An expanded toolkit for gene tagging based on MiMIC and scarless CRISPR tagging in Drosophila
Figures
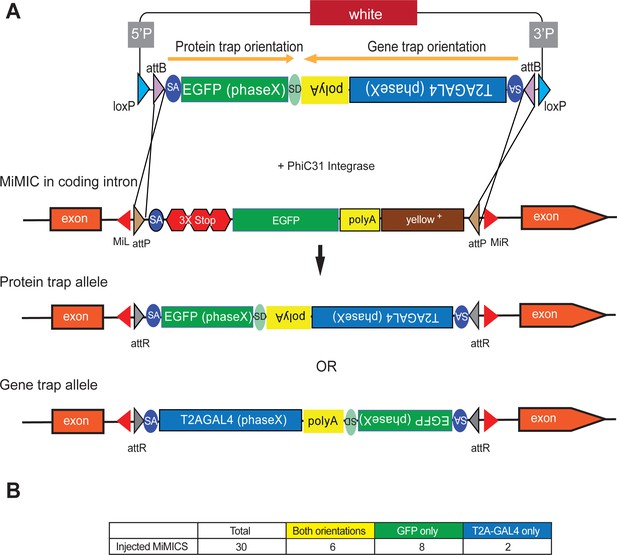
Double Header optimizes RMCE outcome of MiMICs.
(A) Schematics of the Double Header construct and RMCE outcomes. Double Header constructs contain a Splice Acceptor (SA)- super folder GFP-FlAsH-StrepII-TEV-3xFlag (EGFP) – Splice Donor (SD) in one orientation and a SA-T2A-GAL4-polyA in the other orientation. Insertion in the GFP orientation results in GFP protein trap whereas insertion in the T2A-GAL4 orientation results in T2A-GAL4 gene trap. (B) Double Header injection statistics.
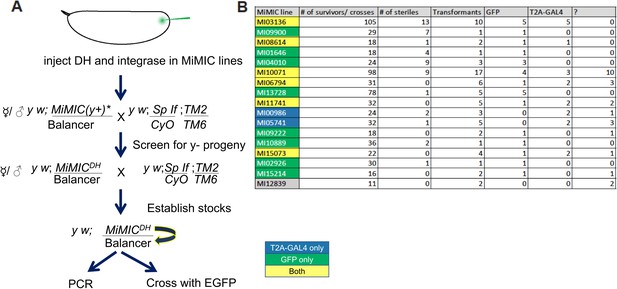
Injection data for Double Header.
(A) The crossing scheme to generate Double Header RMCE events through embryo injection. (B) PCR determination of the Double Header orientation. ? indicates the number of lines where the PCR pattern was ambiguous. Yellow MiMICs: Double Header insertions in both orientations, Green MiMICs: only GFP protein trap orientation, Blue MiMICs: only T2A-GAL4 gene trap orientation.
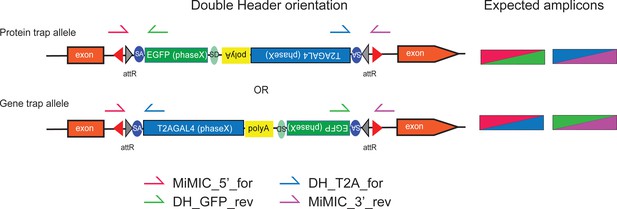
PCR strategy to identify Double Header orientation.
Primers are indicated on the Double Header construct that inserted in an intronic MiMIC. For each Double Header insertion four single fly PCR reactions were set with MiMIC inwards primers that bind outside the attP sites and are directed inwards (MiMIC_5’_for, MiMIC_3’_rev) and GFP and T2A-GAL4 specific outwards primers (DH_GFP_rev, DH_T2A-for). A correct insertion results in amplicons in two out of four PCRs.
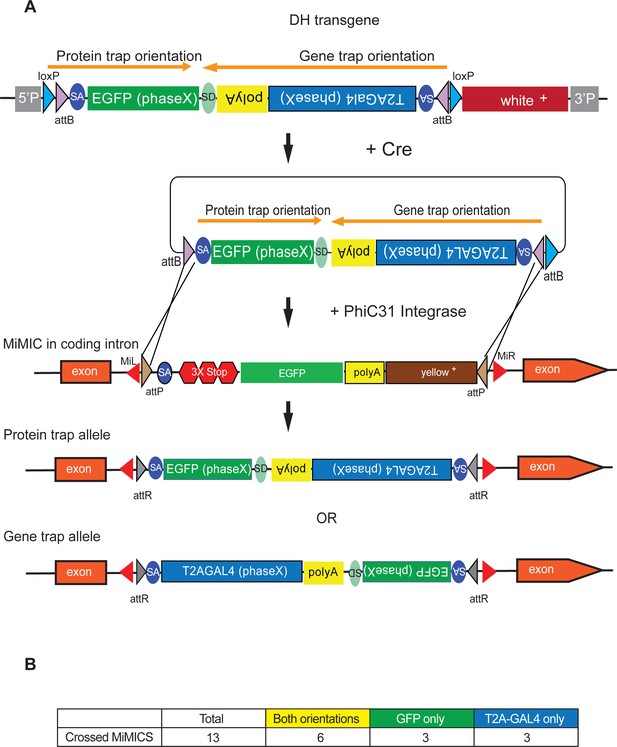
Double Header integration through crosses facilitates RMCE.
(A) Schematics of the Double Header transgene mobilization in vivo. Double Header transgenes contain loxP sites that can be used to mobilize the RMCE cassette in vivo, without the need for injection. (B) Double header crossing statistics.
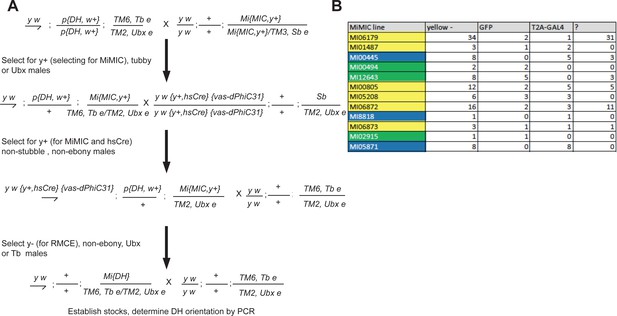
Crossing scheme for Double Header and data of integration.
(A) Crossing scheme for mobilizing Double Header RMCE cassette and selecting RMCE events. (B) PCR determination of the Double Header orientation. ? indicates the number of lines where PCR pattern was ambiguous. Yellow MiMICs: Double Header insertions in both orientations, Green MiMICs: only GFP protein trap orientation, Blue MiMICs: only T2A-GAL4 gene trap orientation.
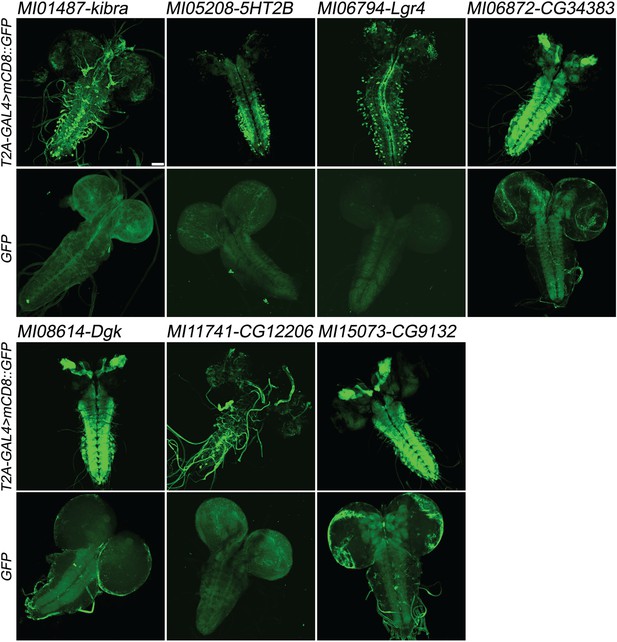
Examples of gene expression patterns obtained by Double Header.
Each MiMIC, MI01487, MI05208, MI06794, MI06872, MI08614, MI11741 and MI15073, was converted to either T2A-GAL4 protein traps or GFP protein traps by Double Header insertion. The expression in the larval CNS is shown with either T2A-GAL4 > UAS-mCD8::GFP or GFP-tag (GFP and mCD8::GFP, green). The affected genes are labelled above. Scale bar: 50 µm.
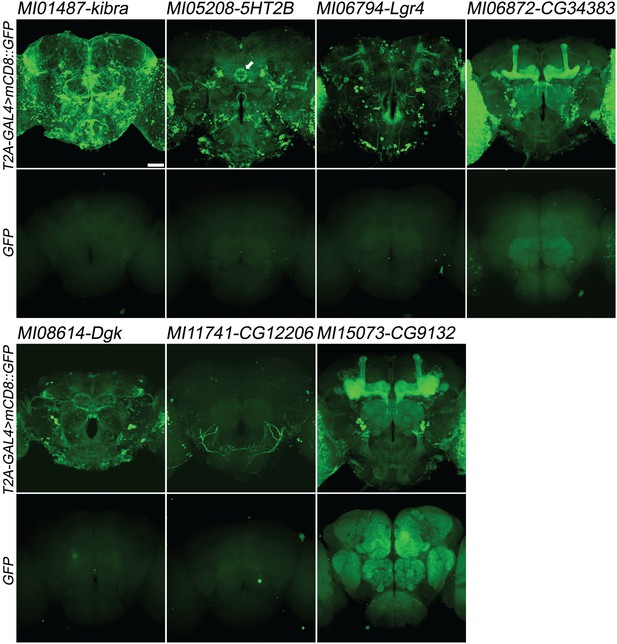
Examples of gene expression patterns obtained by Double Header insertions in MiMICs in adult brain.
Each MiMIC MI01487, MI05208, MI06794, MI06872, MI08614, MI11741 and MI15073, was converted to either a T2A-GAL4 gene trap or GFP protein trap by Double Header insertion. The expression in the adult brain is shown with either T2A-GAL4 > UAS-mCD8::GFP or GFP-tag (GFP and mCD8::GFP, green). The affected genes are labelled above. Arrow: Ellipsoid body (MI05208-5HT2B). Scale bar: 50 µm.
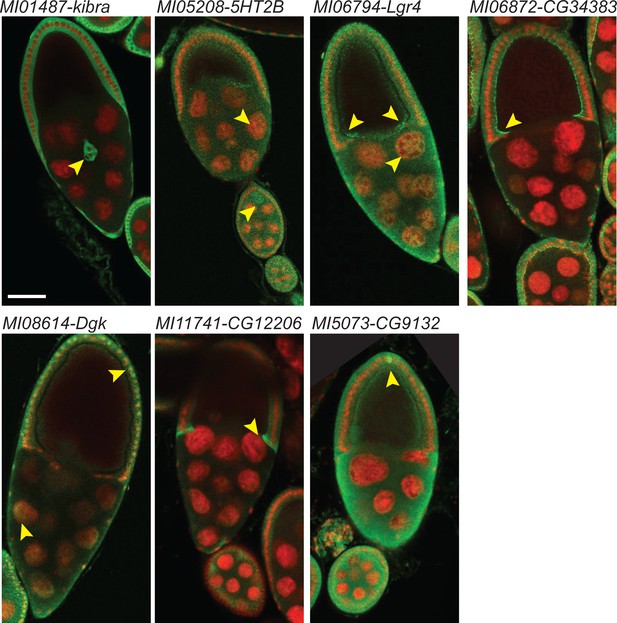
Examples of cellular expression patterns and subcellular localization of tagged proteins in egg chambers at stage 9 and 10.
Double header GFP protein traps of MIMIC lines shown in Figure 3 were dissected and ovaries were stained with anti-GFP antibody (green) and DAPI (red). Arrowheads indicate features that are referred to in the text; border cells for kibra; nurse cells, follicle cels and oocytes for 5HT2B; GFP is broadly expressed and distributed for Lgr4; note the apical enrichment in follicle cells in CG34383; nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in nurse cells and follicle cells are observed in Dgk; centripedal cells cytoplasm is mostly labeled in CG12206; broad expression and localization with pole cell enrichment in CG9132. Scale bar: 50 µm.
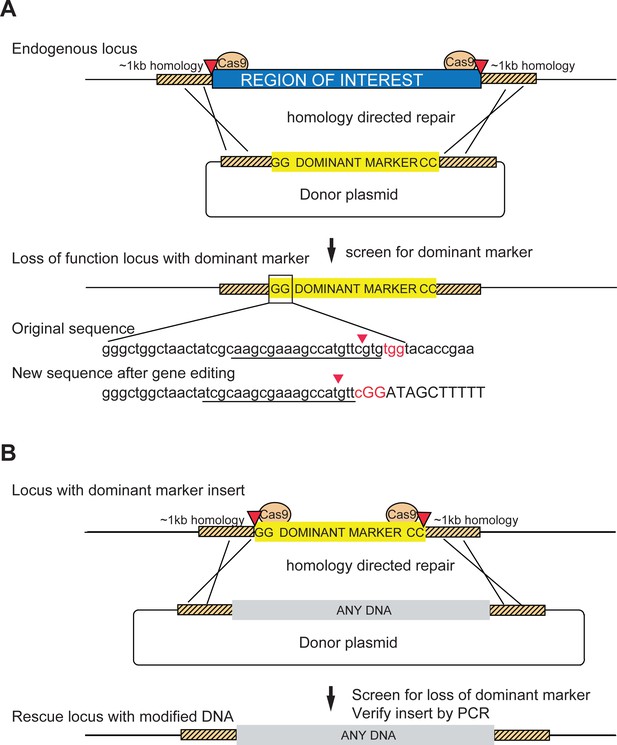
Schematic of a two-step system for scarless gene editing.
(A) In step 1, a cassette containing a dominant marker flanked by nucleotides GG and CC replaces an endogenous locus via Homology Directed Repair (HDR) following double strand breaks produced by Cas9 cleavage (marked by red arrowheads). The removal of the intervening sequence between the Cas9 cut sites alters the sgRNA target sequences (underlined) preventing cleavage of the donor construct or the modified DNA. Screening for the dominant marker facilitates identification of CRISPR gene editing events while the flanking nucleotides GG (boxed inset) and CC create novel Cas9 target sites, allowing subsequent excision. (B) In step two the insert is removed and replaced with any DNA via a second round of HDR with new sgRNA sequences, facilitating the scarless insertion of any DNA sequence desirable.
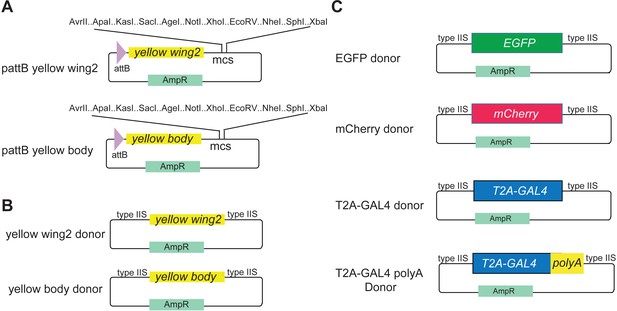
Template vectors for cloning yellow expression constructs.
(A) Vectors for ΦC31-mediated site-specific integration with yellow wing and body expression constructs. (B) yellow wing and body expression constructs compatible with Golden Gate cloning for SIC insertion via HDR. (C) Template donors compatible with Golden Gate cloning for yellow cassette swapping via HDR.
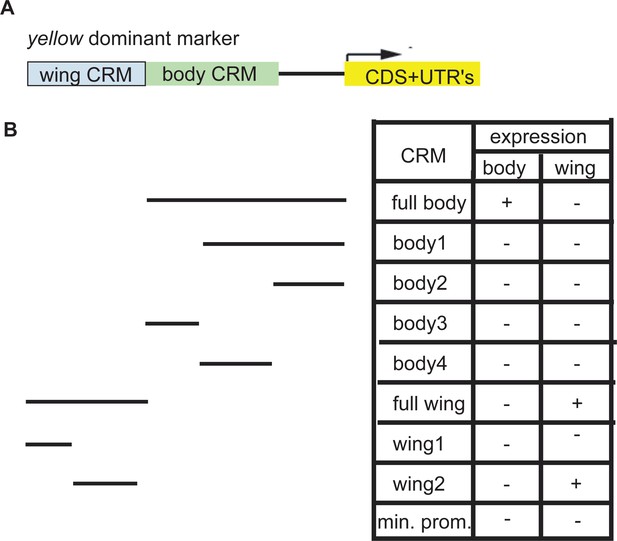
Mapping cis-regulatory modules for the yellow gene.
(A) Structure of the yellow dominant marker showing previously characterized enhancers for wing and body (Geyer and Corces, 1987). (B) regions tested for yellow expression (black lines) when fused to a minimal promoter and the yellow gene. The table at the bottom right indicates the presence/absence of dark pigmentation in either the body or the wing for each cis-regulatory module (CRM) tested.
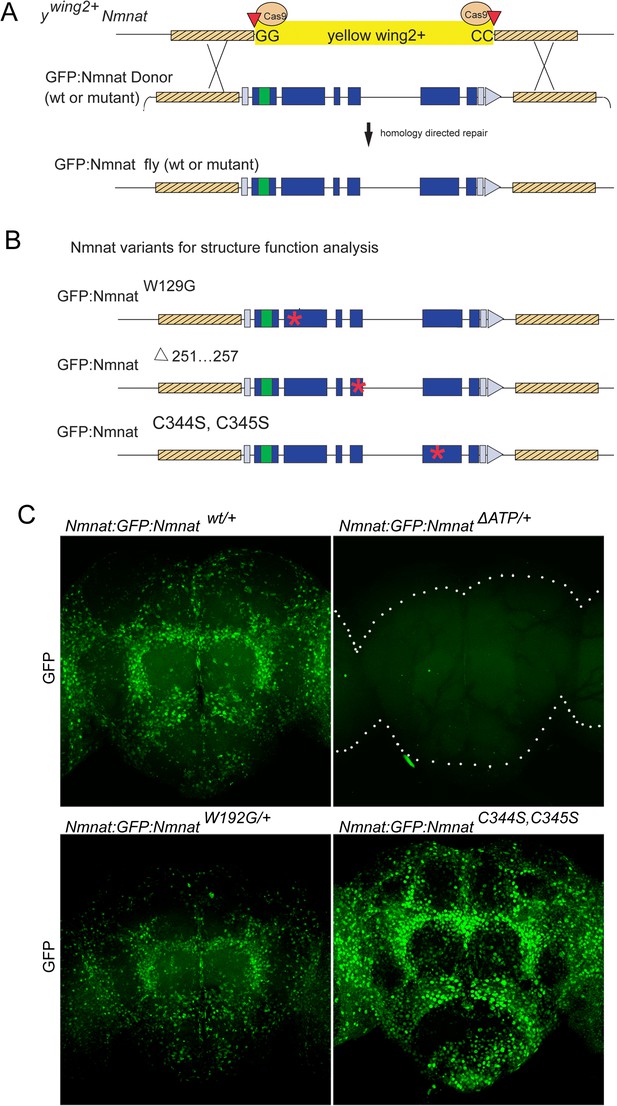
ywing2+ cassette swapping facilitates structure-function analyses.
(A) Schematic of the Nmnat::GFP::Nmnat donor construct for replacing the inserted ywing2+ SIC at the Nmnat locus. (B) Nmnat::GFP::Nmnat variants used in the structure function experiment. Red * denotes approximate location of altered sequence(s). (C) Images of adult brains of Nmnat::GFP::Nmnat wt (Top left) Nmnat::GFP::NmnatW129G (Bottom left) Nmnat::GFP::NmnatΔ251…257 (Top right) and Nmnat:GFP:NmnatC344S, C345S (bottom right).
Tables
Summary statistics for cassette knock-in experiments
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38709.014| Construct | Genotype injected: | No. independent positive lines obtained | Lethality | Rescue of lethality/failure to complement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ywing2+ ΔNmnat | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 6 | lethal | Genomic Fragment (Zhai et al., 2006)/NmnatΔ4790–1 |
| ywing2+ ΔStub1 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 4 | Viable/Fertile* | ND |
| ywing2+ ΔUbqn | yw iso#6; +/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9} | 2 | lethal | Fails to complement Ubqn1 |
| ywing2+ ΔItp-r83A | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 1 | lethal | ND |
| ywing2+ ΔCG18769 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 2 | lethal | ND |
| ywing2+ ΔCG13390 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 2 | lethal | Rescued by Genomic Fragment (this study) |
| ywing2+ ΔMed27 | yw iso#6; +/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9} | 1 | lethal | Rescued by Genomic Fragment (this study) |
| ywing2+ ΔCG11679 | yw iso#6; +/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9} | 2 | lethal | Rescued by genomic duplication BSC Dp(1:3) 304 |
| Ywing2+ Δrho | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w* | 0 | NA | NA |
| ywing2+ Δamx | yw iso#6; +/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9} | 2 | Female sterile | Rescued by Genomic Fragment |
-
*two of four lines
Summary statistics for cassette swapping experiments
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38709.015| Construct | Injected genotype: | No. embryos injected | No. fertile adults | No vials with y- flies | % of y- flies confirmed positive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nmnat:GFP:Nmnat wt #1 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;+; ywing2+ ΔNmnat/TM6B | 514 | 7 | 4 | 6% |
| Nmnat:GFP:Nmnat wt #2 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;+; ywing2+ ΔNmnat/TM6B | 607 | 16 | 5 | 21% |
| Nmnat:GFP:NmnatW129G #1 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;+; ywing2+ ΔNmnat/TM6B | 653 | 0 | - | - |
| Nmnat:GFP:NmnatW129G #2 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;3 KB NMNAT GRC; ywing2+ ΔNmnat | 418 | 31 | 3 | 55% |
| Nmnat:GFP:NmnatΔ251…257 | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;3 KB NMNAT GRC; ywing2+ ΔNmnat | 496 | 29 | 11 | 24% |
| Nmnat:GFP:NmnatC344S, C345S | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;3 KB NMNAT GRC; ywing2+ ΔNmnat | 386 | 30 | 12 | 14% |
| Stub1:GFP | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*; ywing2+ ΔStub1 | 235 | 62 | 2 | 66% |
| CG11679:Flag | ywing2+ ΔCG11679/FM7 Kgal4,UAS GFP;+/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9 | 976 | 12* | 3 | 33% |
| Med27:flag | y1 M{nos-Cas9.P}ZH-2A w*;+; ywing2+ ΔMed27 | 833 | 17 | 3 | 29% |
| Amx:GFP | ywing2+ Δamx;+/+; attP2(y-){nos-Cas9 | 648 | 34 | 0 | - |
-
*excluding FM7 homozygotes and hemizygotes
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase 0 on chromosome II | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase one on chromosome II | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase two on chromosome II | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase 0 on chromosome III | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase one on chromosome III | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Double Header Jump Starter phase two on chromosome III | This study | Fly strain containing DH flanked by LoxP sites | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI01487 (kibra) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0040175; RRID:BDSC_40175 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI05208 [5-HT2B (5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B)] | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0042994; RRID:BDSC_42994 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI06794 [Lgr4(Leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4)] | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0042179: RRID:BDSC_42179 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI06872 (CG34383) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0041111; RRID:BDSC_41111 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI08614 [Dgk (Diacyl glycerol kinase)] | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0044991; RRID:BDSC_44991 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI11741 (CG12206) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0056687; RRID:BDSC_56687 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI15073 (CG9132) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0059739; RRID:BDSC_59739 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI02926 (Pits) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0036165; RRID:BDSC_36165 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI00805 (CG6966) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0034113; RRID:BDSC_34113 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI12643 (fz) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0058645; RRID:BDSC_58645 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI05871 (Doa) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0043880; RRID:BDSC_43880 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI08818 (qless) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0051110; RRID:BDSC_51110 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI06179 (DCX-EMAP) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0043047; RRID:BDSC_43047 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI14396 (CG6293) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0059511; RRID:BDSC_59511 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI00445 (Nlg3) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0031005; RRID:BDSC_31005 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI09222 (CG1578) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0051263; RRID:BDSC_51263 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI00494 (wnd) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015b | flybaseID# _FBst0031028; RRID:BDSC_31028 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI02915 (Ask1) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0036163; RRID:BDSC_36163 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI03136 (LPCAT) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0036425; RRID:BDSC_36425 | |
| Gnetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI10071 (Trpl) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0053455; RRID:BDSC_53455 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI09900 (Sap47) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID# _FBst0053794; RRID:BDSC_53794 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI01646 (CG1815) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0035948; RRID:BDSC_35948 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI04010 (Tbh) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0056660; RRID:BDSC_56660 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI13728 (CG17841) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0059189; RRID:BDSC_59189 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI05741 (CG1632) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0042106; RRID:BDSC_42106 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI10889 (CG17167) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0056092; RRID:BDSC_56092 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI00986 (CG32698) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0035095; RRID:BDSC_35095 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | MI15214 (CG13375) | Venken et al. (2011a); Nagarkar-Jaiswal et al., 2015a | flybaseID#_ FBst0060995; RRID:BDSC_60995 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Nmnatywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the geneNmnat | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Stub1ywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene Stub1 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Ubqnywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene Ubqn | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Itp-r83Aywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene Itp-r83 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | CG18769ywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene CG18769 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | CG13390ywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene CG13390 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Med27ywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene Med27 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | CG11679ywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene CG11679 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | amxywing2+ | This study | fly strain carrying the ywing2+ dominant marker replacing the gene amx | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Nmnat::GFP::NmnatWT | This study | fly strain carrying the Nmnat gene with S(GSS)4... EGFP coding sequence… (GSS)4 integrated internally into the protein between 3R:24945353 and 3R:24945353 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Nmnat::GFP::NmnatW129G | This study | fly strain carrying the Nmnat gene with S(GSS)4...EGFP coding sequence…(GSS)4 integrated internally into the protein between 3R: 24945353 and 3R:24945353 and bearing a mutation producing W192G | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Nmnat::GFP::NmnatΔ251…257 | This study | fly strain carrying the Nmnat gene with S(GSS)4...EGFP coding sequence…(GSS)4 integrated internally into the protein between 3R: 24945353 and 3R:24945353 and bearing a deletion removing amino acids 251…257 | |
| Genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Nmnat::GFP::NmnatC344S, C345S | This study | fly strain carrying the Nmnat gene with S(GSS)4... EGFP coding sequence… (GSS)4 integrated internally into the protein between 3R: 24945353 and 3R:24945353 and bearing a mutation producing C344S, C345S | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Double Header | This study | Recombination Mediated Cassette Exchange donor plasmid containing SA-T2A -GAL4-polyA and SA-GFP-SD in the opposite orientation | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pattB ywing2+ | This study | Vector for φC31 integrated transgenesis that expresses the yellow gene product in the wings | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pattB ybody+ | This study | Vector for φC31 integrated transgenesis that expresses the yellow gene product in the body | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{ywing2+} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the yellow wing2 + dominant marker flanked by nucleotides ‘GG’ and ‘CC’ upstream and downstream, respectively | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{ybody+} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the yellow body dominant marker flanked by nucleotides ‘GG’ and ‘C C’ upstream and downstream, respectively | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{EGFP Donor} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the EGFP coding sequence flanked by (GSS) linker sequences | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{mCherry Donor} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the mCherry coding sequence flanked by (GSS) linker sequences | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{T2a-GAL4 Donor}} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the T2a viral peptide sequence in frame with the GAL4 transcription factor coding sequence | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | p{T2a-GAL4-PolyA Donor}} | This study | Donor vector compatible with Golden Gate cloning carrying the T2a viral peptide sequence in frame with the GAL4 transcription factor coding sequence terminating in the SV40 transcriptional terminator | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCFD3-dU6:3gRNA | Port et al. (2014) | Addgene_ plasmid_#49410 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Double Header | This study | Recombination Mediated Cassette Exchange donor plasmid containing SA-T2A-GAL4-polyA and SA-GFP-SD in the opposite orientation | |
| Antibody | anti-GFP antibody conjugated with FITC | Abcam | RRID: AB_305635 | used at 1:500 |
| Antibody | anti-GFP | Invitrogen | Cat#_ A11122 | used at 1:500 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Sequences of oligonucleotides, sgRNAs and key vectors used in this study are shown along with a protocol for designing donor templates using the yellow wing2+ swappable insertion cassette.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38709.017
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.38709.018





