The visual speech head start improves perception and reduces superior temporal cortex responses to auditory speech
Figures
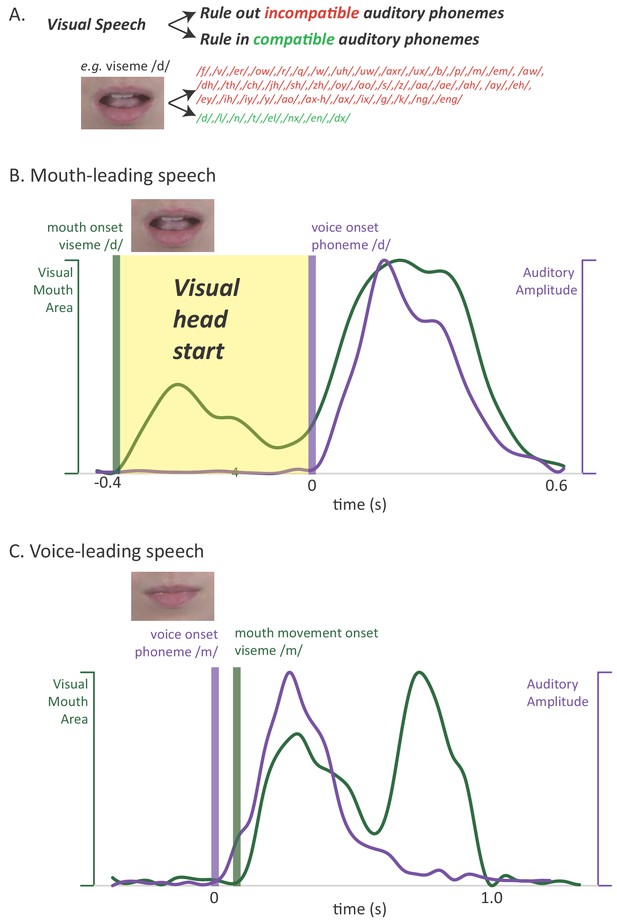
Relationship between auditory and visual speech.
(A) Visual speech provides independent information about speech content. Any given visual speech feature, such as the open mouth visible when pronouncing ‘d’, is incompatible with many auditory phonemes (red) and compatible with a few auditory phonemes (green). (B) Visual speech provides a processing head start on auditory speech (yellow region) as shown by auditory and visual speech feature asynchrony for the word ‘drive.’ Audiovisual speech is composed of visual mouth movements (green line showing visual mouth area) and auditory speech sounds (purple line showing auditory sound pressure level). Lip and mouth movements (visual speech onset, green bar) occur prior to vocalization (auditory speech onset, purple bar). Time zero is the auditory speech onset. This word is classified as ‘mouth-leading’ as visual mouth movements begin before auditory speech. (C) For the word ‘known,’ mouth movements begin after auditory vocalization (green bar comes after purple bar) and there is no visual head start. This word is termed as ‘voice-leading’ because vocalization begins before visible mouth movements.
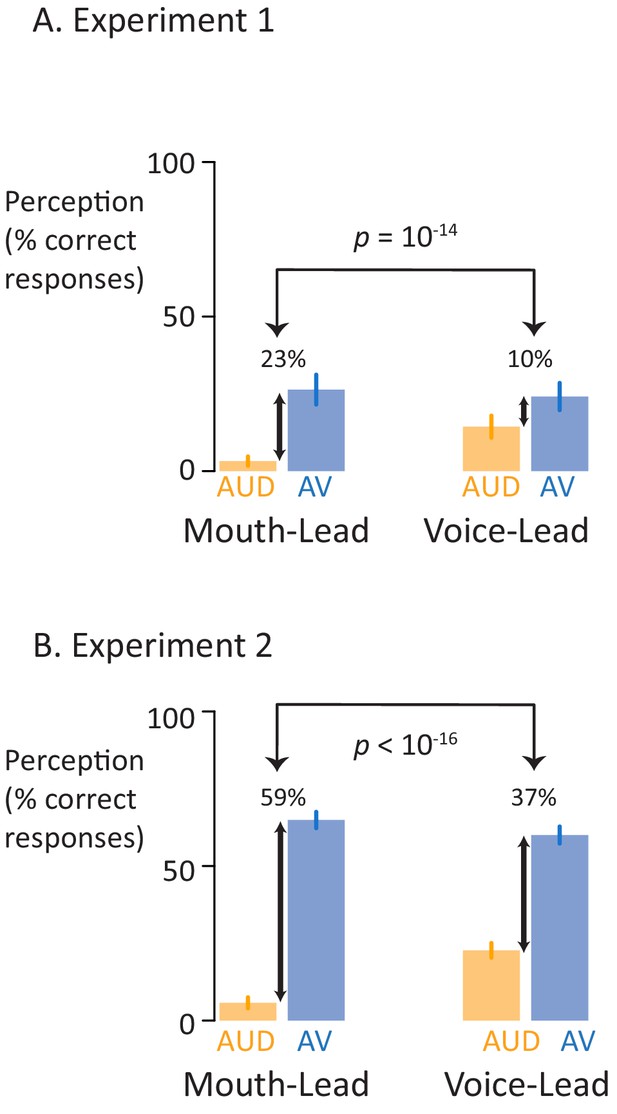
Perceptual performance on speech-in-noise recognition tasks.
(A) Results of the first perceptual experiment on two mouth-leading words and two voice-leading words. For the mouth-leading words (left plot), the addition of visual speech increased comprehension of noisy auditory words by 23% (small black arrow showing difference between noisy auditory-only speech, orange bar labeled AUD, and noisy audiovisual speech, blue bar labeled AV). In contrast, for voice-leading words (right plot) the addition of visual speech increased accuracy by only 10%. The interaction (difference of the differences) was significant (p=10−14). Error bars represent standard error of the mean across subjects. (B) Results of the second perceptual experiment on five mouth-leading words and five voice-leading words, all different than those used in the first perceptual experiment. Adding visual speech to noisy auditory speech produced a significantly greater enhancement (p<10−16) for mouth-leading words (left plot) than for voice-leading words (right plot).
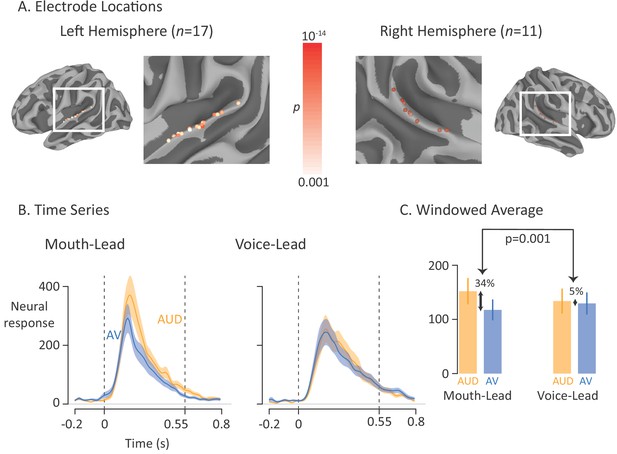
Average broadband high-frequency activity by experimental condition.
(A) The location of 17 left-hemisphere (left panel) and 11 right-hemisphere (right panel) electrodes that met both an anatomical criterion (located over the posterior superior temporal gyrus) and a functional criterion (significant response to auditory-only speech). The color of each electrode shows the significance (corrected for multiple comparisons using p<0.001 Bonferroni-corrected) of each electrode’s response to the auditory-only condition during the period from auditory speech onset to offset. (B) For mouth-leading words (left panel), the neural response to auditory-only words (AUD; orange line) was greater than the response to audiovisual words (AV; blue line). For voice-leading words (right panel), the responses were similar. Shaded regions show standard error of the mean across electrodes (n = 28) and dashed lines show auditory speech onset (0 s) and offset (0.55 s). (C) To quantify the difference between word types, the neural response was averaged within the window defined by auditory speech onset and offset. For mouth-leading words (left panel), the auditory-only format evoked a significantly greater response than the audiovisual format (34% difference, p=10−5). For voice-leading words, there was little difference (5%, p=0.41), resulting in a significant interaction between word format and word type (34% vs. 5%, p=0.001). Error bars show standard error of the mean across electrodes (n = 28).
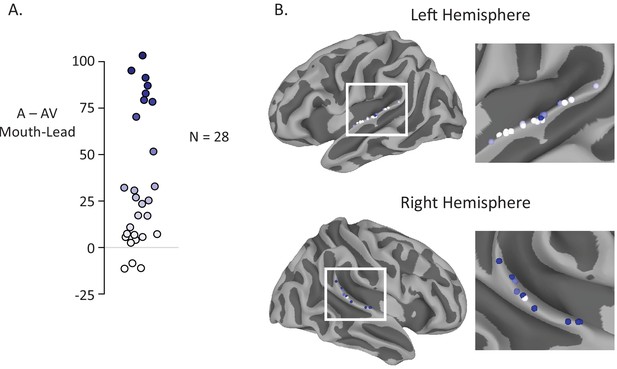
Anatomic distribution of multisensory gain by electrode.
(A) The reduction in neural response to audiovisual compared to auditory-only speech for mouth-leading words was measured for each electrode (difference in average BHA to audiovisual stimuli and average BHA to auditory-only stimuli over time window 0 ms to 550 ms). Most electrodes (25 of 28) had a decreased neural response to audiovisual compared to auditory only stimuli. Color on the white-to-blue gradient corresponds to amount of reduction. (B) All electrodes from all participants displayed on a template brain (same color scale as A). No consistent organization of multisensory influence was observed.
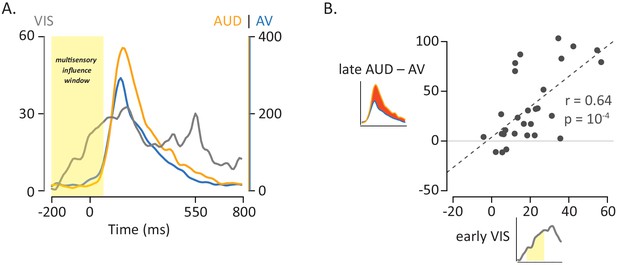
Influence of Visual Speech on Multisensory Integration.
(A) Responses to the three formats of mouth-leading words (visual-only, gray; auditory-only, orange; audiovisual, blue). Responses were aligned to auditory onset at t = 0 (or to the time when auditory onset would have occurred for visual-only stimuli). The left vertical axis contains the scale for visual-only neural responses (0% to 60%), which were much smaller than auditory-only and audiovisual responses (scale given in right-hand vertical axis; 0% to 400%). The visual-only response onset occurred prior to auditory-only response onset, creating a multisensory influence window (yellow region) in which visual speech could influence processing of auditory speech, resulting in a reduced response to audiovisual compared with auditory-only speech. (B) The amplitude of the early neural response (BHA) to visual-only stimuli was positively correlated with the difference in the neural response between audiovisual and auditory-only speech (N = 28; r = 0.64, p=10−4). The early visual-only response (horizontal axis) for each electrode was the average BHA for the 200 ms period following visual speech onset (−100 ms to 100 ms; yellow region in axis inset). The difference between the audiovisual and auditory-only neural response (vertical axis) was calculated as the difference in average BHA during auditory speech (0 ms to 550 ms; red region in axis inset).
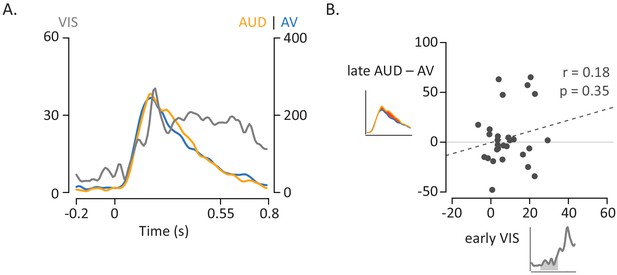
Influence of Visual Speech for Voice-Leading Words.
(A) Responses to the three formats of voice-leading words (visual-only, gray; auditory-only, orange; audiovisual, blue). Responses were aligned to auditory onset at t = 0 (or to the time when auditory onset would have occurred for visual-only stimuli). The left vertical axis contains the scale for visual-only neural responses (0% to 60%), which were much smaller than auditory-only and audiovisual responses (scale given in right-hand vertical axis; 0% to 400%). The neural response to the three word began at similar times. (B) Correlation between the amplitude of the early neural response to visual-only words and the difference in the neural response between audiovisual and auditory-only speech. The early visual-only response (horizontal axis) for each electrode was the average BHA for the 200 ms period following visual speech onset (time −100 ms to 100 ms; gray region underneath curve in axis inset). The reduction in neural response to audiovisual vs. auditory-only speech (vertical axis) was calculated as the difference in average BHA during the duration of the entire auditory stimulus (0 ms to 550 ms; red region in axis inset).
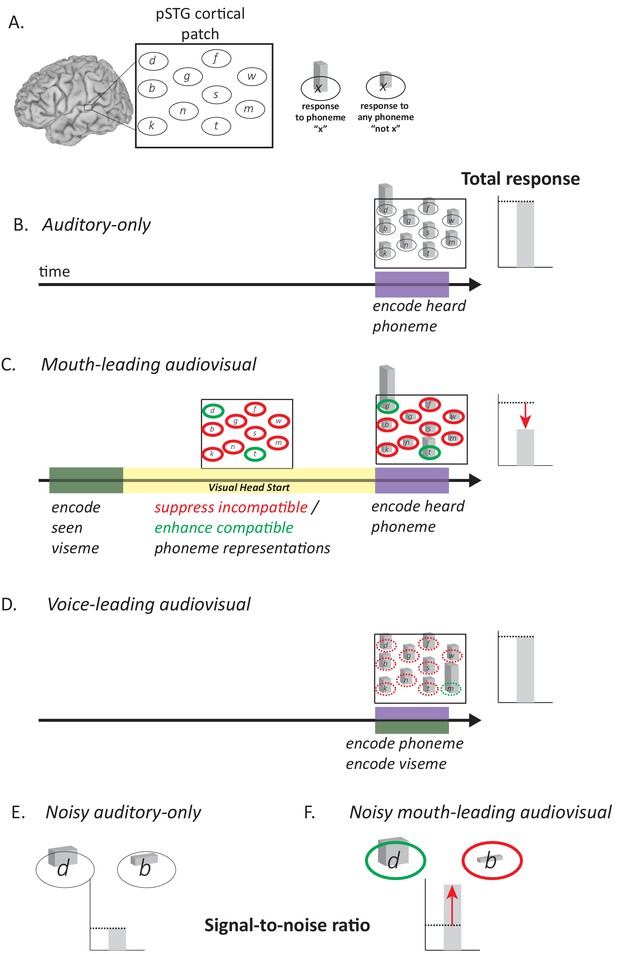
Model of Audiovisual Interactions in pSTG.
(A) In the pSTG, small populations of neurons are selective for specific speech sounds (phonemes). Each population is shown as an ellipse labeled by its preferred phoneme. The ellipses are shown spatially separated but the model is equally applicable if the neurons are intermixed instead of spatially segregated. Selectivity is only partial, so that for the population of neurons selective for a given phoneme ‘x’ (ellipse containing ‘x’) presentation of the phoneme ‘x’ evokes a larger response than presentation of any other phoneme (‘not x’). (B) When an auditory phoneme is presented, all populations of neurons respond, with the highest response in the population of neurons selective for that phoneme. Example shown is for presentation of auditory ‘d’; the amplitude of the response in each population of neurons is shown by the height of the bar inside each ellipse, with highest bar for ‘d’ population. The total response summed across all populations is shown at right. (C) For mouth-leading speech, early arriving visual speech provides a head start (yellow region). During this time, activity in neuronal populations representing incompatible phonemes is suppressed (red outlines) and activity in neuronal populations representing compatible phonemes in enhanced (green outlines). Arrival of auditory speech evokes activity in all populations. Because there are more suppressed populations than enhanced populations, the total response across all populations is decreased relative to the auditory-only format (dashed line and red arrow). Example shown is for audiovisual ‘d’, resulting in larger responses in populations representing the compatible phonemes ‘d’ and ‘t’, smaller responses in all other populations. (D) For voice-leading speech, visual speech and auditory speech onset at similar times, resulting in no opportunity for suppression or enhancement (dashed outlines; example shown is for audiovisual ‘m’). The total response is similar to the auditory-only format (dashed line). (E) For noisy speech, there is a reduction in the amplitude of the response to auditory phonemes for both preferred and non-preferred populations (example shown is for noisy auditory ‘da’; only two neuronal populations are shown for simplicity). The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is defined as the ratio the response amplitude of the preferred to the non-preferred population. (F) For noisy audiovisual speech that is mouth-leading (example shown is for noisy audiovisual ‘da’) the response to the compatible neuronal populations are enhanced and the response to the incompatible neuronal populations are suppressed (visible as differences in bar height inside green and red outlines), resulting in increased SNR (red arrow).
Additional files
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48116.009





