Distinct inflammatory and wound healing responses to complex caudal fin injuries of larval zebrafish
Figures
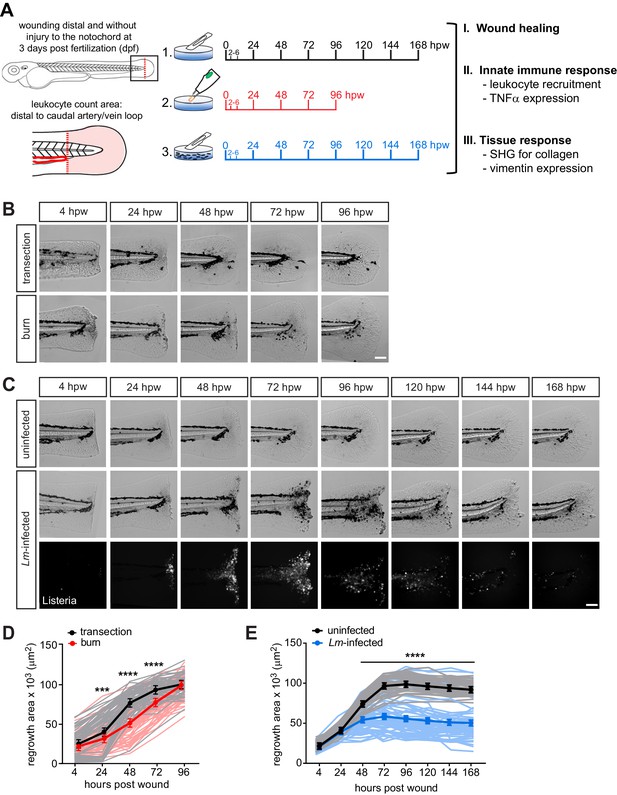
Caudal fin recovers from thermal injury, while wound healing is impaired in the presence of infection.
(A) Experimental schematic and analyses. (B) Single-plane brightfield images of caudal fin area of individual wild-type larvae over time in response to simple transection or thermal injury, and in (D) the corresponding quantification of tissue regrowth area. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates with associated p values. Total N = 62–71 larvae per time point for each treatment. (C) Single-plane brightfield or fluorescent images of caudal fin area of individual wild-type larvae over time in response to uninfected transection or L. monocytogenes (Lm)-infected transection using mCherry-expressing L. monocytogenes, and in (E) the corresponding quantification of tissue regrowth area over time are shown. Values are arithmetic means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. Total N = 39–58 larvae per time point for each treatment. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Lines in lighter color depict values for every larva measured over three biological replicates. Scale bar is 100 microns.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Related to Figure 1D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.004
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Related to Figure 1E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.005
-
Figure 1—source code 1
Related to Figure 1D and E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.006

L. monocytogenes infection during tail wound infection is associated with minimal dissemination and negligible effect on host survival.
(A) Wild-type larvae were wounded (B) or unwounded in presence of mCherry-expressing L. monocytogenes and fixed at indicated time points. 200-micron size z series at 5-micron steps was acquired using Zeiss zoomscope by tile imaging of the whole embryo. Maximal intensity projections of mCherry channel are displayed. Scale bar is 500 micron in whole embryo images, and 100 micron in the zoomed inset. Representative images are shown from three biological replicates; at least 10 embryos were imaged per time point per replicate. (C) an example where L. monocytogenes has disseminated is shown from each biological repeat. (D) Wild-type larvae were wounded in presence of unlabeled L. monocytogenes and survival was monitored. Data represents three biological replicates, where N indicates the total number of embryos pooled from the replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using R version 3.4 (www.r-project.org) as previously described (Vincent et al., 2016).
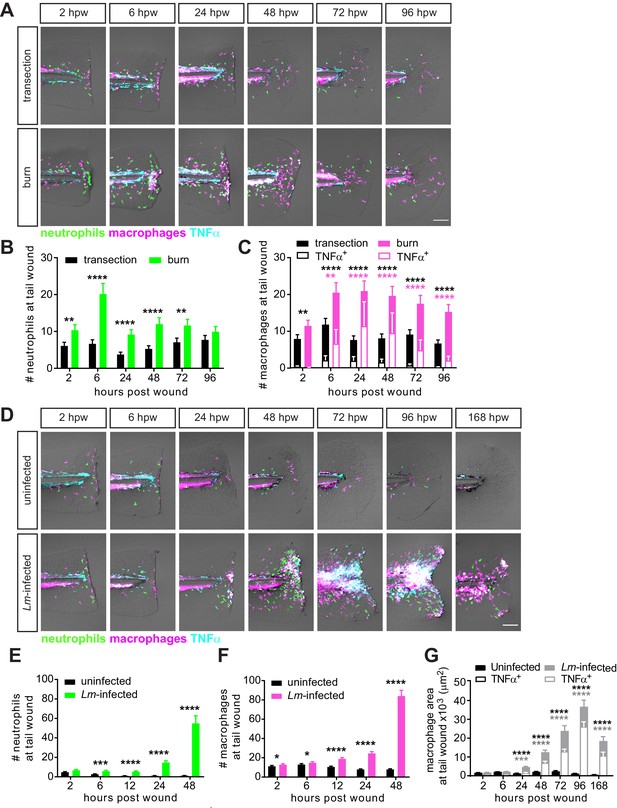
Caudal fin injuries trigger distinct inflammatory responses.
(A) Sum-projections of z-stacks acquired by laser scanning confocal microscope using triple transgenic larvae (Tg(tnf:GFP) x Tg(lysC:BFP/mpeg1:mCherry-CAAX)) over time in response to simple transection or thermal injury. Merged channels are displayed; single channels are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Scale bar is 100 microns. Leukocyte recruitment was quantified by counting (B) neutrophils and (C) macrophages in the caudal fin tissue distal to the caudal artery/vein loop (Figure 1A). In parallel, TNFα expression in macrophages was monitored using TNFα reporter and scored as negative or positive for expression, and TNFα-positive counts are shown in (C). Values in (B) and (C) are least square means and SE from four biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 28–44 larvae per time point for each treatment. **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001; black and magenta * depict p values for leukocyte and TNFα-positive counts, respectively. p values for comparing time points within each injury are provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 2A,B. (D) Sum-projections of z-stacks acquired by laser scanning confocal microscope using triple transgenic larvae (Tg(tnf:GFP) x Tg(lysC:BFP/mpeg1:mCherry-CAAX)) over time in response to uninfected or Lm-infected transection. Merged channels are displayed; single channels are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Scale bar is 100 microns. Leukocyte recruitment was quantified using double transgenic larvae (Tg(lysC:mCherry-histone2b) x Tg(mpeg1:GFP-histone2b)) where (E) neutrophils and (F) macrophages were counted in caudal fin area distal to the caudal artery/vein loop in single-plane images acquired by Zeiss Zoomscope. TNFα expression in macrophages (G) was quantified by area thresholding (see Materials and methods and Figure 2—figure supplement 2E) using images in (D). For clarity, values in (G) for the uninfected transection are also shown separately in Figure 2—figure supplement 2F. Values in (E) and (F) are least square means and SE from four biological replicates, with associated p values. Values for macrophages were fitted with poisson distribution. Total N = 30–60 larvae per time point for each treatment. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Values in (G) are arithmetic means and SE from three experimental replicates with associated p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. Total N = 12–27 larvae per time point for each treatment. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; black and gray * depict p values for macrophage and TNFα-positive areas, respectively.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Related to Figure 2B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.011
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Related to Figure 2C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.012
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Related to Figure 2C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.013
-
Figure 2—source data 4
Related to Figure 2E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.014
-
Figure 2—source data 5
Related to Figure 2F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.015
-
Figure 2—source data 6
Related to Figure 2G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.016
-
Figure 2—source data 7
Related to Figure 2G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.017
-
Figure 2—source code 1
Related to Figure 2B,C and E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.018
-
Figure 2—source code 2
Related to Figure 2F.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.019
-
Figure 2—source code 3
Related to Figure 2G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.020
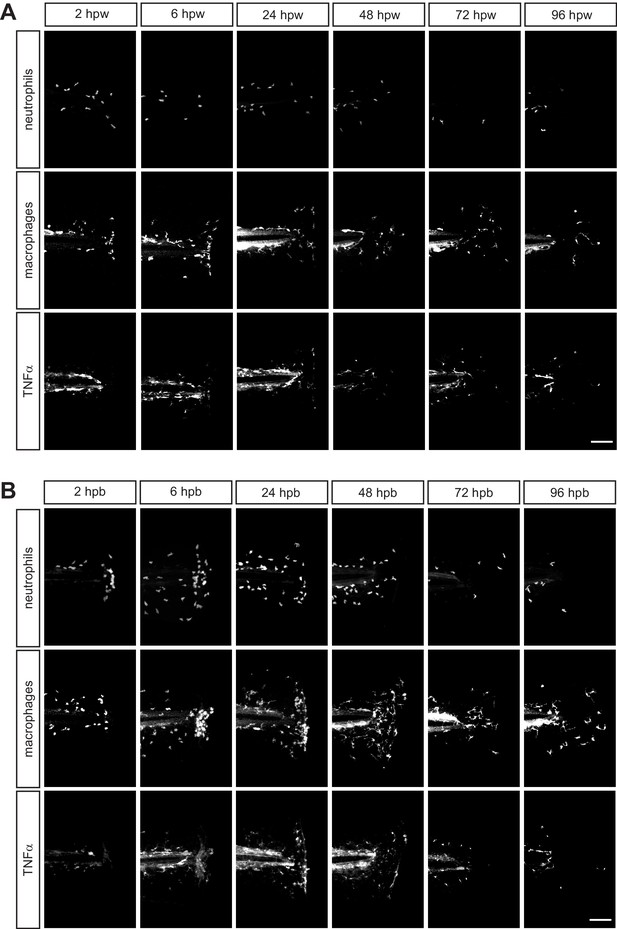
Leukocyte recruitment in response to thermal injury.
Single channels associated with merged images in Figure 2A showing (A) transection and (B) burn image sets. Neutrophils, macrophages and TNFα were labeled with BFP, mCherry and GFP respectively. Scale bar is 100 micron.
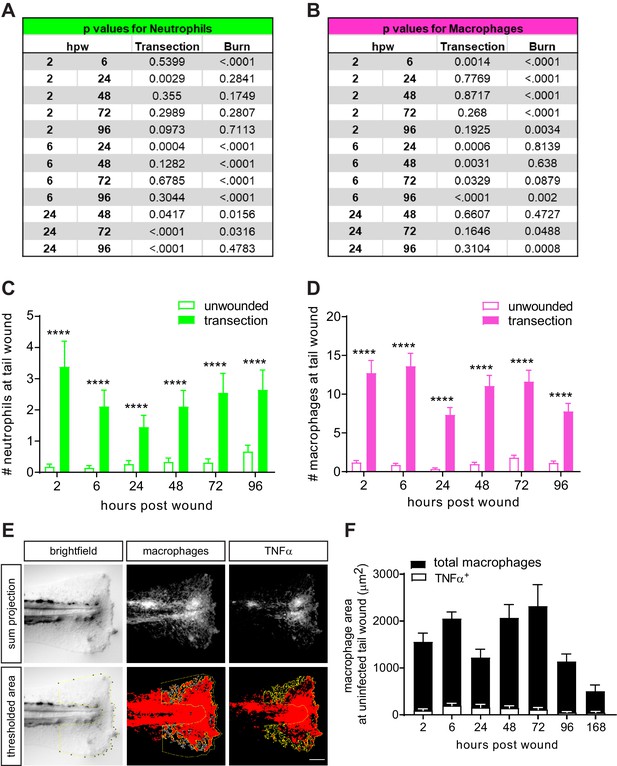
Leukocyte recruitment in the caudal fin tissue is minimal in unwounded larvae.
Additional p values associated with Figure 2B and C are provided for (A) neutrophils and (B) macrophages to reflect changes over time within each injury. Leukocyte recruitment in unwounded larvae or following simple transection was quantified using double transgenic larvae (Tg(lysC:mCherry-histone2b) x Tg(mpeg1:GFP-histone2b)). (C) Neutrophils and (D) macrophages were counted in caudal fin area distal to the caudal vein loop in single-plane images acquired by Zeiss Zoomscope. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 29–34 larvae per time point for each treatment. ****<0.0001. (E) Example of quantitation by area thresholding (see Materials and methods). (F) For clarity, values for uninfected transection from Figure 2G were plotted alone to show full data range.
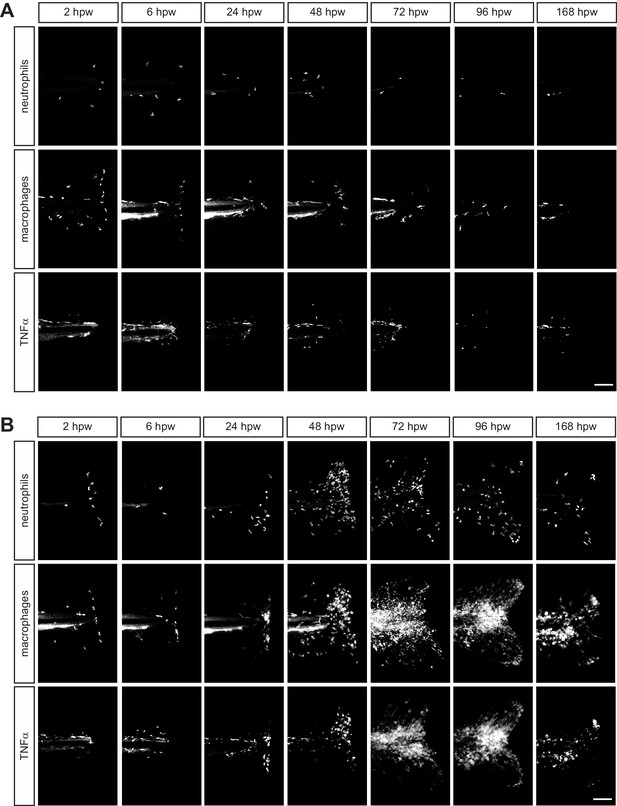
Leukocyte recruitment in response to transection in the presence of infection.
Single channels associated with merged images in Figure 2D showing (A) uninfected and (B) L. monocytogenes (Lm)- infected image sets. Neutrophils, macrophages and TNFα were labeled with BFP, mCherry and GFP respectively. Scale bar is 100 micron.
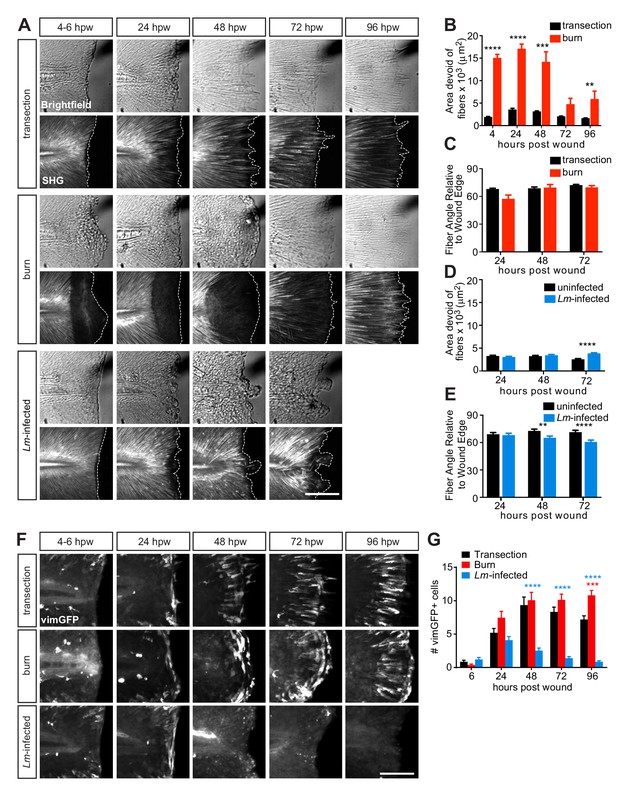
Multiphoton microscopy of collagen and vimentin-expressing cells identify differences in tissue remodeling over time amongst the injuries.
(A) Z-projections of caudal fins imaged at different times after transection, thermal injury (burn) or infected transection showing the tissue wound edge in the bright field and corresponding SHG image. White dotted outline indicates wound edge from brightfield image. Scale bar is 100 microns. (B) Graph showing the area devoid of SHG fibers (from fiber ends to wound edge) following transection or thermal injury. Values are arithmetic means and SE from three biological replicates. p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. Total N = 23–28 larvae per time point for each treatment. (C) Graph showing the angle of fiber segments relative to the wound edge, as quantified by CurveAlign software (see Materials and methods), within 50 microns of the wound edge with transection or thermal injury. 0o is parallel to the wound edge while 90o is perpendicular to the wound edge. Values are arithmetic means and SE from three experimental replicates. p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. Total N = 14–25 larvae per time point for each treatment. (D) Graph showing the area devoid of SHG fibers (from fiber ends to wound edge) following uninfected or Lm-infected transection. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 28-32 larvae per time point for each treatment. (E) Graph showing the angle of fiber segments relative to the wound edge in uninfected or Lm-infected transections. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 17–31 larvae per time point for each treatment. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (F) Z-projections of multiphoton microscopy images of vimGFP-positive cells at the wound edge in caudal fins at different times after simple transection, burn or Lm-infected transection. Scale bars are 100 microns. Merge of z-projections of vimGFP-positive cell images (green) with z-projections of corresponding SHG images (white) are shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B. (G) Graph showing the number of vimGFP-positive cells within a 50 × 100 micron box adjacent to the wound edge and centered vertically with the notochord (Figure 4—figure supplement 1A). Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 19–28 larvae per time point for each treatment. For clarity, only relevant comparisons (burn in red, or Lm-infected transection in blue, to the control transection) are shown on the graph; ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Related to Figure 3B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.024
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Related to Figure 3C.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.025
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Related to Figure 3D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.026
-
Figure 3—source data 4
Related to Figure 3E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.027
-
Figure 3—source data 5
Related to Figure 3G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.028
-
Figure 3—source code 1
Related to Figure 3B and D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.029
-
Figure 3—source code 2
Related to Figure 3B–E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.030
-
Figure 3—source code 3
Related to Figure 3G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.031
-
Figure 3—source code 4
Related to Figure 3G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.032
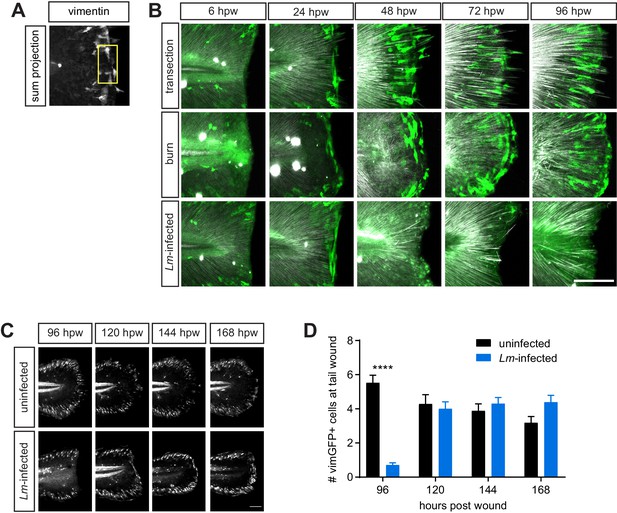
VimGFP-positive cells at the wound recover over time at the Lm-infected tail wound.
(A) an example of an image with vimentin expression showing a 50 × 100 micron box placed strategically to count vimGFP-positive cells is shown (see Materials and methods). (B) Merge of z-projections of vimGFP-positive cell images (green) with z-projections of corresponding SHG images (white) from Figure 3F. (C) sum projections of z series acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae following uninfected or Lm-infected transection. Scale bar is 100 micron. (D) Graph showing quantitation of vimGFP-positive cells at the wound over time. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 27–48 larvae per time point for each treatment. ***<0.0001.

Tail wound infection in the presence of hly mutant of L. monocytogenes causes no delay in vimGFP-positive cells and is associated with limited inflammation.
(A) representative images of sum projections of z series acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae following tail transection in the presence of mCherry-expressing wild-type (Wt) or hly Lm over time. Scale bar is 100 micron. N = 4–6 larvae per time point for Wt Lm and N = 11–12 larvae per time point for hly Lm; one experimental repeat. (B) representative images of sum projections of z series acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using transgenic larvae Tg(mpeg1:GFP) larvae following tail transection in the presence of mCherry-expressing wild-type (Wt) or hly Lm over time. Scale bar is 100 micron. N = 5–7 larvae per time point for Wt Lm and N = 12 larvae per time point for hly Lm; one biological repeat.
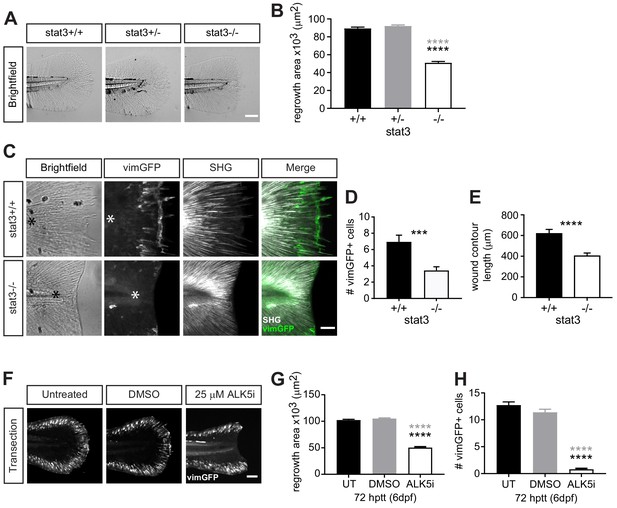
Wound healing and wound-associated vimentin-expressing cells are regulated by Stat3 and TGFβ signaling.
(A) Single-plane brightfield images of wild-type, heterozygous and stat3 mutant larvae showing tissue regrowth of caudal fins at 72 hr post tail transection (hptt) and (B) corresponding quantification of area of tissue regrowth. Values are arithmetic means and SE from three biological replicates. p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. N = 41–50 larvae from het incross, per biological repeat, followed by genotyping. ****p<0.0001; black and gray * depict p values in comparison to wild-type and heterozygous, respectively. (C) Z-projections of multiphoton microscopy images showing the location of vimGFP-positive cells and SHG fiber organization in wild-type and stat3 mutant larval caudal fins at 72 hptt. Asterisk denotes region just posterior to tip of notochord. Scale bar is 50 microns. (D) Quantification of the number of vimGFP-positive cells at the wound edge in wild-type and stat3 mutant larvae. Values are least square means and SE from three replicates; Total N = 28–32 larvae per treatment. ***p<0.001 (E) Graph comparing the contour length of the wound edge, measured using SHG images, between wild-type and stat3 mutant larvae. Values are arithmetic mean and SE from three experimental replicates with associated p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. ****p<0.0001. Total N = 28–32. (F) Sum-projections of z-stacks acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae, following tail transection at 72 hptt (6 dpf) in E3 medium only (untreated, UT) or in the presence of 25 µM ALK5 (TGFβRI) inhibitor or 0.5% DMSO as vehicle control. (G) Corresponding quantification of area of tissue regrowth. Values are arithmetic means and SE from three biological replicates. p values obtained by analyzing ranks due to residuals not being normally distributed. (H) corresponding quantification of vimGFP-positive cells at the wound edge. Values are least square means and SE from three biological replicates, with associated p values. Total N = 36–43 larvae for each treatment in (G) and (H). ****p<0.0001; black and gray * depict p values in comparison to untreated and DMSO-treated respectively.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Related to Figure 4B.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.036
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Related to Figure 4D.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.037
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Related to Figure 4E.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.038
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Related to Figure 4G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.039
-
Figure 4—source data 5
Related to Figure 4H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.040
-
Figure 4—source code 1
Related to Figure 4B,E and G.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.041
-
Figure 4—source code 2
Related to Figure 4D and H.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.042
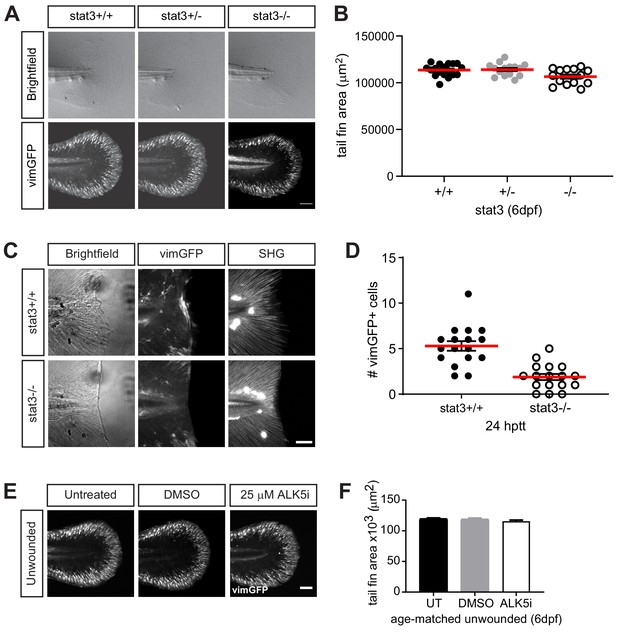
Stat3 or TGFβ signaling does not affect the presence of vimGFP-positive cells associated with development.
(A) Sum-projections of z-stacks acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae in stat3 mutant background, showing tail fin of age-matched unwounded larvae at 6 dpf. Scale bar is 100 microns. (B) the corresponding quantification of the tail fin area. Total N = 47 larvae from het incross; one biological replicate, thus no statistical analysis was performed. (C) z-projections acquired by multiphoton microscropy using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae in stat3 mutant background, showing vimentin-expressing cells and SHG fiber organization in caudal fins at 24 hptt. Scale bar is 50 microns. (D) the corresponding quantification of vimentin-positive cells at the wound edge. Total N = 17 larvae per genotype; two biological replicates, thus no statistical analysis performed. (E) Sum-projections of z-stacks acquired by spinning disk confocal microscope using Tg(vim:GFP) larvae, showing tail fin area and vimentin-expressing cells of unwounded larvae at 6 dpf in E3 medium only (untreated, UT) or in the presence of 25 µM ALK5 (TGFβRI) inhibitor or 0.5% DMSO as vehicle control. Scale bar is 100 microns. (F) the corresponding quantification of tail fin area in unwounded larvae. Values are arithmetic mean and SE from three biological replicates. No statistically significant differences were detected. Total N = 36–39 for each treatment.

Table summarizing the characteristics of the three wound models.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.035Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (10403S) | Listeria monocytogenes (strain 10403S) | Vincent et al., 2016 | was be obtained from JD Sauer Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | WT (AB) | ZIRC | ZL1 | https://zebrafish.org/home/guide.php |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(tnf:GFP) | Marjoram et al., 2015 | was obtain from M Bagnat Lab, Duke University | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(vim:GFP) | LeBert et al., 2018 | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(lysC:mCherry-histone2b) | Lam et al., 2014 | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(mpeg1:mCherry-histone2b) | Vincent et al., 2016 | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(mpeg1:GFP-histone2b) | this paper | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(lysC:BFP) | Rosowski et al., 2018 | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(mpeg1:mCherry-CAAX) | Bojarczuk et al., 2016 | was obtained from LI Zon Lab, Boston Children's Hospital, Dana Farber Cancer Institute | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | Tg(lysC:BFP/mpeg1:mCherry-CAAX) | de Oliveira et al., 2019 | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | casper | White et al., 2008 | ZL1714 | https://zebrafish.org/home/guide.php |
| Strain, strain background (D. Rerio) | stat3stl27/+ | Liu et al., 2017b | was obtained from L Solnica-Krezel Lab, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (D. Rerio) | tol2-mpeg1:GFP-histone2b | this paper | can be obtained from A Huttenlocher Lab, University of Wisconsin - Madison | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ALK5 inhibitor (ALK5i) | Selleckchem | item no. SB431542; RRID:SCR_003823 | 25 µM in DMSO; no pretreatment, start treatment upon wounding, refresh daily |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | RRID:SCR_002798 | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ | |
| Software, algorithm | SAS | RRID:SCR_008567 | https://www.sas.com/en_us/home.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji, ImageJ | Schindelin et al., 2012 | RRID:SCR_002285 | https://fiji.sc/ |
| Software, algorithm | CurveAlign | Liu et al., 2017a | https://loci.wisc.edu/software/curvealign | |
| Other | High temperature cautery pen, fine tip | Bovie | AA01 | http://www.boviemedical.com/hightempcauteries/ |
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.45976.043





