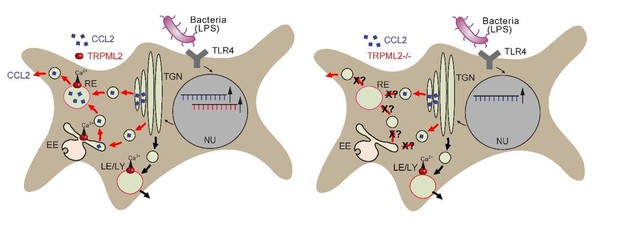
Selective agonist of TRPML2 reveals direct role in chemokine release from innate immune cells
Figures
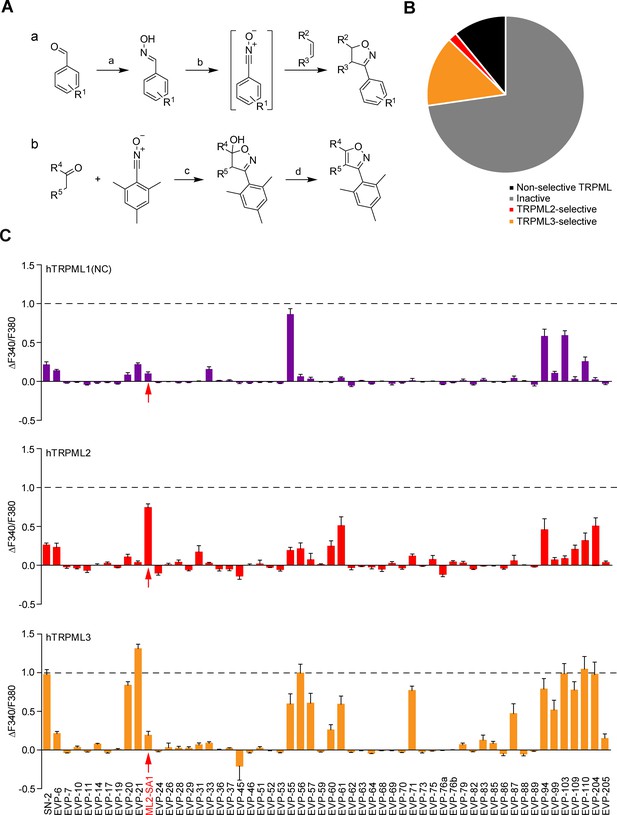
Chemical synthesis strategies and functional evaluation of SN-2 analogous compounds using calcium imaging.
(A) Shown are synthesis strategies a and b used to generate most of the SN-2 analogous compounds shown in Suppl. Figure 1. R1 = alkyl/ halogen/nitro/ methoxy; R2 / R3 = (cyclo)alkyl/phenyl/ hydroxyalkyl; R4 / R5=alkyl/ phenyl / (hetero)cycles; a) H2N-OH ∙ HCl (1.5 eq.), NaOH (3 eq.), H2O:EtOH (1:1), 0°C - rt, 18 hr; b) PIFA (1.2 eq.), alkene (1.5 eq.), H2O:MeOH (1:2), rt, 1–24 hr; c) ketone (2 eq.), LDA (2 eq.), THF, −78°C, 2 hr, mesitonitrile oxide, −78°C - rt, 2–15 hr; d) Na2CO3, MeOH:H2O (2:1), 95°C, 2 hr. (B) Cartoon showing schematically the fractions of inactive, non-selective TRPML activating, TRPML2-selective, and TRPML3-selective agonists (total number = 55). (C) Fura-2 calcium imaging results showing the effect of SN-2 and its analogues (10 μM) on hTRPML1(NC)-YFP, hTRPML2-YFP, and hTRPML3-YFP transfected HEK293 cells. Mean values normalized to basal (200 s after compound application)±SEM of up to >100 independent experiments with 3–10 cells per experiment are shown.
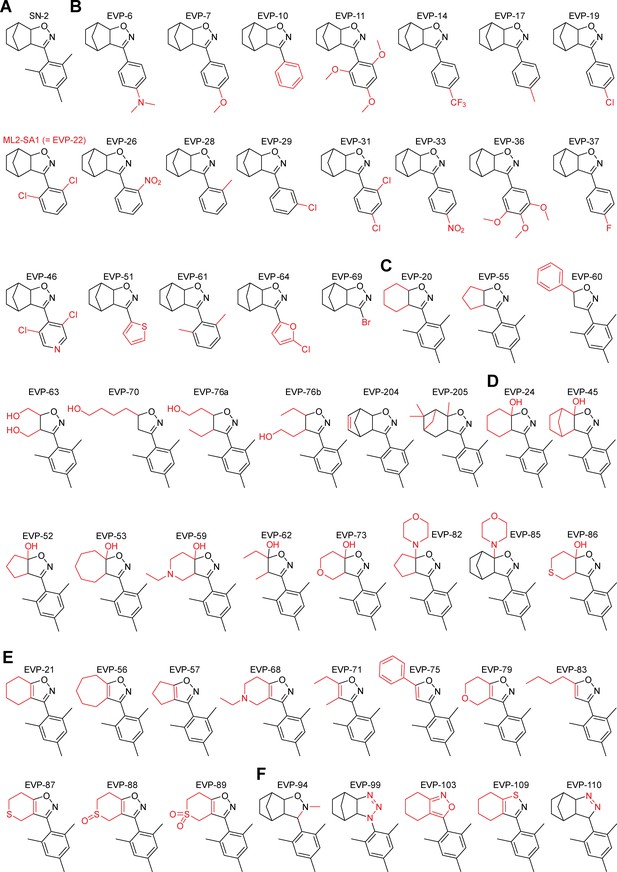
Structures of SN-2 analogues.
Shown are the chemical structures of all generated SN-2 analogous compounds. Changes in comparison to SN-2 are highlighted in red. (A) Structure of the lead compound SN-2. (B) Variations in the aryl ring. (C) Isoxazolines with variations in the aliphatic residue. (D) Different 5-hydroxy- and 5-morpholino-isoxazolines. (E) Different isoxazoles. (F) Variations in the heterocycle. With synthesis strategy a we performed numerous variations of the residues on SN-2. Starting with suitable aromatic aldehydes (such as variably substituted mono- and poly-methoxybenzaldehydes, chloro- and fluorobenzaldehydes, trifluoromethyl- and nitrobenzaldehydes, thiophene- and furan-carbaldehydes), the appropriate oximes were prepared. Subsequent conversion into nitrile oxides with PIFA (= [bis (trifluoroacetoxy)iodo]benzene) and reaction with norbornene and other cyclic and acyclic olefins in a Huisgen [3 + 2] cycloaddition led to analogues of SN-2 with a broad range of variations in the aromatic ring and the ring/substituents attached to the isoxazoline ring. Synthesis strategy b (Figure 1A) resulted in fully aromatic isoxazole analogues of SN-2, bearing annulated ring systems or open chain substituents (R4, R5). Starting from enolates of appropriate cyclic or acyclic ketones, substituted 5-hydroxyisoxazolines were generated via a Huisgen cycloaddition with mesitonitrile oxide. Dehydration with sodium carbonate resulted in aromatic analogues of SN-2. 5-Morpholinoisoxazolines (EVP-82, EVP-85) were generated in a similar manner from the ketones via enamines (Fos et al., 1992; Kuehne et al., 1964). Other 5-membered ring heterocycles like isoxazolidines (EVP-94) (Cerri et al., 1974), isomeric isoxazoles (EVP-103) (Fos et al., 1992), triazolines (EVP-199), pyrazolines (EVP-110) (Wulfman et al., 1988), and isothiazoles (EVP-109) (Akiba et al., 1985) were obtained by following established procedures of heterocyclic chemistry.
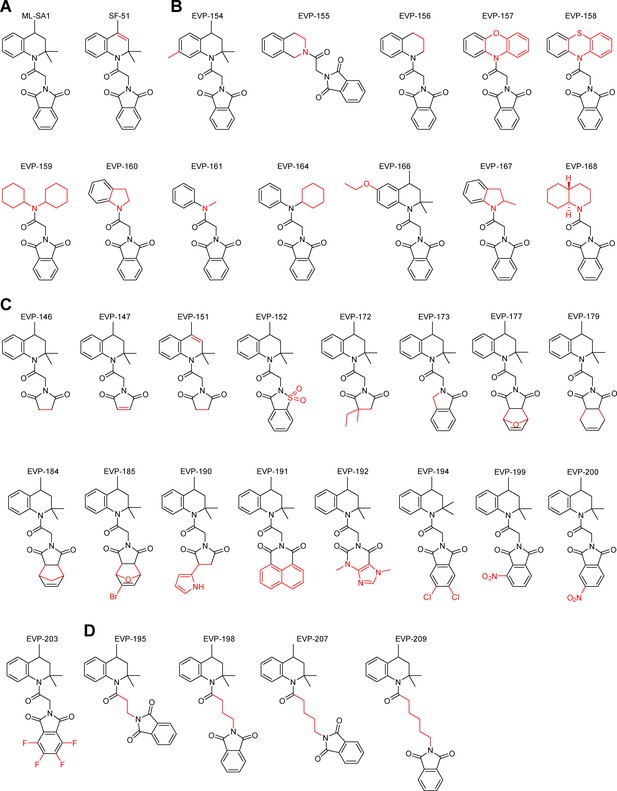
Structures of SF-51/ML-SA1 analogues.
Shown are the chemical structures of all generated SF-51/ML-SA1 analogous compounds. Changes in comparison to SF-51/ML-SA1 are highlighted in red. (A) Structure of the lead compounds ML-SA1 and SF-51. (B) Modifications of the acetone anile residue. (C) Modifications of the phthalimide residue. (D) Modifications of the length of the acyl spacer.
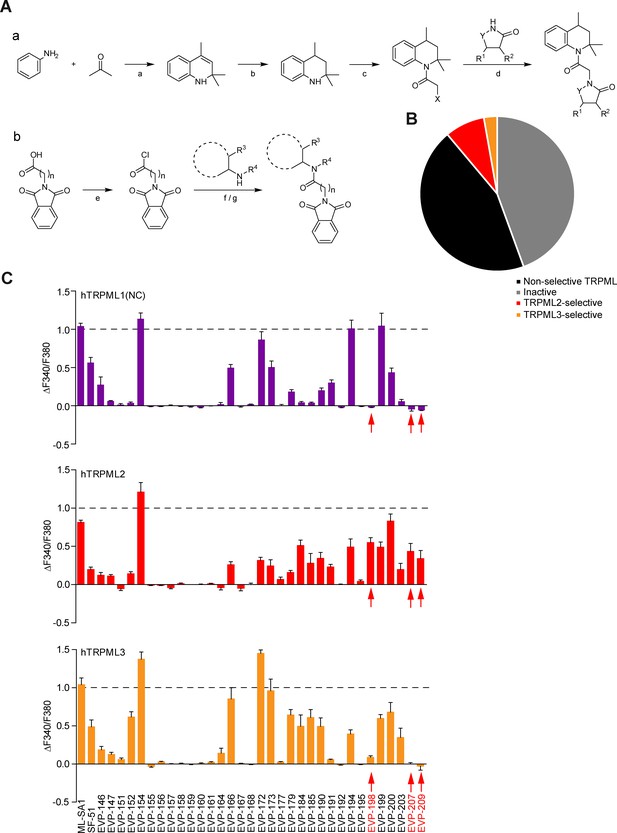
Chemical synthesis strategies and functional evaluation of SF-51/ML-SA1-analogous compounds using calcium imaging.
(A) Shown are synthesis strategies a and b used to generate the 35 SF-51/ML-SA1-analogous compounds shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 2. X = Cl/ Br; Y = CO/SO2 / CH2; R1 / R2 / R3 / R4=H/(cyclo)alkyl/aryl; n = 1–5; reaction conditions: a) p-toluenesulfonic acid, cyclohexane, 85°C, 15 hr. (b) H2, Pd/C, ethyl acetate, rt, 15 hr. (c) K2CO3, acetone, 0°C, 30 min, chloroacetyl chloride/bromoacetyl bromide, 0°C - rt, 15 hr. (d) LiHMDS (lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide), NaI, molecular sieves 4 Å, THF (dry), 70°C, 15 hr. (e) SOCl2, reflux, 1 hr. (f) Et3N, DCM, RT, 15 hr. (g) DCM, 0°C – rt, 15 hr. (B) Cartoon showing schematically the fractions of inactive, non-selective TRPML activating, TRPML2-selective, and TRPML3-selective agonists (total number = 35). (C) Fura-2 calcium imaging results showing the effect of SF-51/ML-SA1 and their analogues (10 μM) on hTRPML1(NC), hTRPML2, and hTRPML3 transfected HEK293 cells. Mean values (normalized to basal)±SEM of at least three up to >100 independent experiments with 3–10 cells per experiment are shown. With synthesis strategy a we performed numerous variations of the phthalimide residue of ML-SA1. Acetone anile was prepared following a known procedure (Chen et al., 2007) and hydrogenated according to a protocol from Venturini et al., 2010. Coupling with chloroacetyl chloride or bromoacetyl bromide respectively (Li et al., 2013) yielded haloacetamides suitable to undergo SN-reactions with a broad range of imides, lactams or sulfimides under anhydrous conditions (Escudero et al., 2011; Bansode et al., 2009). Synthesis strategy b was used both for variations in the northern acetone anile part of ML-SA1 as well as differentiations in the length of the acyl spacer. Starting from commercially available N-phthaloylglycine the acid chloride was prepared following a standard procedure (Bala et al., 2012) followed by amide coupling with different 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines and other cyclic and acyclic secondary amines (Volkov et al., 2014). Starting from phthalic anhydride and variable ω-aminocarboxylic acids, the southern part of the lead compounds was prepared with variable length of the acyl spacer (Tan et al., 2004) followed by chlorination with thionyl chloride (Tan et al., 2004) and amide coupling with hydrogenated acetone anile (Tagle et al., 2017) or other appropriate secondary amines.
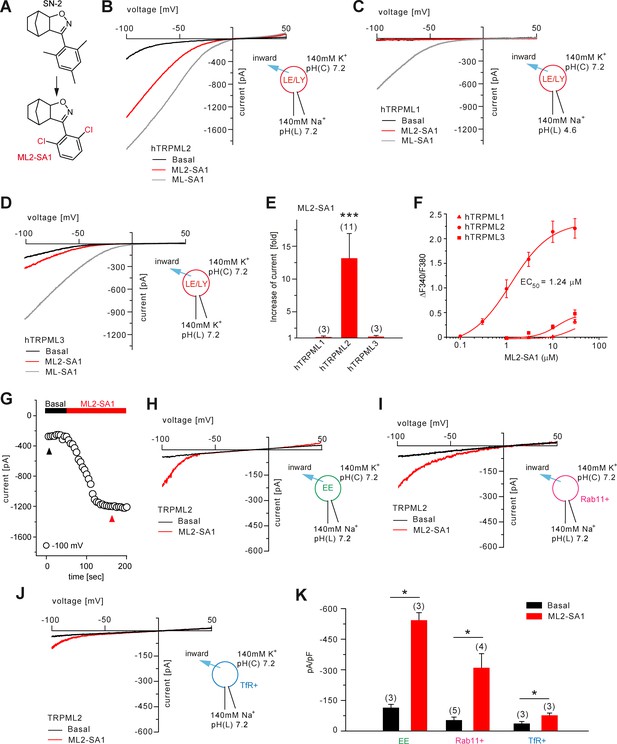
Effect of ML2-SA1 on TRPML channels.
(A) Cartoon depicting chemical structures of SN-2 and ML2-SA1. (B) Representative ML2-SA1 or ML-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML2 expressing HEK293 cells. (C–D) Representative ML2-SA1 or ML-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML1 or hTRPML3 expressing HEK293 cells. (E) Statistical summary of ML2-SA1 data as shown in B-D as fold increase compared to the respective basal currents in LE/LY. Shown are mean values ± SEM at −100 mV of n independent experiments as indicated, each. (F) Dose-response curves obtained from fura-2 calcium imaging experiments with hTRPML1(NC), hTRPML2, and hTRPML3 expressed in HEK293 cells and elicited with ML2-SA1 at varying concentrations. The calculated EC50 value for hTRPML2 is: 1.24 ± 0.12 μM (mean ± SEM). (G) Time course of TRPML2 activation by ML2-SA1 taken from experiments as shown in B. Black and red arrows indicate time points for basal and ML2-SA1 induced TRPML2 activity that were used for the IV relationship. (H–J) Representative basal and ML2-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from Wort./Lat.B-enlarged EE, from vacuolin-enlarged Rab11+, or form TfR+ vesicles isolated from hTRPML2 expressing HEK293 cells. (K) Statistical summary of data as shown in G-I. * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, *** indicates p<0.001, Figure 2E, one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test, Figure 2J, paired t-test.
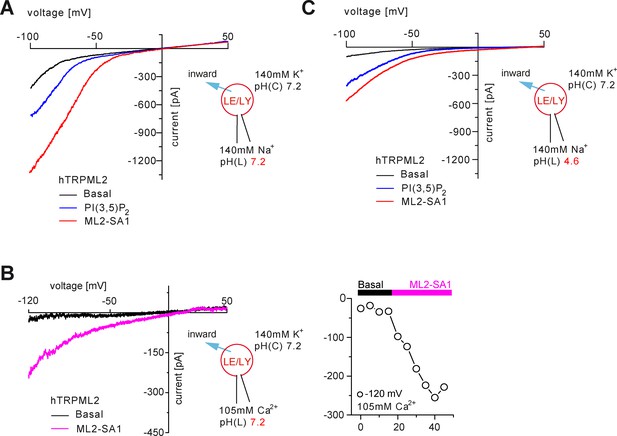
Effect of ML2-SA1 on TRPML2 under different pH conditions.
(A) Representative basal, PI(3,5)P2 (1 μM) or ML2-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML2 expressing HEK293 cells (neutral luminal pH). (B) Representative basal and ML2-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents measured in 105 mM luminal Ca2+ (isotonic) from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML2 expressing HEK293 cells. The right panel shows the corresponding time course. (C) Representative basal, PI(3,5)P2 (1 μM) or ML2-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML2 expressing HEK293 cells (highly acidic luminal pH).
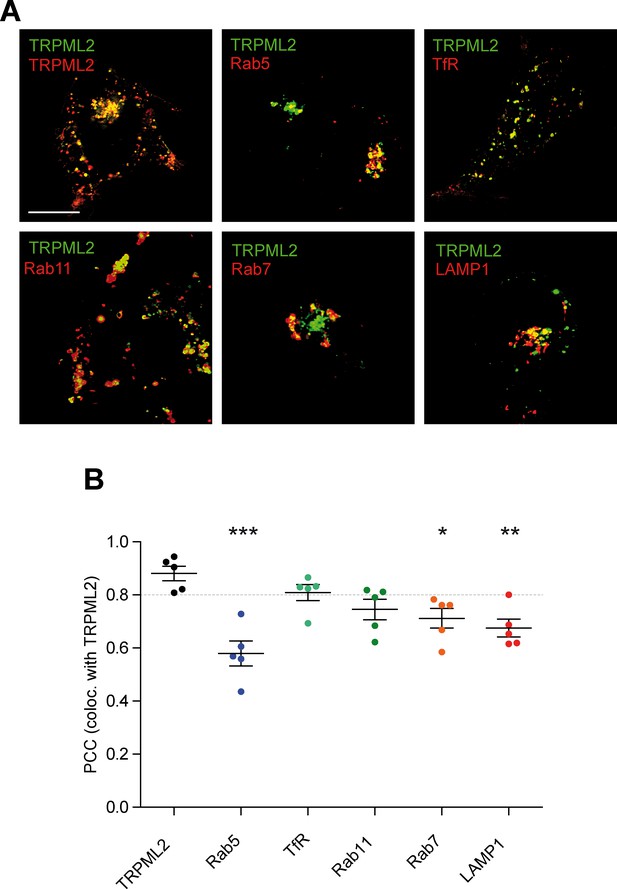
Co-transfection of HEK293 cells with fluorescently labelled TRPML2 and vesicle-specific markers of the endolysosomal system.
(A) Shown are representative images of TRPML2 (green) transiently cotransfected with either TRPML2 (red) or markers of the endolysosomal system (red): Rab5 (early endosomes), TfR (early/recycling endosomes), Rab11 (recycling endosomes), Rab7 (late endosomes), or LAMP1 (late endosomes/lysosomes). Scale bar (identical for all images)=10 μm. (B) TRPML2 colocalisation quantification. Pearson’s Correlation Coefficients were calculated by marking and isolating single cells in ImageJ, using the ImageJ plugin ‘JACoP’ to quantify the localization correlation. Individual PCC values are plotted alongside overall mean values ± SEM of five individual cells. Colocalization of TRPML2 did not significantly differ from TRPML2 (0.880 ± 0.028) with either TfR (0.809 ± 0.030) or Rab11 (0.745 ± 0.039), while it appeared to colocalize significantly less with Rab5 (0.579 ± 0.047), Rab7 (0.712 ± 0.037), and LAMP1 (0.675 ± 0.034). * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, *** indicates p<0.001, one-way ANOVA test followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test comparing against TRPML2/TRPML2.
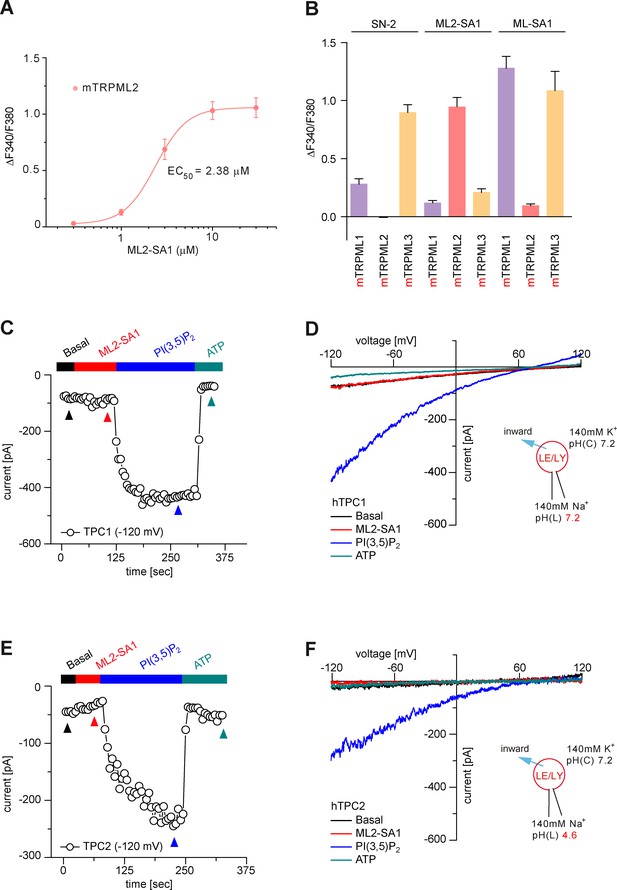
DRC of ML2-SA1 effect on mTRPML2, effects of ML2-SA1, SN2, and ML-SA1 on mTRPML channel isoforms, and cytotoxicity of ML2-SA1.
(A) Dose-response curve (DRC) for ML2-SA1 effect on mouse TRPML2 in HEK293 cells, obtained from fura-2 calcium imaging experiments. The calculated EC50 value for mTRPML2 is: 2.38 ± 0.001 μM (mean ± SEM). (B) Summary of fura-2 calcium imaging results showing the effect of SN-2, ML2-SA1, and ML-SA1 (10 μM, each) on mouse TRPML1, 2, and 3. (C, E) Representative time courses of continuous recordings using a ramp protocol (−120 mV to +120 mV in 500 ms, every 5 s, holding potential = 0 mV). Data obtained at +120 mV were plotted against time. Recordings at the time points as indicated were used for the IV relationships (D, F), respectively. No significant ML2-SA1 (10 μM) elicited current was detectable in vacuolin-enlarged endolysosomes isolated from hTPC1 (C–D) or hTPC2 (E–F) expressing HEK293 cells. PI(3,5)P2 (1 μM, batch solution) was applied as positive control to elicited TPC currents. ATP (1 mM, bath solution) was applied to inhibit PI(3,5)P2-evoked TPC currents.
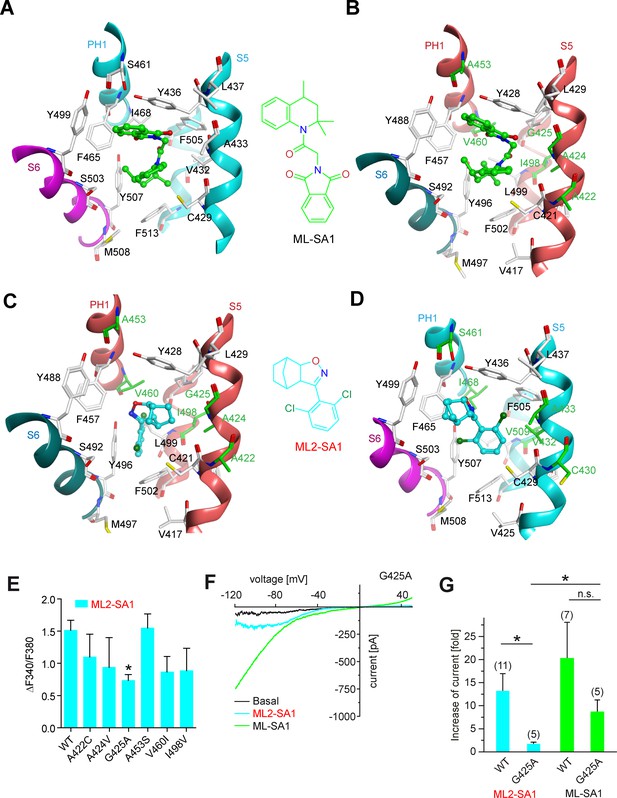
Molecular modeling of ML2-SA1 and ML-SA1 binding.
(A) Binding mode of ML-SA1 (green colored carbon atoms) at hTRPML1, showing residues within 5 Å of ML-SA1, as observed in one of the four identical binding pockets of the cryo-EM structure (PDB ID: 5WJ9). The S6 helix of monomer A of hTRPML1 is colored magenta, the PH1 and S5 helices of monomer B are colored cyan. (B) Binding mode of ML-SA1 (green colored carbon atoms) at hTRPML2 (homology model generated with MODELLER) as predicted by the ligand docking. Only residues within 5 Å of ML-SA1 in one of the four identical binding pockets are displayed. The S6 helix of monomer A of hTRPML2 is colored petrol blue, the PH1 and S5 helices of monomer B are colored salmon. Amino acid residues that are different in hTRPML1 and hTRPML2 are colored green (C) Binding mode of one ML2-SA1 enantiomer (cyan colored carbon atoms; 3aS, 4S, 7R, 7aS) at hTRPML2 as predicted by ligand docking. Only residues within 5 Å of ML2-SA1 in one of the four identical binding pockets are displayed (same coloring and representation style as in Figure 3B). Binding of the other ML2-SA1 enantiomer (3aR, 4R, 7S, 7aR) resulted in a similar binding mode that is shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B (D) Binding mode of one ML2-SA1 enantiomer (cyan colored carbon atoms; 3aS, 4S, 7R, 7aS) at hTRPML1 as predicted by ligand docking. Only residues within 5 Å of ML2-SA1 in one of the four identical binding pockets are displayed (same coloring and representation style as in Figure 3a). (E) Fura-2 calcium imaging results showing the effect of ML2-SA1 (10 μM) on hTRPML2-YFP WT and mutant transfected HEK293 cells. Mean values normalized to basal (120 s after compound application)±SEM of at least three independent experiments, each. * indicates p<0.05, one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnet post-hoc test. (F) Representative ML2-SA1 or ML-SA1 (10 μM) elicited currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from hTRPML2(G425A) expressing HEK293 cells. (G) Statistical summary of data as shown in F as fold increase compared to the respective basal currents in LE/LY. Shown are mean values ± SEM at −100 mV of at n independent experiments as indicated. * indicates p<0.05, unpaired t-test.
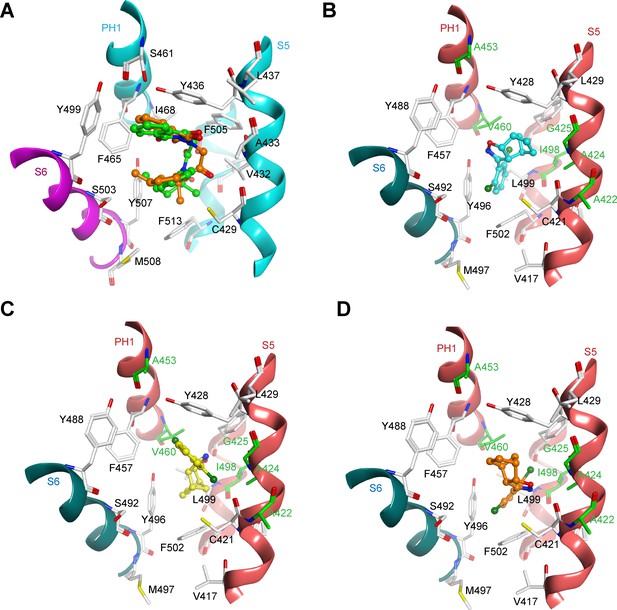
Additional molecular modeling of ML2-SA1 and ML-SA1 binding.
(A) Comparison of the experimentally derived binding mode of ML-SA1 (green colored carbon atoms) and the docking pose (obtained with program GLIDE) at the hTRPML1 binding pocket (orange colored carbon atoms). The RMSD of the heavy atoms is 1.22 Å for the top-ranked solution. (B) Binding mode of the second ML2-SA1 enantiomer (cyan colored carbon atoms; absolute configuration: 3aR, 4R, 7S, 7aR) at hTRPML2 as predicted by ligand docking. The orientation is similar as observed for the enantiomer shown in Figure 3c and only the norbornane ring adopts a slightly different orientation. Only residues within 5 Å of ML2-SA1 in one of the four identical binding pockets are displayed. Binding was not different from the enantiomer (3aS, 4S, 7R, 7aS) shown in Figure 3D. (C–D) Alternative orientations (rank 2 and 3 of the GLIDE docking results) to that shown in Figure 3C of ML2-SA1 binding at hTRPML2.
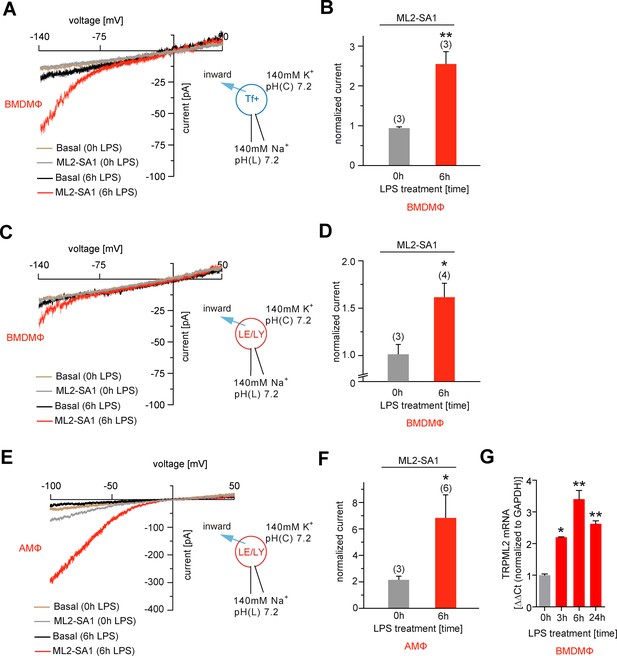
Effect of ML2-SA1 on channel currents in endolysosomal organelles isolated from different primary mouse macrophages.
(A) Representative currents from vacuolin-enlarged/Tf+ vesicles isolated from murine (LPS 6 hr or LPS 0 hr) primary WT BMDMΦ, basal or elicited by an application of 10 μM ML2-SA1. All currents are normalized to basal current without ML2-SA1. (B) Statistical summary of data shown in A. (C) Representative currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from murine (LPS 6 hr or LPS 0 hr) primary WT bone marrow macrophages (BMDMΦ), basal or elicited by an application of 10 μM ML2-SA1. (D) Statistical summary of data shown in C. (E) Representative currents from YM201636-enlarged LE/LY isolated from murine (LPS 6 hr or LPS 0 hr) primary WT alveolar macrophages (AMΦ), basal or elicited by an application of 10 μM ML2-SA1. (F) Statistical summary of data shown in E. * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, Student’s t test, unpaired. (G) qPCR data showing levels of TRPML2 expression after 3, 6, and 24 hr LPS treatment compared to untreated (0 hr). * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test.
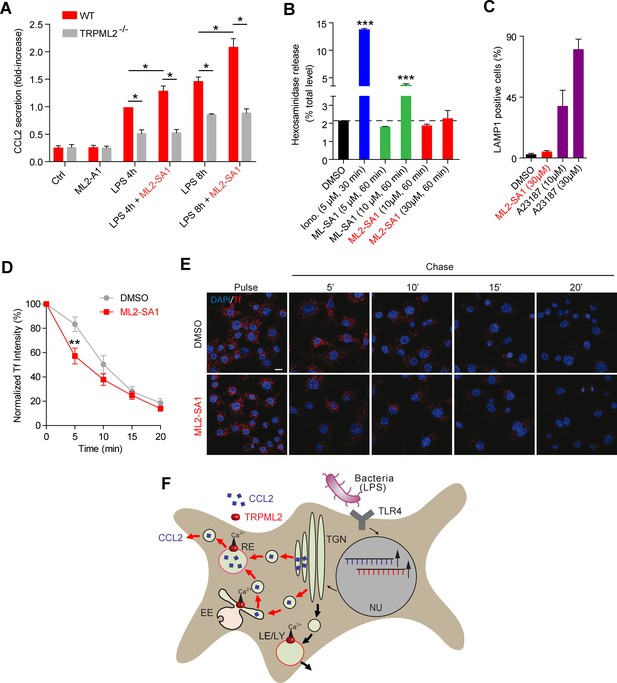
Effect of ML2-SA1 on chemokine release from primary mouse macrophages.
(A) Shown are data obtained from primary WT and TRPML2-/- mouse bone marrow macrophages (BMDMΦ) with and without LPS treatment for 4 hr and 8 hr, respectively. The fraction treated with LPS and 10 μM ML2-SA1 showed significantly increased CCL2 secretion compared to WT controls treated with LPS only. TRPML2-/- cells displayed strongly reduced CCL2 secretion. Shown are normalized mean values ± SEM of 5 mice each. * indicates p<0.05, Student’s t test, unpaired. (B) Lysosomal exocytosis assay showing the increase in beta-hexosaminidase release upon stimulation with either ionomycin, ML-SA1, or ML2-SA1 (conc. as indicated) from LPS (6 hr) stimulated BMDMΦ. *** indicates p<0.001, one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. (C) Lysosomal exocytosis assay by flow cytometry showing the percentage of cells which show an increase in LAMP1 fluorescence on the plasma membrane. Cells were treated with DMSO, calcium ionophore A23187 (calcimycin), and 30 μM ML2-SA1. (D–E) Recycling endosome assay showing the decrease of Tf mean fluorescence in LPS stimulated RAW264.7 cells, treated with either DMSO or 30 μM ML2-SA1. Scale bar (identical for all images)=10 μm. Plot shows the normalized Tf intensity (shown is the average of 3 independent experiments, each). **p<0.01, two-way ANOVA, repeated measures, followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. (F) Cartoon showing organelles with functional TRPML2 expression as confirmed by endolysosomal patch-clamp analysis (EE, RE, LE/LY). CCL2 (MCP-1) is hypothesized to be trafficked and secreted via the EE/RE pathway, based on the observation that ML2-SA1 promotes Tf trafficking in the EE/RE compartment, while no effect on lysosomal exocytosis was found. No secretory vesicles are reported to exist in macrophages.
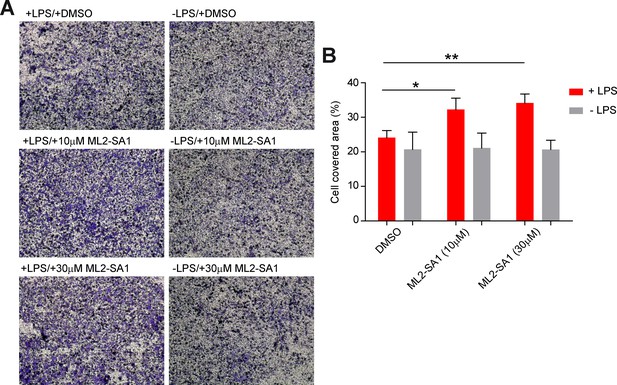
Effect of ML2-SA1 on macrophage migration.
(A) Shown are representative images obtained from a modified Boyden chamber experiment. Images show fixed and crystal violet stained BMDMΦ after 3 hr migration through a transwell chamber along a chemotactic gradient created by BMDMΦ in the lower compartment. Indicated treatments refer to treatment of the cells in the lower compartment. (B) Quantification of migration in the modified Boyden chamber setup (A) shows a significant increase in migration when LPS pre-treated cells in the lower compartment were subjected to 10 or 30 µM ML2-SA1. Shown are mean values ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.01, repeated measures, one-way ANOVA with Greenhouse-Geisser correction, followed by Dunnet post-hoc test.
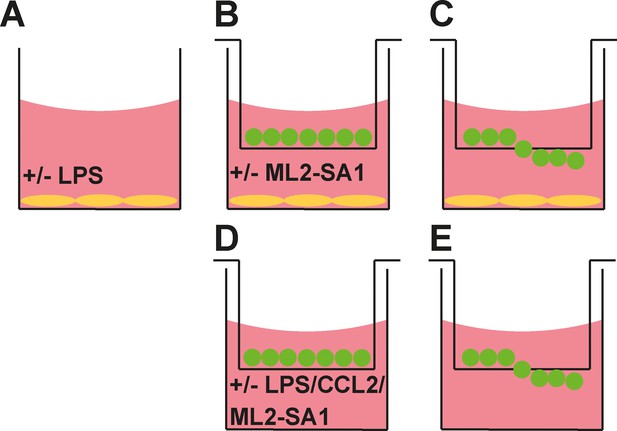
Modified and classical Boyden chamber setup.
In the modified Boyden chamber setup (A–C) BMDMΦ plated on poly-L-lysine coated cover slips in a twenty-four well plate are treated with 1 µg/mL LPS or equal volume of DMSO for 6 hr (A). After 6 hr media is replaced for media containing 10 or 30 µM ML2-SA1 or equal volume of DMSO and a transwell chamber containing 1 × 105 BMDMΦ is inserted (B). After 3 hr migration, cells translocated through the transwell chamber and stick to the bottom (C). In the classical Boyden chamber setup (D–E) a twenty-four well plate is filled with media containing either DMSO, 1 µg/mL LPS and DMSO, 1 µg/mL LPS and 30 µM ML2-SA1, or 10 ng/mL CCL2 and a transwell chamber containing 1 × 105 BMDMΦ is inserted (D). After 3 hr migration, cells translocated through the transwell chamber and stick to the bottom (E). Migrated cells can be fixed and stained with crystal violet for quantification of cell covered area.
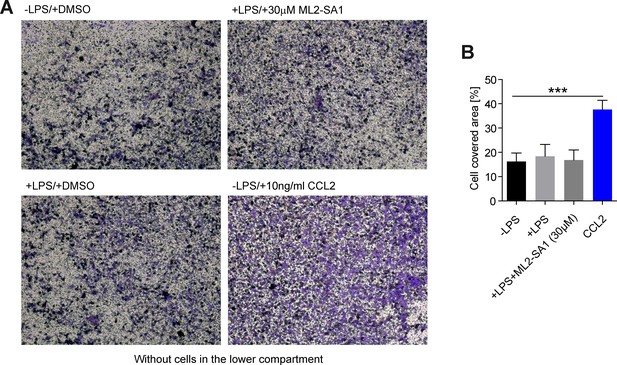
Migration assay without cells in the lower compartment of the classical Boyden chamber.
(A) Representative images obtained from a classical Boyden chamber setup showing fixed and crystal violet stained BMDMΦ after 3 hr migration through a transwell chamber. The respective conditions in the lower compartment (media) are indicated. (B) Quantification of migration in the classical Boyden chamber setup showing a significant increase in migration when 10 ng/mL CCL2 was present in the lower compartment but not when LPS or ML2-SA1 were present (1 µg/mL LPS or 30 µM ML2-SA1). Shown are mean values ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *** indicates p<0.001, one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnet post-hoc test.
Tables
| Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | DSMZ | ACC 305 | |
| HEK 293 stable stably expressing TRPML3-YFP | Grimm et al. (2010); PMID: 20189104 | ||
| HEK 293 stable stably expressing TRPML1-YFP | Chen et al. (2014), PMID: 25119295 | ||
| TRPML1 (encoded by the Mcoln1 gene) KO mouse; Mcoln1tm1Sasl, C57BL/6 | Venugopal et al. (2007); PMID: 17924347 | MGI ID: 3794204 | |
| TRPML2 (encoded by the Mcoln2 gene) KO mouse; C57BL/6 | Sun et al. (2015); PMID: 26432893 | MGI: 1915529 | |
| TRPML3 (encoded by the Mcoln3 gene) KO mouse; Mcoln3tm1. 1Hels, FVB/NJ | Jörs et al. (2010); PMID: 21179200 | MGI ID: 5319089 | |
| anti-LAMP-1 (1D4B) (rat monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | Cat#A-11006; RRID: AB_2134495 | (1:100) |
| Goat anti-Rat IgG (H + L) Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | ThermoFisher | Cat#sc-19992; RRID: AB_2534074 | (1:1000) |
| mcherry-Transferrin Receptor 20 (plasmid) | N/A | Addgene Plasmid #55144 | |
| DsRed-Rab11 (plasmid) | Choudhury et al. (2002); PMID: 12070301 | Addgene Plasmid #12679 | |
| TRPML1-YFP (plasmid) | Grimm et al. (2010), PMID: 20189104 | ||
| TRPML2-YFP (plasmid) | Grimm et al. (2010), PMID: 20189104 | ||
| TRPML3-YFP (plasmid) | Grimm et al. (2010), PMID: 20189104 | ||
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP A422C | this paper | forward: CTTCGGTTTTGTTGTTGTG CTGGTATGATTTATCTGGG reverse: CCCAGATAAATCATACCAGC ACAACAACAAAACCGAAG | |
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP A424V | this paper | forward: CGGTTTTGTGCTTG TGTTGGTATGATTTATCTGGGTTACAC reverse: GTGTAACCCAGATAAATCAT ACCAACACAAGCACAAAACCG | |
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP G425A | this paper | forward: CGGTTTTGTGCTTGT GCTGCTATGATTTATCTGGGTTACAC reverse: GTGTAACCCAGATAAATCA TAGCAGCACAAGCACAAAACCG | |
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP A453S | this paper | forward: CTGAACACAGTTTCTG AGTGTCTGTTTTCTCTGG reverse: CCAGAGAAAACAGACA CTCAGAAACTGTGTTCAG | |
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP V460I | this paper | forward: TGTCTGTTTTCTCTGATCA ACGGTGATGACATG reverse: CATGTCATCACCGTTGATC AGAGAAAACAGACA | |
| Quikchange primers for TRPML2:YFP I498V | this paper | forward: CCTTCATCAGCCTTTTTATATATA TGGTTCTCAGTCTTTTTATTGC reverse: GCAATAAAAAGACTGAGAACCA TATATATAAAAAGGCTGATGAAGG | |
| qPCR Primer for TRPML1 (NM_053177) | www.pga.mgh.harvard.edu/primerbank | PrimerBankID: 16716462 c2 | forward: GCCTTGGGCCAATGGATCA reverse: CCCTTGGATCAATGTCAAAGGTA |
| qPCR Primer for TRPML2 (NM_026656) | this paper | forward: AATTTGGGGTCACGTCATGC reverse: AGAATCGAGAGACGCCATCG | |
| qPCR Primer for TRPML3 (NM_134160) | this paper | forward: GAGTTACCTGGTGTGGCTGT reverse: TGCTGGTAGTGCTTAATTGTTTCG | |
| qPCR Primer for HPRT (NM_013556) | Hruz et al. (2011); PMID: 21418615 | N/A | forward: GCTCGAGATGTCATGAAGGAGAT reverse: AAAGAACTTATAGCCCCCCTTGA |
| Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Escherichia coli O26:B6 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#L2762 | |
| Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Escherichia coli O111:B4 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#L4391 | |
| Fura-2, AM, cell permeant | ThermoFisher | Cat#F1201 | |
| Mouse M-CSF, premium grade | Miltenyi Biotech | Cat#130-101-703 | |
| Transferrin from human serum, Alexa FluorTM 546-conjugated | TermoFisher | Cat# T23364 | |
| Transferrin from human serum, Alexa FluorTM 555-conjugated | Thermo Fisher | Cat#T35352 | |
| JE/MCP-1/CCL2 from mouse, recombinant | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# SRP4207 | |
| YM201636 | Chemdea | Cat#CD0181 | |
| MLSA-1 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#SML0627 | |
| PI(3,5)P2 | AG Scientific | Cat#P-1123 | |
| Wortmannin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#W1628 | |
| LatrunculinB | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#L5288 | |
| Vacuolin | Santa Cruz | Cat# sc-216045 | |
| Calcium ionophore A23187 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#C7522 | |
| 4-Methylumbelliferyl N-acetyl-b-D-glucosaminide | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#M2133 | |
| RNeasy Plus Mini Kit | Qiagen | Cat# 74134 | |
| RevertAid first strand cDNA synthesis Kit | ThermoScientific | Cat# K1621 | |
| CD11b MicroBeads, human and mouse | Miltenyi Biotech | Cat#130-049-601 | |
| QuikChange II Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit | Agilent | Cat#200523 | |
| Mouse/rat CCL2/ JE/MCP-1 Quantikine ELISA Kit | BioLegend | Cat#432707 | |
| Origin8 | OriginLab | ||
| GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Software Inc. |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Synthesis details and analytical data
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39720.017
-
Supplementary file 2
Summary of characteristics of TRPML channels
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39720.018
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.39720.019