Insulin-like peptides and the mTOR-TFEB pathway protect Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodites from mating-induced death
Figures
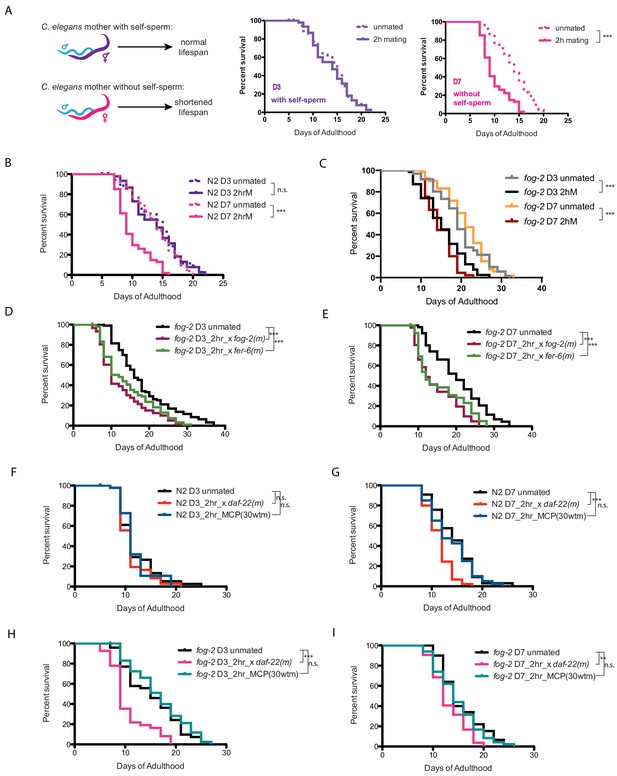
Brief mating-induced death is dependent on self-sperm and acts through male seminal fluid.
(A) Schematic and representative survival curves illustrating survival after a brief (2 hr) mating; C. elegans hermaphrodite lifespan is dependent on the presence of self-sperm. (B) Wild-type N2 hermaphrodites have reduced lifespan after 2 hr mating on day 7 of adulthood, but have normal lifespan when such brief mating occurs on day 3. Day 3 N2 unmated: 14.1 ± 0.7 days; mated: 13.9 ± 0.6 days, p=0.8481; Day 7 N2 unmated: 13.8 ± 0.5 days; mated: 10.0 ± 0.4 days, p<0.0001. In this study, we define day 0 as the beginning of the adulthood for all lifespans. Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank (Mantel-Cox) method was performed to compare the lifespans of different groups in this study. See Supplementary file 1 for all lifespan data summary. (C) Self-spermless fog-2(q71) are susceptible to 2 hr mating on both day 3 and day 7 of adulthood. Day three fog-2 unmated: 19.7 ± 0.7 days; mated: 15.4 ± 0.7 days, p<0.0001; Day seven fog-2 unmated: 21.0 ± 0.6 days; mated: 14.8 ± 0.5 days, p<0.0001. (D–E) Mating with fog-2 males (which are functionally wild type) or with fer-6 males (which lack sperm) leads to a similar magnitude of lifespan decrease in fog-2 self-spermless hermaphrodites. Day 3 fog-2 unmated: 18.2 ± 0.8 days; mated with fog-2 males: 12.6 ± 0.7 days, p<0.0001; mated with fer-6 males: 14.1 ± 0.7 days, p=0.0002 (compared to unmated). Day 7 fog-2 unmated: 20.3 ± 1.0 days; mated with fog-2 males: 14.6 ± 0.9 days, p<0.0001; mated with fer-6 males: 15.6 ± 1.0 days, p=0.0016 (compared to unmated). (F–G) N2 hermaphrodites are not short-lived after 2 hr exposure to male pheromone-conditioned plates (conditioned by 30 wild-type males for 2 days) either on day 3 or day 7 of adulthood. Only old day 7 N2 hermaphrodites have a shorter lifespan after 2 hr mating with daf-22 male pheromone production defective males (F). Day 3 N2 unmated: 11.9 ± 0.6 days; mated with daf-22 males: 11.1 ± 0.4 days, p=0.3058; unmated on male-conditioned plates (MCP; pre-conditioned with 30 males, see Materials and methods for details): 11.7 ± 0.5 days, p=0.9696 (compared to unmated). Day 7 N2 unmated: 14.3 ± 0.7 days; mated with daf-22 males: 11.4 ± 0.4 days, p=0.0001; unmated on male-conditioned plates (MCP): 13.7±0.7 days, p=0.5984 (compared to unmated). (H–I) Like N2 hermaphrodites, the lifespans of fog-2 hermaphrodites are not affected by 2 hr male pheromone exposure. However, both young (G) and old (H) fog-2 hermaphrodites live significantly shorter after brief mating with daf-22 males. Day 3 fog-2 unmated: 15.3 ± 0.8 days; mated with daf-22 males: 10.4 ± 0.6 days, p<0.0001; unmated on male-conditioned plates (MCP): 16.5 ± 0.8 days, p=0.3459 (compared to unmated). Day 7 fog-2 unmated: 15.5±0.6 days; mated with daf-22 males: 13.1 ± 0.4 days, p=0.0017; unmated on male-conditioned plates (MCP): 14.7±0.6 days, p=0.4493 (compared to unmated).
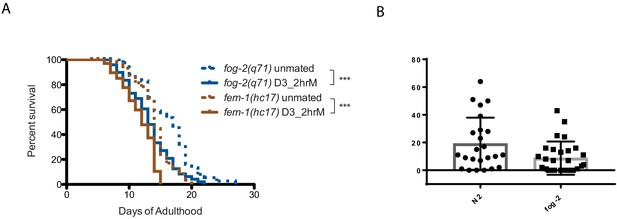
The presence of self-sperm protects the hermaphrodites from brief mating-induced death.
(A) Both self-spermless fog-2(q71) and fem-1(hc17) hermaphrodites are susceptible to 2 hr mating on day 3 of adulthood. fog-2 unmated: 16.3 ± 0.7 days; mated: 13.4 ± 0.5 days, p=0.0010. fem-1 unmated: 14.2 ± 0.4 days; mated: 11.7 ± 0.3 days, p<0.0001. (B) Young N2 hermaphrodites’ resistance to brief mating-induced death is not due to low mating efficiency. Total male progeny from 2 hr mated N2 were counted (we only counted male progeny because we did not want to include progeny from self-fertilization. 2x male progeny from mated N2 hermaphrodites is a good estimate of the total number of cross-progeny) as well as total progeny (fog-2 does not have self sperm, so all the progeny produced after mating are cross-progeny) from 2 hr mated fog-2 hermaphrodites (All hermaphrodites were mated on Day 3 of adulthood). Mated N2 hermaphrodites produce at least two-fold more male progeny than total progeny produced by mated fog-2. Therefore, potentially more male sperm and seminal fluid were transferred to N2 hermaphrodites. Still, young N2 are resistant to brief mating-induced death, suggesting that young N2 hermaphrodites’ resistance to brief mating-induced death is not due to lower mating efficiency or the transfer of less male sperm or seminal fluid.
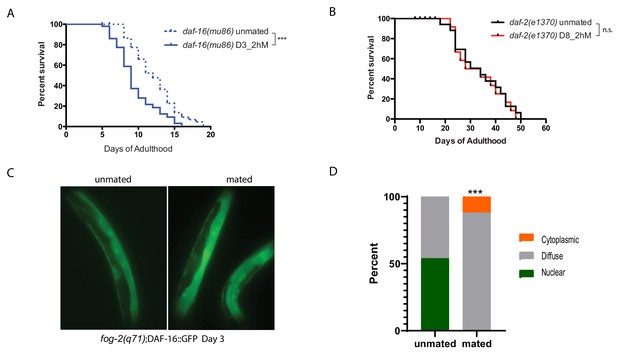
IIS/FOXO in brief mating-induced death.
(A) daf-16(mu86) mutants lived shorter after 2hr mating on Day 3 of adulthood. Unmated: 12.2±0.5 days; mated: 9.5±0.5 days, p=0.0003. (B) daf-2(e1370) mutants are resistant to 2 hr mating in the absence of self-sperm on Day 8 of adulthood. Unmated: 33.2±2.6 days; mated: 32.7±2.9 days, p=0.7519. (C–D) Nuclear DAF-16::GFP in self-spermless fog-2 hermaphrodites becomes diffuse after mating. (C) Representative images of DAF-16::GFP in unmated and mated fog-2 hermaphrodites (Day 3). (D) Quantitation of DAF-16::GFP, p=0.0006. Each worm was assigned a category based on DAF-16::GFP localization. Chi-square test was used to determine the significance.
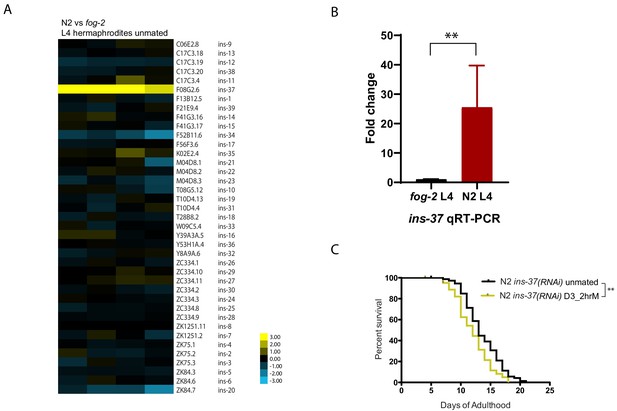
INS-37 is required for self-sperm protection from brief mating-induced death.
(A) Heatmap of all the insulin genes from microarray-based transcriptome comparison between N2 and fog-2 L4 hermaphrodites. (Four biological replicates) (B) qRT-PCR reveals over 25 fold up-regulation of ins-37 in N2 L4 hermaphrodites compared to fog-2 L4 hermaphrodites, p=0.0043. Reference gene pmp-3 was used for normalization. RNA was extracted from three additional biological replicates (different from the sample used for microarray in Figure 3A). (C) Knocking down ins-37 in N2 hermaphrodites makes them susceptible to 2 hr mating on day 3 of adulthood. (see Figure 3—figure supplement 2B for results of N2 on control RNAi vector) N2 ins-37 RNAi unmated: 13.6 ± 0.4 days; N2 ins-37 RNAi mated: 12.0 ± 0.4 days, p=0.0040.
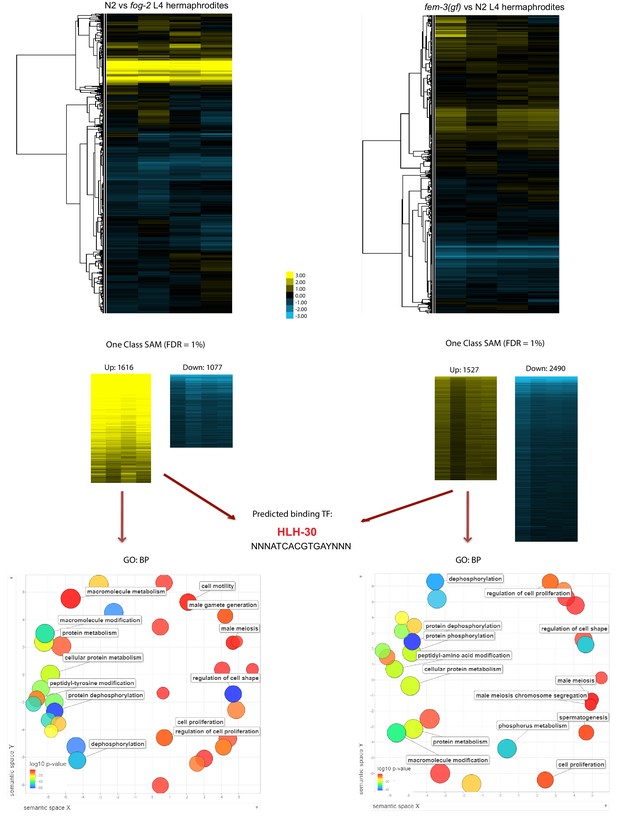
Transcriptomic comparison between self-spermless, wild type, and excess self-sperm mutants reveals HLH-30 binding motif.
L4 hermaphrodites of each genotype were collected for RNA extraction and microarray-based transcriptome analysis. One-class SAM was used to determine genes with significant changes in expression between each comparison. The gene lists from SAM (FDR = 1%) were then imported to g:Profiler for GO terms and TF binding motifs analysis.

Ins-7 is highly up-regulated in L4 hermaphrodites with self-sperm.
(A) qRT-PCR of ins-37. Ins-37 has an over 25-fold increase in N2 L4 hermaphrodites compared to fog-2 L4 hermaphrodites (same figure shown in Figure 3B). Mating has very little impact on ins-37 expression compared to the presence of self-sperm. Expression level of ins-37 increased about twofold in Day 2 mated fog-2 compared to unmated fog-2 (p=0.0137). (B) Control of Figure 3C,N2 hermaphrodites do not live shorter after 2 hr mating on day 3 of adulthood. N2 vector RNAi unmated: 12.1 ± 0.5 days; N2 vector RNAi mated: 11.6 ± 0.5 days, p=0.6335. .
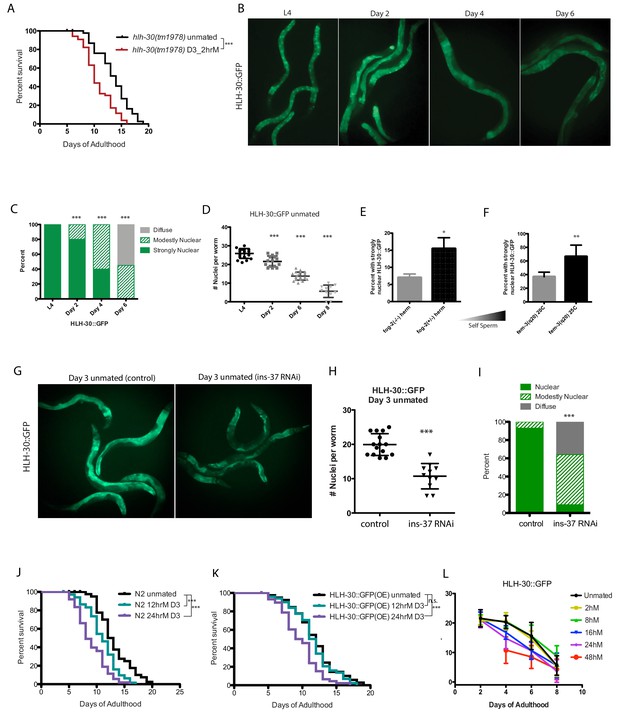
HLH-30 protects against brief mating-induced death.
(A) hlh-30(tm1978) mutants live shorter after brief mating on day 3, unlike wild type (N2) hermaphrodites, which are resistant to 2 hr mating on day 3 of adulthood (Figure 4—figure supplement 1L). hlh-30 unmated: 11.7 ± 0.3 days; mated: 9.8 ± 0.3 days, p=0.0002. (B) Nuclearly localized HLH-30::GFP becomes diffuse with age. Representative images of HLH-30::GFP (BC11288) in unmated hermaphrodites at various ages. Worms were imaged under free moving conditions; no anesthetic was used, to prevent possible artificial perturbation of HLH-30 localization. (C–D) Quantitation of HLH-30::GFP in B). In C), each worm was assigned a category based on HLH-30::GFP localization. Chi-square test was used to determine the significance. In D), number of nuclei with nuclearly localized HLH-30::GFP was counted for each worm. The average of each group was compared to L4 using the unpaired t-test. (E–F) The amount of self-sperm is positively correlated with the number of worms having strongly nuclearly localized HLH-30::GFP. (Three biological replicates per condition; average was compared by t-test). In F), fem-3 worms were grown at 25C to induce excess self-sperm phenotype, control fem-3 were grown at 20 C. (G–I) Knockdown of ins-37 reduces nuclearly localized HLH-30::GFP in unmated hermaphrodites. (G) Representative images of day 3 HLH-30::GFP hermaphrodites on control RNAi (left) and ins-37(RNAi) (right). (H–I) Quantitation of HLH-30::GFP in G), same method used in C-D. (J–K) HLH-30::GFP strain is more resistant to longer mating, compared to wild-type (N2) hermaphrodites. Wild-type are already susceptible to 12 hr mating (J), whereas HLH-30::GFP worms are resistant (K). 24 hr mating reduces lifespan of both strains. N2 unmated: 13.2 ± 0.5 days; 12 hr mated: 11.0 ± 0.3 days, p=0.0005; 24 hr mated: 9.0 ± 0.4 days, p<0.0001 (compared to unmated). HLH-30::GFP unmated: 11.9 ± 0.4 days; 12 hr mated: 11.6 ± 0.4 days, p=0.4471; 24 hr mated: 9.7 ± 0.4 days, p=0.0001 (compared to unmated). (L) Summary of nuclear HLH-30::GFP quantitation of worms with age and after mating for various time on day 3. (See Figure 4—figure supplement 1A–K for more detailed information).
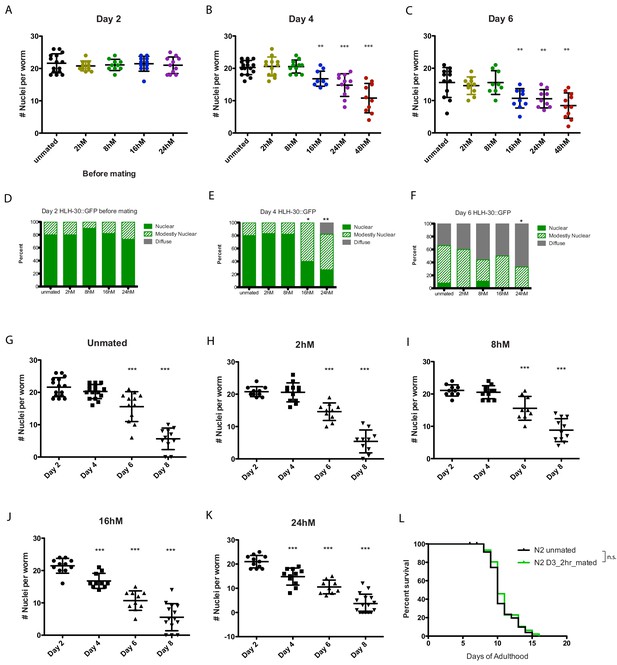
Quantitation of HLH-30::GFP in worms at different ages and after mating for various lengths of time.
(A–K) HLH-30::GFP becomes more diffuse with age, even if the hermaphrodites have not been mated; however, mating accelerates this process. All worms were mated on Day 3 of adulthood. (B, C; E–K) 2 hr and 8 hr mating seem to have no impact on HLH-30::GFP localization (same as unmated control). However, starting from 16 hr mating, HLH-30::GFP become less nuclearly localized. (L) Control of Figure 4A,N2 hermaphrodites do not live shorter after 2 hr mating on day 3 of adulthood. N2 unmated: 13.4 ± 0.5 days; N2 mated: 12.7 ± 0.4 days, p=0.2263.

Mating also decreases nuclear HLH-30::GFP in fog-2 self-spermless hermaphrodites.
Left: representative images of HLH-30::GFP in unmated and mated fog-2 hermaphrodites (Day 4). Quantitation of HLH-30::GFP in fog-2. (p=0.0328) Each worm was assigned a category based on HLH-30::GFP localization. Chi-square test was used to determine the significance.
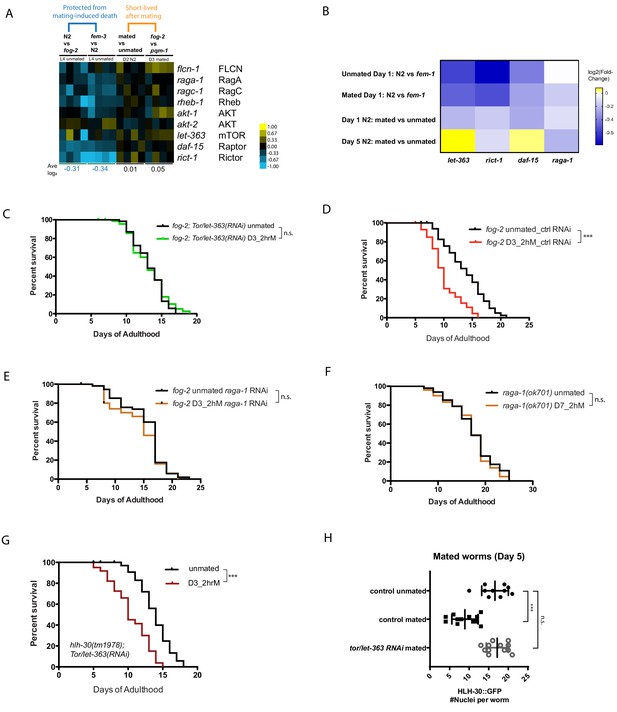
TOR signaling components promote Seminal Fluid-induced killing/brief mating-induced death.
(A) Most positive regulators of TOR signaling (e.g., Rictor/rict-1) were modestly downregulated in conditions in which worms have self-sperm and are protected from brief mating-induced death (left block, blue), but rise in mated or short-lived conditions (right block). (B) Independent RNA-seq confirmed the modest downregulation of TOR signaling components in worms that are protected from brief mating-induced death. Note the first two rows are conditions in which the hermaphrodites have self-sperm protection against brief mating. (C) Knockdown of tor/let-363 in self-spermless fog-2 protects the hermaphrodites from SF killing. fog-2;TOR/let-363(RNAi) unmated: 13.3 ± 0.3 days; mated: 13.2 ± 0.4 days, p=0.7368. (D) Control of Figure 5C: fog-2 on vector control RNAi unmated: 13.7 ± 0.6 days; mated: 10.1 ± 0.4 days, p<0.0001. (E) fog-2;raga-1(RNAi) unmated: 15.3 ± 0.5 days; mated: 14.3 ± 0.6 days, p=0.2378. (F) Day 7 self-sperm depleted raga-1(ok701) are also resistant to brief 2 hr mating. Unmated: 18.5 ± 0.7 days; mated: 18.1 ± 0.7 days, p=0.5833. (G) TOR/let-363 knockdown in hlh-30(tm1978) mutants fails to protect the hermaphrodites from brief mating-induced death. hlh-30;TOR/let-363(RNAi) unmated: 13.8 ± 0.3 days; mated: 10.5 ± 0.4 days, p<0.0001. (H) Quantitation of nuclear HLH-30::GFP in mated hermaphrodites treated with let-363 RNAi.
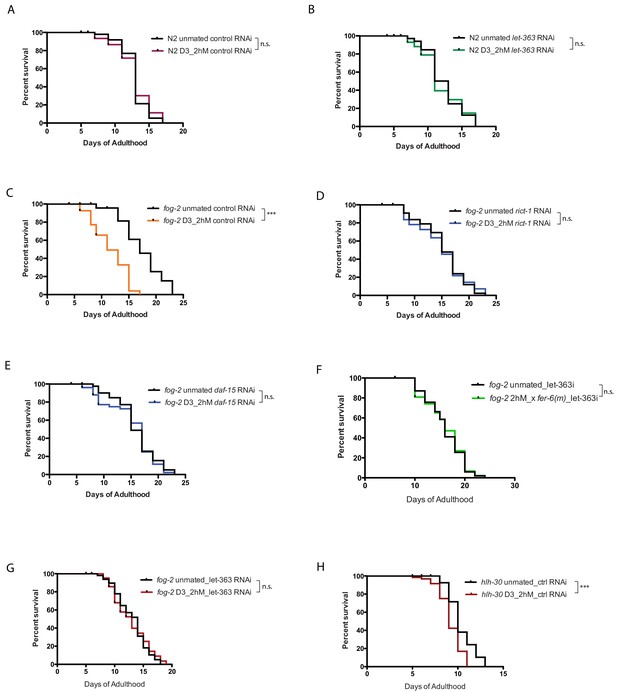
TOR signaling mediates self-sperm protection from brief mating.
(A–B) Knockdown of let-363 has no impact on lifespan of N2 upon brief mating. (A) N2 on vector control RNAi unmated: 14.9 ± 0.3 days; mated: 14.9 ± 0.4 days, p=0.7888. (B) N2 on TOR/let-363 RNAi unmated: 12.3 ± 0.5 days; mated: 12.1 ± 0.6 days, p=0.8791. (C–F) Individual TOR components knockdown prevents SF killing in spermless females. (D) fog-2;rict-1(RNAi) unmated: 15.2 ± 0.6 days; mated: 14.9 ± 0.6 days, p=0.8375. (E) fog-2;daf-15(RNAi) unmated: 15.9 ± 0.6 days; mated: 15.2 ± 0.6 days, p=0.6903. (C) fog-2; control (RNAi) unmated: 17.4 ± 0.8 days; mated: 11.7 ± 0.6 days, p<0.0001. (F) Knockdown of let-363 in self-spermless fog-2 protects the hermaphrodites from SF killing. fog-2 on TOR/let-363 RNAi unmated: 16.0 ± 0.5 days; mated with fer-6 males: 16.0 ± 0.6 days, p=0.8488. (G–H) Lifespan control for Figure 5G. (G) fog-2 on TOR/let-363 RNAi unmated: 13.0 ± 0.4 days; mated: 12.9 ± 0.4 days, p=0.8275. (H) hlh-30 on vector control RNAi unmated: 10.4 ± 0.2 days; mated: 9.2 ± 0.2 days, p<0.0001.

Insulin and mTOR signaling pathways influence HLH-30 and DAF-16 localization in mated hermaphrodites.
(A–B) Knocking down pqm-1, insulins, and Tor/let-363 does not affect HLH-30::GFP localization in unmated worms; (C) By contrast, knocking down pqm-1, ins-7, ins-8, or let-363 largely prevent HLH-30::GFP from localizing to the cytoplasm. (D) Mating-induced DAF-16::GFP localization movement was inhibited in fog-2 after knocking down let-363. (in contrast to Figure 2B–C) .
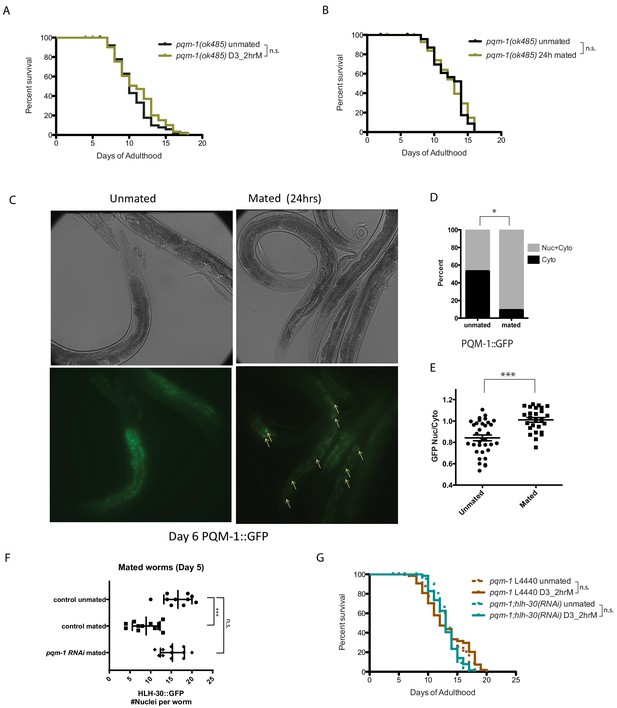
PQM-1 is required for SF and brief mating-induced killing.
(A–B) pqm-1(ok485) mutant hermaphrodites are resistant to short term (2 hr) mating-induced death (A), as well as long term (24 hr) mating (B) 2 hr pqm-1 unmated: 10.5 ± 0.3 days; mated: 11.1 ± 0.4 days, p=0.2070. 24 hr pqm-1 unmated: 12.5 ± 0.5 days; mated: 12.5 ± 0.5 days, p=0.8407. (See Figure 6—figure supplement 1A–B for more controls) (C) Representative images of PQM-1::GFP hermaphrodites. Left: unmated pqm-1 control, Right: mated pqm-1 (mated on day 1 of adulthood for 24 hr). Images are taken on day 6 of adulthood. White arrows indicate nuclearly localized PQM-1::GFP. (D–E) Quantitation of PQM-1::GFP localization. (D) Non-parametric comparison; E) nuclear and cytoplasmic GFP intensity was measured in the most anterior nuclei (easily recognizable) of the intestine for worms in each group. Averages were compared using a t-test. (F) Knocking down pqm-1 restores nuclearly localized HLH-30 in mated hermaphrodites. Quantitation of nuclear HLH-30::GFP in mated hermaphrodites treated with pqm-1 RNAi (same as Figure 5H). (G) Knocking down pqm-1 blocks the lifespan decrease normally induced by 2 hr mating in hlh-30(tm1978) mutants. pqm-1 on vector control RNAi: unmated:13.2 ± 0.4 days, mated: 13.1 ± 0.5 days, p=0.4169. pqm-1;hlh-30(RNAi): unmated:13.2 ± 0.3 days, mated: 13.1 ± 0.3 days, p=0.9161.
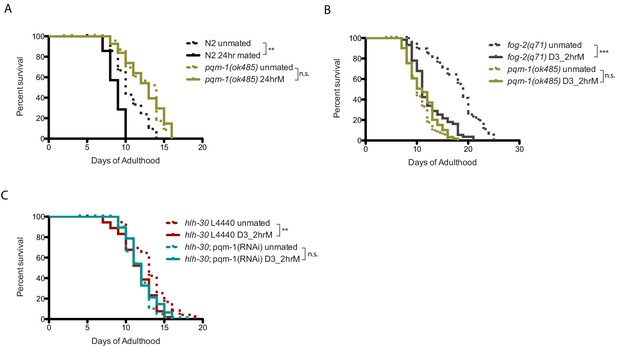
PQM-1 is required for SF killing.
(A–B) pqm-1 mutants are resistant to both long-term (24 hr; B) and brief (2 hr) mating (C). (C) Knocking down hlh-30 in pqm-1 mutants does not make them susceptible to brief mating-induced death. hlh-30 on vector control RNAi: unmated:13.1 ± 0.4 days, mated: 11.6 ± 0.3 days, p=0.0015. hlh-30 on pqm-1 RNAi:unmated:11.7 ± 0.2 days, mated: 12.0 ± 0.2 days, p=0.3601.
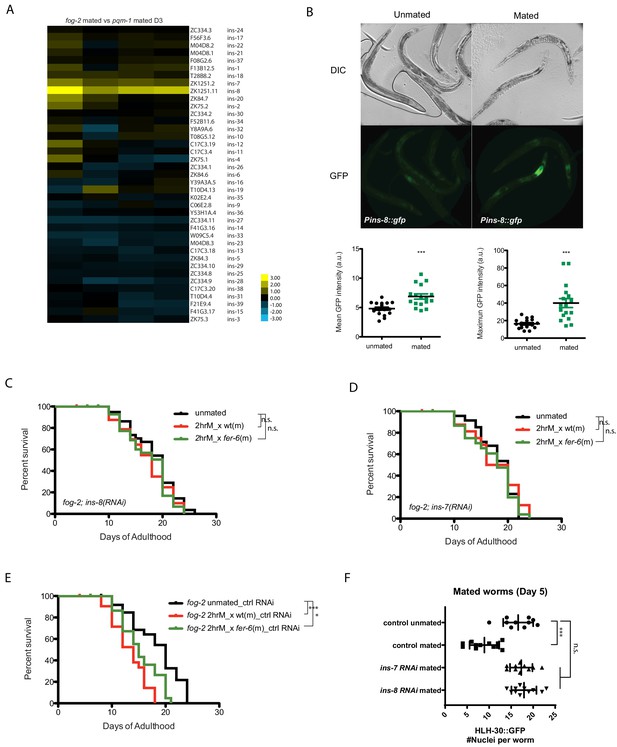
Insulins mediate seminal fluid killing.
(A) Heatmap of insulin gene expression comparisons between fog-2 mated worms (short-lived after mating) and pqm-1 mated worms (no lifespan decrease after mating). (B) Both mean and maximum Pins-8::gfp expression increased in mated worms (right), correlating with gene expression data (A). (C, D) Knockdown of ins-8 (C) or ins-7 (D) protects hermaphrodites from seminal fluid killing. (C) fog-2;ins-8(RNAi) unmated: 18.4 ± 0.7 days; mated with fog-2 males: 17.2 ± 0.9 days, p=0.2879; mated with fer-6 males: 17.3 ± 0.7 days, p=0.2582 (compared to unmated). (D) fog-2;ins-7(RNAi) unmated: 18.2 ± 0.6 days; mated with fog-2 males: 17.7 ± 1.1 days, p=0.9380; mated with fer-6 males: 17.2 ± 0.7 days, p=0.3994 (compared to unmated). (E) Controls for Figure 7C–D. fog-2 on vector control RNAi unmated: 18.4 ± 0.9 days; mated with fog-2 males: 13.3 ± 0.7 days, p<0.0001; mated with fer-6 males: 15.4 ± 0.6 days, p=0.0032 (compared to unmated). (F) Knocking down ins-7 and ins-8 also restores nuclearly localized HLH-30 in mated hermaphrodites.
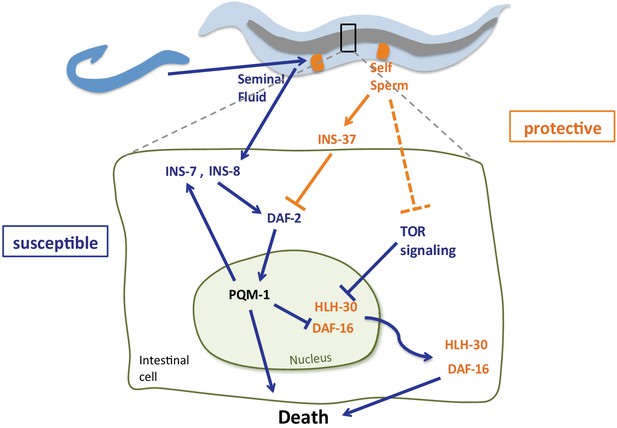
Model of self-sperm mediated protection from seminal fluid killing Prior to mating, the presence of self-sperm maintains high ins-37 expression.
INS-37 antagonizes DAF-2 activity and promotes DAF-16 and HLH-30 maintenance in the nucleus. Self-sperm also inhibits TOR signaling, which regulates HLH-30 nuclear localization. Seminal fluid transfer upon mating increases expression of ins-8 and ins-7; these agonists activate DAF-2, promoting PQM-1 nuclear localization and DAF-16 and HLH-30 nuclear exit, resulting in premature death. INS-7 acts in a feed-forward loop (Murphy et al., 2007), further accelerating DAF-2 activation.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Lifespan results summary.
Summary of all the lifespan results in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46413.019
-
Supplementary file 2
N2 vs fog2(q71) L4 unmated hermaphrodites microarray analysis.
List of significantly up- and down-regulated genes in N2 vs fog2(q71) L4 unmated hermaphrodites transcriptome comparison identified by Significant Analysis of Microarrays (SAM), and functional enrichment analysis of these genes by g:Profiler.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46413.020
-
Supplementary file 3
fem-3(q20) vs N2 L4 unmated hermaphrodites microarray analysis.
List of significantly up- and down-regulated genes in fem-3(q20) vs N2 L4 unmated hermaphrodites transcriptome comparison identified by Significant Analysis of Microarrays (SAM), and functional enrichment analysis of these genes by g:Profiler.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46413.021
-
Supplementary file 4
fog-2(q71) vs pqm-1(ok485) mated hermaphrodites (Day 3) microarray analysis.
List of significantly up- and down-regulated genes in fog-2(q71) vs pqm-1(ok485) mated hermaphrodites (Day 3) transcriptome comparison identified by Significant Analysis of Microarrays (SAM), and functional enrichment analysis of these genes by g:Profiler.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46413.022
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46413.023





