Downsizing the molecular spring of the giant protein titin reveals that skeletal muscle titin determines passive stiffness and drives longitudinal hypertrophy
Figures
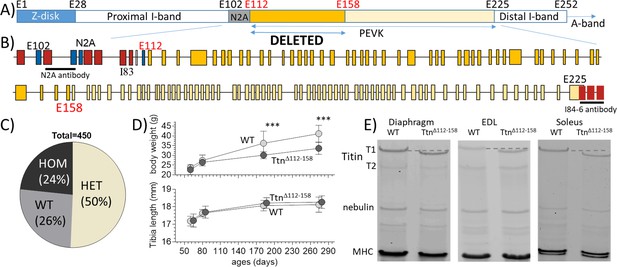
The TtnΔ112-158 mouse model.
(A and B) Titin’s I-band region is shown schematically in (A) and the exon composition of the PEVK and flanking region is indicated in B). The region targeted for deletion is highlighted. (Yellow: PEVK exons; dark yellow: targeted exons; red: Ig domains, blue: unique sequence; the horizontal lines indicate the binding sites of the antibodies used in Figure 3). (C) Genotype distribution of mice born to heterozygous parents is Mendelian. (D) Comparison between WT and homozygous TtnΔ112-158 mice of body weight (top) and Tibia length (bottom). Two-way ANOVA reveals a significantly reduced BW in TtnΔ112-158 mice with a multiple comparison analysis revealing a significant reduction at 180 and 275 days. No significant differences in tibia length were found. (All male mice, for female mice, see S1B). (E) Protein Gels. Full-length titin (T1) has a higher mobility in TtnΔ112-158 mice but the mobility of T2 is the same. (T2 is a degradation product of T1 that is present in diaphragm and EDL but absent in soleus). MHC: myosin heavy chain.
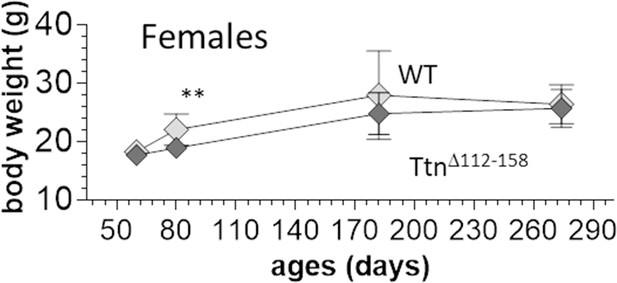
Body weight comparison between WT and homozygous Ttn∆112-158 female mice.
Two-way ANOVA reveals a significantly reduced BW in Ttn∆112-158 with a multiple comparison analysis revealing a significant reduction at 80 days. Note that the number of mice was less at 290 d (5 mice), likely explaining the relatively low WT weights.
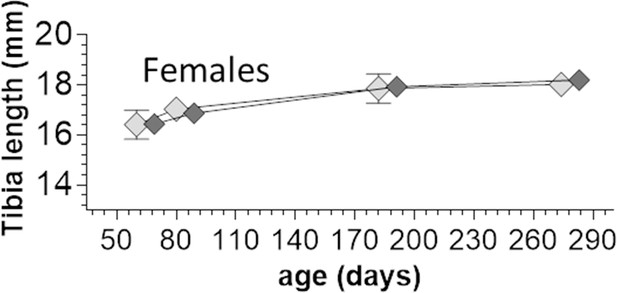
Tibia length comparison between WT and homozygous Ttn∆112-158 female mice.
Two-way ANOVA reveals no significant differences in tibia length between the genotypes.
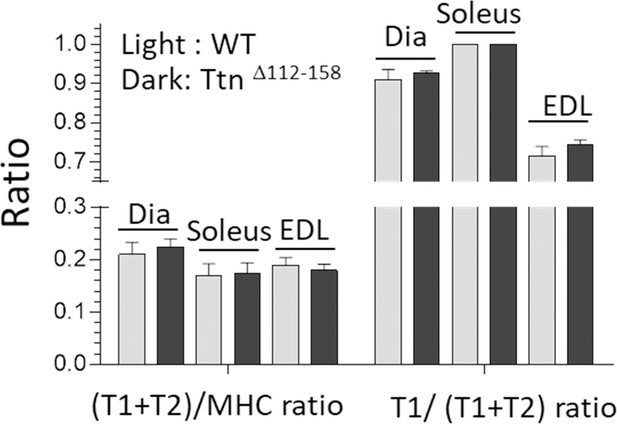
Titin expression analysis.
The total amount of titin, T1 + T2 (relative to myosin heavy chain, MHC) and the fractional content of T1 (relative to total titin) are unaltered in the Ttn∆112-158 mice.
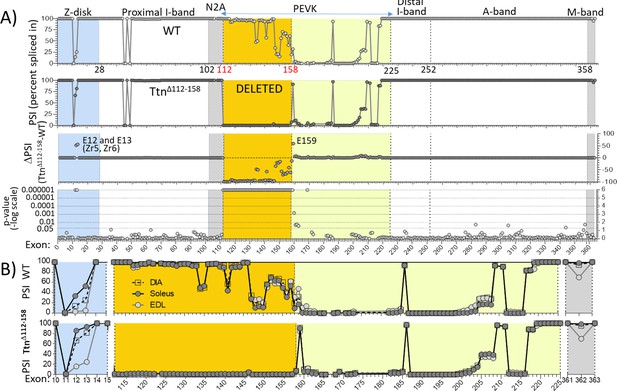
Titin exon expression analysis.
(A) RNAseq-based titin exon expression of diaphragm muscle, expressed as percent spliced-in (PSI) in WT and TtnΔ112-158 mice (top and below), and the PSI difference between the two genotypes and the p-value of PSI difference (bottom and above). The targeted exons are absent in the TtnΔ112-158 mouse with minimal changes in the Z-disk and M-band. (p-value scale is –log(p-value) with values > 6 shown as 6.) (B) PSI of Diaphragm, EDL and soleus muscle of WT (top) and TtnΔ112-158 (bottom) mice. Only shown are areas within the gene where PSI differences exist between the genotypes. Z-disk (blue), PEVK (yellow) and M-band (gray). Zr: Z repeat.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Percent Spliced In source data.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40532.010
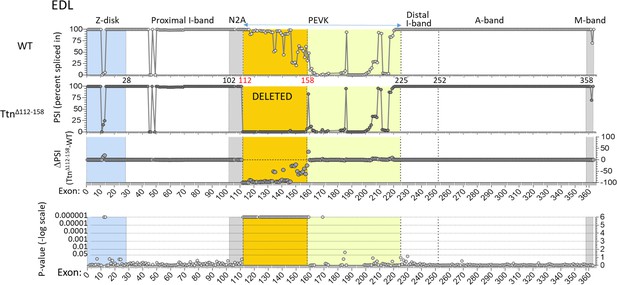
Titin expression analysis in EDL muscle.
RNAseq-based titin exon expression of EDL muscle, expressed as percent spliced-in (PSI) in WT and Ttn∆112-158 mice (top and below), and the PSI difference between the two genotypes and the p-value of the PSI difference (bottom and above). The targeted exons are absent in the Ttn∆112-158 mouse with minimal changes elsewhere. p-value scale is –log(p-value) with values > 6 shown as 6.
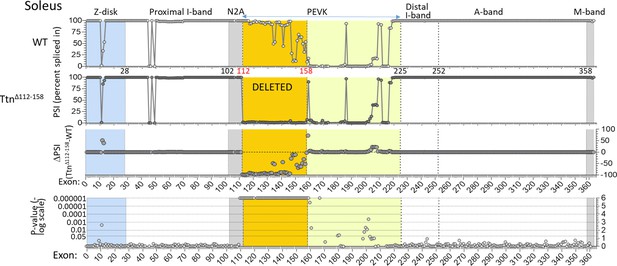
Titin expression analysis in soleus muscle.
RNAseq-based titin exon expression of EDL muscle, expressed as percent spliced-in (PSI) in WT and Ttn∆112-158 mice (top and below), and the PSI difference between the two genotypes and the p-value of the PSI difference (bottom and above). The targeted exons are absent in the Ttn∆112-158 mouse with minimal changes elsewhere. The p-value scale is –log(p-value) with values > 6 shown as 6.
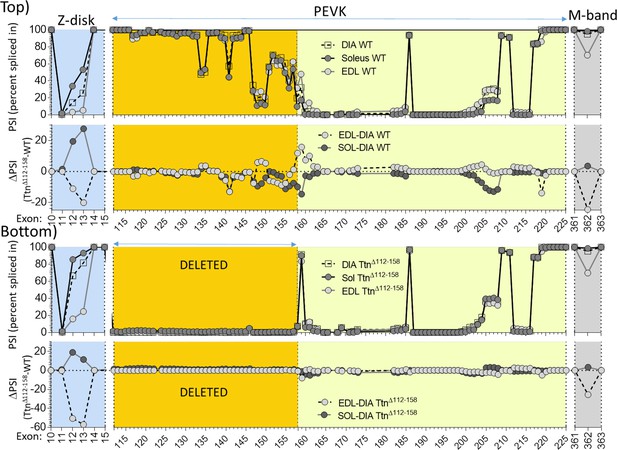
Titin expression analysis in diaphragm, EDL and soleus muscle, in part of Z-disk, complete PEVK and part of M-band regions.
Top: superimposed results of WT (top) and PSI difference between EDL and diaphragm and between soleus and diaphragm (bottom). Bottom: superimposed results of Ttn∆112-158 mice (top) and PSI difference between EDL and Diaphragm and between soleus and diaphragm (bottom).
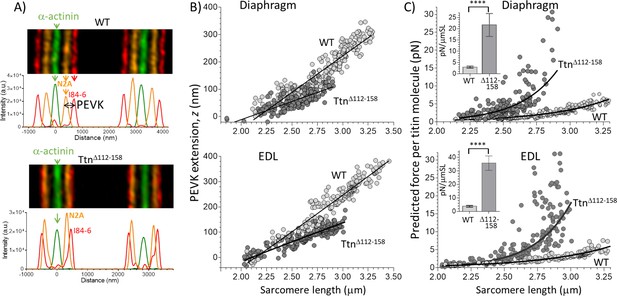
Extension of the PEVK segment and predicted titin-based force.
(A) Example immuno-fluorescence images and densitometry of sarcomeres labeled with N2A and I84-86 antibodies that flank the PEVK (Figure 1B shows binding sites). (B) PEVK extension (z) as function of sarcomere length in muscles stretched to different lengths. (C) Force per titin molecule as a function of sarcomere length. Inset shows the average stiffness of titin in the 2.45–2.75 μm SL range. The measured PEVK extension predicts a large increase in titin-based stiffness in TtnΔ112-158.
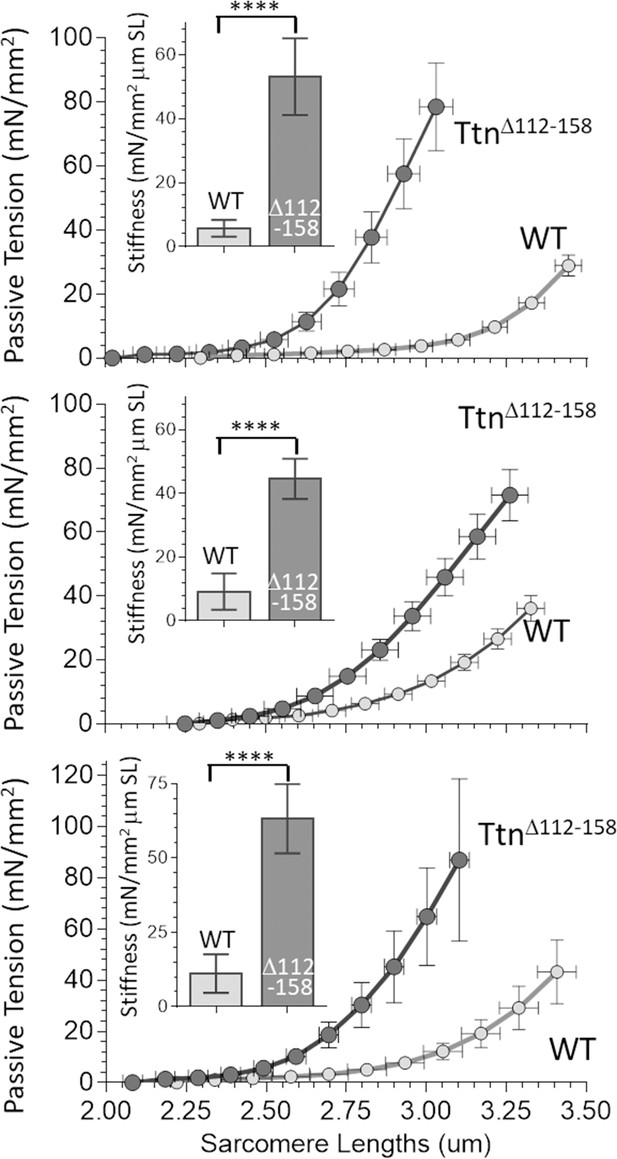
Passive Muscle stiffness.
The passive tension – sarcomere length relation was determined in Diaphragm (top), EDL (middle) and soleus (bottom) intact muscle from WT and TtnΔ112-158 mice. Passive tension is highly increased in TtnΔ112-158. The insets show average passive stiffness in the 2.45–2.75 μm SL range. Passive stiffness is increased ~5–10 fold in TtnΔ112-158 mice.
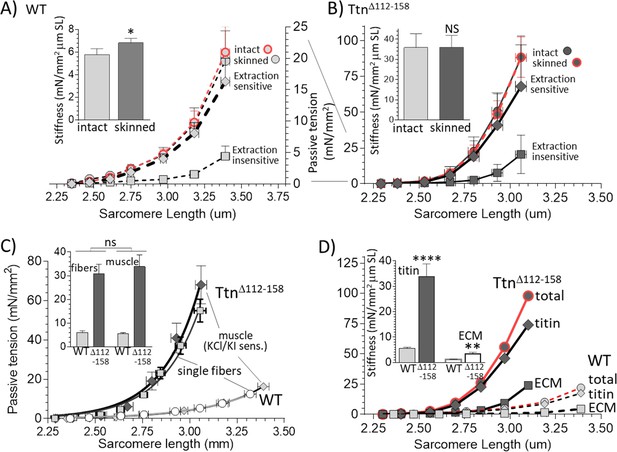
Functionally dissecting passive muscle stiffness.
(A and B) Passive tension in EDL muscle (5th toe muscle) was measured in intact muscle, then again after skinning, and a final time after KCl/KI extraction (extraction insensitive tension). The tension is minimally affected by skinning and tensions before and after skinning largely overlap. The difference between before and after KCl/KI extraction is the extraction-sensitive tension. (A) WT, (B) TtnΔ112-158 muscles (note ~4 fold different vertical scales). Insets of A and B show passive stiffness of intact and skinned muscle (SL range 2.45–2.75 μm). Skinning minimally impacts passive stiffness. (C) Comparison of extraction sensitive muscle tension with the passive tension of mechanically skinned single EDL fibers. The inset shows the average stiffness (SL range 2.45–2.75 μm) for single fibers (left two bars) and whole muscle (right two bars). Results are not significantly different, supporting that the extraction-sensitive tension is titin-based (see text for details). (D) Overlay of WT and TtnΔ112-158 skinned muscle total tension, titin-based tension and ECM-based tension. The inset shows the stiffness (SL 2.45–2.75 μm) for titin and ECM stiffness. Both titin and ECM have increased stiffness in TtnΔ112-158 muscles, but the effect is much larger for titin.
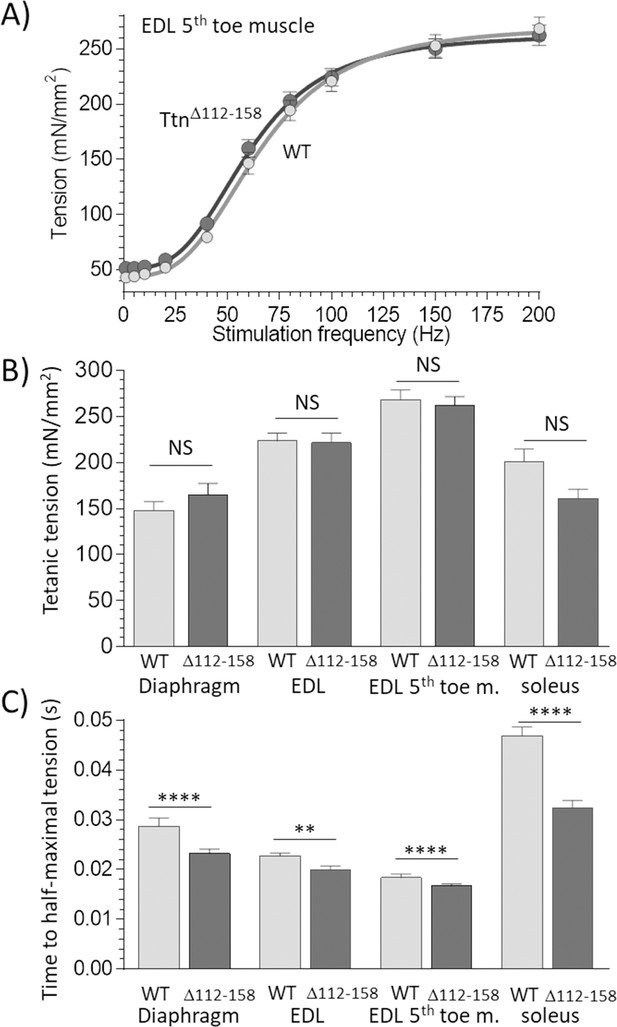
Active tension.
(A) Example results of tetanic tension vs. stimulation frequency. Results of EDL 5th toe muscle are shown. Results of WT and TtnΔ112-158 muscles closely overlap. (B) Maximal tetanic tension in Diaphragm (150 Hz), whole EDL muscle (200 Hz), 5th toe muscle of the EDL (200 Hz) and soleus muscle (150 Hz). Two-way ANOVA reveals that there is no significant difference in maximal tetanic tension in TtnΔ112-158 muscles with a multiple comparison analysis revealing also no effects in individual muscle types. (C) Time to reach half-maximal active tetanic tension is significantly altered in TtnΔ112-158 muscles (two-way ANOVA) with a multiple comparison analysis revealing a significant reduction in all TtnΔ112-158 muscle types.
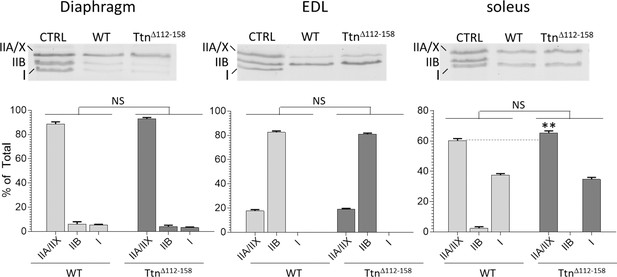
Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) isoform analysis.
Two-way ANOVA reveals that there is no significant difference in MHC isoforms in either diaphragm, EDL, or soleus Ttn∆112-158 muscles compared to WT controls. A multiple comparison analysis only reveals a difference in soleus muscle where IIA/IIX MHC is increased from 60% in WT to 65% in Ttn∆112-158 mice.
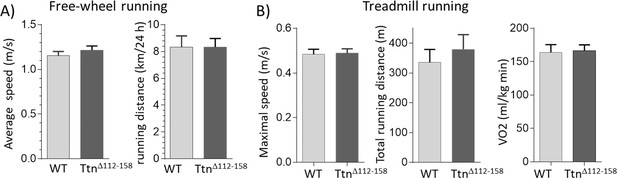
Exercise capacity.
(A) Free-wheel running exercise. Left, average running speed; Right, average distance ran in a 24 hr period. There is no significant difference in running speed and running between Ttn∆112-158 and WT mice. (B) Treadmill running exercise in which the mice had to run uphill and at a progressively increasing speed until they failed to keep up (see Materials and methods). Maximal running speed total running distance and VO2 consumption at maximal running speed (normalized to body weight) revealed no genotype effects. (Female mice were used.).
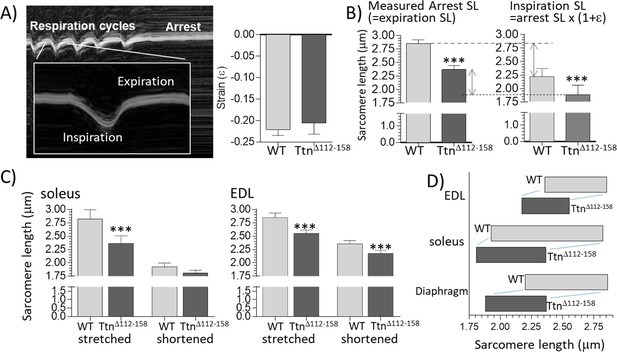
Sarcomere length working range.
(A) Motion-mode Echo image of the diaphragm in a WT mouse. The change in strain was measuring during inspiration (shortening) and then the mouse was perfusion-fixed which arrested the diaphragm in the expiration state. (A) Right: Strain amplitude (ε) measured on echo images during inspiration is the same in WT and TtnΔ112-158 mice. (Strain amplitude is defined as the fractional muscle shortening during inspiration.) (B) Left: measured sarcomere length (SL) in muscle strips dissected from the perfusion-fixed diaphragm is much less in TtnΔ112-158 than in WT mice. Right: calculated SL at end-inspiration, determined from the measured arrest SL and strain amplitude. (C) Measured sarcomere length in perfusion-fixed soleus muscle (left) and EDL muscle (right) in mice in which one hind leg was in a fully plantarflexed position while the other hind leg was held in a fully dorsiflexed position. (D) Sarcomere working range. The working range of all examined muscle types is reduced in TtnΔ112-158 mice. (Right side of the box is the maximal length and the left side the minimal length).
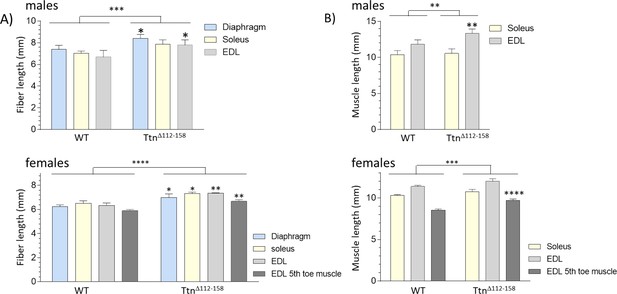
Fiber lengths and muscle lengths are increased in Ttn∆112-158 mice.
(A) Fibers were carefully dissected from chemically fixed muscle at their slack length and their end-to-end length was measured. Fibers are longer in muscles from Ttn∆112-158 mice in male (top) and female (bottom) mice. (B) Since fibers do not span the full muscle length in soleus and EDL we also measured the end-to-end length of the muscle. Muscle lengths are increased in males and female Ttn∆112-158 mice.
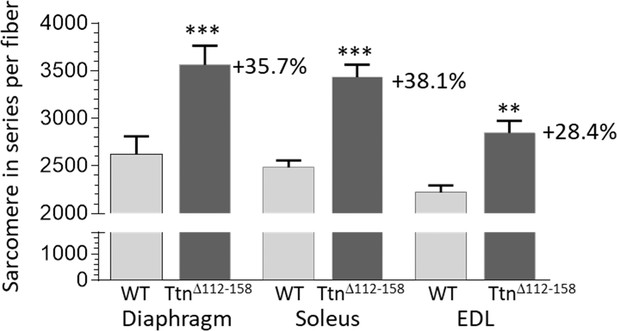
Sarcomere in series per muscle fiber.
Two-way ANOVA reveals a significantly increased number of sarcomeres in single fibers in all studied muscle types in TtnΔ112-158 mice. The average increase in the number of sarcomeres in series in all muscle types is 34%.
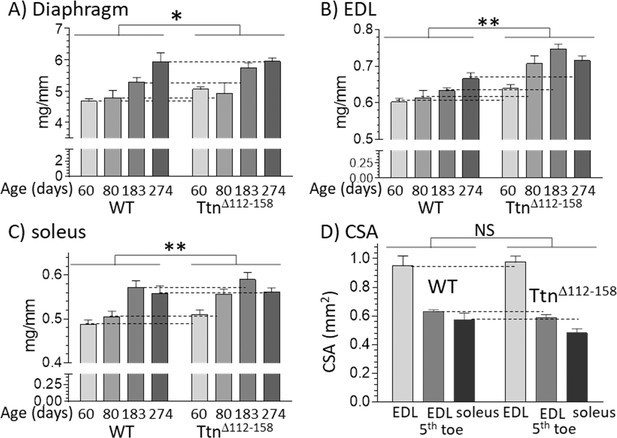
Muscles of TtnΔ112-158 mice are hypertrophied without an increase in cross-sectional area.
(A–C) Hypertrophy is expressed as muscle weight (mg) normalized to tibia length (mm). Two-way ANOVA reveals a significantly increased hypertrophy in all muscle types of the TtnΔ112-158 mice (male mice, group sizes, 5–13). (D) Cross-sectional area (CSA) of muscles. CSA was measured in passive muscles held at their slack length in 2 month-old mice (group size 5–9). Two-way ANOVA reveals no significant genotype effect on CSA with a multiple comparison analysis revealing no genotype differences for individual muscle types.
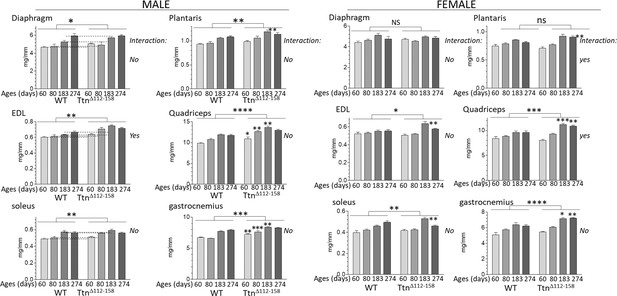
Muscles of Ttn∆112-158 mice are hypertrophied.
Hypertrophy is expressed as muscle weight (mg) normalized to tibia length (mm). Two-way ANOVA reveals a significantly increased hypertrophy in most muscle types of the Ttn∆112-158 mice. Most of the muscle types do not have a significant interaction term with age indicating that the genotype effect on muscle weight does not vary with age.
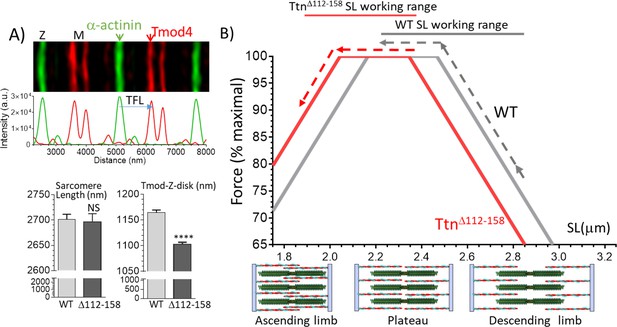
Thin filament length (TFL) and predicted force-sarcomere length (SL) relation.
(A) TFL was measured in diaphragm muscle by super-resolution optical microscopy using the TFL-pointed end capping protein Tmod4. Top shows a WT example. Bottom: analyzed results. Sarcomere length (left) is not different. TFL (Tmod-Z-disk distance) is significantly reduced from 1165 nm in WT to 1102 nm in TtnΔ112-158 diaphragm. (B) Top, Predicted force-sarcomere length relation using the measured TFLs: WT grey; TtnΔ112-158 red. Broken lines indicate the sarcomere length working ranges of the WT and TtnΔ112-158 diaphragm (from Figure 8D). (B) Bottom, schematic of sarcomeres on ascending limb (left), plateau (middle) and descending limb (right) of the force-SL relation. Green: thick filaments, red: thin filaments. (Note the central region of the thick filament that is devoid of myosin heads is known as the bare zone.).
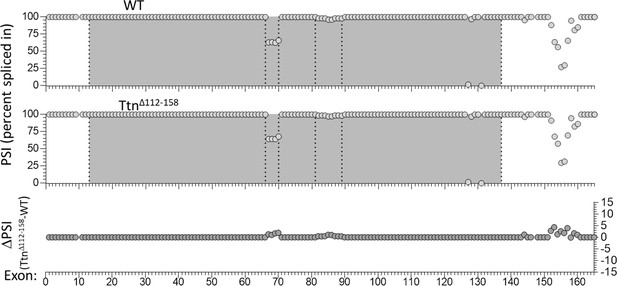
Nebulin exon expression analysis in diaphragm muscle.
RNAseq-based nebulin exon expression of diaphragm muscle, expressed as percent spliced in (PSI) in WT (top) and Ttn∆112-158 mice (middle), and the PSI difference between the two genotypes (bottom). Several exons in the middle of the gene (exons 66–70 and exons 82–89) are slightly upregulated (<5%) in the Ttn∆112-158 diaphragm but differences are not significant. In these regions a super-repeat duplication and a super-repeat triplication are found (making for 25 super-repeats in the mouse Neb gene). Several exons towards the C-terminus (Z-disk region) are also slightly upregulated, but differences are not significant.
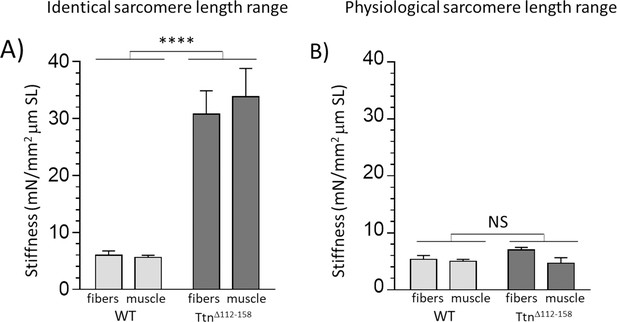
Passive muscle stiffness at the physiological sarcomere length range.
Passive stiffness in Ttn∆112-158 and WT EDL 5th toe muscle at an identical sarcomere length range (A) and at the physiological sarcomere length of each genotype (B). Data in A represent the average stiffness in the sarcomere length range 2.45–2.75 μm (data from Figure 5C, inset) and data in B represent the average stiffness in the sarcomere length range 2.35–2.85 μm for WT and 2.12–2.55 μm for Ttn∆112-158, representing the physiological sarcomere length range determined in Figure 8D. It is notable that within the physiological sarcomere length range (B) passive stiffness of the two genotypes is the same. (No differences between results of single fibers and whole muscle.). Legends for the supplementary figures.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene (Mus musculus) | Titin (Ttn) | NA | Ensembl: ENSMUSG00000051747 | |
| genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Ttn∆112-158 | this paper | Deletion of (GRCm38/mm10) chr2:76,839,202–76,867,333 | |
| strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | ‘mixed C57BL/6J and 129P2/OlaHsd " | other | Homologous recombination in E14TG2a cells (129/Ola strain, PMID: 3683574). Mice backcrossed seven generations to C57BL/6J (JAX stock#664) | |
| antibody | anti-titin N2A (chicken polyclonal) | Biogenes | Biogenes: anti-X105-X106 | (5.75 μg/mL) |
| antibody | anti-titin I84-86 (rabbit polyclonal) | Biogenes | Biogenes: anti-BK283-BK284 | (1 μg/mL) |
| antibody | anti-α-actinin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Sigma-Aldrich:A7811; RRID:AB_476766 | (1:1000) |
| antibody | anti-Tmod4 (rabbit polyclonal) | Proteintech Group Inc | Proteintech Group:11753–1-AP; RRID:AB_2205433 | (1:750) |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-488 conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG | Invitrogen | (1:500) | |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-568 conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG | Invitrogen | (1:250) | |
| antibody | AlexaFluor-647 conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG | Invitrogen | (1:250) | |
| antibody | CF-633 conjugated donkey anti-chicken IgY | Biotium | (1:200) | |
| other | AlexaFluor-488 conjugated phalloidin | Invitrogen | (1:1000) |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40532.025





