Compensatory growth renders Tcf7l1a dispensable for eye formation despite its requirement in eye field specification
Figures
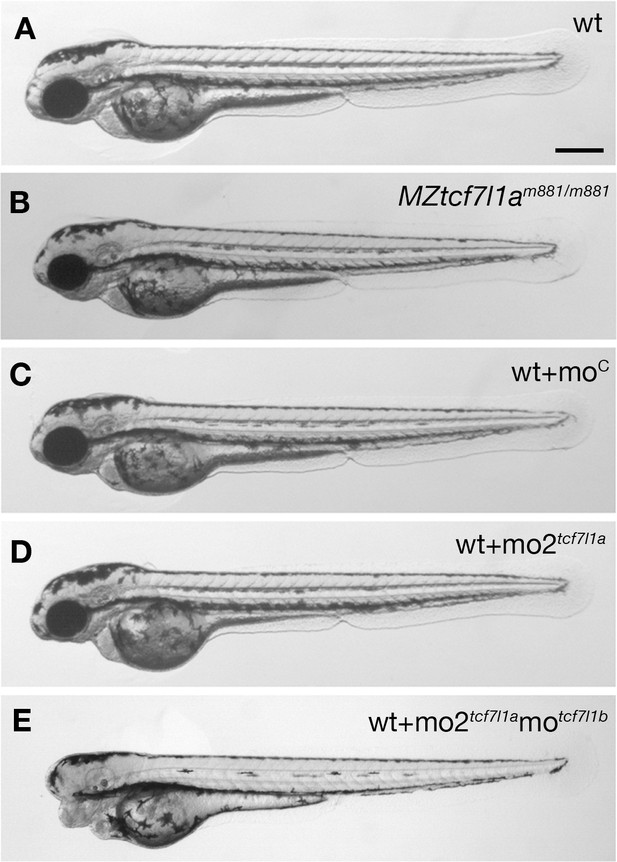
Tcf7l1a maternal zygotic (MZ) mutants and tcf7l1a morphants have no overt eye phenotype.
Lateral views of typical wildtype (A) MZtcf7l1a-/- (B) wildtype injected with control morpholino (C) tcf7l1a morphant (D) and tcf7l1a/tcf7l1b double morphant (E) embryos at 2 days post fertilisation. All conditions n > 100 and over three independent experiments except when specified. Dorsal up, anterior to the left. Scale Bar = 250 µm.
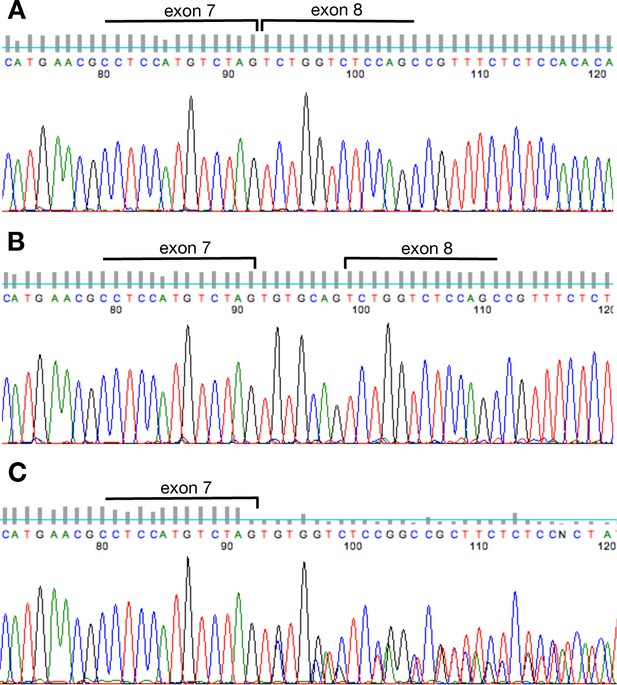
Sequence of the tcf7l1a exon7/8 boundary.
RT-PCR chromatogram sequence of tcf7l1a exon7/8 fragment showing the expected intron splice in wildtype embryos (A). tcf7l1a-/- mutants show an unambiguous inclusion of 7 nucleotides from intron 7 (B) and a mixed read in mRNA coming from heterozygous siblings (C).
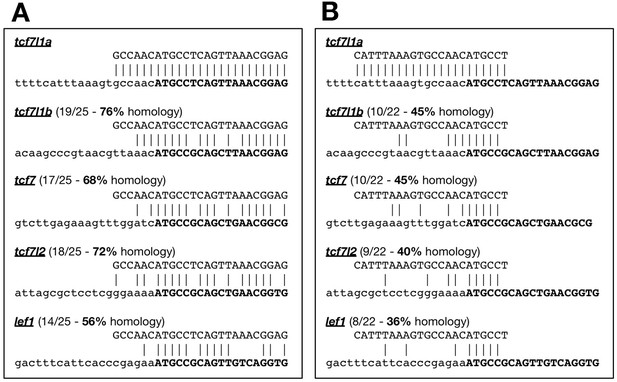
Alignment of tcf7l1a, morpholinos to lef1 and other tcf genes.
Alignment of the previously published tcf7l1a morpholino (A) mo1tcf7l1a, Dorsky et al., 2003), and mo2tcf7l1a (B) with less homology to other lef/tcf genes. Target genes in bottom sequence, 5’UTR in lowercase, gene open-reading frame in bold uppercase.
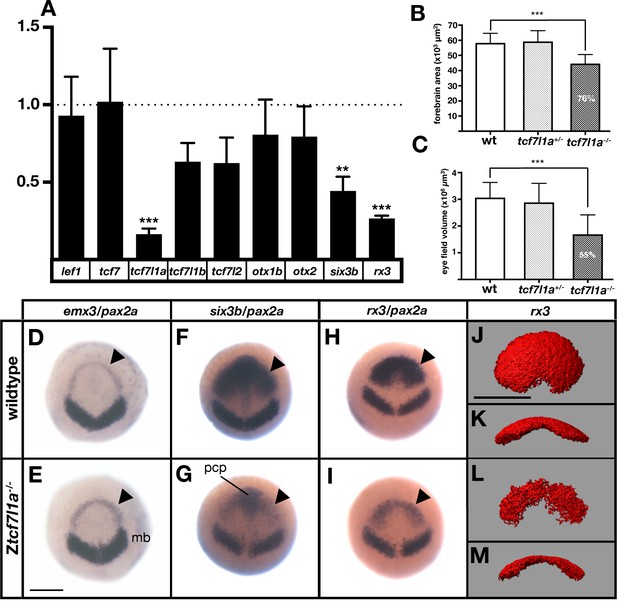
The prospective forebrain and eye field domains of the neural plate are reduced in Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants.
(A) Graph showing RT-qPCR quantification of the mRNA levels of lef1, tcf7, tcf7l1a, tcf7l1b, tcf7l2, otx1b, otx2, six3b and rx3 in Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants relative to wildtype embryos at 10hpf. Biological and technical triplicates, two independent experiments. (B, C) Quantification of the forebrain domain of the anterior neural plate (B) enclosed by emx3 up to pax2a (D, E) expression by in situ hybridisation (reduction to an average of 76%, n = 11, one experiment, data in Supplementary file 1B), and eye field volume (C) by rx3 fluorescent in situ hybridisation confocal volume reconstruction (J–M) (reduction to an average of 55%, n = 10, one experiment, data in Supplementary file 1C). (D–I) Expression of emx3 (arrowhead)/pax2a (D, E), six3b (arrowhead)/pax2a (F, G) and rx3 (arrowhead)/pax2a (H, I) in wildtype (D, F, H) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (E, G, I) embryos detected by in situ hybridisation at 10hpf. Reduction of six3b and rx3 expression 100%, n > 40, three experiments. (J–M) Confocal volume reconstruction of rx3 fluorescent in situ hybridisation in wildtype (J, K) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (L, M) mutants at 10hpf. (J, L) Dorsal view, anterior to top, and (K, M) transverse view from posterior, dorsal up. Abbreviations: mb, midbrain; pcp, prechordal plate Scale Bars = 250 µm.
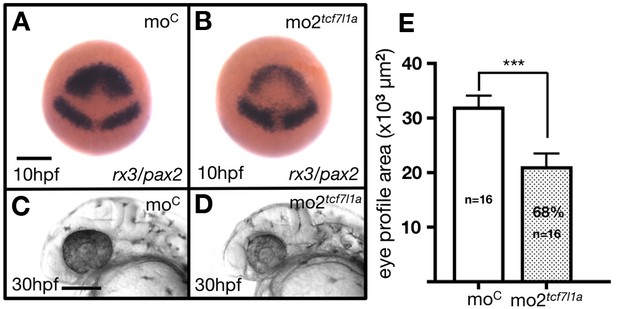
tcf7l1a morpholino (mo2tcf7l1a) phenocopies the Ztcf7l1a-/- mutant.
(A, B) Dorsal views of rx3/pax2a in situ hybridisation at 100%epibly and (C, D) lateral views of 30hpf wildtype embryos injected with 400pmols of (A, C) control morpholino or (B, D) mo2tcf7l1a. Scale bar = 250 µm. (E) Plot showing the quantification of the eye profile area in wildtype embryos injected with control morpholino (first bar) or mo2tcf7l1a (second bar) at 30hpf. Scale bar = 200 µm.
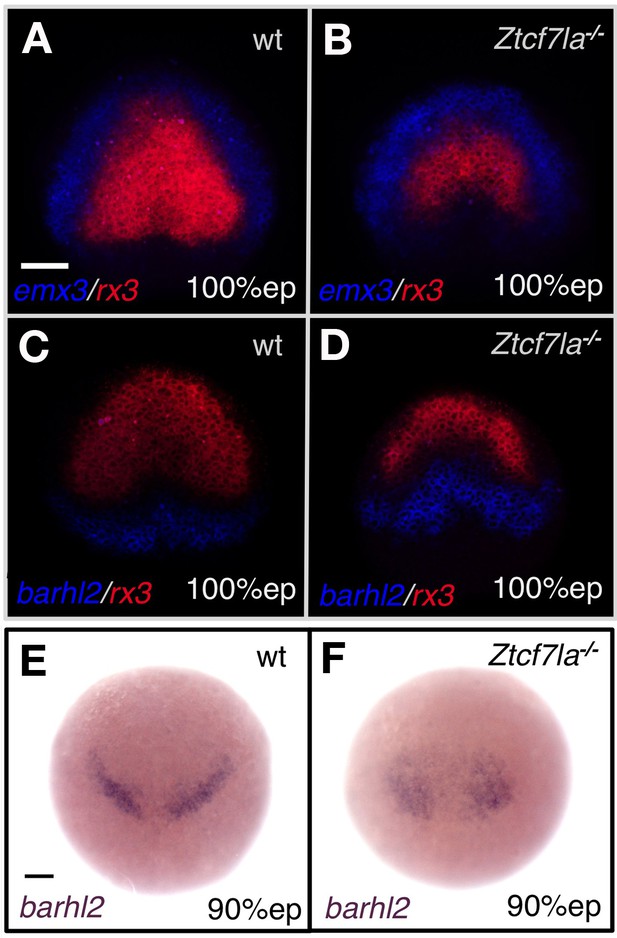
The eye field domain of the anterior neural plate is caudalised in Ztcf7l1a mutants.
Dorsal views of anterior neural plates, anterior up. (A–D) Double fluorescent in situ hybridisation of prospective telencephalic marker emx3 (blue) and prospective eye field marker rx3 (red) (A, B), and prospective diencephalic marker barhl2 (blue) and rx3 (red) (C, D) in wildtype (A, C) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (B, D) embryos at 10hpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. (E, F) In situ hybridisation of barhl2 in wildtype (E) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (F) embryos at 9hpf. All conditions n = 5, one experiment each. Scale bars = 100 µm.
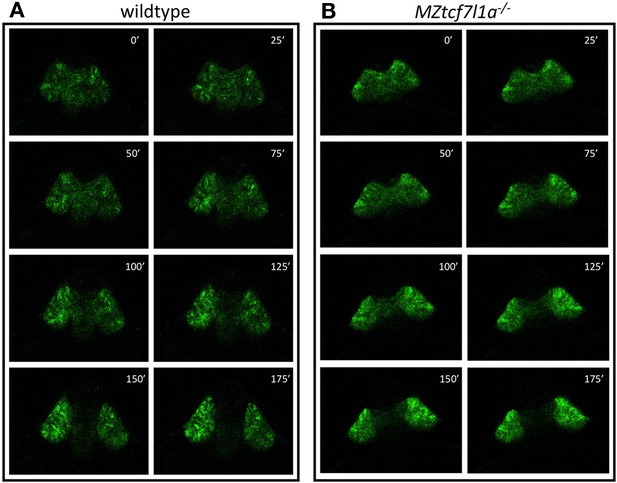
Eye vesicle evagination in heterozygous and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants.
Confocal time lapse movie snapshots (1 frame every 25 min) of heterozygous sibling (A) and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (B) expressing the Tg(rx3:GFP)zf460Tg transgene. First frame taken at 11hpf. Minutes after movie has started indicated in each frame. From two independent experiments n = 6 for both conditions.
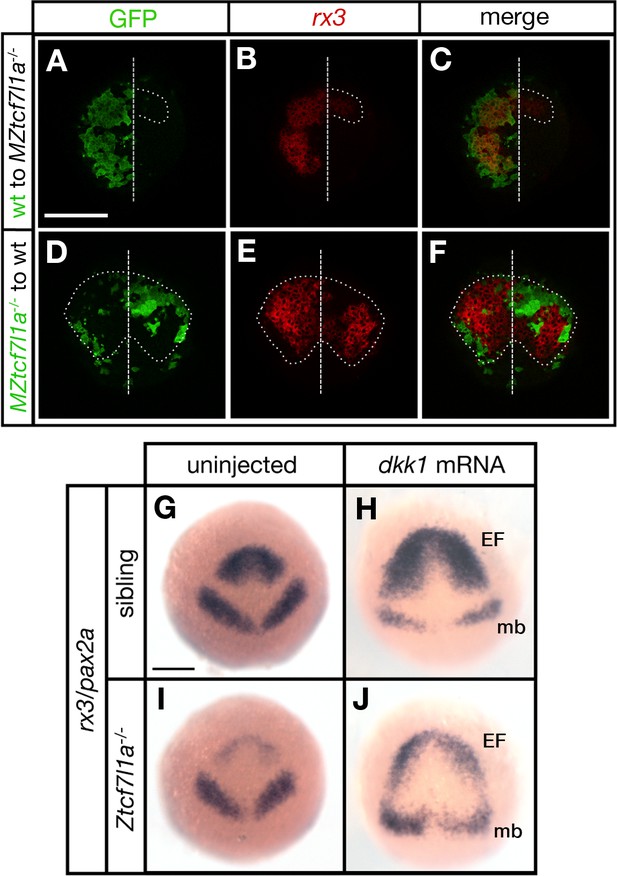
Tcf7l1a cell autonomously promotes rx3 expression in the eye field.
(A–F) Dorsal views of confocal images of rx3 mRNA expression (red) detected by fluorescent in situ hybridisation at 10hpf in the anterior neural plates of chimeric embryos containing transplants of (A–C) wildtype (GFP+) donor cells in MZtcf7l1a-/- host embryos (100%, n = 13), and (D–F) MZtcf7l1a-/- (GFP+) donor cells in wildtype host embryos (100%, n = 9). Dotted line outlines eye fields; note in A-C that rx3 expression extends considerably caudal to the reduced mutant eye field on the side of the neural plate containing wild-type cells. Dashed line marks the embryo midline. (G–J) In situ hybridisation of rx3 and pax2a in sibling (G, H) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (I, J) 9hpf embryos, uninjected (G, I) or injected with 50 pg of dkk1 mRNA (H, J). Abbreviations; EF, eyefield; mb, midbrain Scale Bars = 200 µm.
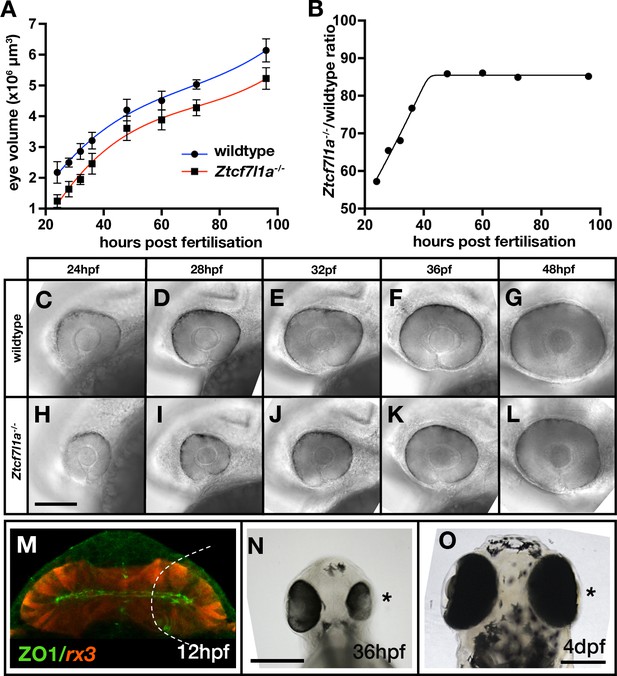
Eye size recovers in Ztcf7l1a-/- mutant and eye vesicle-cell removed embryos.
(A) Growth kinetics of the eye in wildtype (blue line) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (red line) embryos at stages indicated (data in Supplementary file 1F, one experiment, 24hpf, wt n = 12, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 14; 28hpf, wt n = 15, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 12; 32hpf, wt n = 13, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 15; 36hpf, wt n = 16, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 14; 48hpf, wt n = 11, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 19; 60hpf, wt n = 11, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 14; 72hpf, wt n = 13, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 19; 96hpf, wt n = 13, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 15). (B) Plot showing the ratio of Ztcf7l1a-/- to wildtype eye volume from data in (A). (C–L) Lateral views (dorsal up, anterior to left) of wildtype (C–G) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (H–L) eyes at stages indicated above panels. (M–O) Eye development following partial ablation of the optic vesicle in wildtype embryos at five somite stage. (M) Coronal confocal section of evaginating optic vesicles (red) in a wildtype Tg(rx3:RFP) five somite stage embryo. Dashed line indicates the approximate extent of ablations performed. 36hpf (N) and 4dpf (O) eyes in embryos in which cells were unilaterally removed from one optic vesicle (from n = 20). Asterisk indicates the eye that develops from the partially ablated optic vesicle. ZO1, zona ocludens 1. Scale bars = 200 µm.
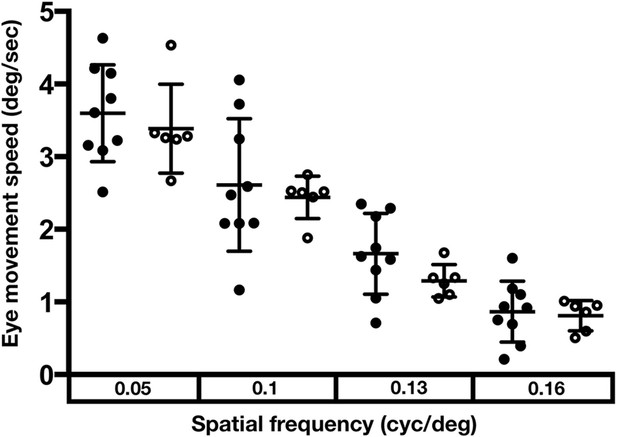
Optokinetic response analysis of wildtype and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants.
Average of left and right eye movement speed in degrees(deg)/second(sec), when wildtype (n = 9, filled circles) and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (n = 6, empty circles) embryos were presented with vertical moving stripes at increasing angular speeds, 0.05, 0.1, 0.13 and 0.16 cycles(cyc)/deg. Two independent experiments (data in Supplementary file 1E).
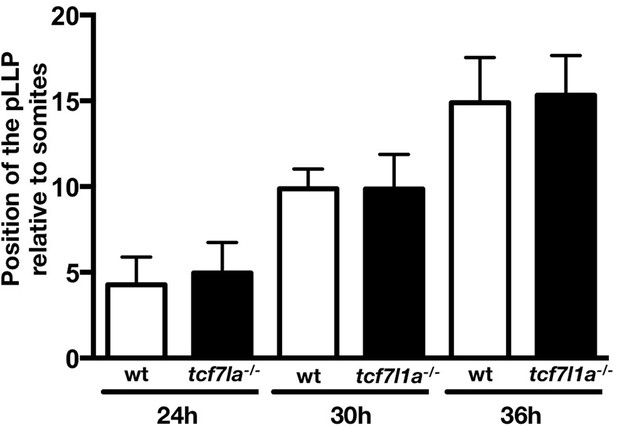
Quantification of the posterior lateral line primordium position in wildtype and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants.
Plot showing the position of the posterior lateral line primordium relative to somite number in wildtype (white bars) and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (black bar) at 24, 30 and 36hpf, (data in Supplementary file 1G).
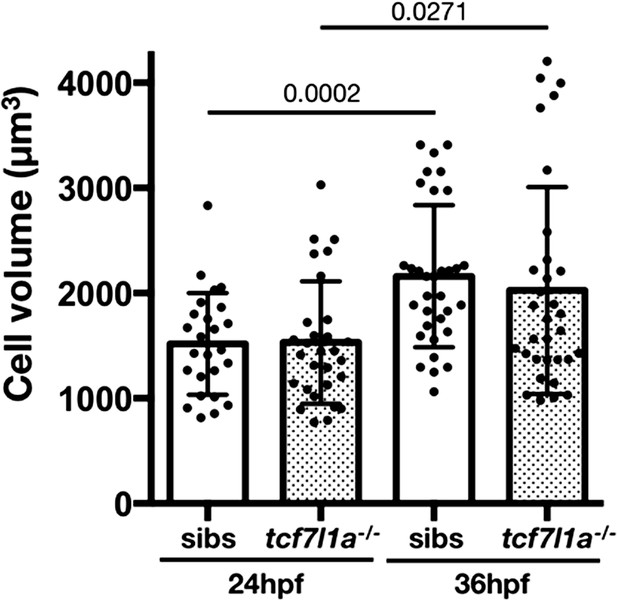
Cell volume quantification in tcf7l1a mutants and siblings.
Plot showing individual cell volume quantification in siblings and tcf7l1a-/- mutants at 24 and 36hpf. Volume was measured in cells expressing GFP and mRFP, data in Supplementary file 1H. Wildtype and heterozygous tcf7l1a embryos were pooled in a single sibling group at each timepoint. Three independent experiments, sibs 24hpf n = 25, tcf7l1a-/- 24hpf n = 29, p=0.935; sibs 36hpf n = 33, tcf7l1a-/- 36hpf n = 32, p=0.519, unpaired t-test.
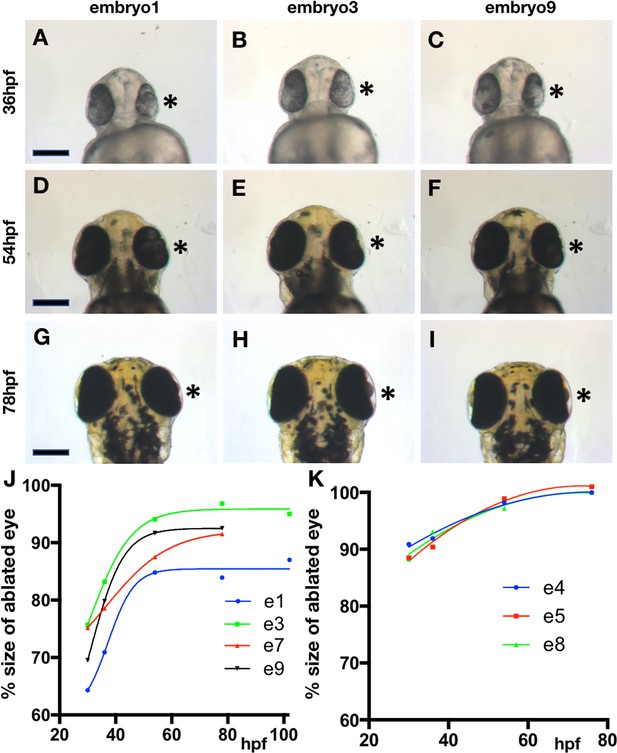
Growth kinetics of the eye from eye vesicle cell-removed embryos.
(A–I) Wildtype embryo example 1 (A, D, G), 3 (B, E, H) and 9 (C, F, I) from which cells were removed from the right eye vesicle at 12hpf imaged at 36hpf (A–C), 54hpf (D–F) and 78hpf (G–H). Ventral view (A–F), dorsal view (H–I), anterior up. Images have been flipped such that the cell-removed eye is always on the right side of the embryo (asterisk). Scale bars = 200 µm. (J, K) Plots showing the ratio of control eye to cell-removed eye volume from data in Supplementary file 1I generated from lateral view imaging of both eyes in each embryo.
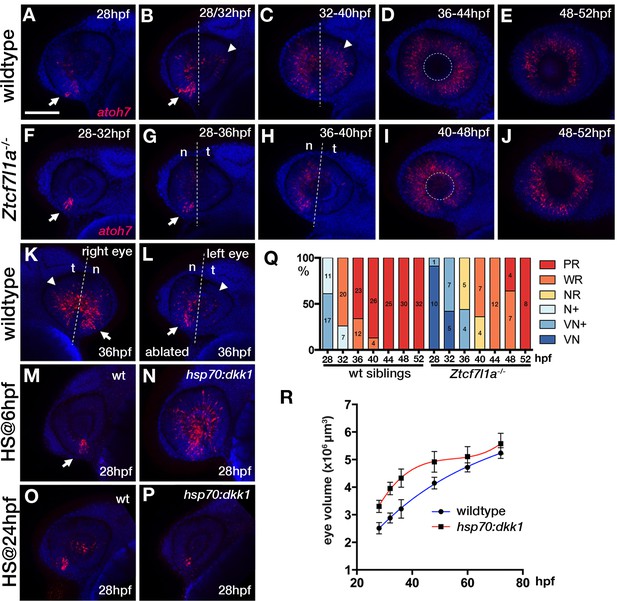
Neurogenesis is delayed in small tcf7l1a-/- eyes and accelerated in large eyes following hsp70:dkk1 overexpression.
(A–P) Lateral views of eyes showing atoh7 fluorescent in situ hybridisation in typical wildtype (A–E, M, O), Ztcf7l1a-/- (F–J), wildtype left-side optic vesicle-ablated (K, L); from n = 5 embryos) and Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 (N, P) embryos at stages indicated. (M–P) Wildtype (M, O) and heterozygous sibling Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 embryos (N, P) heat-shocked at 6hpf (M, N); from n = 7/9 embryos) or 24hpf (O, P); from n = 10/10 embryos) for 45’ at 37°C and grown to 28hpf. Anterior is to the left except in (K) in which anterior is to the right. Arrows indicate ventro-nasal retina; arrowheads indicate dorso-temporal retina; dashed line approximate the nasal-temporal division; dashed circle marks lens position. Abbreviations: n, nasal, t, temporal. Scale bar = 100 µm. (Q) Histogram showing the spatial distribution of atoh7 expression in sibling and Ztcf7l1a-/- retinas at the indicated hours post-fertilisation (data in Supplementary file 1F). VN, ventro nasal expression; VN+, ventro-nasal expression plus a few scattered cells; N+, nasal expression plus scattered cells covering the whole retina; NR, nasal retina expression; WR, whole retina expression; PR, expression localised to the peripheral retina. Numbers in bars represent the number of embryos scored for the particular category of atoh7 expression. (R) Plot showing the growth kinetics of the eye in wildtype (blue line) and Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 (red line) embryos at times indicated (data in Supplementary file 1K).
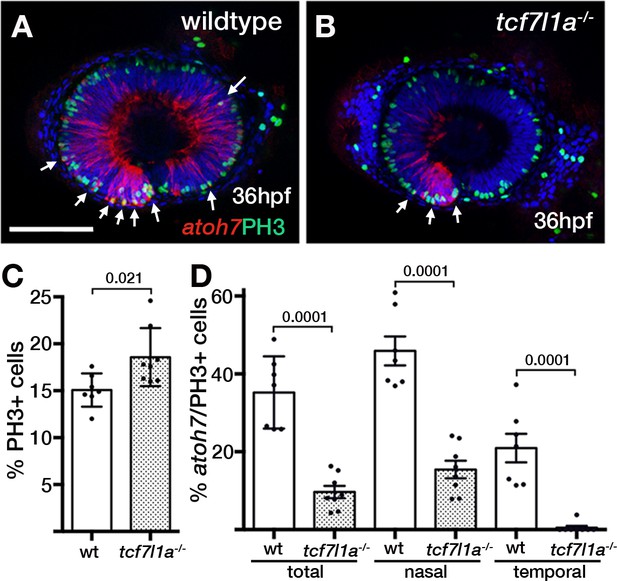
Ztcf7l1a mutants show more retinal progenitor cells undergoing proliferation.
(A–B) Immunostaining detecting phosphohistone3 (PH3, green) and RFP (Tg(atoh7:GAP-RFP)cu2Tg-, red) in wildtype (A) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (B) eyes at 36hpf . Arrows indicate selected double PH3/RFP positive cells. n, nasal; t, temporal. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C–D) Plot showing the percentage of PH3-positive cells (C) data in Supplementary file 1L) and double PH3/RFP-positive cells (D), data in Supplementary file 1L). Single experiment, wildtype n = 7, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 8, figures over the bars show p-values from unpaired t-tests.
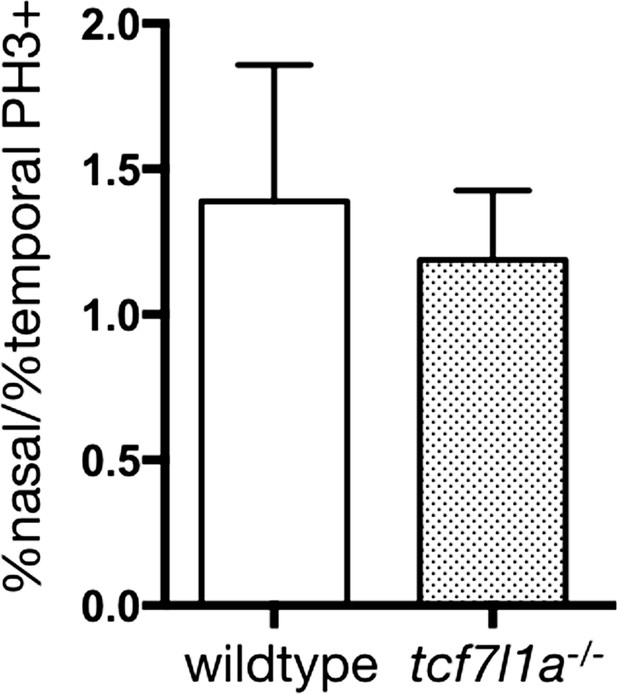
Ratio of double atoh7/phosphohistone3 cells in the nasal and temporal retina.
Plot showing the ratio of atoh7/phosphohistone3 positive cells of nasal over temporal retina in wildtypes (n = 7) and tcf7l1a-/- mutants (n = 8). Data in Supplementary file 1K. Difference in both conditions is not significant, p=0.3, unpaired t-test).
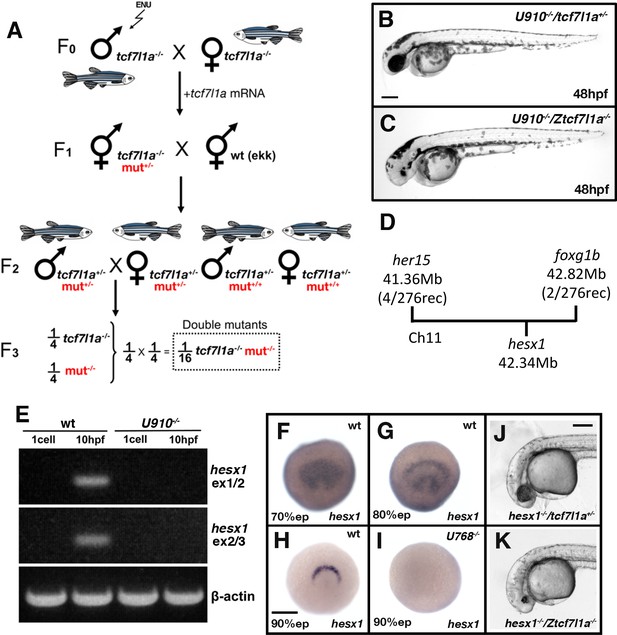
Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants lacking Hesx1 function fail to form eyes.
(A) Schematic of the genetic strategy to isolate mutations that modify the tcf7l1a-/- mutant phenotype. (B–C) U910 modifier of the tcf7l1a-/- mutant phenotype. Lateral views of homozygous U910 embryos that are heterozygous (B) or homozygous (C) for the tcf7l1a mutation. (D) Representation of SSLP segregation linkage analysis mapping of U910 modifier of tcf7l1a to a 1.46 megabase (Mb) interval on chromosome 11 (Ch11; rec, recombinants). (E) RT-PCR for hesx1 spanning exons 1–2 (top panel), exons 2–3 (middle panel) and β-actin (bottom panel) on wildtype (lanes 1 and 2) and U910-/- (lanes 3 and 4) embryo cDNA from 1 cell stage (lanes 1 and 3) and 10hpf (lanes 2 and 4). Single experiment. (F–I) hesx1 in situ hybridisation on wildtype (F–H) and U910-/- (I) embryos at epiboly (ep) stages indicated. Dorsal views, anterior up. (J, K) Lateral views of hesx1-/- (Δex1/2)/tcf7l1a+/- (J) and hesx1-/- (Δex1/2)/Ztcf7l1a-/- (K) embryos. Four independent experiments, n = 53. Scale bars = 200 µm.

Genomic DNA sequence of hesx1 locus spanning exons 1 and 2.
Genomic DNA sequence deleted in U910 fish in bold. hesx1 exons 1 and 2 highlighted in yellow. Open reading frame first codon in exon one is highlighted in red.
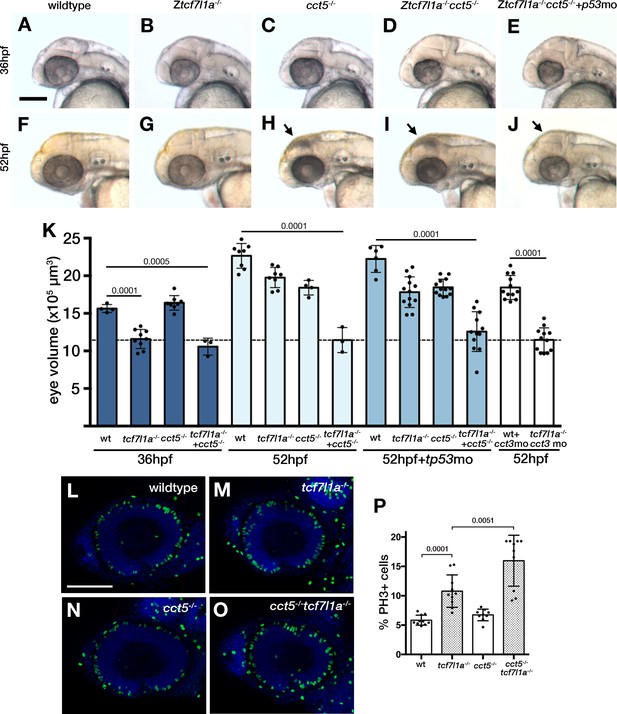
Loss of tcf7l1a modifies the cct5u762 mutant eye phenotype.
(A–J) Lateral views of wildtype (A, F), Ztcf7l1a-/- mutant (B, G) cct5U762/u762 mutants (C, H), double cct5U762/u762/Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (D, I) and double cct5U762/u762/Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants injected with 0.8 pmol of cct3 morpholino (E, J) at indicated stages. Scale bar = 100 µm. Full data in Supplementary file 10O, single experiment, 36hpf, wt n = 4, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 9, cct5-/- n = 8, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 3; 52hpf, wt n = 8, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 8, cct5-/- n = 4, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 3; 52hpf + 2 pmol tp53 morpholino, wt n = 6, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 13, cct5-/- n = 13, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 12; 52hpf + 0.8 pmol cct3 morpholino, wt n = 12, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 12. (K) Eye volume quantification at the indicated timepoints and conditions shown in A–J) (data in Supplementary file 1O). Unpaired t-test. (L–O) Immunostaining detecting phosphohistone3 (PH3, green) in wildtype (L), Ztcf7l1a-/- (M), cct5-/- (N), cct5-/-/Ztcf7l1a-/- (O) eyes at 32hpf. (P) Plot showing the percentage of PH3 positive cells in the eyes shown in L–O) (data in Supplementary file 1Q) Single experiment, wildtype n = 10, Ztcf7l1a-/- n = 10, cct5-/- n = 9, cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/-n = 10, unpaired t-tests.
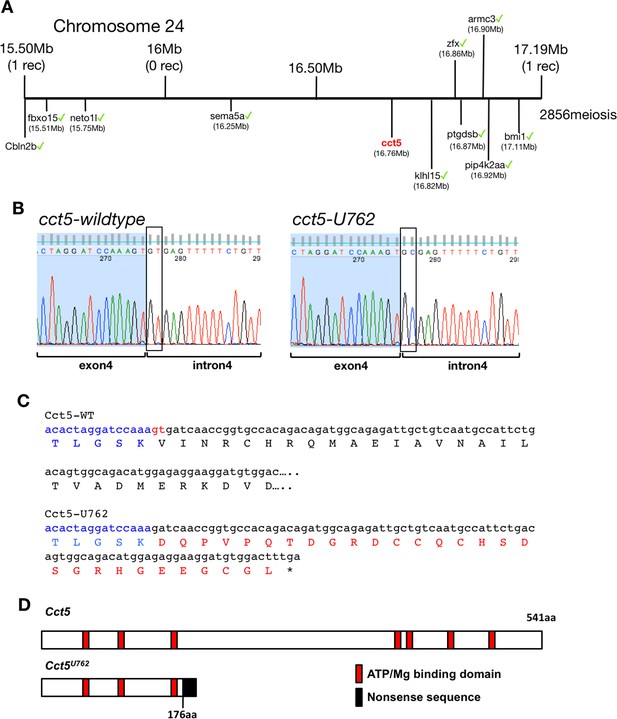
Genetic mapping of U762 and description of the cct5U762 mutation.
(A) Representation of the SSLP segregation linkage analysis mapping of U762) modifier of tcf7l1a to a 1.69 Mb interval on chromosome 12, between 15.50 Megabases (Mb) with one recombinant (rec) and 17.19 Mb with one rec. Green ticks highlight sequenced genes in the interval that show no mutations. (B) DNA sequencing chromatograms of the genomic fragment encompassing the 3’ end of cct5 exon 4 and 5’ end of intron four from wildtype (left) and cct5U762/762(right) embryos. Boxes show the splice donor nucleotides in intron 4. (C) Nucleotide and protein sequence of wildtype (top alignment) and cct5U762 (bottom alignment). cct5 exon four nucleotides and amino acids in blue. The last two 3’ nucleotides in exon four that are used in cct5U762 as a splice donor in red. Nonsense amino acid sequence in cct5U762 in red. (D) Cartoon of wildtype and Cct5U762 protein product. Red boxes show Mg2+/ATP binding domains, black box indicates nonsense mutant protein stretch.
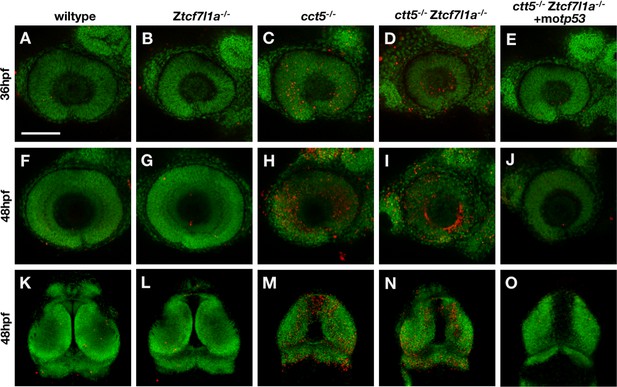
Whole mount Tunel cell death analysis in cct5/tcf7l1a mutants.
Tunel assay labelling detecting apoptotic cells (red) performed in wildtype (A, F, K, 100% n = 8), Ztcf7l1a-/- (B, G, L, 100% n = 10), cct5-/- (C, H, M, 100% n = 9), cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- (D, I, N, 100% n = 4) and cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- + 2 pmol of tp53 morpholino (E, J, O, 100% n = 5). DAPI pseudocoloured in green. Scale bar = 100 µm.
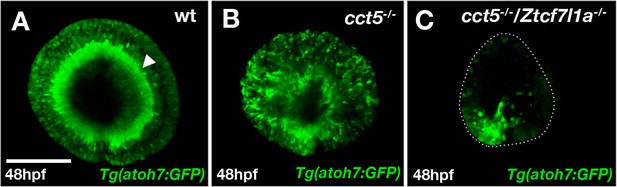
atoh7 expression in cct5/tcf7l1a mutants.
(A–C) Anti-GFP immunocytochemistry (green) showing Tg(atoh7:GFP)- labelled neurons in wildtype. (A) cct5-/- (cct5U762/U762) (B) and cct5-/-/Ztcf7l1a-/- (C) embryos at 48hpf. Dotted line in (C) outlines the eye profile. Arrowhead points to the retina ganglion cell layer. Scale bar = 100 µm.
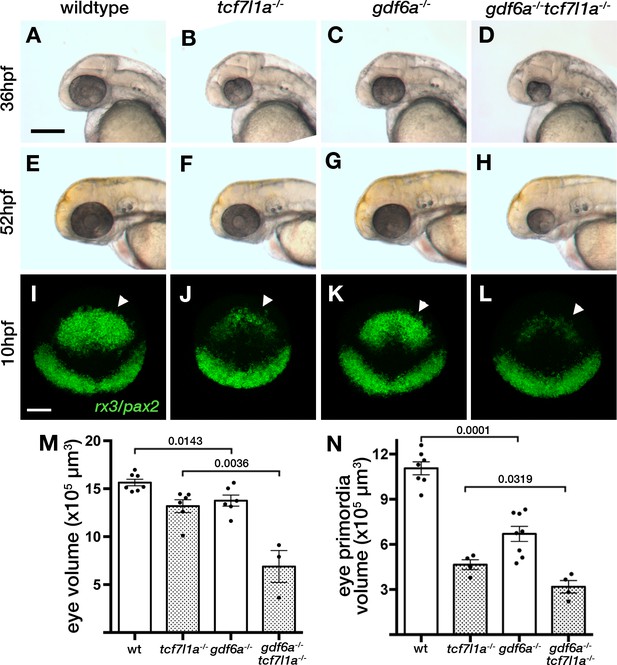
Loss of tcf7l1a modifies the gdf6aU768/U768mutant eye phenotype.
(A–H) Lateral views of eyes in wildtype (A, E), Ztcf7l1a-/- (B, F), gdf6aU768/U768 (C, G) and double gdf6aU768/U768/Ztcf7l1a-/- (D, H) embryos at 36hpf (A–D) and 52hpf (E–H). Dorsal up, anterior to left. Arrows indicate the lens. Scale bar = 200 µm. (I) Whole mount fluorescent in situ hybridisation for rx3 and pax2a in wildtype (I), Ztcf7l1a-/- (J), gdf6aU768/U768(K) and double gdf6aU768/U768/Ztcf7l1a-/- (L) embryos at 10hpf. Dorsal view, anterior up. Arrows point to rx3 eye field expression. Scale bar = 100 µm. (M) Eye volume quantification in wildtype (n = 7), Ztcf7l1a-/- (n = 6), gdf6a-/-(n = 6) and gdf6aU768/U768/Ztcf7l1a-/- double mutant siblings (n = 3) at 36hpf (data in Supplementary file 1R). Single experiment, unpaired t-test. (N) Eye field volume quantification from rx3 fluorescent in situ hybridisation shown in I-L in wildtype (n = 7), Ztcf7l1a-/- (n = 4), gdf6a-/-(n = 8) and gdf6aU768/U768/Ztcf7l1a-/- double mutant siblings (n = 4) at 10hpf (data in Supplementary file 1S). Single experiment, unpaired t-test.
Videos
Time lapse movies of eye vesicle evagination in and Ztcf7l1a+/- siblings.
Confocal time lapse movies (1 frame every 5 min) of Ztcf7l1a+/- sibling (S1, n = 5) expressing the Tg(rx3:GFP)zf460Tg transgene. First frame taken at 11hpf; membrane RFP in red counterstain.
Time lapse movies of eye vesicle evagination in Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants.
Confocal time lapse movies (1 frame every 5 min) of Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (S2, n = 5) expressing the Tg(rx3:GFP)zf460Tg transgene. First frame taken at 11hpf; membrane RFP in red counterstain.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables.
(A) RT-qPCR data on mRNA levels from Ztcf7l1a-/- versus wildtype embryos. Figures represent the fold change of Ztcf7l1a-/- over wildtype RT-qPCR experiments performed as technical and biological triplicates using GAPDH as a reference control. Standard deviation (SD). p-Value calculated by an unpaired t-test. (B) Measurement of the area of the prospective forebrain in wildtype and Ztcf7l1a mutants. Prospective forebrain size data generated by measuring the area enclosed by emx3 expression to the rostral limit of pax2a (mesencephalic marker) expression after whole mount in situ hybridisation in wildtype (+/+), tcf7l1a+/- (+/-) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (-/-) embryos at 10hpf. Data in µm2. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). Not-significant, ns. p-Value calculated by an unpaired t-test. (C) Measurement of the volume of rx3 expression in the eye field by fluorescent in situ hybridisation in wildtype and tcf7l1a mutants. Confocal volume analysis of rx3 fluorescent in situ hybridisation on wildtype (+/+), tcf7l1a+/- (+/-) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (-/-) at 10hpf. Data in µm3. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). Not-significant (ns). p-Value calculated by an unpaired t-test. (D) List of differentially expressed genes between wildtypes and tcf7l1a-/-, and between tcf7l1a-/- and tcf7l1a-/-tcf7l1b+/- double mutants at 8hpf. Ensembl gene ID (Gene ID), p-value (pval), adjusted p-value (adjp), log2 fold change (log2fc), linear fold change (fold change), chromosome (Chr) and gene name (Name). (E) Optokinetic response analysis of wildtype and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants. Tabulation of the data used on the plot (Figure 4—figure supplement 1). No significant difference observed when performing an unpaired t-test. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). (F) Eye volume measurement data in wildtype and tcf7l1a mutants. Data of eye volume measurement (µm3) from wildtype and tcf7l1a-/- embryos at 24, 28, 32, 36, 48, 60, 72 and 96hpf. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD), percentage of Ztcf7l1a-/- eye volume size relative to wildtype eyes (%). (G) Quantification of the posterior lateral line primordium position in wildtype and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants. Tabulation of the data used on the plot (Figure 4—figure supplement 2). No significant difference observed when performing an unpaired t-test. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). (H) Cell volume quantification data in tcf7l1a-/- mutants and sibling eyes. Data of eye cell volume measurement (µm3) in siblings and tcf7l1a-/- mutants at 24 and 36hpf. In sibling columns, wildtype cell data is in bold text and heterozygotes in normal text. Average (Avg), standard deviation (SD). (I) Eye volume measurement data from eye vesicle cell-removed embryos. Data of eye volume measurement (µm3) from control and optic-vesicle ablated eyes at 30, 36, 54, 78 and 102hpf. Percentage of ablated eye volume size relative to the control eye (%). The last time point is missing for embryos 1 and 9 because they died after 78 hr. (J) Classification and quantification of atoh7 expression patterns in wildtype and Ztcf7l1a-/- eyes. Quantification of atoh7 expression categories in the eye at 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48 and 52hpf in wildtype (top table) and Ztcf7l1a-/- (bottom table) embryos. atoh7 expression was classified in the following categories: VN, ventro nasal; VN+, ventro nasal plus a few scattered cells; N+, nasal plus scattered cells covering the whole retina; NR, nasal retina; WR, whole retina; PR, peripheral retina. (K) Eye volume measurement data in heat-shocked control wildtype and Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 embryos. Tabulation of eye volume measurements in µm3 in heat shock control wild-type and Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 embryos at 28, 32, 36, 48, 60 and 72 hpf, used for plot in Figure 5R. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD), percentage of Tg(HS:dkk1)w32 eye volume size relative to heat shock control wildtype eyes (%). (L) Phosphohistone3 (PH3+) and double atoh7/PH3+ cell counts in wildtype and Ztcf7l1a mutant eyes. Tabulation of the PH3+ and double atoh7/PH3+ cell count in wildtypes (A) and Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants (B). The percentage of total PH3+ cells was calculated by dividing the PH3 count by the total number of cells. The percentage of nasal (N), temporal (T) or whole retina (total) atoh7/PH3+ cells was calculated by dividing the atoh7/PH3 +cell count in the N, T or total retina by the PH3+ count in the respective area. Average, avg; Standard deviation, SD. (M) List of genes in the U910 genetic interval. Position of the genes in the U910 interval in megabases (Mb) in the GRCz10 assembly. Mapped gene is highlighted in yellow. (N) Frequency of eyeless embryos and their respective genotypes in four incrosses of hesx1-/-/tcf7l1a ± fish. (O) Eye volume measurement data in wildtype, Ztcf7l1a, cct5 and cct5/tcf7l1a double mutant siblings. Data of eye volume measurement figures in µm3 in embryos at 36 (A) and 52hpf (B-D), injected with 2 pmol of tp53 morpholino (C) or 0.8 pmol of cct3 morpholino (D). Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). (P) List of the genes in the U762 genetic interval. Position of genes in the U762 interval in megabases (Mb) in the GRCz10 assembly. Mapped gene is highlighted in yellow. (Q) PH3 and double atoh7/PH3 positive cell count in cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- mutants. Tabulation of the PH3+ (A) and double atoh7/PH3+ (B) cell count in wildtype, Ztcf7l1a-/-, cct5-/- and cct5/Ztcf7l1a-/- eyes. Avg, average; SD, standard deviation. (R) Eye volume measurement data in wildtype, Ztcf7l1a, gdf6a and gdf6a/Ztcf7l1a double mutant siblings. Data of eye volume measurement figures in µm3 in embryos at 36hpf. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD). (S) Eye field volume measurement data in wildtype, Ztcf7l1a, gdf6a and gdf6a/Ztcf7l1a double mutant siblings. Data of eye field volume quantification in µm3 from rx3 in situ hybridisation in wildtype, Ztcf7l1a-/-, gdf6a-/- and gdf6a/Ztcf7l1a double mutant siblings at 10hpf. Average (avg), standard deviation (SD).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40093.028
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40093.029





