FoxA1 and FoxA2 drive gastric differentiation and suppress squamous identity in NKX2-1-negative lung cancer
Figures
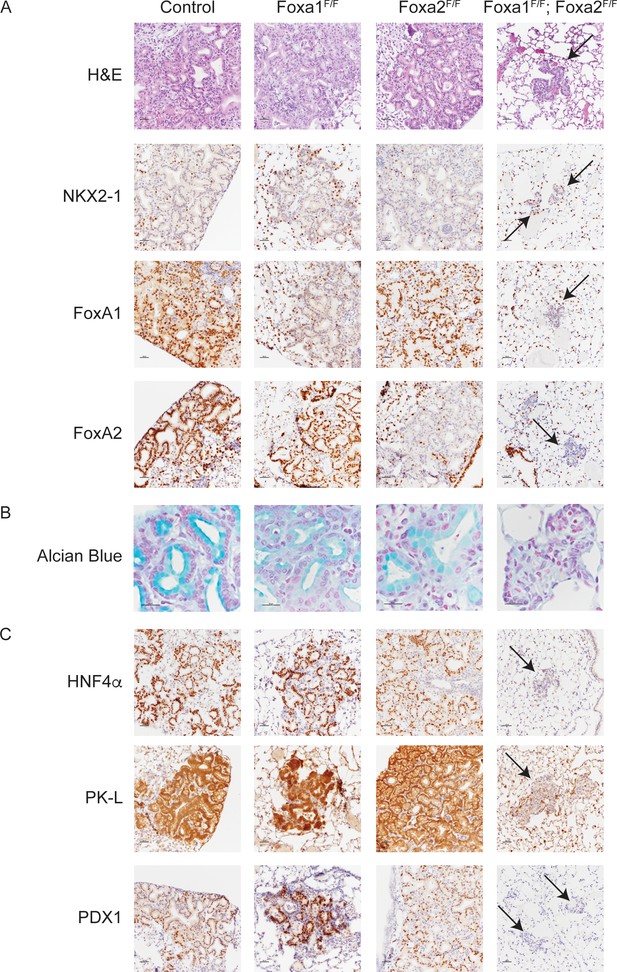
FoxA1 and FoxA2 are required for mucinous lung adenocarcinoma formation.
Photomicrographs of lung neoplasia arising 11 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus. All mice are KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F and harbor conditional alleles of Foxa1 and/or Foxa2 as indicated. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) for NKX2-1, FoxA1 and FoxA2. Arrows indicate neoplasia lacking expression of all three proteins. Scale bar: 100 microns. (B) Alcian blue stain for mucin production. Scale bar: 50 microns. (C) IHC for markers of gastrointestinal differentiation HNF4α, PK-L and PDX1. Scale bar: 100 microns.

FoxA1 and FoxA2 are required for mucinous lung adenocarcinoma formation.
(A) IHC for indicated proteins on primary human mucinous lung adenocarcinoma. Images are representative of six independent primary tumors. Scale bar: 100 microns. (B) FOXA1 and FOXA2 mRNA levels in KRAS-mutant human lung adenocarcinoma and adjacent normal lung. Clusters were defined in Skoulidis et al. (2015) using TCGA data. HNF4α-positive/NKX2-1-negative tumors are found predominantly in KC cluster. (C) IHC for indicated proteins on lung neoplasia arising 11 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus. All mice are KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F and harbor conditional alleles of Foxa1 and/or Foxa2. Scale bar: 100 microns.
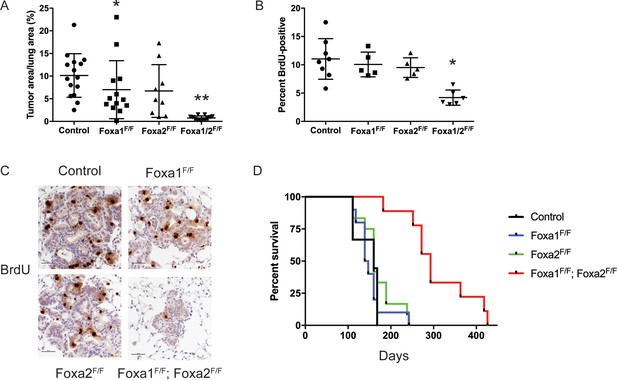
FoxA1 and FoxA2 are required for initiation and proliferation of NKX2-1-deficient lung adenocarcinoma.
(A) Quantitation of tumor burden 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 15), Foxa1F/F (n = 13), Foxa2F/F (n = 9) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 12). **p < 0.0002 vs. each group, Mann-Whitney. *p=0.0425 vs. control. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (B) Quantitation of BrdU incorporation in lung neoplasia 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 7), Foxa1F/F (n = 4), Foxa2F/F (n = 4) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 7). *p < 0.005 vs. each control, Mann-Whitney. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (C) Representative IHC for BrdU in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype quantitated in Figure 2B. Scale bar: 100 microns. (D) Long-term survival after tumor initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 9), Foxa1F/F (n = 10), Foxa2F/F (n = 12) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 9). p < 0.0001, KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mice vs. each control, Log-rank test.

FoxA1 and FoxA2 are required for initiation and proliferation of NKX2-1-deficient lung adenocarcinoma.
(A) Percentage of tumor area expressing HNF4α in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mice analyzed at 5-week (n = 11) and 11-week (n = 7) timepoints and in survival analysis (n = 9). Tumors were initiated by PGK-Cre lentivirus. *p < 0.001 vs. 11 weeks and survival group, Mann-Whitney. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (B) IHC for HNF4α in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse analyzed at 11-week timepoint. Arrow points to HNF4α-negative complete recombinant (left). Brown nuclear stain marks HNF4α-positive incomplete recombinant. Scale bar: 500 microns. (C) Quantitation of average lesion area 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 15), Foxa1F/F (n = 13), Foxa2F/F (n = 9) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 12). **p < 0.001 vs. each group, Mann-Whitney. *p = 0.0251 vs. control. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (D) Quantitation of lesions/mm2 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 15), Foxa1F/F (n = 13), Foxa2F/F (n = 9) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 12). **p < 0.003 vs. each group, Mann-Whitney. *p=0.0171 vs. control. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (E) Quantitation of proliferation marker MCM2 in lung neoplasia 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 7), Foxa1F/F (n = 5), Foxa2F/F (n = 4) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 7). *p < 0.01 vs. each control, Mann-Whitney. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (F) Quantitation of proliferation marker KI67 in lung neoplasia 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype: control (n = 7), Foxa1F/F (n = 5), Foxa2F/F (n = 4) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 7). *p < 0.01 vs. each control, Mann-Whitney. Graphs represent mean ±S.D. (G) Representative IHC for proliferation markers MCM2 and KI67 in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype quantitated in Figure 2—figure supplement 1E–F. Scale bar: 100 microns. (H) Representative IHC for CC3 (cleaved caspase-3) in tumors from mice of indicated genotype. Inset depicts thymus (positive control). Scale bar: 100 microns. (I) H and E demonstrating extracellular mucin secretion (E) in tumors from KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F mice (survival analysis). Scale bar: 100 microns.
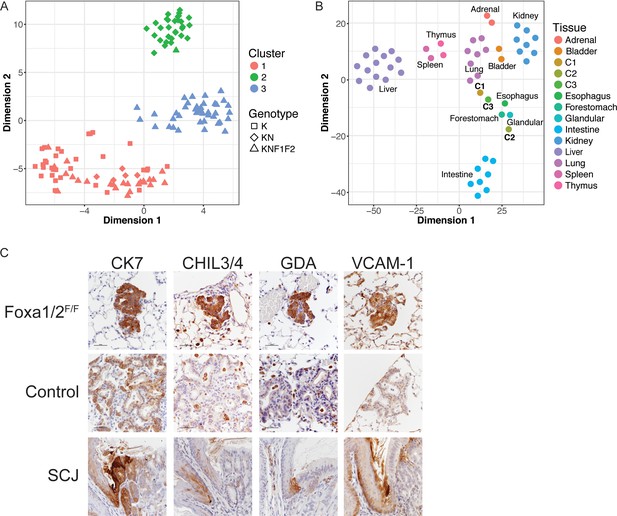
Deletion Nkx2-1, Foxa1 and Foxa2 at initiation blocks gastric differentiation and induces expression of squamocolumnar junctional markers in lung neoplasia.
(A) tSNE plot of single-cell mRNA-Seq data derived from murine lung tumor cells (n = 134). Cells were sorted based on tdTomato expression from mice of the following genotypes: KrasLSL-G12D/+(K), n = 1 mouse), KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F (KN), n = 1 mouse), KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (KNF1F2, n = 2 mice). Color indicates cancer cell cluster. Shape indicates genotype of mouse from which cell was isolated. (B) tSNE plot of three cancer cell clusters (C1–C3) and a panel of normal murine tissue. ‘Glandular’ indicates glandular stomach. (C) IHC for indicated proteins in lung neoplasia 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mice and NKX2-1-negative controls. SCJ: normal squamocolumnar junction (forestomach on left, glandular stomach on right). Scale bar: 100 microns.
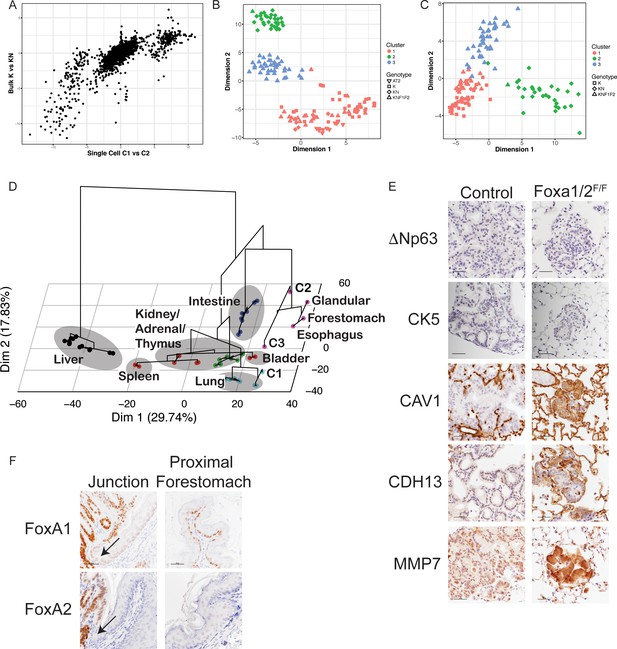
Deletion of Nkx2-1, Foxa1 and Foxa2 at initiation blocks gastric differentiation and induces expression of squamocolumnar junctional markers in lung neoplasia.
(A) Correlation between differentially expressed genes identified in single-cell analysis (C1 vs. C2, X axis) and population analysis (KrasLSL-G12D/+(K) vs. KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F (KN), Y axis). (B) tSNE plot of single high-quality tumor cells (this study) and E18.5 type two pneumocytes (AT2) from murine lung (Treutlein et al.). Color indicates cluster. Shape indicates source of cell. (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) of cancer cell clusters (C1–C3) based on genes comprising invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma signature (Guo et al). (D) Hierarchical clustering on principal components (HCPC) of the three cancer cell clusters (C1–C3) and normal murine tissue. The first two dimensions of a principal component analysis (PCA) is overlayed with the hierarchical clustering of the first five PCA dimensions. Dot color indicates cluster to which sample was assigned in K-means clustering. Gray ovals highlight multiple samples from the same tissue. ‘Glandular’ indicates glandular stomach. (E) IHC for indicated proteins in lung neoplasia 5 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mice and controls. Scale bar: 100 microns. (F) IHC for FoxA1 and FoxA2 at the squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) of glandular stomach and forestomach (left panels) and in proximal forestomach (right panels). Arrows point to SCJ. Scale bars: 100 microns.
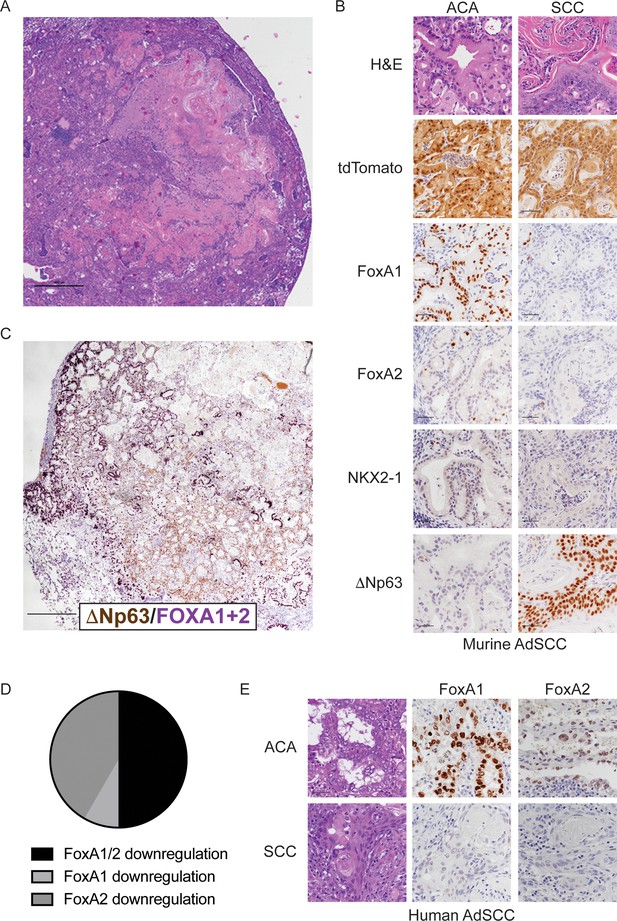
FoxA1 and FoxA2 are downregulated in the squamous component of murine and human adenosquamous lung carcinoma.
(A) H and E of AdSCC arising in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse. Scale bar: 1000 microns. (B) H and E and IHC of adenocarcinoma (left) and squamous (right) components of AdSCC arising in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse. Scale bar: 100 microns. (C) Dual IHC for ΔNp63 (brown) and FoxA1/2 (purple) in AdSCC arising in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse. Scale bar: 1000 microns. (D) Percent of human AdSCC cases (n = 12) exhibiting downregulation of FoxA1 and/or FoxA2 expression in the SCC component as assessed by IHC. (E) Representative IHC for FoxA1 and FoxA2 in a human AdSCC exhibiting downregulation of both proteins in the SCC component. Scale bar: 100 microns.

FoxA1 and FoxA2 are downregulated in the squamous component of murine and human adenosquamous lung carcinoma.
(A) Percent of KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice of indicated genotype with adenosquamous carcinoma (AdSCC) 20 weeks after initiation with PGK-Cre lentivirus. Control (n = 14), Foxa1F/F (n = 10), Foxa2F/F (n = 17) and Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 12). (B) IHC of adenocarcinoma (left) and squamous (right) components of AdSCC arising in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F mouse. Scale bar: 100 microns. (C) IHC for indicated proteins in adenocarcinoma (left) and squamous (right) components of AdSCC arising in KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse. Scale bar: 100 microns.
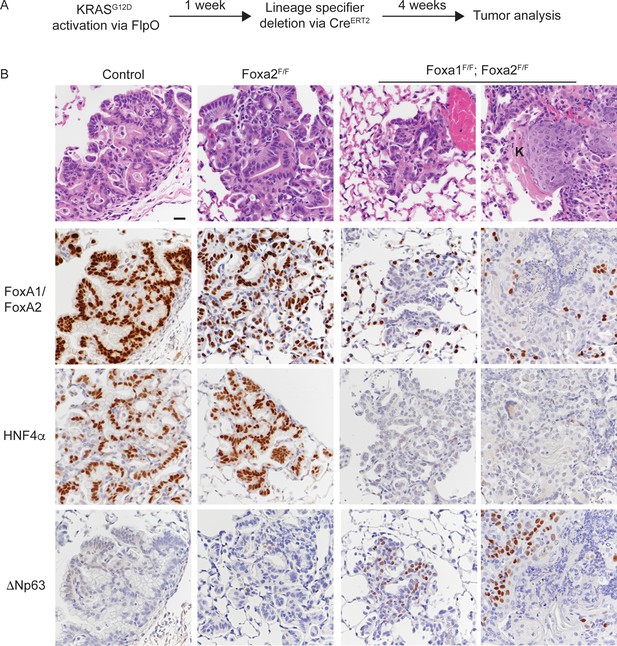
Uncoupling KRASG12D activation from lineage specifier deletion promotes squamous cell carcinoma formation in the lung.
(A) Schematic of experimental design. (B) H and E and IHC for indicated proteins in tumors from mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F (controls) alone and in combination with either Foxa2F/F or Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F. ‘K’ indicates acellular keratin. All mice were given tamoxifen 1 week after tumor initiation. Tamoxifen administration consisted of six intraperitoneal doses over nine days, followed by tamoxifen-containing chow until the end of the experiment. Scale bar: 50 microns.
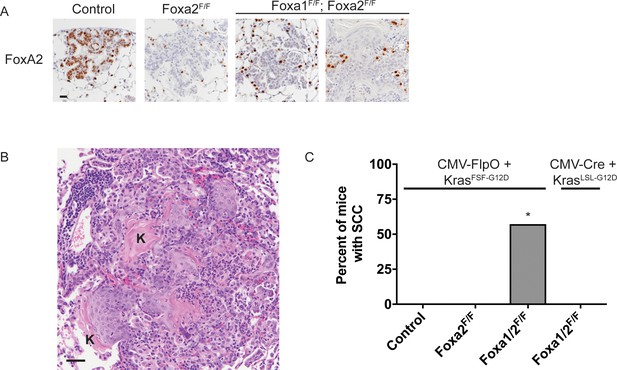
Uncoupling KRASG12Dactivation from lineage specifier deletion promotes squamous cell carcinoma formation in the lung.
(A) IHC for FoxA2 in tumors from mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F (controls) alone and in combination with either Foxa2F/F or Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F. Scale bar: 50 microns. (B) Low power H and E photomicrograph of keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma arising in KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mouse. Scale bar: 100 microns. ‘K’ indicates acellular keratin. (C) Percent of KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F (Control, n = 19), KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 21), KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 8) and KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F mice (n = 6) harboring keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma 5 weeks after initiation with Ad5-CMV-FlpO followed by tamoxifen (KrasFSF-G12D/+ mice) or Ad5-CMV-Cre (KrasLSL-G12D/+ mice). *p < 0.001, Chi-square test.
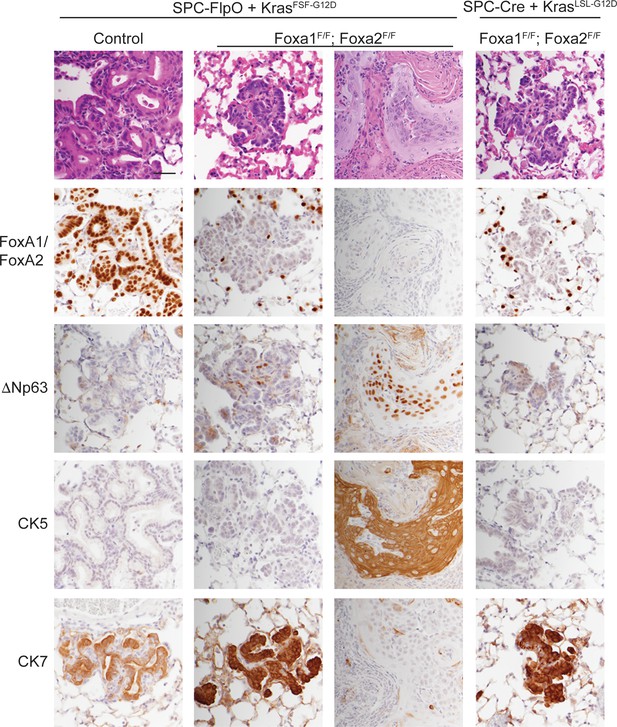
SPC-positive cells give rise to squamous cell carcinoma when KRASG12D activation is uncoupled from lineage specifier deletion.
H and E and IHC for indicated proteins in neoplasia 5 weeks post initiation. In mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F (controls) alone and in combination with Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F, lung tumors were in initiated with Ad5-SPC-FlpO adenovirus. In mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasLSL-G12D/+; RosaLSL-tdTomato; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F, tumors were initiated with Ad5-SPC-Cre (right column). All mice were given tamoxifen 1 week after tumor initiation. Tamoxifen administration consisted of four intraperitoneal doses over 5 days, followed by tamoxifen-containing chow until the end of the experiment. Scale bar: 100 microns.
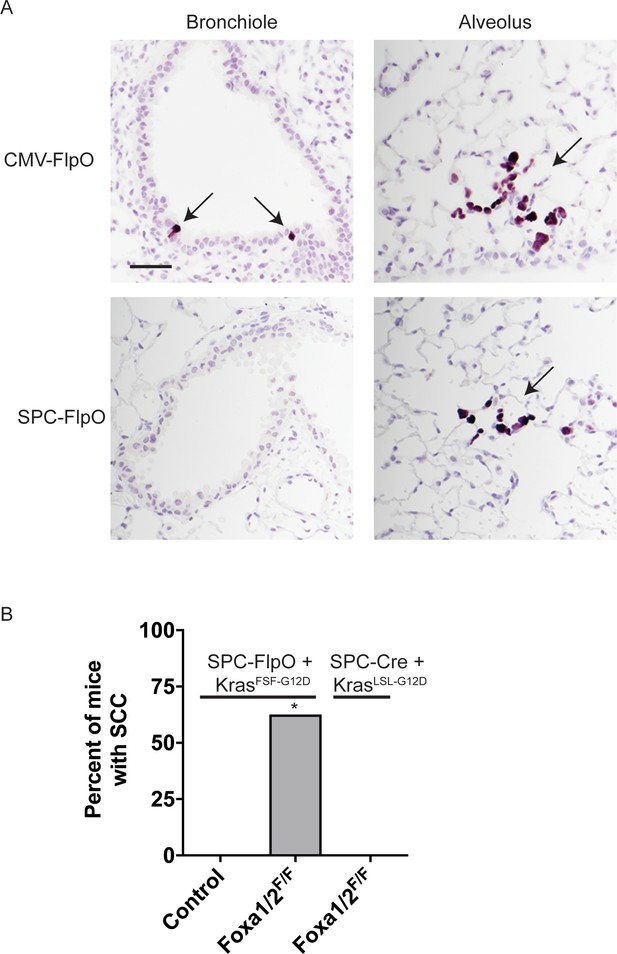
SPC-positive cells give rise to squamous cell carcinoma when KRASG12Dactivation is uncoupled from lineage specifier deletion.
(A) IHC for HA (purple) in lungs from KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; CAG-LSL-HA-UPRT mice infected with Ad5-CMV-FlpO (top) or Ad5-SPC-FlpO (bottom). One week post-infection, mice were given four intraperitoneal injections of tamoxifen over 5 days, followed by tamoxifen chow. Lungs were analyzed 3 weeks post-infection. Scale bar: 100 microns. (B) Percent of mice harboring keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) 5 weeks post tumor initiation. In mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasFSF-G12D/+; RosaFSF-CreERT2; Nkx2-1F/F (controls, n = 5)) alone and in combination with Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 8) lung tumors were initiated with Ad5-SPC-FlpO adenovirus. In mice harboring the conditional alleles KrasLSL-G12D/+; RosaLSL-tdTomato; Nkx2-1F/F; Foxa1F/F; Foxa2F/F (n = 5) tumors were initiated with Ad5-SPC-Cre (right column). All mice were given tamoxifen 1 week after tumor initiation. Tamoxifen administration consisted of four intraperitoneal doses over 5 days, followed by tamoxifen-containing chow until the end of the experiment. *p < 0.03 vs. each control, Chi-square test.
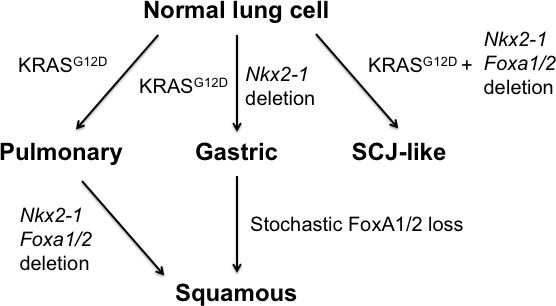
Model of context-specific regulation of lung cancer identity by NKX2-1, FoxA1 and FoxA2.
SCJ: squamocolumnar junction of GI tract.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | KrasLSL-G12D | PMID: 11751630 | Dr. Tyler Jacks (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts) | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | KrasFSF-G12D | PMID: 21512139 | RRID:MGI:5007794 | Dr. Tyler Jacks (Massachusetts Institute of Technology , Cambridge, Massachusetts) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Rosa26LSL-tdTomato | PMID: 20023653 | RRID:MGI:4436847 | Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, Maine) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Rosa26FSF-CreERT2 | PMID: 25326799 | Dr. Dieter Saur (Technische Universität München, München, Germany) | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Nkx2-1F/F | PMID: 16601074 | RRID:MGI:3653706 | Dr. Shioko Kimura (National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Foxa1F/F | PMID: 19141476 | RRID:MGI:3831163 | Dr. Klaus H. Kaestner (University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Foxa2F/F | PMID: 10866673 | RRID:MGI:2177357 | Dr. Klaus H. Kaestner (University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | CAG-LSL-HA-UPRT | PMID: 23307870 | Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, Maine) | |
| Cell line | 293T | PMID: 19561589 | ||
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-BrdU | Abcam | Cat. #: ab6326, RRID: AB_305426 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cadherin 13 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab167407 | IHC (1:250) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Cathepsin E | Lifespan Biosciences | Cat. #: LS-B523, RRID:AB_2087236 | IHC (1:12000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Caveolin 1 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab192869 | IHC (1:4000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-CHIL3/4 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab192029 | IHC (1:20000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cleaved- caspase 3 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat. #: 9664 | IHC (1:800) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cytokeratin-5 | Abcam | Cat #: ab52635 (EP1691Y) | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cytokeratin-7 | Abcam | Cat #: ab181598 (EP17078) | IHC (1:20,000) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-Cytokeratin-8 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat. #: TROMA-I, RRID:AB_531826 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cytokeratin- 14 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab181595 (EPR17350) | IHC (1:4000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-FoxA1 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab173287 | IHC (1:4000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-FoxA2 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab108422, RRID:AB_11157157 | IHC (1:1200) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Galectin 4 | R and D Systems | Cat. #: AF2128, RRID:AB_ 2297050 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Gastrokine 1 | Abnova | Cat. #: H00056287-M01, RRID:AB_1505437 | IHC (1:50) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-GDA | Abcam | Cat. #: ab210606 | IHC (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-HNF4α | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat. #: 3113S, RRID:AB_2295208 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-Ki67 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab16667, RRID:AB_302459 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-MCM2 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab31159, RRID:AB_881276 | IHC (1:800) |
| Antibody | Polyclonal goat anti-MMP7 | R and D Systems | Cat. #: AF2967, RRID:AB_664120 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Muc5AC | Abnova | Cat. #: MAB13117 | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-NKX2-1 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab76013, RRID: AB_1310784 | IHC (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-p40 (∆Np63) | Biocare Medical | Cat. #: ACI 3066 C | IHC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-PDX1 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | Cat. #: F109-D12, RRID:AB_1 157903 | IHC (1:10) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-PIGR | Abcam | Cat. #: ab170321 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-PK-LR | Abcam | Cat. #: ab171744 | IHC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-proSPC | Millipore | Cat. #: AB3786, RRID: AB_91588 | IHC (1:4000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-RFP | Rockland | Cat. #: 600-401-379 | IHC (1:400) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-SOX2 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat. #: 3728, RRID: AB_2194037 | IHC (1:250) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-VCAM1 | Abcam | Cat. #: ab134047, RRID:AB_2721053 | IHC (1:1000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Ad5-CMVCre | Gene Transfer Vector Core, University of Iowa, IA | VVC-U of Iowa-5-HT | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Ad5-CMVFlpo | Gene Transfer Vector Core, University of Iowa, IA | VVC-U of Iowa-530HT | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Ad5-SPC-Cre | Gene Transfer Vector Core, University of Iowa, IA | VVC-Berns- 1168 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Ad5-SPC-FlpO | Gene Transfer Vector Core, University of Iowa, IA | VVC-Snyder- 6695 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | PGK-Cre | PMID: 19561589 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | VSVg | PMID: 19561589 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Δ8.9 | PMID: 19561589 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | SPC-FlpO shuttle plasmid | this paper | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen | Sigma-Aldrich | T5648-5G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen supplemented chow | Envigo | TD.130858 | 500 mg/kg of diet |
| Chemical compound, drug | 1X PBS | ThermoFisher Scientific | 20012050 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trizol | ThermoFisher Scientific | 15596026 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Bloxall | Vector Laboratories | SP-6000 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Horse serum | Vector Laboratories | S-2012 | |
| commercial assay, kit | Rodent Block M | Biocare Medical | RBM961 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ImmPRESS anti-rabbit HRP | Vector Laboratories | MP-7401 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ImmPRESS anti-rat HRP | Vector Laboratories | MP-7444 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ImmPRESS anti-goat HRP | Vector Laboratories | MP-7405 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Anti-mouse secondary | Biocare Medical | MM620 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ImmPACT DAB Peroxidase (HRP) Substrate | Vector Laboratories | SK-4105 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | ImmPACT VIP Peroxidase (HRP) Substrate | Vector Laboratories | SK-4605 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Hematoxylin | Fisher Scientific | 6765003 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Collagena se type I | ThermoFisher Scientific | 17100017 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Elastase | Worthington Biochemical Corporation | LS002280 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Dispase | Corning | 354235 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Deoxyribonuclease I | Sigma-Aldrich | DN25 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Red Blood Cell Lysis Buffer | eBioscience | 00-4333-57 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | PureLink RNA Mini kit | ThermoFisher Scientific | 12183018A |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of all single cells used in analysis with quality control metrics, genotype of mouse and cluster each cell was assigned.
In cells that failed quality control, cluster is not assigned and failed QC metric(s) are highlighted.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.016
-
Supplementary file 2
Table of gene expression levels in all high quality cells used in downstream analysis.
Cells are organized by cluster (C1: gray, C2: yellow, C3: green).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.017
-
Supplementary file 3
Marker genes from each cluster (generated with S3).
Genes differentially expressed between each cluster (pairwise comparisons, SCDE).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.018
-
Supplementary file 4
Genes differentially expressed between tumor cells sorted from KrasLSL-G12D/+ mice (K, n = 3 mice) and KrasLSL-G12D/+; Nkx2-1F/F mice (KN, n = 3 mice)
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.019
-
Supplementary file 5
List of normal murine tissues used and their source.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.020
-
Supplementary file 6
Cosine similarity table quantitating similarity between single cell clusters and each normal tissue evaluated.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.021
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38579.022





