Transcriptional landscape of myogenesis from human pluripotent stem cells reveals a key role of TWIST1 in maintenance of skeletal muscle progenitors
Figures
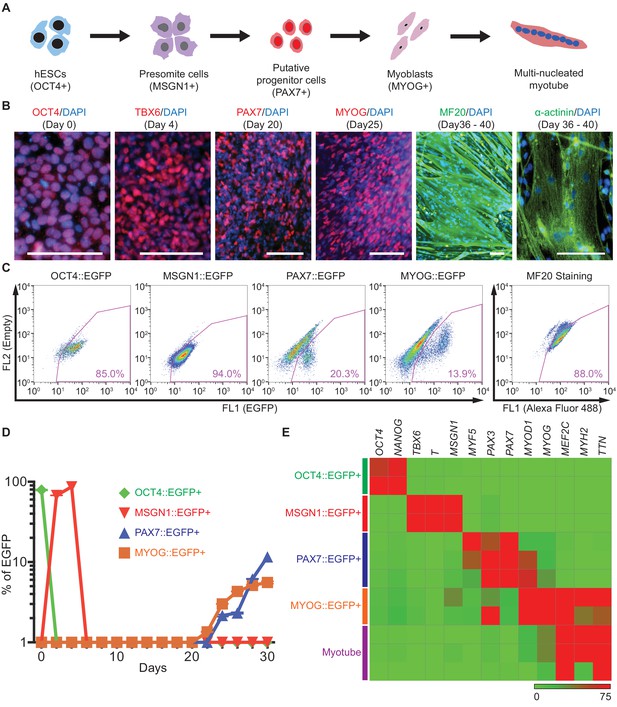
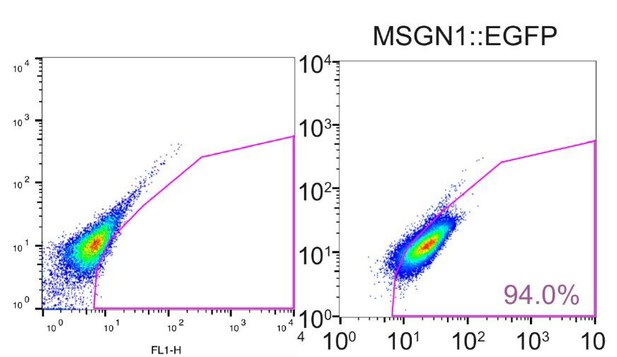
Generation and characterization of genetic reporter hPSC lines for stage-specific markers during human skeletal muscle specification.
(A) Schematic illustration of the embryonic myogenesis of hPSCs with stage-specific marker genes. (B) Immunocytochemistry of OCT4, TBX6, PAX7, MYOG, MF20 and α-actinin during in vitro muscle differentiation. (bars, 100 μm) (C) FACS plots of multiple reporter lines during in vitro muscle differentiation with two chemical compounds and expression of MF20, myotube marker. (D) Plot of EGFP percentage for each marker in multiple reporter lines during in vitro muscle differentiation. Values were detected every 2 days. (E) Heatmap of stage-specific marker genes expression in FACS-sorted positive population for each marker in multiple reporter lines (OCT4::EGFP+ cells at day 0, MSGN1::EGFP+ cells at day 4, PAX7::EGFP+ cells between day 26 and day 30, MYOG::EGFP+ cells between day 34 and day 37, and myotube isolation at day 36–40. The maximum values in each column were adjusted to 100.).
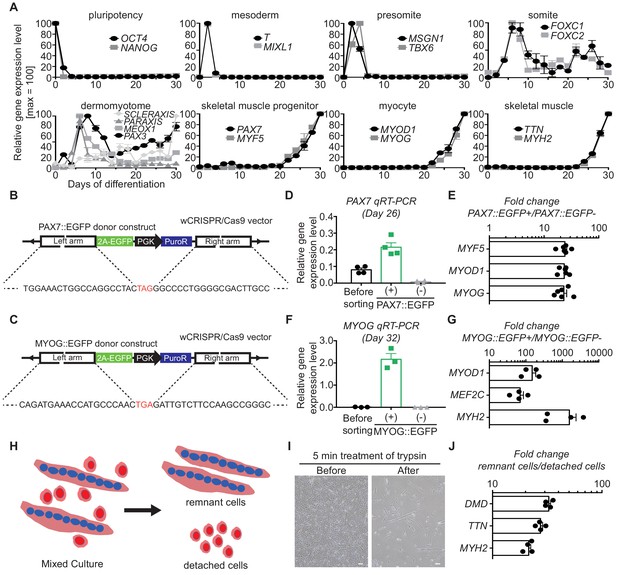
Generation and validation of stage-specific hPSC reporter lines for myogenesis.
(A) mRNA expression pattern of stage-specific marker genes for in vitro muscle specification. (B–C) The constructs for generation of PAX7::EGFP reporter line and MYOG::EGFP reporter line. (D) PAX7 gene expression levels in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and PAX7::EGFP- cells. (E) Early skeletal muscle specific marker gene expression levels in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and PAX7::EGFP- cells. (F) MYOG gene expression levels in MYOG::EGFP+ cells and MYOG::EGFP- cells. (G) Known myogenic key marker gene expression levels in MYOG::EGFP+ cells and MYOG::EGFP- cells. (H) Novel method for isolation of myotube from heterogeneous culture using differential rate of detachment of cell types upon trypsin. (I) Morphology of myotube culture before and after cell detachment by trypsin. (J) Expression of skeletal muscle regulation marker genes in detached cell group (myoblast) and remaining cell group (myotube).
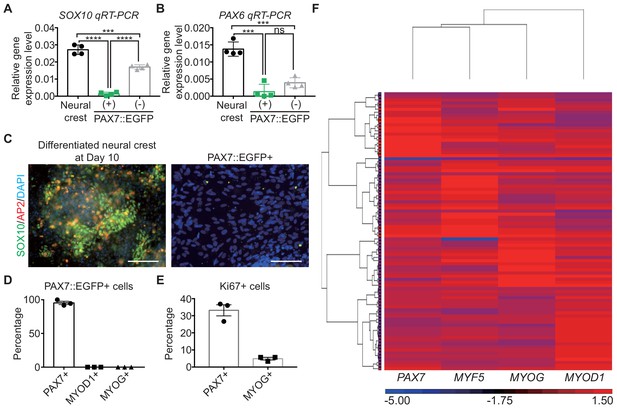
Characterization of PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
(A) SOX10 gene expression levels of differentiated neural crest cells at day 10 as a positive control, PAX7::EGFP+, and PAX7::EGFP- cell populations (****, p value < 0.0001; ***, p value < 0.001; unpaired t-test). (B) PAX6 gene expression levels of differentiated neural crest cells at day 10 as a positive control, PAX7::EGFP+, and PAX7::EGFP- cell populations (***, p value < 0.001; ns, not significant; unpaired t-test). (C) Immunohistochemistry of SOX10 and AP2 in differentiated neural crest and PAX7::EGFP+ cell populations (bar, 100 μm). (D) Proportion of PAX7-positive cells, MYOD1-positive cells, and MYOG-positive cells in PAX7::EGFP+ cells. (E) Plot for percentage of Ki67-positive cells in PAX7-positive cells and MYOG-positive cells during in vitro skeletal muscle specification. (F) Heatmap of single-cell qRT-PCR of PAX7, MYF5, MYOD1, and MYOG in a PAX7::EGFP+ cell.
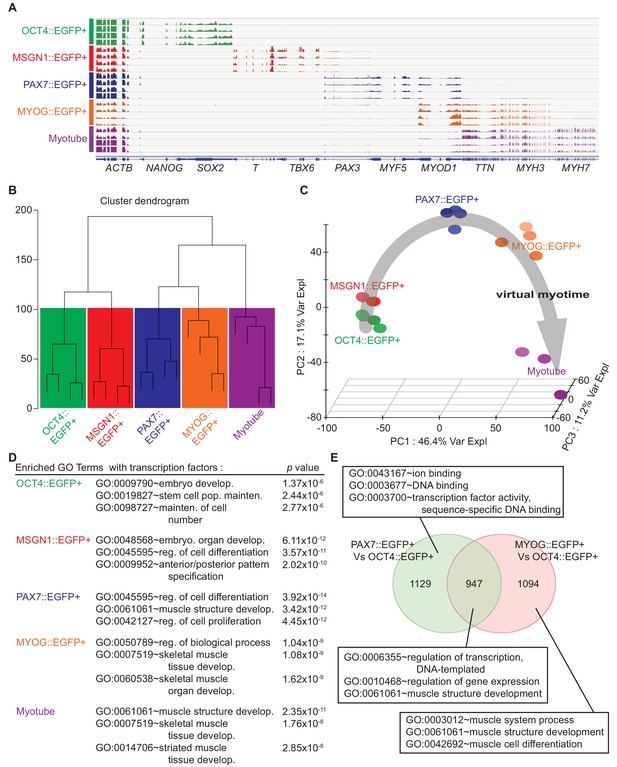
Cell population network analysis with RNA-sequencing data from five different cell types.
Each sample of cell population was collected as described in Figure 1E. (A) Coverage profiles of total RNA from each group: NANOG, SOX2, T, TBX6, PAX3, MYF5, MYOD1, TTN, MYH3, MYH7, and universally expressed gene ACTB. (B) Dendrogram of RNA-seq result produced by hierarchical clustering of five cell populations. (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of five cell populations during in vitro myogenesis. Gray arrow indicates ‘Virtual myotime’ from OCT4::EGFP+ to Myotube samples. (D) Enriched Gene ontology (GO) terms with transcription factors that had high p values in five cell populations from RNA-seq data. (E) Venn diagram of the upregulated genes and their GO terms in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and MYOG::EGFP+ cells compared to OCT4::EGFP+ cells.
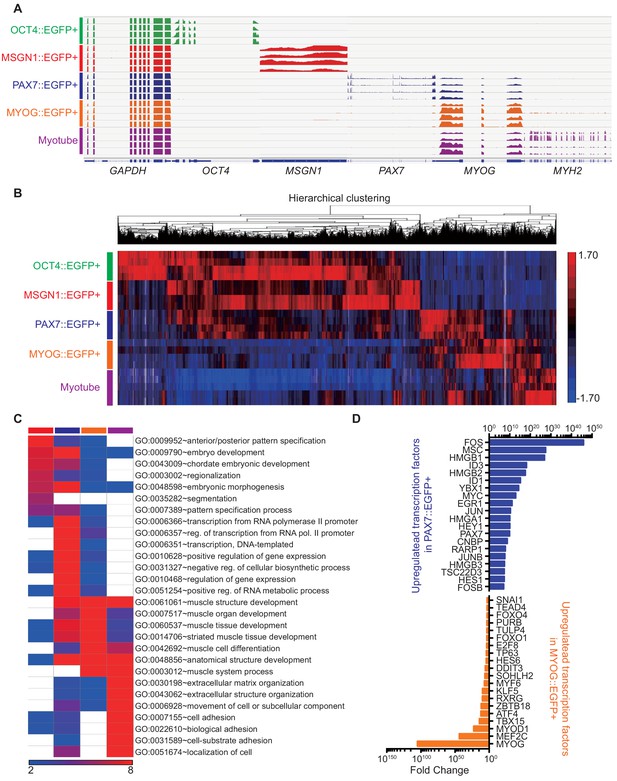
Transcriptome in cell populations at each stage of embryonic myogenesis.
(A) Representative coverage profile of stage-specific genes (OCT4, MSGN1, PAX7, MYOG, MYH2) including housekeeping gene (GAPDH). (B) Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of RNA-seq data. (C) Heatmap of GO term analysis pattern during in vitro myogenesis. (D) List of upregulated TFs in each PAX7::EGFP+ group and MYOG::EGFP+ group compared to each other.
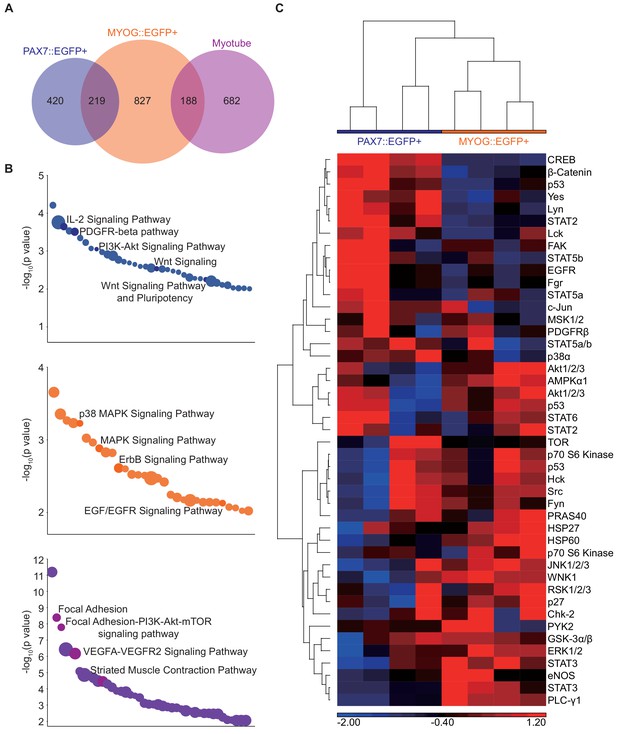
Differential gene expression analysis among PAX7::EGFP+ cells, MOYG::EGFP+ cells, and Myotubes.
(A) Venn diagram of the PAX7::EGFP+, MYOG::EGFP+, and Myotube samples. (B) Pathway analysis of cell-type-specific gene signatures. (C) Heatmap of phosphorylation for multiple protein substrates in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and MYOG::EGFP+ cells.
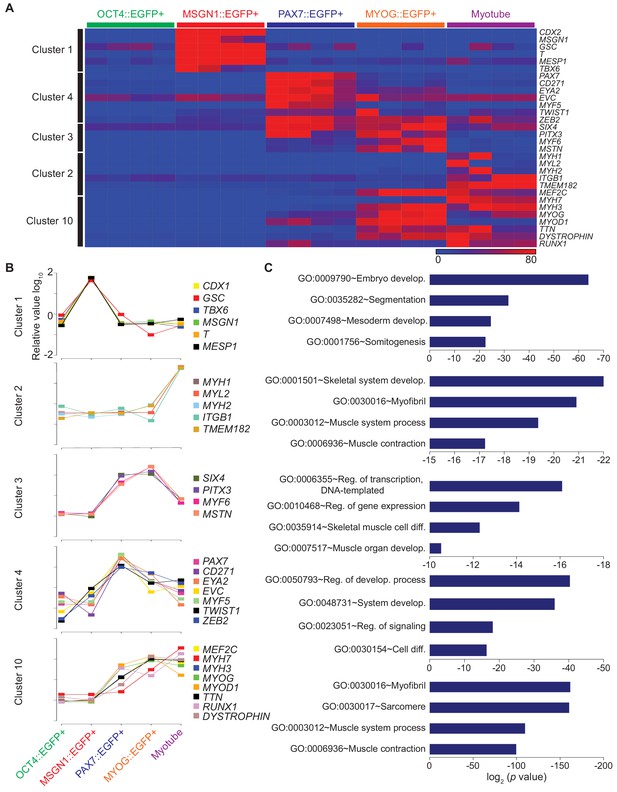
Clustering analysis of differential gene expression patterns.
(A) Validation of clustering analysis from RNA-seq data. The heatmap of gene sets from clusters in each cell population during myogenesis showed similar expression patterns of genes in the same cluster. (B) The expression patterns of multiple genes from each cluster; Cluster 1, Cluster 2, Cluster 3, Cluster 4, and Cluster 10 during muscle differentiation and their GO terms (C).
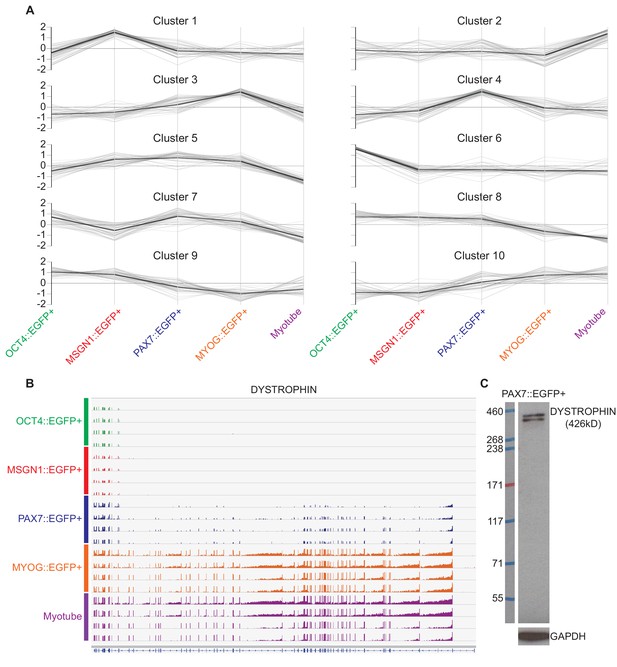
Ten clustering patterns from RNA-seq data analysis.
(A) A total of 10 clustering categories were created by gene expression patterns in each stage of OCT4::EGFP+, MSGN1::EGFP+, PAX7::EGFP+, MYOG::EGFP+, and Myotube populations. (B) Coverage profiles of DMD gene from each group. (C) Western blot of DMD in PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
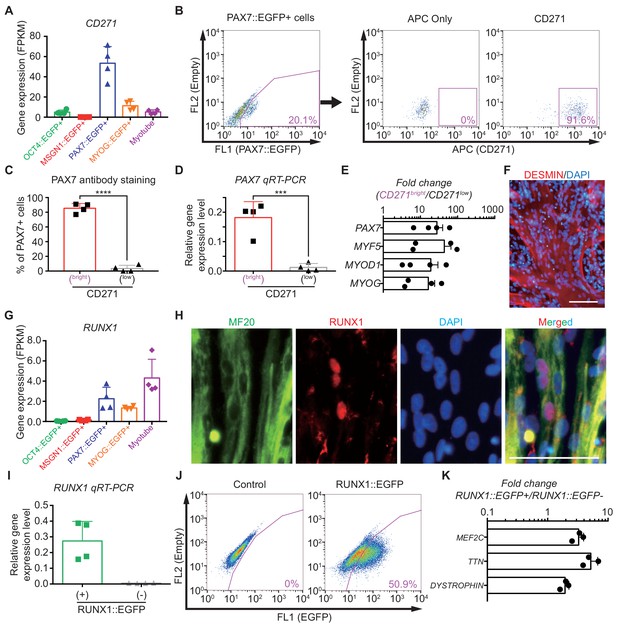
Characterization of CD271 and RUNX1 expression during in vitro myogenesis in hPSCs.
(A) CD271 expression profile with RNA-seq data in five different cell populations during muscle specification. (B) FACS plots of CD271 in PAX7::EGFP+ cell population at day 30 of skeletal muscle specification. (C) The percentages of PAX7+ cells in CD271bright cells and CD271low cells at 4 hr after cell sorting (****, p value < 0.0001; unpaired t-test). (D) PAX7 gene expression levels of CD271bright/CD271low populations (***, p value < 0.001; unpaired t-test). (E) Fold changes of expression levels with myogenic-specific marker genes, PAX7, MYF5, MYOD1 and MYOG in the CD271bright/CD271low populations. (F) Myotube formation ability of CD271bright cells confirmed by DESMIN expression. (G) RUNX1 expression profile with RNA-seq data in five different cell populations during muscle differentiation. (H) Co-localization of RUNX1 and MF20 in differentiating muscle cells at day 30. (bars, 100 μm) (I) The validation of reporting ability of the RUNX1::EGFP reporter line by measuring RUNX1 levels in both RUNX1::EGFP+ and RUNX1::EGFP- cell populations. (J) FACS plots for EGFP reporting RUNX1 expression in RUNX1::EGFP reporter line at day 35 of in vitro myogenesis. (K) Myotube related gene expression levels in both RUNX1::EGFP+ and RUNX1::EGFP- cell populations.
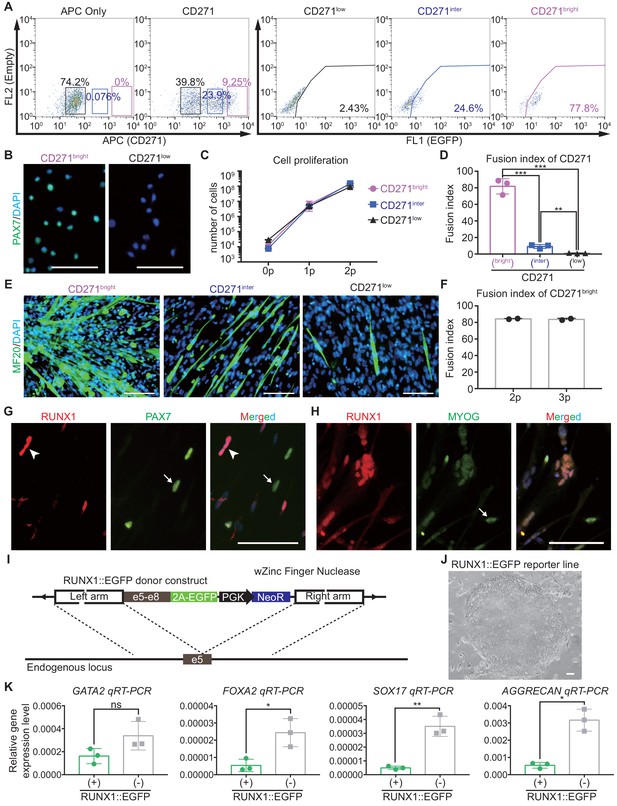
Stage-specific gene expression patterns in selected clusters.
(A) Proportion of PAX7::EGFP+ cells in CD271bright cells, CD271inter, and CD271low cells at day 30 of skeletal muscle specification. (B) Immunocytochemistry for the quantitative evaluation of PAX7 protein in CD271bright cells and CD271low cells 4 hr after cell sorting. (C) Cell proliferation ratio of CD271bright cells, CD271inter cells, and CD271low cells after sorting for two passages. (D) Fusion index of CD271bright cells, CD271inter cells, and CD271low cells at passage 1 (***, p value < 0.001; **, p value < 0.01; unpaired t-test). (E) Immunohistochemistry of MF20 in cultured CD271bright cells, CD271inter cells, and CD271low cells. (F) Fusion index in CD271bright cells during passages. (G) Co-localization of RUNX1 and PAX7 in differentiated skeletal muscle cells (bars, 100 μm). (H) Co-localization of RUNX1 and MYOG in differentiated skeletal muscle cells (bars, 100 μm). (I) Construct for the generation of the RUNX1::EGFP reporter line. (J) Morphology of undifferentiated RUNX1::EGFP reporter hESCs in the bright field. (K) mRNA expression pattern of several marker genes (GATA2, FOXA2, SOX17, and AGGRECAN) in RUNX1::EGFP+ cells and RUNX1::EGFP- cells (**, p value < 0.01; *, p value < 0.05; ns, not significant; unpaired t-test).
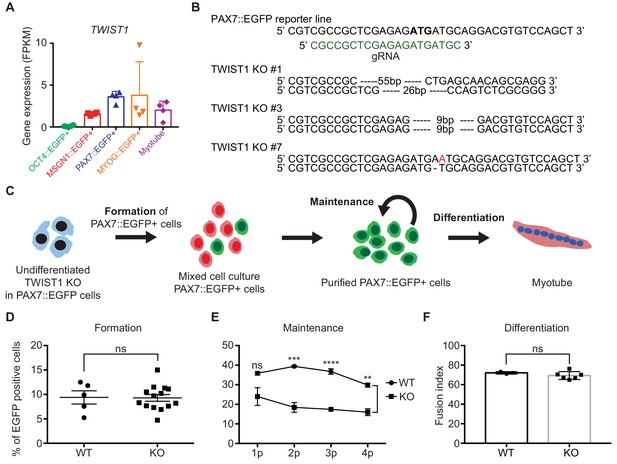
Establishment of TWIST1 knock-out (KO) lines in PAX7::EGFP reporter line and functional analysis of TWIST1 during human in vitro myogenesis.
(A) TWIST1 gene expression pattern of RNA-seq data in five different cell populations during muscle differentiation. (B) The position of genomic DNA and the sequence of gRNA for KO of the TWIST1 gene and the clone numbers with deleted sequences. (C) The experimental scheme of skeletal muscle specification, purification and differentiation. (D) The formation of PAX7::EGFP+ cells in WT and TWIST1 KO lines. (E) The maintenance of PAX7::EGFP+ cell population in WT and TWIST1 KO lines during PAX7::EGFP+ cell expansion. (F) The ability of multinucleated myotube formation in WT and TWIST1 KO lines.
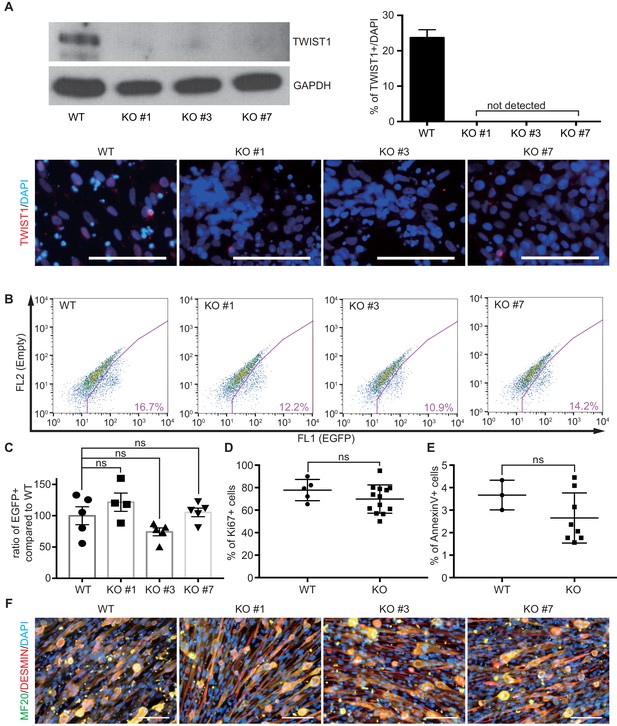
The characterization of TWIST1 KO lines in PAX7::EGFP reporter line.
(A) Validation of TWIST1 KO lines with western blot and quantification of TWIST1+ cells at day 30 of in vitro skeletal muscle specification. (B) FACS analysis of PAX7::EGFP in WT and TWIST1 KO clones (#1, #3, #7) at day 30 of in vitro muscle specification. (C) The formation ratio of PAX7::EGFP+ cells in each TWIST1 KO lines compared to WT (ns, not significant; unpaired t-test). (D) The percentage of Ki67+ cells in WT and TWIST1 KO lines. (E) The percentage of Annexin V+ cells in WT and TWIST1 KO lines. (F) Immunocytochemistry of MF20 and DESMIN in WT and TWIST1 KO lines.
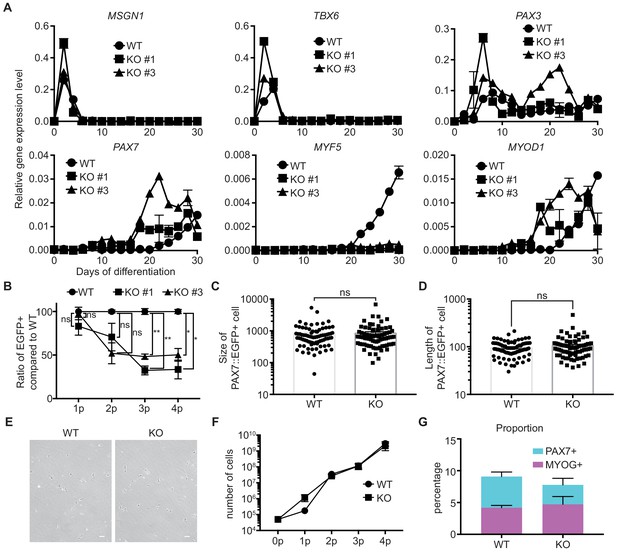
Characterization of TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
(A) mRNA expression pattern of stage-specific marker genes for in vitro skeletal muscle specification. (B) Ratio of EGFP+ percentages in each TWIST1 KO clone (#1 and #3) compared to those of WT cells (**, p value < 0.01; *, p value < 0.05; ns, not significant unpaired t-test). (C) Quantification of cell size for cultured cells of WT and TWIST1 KO line (ns, not significant unpaired t-test). (D) Quantification of cell length for cultured cells of WT and TWIST1 KO line (ns, not significant unpaired t-test). (E) Images for cultured cells of WT and TWIST1 KO line. (F) Cell proliferation rates of WT and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells after sorting. (G) Proportions of PAX7+ cells and MYOG+ cells in WT and TWIST1 KO lines during in vitro skeletal muscle specification.
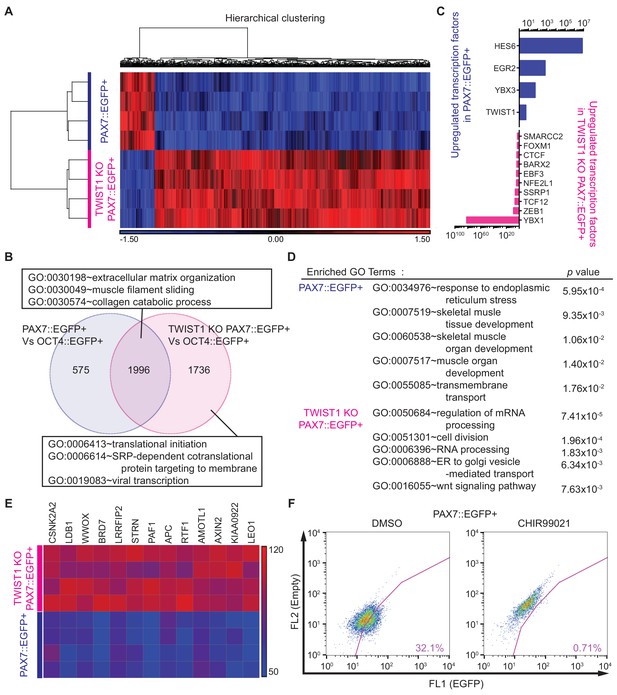
Whole transcriptome analysis between PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
(A) Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of RNA-seq data for PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells. (B) Venn diagram of the upregulated genes and their GO terms in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells compared to OCT4::EGFP+ cells. (C) List of upregulated TFs in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells compared to each other. (D) Enriched Gene ontology (GO) terms with whole transcriptome that had high p values between PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells from RNA-seq data. (E) Heatmap of Wnt signaling downstream target gene expression patterns in PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells. (F) FACS plots of EGFP percentage with Wnt activator (CHIR99021) in PAX7::EGFP+ cells during in vitro cell proliferation.
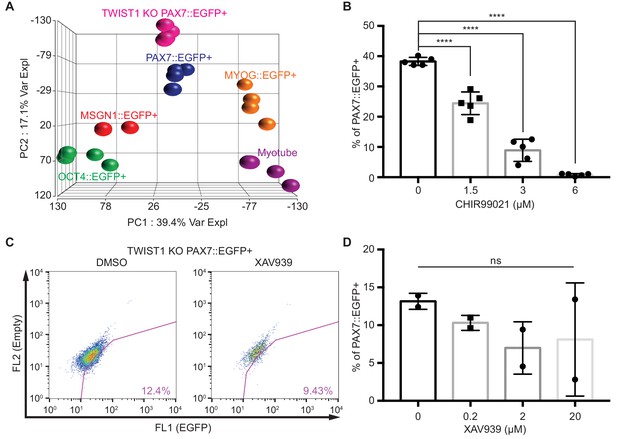
Transcriptome analysis between PAX7::EGFP+ cells and TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
(A) The PCA plot including the TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cell population during in vitro myogenesis. (B) The percentage of PAX7::EGFP+ cells with serial dose-dependent treatments of CHIR99021 during in vitro cell culture for maintaining PAX7 gene expression. (C) The FACS plots of EGFP percentage with Wnt inhibitor (XAV939) in TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells during in vitro cell proliferation. (D) The quantification of TWIST1 KO PAX7::EGFP+ cells with dose-dependent treatments of XAV939 and DMSO as a control during in vitro cell proliferation for maintaining PAX7 gene expression.
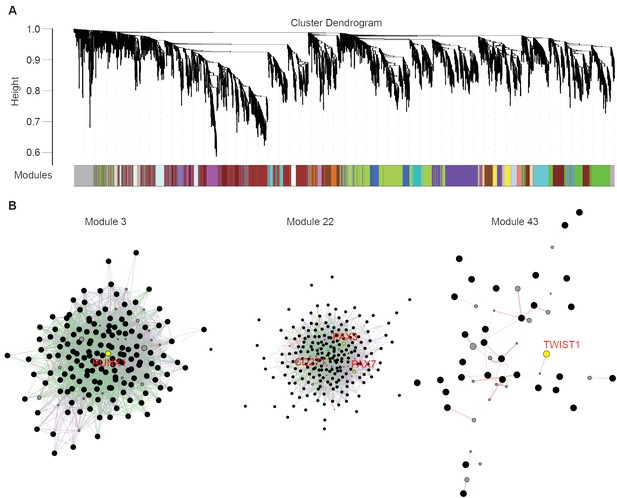
Stage-specific modules of RNA-seq data from five different cell types with weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
(A) WGCNA dendrogram of five different cell types. (B) Protein interaction network plots of module 3, module 22, and module 43.
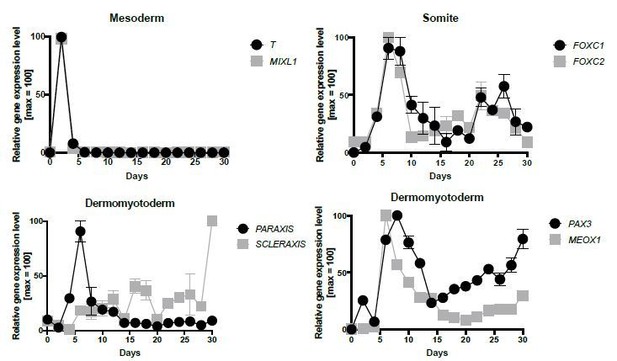
mRNA expression pattern of several marker genes during in vitro skeletal muscle specification (n = 2, independent biological repeats).
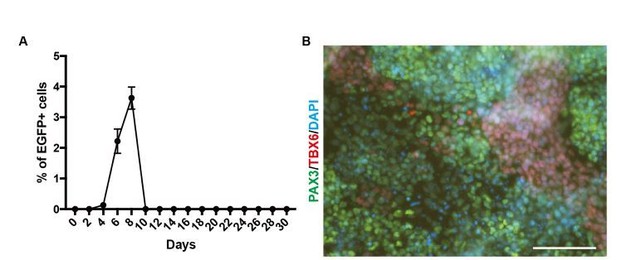
PAX3 gene expression during in vitro skeletal muscle differentiation.
(A) EGFP expression pattern for PAX3 gene during skeletal muscle specification (n = 2). (B) Immunohistochemistry for the PAX3 and TBX6 at Day 4 (bar, 100μm).
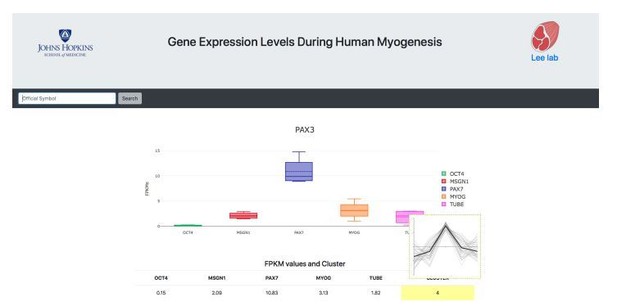
A representative screen-shot of inclusive gene expression atlas during human myogenesis.
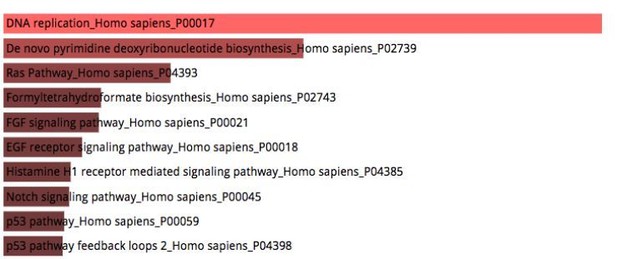
Pathway analysis of cell type specific gene signatures between MYOG::EGFP+ cells and Myotubes.
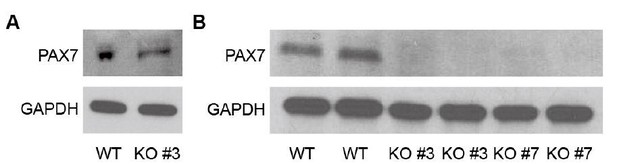
Western blot of PAX7 in WT and TWIST1 KO lines.
(A) Western blot of PAX7 in WT and TWIST1 KO lines (clone #3) at Day 30 of myogenic specification. (B) Western blot of PAX7 in WT and TWIST1 KO lines (clone #3 and #7) during expansion of PAX7::GFP+ cells after cell sorting at passage 4.
Videos
Twitching multinucleated myotubes derived from FACS-purified PAX7::EGFP+ cells.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Degignation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | H9 Human ES | WiCell | WAe009-A | |
| Antibody | α-ACTININ (Sarcomeric) (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: A7811 RRID: AB_476766 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | AP2 (rabbit polyclonal) | DSHB | Cat#: 3B5 RRID: AB_528084 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | CD271 (mouse monoclonal) | Advanced Targeting Systems | Cat#: AB-N07 RRID: AB_171797 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | DESMIN (mouse monoclonal) | DAKO | Cat#: M0760 RRID: AB_2335684 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | DYSTROPHIN (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat#: MANDYS1(3B7) RRID:AB_528206 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | MF20 (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat#: MF20 RRID: AB_2147781 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | MYOG (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat#: F5D RRID: AB_2146602 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | NANOG (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat#: 3580 RRID:AB_2150399 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | OCT4 (mouse monoclonal) | SANTA CRUZ | Cat#: sc-5279 RRID:AB_628051 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | PAX7 (mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | Cat#: pax7 RRID:AB_528428 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | RUNX1 (rabbit polyclonal) | abcam | Cat#: ab23980 RRID:AB_2200834 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | SOX10 (mouse monoclonal) | SANTA CRUZ | Cat#: sc-17343 RRID:AB_2255319 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | TRA1-81 (mouse monoclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat#: 4745 RRID:AB_2119060 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | TWIST1 (mouse monoclonal) | abcam | Cat#: ab175430 | (1:100) |
| Commercial assay or kit | Proteome Profiler Human Phospho-Kinase Array kit | R and D Systems | Cat#: ARY003B | |
| Other | DAPI | Invitrogen | D1306 | (1 ug/ml) |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Gene expression levels and GO terms of Five groups during myogenesis, Related to Figure 2 and Figure 2—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
DGEs and GO terms of Three groups and DGEs of Two groups, Related to Figure 2E and Figure 2—figure supplement 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Clustering and GO terms of Five Clusters, Related to Figure 3 and Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Gene expression levels, DGEs and GO terms of Three groups and DGEs of TWIST1 KO lines, Related to Figure 6 and Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Resources table for the primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-supp5-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/46981/elife-46981-transrepform-v1.docx