NHR-8 and P-glycoproteins uncouple xenobiotic resistance from longevity in chemosensory C. elegans mutants
Figures
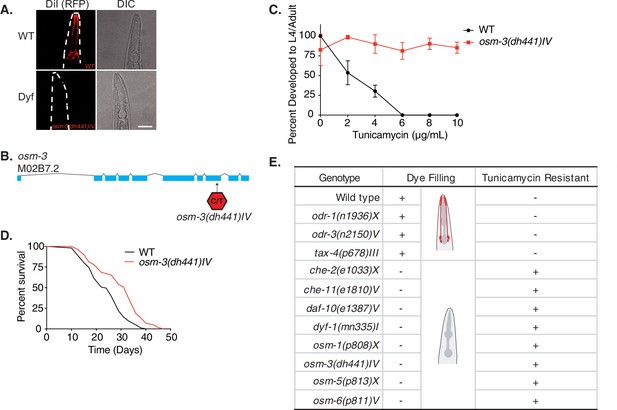
Tunicamycin resistance occurs in dye filling defective long-lived chemosensory C. elegans mutants.
(A) Fluorescence and differential interference contract confocal microscopy images of WT and osm-3(dh441)IV C. elegans after DiI treatment (scale bar 40 µm). (B) Depiction of the osm-3(dh441) locus. osm-3(dh441)IV has a C to T mutation at position 3796925 of exon 8. (C) Developmental tunicamycin (TM) resistance assay using the indicated concentrations with WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments with >15 scored animals each). (D) Demographic lifespan analysis of WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals. WT mean lifespan = 24 days, osm-3(dh441)IV mean lifespan = 29 days, p<0.0001. See Supplementary file 1 for statistical analysis. (E) Table of dye filling phenotype and TM resistance. In the dye filling column,+ is positive for DiI filling as in (A) and − is Dyf. In the TM resistant column, + is resistant and − is not resistant to 10 µg/mL TM.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and osm-3(dh441) animals (Figure 1C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
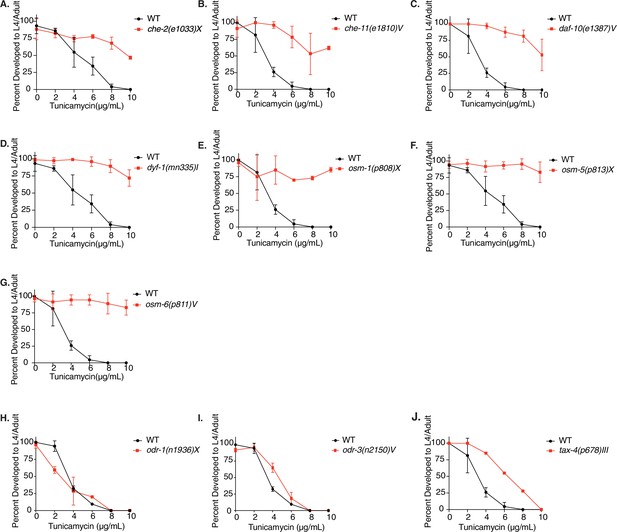
Tunicamycin resistance occurs in dye filling defective long-lived chemosensory C. elegans mutants.
(A–J) Developmental TM resistance assay with WT, che-2(e1033)X, che-11(e1810)V, daf-10(e1387)V, dyf-1(mn335)I, osm-1(p808)X, osm-5(p813)X, osm-6(p811)V, odr-1(n1936)X, odr-3(n2150)V, and tax-4(p678)III animals. Data are mean ± SD (n = 1 for J; n = 2 for B, C, E, G, H and I; n = 3 for A, D, and F independent experiments with >15 scored animals each).
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and che-2(e1033)X animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and che-11(e1810)V animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 3
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and daf-10(e1387)V animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 4
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and dyf-1(mn335)I animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 5
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and osm-1(p808)X animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data5-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 6
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and osm-5(p813)X animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data6-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 7
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and osm-6(p811)V animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data7-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 8
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and odr-1(n1936)X animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data8-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 9
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and odr-3(n2150)V animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data9-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 10
Developmental TM resistance assay with WT and tax-4(p7689)III animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig1-figsupp1-data10-v2.xlsx
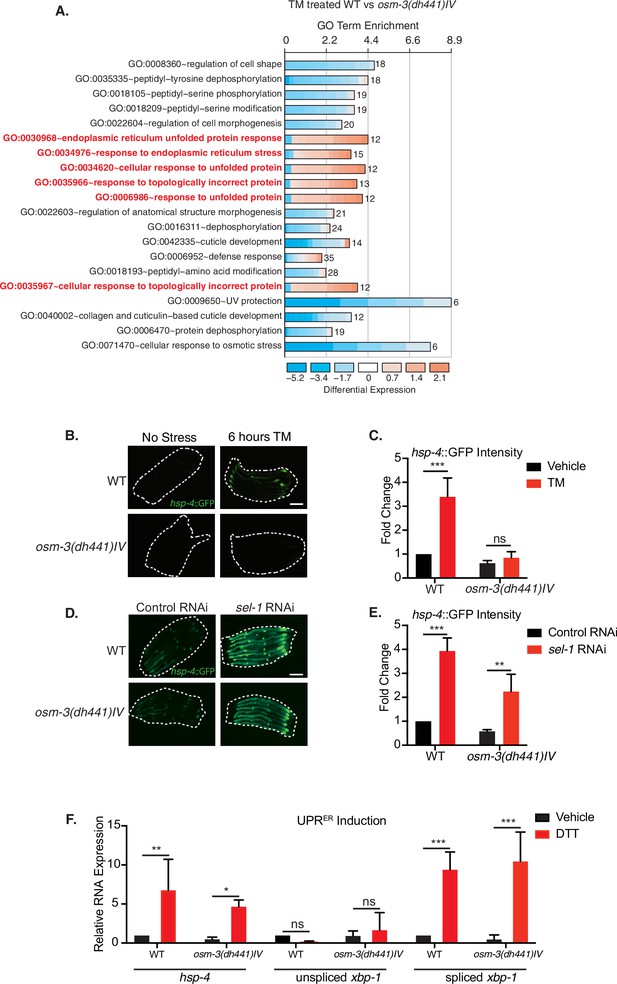
Reduced tunicamycin-induced ER stress signaling in osm-3 mutants despite functional ER-UPR pathway.
(A) DAVID gene ontology (GO) terms that are enriched in TM-treated WT compared to TM-treated osm-3(dh441)IV worms. Red = upregulated and blue = downregulated. The fold enrichment is plotted as x axis. The numbers of genes is indicated next to the bar for each term. (B) Green fluorescent images of WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals in the hsp-4::GFP reporter background after 6 hr of 10 µg/mL TM treatment. Worms are outlined in the images (scale bar 100 µm). (C) Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background after 6 hr of control or TM treatment. Fold change represents GFP intensity normalized to WT treated with vehicle. Data are mean + SEM, n = 4, ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (D) Green fluorescent images of WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals in the hsp-4::GFP background after development on control or sel-1 RNAi. Worms are outlined in the images (scale bar 100 µm). (E) Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background raised on control or sel-1 RNAi. Fold change represents GFP intensity normalized to WT treated with vehicle. Data are mean + SEM, n = 3, **p<0.005 ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (F) Quantitative PCR measuring relative hsp-4 and spliced and unspliced xbp-1 mRNA levels in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals after 2 hr of 10 mM DTT treatment. Relative mRNA expression is mRNA expression levels normalized to WT treated with vehicle. Data are mean + SEM, n = 3, *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background after 6 hr of control or TM treatment (Figure 2C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background raised on control or sel-1 RNAi.
(Figure 2E).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Quantitative PCR measuring relative hsp-4 and spliced and unspliced xbp-1 mRNA levels in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals after 2 hr of 10 mM DTT treatment (Figure 2F).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig2-data3-v2.xlsx
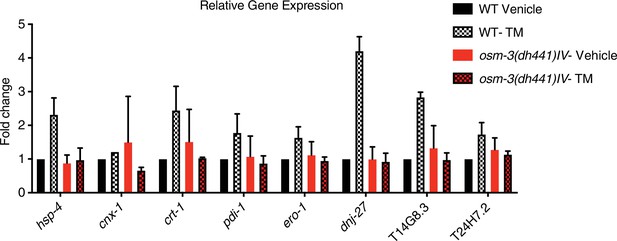
Quantitative PCR measuring relative mRNA expression of indicated genes in WT animals and osm-3(dh441)IV mutants after 6 hr of vehicle or TM treatment.
Fold change represents mRNA expression levels of the targeted genes normalized to WT treated with vehicle. Data are mean + SEM, n = 2.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantitative PCR measuring relative mRNA expression of indicated genes in WT animals and osm-3(dh441)IV mutants after 6 hr of vehicle or TM treatment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
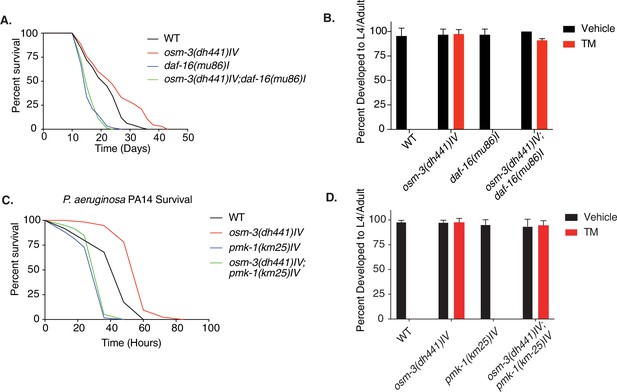
Tunicamycin resistance in osm-3 mutants is not daf-16 or pmk-1 dependent.
(A) Demographic lifespan analysis of WT, osm-3(dhh441)IV, daf-16(mu86)I and osm-3(dh441)IV; daf-16(mu86)I animals. WT mean lifespan = 22 days, osm-3(dh441)IV mean lifespan = 25 days p<0.005 compared to WT, daf-16(mu86)I mean lifespan = 16 days p<0.0001 compared to WT, osm-3(dh441)IV; daf-16(mu86)I mean lifespan = 16 days p<0.0001 compared to WT. See Supplementary file 1 for statistical analysis. (B) Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441) IV, daf-16(mu86)I, and osm-3(dh441)IV; daf-16(mu86)I animals. No viable WT or daf-16(mu86) animals were observed in the TM condition. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments with >15 scored animals each). (C) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 survival assay with WT, osm-3(dh441) IV, pmk-1(km25)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; pmk-1(km25)IV animals. WT mean survival = 44 hr, osm-3(dh441)IV mean survival = 58 hr p<0.001 compared to WT, pmk-1(km25)IV mean survival = 31 hr p<0.001 compared to WT, osm-3(dh441)IV; pmk-1(km25)IV mean survival = 34 hr p<0.001 compared to WT and p=0.06 compared to pmk-1(km25)IV. See Supplementary file 1 for statistical analysis. (D) Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, pmk-1(km25)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; pmk-1(km25)IV animals. No viable WT or pmk-1(km-25) animals were observed in the TM condition. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments with >15 scored animals each).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, daf-16(mu86)I, and osm-3(dh441)IV; daf-16(mu86)I mutants.
(Figure 3B).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, pmk-1(km25)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; pmk-1(km25)IV mutants.
(Figure 3D).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
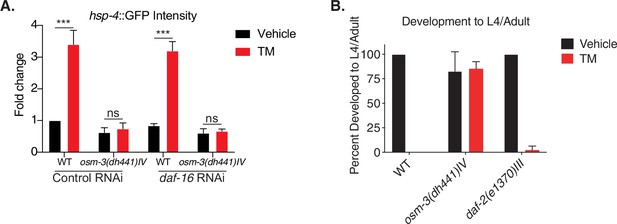
Tunicamycin resistance in osm-3 mutants is not daf-16 or pmk-1 dependent.
(A) Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background raised on control or daf-16 RNAi. Data are mean + SEM, n = 4, ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (B) Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV and daf-2(e1370)III animals. No viable animals were observed in TM-treated WT. Data are mean + SEM, n = 3.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Biosorter analysis of osm-3(dh441)IV vs. WT animals in the hsp-4::GFP background raised on control or daf-16 RNAi.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Developmental resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM with WT, osm-3(dh441) IV, and daf-2(e1370) III mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig3-figsupp1-data2-v2.xlsx
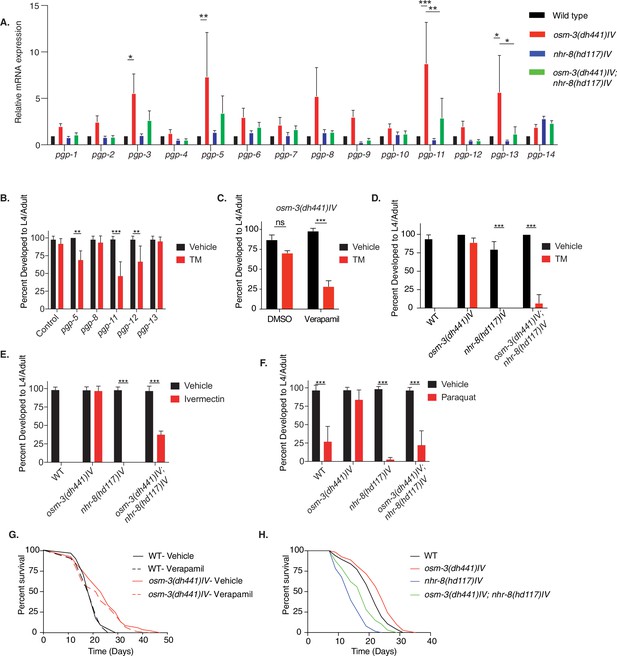
nhr-8 signaling regulates xenobiotic detoxification response through PGPs.
(A) Quantitative PCR measuring relative PGP mRNA expression in WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals. Relative mRNA expression is mRNA expression levels normalized to WT. There was no TM treatment. Data are mean + SEM, n = 3, *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (B) Developmental TM resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM and the indicated RNAi treatments with osm-3(dh441)IV mutants. Data are mean + SD, n = 3, **p<0.05, ***p<0.001 by two-way ANOVA. (C) Developmental TM resistance assay using the PGP inhibitor verapamil (VPL) using 10 µg/mL TM supplemented with vehicle or 1 nM VPL. Data are mean + SD, n = 3, ***p<0.001 by two-way ANOVA. (D) Developmental TM resistance assay on 10 µg/mL TM and control with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals. Data are mean + SD, n = 3, *p<0.05, ***p<0.0001 by t-test. (E) Developmental ivermectin resistance assay of WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals using 6 ng/mL ivermectin and vehicle control. Data are mean + SD, n = 3, ***p<0.001 by two-way ANOVA. (F) Developmental paraquat resistance assay of WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals using 0.2 mM paraquat and vehicle control. Data are mean + SD, n = 3, ***p<0.001 by two-way ANOVA. (G) Demographic lifespan analysis on vehicle and verapamil-treated WT and osm-3(dh441)IV worms. Vehicle treated.WT mean lifespan = 19 days; osm-3(dh441)IV mean lifespan = 24 days p<0.0001 compared to WT vehicle. verapamil treated.WT mean lifespan = 19 days; osm-3(dh441)IV mean lifespan = 22 days, p<0.005 compared to WT Vehicle. (H) Demographic lifespan analysis of WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV;nhr-8(hd117)IV animals. WT mean lifespan = 22 days, osm-3(dh441)IV mean lifespan = 24 days p<0.0001 compared to WT, nhr-8(hd117)IV mean lifespan = 14 p<0.0001 compared to WT, osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV mean lifespan = 19 days p<0.0001 compared to WT.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Quantitative PCR measuring relative PGP mRNA expression in WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals (Figure 4A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Developmental TM resistance assay using 10 µg/mL TM and the indicated PGPs RNAi treatment.
(Figure 4B).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 3
Developmental TM resistance assay using the PGP inhibitor verapamil (VPL) using 10 µg/mL TM supplemented with vehicle or 1 nM VPL.
(Figure 4C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data3-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 4
Developmental TM resistance assay on 10 µg/mL TM and control with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals (Figure 4D).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data4-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 5
Developmental ivermectin resistance assay of WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals using 6 ng/mL ivermectin and vehicle control (Figure 4E).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data5-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 6
Developmental paraquat resistance assay of WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals using 0.2 mM paraquat and vehicle control (Figure 4F).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-data6-v2.xlsx
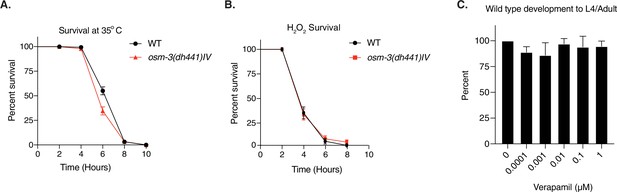
nhr-8 signaling regulates xenobiotic detoxification response through PGPs.
(A) Heat shock assay at 35°C in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals on day 1 of adulthood. See Supplementary file 1 for statistical analysis. (B) Hydrogen peroxide survival assay using 1 µM H2O2 on day 1 of adulthood in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals. See Supplementary file 1 for statistical analysis. (C) WT development on 0–1 µM Verapamil. No significant difference in development. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments with >9 scored animals each).
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Heat shock assay at 35 °C in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals on day 1 of adulthood.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Hydrogen peroxide survival assay using 1 mM H2O2 on day 1 of adulthood in WT and osm-3(dh441)IV animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-figsupp1-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 3
WT development on 0–1 µM Verapamil.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig4-figsupp1-data3-v2.xlsx
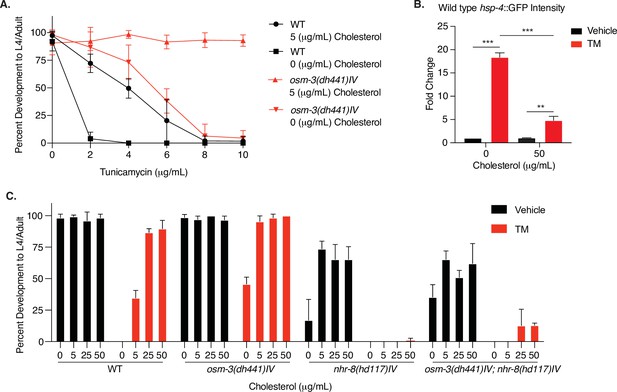
Cholesterol modulates TM resistance through NHR-8.
(A) Developmental dose–response TM resistance assay using the indicated TM concentrations with WT animals and osm-3(dh441)IV mutants raised on 0 or 5 µg/mL cholesterol. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5 independent experiments with >15 scored animals each). (B) Biosorter analysis of WT animals with the hsp-4::GFP reporter raised on 0 or 50 µg/mL cholesterol after 6 hr of vehicle or 5 µg/mL TM treatment. Data are mean + SEM, n = 3, *p<0.05, ***p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. (C) Cholesterol dose–response developmental assay with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals on vehicle or 5 µg/mL TM. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments with >15 scored animals each).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Developmental dose–response TM resistance assay using the indicated TM concentrations with WT animals and osm-3(dh441)IV mutants raised on 0 or 5 µg/mL cholesterol.
(Figure 5A).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
Biosorter analysis of WT animals with the hsp-4::GFP reporter raised on 0 or 50 µg/mL cholesterol after 6 hr of vehicle or 5 µg/mL TM treatment.
(Figure 5B).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Cholesterol dose–response developmental assay with WT, osm-3(dh441)IV, nhr-8(hd117)IV, and osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV animals on vehicle or 5 µg/mL TM.
(Figure 5C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-fig5-data3-v2.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::sel-1] | Source Bioscience | CELE_F45D3.5 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::daf-16] | Source Bioscience | CELE_R13H8.1 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::pgp-5] | Source Bioscience | CELE_C05A9.1 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::pgp-8] | Source Bioscience | CELE_T21E8.3 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::pgp11] | Source Bioscience | CELE_DH11.3 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::pgp-12] | Source Bioscience | CELE_F22E10.1 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Strain, strain background(E. coli) | HT115 [L4440::pgp-13] | Source Bioscience | CELE_F22E10.2 | Ahringer RNAi library |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-3(dh441)IV | Other | AA1962 | available from A. Antebi or M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | daf-16(mu86)I | CGC | CF1038 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | pmk-1(km25)IV | CGC | KU25 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-3(dh441)IV; nhr-8(hd117)IV | This paper | MSD420 | available from M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-3(dh441)IV; daf-16(mu86)I | This paper | MSD422 | available from M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-3(dh441)IV; pmk-1(km25)IV | This paper | MSD423 | available from M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | odr-1(n1936)X | CGC | CX2065 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | odr-3(n2150)V | CGC | CX2205 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-6(p811)V | CGC | PR811 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | tax-4(p678)III | CGC | PR678 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | nhr-8(hd117)IV | other | AA968 | available from A. Antebi or M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | N2; dhEx451(nhr-8::gfp; coel::RFP) | CGC | AA1027 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-3(dh441)IV; zcIs4 [hsp-4::GFP]V | other | AA2774 | available from A. Antebi or M.S. Denzel |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | zcIs4[hsp-4::GFP]V | CGC | SJ4005 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | che-11(e1810)V | CGC | CB3330 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | daf-10(e1387)IV | CGC | CB1387 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-1(p808)X | CGC | PR808 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | dyf-1(mn335)I | CGC | SP1205 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | che-2(e1033)X | CGC | CB1033 | |
| Genetic reagent(C. elegans) | osm-5(p813)X | CGC | PR813 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Direct-zol RNA Microprep | Zymo Research | R2060 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SMARTer Stranded RNA-Seq HT Kit | Takara | 634,838 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ribo-zero Gold kit | Illumina | MRZG12324 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tunicamycin | Calbiochem | CAS 11089-65-9 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dithiothreitol | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 3483-12-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Methyl viologen dichloride hydrate | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 75365-73-0 | Paraquat |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ivermectin | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 70288-86-7 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Verapamil hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 152-11-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cholesterol | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 57-88-5 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 1,1′-Dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′- tetramethylindocarbo cyanine perchlorate | Sigma-Aldrich | CAS 41085-99-8 | DiI |
| Software, algorithm | R statistical software | cran.r-project.org | DESeq2 1.16.1 | PMID.25516281 |
| Other | Reference Genome | ENSEMBL | WBCel235 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table containing the statistical analysis of the lifespan, PA14, heat shock and H2O2 resistance assays.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of qPCR primers used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53174/elife-53174-transrepform1-v2.pdf





