Preserved extrastriate visual network in a monkey with substantial, naturally occurring damage to primary visual cortex
Figures
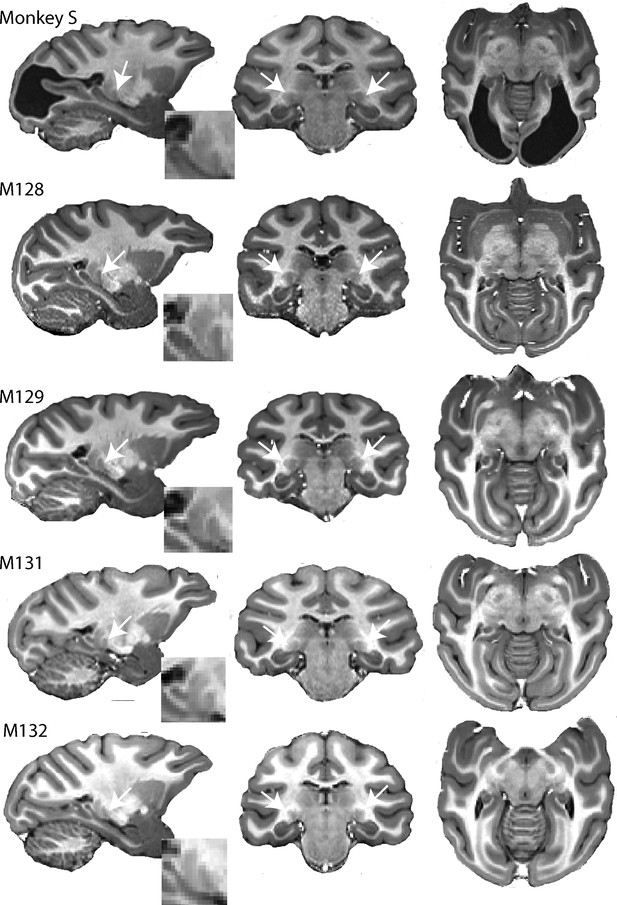
High resolution structural images of five adult female macaques of similar age and weight.
The large bilateral lesions of monkey S to the occipital cortex are clearly visible. LGN (white arrow) and pulvinar (posterior and dorsal to LGN) are shown in parasagittal section (with high magnification inset) as well as in the coronal and horizontal sections.

Visual map estimate of monkey S.
Based on established neurophysiological maps of V1 retinotopy in relation to the cortical folding pattern and approximate slice position (their Figure 11, Van Essen et al., 1984), we estimated the visual field loss of monkey S. The visual map is shown on post mortem T2*-weighted images – deformations of the occipital cortical surface were post mortem. Given the extent of the loss of white matter directly underneath V1, we expect bilateral visual field loss, for the central 10° as well as for more peripheral parts, potentially around 15°−20° eccentricity.
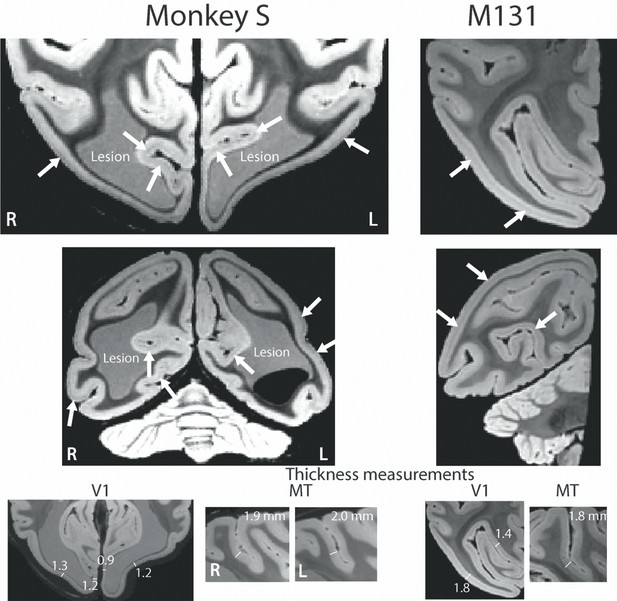
Post mortem high resolution scan of V1.
A post mortem T2*-weighted structural scan at high field (7T) revealed the stripe of Gennari in V1 (white arrows for example sites) of both monkey S and a control monkey (M131), although the position relative to the cortical surface within the cortical ribbon appeared to differ. The V1 grey matter in monkey S was reduced in thickness to 0.9–1.3 mm around the enlarged ventricles (1.4–1.8 mm in the control). The appearance of increased thickness more laterally in the sulcus is due to the angle of the slice through cortex at this point. By contrast, the grey matter at the location for V5/MT appeared intact with a typical thickness of 1.9–2.0 mm. Note that the lesion is partially light grey in appearance as well partially black. As the brain was still inside the skull during the scan, we speculate that this might be a result of slow incursion of ‘fluorinert’, in which the skull was immersed for this scan.
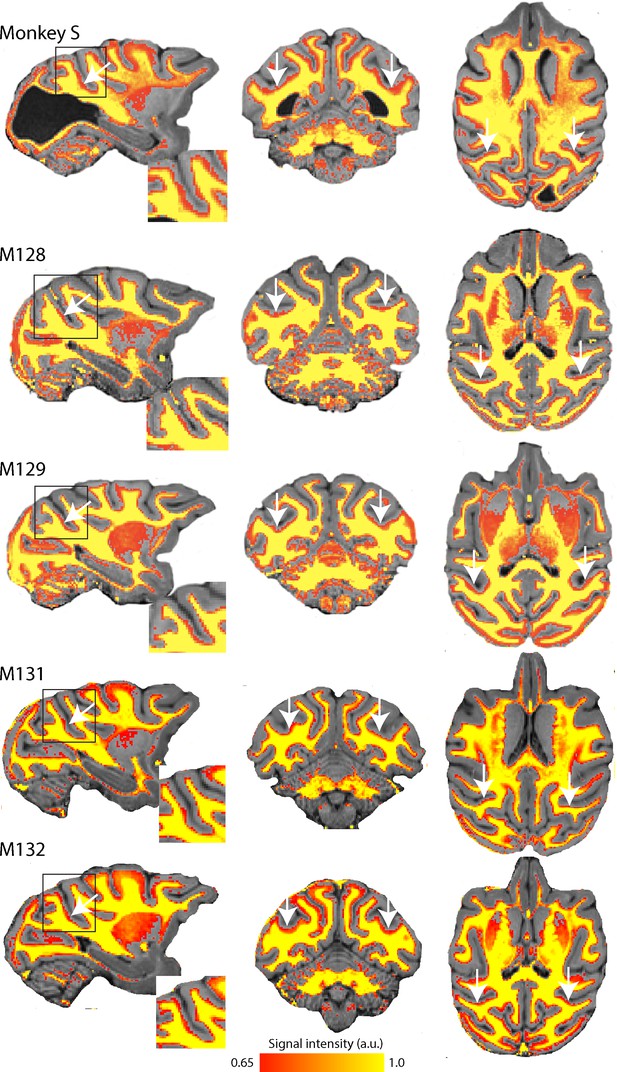
Myelin-weighted T1w/T2w images obtained in vivo show the expected pattern of dense myelination.
Yellow represents the highest intensity signal in the images, corresponding to the dense white matter, while red is less dense white matter, corresponding either to myelin within the cortical ribbon, as in the case of area V5/MT, or subcortical grey matter. The white arrows indicate the location of V5/MT in each view, and the red voxels within the cortical ribbon indicate the increased myelination expected in controls and monkey S.
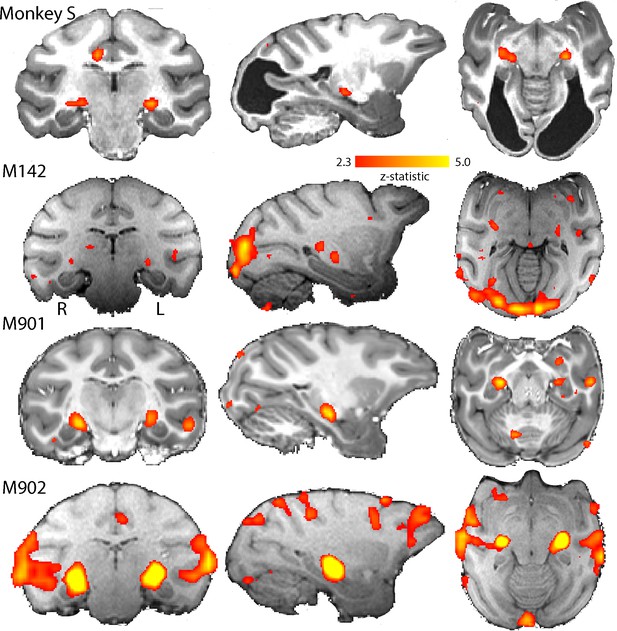
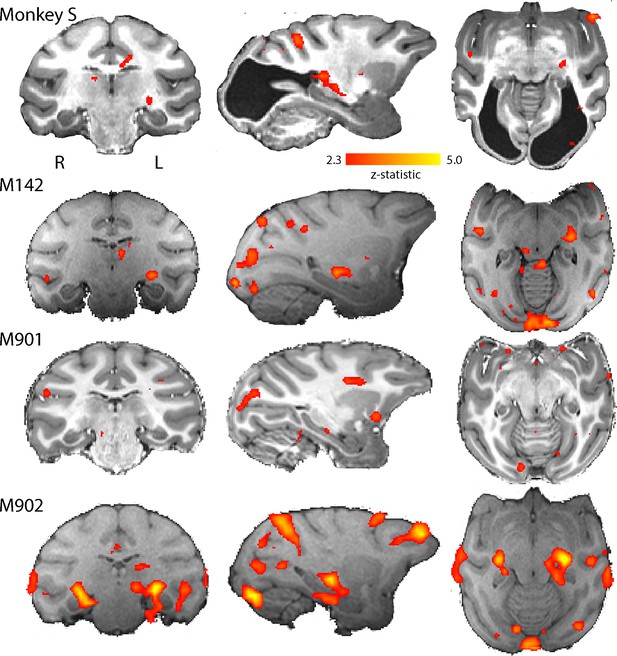
BOLD Activation by high contrast stimuli.
LGN was significantly activated in all monkeys by flickering checkerboards (z > 2.3). Cortical activation is less consistent across the control monkeys and not really evident in monkey S. The parasagittal sections show that the pulvinar was not consistently activated by this stimulus.

Anaesthesia, weight, and significant visual responses.
In anaesthetised monkeys, visual activation can vary for a number of reasons, including accommodation, drifting eye movements and level of anaesthesia (Hutchison et al., 2014). Average %isoflurane inspired during the acquisition of visual sequences in our study is plotted against the weight of the monkey at the time of the functional MRI scan. Data in red are from fMRI sessions with significant BOLD activation of the LGN due to visual stimulation (z > 2.3), in blue from sessions without a significant response. The two scanning sessions for monkey S are indicated with a black ring, the only female Rhesus macaque in the control sample with a grey dashed circle. Vertical bars depict the range of %isoflurane levels throughout the visual functional scan. The table underneath summarizes weight, mean %isoflurane level inspired, minimum and maximum values, time from onset of sedation, and mean %isoflurane expired.
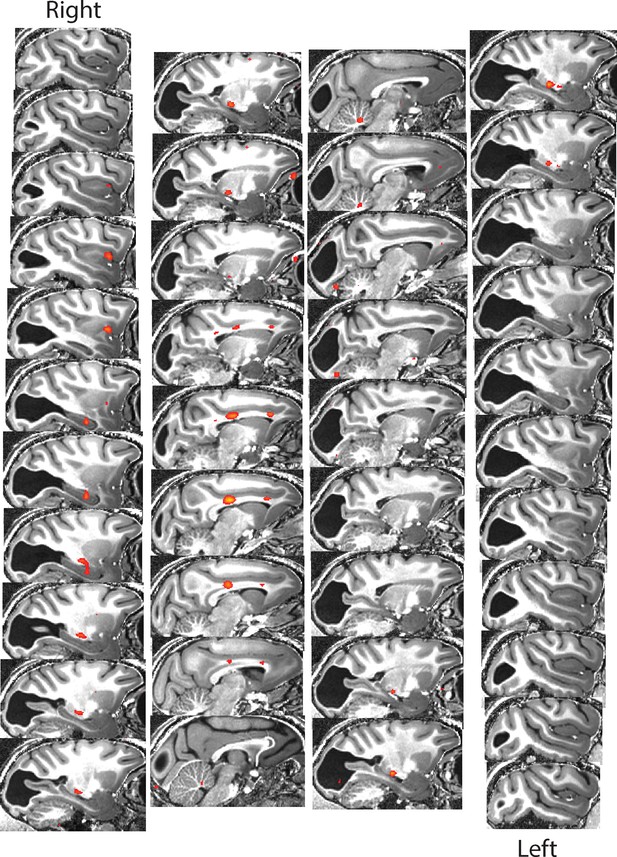
BOLD activation by high contrast stimuli for monkey S.
Parasagittal sections (1 mm spaced) through the brain of monkey S. Regions of significant activation (z > 2.3) for the checkerboard are shown in red-yellow. There was no activation evident in V1.
BOLD activation by visual motion.
Activation to the moving dot stimulus generated less activity in all monkeys than the flickering checkerboard. In particular, the LGN activation levels were lower in all monkeys. Monkey S showed LGN activation in the left hemisphere only, but in this case pulvinar activation was also evident (z > 2.3).
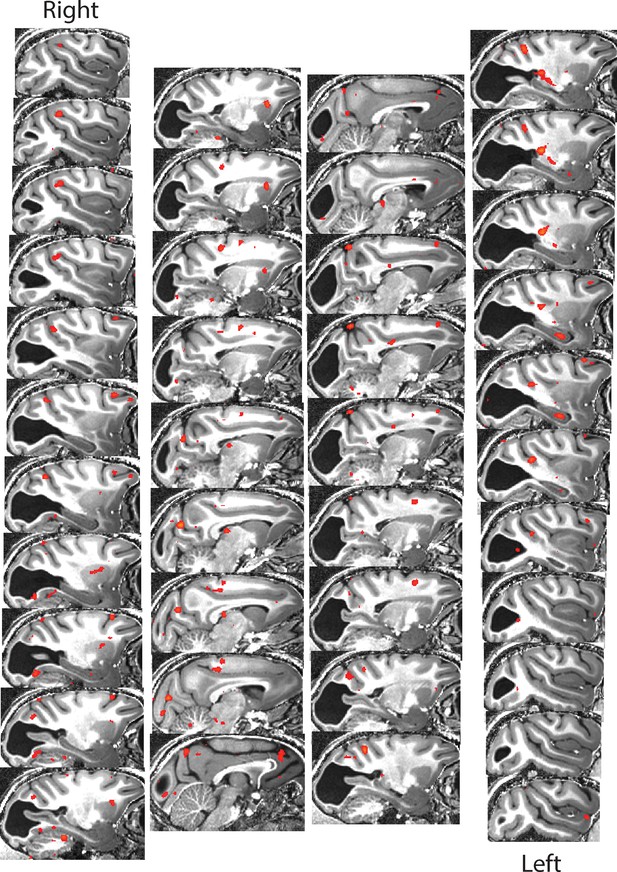
BOLD activation by visual motion for monkey S.
Parasagittal sections (1 mm spaced) through the brain of monkey S. Regions of significant activation (z > 2.3) for visual motion are shown in red-yellow. Again, there was little evidence of stimulus-evoked activation in V1.
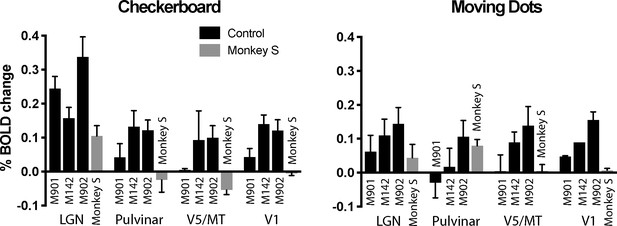
% BOLD change to visual stimulation.
Change in BOLD signal to checkerboard and moving dot stimuli. In response to the flickering checkerboard stimulus, we saw robust BOLD activation of the LGN in monkey S and the three control monkeys. The activation level to the moving dots was lower in the LGN, although monkey S showed clear activation in the pulvinar only in response to moving dots. V1 was activated in all three control monkeys but not monkey S. Plotted are mean ± SEM of the right and left hemisphere for each monkey.

The mean timeseries of the BOLD response for monkey S averaged across the 16 cycles of one scan.
The data points show the average of all voxels in the left LGN mask to the checkerboard stimulus and of all the voxels in the right pulvinar mask to the moving dots.
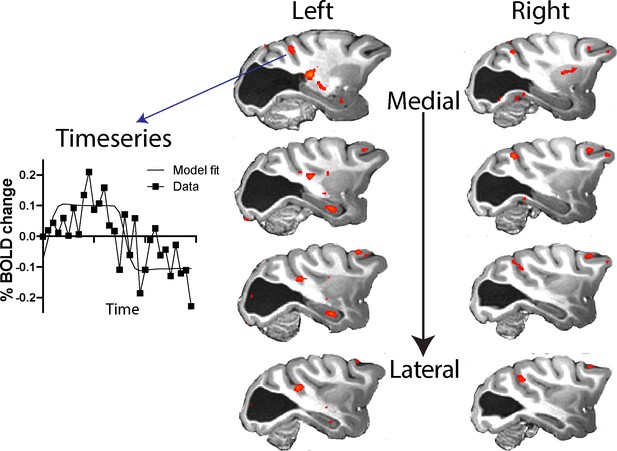
Response to visual motion in dorsal STS.
Illustration of BOLD activation (z > 2.3) in series of slices through V5/MT in both hemispheres of monkey S. While there was no extended area of activation to the moving dot stimulus, there were a number of small regions of activation across dorsal regions of the STS. The timeseries plot shows the average signal extracted from one of these regions of activation (z > 2.3) shown in the top left panel.
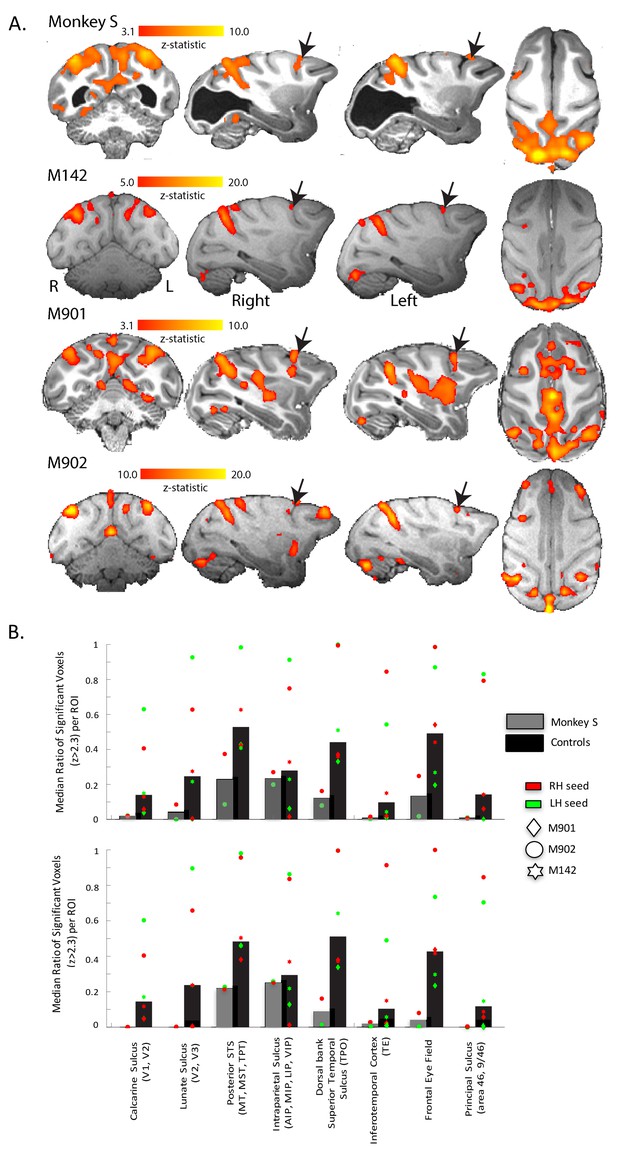
Functional connectivity of V5/MT.
(A) Regions showing significant correlation with the time-series extracted from area V5/MT in the right hemisphere. The colourbar indicates the significance of the correlations (z-statistic) but note that the scales differ across monkeys. The network of cortical regions showing significant correlation is consistent across all animals, including monkey S, and consists predominantly of dorsal occipital and parietal regions as well as area FEF (black arrows). (B) Quantitative comparison of activation (z-statistic) of key visual, parietal and frontal brain regions. Upper bar graph shows ipsilateral and bottom contralateral connectivity expressed as the median ratio of significantly activated voxels over total number of voxels within each region of interest. Dots depict results separately for monkeys and seed regions. Despite individual differences in the level of cortical activation, a bilateral pattern of dorsal but not ventral visual activation emerged.
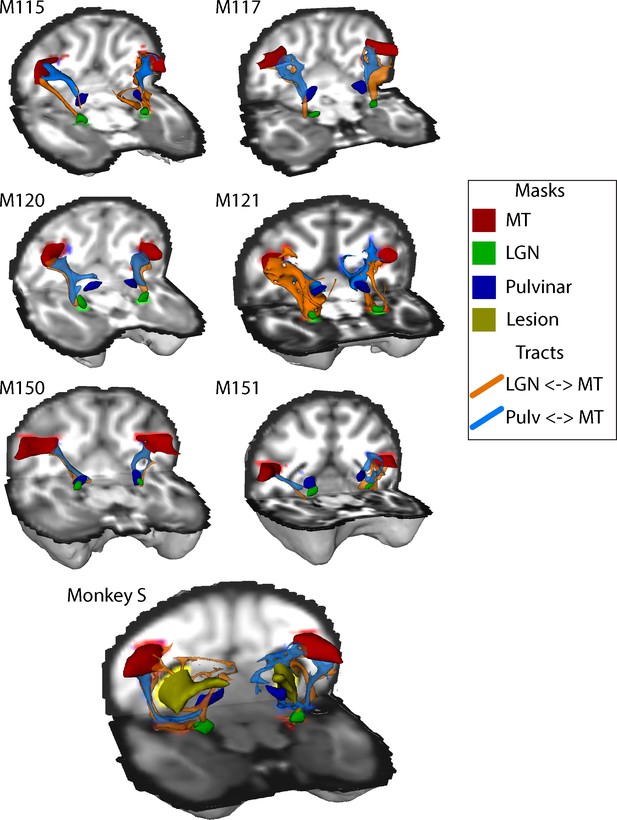
White-matter tracts between LGN, pulvinar and V5/MT.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and probabilistic tractography were used to investigate tracts between extra striate visual motion area V5/MT (red) and the LGN (green) and V5/MT and the pulvinar (blue). All tracts could be traced in the control monkeys and monkey S. In monkey S, the tracts appeared fragmented and took different routes, likely due to the presence of the lesion (shown in yellow).
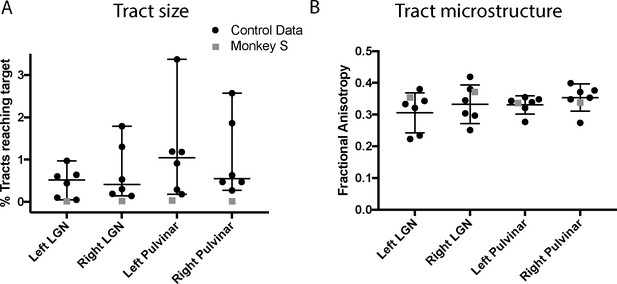
Quantification of tractography results.
(A) Quantification of the percentage of streamlines from the seeds in subcortical areas LGN and pulvinar reaching cortical area V5/MT in the two hemispheres. While there was considerable variability between control monkeys (black circles), the number of tracts in monkey S (grey square) is consistently lower for all tracts. (B) By contrast, the functional anisotropy values for the tracts in monkey S were comparable to the control values for both pathways. This suggests that the white matter microstructure within the tracts between V5/MT and each target structure was intact. Data points show results from individual hemispheres, the horizontal lines give the median and the 95% confidence interval for the control group.
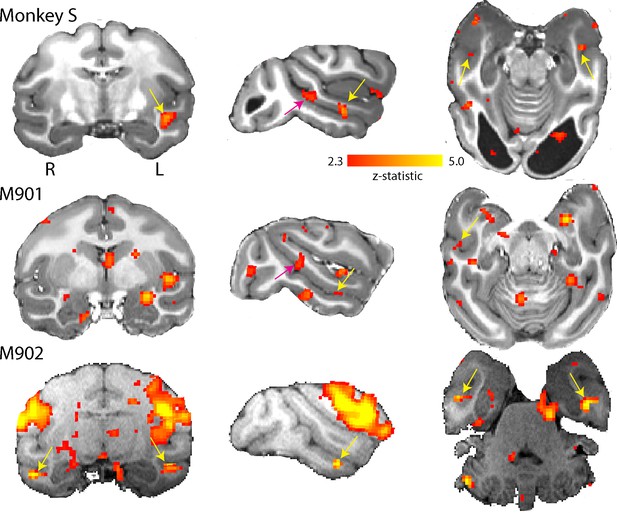
Activation of anterior and middle face patch for face stimuli.
Images show the BOLD signal for blocks of neutral and threatening faces and compared to a mid-grey screen. Monkey S showed activation of the middle fundus (pink arrow) and anterior fundus (yellow arrow) face patch along the mid- and temporal STS regions. Both controls showed activation of the anterior face patch and one also showed activation of the middle face patch. (2.3 < zstat < 5).
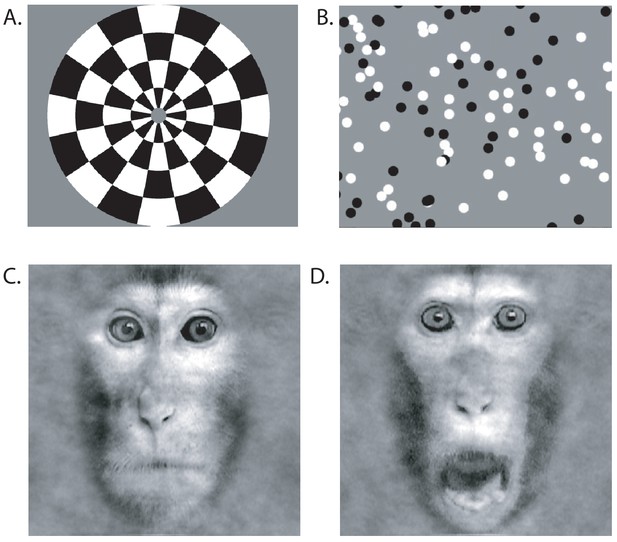
Visual Stimuli for functional MRI.
(A) Contrast reversing checkerboard was used for eliciting basic visual activations (one of two images shown). (B) For eliciting motion-related visual responses, black and white random dots were shown full screen on a mid-grey background moving coherently in one of the four cardinal direction. (C) Face stimuli were either neutral or (D) threatening.
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.42325.020





