Meta-Research: Why we need to report more than 'Data were Analyzed by t-tests or ANOVA'
Figures
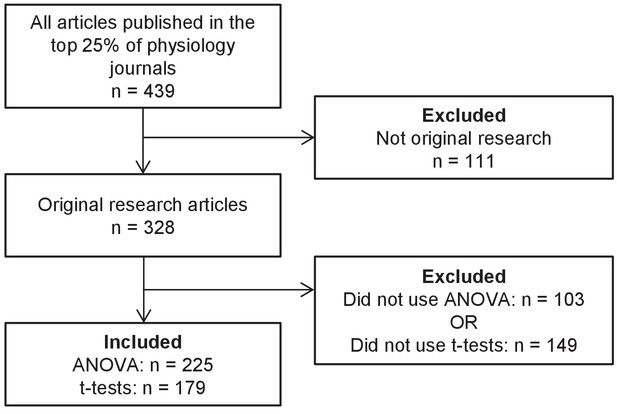
Systematic review flow chart.
The flow chart illustrates the selection of articles for inclusion in this analysis at each stage of the screening process.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Data from systematic review.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.003
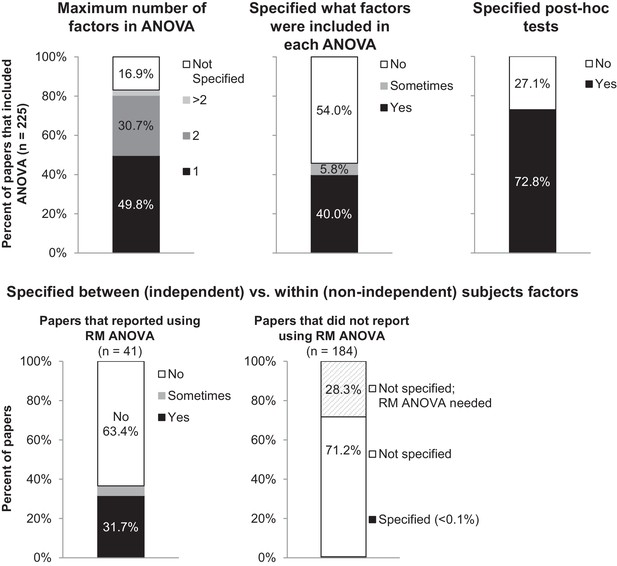
Many papers lack the information needed to determine what type of ANOVA was performed.
The figure illustrates the proportion of papers in our sample that reported information needed to determine what type of ANOVA was performed, including the number of factors, the names of factors, and the type of post-hoc tests. The top panel presents the proportion of all papers that included ANOVA (n = 225). 'Sometimes' indicates that the information was reported for some ANOVAs but not others. The bottom row examines the proportion of papers that specified whether each factor was between vs. within-subjects. Papers are subdivided into those that reported using repeated measures ANOVA (n = 41), and those that did not report using repeated measures ANOVA (n = 184). RM: repeated measures.
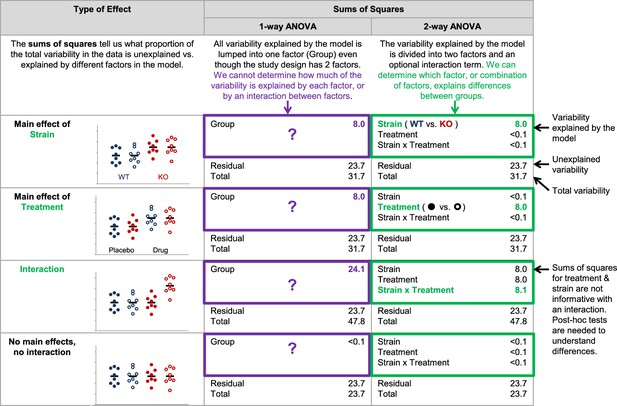
Why it matters whether investigators use a one-way vs two-way ANOVA for a study design with two factors.
The two-way ANOVA allows investigators to determine how much of the variability explained by the model is attributed to the first factor, the second factor, and the interaction between the two factors. When a one-way ANOVA is used for a study with two factors, this information is missed because all variability explained by the model is assigned to a single factor. We cannot determine how much variability is explained by each of the two factors, or test for an interaction. The simulated dataset includes four groups – wild-type mice receiving placebo (closed blue circles), wild-type mice receiving an experimental drug (open blue circles), knockout mice receiving placebo (closed red circles) and knockout mice receiving an experimental drug (open red circles). The same dataset was used for all four examples, except that means for particular groups were shifted to show a main effect of strain, a main effect of treatment, and interaction between strain and treatment or no main effects and no interaction. One- and two-way (strain x treatment) ANOVAs were applied to illustrate differences between how these two tests interpret the variability explained by the model.
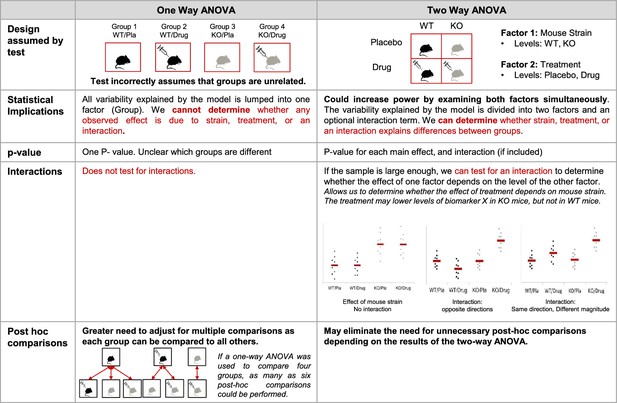
Additional implications of using a one-way vs two-way ANOVA.
This figure compares key features of one- and two-way ANOVAs to illustrate potential problems with using a one-way ANOVA for a design with two or more factors. When used for a study with two factors, the one-way ANOVA incorrectly assumes that the groups are unrelated, generates a single p-value that does not provide information about which groups are different, and does not test for interactions. The two-way ANOVA correctly interprets the study design, which can increase power. The two-way ANOVA also allows for the generation of a set of p-values that provide more information about which groups may be different, can test for interactions, and may eliminate the need for unnecessary post-hoc comparisons. This figure uses an experimental design with four groups (wild-type mice receiving placebo, wild-type mice receiving an experimental drug, knockout mice receiving placebo and knockout mice receiving an experimental drug). See Figure 2 for a detailed explanation of the material in the statistical implications section. KO: knockout; WT: wild-type; Pla: placebo.
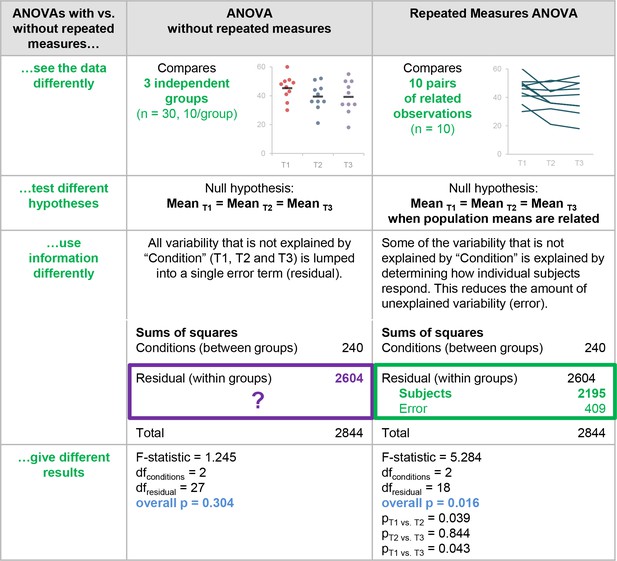
Why it matters whether investigators used an ANOVA with vs. without repeated measures.
This figure highlights the differences between ANOVA with vs. without repeated measures and illustrates the problems with using an ANOVA without repeated measures when the study design includes longitudinal or non-independent measurements. These two tests interpret the data differently, test different hypotheses, use information differently when calculating the test statistic, and give different results.
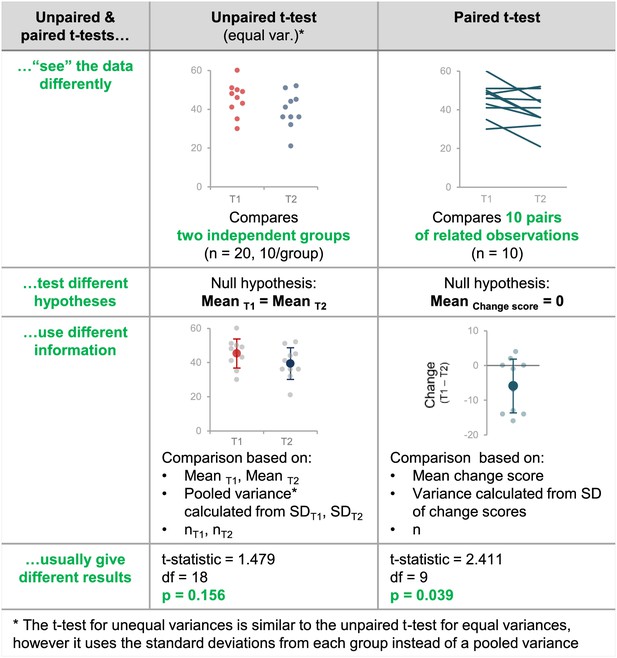
Why papers need to contain sufficient detail to confirm that the appropriate t-test was used.
This figure highlights the differences between unpaired and paired t-tests by illustrating how these tests interpret the data differently, test different hypotheses, use information differently when calculating the test statistic, and give different results. If the wrong t-test is used, the result may be misleading because the test will make incorrect assumptions about the experimental design and may test the wrong hypothesis. Without the original data, it is very difficult to determine what the result should have been (see Figure 6).
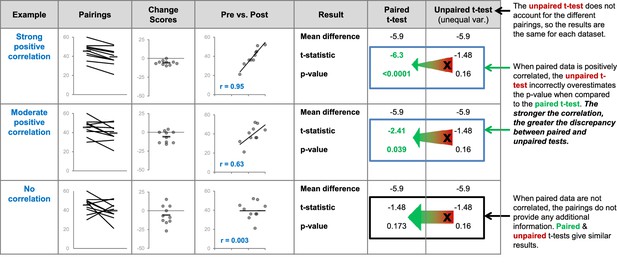
Differences between the results of statistical tests depend on the data.
The three datasets use different pairings of the values shown in the dot plot on the left. The comments on the right side of the figure illustrate what happens when an unpaired t-test is inappropriately used to compare paired, or related, measurements. We expect paired data to be positively correlated – two paired observations are usually more similar than two unrelated observations. The strength of this correlation will vary. We expect observations from the same participant to be more similar (strongly correlated) than observations from pairs of participants matched for age and sex. Stronger correlations result in greater discrepancies between the results of the paired and unpaired t-tests. Very strong correlations between paired data are unusual but are presented here to illustrate this relationship. We do not expect paired data to be negatively correlated – if this happens it is important to review the experimental design and data to ensure that everything is correct.
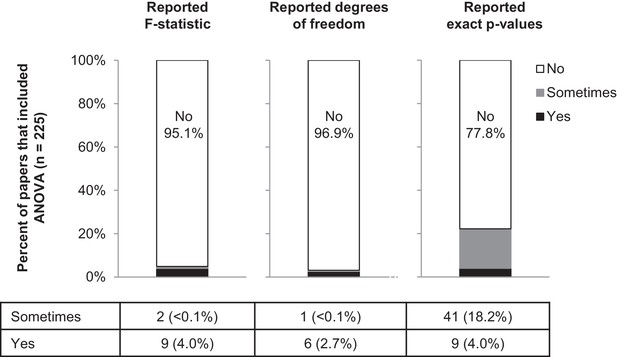
Few papers report the details needed to confirm that the result of the ANOVA was correct.
This figure reports the proportion of papers with ANOVAs (n = 225) that reported the F-statistic, degrees of freedom and exact p-values. Sometimes indicates that the information was reported for some ANOVAs contained in the paper but not for others.
Tables
Reporting of details needed to verify the results of a t-test.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.013| Reported t-statistic | Reported exact sample size or degrees of freedom | Reported exact p-values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No | 156 (95.7%) | 11 (6.7%) | 113 (69.3%) |
| Sometimes | 0 | 27 (16.6%) | 17 (10.4%) |
| Yes | 7 (4.3%) | 125 (76.7%) | 33 (20.2%) |
-
We analyzed the 179 papers in our sample that included t-tests to check if they reported the details that are needed to verify the results of these tests: we had to exclude 16 papers from this analysis because we were unable to determine what data were analyzed by t-tests or to identify a two-group comparison. Most of the papers (95.7%; 156/163) did not report the t-statistic (column 2) and over two-thirds (69.3%; 113/163) did not report exact p-values (column 4), but over three-quarters (76.7%; 125/163) reported the exact sample size or degree of freedom for all of the t-tests in the paper (column 3).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Number of articles examined by journal.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.014
-
Supplementary file 2
Abstraction protocol for systematic review.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.015
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.016
-
Reporting standard 1
PRISMA 2009 checklist.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36163.017





