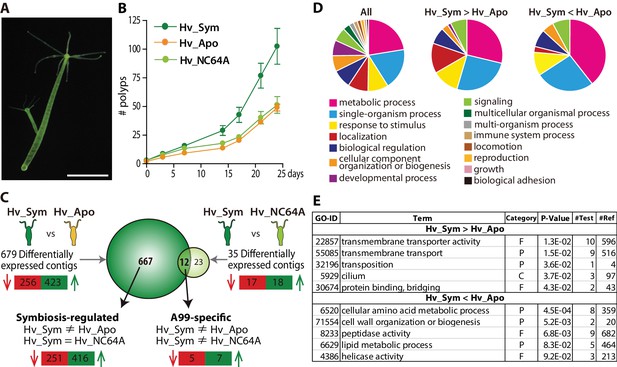
Hydra growth and differential expression of Hydra genes resulting from symbiosis.
(A) Hydra viridissima strain A99 used for this study. Scale bar, 2 mm. (B) Growth rates of polyps grown with native symbiotic Chlorella A99 (Hv_Sym, dark green), Aposymbiotic polyps from which Chlorella were removed (Hv_Apo, orange) and aposymbiotic polyps reinfected with Chlorella variabilis NC64A (Hv_NC64A, light green). Average of the number of hydra in each experimental group (n = 6) is represented. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (C) Graphic representation of differentially expressed genes identified by microarray. The transcriptome of Hv_Sym is compared with that of Hv_Apo and Hv_NC64A with the number of down-regulated contigs in Hv_Sym shown in red and those up-regulated in green. Genes differentially expressed in Hv_Sym compared to both Hv_Apo and Hv_NC64A are given as ‘A99-specific’, those differentially expressed between Hv_A99 and Hv_Apo but not Hv_NC64A as ‘Symbiosis-regulated’. (D) GO distribution of Biological Process at level two in all contigs (All), up-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo) and down-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo) in Hv_Sym. (E) Overrepresented GO terms in up-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo) and down-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo). Category, F: molecular function, C: cellular component, P: biological process. P-values, probability of Fisher’s exact test. #Test, number of corresponding contigs in differentially expressed contigs. #Ref, number of corresponding contigs in all contigs.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
GO distribution of Biological Process in all contigs (All), up-regulated contigs (up: Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo) and down-regulated contigs (down: Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo) in Hv_Sym.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.007
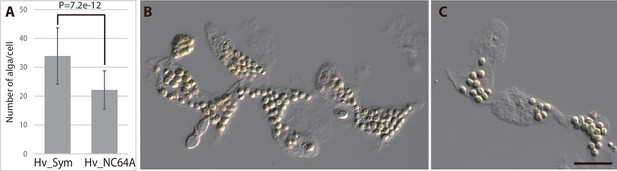
Chlorella sp. A99 and Chlorella variabilis NC64A in Hydra viridissima A99.
(A) Average number of algae per Hydra cell, for native Chlorella sp. A99 (Hv_Sym) and aposymbiotic Hydra re-infected with Chlorella variabilis NC64A (Hv_NC64A). P: p-value of student t-test. (B) Endodermal epithelial cells of Hv_Sym showing intracellular algae (C) Endodermal epithelial cells of Hv_NC64A. Scale bar, 20 µm.
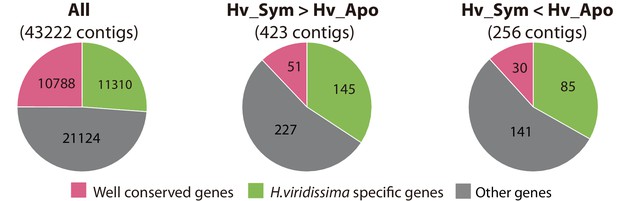
Conserved genes and species-specific genes differentially expressed in symbiotic Hydra.
Distribution of well-conserved Hydra viridissma genes (pink), Hydra viridissima-specific genes (green) and other genes (shared by some but not all metazoans, gray) among eight metazoans: Hydra magnipapillata, Acropora digitifera, Nematostella vectensis, Strongylocentrotus pupuratus, Branchiostoma floridae, Homo sapiens and Drosophila melanogaster and Hydra viridissima A99. Pie charts are shown for all contigs (All), up-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo) and down-regulated contigs (Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo).

Glutamine synthetase (GS) genes in Cnidarians.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the GS gene of four species in Cnidarians. While anthozoans (Nematostella vectensis, Acropora digitifera) have a single GS gene, Hydra magnipappilata (Hma) has five genes and Hydra viridissima A99 has three genes, Hv_1046 (GS-1), Hv_315 (GS-2) and Hv_4671 (GS-3). (B) Average of relative expression level of the three GS genes in Hv_Sym, Hv_NC64A and Hv_Apo as determined by microarray analysis. Error bars indicate standard deviation. P-value of t-test, *<0.05.
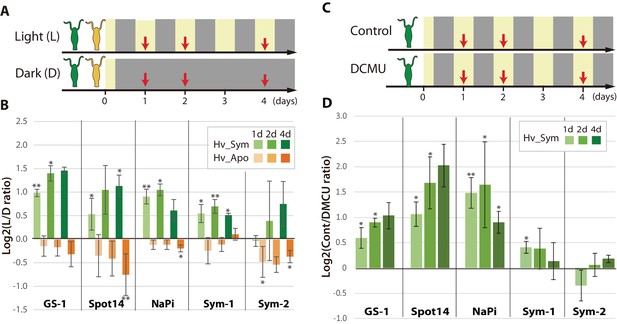
Differential expression of Hydra genes under influence of Chlorella photosynthesis.
(A) Sampling scheme. Hv_Sym (green) and Hv_Apo (orange) were cultured under a standard light-dark regime (Light: L) and in continuous darkness (Dark: D), and RNA was extracted from the polyps at the days indicated by red arrows. (B) Expression difference of five A99-specific genes in Hv_Sym (green bars) and Hv_Apo (orange bars) between the light-dark condition and darkness. The vertical axis shows log scale (log2) fold changes of relative expression level in Light over Dark. (C) Sampling scheme of inhibiting photosynthesis. (D) Differential expression of the five A99-specific genes under conditions allowing (Control) or inhibiting photosynthesis (DCMU). The vertical axis shows log scale (log2) fold changes of relative expression level in Control over DCMU treated. T-tests were performed between Light and Dark (B), and DCMU and Control (D). For each biological replicate (n = 3) 50 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction. Error bars indicate standard deviation. P-value of t-test, *<0.05, **<0.01.
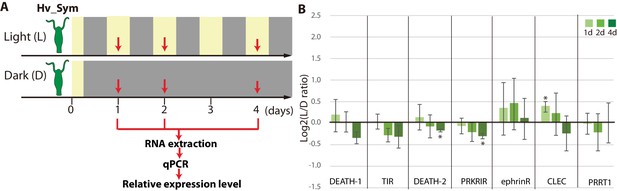
Differential expression of symbiosis-dependent Hydra genes grown under light/dark condition and in darkness.
(A) Sampling scheme. Hv_Sym was cultured in the light-dark condition (Light: L) and in the continuous dark (Dark: D). Gene expression levels were examined by qPCR at 1, 2, 4 days for each condition (red arrows). (B) Expression difference of the genes in Hv_A99 between the two conditions. DEATH-1 and DEATH-2: Death domain containing proteins (gene ID: 6508 and rc_2417), TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain containing protein (gene ID: 5168), PRKRIR: protein-kinase interferon-inducible double stranded RNA dependent inhibitor, repressor of (p58 repressor) (gene ID: rc_9398), ephrinR: ephrin receptor (gene ID: 26108), CLEC: C-type mannose receptor (gene ID: 11411), PRRT1: proline-rich transmembrane protein 1 (gene ID: rc_24563). For each biological replicate (n = 3) 50 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction. The vertical axis shows log scale (log2) fold change of relative expression levels in the light condition over the dark condition. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Pvalue of t-test, *<0.05, **<0.01.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Hydra genes under influence of Chlorella photosynthesis examined by qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.014
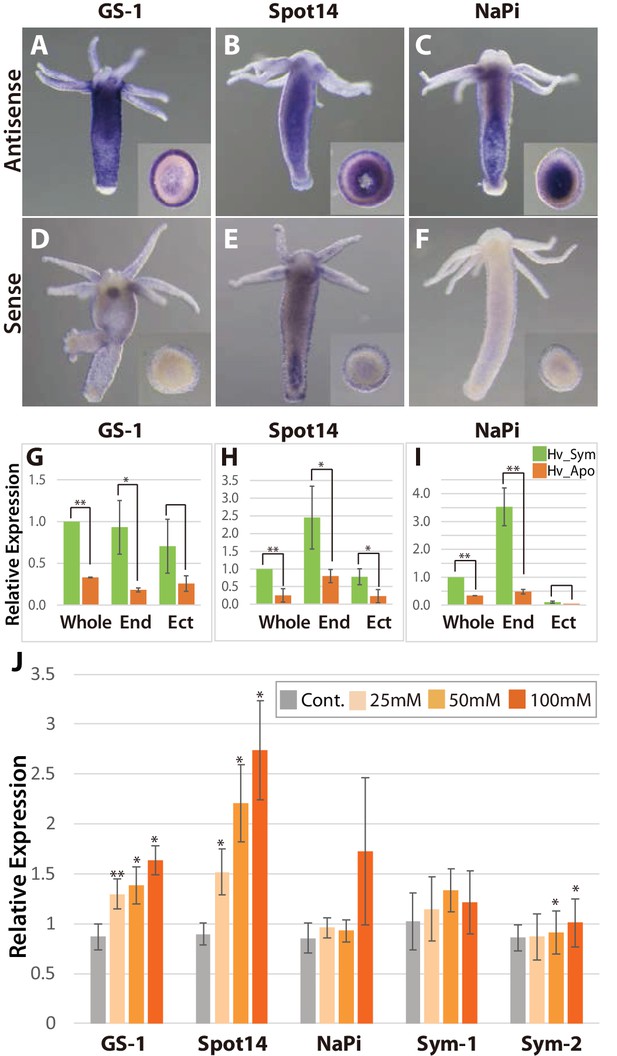
Spatial expression patterns of genes coding for glutamine synthetase, Spot 14 and Na/Pi-transporter.
(A-F); Whole mount in situ hybridization using antisense (A–C) and sense probes (D-F; negative controls) for glutamine synthetase-1 (GS-1; left), Spot 14 (center) and Na/Pi-transporter (NaPi; right). Inserts show cross sections of the polyp’s body. (G–I) Relative expression levels of whole animal (whole), isolated endoderm (End) and isolated ectoderm (Ect) tissue of Hv_Sym (green bars) and Hv_Apo (orange bars). For each biological replicate (n = 3) 10–20 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction of endodermal and ectodermal tissue. T-test was performed between Hv_Sym and Hv_apo. Pvalue, *<0.05, **<0.01. (J) Expression change of genes GS-1, Spot14, NaPi, Sym-1 and Sym-2 following exposure to 25, 50 and 100 mM maltose in Hv_Apo. For each biological replicate (n = 3) 50 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction The vertical axis shows log scale (log2) fold changes of relative expression level of maltose-treated over the untreated Hv_Apo control. T-test was performed between maltose-treated in each concentration and control (*: p value <0.05) and Kruskal-Wallis test (†: p value <0.05) in the series of 48 hr treatment were performed. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Expression change of genes GS-1, Spot14, NaPi, Sym-1 and Sym-2 following exposure to 25, 50 and 100 mM maltose in Hv_Apo examined by qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.021
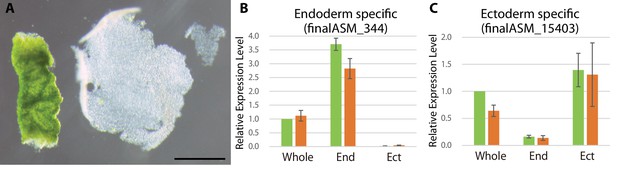
Tissue isolation of green hydra.
(A) Isolated endoderm (left) and isolated ectoderm (right). Scale bar, 1 mm. Expression levels of an endoderm-specific gene finalASM_15403 (B) and that of an ectoderm specific gene finalASM_344 (C) in whole hydra (Whole) and isolated endoderm (End) and ectoderm (Ect) were examined to confirm whether tissue isolation had performed properly. For each biological replicate (n = 3) 10–20 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction of endodermal and ectodermal tissue. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
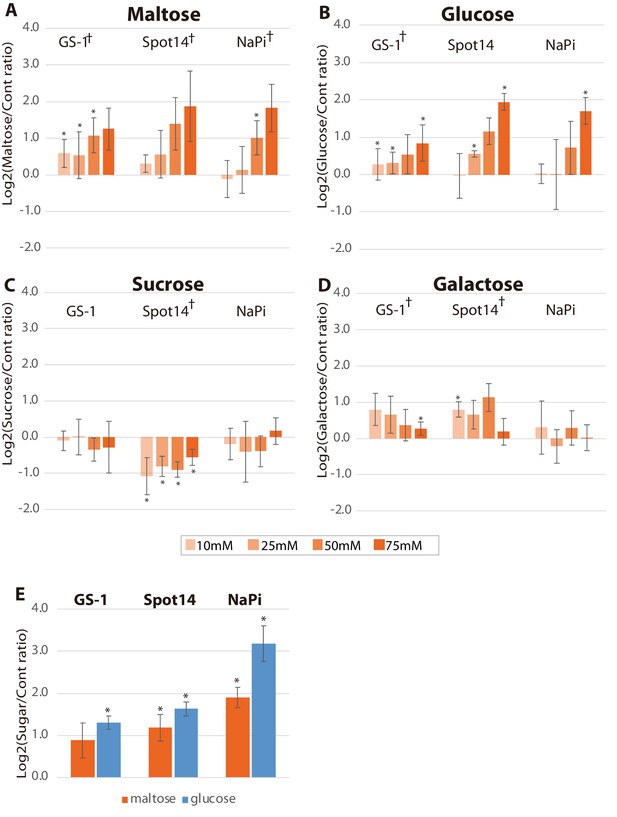
Effects of sugars on Hydra growth.
Effects of growth in presence of maltose (A), glucose (B), sucrose (C) and galactose (D) on gene expression of GS-1, Spot14 and NaPi. Hv_Apo were cultured in medium containing 10, 25, 50 or 75 mM of each sugar for 48 hr, and 75 mM maltose (orange) and glucose (blue) for 6 hr (E). RNA was extracted from the polyps in the light condition. Expression difference of the genes was examined by qPCR. For each biological replicate (n = 3) 50 hydra polyps were used for total RNA extraction. The vertical axis is log scale (log2) fold change of relative expression level of sugar-treated hydras over controls. T-test (*: p-value<0.05) in each concentration and Kruskal-Wallis test (†: pvalue <0.05) in the series of 48 hr treatment were performed. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Effects in presence of maltose, glucose, sucrose and galactose on gene expression of GS-1, Spot14 and NaPi in Hv_Apo examined by qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.020
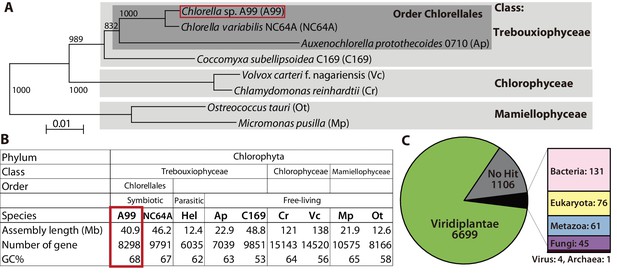
Comparison of key features deduced from the Chlorella A99 genome with other green algae.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of eight genome sequenced chlorophyte green algae including Chlorella sp. A99. The NJ tree is based on sequences of the 18S rRNA gene, ITS1, 5.8S rRNA gene, ITS2 and 28S rRNA gene. (B) Genomic features and taxonomy of the sequenced chlorophyte green algae. Hel: Helicosporidium sp. ATCC50920. (C) The proportion of similarity of Chlorella A99 gene models to those of other organisms.
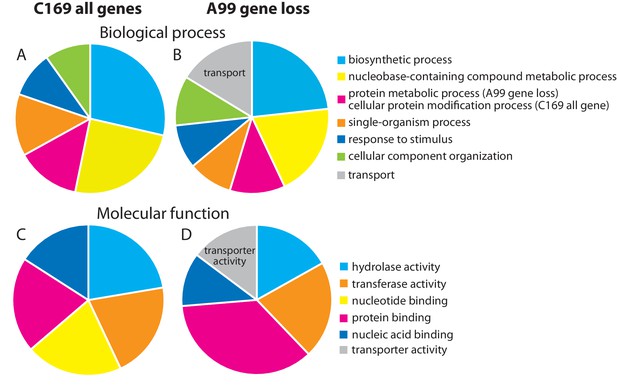
Genes missing in the genome of Chlorella A99.
Functional categorization of genes present in Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (A, C) and genes missing in Chlorella A99 (B, D) by GO terms using Bast2GO. Multilevel pie charts show enrichment of GO’ Biological Process’ terms (A, B) and GO ‘Molecular Function’ terms (C, D) on the lowest level, which cover at least 10% of the total amount of annotated sequences.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Functional categorization of genes present in Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (C169_all) and genes missing in Chlorella A99 (A99 gene loss) by GO terms’ Biological Process’ terms and ‘Molecular Function’ on the lowest level, which cover at least 10% of the total amount of annotated sequences.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.026
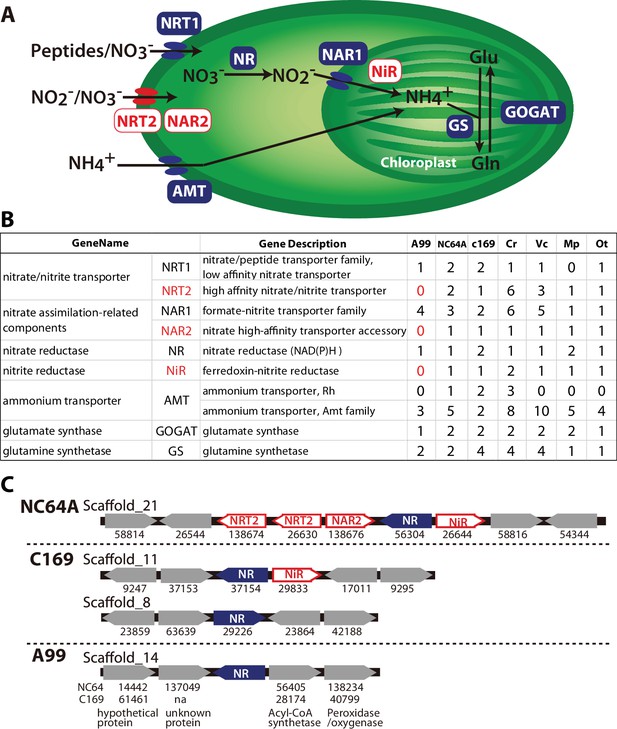
Nitrogen assimilation pathways in Chlorella A99.
(A) Schematic diagram of the nitrogen assimilation pathway in plants showing the function of nitrate transporters NRT1 (peptides/nitrate transporter) and NRT2 (nitrate/nitrite transporter), nitrate assimilation-related components NAR1 and NAR2, nitrate reductase NR, nitrite reductase NiR, ammonium transporter AMT, glutamate synthetase GOGAT and glutamine synthetase GS. Genes shown in red boxes (NRT2, NAR2 and NiR) were not found in the Chlorella sp. A99 genome. (B) Table showing the number of nitrogen assimilation genes in Chlorella sp. A99 (A99), Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (C169), Volvox carteri f. nagariensis (Vc), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr), Ostreococcus tauri (Ot) and Micromonas pusilla (Mp). (C) Gene clusters of nitrate assimilation genes around the shared NR genes (blue) in the genomes of NC64A, C169 and A99. Red boxes show nitrate assimilation genes absent in A99 and gray boxes depict other genes. Numbers below the boxes are JGI protein IDs of NC64A and C169. Numbers below the genes of A99 are JGI protein IDs of the best hit genes in NC64A and C169 and their gene name.
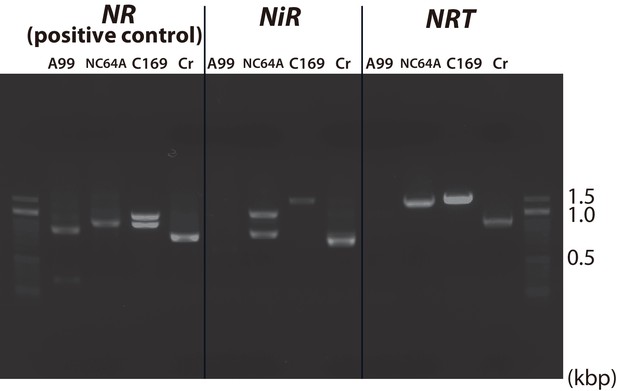
PCR of nitrate assimilation genes.
PCR amplification of genomic DNA corresponding to the genes NRT2, NiR and NR (positive control) was performed in Chlorella sp. A99 (A99), Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (C169) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr).
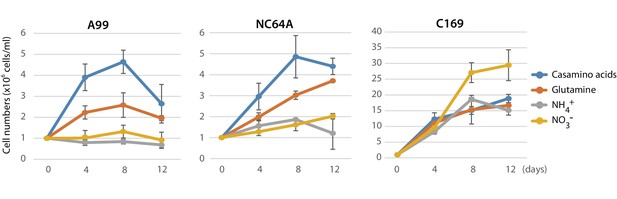
Growth of green algae in presence of various nitrogen sources.
The growth rate of Chlorella A99 (A99), Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A) and Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 (C169) by in vitro culture was assessed for different nitrogen sources with casamino acids (blue), glutamine (orange), ammonium (gray) and nitrate (yellow). Mean number of algae per ml were determined at 4, 8, 12 days after inoculation with 106 cell/ml. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
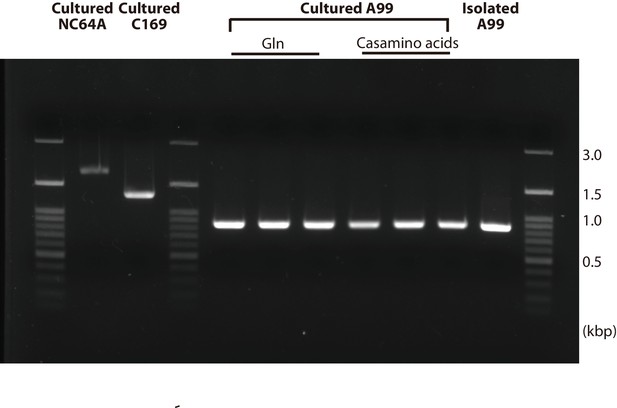
PCR of 18S rRNA genes in cultured algae.
PCR amplification of genomic DNA of the 18S rRNA gene was performed in Chlorella A99 shortly after isolation from H. viridissima A99 (Isolated A99), cultured in medium containing glutamine (Glu) and in medium with casamino acids for 12 days, with cultured NC64A and C169 added for comparison.
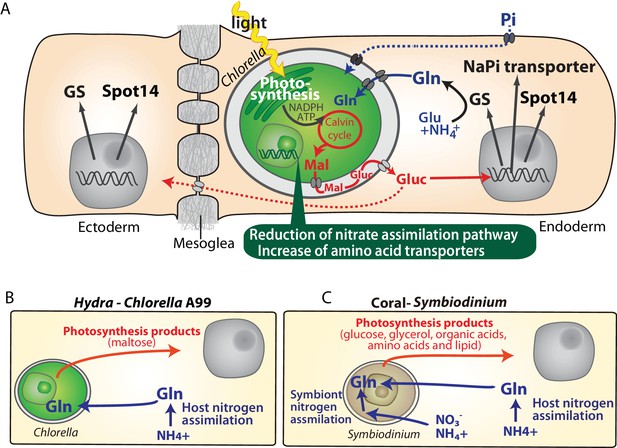
Molecular interactions in the symbiosis of cnidarians.
(A) Summary of symbiotic interactions between Hydra and Chlorella A99. During light conditions, Chlorella A99 performs photosynthesis and produces maltose (Mal), which is secreted into the Hydra symbiosome where it is possibly digested to glucose (Gluc), shown in red. The sugar induces expression of Hydra genes encoding glutamine synthetase (GS), Na/Pi transporter (NaPi) and Spot14. GS catalyzes the condensation of glutamate (Glu) and ammonium (NH4+) to form glutamine (Gln), which is used by Chlorella as a nitrogen source. Since the sugar also up-regulates the NaPi gene, which controls intracellular phosphate levels, it might be involved in the supply of phosphorus to Chlorella as well (blue broken line). The sugar is transported to the ectoderm (red broken line) and there induces the expression of GS and Spot14. In the Chlorella A99 genome, degeneration of the nitrate assimilation system and an increase of amino acid transporters was observed (green balloon). (B, C) Comparison between Hydra-Chlorella symbiosis and coral-Symbiodinium symbiosis. Red indicates transfer of photosynthesis products from the symbiont to the host, and blue indicates transfer of nitrogen sources from the host to the symbiont. While the host organisms Hydra and coral can assimilate NH4+ to Gln (B, C), assimilation of inorganic nitrogen by Symbiodinidium plays an important role for the symbiotic system in coral (C).
Tables
List of differentially expressed genes between Hv_Sym and Hv_Apo, which are likely to be involved in symbiotic relationship
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.008| Probename | Fold change | Human_BestHit | blast2GO_Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hv_Sym /Hv_Apo | Hv_Sym_sexy /Hv_Apo | Hv_NC64A /Hv_Sym | ||||
| Localization and Transport | ||||||
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||||
| rc_6788 | 9.87 | 8.00 | 1.01 | helicase conserved c-terminal domain containing protein | ||
| rc_10246 | 8.26 | 5.15 | 1.82 | protein | ||
| rc_6298 | 7.10 | 4.73 | 0.99 | hypothetical protein LOC220081 | protein fam194b | |
| 2268 | 6.96 | 3.58 | 1.26 | protein Daple | viral a-type inclusion protein | |
| 10548 | 6.74 | 6.89 | 0.73 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member three isoform d | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily m member 3-like | |
| rc_1290 | 6.44 | 7.18 | 0.99 | tetratricopeptide repeat protein eight isoform B | tetratricopeptide repeat protein 8 | |
| 18736 | 6.04 | 6.34 | 1.03 | BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD9 | btb poz domain-containing protein kctd9-like; unnamed protein product | |
| rc_9270 | 5.96 | 10.03 | 1.37 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein LOC100131693 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4e | |
| NPNHRC_15697 | 3.85 | 2.74 | 0.62 | major facilitator superfamily domain- containing protein 1 | ||
| 290 | 3.68 | 3.73 | 1.32 | splicing factor, arginine/ serine-rich 6 | splicing arginine serine-rich 4 | |
| rc_9596 | 3.56 | 4.19 | 1.62 | BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD10 | btb poz domain-containing adapter for cul3-mediated degradation protein 3 | |
| rc_6774 | 3.34 | 3.32 | 1.31 | solute carrier family 43, member 2 | large neutral amino acids transporter small subunit 4 | |
| rc_26218 | 3.29 | 2.91 | 0.41 | sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2A isoform 1 | sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2b | |
| NPNHRC_26094 | 3.20 | 3.98 | 1.31 | SPE-39 proteinid="T5" | spe-39 protein | |
| 9096 | 3.10 | 2.20 | 0.69 | otoferlin isoform d | otoferlin | |
| rc_21349 | 2.89 | 4.25 | 0.78 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | |
| npRC_14488 | 2.88 | 2.65 | 0.71 | solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 8 | solute carrier family facilitated glucose transporter member 8-like | |
| 8863 | 2.75 | 2.70 | 0.81 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B, member 10 precursor | abc transporter b family protein | |
| rc_11896 | 2.49 | 2.56 | 1.52 | ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B, member 10 precursor | abc transporter b family member 25-like | |
| rc_6842 | 2.41 | 3.35 | 1.59 | hypothetical protein LOC112752 isoform 2 | intraflagellar transport protein 43 homolog | |
| 5242 | 2.36 | 3.35 | 1.22 | growth arrest-specific protein 8 | growth arrest-specific protein 8 | |
| 5815 | 2.23 | 2.47 | 0.78 | plasma membrane calcium- transporting ATPase 4 isoform 4a | plasma membrane calcium atpase | |
| 8765 | 2.22 | 3.25 | 0.91 | growth arrest-specific protein 8 | growth arrest-specific protein 8 | |
| NPNH_14052 | 2.19 | 2.17 | 0.79 | V-type proton ATPase 21 kDa proteolipid subunit isoform 2 | v-type proton atpase 21 kda proteolipid subunit-like | |
| rc_2499 | 2.18 | 2.03 | 1.47 | endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment protein three isoform a | endoplasmic reticulum-golgi intermediate compartment protein 3 isoform 2 | |
| rc_13969 | 2.08 | 3.09 | 0.97 | major facilitator superfamily | ||
| (IPR023561) Carbonic anhydrase, alpha-class | ||||||
| rc_24825 | 2.49 | 2.38 | 0.83 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, G precursor | receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase gamma | |
| Cell Adhesion and extracelluar matrix | ||||||
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||||
| 7915 | 4.01 | 5.09 | 0.94 | fibrillin-2 precursor | fibrillin-1- partial | |
| npRC_24163 | glutamate3.69 | 3.59 | 1.32 | semaphorin 5A precursor | rhamnospondin 1 | |
| Immunity, apoptosis and recognition | ||||||
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||||
| (IPR000157) Toll/interleukin-1 receptor homology (TIR) domain | ||||||
| 5168 | 9.28 | 4.92 | 0.61 | protein; PREDICTED: uncharacterized protein LOC100893943 | ||
| 12749 | 5.13 | 3.35 | 1.26 | PREDICTED: uncharacterized protein LOC100893943 [Strongylocentrotus purpuratus] | ||
| (IPR011029) DEATH-like | ||||||
| 6508 | 6.70 | 5.10 | 0.64 | PREDICTED: hypothetical protein [Hydra magnipapillata] | ||
| rc_2417 | 5.39 | 2.70 | 1.01 | nod3 partial; PREDICTED: uncharacterized protein LOC100206003 | ||
| (IPR002398) Peptidase C14, caspase precursor p45 | ||||||
| NPNH_21275 | 2.36 | 3.53 | 1.18 | caspase seven isoform alpha precursor | caspase d | |
| (IPR016187) C-type lectin fold | ||||||
| 11411 | 2.93 | 2.98 | 0.75 | C-type mannose receptor 2 | PREDICTED: similar to predicted protein, partial [Hydra magnipapillata] | |
| Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo | ||||||
| (IPR000488) Death | ||||||
| 7319 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 1.10 | probable ubiquitin carboxyl- terminal hydrolase CYLD isoform 2 | ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase cyld | |
| (IPR001875) Death effector domain | ||||||
| RC_FV81RT001CSTY | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.93 | astrocytic phosphoprotein PEA-15 | fadd | |
| Chitinase | ||||||
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||||
| (IPR001223) Glycoside hydrolase, family 18, catalytic domain | ||||||
| rc_4450 | 2.78 | 3.83 | 0.66 | chitinase 2 | ||
| Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo | ||||||
| (IPR000726) Glycoside hydrolase, family 19, catalytic | ||||||
| FPVQZVL01EAWBY | 0.21 | 0.16 | 1.78 | endochitinase 1-like | ||
| 1028 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 1.47 | endochitinase 1-like | ||
| Oxidative Stress Response | ||||||
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||||
| np_1276 | 5.99 | 7.16 | 0.78 | glutaredoxin-2, mitochondrial isoform 2 | cpyc type | |
| 10926 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 0.8 | hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase- like protein 2 | hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-like protein 2 | |
| 469 | 2.97 | 3.53 | 0.76 | cytochrome P450 3A7 | cytochrome p450 | |
| FV81RT001DCTAQ | 2.69 | 2.50 | 0.75 | oxidoreductase NAD-binding domain-containing protein one precursor | oxidoreductase nad-binding domain- containing protein 1 | |
| 696 | 2.30 | 3.24 | 0.69 | methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase B1 | selenoprotein 1; methionine-r-sulfoxide reductase b1-a-like | |
| 6572 | 2.23 | 2.15 | 1.06 | L-xylulose reductase | l-xylulose reductase | |
| 13298 | 2.10 | 3.49 | 0.64 | eosinophil peroxidase preproprotein | peroxidase | |
| npRC_6975 | 2.04 | 2.77 | 1.42 | methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase B1 | selenoprotein 1; methionine-r-sulfoxide reductase b1-a-like | |
| (IPR024079) Metallopeptidase, catalytic domain | ||||||
| Hv_array_4952 | 4.77 | 13.31 | 0.72 | meprin A subunit beta precursor | zinc metalloproteinase nas-4-like | |
| Hv_array_rc_3992 | 2.66 | 2.23 | 1.27 | matrix metalloproteinase seven preproprotein | matrix metalloproteinase-24-like | |
| Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo | ||||||
| RC_FWZAEML02HKSC | 0.255 | 0.153 | 1.444 | ascorbate peroxidase | ||
| np_14962 | 0.293 | 0.455 | 1.390 | tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 2 | phenylalanine hydroxylase | |
| rc_4151 | 0.318 | 0.463 | 1.693 | phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | phenylalanine hydroxylase | |
| 2835 | 0.384 | 0.344 | 1.787 | u1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70 kda | ||
| rc_11426 | 0.413 | 0.458 | 1.591 | short-chain dehydrogenase/ reductase family 9C member 7 | uncharacterized oxidoreductase -like | |
| FWZAEML02IC34R | 0.427 | 0.448 | 1.159 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 5A1 isoform two precursor | succinate-semialdehyde mitochondrial-like | |
| FWZAEML02HKSCO | 0.454 | 0.307 | 0.833 | ascorbate peroxidase | ||
| (IPR004045) Glutathione S-transferase, N-terminal | ||||||
| RC_FWZAEML02GGHN | 0.09 | 0.07 | 1.81 | hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase | glutathione s-transferase family member (gst-7) | |
| (IPR024079) Metallopeptidase, catalytic domain | ||||||
| rc_11270 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 1.33 | meprin A subunit beta precursor | protein; zinc metalloproteinase nas-4-like | |
| rc_RSASM_15059 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 1.42 | ---NA--- | ||
| 2111 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 1.74 | meprin A subunit beta precursor | zinc metalloproteinase nas-4-like | |
| 12451 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.78 | meprin A subunit alpha precursor | zinc metalloproteinase nas-13- partial | |
| (IPR013122) Polycystin cation channel, PKD1/PKD2 | ||||||
| 28854 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.94 | polycystin-2 | receptor for egg jelly partial | |
| 15774 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.76 | polycystic kidney disease protein 1-like two isoform a | protein | |
List of genes differentially expressed in Hv_Sym compared to both Hv_Apo and Hv_NC64A (‘A99-specific’)
Fold change of expression level determined by microarray analysis and qPCR analysis
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo, Hv_NC64A | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe name (gene ID) | Microarray | qPCR | Gene annotation | InterProScan | ||
| Sym/Apo | Sym/NC64A | Sym/Apo | Sym/NC64A | |||
| rc_13579 | 12.8 | 4.0 | 11.2 | 4.0 | (Hydra specific) | |
| rc_12891 | 9.0 | 2.9 | 14.6 | 6.9 | (Hydra viridis specific) | |
| 27417 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 3.0 | 3.0 | IPR009786 Spot_14 | |
| rc_26218 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.3 | sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein | PTHR10010 Sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2C |
| 1046 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 1.6 | glutamine synthetase | |
| Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo, Hv_NC64A | ||||||
| Probe name (gene ID) | Microarray | qPCR | Gene Annotation | InterProScan | ||
| Apo/Sym | NC64A/Sym | Apo/Sym | NC64A/Sym | |||
| NPNHRC_26859 | 83.2 | 9.7 | ∞ | ∞ | (Hydra viridis specific) | |
| RC_FVQRUGK01AXSJ | 13.7 | 2.6 | 2.1 | 1.5 | acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase | |
| rc_14793 | 7.2 | 4.1 | 9.4 | 4.8 | 2-isopropylmalate synthase | IPR013785 Aldolase_TIM, |
| FV81RT002HT2FL | 2.8 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 1.8 | histidine ammonia-lyase | IPR001106 Aromatic_Lyase IPR008948 L-Aspartase-like |
| NPNHRC_12201 | 2.7glutamate | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.5 | (Hydra viridis specific) | |
-
Table 2—source data 1
Expression level of ‘A99-specific’ genes and ‘Symbiosis related’ genes examined by microarray and qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.010
List of annotated genes up-regulated in Hv_NC64A compared to Hv_Sym
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.011| Probename | Hv_NC64A/ Hv_Sym | Hv_Apo/ Hv_Sym | Hv_Sym_sexy/ Hv_Sym | Blast2GO description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rc_1623 | 4.57 | 1.64 | 5.98 | methylase involved in ubiquinone menaquinone biosynthesis |
| 28947 | 3.52 | 1.59 | 0.63 | non-ribosomal peptide synthetase |
| 1353 | 3.13 | 1.63 | 0.10 | nuclear protein set |
| 14347 | 2.69 | 2.40 | 0.54 | n-(5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl)-l -cysteinyl-d-valine synthase |
| SSH_397 | 2.67 | 2.39 | 0.50 | n-(5-amino-5-carboxypentanoyl)-l -cysteinyl-d-valine synthase |
| RC_FWZAEML01C7BP | 2.28 | 0.82 | 0.41 | ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase family protein |
| RC_FVQRUGK01EOXS | 2.25 | 1.52 | 0.53 | ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase family protein |
| rc_11710 | 2.15 | 1.26 | 0.31 | ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase family protein |
| 1677 | 2.10 | 1.19 | 0.38 | ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase family protein |
| rc_363 | 2.21 | 1.04 | 0.76 | gcc2 and gcc3 family protein |
List of the genes differentially expressed between Hv_Sym and Hv_Apo
Fold change of expression level determined by microarray analysis and qPCR
| Hv_Sym > Hv_Apo | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probe name (gene ID) | Microarray | qPCR | Gene annotation | InterProScan |
| Sym/Apo | Sym/Apo | |||
| 5168 | 9.3 | 7.4 | IPR000157 TIR_dom PTHR23097 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member | |
| 6508 | 6.7 | 2.9 | IPR011029:DEATH-like_dom | |
| 11411 | 2.9 | 2.0 | C-type mannose receptor 2 | IPR000742 EG-like_dom IPR001304 C-type_lectin |
| 26108 | 7.2 | 7.2 | ephrin type-A receptor six isoform a | |
| rc_2417 | 5.4 | 3.5 | IPR000488 Death_domain | |
| rc_24563 | 6.1 | 6.7 | Proline-rich transmembrane protein 1 | IPR007593 CD225/Dispanin_fam PTHR14948 NG5 |
| rc_9398 | 6.2 | 5.4 | protein-kinase, interferon-inducible double stranded RNA dependent inhibitor, repressor of (P58 repressor) | PTHR11697 general transcription factor 2-related zinc finger protein |
| Hv_Sym < Hv_Apo | ||||
| Probe name (gene ID) | Microarray | qPCR | Gene Annotation | InterProScan |
| Apo/Sym | Apo/Sym | |||
| rc_10789 | 2.5 | 3.7 | endoribonuclease Dicer | IPR000999 RNase_III_dom PTHR1495 helicase-related |
| rc_12826 | 3.0 | 2.3 | interferon regulatory factor 1 | IPR001346 Interferon_reg_fact_DNA-bd_dom; IPR011991 WHTH_DNA-bd_dom PTHR11949 interferon regulatory factor |
| rc_8898 | 6.1 | 4.1 | leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 15 isoform b | IPR001611 Leu-rich_rp PTHR24373 Toll-like receptor 9 |
| FV81RT001CSTY | 3.2 | 2.0 | astrocytic phosphoprotein PEA-15 | IPR001875 DED, IPR011029 DEATH-like_dom |
| RSASM_17752 | 4.0 | 2.1 | CD97 antigen isoform two precursor | IPR000832 GPCR_2_secretin-like PTHR12011 vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor 2 |
-
Table 4—source data 1
Expression level of 'Symbiosis related' genes examined by microarray and qPCR.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.016
Summary of sequence data for assembling Chlorella sp. A99 genome sequences
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.023| Number of reads | 85469010 | |
| Number of reads assembled | 61838513 | |
| Number of bases | 17398635102 | |
| Scaffolds | Contigs | |
| Total length of sequence | 40934037 | 40687875 |
| Total number of sequences | 82 | 7455 |
| Maximum length of sequence | 4003385 | 171868 |
| N50 | 1727419 | 12747 |
| GC contents (%) | 68.07% | 69.95% |
Amino acid transporter genes in Chlorella sp. A99 (A99), Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 (C169), Volvox carteri (Vc), Micromonas pusilla (Mp) and Ostreococcus tauri (Ot) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr)
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.024| A. The number of Pfam domains related to amino acids transport | |||||||
| Pfam domain name | A99 | NC64A | c169 | Cr | Vc | Mp | Ot |
| Aa_trans | 30 | 38 | 21 | 9 | 7 | 9 | 8 |
| AA_permease | 4 | 6 | 15 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
| B. Ortholog groups including Aa_trans domain containing genes overrepresented in symbiotic Chlorella | |||||||
| Ortholog group ID: Gene annotation | A99 | NC64A | c169 | Cr | Vc | Mp | Ot |
| OG0000040: amino acid permease 2 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| OG0000324: transmembrane amino acid transporter family protein (solute carrier family 38, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter) | 6 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
List of Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (C169) genes, which are present in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Volvox carteri, but missing in the genome of Chlorella A99
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.027| UniProt ID in C169 | Description |
|---|---|
| F1DPL8_9CHLO | ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 (mitochondrion) |
| F1DPL7_9CHLO | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 3 (mitochondrion) |
| I0YZU4_9CHLO | equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 |
| I0Z311_9CHLO | equilibrative nucleoside transporter family |
| I0YZC9_9CHLO | high affinity nitrate transporter |
| I0Z2L2_9CHLO | hypothetical protein COCSUDRAFT_28432 |
| I0YJ99_9CHLO | hypothetical protein COCSUDRAFT_34498 |
| I0YKQ1_9CHLO | hypothetical protein COCSUDRAFT_45098 |
| I0YYD3_9CHLO | hypothetical protein COCSUDRAFT_65897 |
| I0YYP5_9CHLO | importin-4 isoform X1 |
| I0YQQ1_9CHLO | low-CO2-inducible membrane |
| I0YJD4_9CHLO | MFS transporter |
| I0YTY0_9CHLO | molybdate transporter 2 |
| F1DPM0_9CHLO | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 (mitochondrion) |
| F1DPM4_9CHLO | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 (mitochondrion) |
| F1DPM8_9CHLO | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 9 (mitochondrion) |
| I0Z357_9CHLO | plasma membrane phosphate transporter Pho87 |
| I0Z9Y1_9CHLO | pre translocase subunit |
| I0YPT2_9CHLO | transcription and mRNA export factor ENY2-like |
| I0Z976_9CHLO | transport SEC23 |
| I0Z3Q6_9CHLO | tyrosine-specific transport -like isoform X1 |
| I0YXU9_9CHLO | urea active transporter |
| I0YRT0_9CHLO | urea active transporter |
| I0YRL4_9CHLO | urea-proton symporter DUR3 |
| I0YUF9_9CHLO | urea-proton symporter DUR3 |
| I0YJS6_9CHLO | urea-proton symporter DUR3 |
| I0YQ78_9CHLO | urea-proton symporter DUR3-like |
| I0YIH7_9CHLO | Zip-domain-containing protein |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Hydra viridissima A99) | Hydra viridissima A99 | PMID: 16351895 | ||
| Strain, strain background (Chlorella sp. A99) | Chlorella sp. A99 | PMID: 16351895 | NCBI BioProject ID: PRJNA412448 | |
| Strain, strain background (Chlorella variabilis NC64A) | Chlorella variabilis NC64A | Microbial Culture Collection at the National Institute for Environmental Studies | NIES-2541 | |
| Strain, strain background (Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169) | Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 | Microbial Culture Collection at the National Institute for Environmental Studies | NIES-2166 | |
| Strain, strain background (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Microbial Culture Collection at the National Institute for Environmental Studies | NIES-2235 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TruSeq DNA LT Sample Prep Kit | Illumina | FC-121–2001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Nextera Mate Pair Sample Preparation Kit | Illumina | FC-132–1001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Miseq reagent kit v3 | Illumina | MS-102–3003 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiSeq SBS kit v4 | Illumina | FC-401–4003 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 4337454 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 4 × 44K Hydra viridissima A99 Custom-Made Microarray | Agilent Technologies | NCBI GEO Platform ID: GPL23280 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | GE Hybridization Kit and GE Wash Pack | Agilent Technologies | 5188–5242, 5188–5327 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | High Sensitivity DNA Kit | Agilent Technologies | 5067–4626 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNA6000 nano kit | Agilent Technologies | 5067–1511 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Low Input Quick Amp Labeling Kit | Agilent Technologies | 5190–2305 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PureLink RNA Mini Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12183018A | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Fermentas First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | K1621 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trizol reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15596026 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | AmpliTaq Gold 360 Master Mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 4398901 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ISOPLANT II | Nippon Gene | 316–04153 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | GoTaq qPCR Master Mix | Promega | A6002 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | KOD FX Neo | TOYOBO | KFX-201 | |
| Software, algorithm | Feature Extraction Software | Agilent Technologies | RRID:SCR_014963 | |
| Software, algorithm | Newbler | 454 Life Sciences, Roche Diagnostics | RRID:SCR_011916 | |
| Software, algorithm | SSPACE | PMID: 21149342 | RRID:SCR_005056 | |
| Software, algorithm | GapCloser | PMID: 23587118 | RRID:SCR_015026 | |
| Software, algorithm | NCBI BLAST | PMID: 2231712 | RRID:SCR_004870 | |
| Software, algorithm | CEGMA | PMID: 17332020 | RRID:SCR_015055 | |
| Software, algorithm | Augustus: Gene Prediction | PMID: 16845043 | RRID:SCR_008417 | |
| Software, algorithm | Blast2GO | PMID: 16081474 | RRID:SCR_005828 | |
| Software, algorithm | Hmmer | PMID: 9918945 | RRID:SCR_005305 | |
| Software, algorithm | CLUSTALX2 | PMID: 17846036 | RRID:SCR_002909 | |
| Software, algorithm | BioEdit | Nucleic Acid Symposium Series 41, 95–98 | RRID:SCR_007361 | |
| Software, algorithm | Njplot | Biochimie 78, 364–369 | NA | |
| Software, algorithm | OrthoFinder | PMID: 26243257 | NA |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Results of microarray analysis and list of differentially expressed genes.
Gene expression of green hydra with native symbiotic Chlorella A99 (Hv_Sym), that in sexual phase (Hv_Sym_sexy), aposymbiotic polyps from which symbiotic Chlorella were removed (Hv_Apo) and aposymbiotic polyps reinfected with Chlorella variabilis NC64A (Hv_NC64A) were compared.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.033
-
Supplementary file 2
(A) Ortholog groups of Aa_trans containing protein in Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 (C169), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr), Volvox carteri (Vc), Micromonas pusilla (Mp) and Ostreococcus tauri (Ot).
(B) Blast best hit genes of Arabidopsis thaliana in Chlorella sp. A99 genes belonging to OG0000040 and OG0000324.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.034
-
Supplementary file 3
List of Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C169 (C169) and their BLAST best hit genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr), Volvox carteri (Vc) and Chlorella A99 (A99) gene model and genome scaffolds.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.035
-
Supplementary file 4
Sequence ID of nitrogen assimilation genes in Symbiodinium.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.036
-
Supplementary file 5
Sequence ID of nitrogen assimilation genes in Chlorella variabilis NC64A (NC64A), Coccomyxa subellipsoidea C-169 (C169), Volvox carteri (Vc), Micromonas pusilla (Mp) and Ostreococcus tauri (Ot) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Cr).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.037
-
Supplementary file 6
Primers used in this study, for quantitative real time RT-PCR. (A), in situ hybridization probes (B), PCR amplification of nitrogen assimilation genes in green algae (C) and PCR amplification of 18S ribosomal DNA gene in green algae (D).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.038
-
Supplementary file 7
Composition of modified Bold’s Basal Medium for one liter (pH. 7).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.039
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35122.040





