A cis-carotene derived apocarotenoid regulates etioplast and chloroplast development
Figures
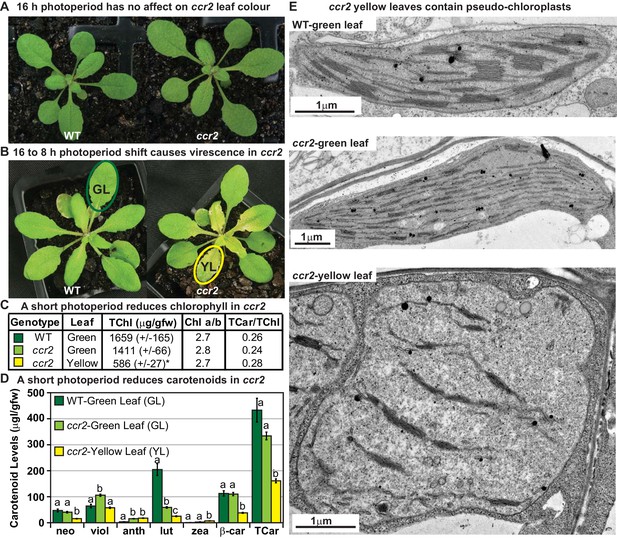

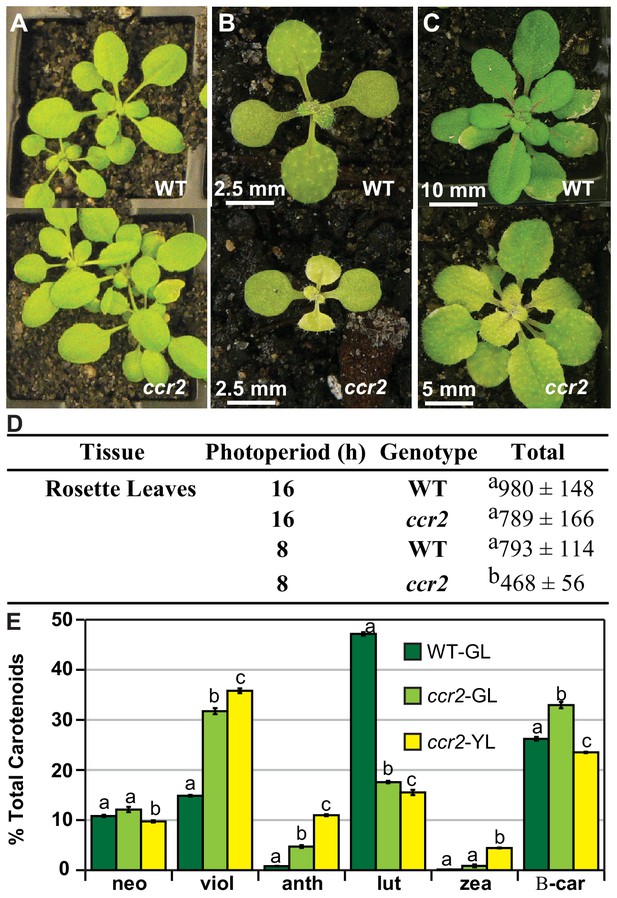
A shorter photoperiod alters plastid development and pigmentation in ccr2.
(A) Three-week-old wild type (WT) and ccr2 plants growing under a 16 hr light photoperiod. (B) Two-week-old plants were shifted from a 16 hr to 8 hr photoperiod for one week and newly emerged or expanded leaves appeared yellow in ccr2 (YL; yellow outline), while WT displayed green leaves (GL; green outline). (C) Chlorophyll levels (µg/gfw) and pigment ratios in green (WT and ccr2) and yellow (ccr2) leaves formed one week after a photoperiod shift from 16 hr to 8 hr. Standard error is shown for TChl (n = 5, single leaf from five plants). Star denotes significant differences (ANOVA; p<0.05). (D) Absolute carotenoid levels (μg/gfw) in green (WT and ccr2) and yellow (ccr2) leaves formed one week after a photoperiod light shift from 16 hr to 8 hr. Values represent average and standard error bars are displayed (n = 5, single leaf from five plants). Lettering denotes significance (ANOVA; p<0.05). Neoxanthin (neo), violaxanthin (viol), antheraxanthin (anth), lutein (lut), zeaxanthin (zea), β-carotene (β-car), Total Chlorophyll (TChl), Chlorophyll a/b ratio (Chl a/b), Total carotenoids (TCar). (E)Transmission electron micrograph images showing representative chloroplasts from WT and ccr2 green leaf sectors as well as yellow leaf sectors of ccr2.
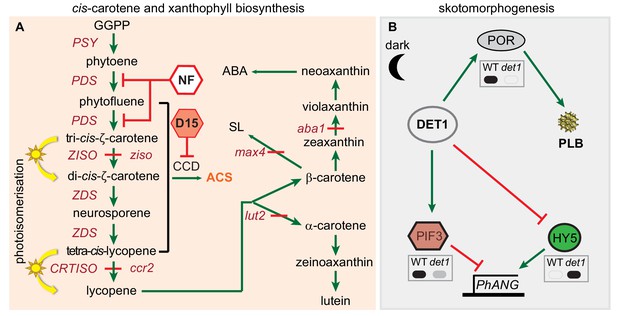
cis-carotene biosynthesis and regulation of PLB formation during skotomorphogenesis.
(A) A pathway for cis-carotene and xanthophyll synthesis. Tri-cis-ζ-carotene and tetra-cis-lycopene are isomerised by ZISO and CRTISO to form di-cis-ζ-carotene and lycopene, respectively. ziso and ccr2 mutants accumulate cis-carotenes (Park et al., 2002; Chen et al., 2010). In the light, photoisomerisation facilitates cis-carotene isomerisation. Norflurazon (NF) inhibits PDS activity. CAROTENOID CLEAVAGE DIOXYGENASE (CCD) activity may cleave cis-carotenes to generate an apocarotenoid signal (ACS) (Kachanovsky et al., 2012; Fantini et al., 2013; Avendaño-Vázquez et al., 2014; Álvarez et al., 2016). Chemical treatment of seedlings with D15 can inhibit CCD activity and enhance carotenoid accumulation (Van Norman et al., 2014). Mutants that block the production of lutein (lut2; lutein-deficient 2), strigolactone (max4-3; more axillary branching 4) and abscisic acid (aba1-3; aba deficient 1) were utilised to interrogate the cause of the ccr2 leaf virescence phenotype. (B) Control of prolamellar body (PLB) formation and protein levels during skotomorphogenesis. DET1 acts as a repressor of photomorphogenesis in etiolated tissues to maintain high PIF3 and low HY5 protein levels, which reduce PHOTOSYNTHESIS ASSOCIATED NUCLEAR GENE (PhANG) expression. det1 mutants do not accumulate PORA and do not form a PLB within the etioplast. Upon de-etiolation, the protein levels DET1 and PIF3 decline and HY5 increases, which induces PhANG expression. Grey insert boxes digitally represent published western protein blots for PORA (Lebedev et al., 1995), PIF3 (Dong et al., 2014) and HY5 (Osterlund et al., 2000) in WT and det1 mutant genotypes. Solid black and grey fills represents high and low protein expression, respectively. Green arrows and red lines represent positive and negative regulation, respectively. Abbreviations: GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate; PSY, PHYTOENE SYNTHASE; PDS, PHYTOENE DESATURASE, ZDS, ζ-CAROTENE DESATURASE; ZISO, ζ-CAROTENE ISOMERASE; CRTISO, CAROTENOID ISOMERASE.
A shorter photoperiod promotes yellow leaf virescence affecting chlorophyll levels and carotenoid composition in ccr2.
(A) WT and ccr2 plants were grown under a lower intensity of light (50 µmol m−2 s−1) and representative images taken 14 DAG. (B) and (C) WT and ccr2 plants were grown under a very short 8 hr photoperiod and representative images taken after 14 (B) and 21 (C) days of growth. (D) Chlorophyll content in immature leaves that recently emerged from WT and ccr2 rosettes 14 DAG. Values represent the average and standard deviations of total chlorophyll content (µg/gfw) from a single leaf sector (n = 2–7 plants). Lettering denotes significance by ANOVA using a post-hoc Tukey test (p<0.05). (E) Percentage carotenoid composition (relative to total) in green (WT and ccr2) and yellow (ccr2) virescent leaves developed one week after a 16 hr to 8 hr photoperiod shift. Values represent average and standard error of means are displayed (n = 5, single leaf from five plants). Lettering denotes significance by ANOVA using a post-hoc Tukey test (p<0.05). Neoxanthin (neo), violaxanthin (viol), antheraxanthin (anth), lutein (lutein), zeaxanthin (zea), β-car (β-carotene), Green Leaf (GL), Yellow Leaf (YL).
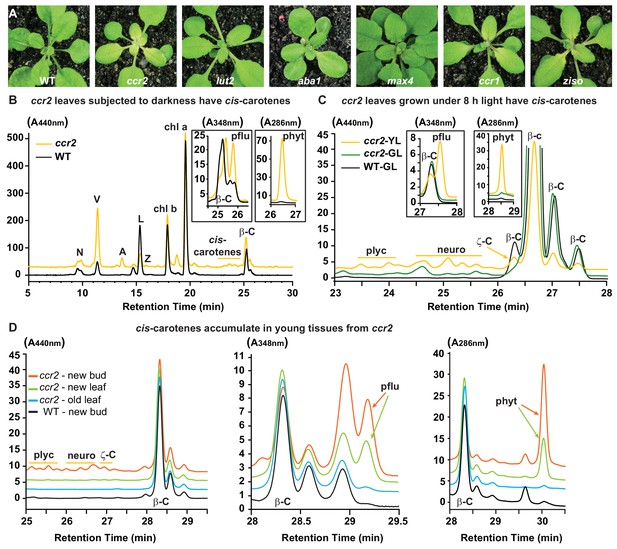
Altered plastid development in ccr2 is linked with cis-carotene accumulation and not to a perturbation in ABA or SL.
(A) Mutants that perturb the levels of lutein, ABA, SL and accumulate cis-carotenes (ccr2, ccr1 and ziso) were grown for two weeks under a 16 hr photoperiod and then shifted to a shorter 8 hr photoperiod for one week. Representative images showing newly emerged and expanding leaves from multiple experimental and biological repetitions (n > 20 plants per line) are displayed. Genetic alleles tested include Col-0 (WT), ccr2-1 (carotenoid isomerase), lut2-1 (epsilon lycopene cyclase), aba1-3 (Ler background) (zeaxanthin epoxidase), max4/ccd8 (carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 8), ccr1-1/sdg8 (set domain group 8) and ziso1-3 (ζ-carotene isomerase). (B) Carotenoid profiles in rosette leaves from three-week-old plants grown under a 16 hr photoperiod and subjected to 6-d of extended darkness. (C) Carotenoid profiles in three-week-old rosette leaves from plants grown under a constant 8 hr light photoperiod. Pigments were profiled in a yellow leaf (YL) and green leaf (GL) from WT and ccr2. (D) Carotenoid profiles in newly emerged floral bud and rosette leaf tissues harvested from four-week-old plants growing under a 16 hr photoperiod. Carotenoid profile traces of various tissue extracts from wild type (WT) and ccr2 show pigments at wavelengths close to the absorption maxima of A440nm (Neoxanthin; N, violaxanthin; V, antheraxanthin; A, lutein; L, zeaxanthin; Z, β-carotene isomers; β-C, chlorophyll a; Chl a, chlorophyll b; chl b, tetra-cis-lycopene; plyc, neurosporene isomers; neuro, and ζ-carotene; ζ-C), A348nm (phytofluene; pflu) and A286nm (phytoene; phyt). HPLC profile y-axis units are in milli-absorbance units (mAU). HPLC traces are representative of multiple leaves from multiple experimental repetitions and retention times vary due to using different columns.
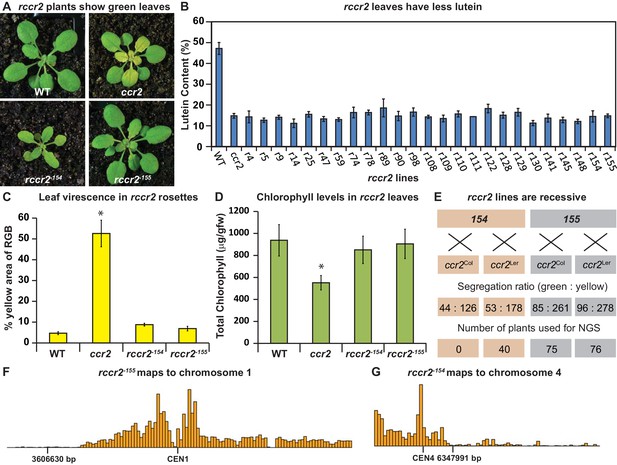
A forward genetics screen identified revertant lines of ccr2 having reduced lutein and normal chlorophyll accumulation when grown under a shorter photoperiod.
(A) Representative images of rccr2−155 and rccr2−154 rosettes one week after shifting two-week old plants from a 16 hr to 8 hr photoperiod. (B) Percentage lutein relative to total carotenoids in immature leaves from WT, ccr2 and rccr2 lines. (C) The degree of leaf virescence detected in rosettes following a reduction in photoperiod. Leaf virescence (% of yellow relative to RGB; Red-Green-Blue) in WT, ccr2, rccr2−154 and rccr2−155 rosettes was quantified using the Lemnatec Scanalyser system and software. (D) Total chlorophyll content in rosette leaves from WT, ccr2, rccr2−154 and rccr2−155 plants exposed to a shorter photoperiod. (E) Segregation ratios of rccr2−154 and rccr2−155 after backcrossing to the ccr2 parent in both Columbia (Col-0) and Landsberg erecta (Ler) ecotypes. (NGS; next generation sequencing) (F) and (G). Leaves were pooled from a segregating F2 progeny of rccr2−155 (F) and rccr2−154 (G) plants and genomic DNA purified for NGS. Bars reflect independent polymorphisms for Ler and/or Columbia SNPs across the Chromosome. The SNP desert indicates there is only Columbia SNP, indicating linkage disequilibrium and less recombination around the location of the causative mutation for ziso−155 (3606630 bp; G to A) and det1−154 (6347991 bp; G to A). Error bars denote standard error of means (SEM) and stars denote statistical significance (ANOVA; p<0.05).
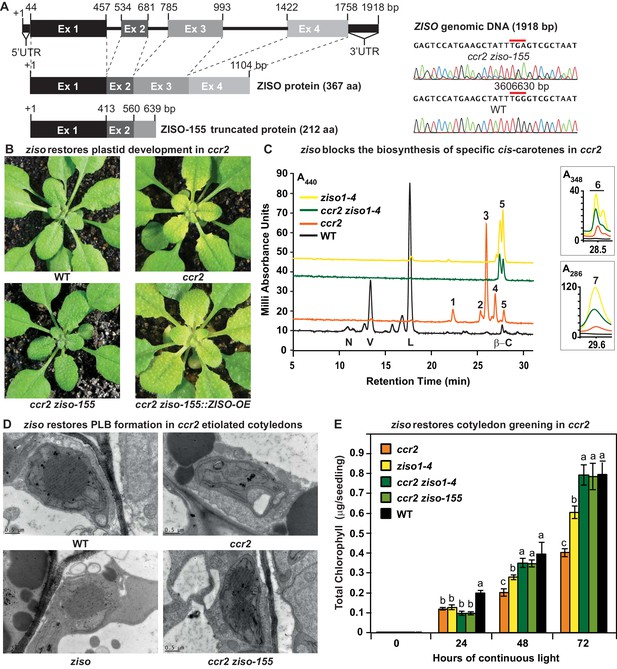
ziso alters cis-carotene profile to restore PLB formation, plastid development and cotyledon greening in ccr2.
(A) Schematic structure of the wild type ZISO gDNA, ZISO protein and the truncated version of the ZISO-155 genomic sequence. ccr2 ziso-155 contains a G->A mutation in AT1G10830 (3606630 bp) as confirmed by Sanger sequencing that results in a premature stop codon (TGA) in exon 3. (B) Rosette images of WT, ccr2, ccr2 ziso-155, and ccr2 ziso-155::ZISO-OE#5 showing leaf pigmentations in newly emerged leaves following a reduction in photoperiod. Images are representative of 84/89 T4 generation ccr2 ziso-155 plants and six independent lines of ccr2 ziso-155::ZISO-OE. (C) Carotenoid profiles of dark grown cotyledons from WT, ccr2, ziso1-4, and ccr2 ziso1-4. Wavelengths close to the absorption maxima of A440nm (major carotenoids and ζ-carotene isomers), A348nm (phytofluene) and A286nm (phytoene) are shown. Neoxanthin (N); violaxanthin (V); lutein (L); β-carotene (β-C); neurosporene (1 and 2); tetra-cis-lycopene (3); pro-neurosporene (4); ζ-carotene (5); phytofluene (6); phytoene (7). (D) Transmission electron micrographs of a representative etioplast from 5-d-old dark grown cotyledons. The etioplasts of WT, ziso and ccr2 ziso-155 show well-developed PLBs, while ccr2 does not have any. Images are representative of 15 plastids from at least 5 TEM sections. (E) Total chlorophyll levels in cotyledons following de-etiolation. WT, ccr2, ziso1-4, ccr2 ziso-155, and ccr2 ziso1-4 were grown in darkness for 4 d, exposed to continuous white light and chlorophyll measured at 0, 24, 48 and 72 hr. Letters within a time point denote statistical analysis by ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test (n > 20 seedlings). Error bars denote standard error of means (SEM).
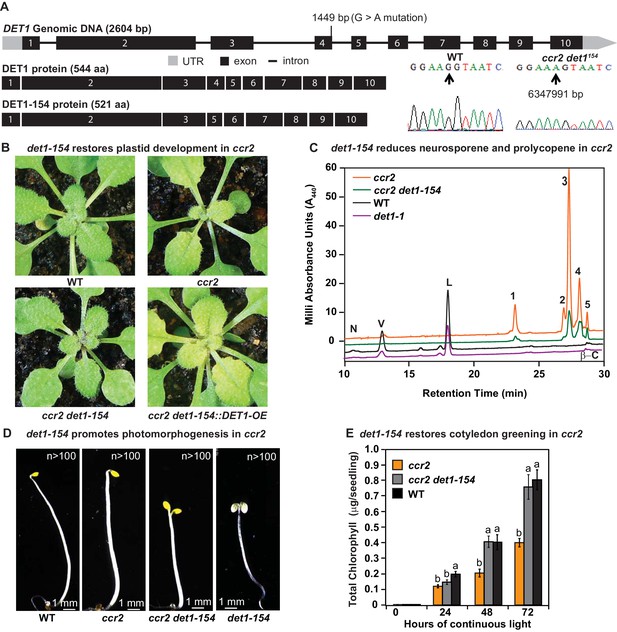
det1 restores PLB formation, plastid development and cotyledon greening in ccr2.
(A) Schematic structure of the wild type DET1 gDNA, DET1 protein and alternative spliced DET1-154 protein. A G->A mutation at the end of exon 4 (1449 bp) of AT4G10180 (6347991 bp) was confirmed by Sanger sequencing that leads to the skipping of exon 4 (69 bp). The DET1-154 splice variant produces a shorter protein (521 aa). Exon 4 comprises 23 amino acids in-frame, having homology to the six-hairpin glycosidase-like (IPR008928) domain. (B) Rosette images of WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154, and ccr2 det1-154::DET1-OE showing leaf pigmentations in newly emerged leaves from plants shifted from a 16 hr photoperiod (2 weeks old) to an 8 hr photoperiod for 1 week. Images are representative of 122/149 T1 generation ccr2 det1-154 plants from 12 independent lines surviving Basta herbicide selection after being transformed with pEARLEY::DET1-OE. (C) Carotenoid profiles of 7-d-old dark grown cotyledons from WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-1 etiolated seedlings. Wavelengths close to the absorption maxima of A440 (major carotenoids and ζ-carotene isomers) show neoxanthin (N); violaxanthin (V); lutein (L), β-carotene (β-C) in WT and neurosporene isomers (1 and 2) tetra-cis-lycopene (3); pro-neurosporene (4), and pro-ζ-carotene (5) in ccr2 and to a less extent in ccr2 det1-154. (D) Etiolated seedling morphology of WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154. Seedlings were grown in the dark for 7 d on MS media without sucrose. Representative images (>100 seedlings from independent experiments) depict a typical apical hook for WT and ccr2, and shorter hypocotyl with open cotyledons for ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154. (E) Chlorophyll levels in cotyledons following de-etiolation. ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and WT were etiolated for 4 d in darkness and thereafter exposed to continuous white light. Chlorophyll measurements were taken at 0, 24, 48 and 72 hr after de-etiolation. Letters within a time point denote statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test (n > 20 seedlings). Error bars denote standard error of means.
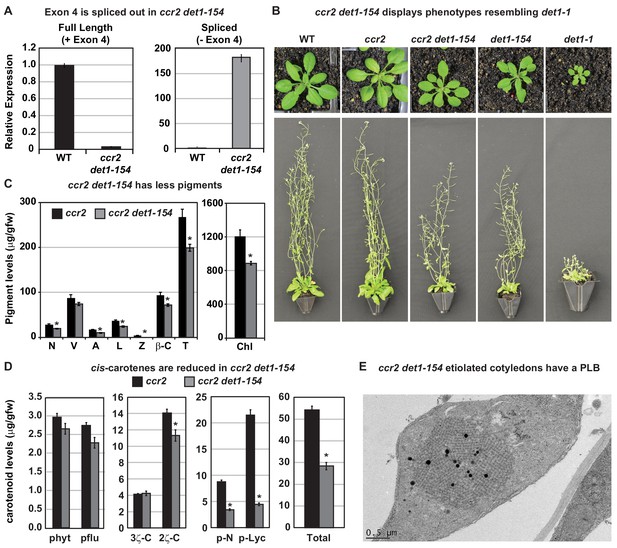
det1-154 has alternative splicing and reduced pigments, cis-carotenes and restored PLB formation in ccr2.
(A) qRT-PCR confirms alternative splicing of exon four in ccr2 det1-154 leaf tissues. Primers were designed to quantify the full length (+ Exon 4; spanning exons 3–4 and 4–5 junctions) and the spliced (- Exon 4: spanning exon 3–5 and 6–7 junctions) DET1-154 mRNA transcript levels in WT and ccr2 det1-154 leaf tissues, respectively. Standard error bars are shown (n = 4). (B) ccr2 det1-154 displays phenotypes resembling det1-1, including a small rosette, shorter floral architecture and partial sterility in comparison to WT and ccr2. (C) ccr2 det1-154 shows reduced pigment levels compared to ccr2. Neoxanthin (N); violaxanthin (V); antheraxanthin (A), lutein (L), β-carotene (β-C), total carotenoids (T) and total chlorophylls (Chl) were quantified at a 440 nm. Mean values are displayed and error bars denote standard error (n = 3). Star denotes significance (ANOVA, p<0.05). Data is representative of multiple experiments. (D) det1-154 reduces cis-carotene content in ccr2. phytoene (phyt), phytofluene (pflu), tri-cis-ζ-carotene (3ζ-C), di-cis-ζ-carotene (2ζ-C), pro-neurosporene (p-N), tetra-cis-lycopene (p-lyc) and total cis-carotenes were quantified at absorption wavelengths providing maximum detection. Star denotes significance (ANOVA, p<0.05). Data is representative of two independent experiments and error bars show standard error (n = 4). (E) Transmission electron micrographs of a representative etioplast from 5-d-old dark grown cotyledons showing a well-developed PLB in ccr2 det1-154.
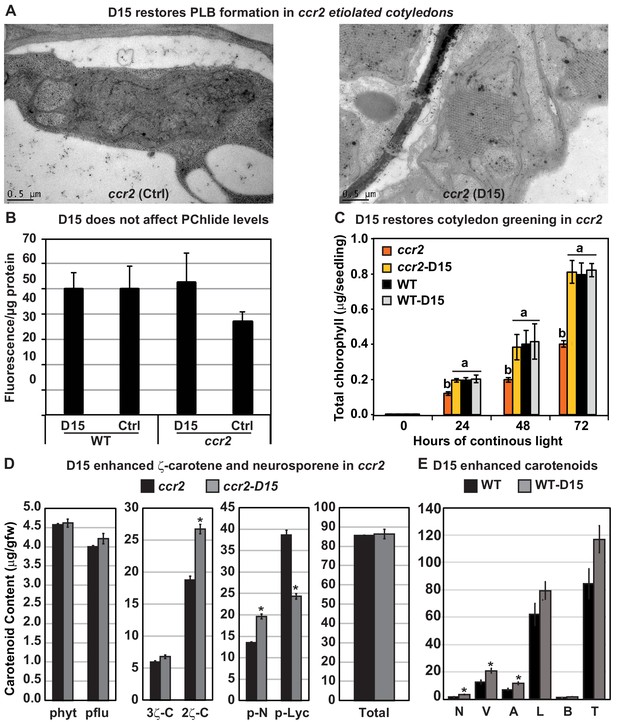
The carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (CCD) inhibitor, D15, restores PLB formation in etiolated ccr2 seedlings, cotyledon greening following de-etiolation and alters cis-carotene accumulation.
(A) Transmission electron micrographs of a representative etioplast from 5-d-old dark grown cotyledons reveal a well-developed PLB in ccr2 treated with the D15, but not in ccr2 treated with ethanol only (control; ctrl). (B) Pchlide levels in Wild Type (WT) and ccr2 treated + /- D15. Fluorescence was measured at 638 nm and 675 nm with an excitation at 440 nm. Net fluorescence of Pchlide was calculated and normalised to protein content. (C) D15 restores chlorophyll accumulation in ccr2 de-etiolated seedlings exposed to continuous light. Twenty seedlings from each of three biological replicates were harvested for chlorophyll determination in every 24 hr under continuous light. Statistical analysis was by ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test (n = 20 seedlings). (D) cis-carotene quantification in etiolated cotyledons of ccr2 treated with D15. phytoene (phyt), phytofluene (pflu), tri-cis-ζ-carotene (3ζ-C), di-cis-ζ-carotene (2ζ-C), pro-neurosporene (p-N), tetra-cis-lycopene (p-lyc) and total cis-carotenes were quantified at absorption wavelengths providing maximum detection. Star denotes significance (ANOVA, p<0.05). Error bars show standard error (n = 4). (E) Quantification of carotenoid levels in etiolated tissues of WT treated with D15. Neoxanthin (N); violaxanthin (V); antheraxanthin (A), lutein (L), β-carotene (β-C) and total carotenoids (T) were quantified at a 440 nm absorption wavelength providing maximum detection. Star denotes significance (ANOVA, p<0.05). Data is representative of two independent experiments.
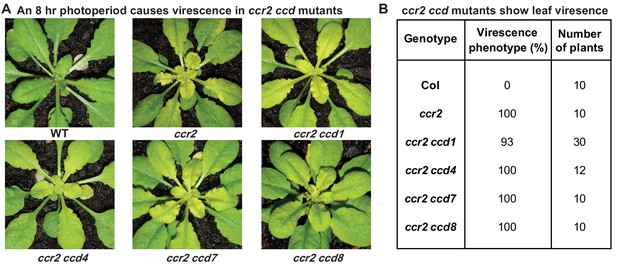
The loss-of-function in individual members of the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase gene family cannot restore plastid development in ccr2 rosettes.
Two-week-old WT, ccr2, ccr2 ccd1, ccr2 ccd4, ccr2 ccd7, and ccr2 ccd8 (F3 homozygous double mutant lines) plants were shifted from a 16 hr to 8 hr photoperiod until newly formed leaves in the ccr2 rosette displayed a virescent leaf phenotype. (A) Representative images of plants showing newly developed leaves in the rosette. (B) Quantification of yellow leaf virescence in individual rosettes from ccr2 ccd double mutants. Data is representative of multiple independent experiments. Statistical analysis by ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey test showed no significant difference in the number of ccr2 and ccr2 ccd plants displaying a virescent phenotype.
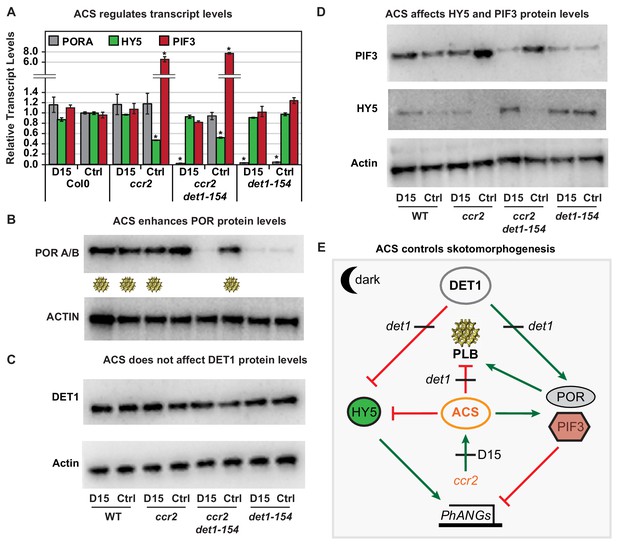
Chemical inhibition of CCD activity revealed how a ccr2 generated apocarotenoid signal transcriptionally up-regulates POR and PIF3 in parallel to det1-154 during skotomorphogenesis.
(A) Transcript levels of PORA, PIF3 and HY5 in WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154 etiolated seedlings growing on MS media (+ /- D15). Statistical analysis denoted as a star was performed by a pair-wise t-test (p<0.05). Error bars represent standard error of means. (B), (C) and (D) Representative western blot images showing POR, DET1, PIF3 and HY5 protein levels, respectively. Proteins were extracted from WT, ccr2 and ccr2 det1-154 etiolated seedlings grown on MS media without (control; Ctrl) or with the chemical inhibitor of CCD activity (D15). The membrane was re-probed using anti-Actin antibody as an internal loading control. Lattice-like symbol below POR western (B), represents formation of a PLB in etiolated cotyledons from that genotype and treatment. (E) Model describing how a cis-carotene derived cleavage product, ACS, regulates POR, HY5, PIF3 and PLB formation during skotomorphogenesis. DET1 maintains skotomorphogenesis by post-transcriptionally maintaining a higher and lower PIF3 and HY5 protein levels, respectively. HY5 promotes and PIF3 represses PhANG expression. det1 mutants trigger photomorphogenesis in that they lack POR mRNA transcripts, protein and a PLB. ccr2 generates ACS that enhances POR mRNA transcript and protein levels that enable PLB formation in det1-154. det1-154 restores PLB formation in ccr2 by blocking a signalling pathway acting independent of POR.
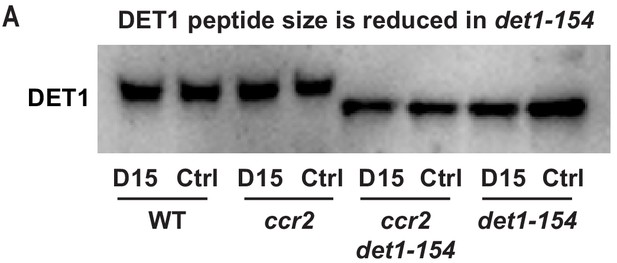
The DET1-154 peptide is smaller in det1-154 mutant genotypes.
(A) Representative western blot image showing the reduced DET1 peptide size in ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154 (59 kDa) compared to WT and ccr2 (62 kDa). Gel electrophoresis of the gel membrane from Figure 7C (electrophoresis for 38 min at 165 volt) was extended for 120 min at 100 volts to resolve the 3 kDa difference in DET1-154 protein size. Under these conditions, the 37 kDa ACTIN peptide and pre-stained ladder were not detected on the membrane. Proteins were extracted from WT, ccr2 and ccr2 det1-154 etiolated seedlings grown on MS media without (control; Ctrl) or with the chemical inhibitor of CCD activity (D15).
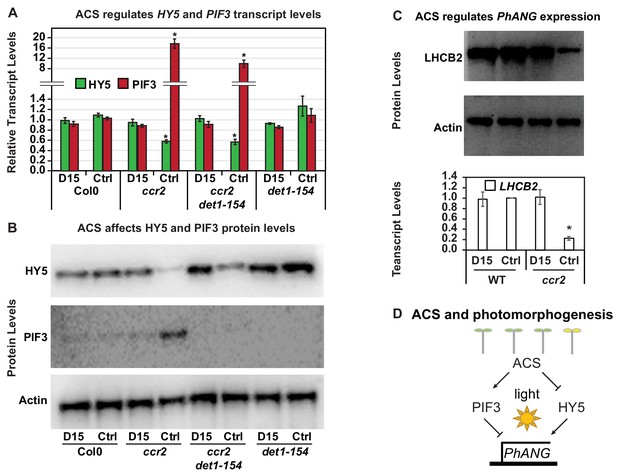
Chemical inhibition of CCD activity revealed how a ccr2 generated apocarotenoid signal transcriptionally represses HY5 and LHCB2 expression during photomorphogenesis.
(A) Transcript levels of PIF3 and HY5 in WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154 de-etiolated seedlings growing on MS media + /- D15. (B) Representative western blot images showing PIF3 and HY5 protein levels in WT, ccr2, ccr2 det1-154 and det1-154 de-etiolated seedlings growing on MS media + /- D15. The membrane was re-probed using anti-Actin antibody as an internal loading control. (C) Protein and transcript levels of LHCB2 expression in WT and ccr2 de-etiolated seedlings growing on MS media + /- D15. (D) Model showing how ACS regulates HY5 and LHCB2 expression in ccr2. Images of seedlings represent are cotyledons are coloured green or yellow to reflect the delay in chlorophyll biosynthesis induced by ACS as evidenced in Figure 6c. De-etiolation of seedlings was performed by transferring 4-d-old etiolated seedlings to continuous light for 3 d to induce photomorphogenesis. Statistical analysis denoted as a star was performed by pair-wise t-test (p<0.05). Error bars represent standard error of means. Ctrl; Control; Ctrl, D15; chemical inhibitor of CCD activity.
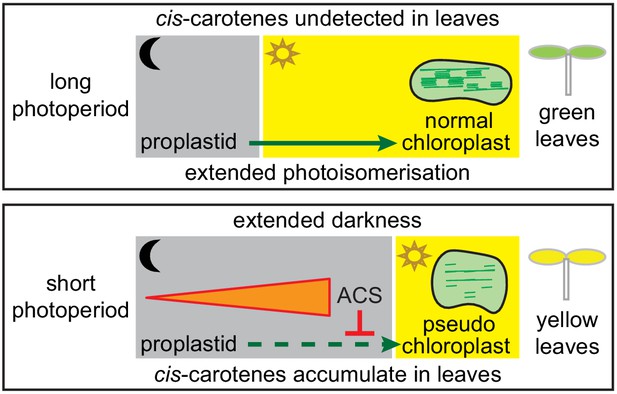
Model showing how a cis-carotene derived apocarotenoid cleavage product controls plastid development in leaves from plants growing under a shorter photoperiod.
Shorter photoperiods that have an extended period of darkness, cause cis-carotenes to accumulate in leaf tissues from plants having impaired or lacking carotenoid isomerase activity. Plants growing under a longer photoperiod are exposed to an extended period of photoisomerisation, which stops cis-carotene from accumulating to detectable levels. A cis-carotene derived apocarotenoid signal (ACS) can perturb proplastid to chloroplast development, leading to the formation of a pseudo-chloroplast with poorly defined thylakoid and grana stacks. As a result, a yellow leaf virescence phenotype becomes visible in newly emerged leaves from carotenoid isomerase mutant plants growing under a shorter photoperiod.
Tables
A cis-carotene derived ACS acts in parallel to DET1 to control PLB formation.
| Germplasm | Hypocotyl Length (mm) | Apical hook | Cotyledon | % PLB (-D15) | % PLB (+D15) | cis-carotenes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | Normal | 13.4 ± 0.2 | Yes | Closed | 100 | 100 | None detected |
| ccr2 | normal | 13.8 ± 0.2 | yes | closed | 0 | 85 | phyt, pflu, ζ-C, p-N, p-Lyc |
| ccr2 det1-154 | shorter | *8.3 ± 0.2 | no | open | 69 | 0 | reduced cis-carotenes |
| det1-154 | shorter | *9.9 ± 0.1 | no | open | ND | ND | phyt, pflu and ζ-C |
-
ND; not determined; p-N; pro-neurosporene, p-Lyc; pro-lycopene (tetra-cis-lycopene), phyt; phytoene, pflu; phytoflurene, ζ-c; ζ-carotene, *; denotes statistical significance (ANOVA, p<0.05).
Contra-regulated differential gene expression in etiolated seedlings and young leaves of ccr2 ziso-155.
| Gene id | GENE | PhANG | Protein encoding description | Etiolated seedlings | Young leaves | det1-1 | NF-1 | NF-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ccr2 | ccr2 ziso-155 | ccr2 | ccr2 ziso-155 | |||||||
| At1g09530 | PIF3 | Transcription factor interacts with photoreceptors and negatively regulates signalling | 30 | 0.1 | 220 | 0.1 | ↓ | −5.0 | NS | |
| At4g10180 | DET1/FUS2 | Encodes a nuclear-localized protein repressor of photomorphogenesis | 5.1 | 0.1 | 5.9 | 0.2 | NS | NS | NS | |
| At3g19390 | Granulin repeat cysteine protease family protein | 4.4 | NS | 6.8 | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| At5g13210 | Unknown conserved expressed protein | 3.8 | NS | 0.4 | NS | ↑ | NS | NS | ||
| At3g45730 | Unknown expressed protein | 2.8 | NS | 2.4 | NS | NS | NS | 10.6 | ||
| At5g43500 | ATARP9 | Encodes an expressed protein similar to actin-related proteins | 2.4 | NS | 2.2 | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| At5g48240 | Unknown expressed protein | 2.1 | NS | 2.2 | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| At2g32950 | COP1/FUS3 | Repressor of photomorphogenesis and induces skotomorphogenesis | 2.0 | 0.0 | 8.9 | 0.1 | ↑ | NS | NS | |
| At5g11260 | HY5 | Transcription factor negatively regulated by COP1, promotes light responsive gene expression | 0.5 | 8.1 | 0.3 | 8.4 | NS | NS | 2.8 | |
| At4g02770 | PSAD1 | Expressed protein with similarity to photosystem I subunit II | 0.5 | NS | 0.5 | NS | ↑ | −12.3 | 0.15 | |
| At3g17070 | Peroxidase family expressed protein | 0.5 | NS | 0.5 | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| At2g31751 | Potential natural antisense gene, expressed protein | 0.4 | NS | 0.5 | NS | NS | NS | NS | ||
| At4g15560 | DXS/CLA1 | yes | 1-deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate synthase activity in MEP pathway | 0.3 | 4.2 | 0.1 | 16.2 | NS | NS | 0.42 |
| At4g34350 | ISPH/CLB6 | yes | 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase in MEP pathway | 0.3 | 9.4 | 0.2 | 11 | ↑ | NS | NS |
| At1g24510 | TCP-1 | T-complex expressed protein one epsilon subunit | 0.3 | 12.0 | 0.1 | 7.9 | NS | NS | NS | |
| At3g59010 | PME35 | Pectin methylesterase that regulates the cell wall mechanical strength | 0.2 | NS | 0.4 | NS | ↓ | NS | NS | |
| At1g29930 | CAB1/LHCB1.3 | yes | Subunit of light-harvesting complex II (LHCII), which absorbs light | 0.2 | 13 | 0.2 | 11 | NS | NS | NS |
| At2g05070 | LHCB2.2 | yes | Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding (LHC) protein that constitute the antenna system | 0.2 | NS | 0.2 | NS | ↑ | −3.6 | NS |
| At5g13630 | GUN5/CHLH | yes | Magnesium chelatase involved in plastid-to-nucleus signalling | 0.2 | 17 | 0.2 | 20 | ↑ | −3.3 | 0.33 |
| At1g67090 | RBCS1a | yes | Member of the Rubisco small subunit (RBCS) multigene family functions in photosynthesis | 0.1 | 67 | 0.1 | 61 | NS | NS | NS |
-
Notes: NS; not significant. Transcriptomic data; det1-1 (Schroeder et al., 2002), norflurazon (NF-1; Page et al., 2017), norflurazon (NF-2; Koussevitzky et al., 2007), PhANG; Photosynthesis associated nuclear gene. Numbers refer to fold change relative to WT = 0 (except for NF-1 where positive and negative numbers indicate up and down-regulation, respectively relative to WT = 1.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Immature ccr2 tissues have an altered cis-carotene and xanthophyll composition.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
D15 and ziso restore PLB formation in ccr2 etiolated cotyledons.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp2-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Transcriptomic analysis of WT, ccr2 and ccr2 ziso-155 etiolated tissues.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Transcriptome analysis of WT, ccr2 and ccr2 ziso-155 immature leaf tissues.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Significantly expressed genes regulated in ccr2 and contra-regulated ccr2 ziso-155 that are common to both etiolated and immature leaf tissues.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp5-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
det1 reduced carotenoids and caused cis-carotenes to accumulate in leaves and etiolated tissues.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp6-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 7
Primer sequences used for qRT-PCR and ccr2 det154 characterisation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-supp7-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/45310/elife-45310-transrepform-v1.docx





