Glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis and remodeling are required for neural tube closure, heart development, and cranial neural crest cell survival
Figures
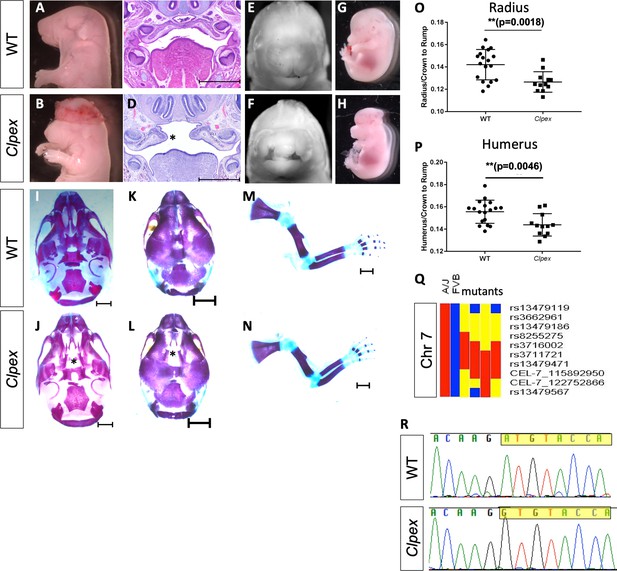
The Clpex mutant phenotype is caused by a hypo-morphic mutation in Pgap2.
Whole mount E18.5 (A,E) and E15.5 (G) WT embryos. Whole mount E18.5 (B, F) and E15.5 (H) Clpex mutant embryos. H&E staining of WT E15.5 (C) and Clpex (D) coronal sections. Skeletal preparation of WT skull ventral view (I), dorsal view (K). Skeletal preparation of Clpex mutant skull ventral view (J) and dorsal view (L). Asterick indicates absent palatine bone in mutant (L). Skeletal preparation of WT limb (M), and Clpex mutant limb (N). Quantification of WT and mutant radial (O) and humeral (P) length normalized to the crown to rump ratio. Mapping data for Clpex mutation (Q). Sanger sequencing of Pgap2 exon three in WT and Clpex mutant with exon three highlighted starting at the initiating methionine (R). Scale bar indicates 500 μm in C,D and 1 mm in I-N. (**p<0.01).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Length of radius and humerus in wildtype and Clpex mutants.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.004
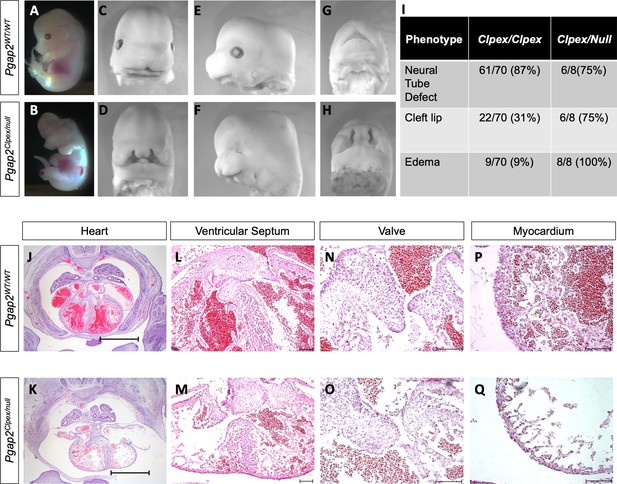
Pgap2null allele fails to complement Pgap2Clpex allele.
Whole mount image of E13.5 WT (A,C,E,G) and Pgap2Clpex/null mutant (B,D,F,H). Penetrance of some key phenotypes is compared in I. Cardiac histology of E14.5 WT (J) and Pgap2Clpex/null mutant (K,), scale bar indicates 1 mm. Higher power images of the ventricular septum (L, M), valve (N, O), and myocardial wall (P, Q). Scale bar indicates 100 μM in L-Q.

Pgap2 alternative transcripts.
UCSC Genome Browser view of Pgap2 with multiple alternative transcripts with Pgap2-225, Pgap2-203, and Pgap2-204 labeled with the start codon mutated in Clpex allele boxed in red and the start codon utilized by Pgap2-203 boxed in blue (A). Protein sequence alignment of canonical transcript Pgap2-225 and variant Pgap2-203 (B). The alignment shows a 89.9% identity in which most of the unaligned amino acids are in the C-terminal tail due to alternative start site usage.
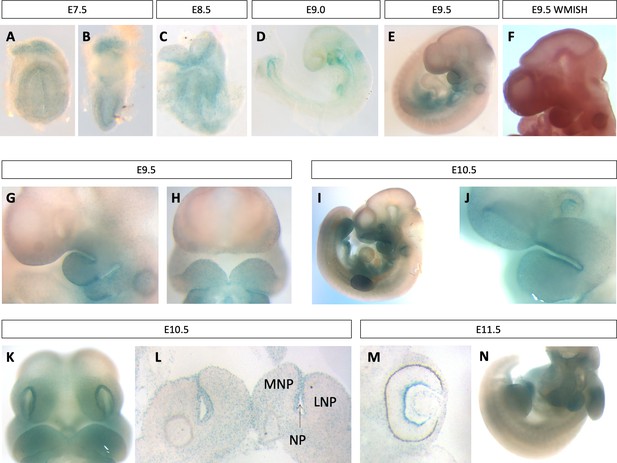
Pgap2 is expressed in neural and craniofacial tissues during development.
Whole mount Pgap2 Xgal staining in E7.5 (A–B), E8.5 (C), E9.0 (D) E9.5 (E, G, H), E10.5 (I–L), and E11.5 (M,N). Pgap2 RNA in situ hybridization at E9.5 (F). Transverse section through the lip at E10.5 (L) at the future site of lip closure. Expression is seen in the ganglion cell layer of the retina at E11.5 (M). LNP = lateral nasal process, MNP = medial nasal process, NP = nasal pit.
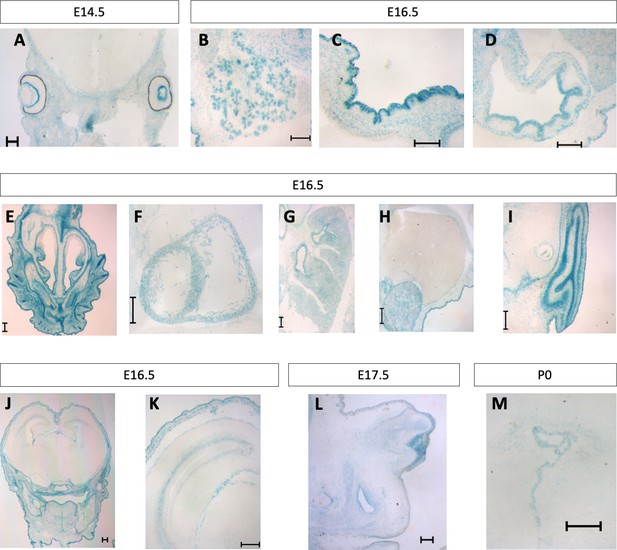
Pgap2 expression at later embryonic and early postnatal stages.
Xgal section staining of Pgap2-LacZ in the eye (A), salivary gland (B), epidermis (C), stomach (D), nasal conchae (E), myocardium (F), lung parenchyma (G), kidney (H), ear (I), cerebral cortex (J, K), genital tubercle (L) and brain/choroid plexus (M). Scale bar indicates 200 um.
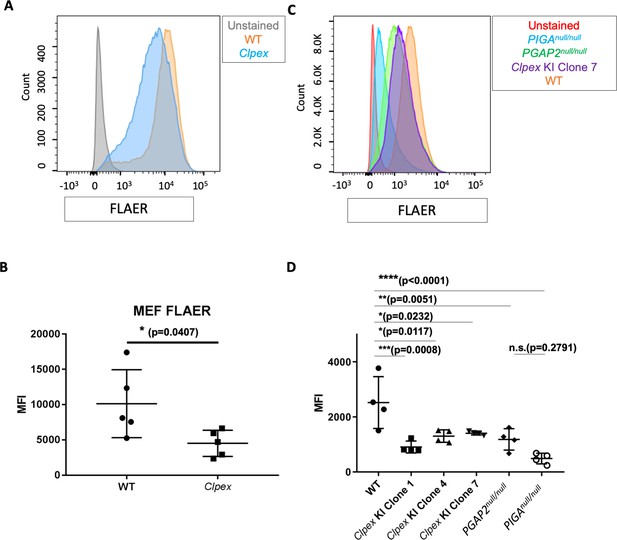
Pgap2 is required for proper anchoring of GPI-APs.
(A) FLAER staining of WT (orange) and Clpex (blue) MEFs, (unstained control in gray) with quantification of Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) (B). FLAER staining of WT (orange) Clpex KI Clone 7 (purple), PGAP2-/- (green), PIGA-/- (blue) HEK293T cells, and unstained control (red) (C) with quantification of MFI (D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
FLAER Staining (MFI) of MEFs and HEK clones.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.012
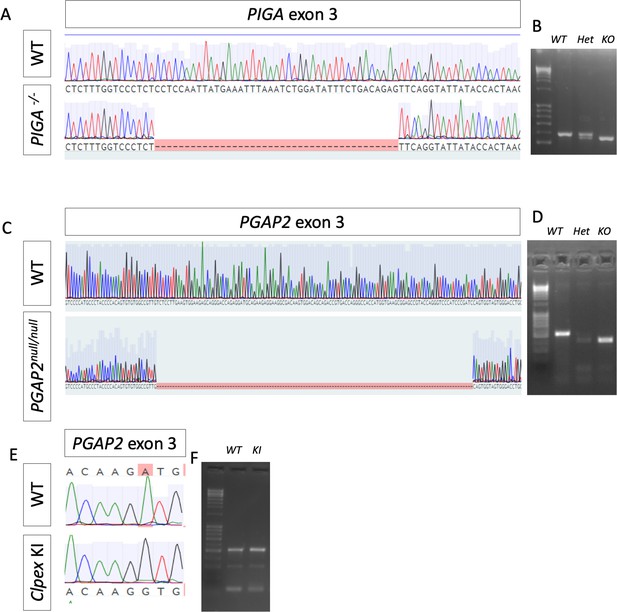
Sequencing of CRISPR/Cas9 generated PIGAnull/null, PGAP2 null/null, and Clpex KI 293T clones.
WT human sequence and Sanger Sequencing of PIGA null/null, clone showing a 29 bp deletion in PIGA exon 3 (A). PCR of exon 3 of PIGA showing a heterozygous clone with a small deletion and the KO with the 29 bp deletion (B). Sanger Sequencing of WT 293T PGAP2 exon three and PGAP2-/- clone showing a 121 bp deletion (C). PCR of PGAP2 exon three showing WT 293T, heterozygous clone with two deletions and the PGAP2-/- clone with a single large deletion (D). Sanger Sequencing of PGAP2 exon three in WT 293T and Clpex Knock-in (KI) clone with the highlighted A > G mutation (E). PCR of PGAP2 exon three with WT 293T and Clpex KI clone DNA (F).
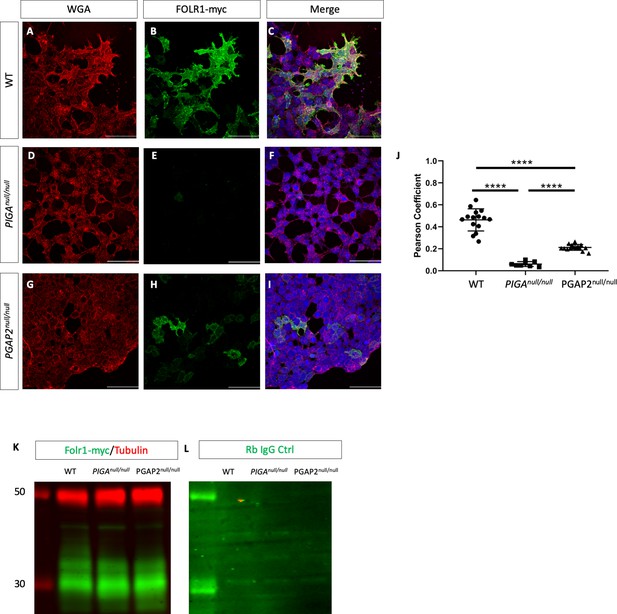
Trafficking of FOLR1 to the cell membrane requires GPI biosynthesis and remodeling.
Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining in WT (A), PIGAnull/null (D), PGAP2null/null (G) HEK293T cells. FOLR1-myc staining in WT (B), PIGAnull/null (E), PGAP2null/null (H) HEK293T cells. Merge of WGA and FOLR1 for WT (C), PIGAnull/null (F), and PGAP2null/null (I). Pearson Coefficient for co-localization of WGA and FOLR1-myc (J). Western blot for αmyc-FOLR1 (green) and αTubulin (red) loading control from cell lysates of WT, PIGAnull/null, and PGAP2 null/null cells overexpressing N-myc tagged FOLR1 (K) and Rabbit IgG control for the same cell lysate (L). ****p<0.0001, Scale bar indicates 100 μM.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of co-localization of WGA and Folr1-myc staining.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.014
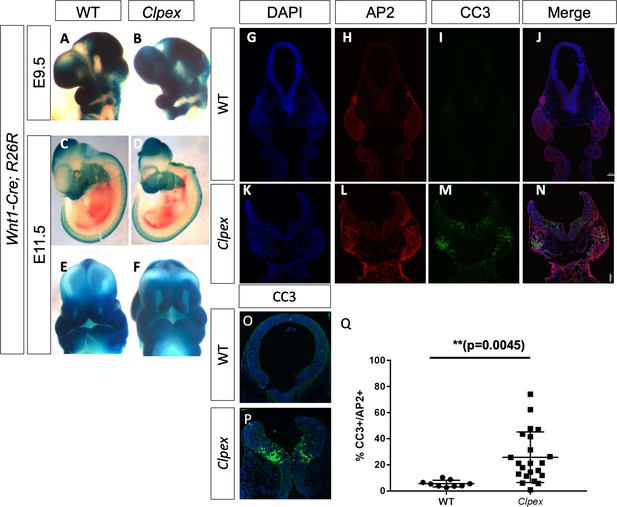
Clpex cNCCs and neuroepithelium undergo apoptosis at E9.5.
Wnt1-Cre, R26R NCC lineage trace in WT (A, C, E) and Clpex mutant (B,D,F) at E9.5 (A,B) and E11.5 (C–F). WT E9.5 embryo stained for DAPI (G), AP2 (H) CC3 (I) and merged image in (J). Clpex E9.5 embryo stained for DAPI (K), AP2 (L) CC3 (M), and merged image in (N). Higher power image of WT (O) and Clpex mutant (P) neuroepithelium stained with CC3 and DAPI. Quantification of CC3+ cells over AP2+ cells in the first branchial arch Region of Interest (Q). **p<0.01. Scale bar indicates 100 μm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Quantification of CC3-positive and AP2-positive cells in wildtype and mutant.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.017
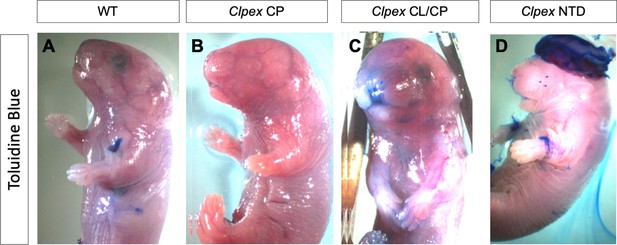
Clpex mutants do not display a defect in barrier formation.
E18.5 WT (A), Clpex cleft palate mutant (B), Clpex cleft lip/cleft palate mutant (C), and Clpex neural tube defect mutant (D) stained with Toludine Blue.
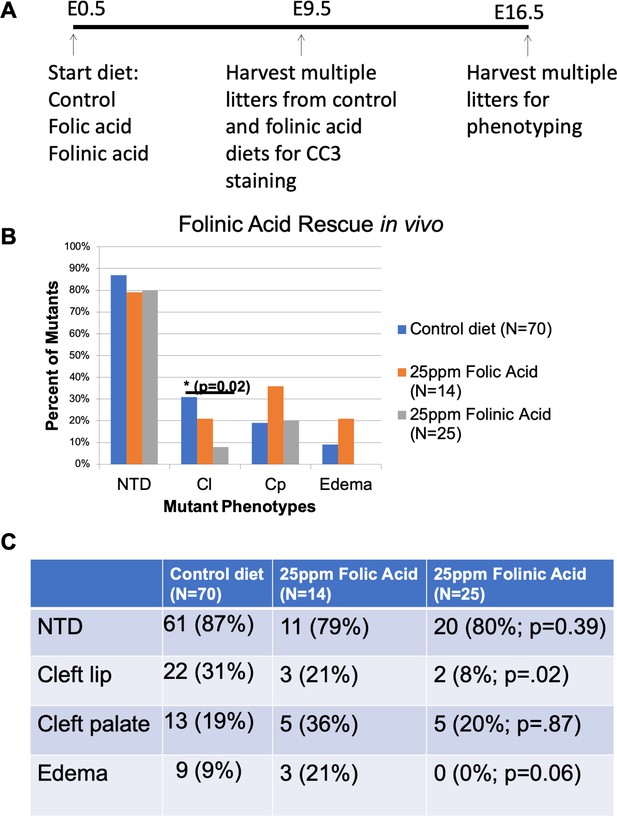
Folinic Acid treatment in utero partially rescues the cNCC apoptosis and cleft lip in Clpex mutants.
Schema of diet regimen to evaluate apoptosis and phenotypic rescue in Clpex mutants treated with control, 25ppm folic acid, or 25ppm folinic acid diet in utero (A). Phenotypes observed in Clpex mutants from litters treated from E0-E16.5 with control diet (blue), 25ppm folic acid (orange), or 25ppm folinic acid (gray) (B). Summary of the phenotypes of Clpex mutants from litters treated with the indicated diets (C). (*p<0.05).
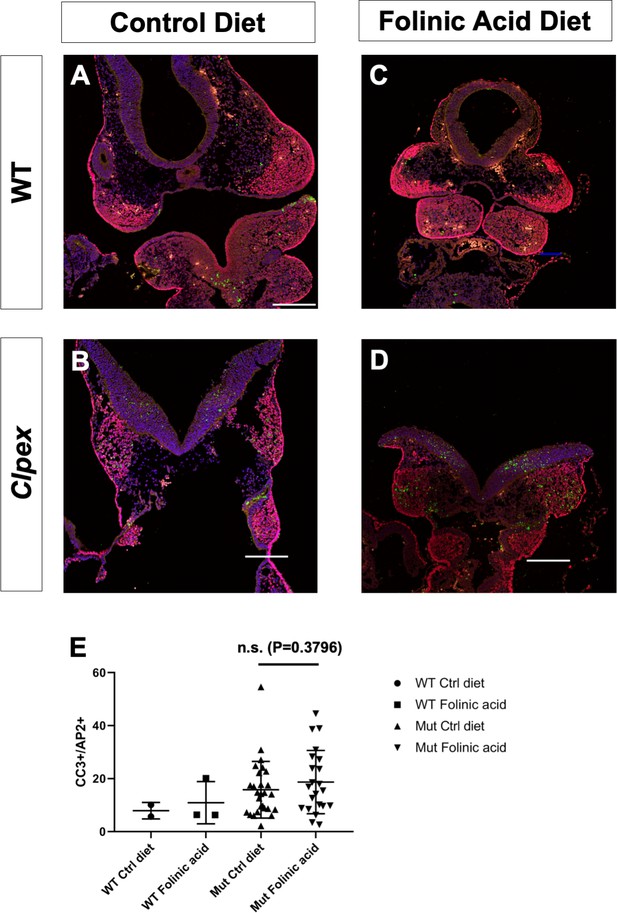
Folinic acid treatment of Clpex embyos does not rescue neural crest cell apoptosis.
WT E9.5 embryo (A) and E9.5 Clpex mutant embryo (B) from litters of pregnant dams fed a control diet from E0.5-E9.5. WT E9.5 embryo (C) and E9.5 Clpex mutant embryo (D) from litters of pregnant dams fed a 25ppm folinic acid diet from E0.5-E9.5. Coronal sections of the first arch stained for AP2 (red), Cleaved Caspase 3 (green), and counterstained with DAPI. Quantification of CC3 +spots/AP2 +spots in the first arch Region of Interest (E). n.s. = not significant.
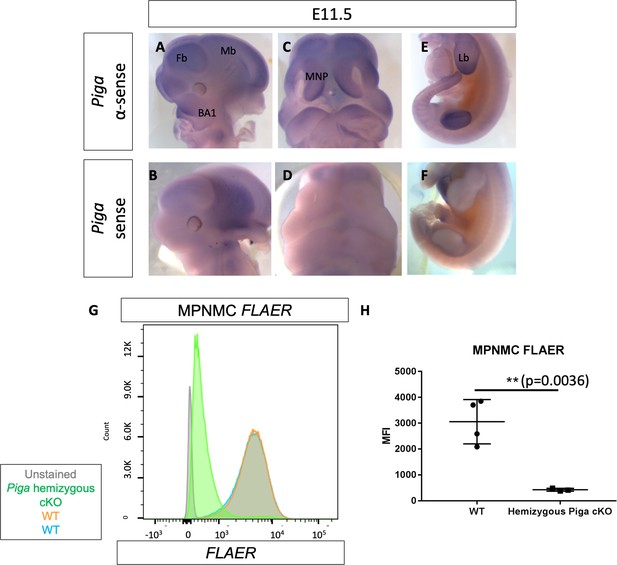
Piga is expressed in the first branchial arch, medial nasal process, limb bud and deletion of Piga in the Wnt1-Cre lineage results in NCC cells that lack GPI biosynthesis.
WMISH of WT E11.5 embryo stained with αsense Piga probe (A, C, E) or sense Piga probe (B, D, E). FLAER flow cytometry staining of WT (orange, blue) and Piga hemizygous cKO MPNMCs (green). FLAER MFI quantified (H). Fb = Forebrain, Mb = Midbrain, BA1 = Branchial Arch 1, MNP = Medial Nasal Process, Lb = Limb bud. **p<0.01.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
MPNMC FLAER MFI.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.024
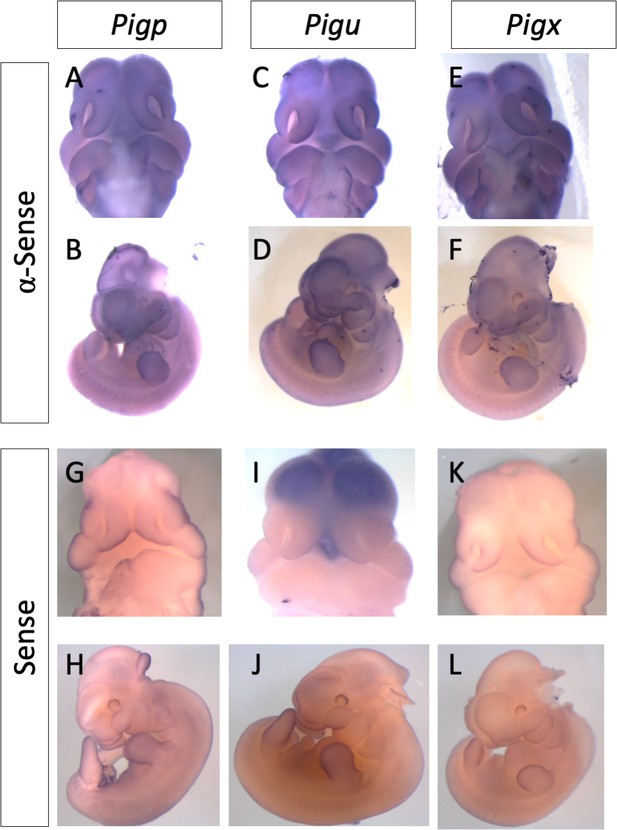
GPI biosynthesis genes show increased expression in the first branchial arch, limb bud, and forebrain.
WT E11.5 RNA in situ hybridization with α-sense (Pigp) (A,B) and sense control probe (G,H); Pigu α-sense probe (C,D) and sense control probe (I,J) and Pigx α-sense probe (E,F) and sense control probes (K,L).
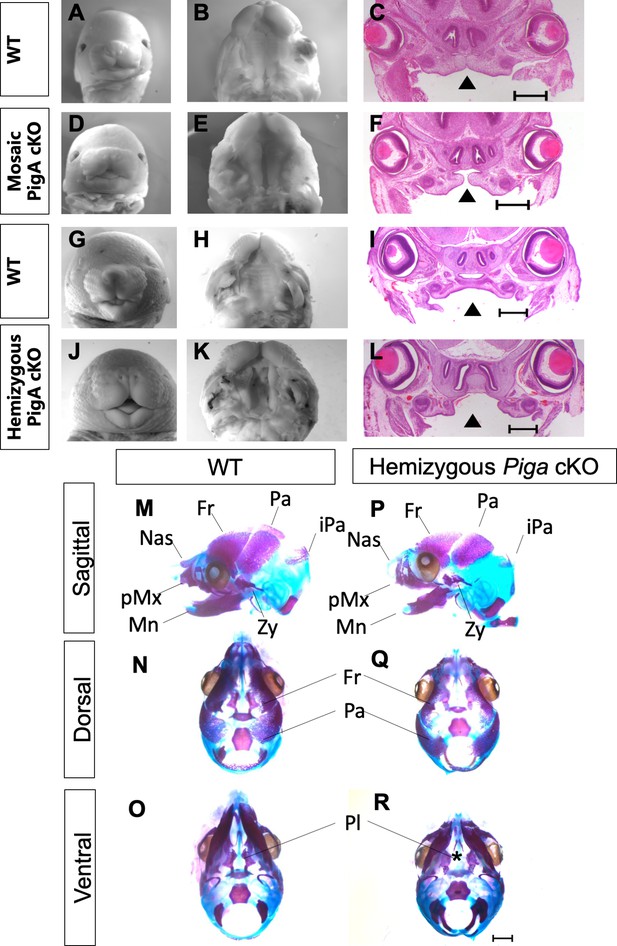
Conditional knockout of Piga abolishes GPI biosynthesis in NCCs and leads to median cleft lip/palate and craniofacial hypoplasia.
Whole mount images of E15.5 WT (A), mosaic Piga cKO (D), E16.5 WT (G) and hemizygous Piga cKO (J). Ventral view of the secondary palate of E15.5 WT (B), Mosaic cKO (E), E16.5 WT (H) and hemizygous cKO (K). H and E staining of E15.5 WT (C), mosaic cKO (F), E16.5 WT (I), and hemizygous cKO (L), arrowhead indicates cleft palate. Alazarin red and alcian blue staining of E16.5 WT skull (M–O) and hemizygous Piga cKO skull (P–R). Asterick indicates cleft palate. Fr = Frontal bone, Pa = Parietal bone, iPa = interparietal bone, Zy = Zygomatic bone, Mn = Mandible, pMx = Premaxilla, Nas = Nasal bone. Scale bar indicates 500 μM in C, F, I, L and 1 mm in M-R.
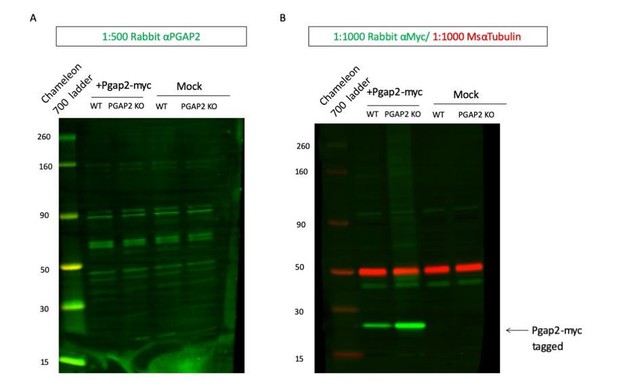
Commercial Pgap2 antibody does not detect overexpressed or endogenous PGAP2.
10μg lysate from overexpression of mouse Pgap2-myc tagged clone (Origene #MR203189) in WT (lane 2) or Pgap2 KO 293T (lane 3) or lysate from mock transfection of WT (lane 4) or Pgap2 KO 293T (lane 5) probed with 1:500 Rb αPGAP (Thermo #PA5-64091, Green). (A) 10μg lysate from overexpression of mouse Pgap2-myc tagged clone in WT (lane 2) or Pgap2 KO 293T (lane 3) or lysate from mock transfection of WT (lane 4) or Pgap2 KO 293T (lane 5) probed with 1:1000 Rb αMyc (Abcam #ab9106, Green) or Ms αTub (Red) (B).
Tables
Exome analysis identifies variant in Pgap2.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.005| Variant filters | Number |
|---|---|
| Total variants | 145,956 |
| Homozygous in all three mutants | 120,393 |
| Chromosome 7 | 5854 |
| 81–125 Mb | 2196 |
| ‘High’ impact | 9 |
| Not in dbSNP | 7 |
| Single base pair change | 1: Pgap2 |
RNA sequencing ToppGene pathway enrichment analysis.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.020| GO Category ID | GO Category Name | p-value | q-value Bonferroni | q-value FDR B&H | q-value FDR B&Y | Hit Count in Query List | Hit Count in Genome | Hit in Query List |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0043565 | Sequence-specific DNA binding | 1.79E-07 | 1.53E-04 | 1.53E-04 | 1.12E-03 | 39 | 1096 | CDX2, CDX4, CIART, MYT1, EVX1, BCL11A, NR6A1, LHX8, HMX1,HNF4A, HOXA1, HOXD11, NHLH1,NHLH1, NHLH2, HAND1, TBXT, CREB3L3,NR1H4, PHF21B, TBX15, ALX3,FOXN4, ESX1, POU6F1, EBF1,IFI16, NKX1-2, HEYL, ZSCAN10,NKX2-4, EGR2, NKX2-1, NR2E1, FOXI2, SIX2 |
| GO:0017127 | Cholesterol transporter activity | 1.10E-06 | 9.41E-04 | 4.71E-04 | 3.45E-03 | 5 | 14 | ABCA1, APOA1, APOA2, APOA4 , APOB |
| GO:0034185 | Apolipoprotein binding | 2.34E-06 | 2.01E-03 | 6.68E-04 | 4.90E-03 | 5 | 16 | ABCA1, MAPT, PLG, PCSK9, LIPC |
Anterior/posterior transcription factors differentially expressed in Clpex mutants compared to controls.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.021| Table 3A | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior TFs | TPM | |||
| Gene | Log2 FC | p-value | Wild-type | Clpex |
| Lhx8 | -1.56 | 0.004589 | 1.95 | 0.59 |
| Alx3 | -0.71 | 0.001724 | 18.68 | 10.36 |
| Nkx2-4 | -2.37 | 0.009815 | 1.89 | 0.31 |
| Hmx1 | -1.75 | 3.308E-06 | 3.9 | 1.04 |
| Table 3B | ||||
| Posterior TFs | TPM | |||
| Gene | Log2 FC | p-value | Wild-type | Clpex |
| Cdx2 | 1.89 | 0 | 4 | 13.53 |
| Cdx4 | 2.04 | 0 | 3.21 | 12.12 |
| Evx1 | 1.60 | 3.14E-08 | 1.06 | 2.97 |
| Hoxc10 | 1.12 | 8.57E-11 | 10.01 | 19.83 |
| Hoxd11 | 1.07 | 1.69E-06 | 2.43 | 4.59 |
| Nkx1-2 | 1.77 | 2.50E-12 | 1.97 | 6.13 |
| Tbxt | 1.69 | 0 | 3.35 | 9.89 |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus Musculus) | Pigaflox | Riken | Riken:B6.129-Pigatm1 RRID:IMSR_RBRC06211 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus Musculus) | Wnt1-Cre | Jackson Laboratories | JAX:B6.Cg-H2afvTg(Wnt1-cre)11RthTg(Wnt1-GAL4)11Rth/J RRID:IMSR_JAX:003829 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus Musculus) | R26R LacZ reporter | Jackson Laboratories | JAX:B6.129S4 Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1Sor/J; R26RTg RRID:MGI:2176735 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus Musculus) | Pgap2null | EUCOMM | EUCCOM: Pgap2tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi RRID:IMSR_EM:09276 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus Musculus) | Clpex | Stottmann et al., 2011 | In house: Pgap2Clpex RRID:MGI:5056383 | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens, kidney) | HEK 293 T cell | ATCC | ATCC: #CRL-11268 RRID:CVCL_1926 | |
| Antibody | sheep polyclonal anti-Digoxigenin | Roche | Roche: #11093274910 RRID:AB_2734716 | (1:5000) |
| Antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-myc | Abcam | Abcam: #ab9106 RRID:AB_307014 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | 488-congugated goat polyclonal anti-rabbit | Thermo | Thermo: #A11008 RRID:AB_143165 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-AP2 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | DSHB: #3B5 supernatant RRID:AB_528084 | (1:20) |
| Antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-Cleaved Caspase 3 | Cell Signaling Technology | CST: #9661 RRID:AB_2341188 | (1:300) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-myc | Sigma | Sigma: #M4439-100UL RRID:AB_439694 | (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Tubulin | Sigma | Sigma: #T6199 RRID:AB_477583 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | goat anti-rabbit IRDye 800CW | LICOR | LICOR: # 926–32211 RRID:AB_621843 | (1:15000) |
| Antibody | goat anti-mouse IRDye 680Rd | LICOR | LICOR: #926–68070 RRID:AB_10956588 | (1:15000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | paired-end RNA sequencing | Beijing Genomics Institute-Americas | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | BBSI enzyme | New England Biolabs | NEB: R0539S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MEGAclear Transcription Clean-up kit | Thermo | Thermo: #AM1908 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Alexafluor-488 proaerolysin (FLAER) | CedarLane Labs, Burlington, Ontario | Cedarlane Labs: #FL1-C, 25 µg | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 25ppm folic acid diet | Envigo | Envigo: Custom diet TD.160472 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 25ppm folinic acid diet | Envigo | Envigo: Custom diet TD.160746 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Control Diet | Envigo | Envigo: Custom diet TD.160112 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-D-galactopyranoside | Sigma | Sigma: #B4252 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Alcian Blue | Sigma | Sigma: #A3157 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Alazarin Red | Sigma | Sigma: #A5533 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Toluidine Blue | Sigma | Sigma: #89640 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | wheat germ agglutinin Texas Red Conjugate | Thermo | Thermo: #W21405 | (5 µL WGA/1 mL PBS) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Folinic acid | Sigma | Sigma: #F7878-500MG | |
| Software, algorithm | Graphpad Prism | GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris 9.2.1, colocalization function | Oxford Instruments | RRID:SCR_007370 | |
| Software, algorithm | Nikon Elements Software, birghtspot analysis | Nikon Instruments Inc. | RRID:SCR_014329 | |
| Software, algorithm | FASTQC | https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ | RRID:SCR_014583 | |
| Software, algorithm | RSEM-v1.3.0 | Li and Dewey, 2011 | RRID:SCR_013027 | |
| Software, algorithm | Toppgene | https://toppgene.cchmc.org/ | RRID:SCR_005726 | |
| Software, algorithm | Computational Suite for Bioinformaticians and Biologists | https://github.com/csbbcompbio/CSBB-v3.0 | RRID:SCR_017234 | |
| Software, algorithm | Benchling sgRNA design software | Benchling, San Fransisco CA | RRID:SCR_013955 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Piga plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR222212 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Pgap2 plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR2031890 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Pigp plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR216742 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Pigu plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR223670 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Pigx plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR201059 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Lhx8 plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR226908 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Tbxt plasmid | Origene | Origene: #MR223752 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mouse Alx3 plasmid | DNASU | DNASU: #MmCD00081160 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CRISPR/Cas9 PX459M2 puromycin-resistance vector | Ran et al., 2013 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Ultramer with 5' and 3' phosphorothiolate bonds | Integrated DNA Technologies | ||
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | Human N-myc tagged Folr1 plasmid | Sinobiological | Sinobiological: #HG11241-NM |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Pgap2 alternatively spliced transcripts.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.026
-
Supplementary file 2
Primers used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.027
-
Supplementary file 3
Clpex mutants display defects in expression of anterior/posterior patterning genes.
E9.5 WT (A,C) and Clpex mutant (B, D) RNA in situ hybridization with α-sense Alx3 probe, an anterior pattering gene. E9.5 WT (E) and Clpex mutant (F) RNA in situ hybridization with α-sense Lhx8 probe, an anterior patterning gene. E9.5 WT (G) and Clpex mutant (H) RNA in situ hybridization with α-sense Tbxt (Brachyury) probe, a posterior patterning gene. E8.5 WT (I) and Clpex mutant (J) RNA in situ hybridization with α-sense Tbxt (Brachyury) probe, a posterior patterning gene.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.028
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45248.029





