Alterations in the amplitude and burst rate of beta oscillations impair reward-dependent motor learning in anxiety
Figures
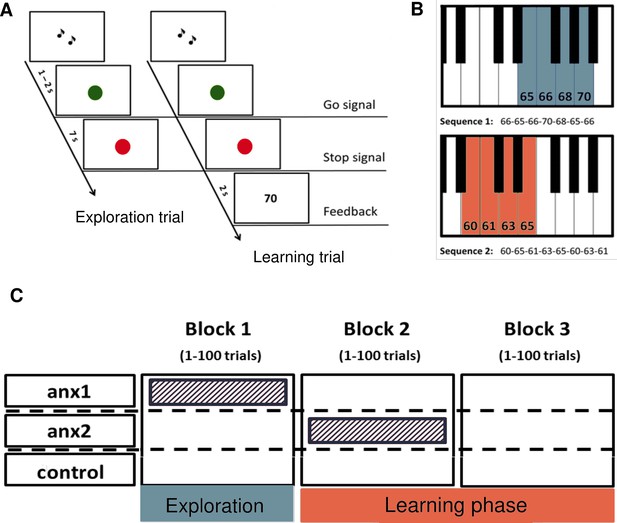
A novel paradigm for testing reward-based motor sequence learning.
(A) Schematic of the task. Participants performed sequence1 during 100 initial exploration trials, followed by 200 trials over two blocks of reward-based learning performing sequence2. During the learning blocks, participants received a performance-related score between 0–100 that would lead to monetary reward. (B) The pitch content of the sequences used in the exploration (sequence1) and reward-based learning blocks (sequence2), respectively. (C) Schematic of the anxiety manipulation. The shaded area denotes the phase in which anxiety was induced in each group, using the threat of an upcoming public speaking task, which took place immediately after that block was completed.
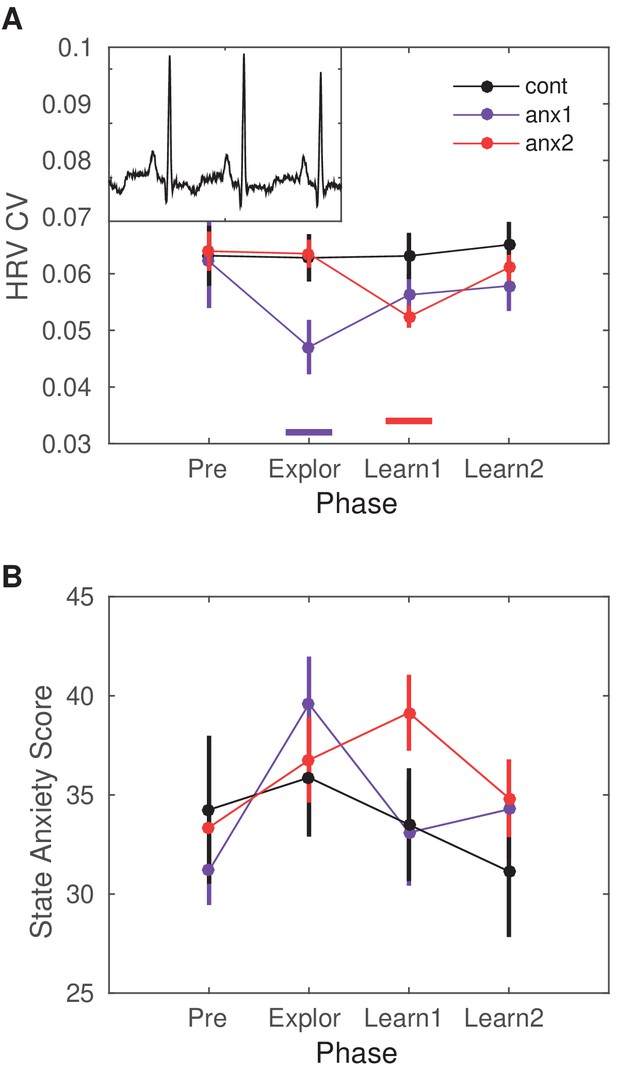
Heart-rate variability (HRV) modulation by the anxiety manipulation.
(A) The average HRV measured as the coefficient of variation (CV) of the inter-beat-interval is displayed across the experimental blocks: initial resting state recording (Pre), initial exploration (Explor), first block of learning (Learn1) and, last block of learning (Learn2). Relative to Pre, there was a significant drop in HRV in anx1 participants during initial exploration (within-subject statistics with paired permutation tests, after controlling the false discovery rate [FDR] at level q = 0.05 due to multiple comparisons, termed ). In anx2 participants, the drop in HRV was found during the first learning block, which was targeted by the anxiety manipulation (). Between-group comparisons revealed that anx1, relative to the control group, exhibited a significantly lower HRV during the exploration phase (, purple bar at the bottom). The anx2 group manifested a significant drop in HRV relative to controls during the first learning block (, red bar at the bottom). These results demonstrate a group-specific modulation of anxiety relative to controls during the targeted blocks. The mean HR did not change within or between groups (). (B) STAI state anxiety score in each group across the different experimental phases. Participants completed the STAI state anxiety subscale first at the start of the experiment before the resting state recording (Pre) and subsequently again immediately before each experimental block (and right after the anxiety induction: Explor, Learn1, Learn2). There was a within-group significant increase in the score for each experimental group during the phase targeted by the anxiety manipulation (anx1: Explor relative to Pre, average score 40 [2] and 31 [2], respectively; ; anx2: Learn1 relative to Pre, average score 39 [2] and 34 [2], respectively; ). Between-group differences were non-significant.
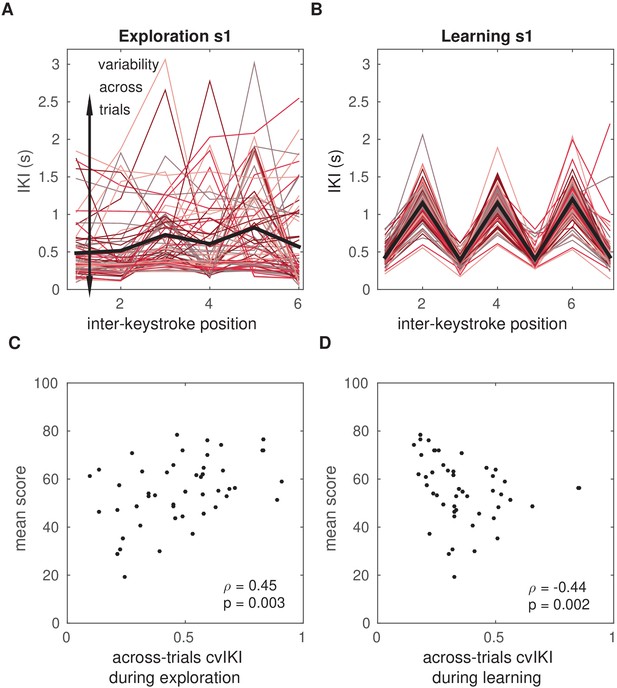
Temporal variability during initial exploration and during reward-based learning.
(A, B) Illustration of timing performance during initial exploration (A) and learning (B) blocks for one representative participant, s1. The x-axis represents the position of the inter-keystroke interval (sequence1: seven notes, corresponding to six inter-keystroke temporal intervals; sequence2: eight notes, corresponding to seven inter-keystroke intervals). The y-axis shows the inter-keystroke interval (IKI) in ms. Black lines represent the mean IKI pattern. Red-colored traces represent the individual timing performance in each of the 100 (A) and 200 (B) trials during exploration and learning blocks, respectively. Task-related temporal variability was measured using the across-trials coefficient of variation of IKI, cvIKI. This measure was computed in successive bins of 25 trials, which allowed us to track changes in cvIKI across time. (C) Non-parametric rank correlation in the total population (N = 60) between the across-trials cvIKI during exploration (averaged across the four 25-trial bins) and the average score achieved subsequently during learning (Spearman ). (D) Same as panel (C) but using the individual value of the across-trials cvIKI from the learning phase (cvIKI was averaged here across all eight 25-trial bins; Spearman ).
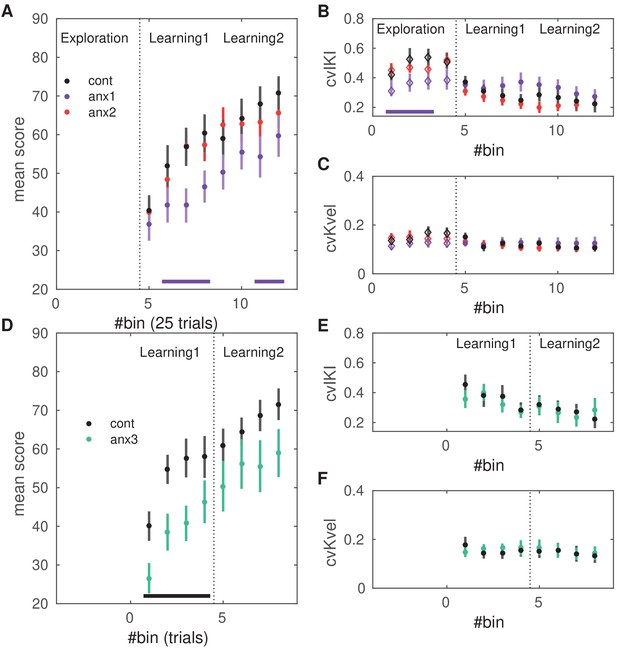
Effects of anxiety on behavioral variability and reward-based learning.
The score was computed as a 0–100 normalized measure of proximity between the norm of the pattern of differences in inter-keystroke intervals performed in each trial and the target norm. All of the behavioral measures shown in this figure are averaged within bins of 25 trials. (A) Scores achieved by participants in the anx1 (N = 20), anx2 (N = 20), and control (N = 20) groups across bins 5:12 (trial range 101–300), corresponding to blocks 2 and 3 and the learning phase. Participants in anx1 achieved significantly lower scores than control participants (, denoted by the bottom purple line). (B) Changes in across-trials cvIKI, revealing a significant drop in task-related exploration during the initial phase in anx1 relative to control participants (). Anx2 participants did not differ from control participants. (C) Same as panel (B) but for the across-trials cvKvel. (D–F) Control experiment: effect of anxiety on variability and learning after removal of the initial exploration phase. Panels (D-F) are displayed in the same way as panels (A–C) for experimental (N = 13) and control (N = 13) groups. Significant between-group differences are denoted by the black bar at the bottom (). (F) In anx3 participants (green), there was a significant drop in the mean scores during the first learning block relative to control participants (). Bars around the mean show ± SEM.
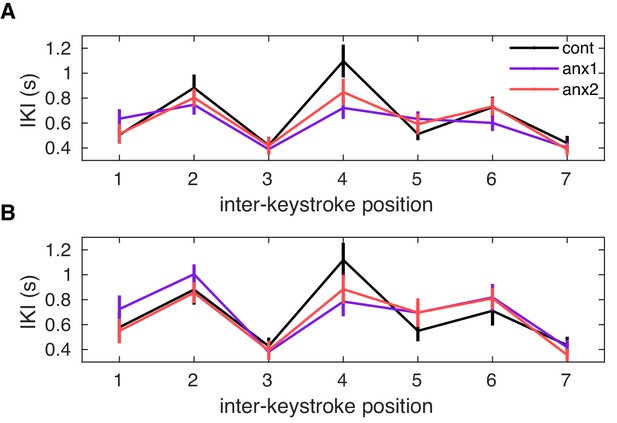
Mean learned solution in each group.
Mean learned solution in each group. On average, the learned performance was not significantly different between experimental and control groups, during either the first (A) or second (B) learning block (; here, a permutation test was carried out to assess differences between groups in the mean IKI at each keystroke position).
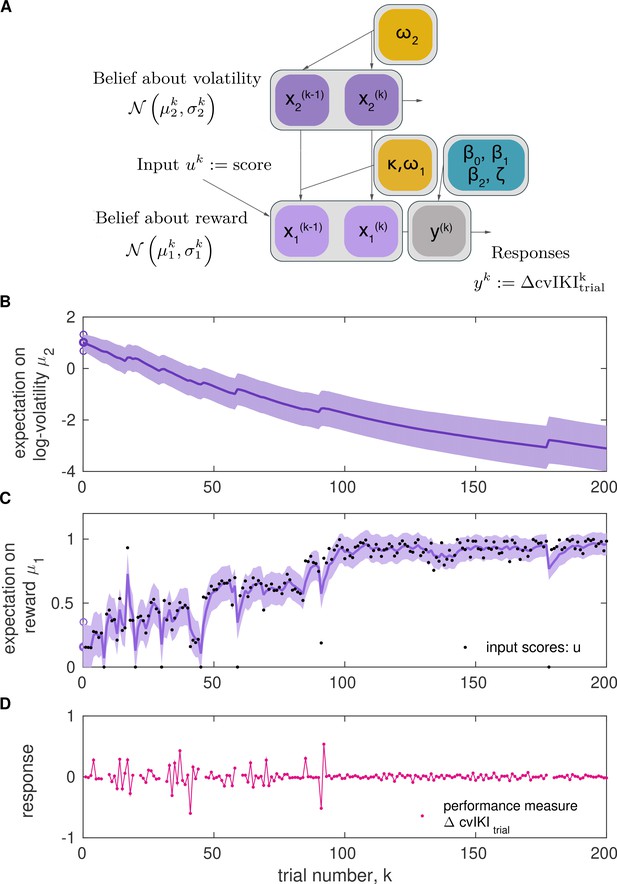
Two-level Hierarchical Gaussian Filter for continuous inputs.
(A) Schematic of the two-level HGF, which models how an agent infers a hidden state in the environment (a random variable), , as well as its rate of change over time (, environmental volatility). Beliefs about those two hierarchically related hidden states (, ) at trial are updated by the sensory input (, observed feedback scores in our study) for that trial via prediction errors (PEs). The states and are continuous variables evolving as coupled Gaussian random walks, where the step size (variance) of the random walk depends on a set of parameters (shown in yellow boxes). The lowest level is coupled to the level above through the variance of the random walk: . The posterior distribution of beliefs about these states is fully determined by the sufficient statistics (mean) and (variance) for levels . The equations describing how expectations () change from trial to are Equation 6 and Equation 10. The response model generates the most probable response, , according to the current beliefs, and is modulated by the response model parameters . In the winning model, the response parameter was the change between trial and in the degree of temporal variability across keystrokes: , normalized to range 0–1. (B, C) Example of belief trajectories (mean, variance) associated with the two levels of the HGF for continuous inputs. Panel (C) displays the expectation on the first level, , which represents an individual’s expectation (posterior mean) of the true reward values for the trial, . Black dots represent the trial-wise input (feedback scores, ). Panel (B) shows the trial-by-trial beliefs about log-volatility , determined by the expectation and associated variance. Shaded areas denote the variance or estimation uncertainty on that level. (D) Illustration of the performance measure used as response in the winning model, .
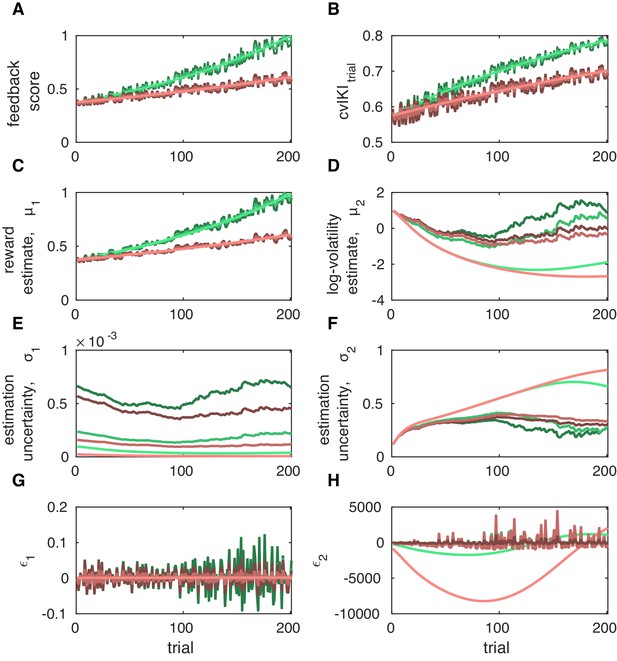
Trial-by-trial belief trajectories for simulated performances.
All belief trajectories were generated using prior values on the HGF parameters as shown in Table 1. We simulated performances in six agents by changing the trial-to-trial difference in IKI values across keystroke positions, thus leading to different trajectories of (B) and feedback scores (A). We started with a pattern of IKI values of [0.2, 0.6, 0.2, 0.6, 0.2, 0.6, 0.2] s and iteratively prolonged the inter-keystroke interval at positions 2, 4, and 6, thereby increasing the temporal difference between IKI values, the vector norm of the total IKI pattern, and the cvIKI value across keystroke positions within the trial, termed . In the plot, steeper and shallower slopes of change across trials in and associated feedback scores are denoted by green and pink colored lines, respectively. In addition, lighter colors denote smoother trial-by-trial transitions in values. Darker colors indicate noisier trial-by-trial changes in this measure, representing an agent with a more variable behavioral strategy every trial. (C, D) Expectation on reward and log-volatility, and (E, F) the associated variance or estimation uncertainty. (G,H) Precision-weighted prediction error on reward, , and volatility, . A steeper slope of change in feedback scores and was associated with higher log-volatility estimates and reduced uncertainty about volatility, . For a fixed slope, increasing levels of noise in the trajectories of the feedback scores and also contributed to higher volatility estimates and reduced . Thus, agents either (i) introducing more fluctuations in behavior from trial to trial or (ii) observing a faster rise in scores had a higher expectation of volatility and lower uncertainty about volatility.
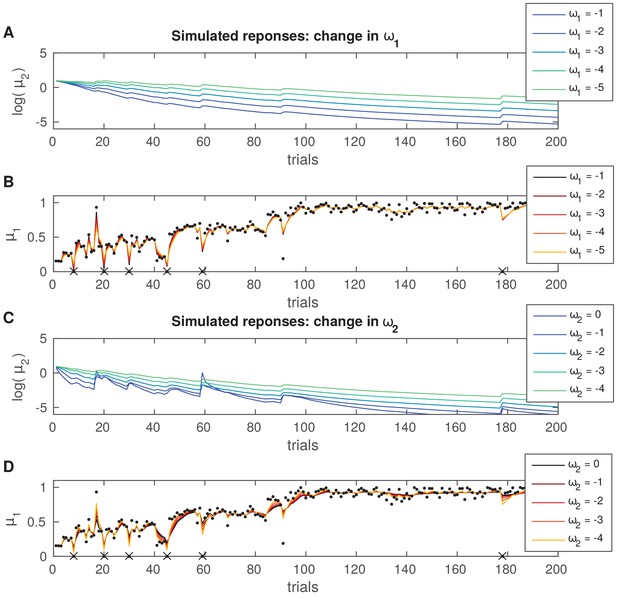
Simulated trial-by-trial belief trajectories in an ideal learner.
Simulated trial-by-trialtrajectories of posterior means of belief distributions in an ideal learner with different values of (A, B) or (C, D). All trajectories were simulated with identical input scores and parameters, except for (A, B) or (C, D): (precision of input). (A) Increasing values of (largest value = −1 in this example) lead to a more pronounced general reduction in the estimate of log-volatility across trials, log(). (B) The time series of the expectation on reward does not vary in a noticeable way as a function of . (C) Increasing values of (largest value = 0 in this example) triggered more phasic trial-by-trial changes in the log-volatility estimate, log(), in response to prediction errors at the lower level (PE about reward, indicated by sharp changes in the trajectories of reward expectations in panel [D]). Increasing values of correspond to higher uncertainty in the prediction on that level (see Equation 13 in 'Materials and methods'). (D) Same as panel (B), but for varying values of . Expectations on reward did not change considerably as a function of in this example.
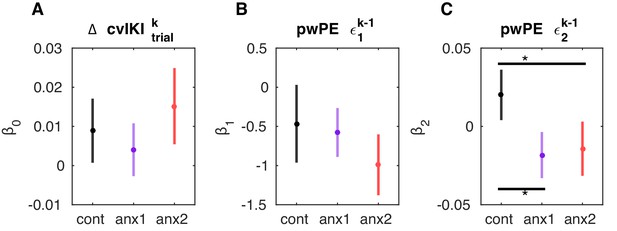
coefficients of the winning response model.
(A–C) Mean (and SEM) values of the coefficients that explain the performance measure in trial as a linear function of (i) a constant value () and (ii) the precision-weighted prediction errors on the previous trial : pwPE concerning reward () and pwPE concerning volatility (). The performance measure in the winning model, , was the change in the degree of temporal variability across keystroke positions from trial to . The values are plotted separately for each control and experimental group. The best response model was obtained using Random Effects Bayesian Model Comparison (BMC) in a set of two families of response models, followed by BMC within the winning family (see main text). The noise parameter did not significantly differ between groups (), and therefore we found no differences in how the model was able to estimate predicted responses to fit the observed responses in each group. (B, C) There were no significant between-group differences in or coefficients (). (C) Control participants had a positive and significantly higher coefficient than anx1 and anx2 participants (, denoted by the horizontal lines and black asterisks). This implies that in control participants an increase in (larger update in the expectation of volatility) contributed to a greater change in the relevant performance measure on the following trial, yet it led to a decrease in anx1 and anx2.
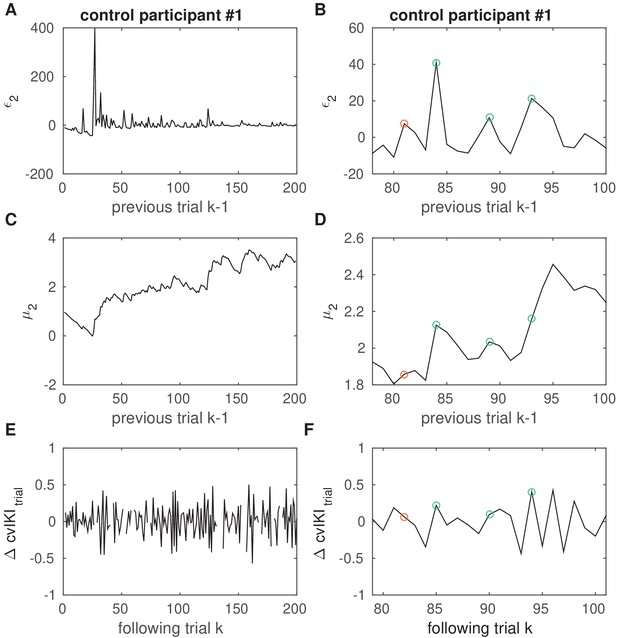
Example in one control participant of the association between pwPEs and performance.
Example in one control participant of the association between pwPEs relating to volatility and subsequent changes in performance. (A, B) Illustration of the trajectory of pwPE relating to volatility on trial , . Right panels are an enlarged display of a section of the corresponding left panel. (C, D) Trajectory of the expectation on log-volatility, . (E, F) Performance measure in the winning response model, , representing the change from trial to in the task-relevant performance variable associated with reward, . Green circles denote trials of large values of that were followed by an increment in the performance measure (larger behavioral change). This figure illustrates the effect of positive coefficients in the response model in control participants, linking large values to large changes in behavior on the next trial. Red circles mark trials of large values that led to smaller changes in the performance variable in the subsequent trial.
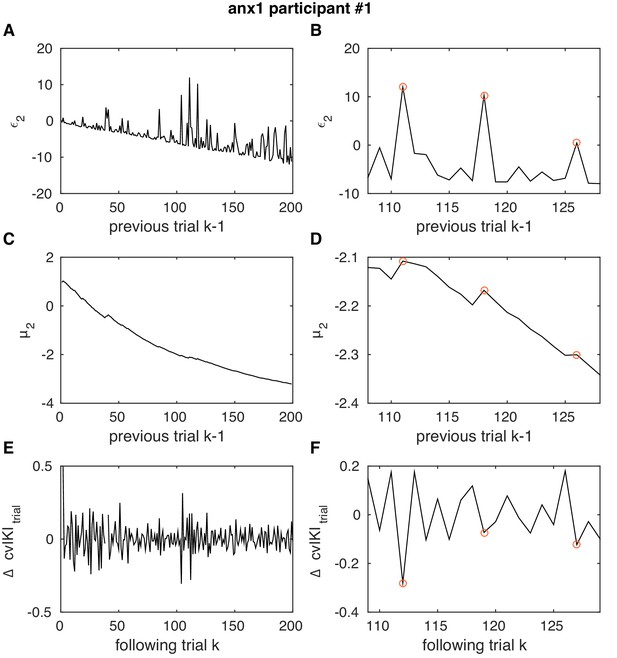
Example in one anx1 participant of the association between pwPEs and performance.
Example in one anx1 participant of the association between pwPEs relating to volatility and subsequent changes in performance. This figure illustrates the effect of negative coefficients in the response model in anx1 and anx2 participants, linking large values to large changes in behavior on the next trial. Same as Figure 5—figure supplement 4 but in one participant from the anx1 group.
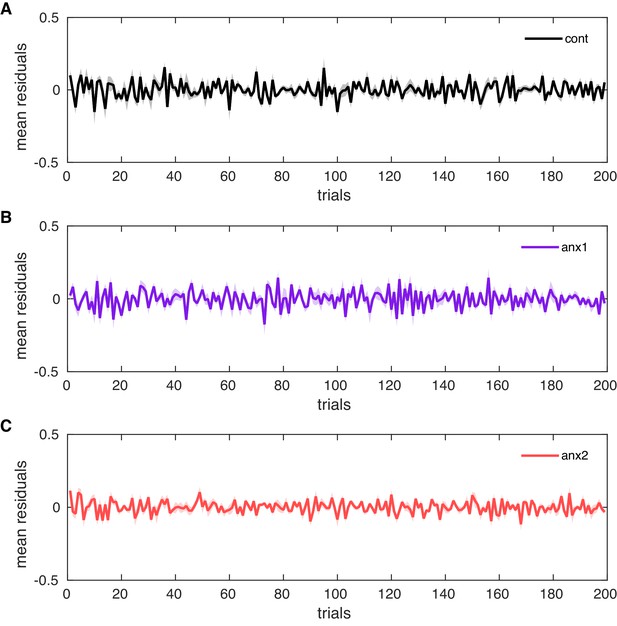
Grand-average trialwise residuals.
Grand-average trialwise residuals resulting from the difference between the observed responses and the responses predicted by the HGF. (A–C) The trialwise residuals in each control and experimental group are shown together as mean and SEM (shaded areas). The winning response model used as response variable the trial-by-trial change in , which is related to the temporal variability of IKI across keystroke positions in a trial. There were no systematic differences in the model fits across groups (; between-group differences in the mean residual, after averaging across trials — cont: ; anx1: ; anx2: ). In the additional control experiment, we also found no significant differences between groups in the mean residual values (mean residual values per group: cont: ; anx3: ).
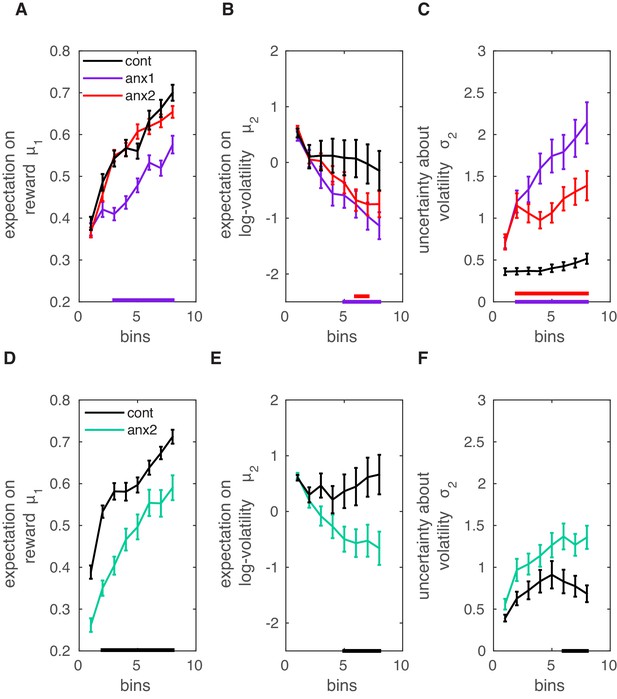
Computational modeling analysis.
Data shown as mean and ± SEM. (A) In the main experiment, anx1 participants underestimated the tendency for (meaning their expectation on reward in the current trial was lower; , purple bar at the bottom). (B) In addition, the expectation on environmental (phasic) log-volatility was significantly smaller in anx1 participants than in control participants (). Similar results were obtained in the anx2 group as compared to the control group (). (C) The uncertainty about environmental volatility was higher in anx1 and anx2 relative to control participants (anx1: ; anx2: ). Larger in the anx1 and anx2 groups contributed to the larger update steps of the estimate , shown in panel (B). (D–F) Same as panels (A–C) but in the separate control experiment. (D) The expectation on the reward tendency, , was lower for anx3 participants relative to control participants (, denoted by the black bar at the bottom). (E) Same as panel (B): anx3 participants had a reduced expectation of environmental volatility (). (F) Anx3 participants were also more uncertain about their phasic volatility estimates relative to control participants (). Thus, the anxiety manipulation in the control experiment biased participants to make larger updates of their expectation of phasic volatility.
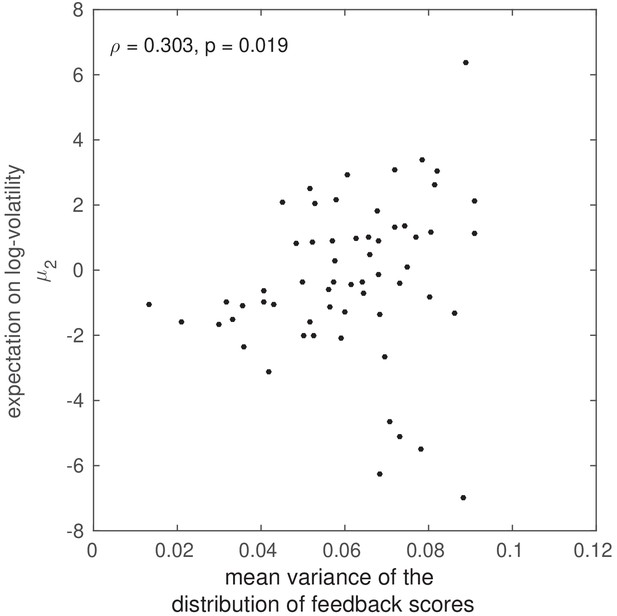
Correlation between HGF volatility estimates and the variance of the distribution of feedback scores.
Correlation between HGF volatility estimates and the variance in the distribution of feedback scores. Non-parametric rank correlation in the total population (N = 60) between the variance of the distribution of feedback scores across the 200 trials, and the average log-volatility estimates . The significant rank correlation () suggests that participants who encountered more variation in feedback scores in association with their performance also had a higher expectation of volatility.
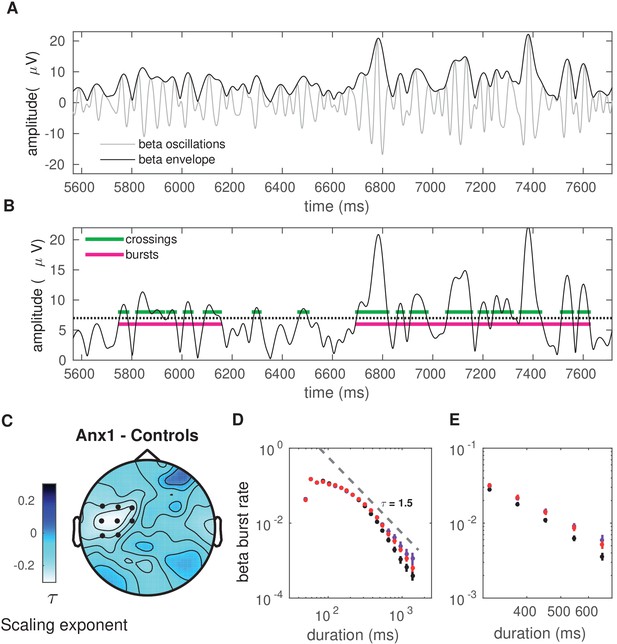
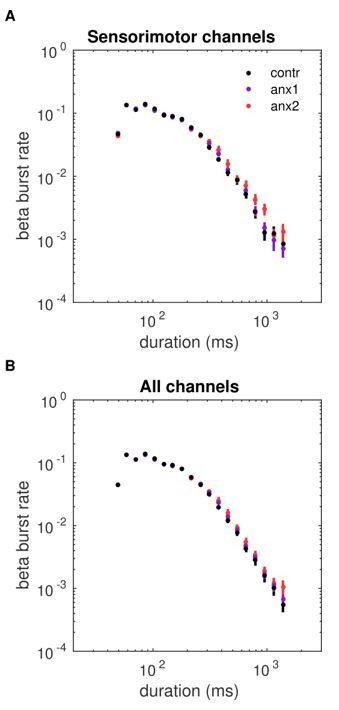
Anxiety during initial exploration prolongs the life-time of sensorimotor beta-band oscillation bursts.
(A) Illustration of the amplitude of beta oscillations (gray line) and the amplitude envelope (black line) for one representative subject and channel. (B) Schematic overview of the threshold-crossing procedure used to detect beta oscillation bursts. A threshold of 75% of the beta-band amplitude envelope was selected and beta bursts extending for at least one cycle were accepted. Windows of above-threshold amplitude crossings detected in the beta-band amplitude envelope (black line) are denoted by the green lines, whereas the windows of the associated bursts are marked by the magenta lines. (C) Scalp topography for between-group changes in the scaling exponent during initial exploration. A significant negative cluster was found in an extended region of left sensorimotor electrodes, resulting from a smaller life-time exponent in anx1 than in control participants. (Black dots indicate significant electrodes, two-tailed cluster-based permutation test, .) (D) Probability distribution of beta-band oscillation-burst life-times within the 50–2000 ms range for each group during initial exploration. The double-logarithmic representation reveals a power law within the fitted range (first duration bin excluded from the fit, as in Poil et al., 2008). For each power law, we extracted the slope, , also termed the life-time exponent. The dashed line illustrates a power law with = 1.5. The smaller scaling exponent found in anx1 participants, as compared to control participants, was associated with long-tailed distributions of burst duration, reflecting the presence of frequent long bursts. Anx2 participants did not differ from control participants in the scaling exponent. Data are shown as mean and ± SEM in the electrodes pertaining to the significant cluster in panel (C). (E) Enlarged display of panel (D) showing that bursts of duration 500 ms or longer were more frequent in anx1 than in control participants.
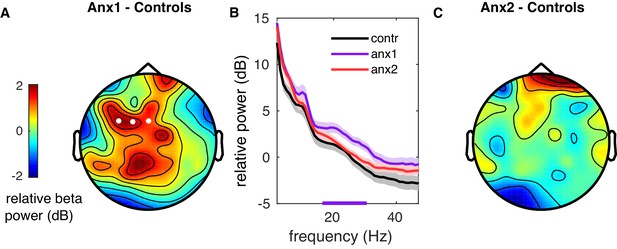
Sensorimotor beta power is modulated by anxiety during initial exploration.
(A) Topographical representation of the between-group difference (anx1–controls) in normalized beta-band power spectral density (PSD) in dB. A larger beta-band PSD increase was found in anx1 participants relative to control participants in a small cluster of contralateral sensorimotor electrodes (white dots indicate significant electrodes, two-tailed cluster-based permutation test, ). (B) The normalized PSD is shown within 4–45 Hz for each experimental and control group after averaging within the cluster of electrodes shown in panel (A). The purple bottom line denotes the frequency range of the significant cluster shown in (A). No significant between-group differences outside the beta range (4–12 Hz or 31–45 Hz) were found (). Anx2 and control participants did not differ in power modulations. Shaded areas denote mean ± SEM. (C) Same as panel (A) but for differences in beta-band PSD between anx2 and control participants. No significant clusters were found.
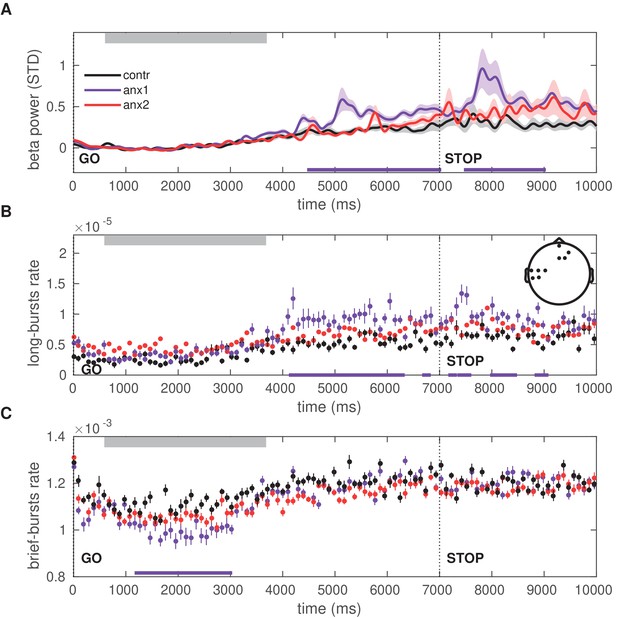
Time course of the beta power and burst rate during trials in the exploration block.
(A) The time representation of the beta power throughout trial performance shows two distinct time windows of increased power in participants affected by the anxiety manipulation: following sequence performance and after the STOP signal (; black bars at the bottom indicate the windows of significant differences). Shaded areas indicate the SEM around the mean. Performance of sequence1 was completed on average between 680 (50) and 3680 (100) ms, denoted by the gray rectangle at the top. The STOP signal was displayed at 7000 ms after the GO signal, and the trial ended at 9000 ms. (B) The rate of oscillation bursts of longer duration ( ms) exhibited a similar temporal pattern, with increased burst rate in anx1 participants following movement and the STOP signal (). (C) In contrast to the rate of long bursts, the rate of brief oscillation bursts was reduced in anx1 relative to control participants, albeit during performance (). All averaged values in panels (A–C) are estimated across the significant sensorimotor and prefrontal electrodes shown in the inset in panel (B).
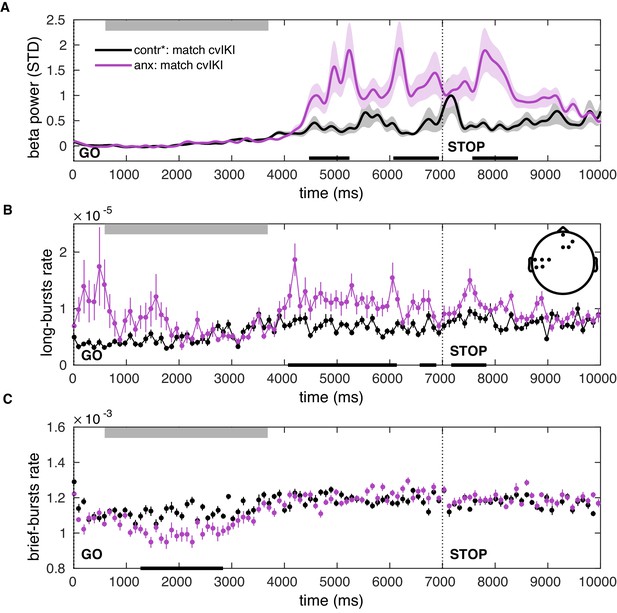
Post-movement increases in the beta-band amplitude and burst rate can be explained by state anxiety after matching participants on temporal variability.
(A–C) A separate control analysis was carried out to determine the influence of the anxiety manipulation alone on the beta PSD and burst rate properties, after controlling for changes in motor variability (cvIKI). Panels (A–C) are similar to Figure 8A, C, but for a comparison between anx1 and participants from an extended control group (contr*, including control and anx2 participants, who were not affected by anxiety during the initial exploration block), after matching them in motor variability. Significant between-group differences are denoted by the black bar at the bottom (). This analysis revealed effects in the same windows as the primary between-group analysis shown in Figure 8. Mean power and burst rate in panels (A–C) are estimated across the significant sensorimotor and prefrontal electrodes shown in the inset in panel (B).
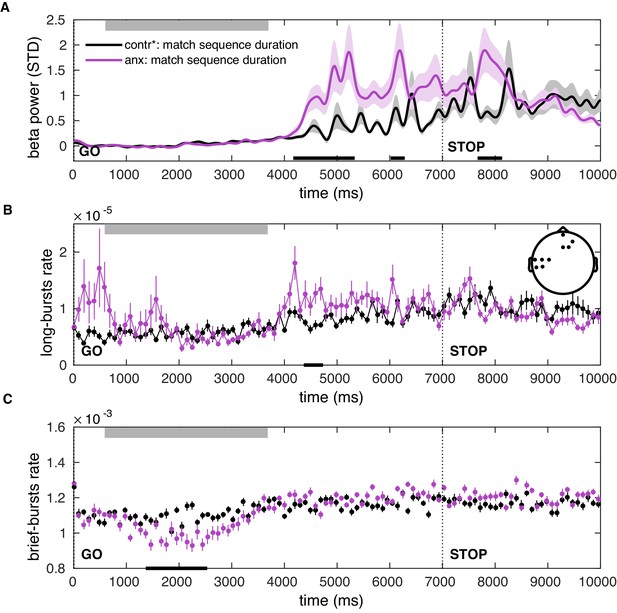
Post-movement increases in the beta-band amplitude and burst rate can be explained by state anxiety after matching participants on the sequence duration.
(A–C) Same as Figure 8—figure supplement 1 but after matching participants in the total duration of the sequence.
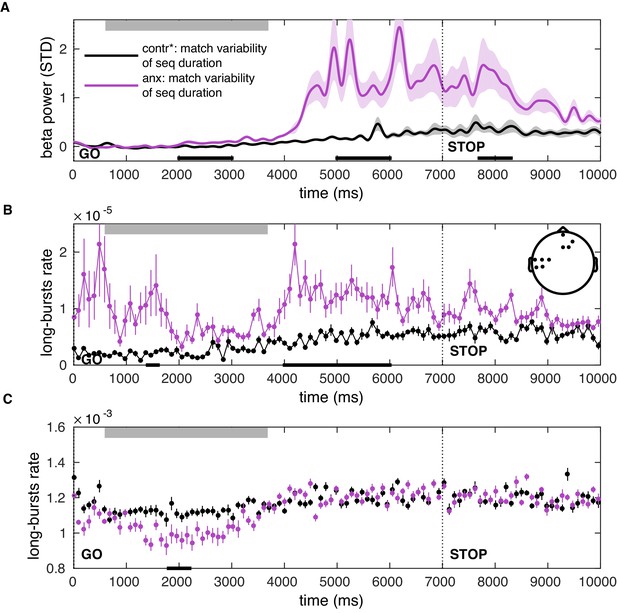
Post-movement increases in the beta-band amplitude and burst rate can be explained by state anxiety after matching participants on the variability of the total sequence duration.
(A–C) Same as Figure 8—figure supplement 1 but after matching participants on the variability of the total sequence duration.
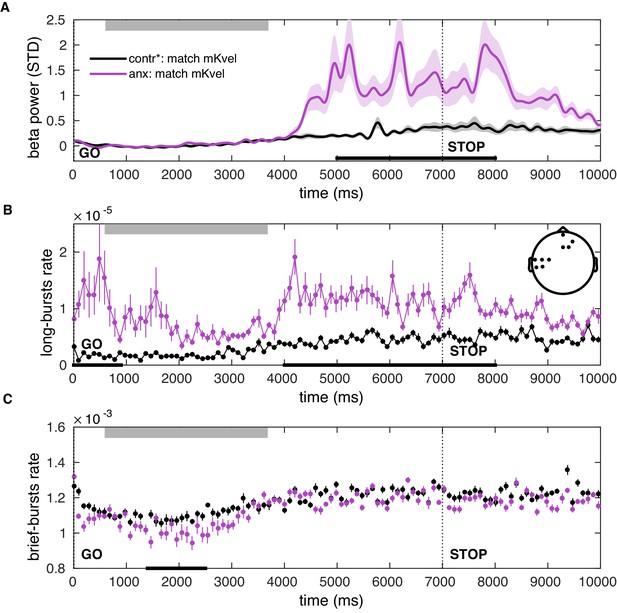
Post-movement increases in the beta-band amplitude and burst rate can be explained by state anxiety after matching participants on the mean keystroke velocity.
(A–C) Same as Figure 8—figure supplement 1 but after matching participants on the mean keystroke velocity, related to loudness.
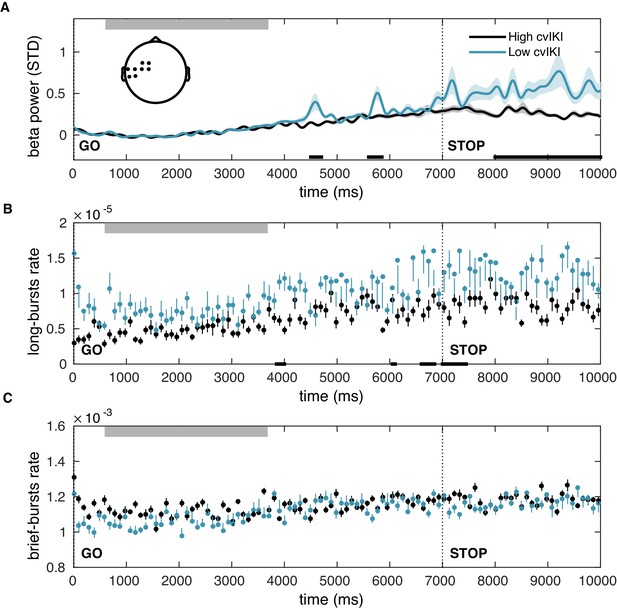
Changes in motor variability without concurrent changes in state anxiety only partially account for the observed alterations in post-movement beta amplitude and burst rate.
(A–C) Same as Figure 8—figure supplement 1, but in a control analysis performed to assess the effect of motor variability on beta PSD changes during exploration, independently of the anxiety manipulation. We compared participants selected from the extended control group (contr*: control + anx2) after doing a median split of the group based on their degree of temporal variability (cvIKI). Between-group differences were associated with small effect sizes (; black bars at the bottom) and were found exclusively in sensorimotor electrodes (shown in the inset topographic map; ).
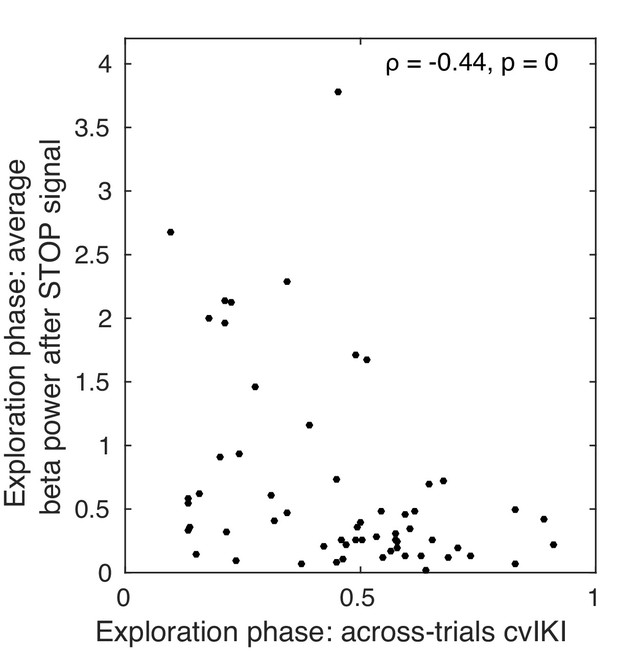
Correlation between average beta power and the degree of task-related behavioral variability across trials during the exploration phase.
Non-parametric rank correlation in the total population (N = 60) between the mean beta power during the time interval following the STOP signal and cvIKI across trials. There was a significant negative correlation (Spearman ), suggesting that an increased use of motor variability during exploration was associated with a reduction in beta power following trial performance.
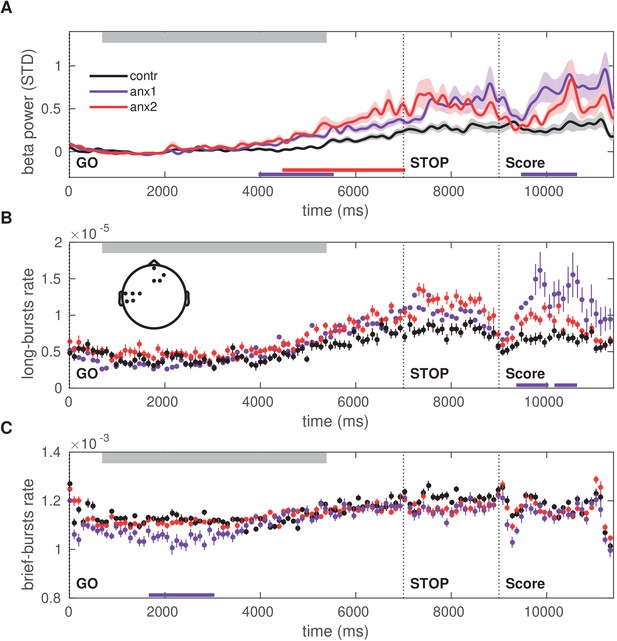
Time course of the beta power and burst rate throughout trial performance and following reward feedback.
(A) Time course of the feedback-locked beta power during sequence performance in the learning blocks, shown separately for anx1, anx2 and control groups. Average across sensorimotor and prefrontal electrode regions as in panel (B). Shaded areas indicate the SEM around the mean. Participants completed sequence2 on average between 720 (30) and 5350 (100) ms, denoted by the top gray box. The STOP signal was displayed 7000 ms after the GO signal, and was followed at 9000 ms by the feedback score. This representation shows two distinct time windows of significant differences in beta activity between the anx1 and control groups: at the end of the sequence performance and subsequently following feedback presentation (, respectively, denoted by the purple bar at the bottom). Anx2 participants also exhibited an enhanced beta power towards the end of the sequence performance (). (B) Time course of the rate of longer ( ms) oscillation bursts during sequence performance in the learning blocks. Anx1 participants exhibited a prominent rise in the burst rate 400–1600 ms following the feedback score, which was significantly larger than the rate in control participants (). Data display the mean and ± SEM. The topographic map indicates the electrodes of significant effects for panels (A–C) (). (C) Same as panel (B) but showing the rate of shorter beta bursts ( ms) during sequence performance in the learning blocks. Between-group comparisons demonstrated a significant drop in the rate of brief oscillation bursts in anx1 participants relative to control participants at the beginning of the performance (), but not after the presentation of the feedback score. In all panels, the traces of the mean power and burst rates were displayed after averaging across the significant sensorimotor and prefrontal electrodes shown in the inset in panel (B).
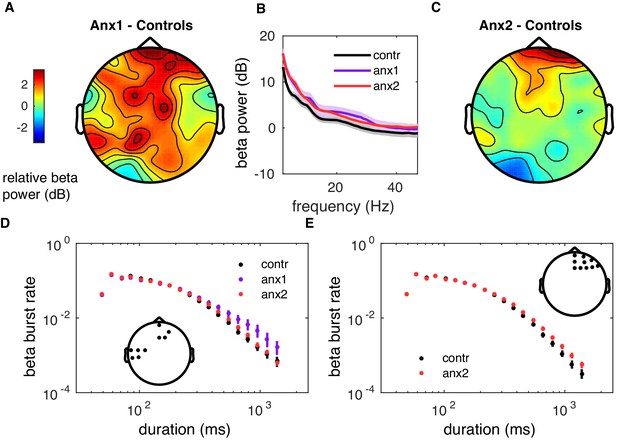
Beta power spectral density and burst rate during reward-based learning.
(A–C) During learning, the general level of normalized PSD did not differ between groups (). The learning-related PSD was normalized into decibels (dB) with the PSD of the initial resting state recording. (D) Probability distribution of beta-band oscillation-burst life-times within range 50–2000 ms for each group during learning blocks. The double-logarithmic representation suggests that longer-tailed distributions were observed in anx1 participants, although there were no between-group significant differences in the scaling exponent of the distribution (). Data are shown as mean and ± SEM across sensorimotor and prefrontal electrodes, corresponding with the inset with a topographic map. (E) Similar to panel (D), but for the representation of the burst distribution in anx2 and control participants across prefrontal electrodes, as shown in the inset. Participants in the anx2 group appeared to exhibit more frequent long bursts than controls in these prefrontal electrodes, but there were no between-group significant differences in the scaling exponents ().
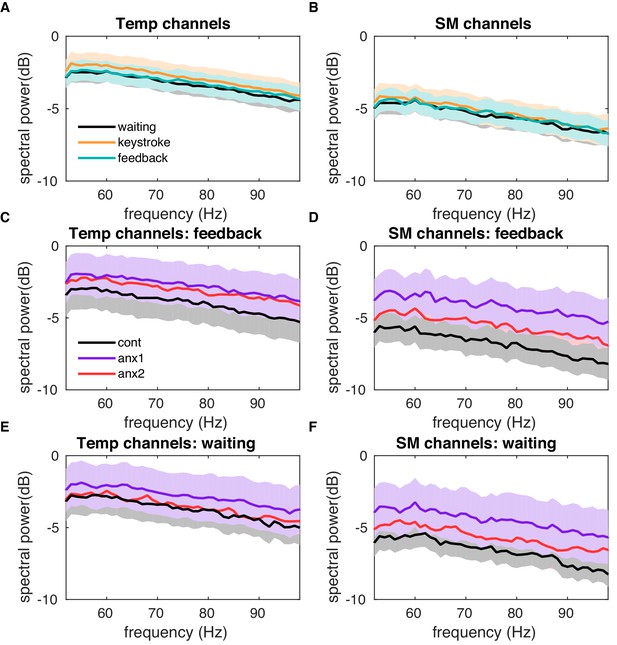
Higher gamma band activity analysis rules out an explanation in which muscle artifacts influence feedback-related changes in power.
Broadband high-frequency gamma band activity, above 50 Hz, has been linked to muscle artifacts (Muthukumaraswamy, 2013). To rule out the possibility that muscle artifacts could explain the feedback-locked beta activity differences between experimental and control groups, we assessed the gamma (50–100 Hz) power activity in different conditions. (A) Gamma power is shown for these intervals: within 0–1 s after feedback presentation, when participants should be at rest after completing the trial performance (green line); within 0–1 s locked to a key press, when participants are moving their fingers (orange line); within 0–1 s locked to the initiation of the trial, when participants are cued to wait for the GO response, and can be expected to be mentally preparing but otherwise at rest (black line). Gamma power was averaged across temporal electrodes, where artifacts usually lead to larger effects. No differences between conditions were found (). (B) Same as panel (A) but after averaging the gamma power values across all sensorimotor (SM) channels. No significant differences were found here either. (C, D) Gamma power locked to the feedback presentation is displayed separately in experimental and control groups in temporal (C) and sensorimotor channels (D). No significant between-group differences were found. (E, F) Same as panels (C–D) but during the waiting interval, when participants were waiting to initiate the trial.
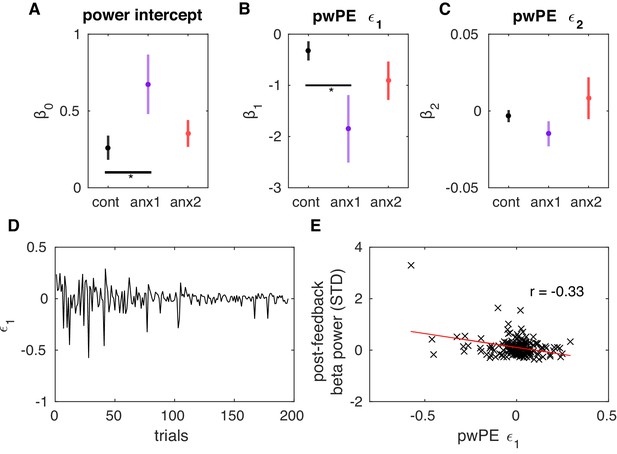
Post-feedback increases in beta power represent attenuated precision-weighted prediction errors about reward estimates.
(A–C) Mean (and SEM) values of the coefficients that explain the post-feedback beta power as a linear function of a constant value (beta power) (A), the precision-weighted prediction errors driving updates in the expectation of reward (pwPE, ) (B), and pwPE driving updates in the expectation of volatility () (C). The measure of beta power used here was the average within 400–1600 ms following feedback presentation and across sensorimotor and prefrontal electrodes ,as shown in Figure 9. The values are plotted separately for each control and experimental group. The and regression coefficients were significantly different from 0 in all groups (). In addition, was larger in the anx1 group relative to the control group (, denoted by the horizontal black line and the asterisk). In anx1 relative to control participants, we found that was negative and significantly smaller in anx1 participants (). Thus, a reduction in contributed to an increase in post-feedback beta power. The multiple regression analysis did not support a significant contribution of the second regressor, pwPE relating to volatility, to explaining the changes in beta power (see main text, also on average did not differ from 0 in any group of participants, ). (D) Illustration of the trajectories of pwPE in one representative anx1 subject. (E) The linear regression between the trial-wise beta power and pwPE for the same representative subject.
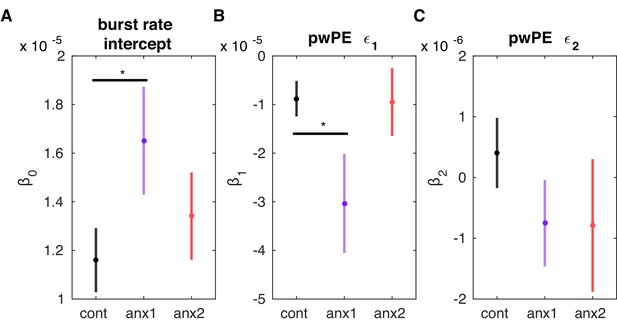
The rate of long beta bursts following feedback is modulated by the magnitude of precision-weighted prediction errors relating to reward.
(A–C) Same as Figure 10A–C but for the grand-averaged rate of post-feedback long beta bursts. The and regression coefficients were significantly different than 0 for each group (). Further to this result, was positive and larger in anx1 than in control participants (). By contrast, the regression coefficient was negative and significantly smaller in the anx1 group than in the control group (). This outcome resembles the results in Figure 10A–C, suggesting that smaller pwPE on reward contributed to a larger rate of long beta bursts. The second regressor coefficient did not differ significantly from zero and changes in did not contribute to better explaining the beta activity (see main text). Anx2 participants did not have significantly different regressor coefficients than the control group. In summary, the multiple regression results linked a higher post-feedback rate of long-lived oscillation bursts (as observed in anx1) with reduced updates about reward.
Topographic map illustrating the EEG channels used for the feedback-locked oscillatory analysis.
Tables
Means and variances of the priors on perceptual parameters and initial values.
Priors on the parameters and initial values of the HGF perceptual model for continuous inputs. The continuous inputs here were the trial-by-trial scores that the participants received, normalized to the 0–1 range. Quantities estimated in the logarithmic space are denoted by log(). Prior mean and variance for , as well as the prior mean for , and the precision of the input, , were defined by the initial 20 input values. When providing prior values that depend on the first 20 input scores, we indicate the median across the total population of 60 participants. For the remaining quantities, the prior mean and variance were pre-defined according to the values indicated in the table.
| Prior mean | Prior variance | |
|---|---|---|
| log() | log(1) | 0 |
| log-variance of 1:20 input scores: −3.04 | 16 | |
| –4 | 16 | |
| log() | negative log-variance of 1:20 input scores: 3.04 | 4 |
| value of the first input score: 0.21 | variance of 1:20 input scores: 0.05 | |
| log() | log-variance of 1:20 input scores: −3.04 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | |
| log() | log(0.01) | 1 |
| individual mean of behavioral parameter | 4 | |
| 0 | 4 | |
| 0 | 4 |