ZCWPW1 is recruited to recombination hotspots by PRDM9 and is essential for meiotic double strand break repair
Figures
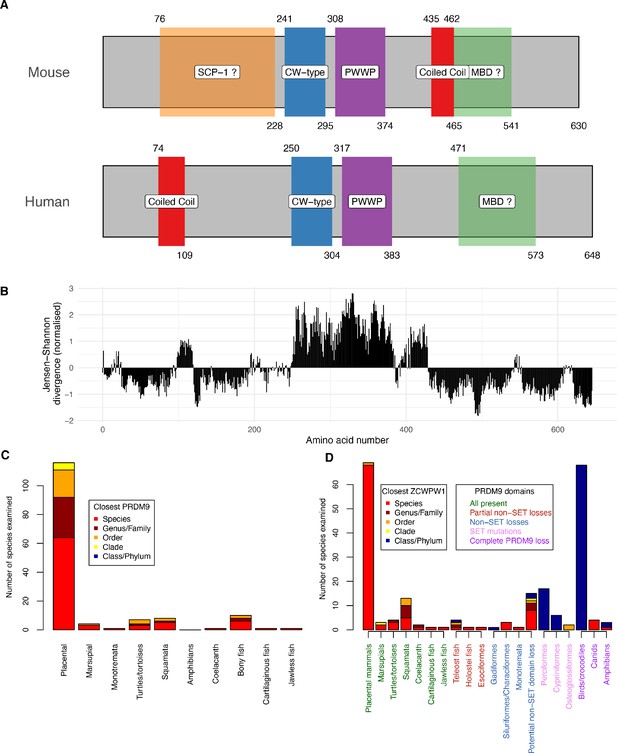
Domain organisation (A) and evolutionary conservation (B) of ZCWPW1, and co-evolution with PRDM9 (C,D).
(A) Protein domains in the human and mouse proteins (source: UniProt). Amino acid start and end positions of each domain are shown above and below the rectangles, respectively. Prediction of SCP-1 (SYCP1) domain from Marchler-Bauer and Bryant, 2004 and of MBDs (methyl-CpG binding domain) from Lobley et al., 2009 (Materials and methods). (B) Conservation of human amino acids, normalised Jensen-Shanon divergence normalised to mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1 is shown on the y-axis (a measure of sequence conservation, see Capra and Singh, 2007 and Johansson and Toh, 2010) computed from using multiple alignment of 167 orthologues (Materials and methods). (C) All species we identified as possessing ZCWPW1 copies were phylogenetically grouped into clades as previously (Baker et al., 2017) (x-axis) and each clade divided (stacked bars) according to whether ZCWPW1-possessing species within it also possess PRDM9 (‘Species’, red) or instead their closest PRDM9-possessing relative is respectively in the same genus/family, order, clade or order/phylum, with colours as given in the ‘Closest PRDM9’ legend. (D) As (C), but now showing the closest relative possessing ZCWPW1 (‘Closest ZCWPW1’ legend) for species possessing complete, partial or no identified PRDM9 copies. As in (C), the x-axis groups species into clades, now further divided based on data from Baker et al., 2017 into subclades according to the domains of PRDM9 lost or mutated across that subclade in all observed copies, reflecting multiple partial losses of particular PRDM9 domains, or complete loss of all PRDM9 copies (Main text). The x-axis labels are ordered and coloured according to the PRDM9 domains present (‘PRDM9 domains’ legend, where ‘SET’ refers to PRDM9’s PR/SET domain and the KRAB and SSXRD domains are grouped as ‘non-SET’, and ‘partial’ losses are seen in some but not all PRDM9 copies in that species). Further details are presented in Materials and methods, and the raw data in Figure 1—source datas 1 and 2.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
ZCWPW1 identified orthologues.
Notes on Table columns: aThe number of 31 perfectly conserved amino acids within strong ZCWPW1 orthologues that match, and are sequenced/align, respectively. bThe number of 78 moderately conserved (entropy <1) amino acids within strong ZCWPW1 orthologues that match, and are sequenced/align, respectively. cStart and end positions of alignment to human reference ZCWPW1. dThe taxonomic relationship of this species to the closest species possessing a copy of PRDM9 with a likely functional SET domain (Baker et al., 2017). eThe number of 37 amino acids, which do not vary in species also shown to possess a copy of PRDM9 with a likely functional SET domain (Baker et al., 2017), which mismatch the expected amino acid in this copy of ZCWPW1 (0 for cases with a perfect match).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 1—source data 2
PRDM9 orthologues (Baker et al., 2017).
Notes on Table columns: fThe taxonomic relationship of this species to the closest species possessing a copy of ZWPW1 we annotated. gData are reproduced from Baker et al., 2017, so columns A, B, C are taken directly from Supplementary File 1 in that paper. hIn Supplementary File 1 (Baker et al., 2017) the identified domains of PRDM9 are given in each observed orthologue. We identified a species-based ‘maximum’ domain set by recording which of three N-terminal domains (SET, KRAB, SSXRD) were present in that species (in one or more orthologues of PRDM9 identified in that species). iIn Supplementary File 1 (Baker et al., 2017), the presence/absence of each of three catalytic tyrosine residues (Y276,341,357) of the human PRDM9 SET domain is given for each PRDM9 ortholog, and we summed these to make a total (0–3). We constructed a species-based maximum value for this sum ‘Y276,341,357.Max.sum’ by taking the maximum value of this sum observed across all PRDM9 orthologues identified in a given species.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig1-data2-v2.xlsx
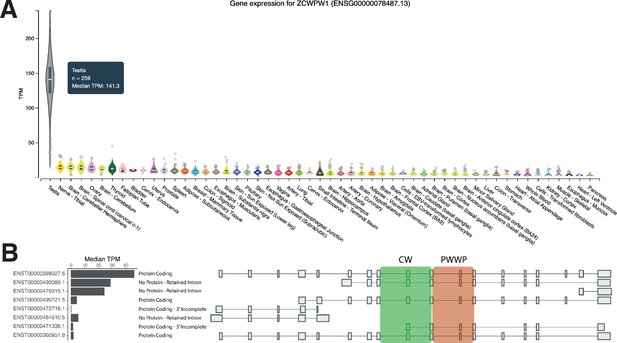
ZCWPW1 is specifically expressed in testis in humans.
Data Source: GTEx Analysis Release V7 (dbGaP Accession phs000424.v7.p2). (A) Total expression by human tissue type. (B) Isoforms of ZCWPW1 expressed in human testis.
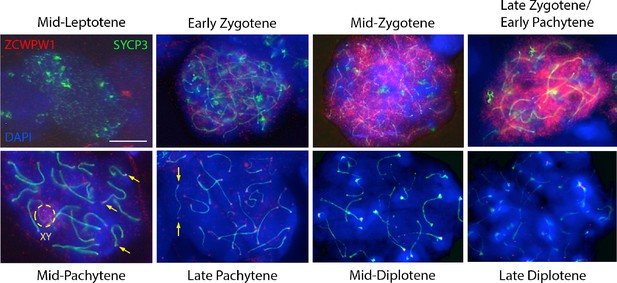
Expression of ZCWPW1 across meiosis prophase I in mouse testis.
Nuclear spreads from 9 to 10 weeks old WT mice were immunostained with antibodies against ZCWPW1 (red) and the synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3 (green) which labels the chromosome axis, and counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualise nuclei. Developmental stages are indicated above and below. Yellow arrows point to ZCWPW1 foci clearly visible at both ends of the synaptonemal complex in mid-late pachytene. Additional evidence is provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 2. The dashed circle shows staining in the XY body. Images for the individual channels are provided in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. These images are representative of the results obtained in three mice. Scale bar: 10 μm.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Immuno-FISH analysis of ZCWPW1 foci localisation at the synaptonemal complex ends in WT testis (mid-Pachytene to Late Diplotene cells).
Only chromosomes clearly identifiable were included in the analysis. X and Y were excluded as they are covered in ZCWPW1 signal (which strong labels the XY body). Stages: P, Pachytene; D, Diplotene. Tel: Telomeric probe. Cen: Centromeric probe.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
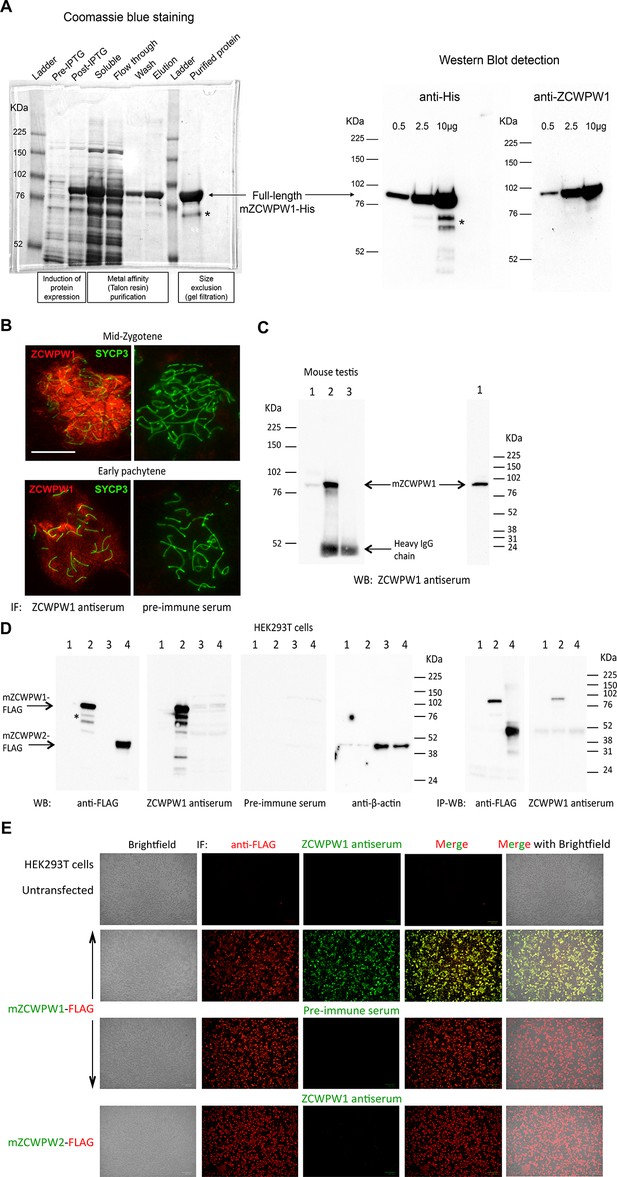
ZCWPW1 antibody generation and validation.
(A) Expression and purification of full-length recombinant mouse ZCWPW1 (mZCWPW1) in E. Coli. Left panel: SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie blue staining of bacterial lysates before (pre-IPTG) and after (post-IPTG) induction of protein expression with IPTG, the soluble protein fraction (after cell sonication) used for purification, the flow through (incompletely depleted from the target protein) after incubating the soluble fraction with Talon resin beads to bind His-tagged mZCWPW1, the wash containing 5mM imidazole, the protein eluate from the beads using 300mM imidazole, and the purified recombinant protein after further purification from low molecular weight (MW) contaminants by size exclusion. Right panel: Western blot detection of purified His-tagged mZCWPW1 using an anti-His and a mouse polyclonal antibody raised against the human protein (previously tested positively against mouse ZCWPW1 overexpressed in HEK293T cells). *Indicates degradation fragments (likely C-terminal). The purified protein was used to immunise rabbits and produce an antiserum against mZCWPW1. (B-E) Validation of the rabbit ZCWPW1 antiserum by immunofluorescence staining (IF), immunoprecipitation (IP) and western blotting (WB) in B6 testis (B,C) and transfected HEK293T cells (D,E). (B) Testis nuclear spreads from 10 weeks old B6 mice were immunostained with the ZCWPW1 antiserum or the pre-immune serum (red), and chromosome axes were labeled with SYCP3 (green). Representative mid-zygotene and early pachytene cells are shown. No signal is detected by the pre-immune serum. Scale bar: 10μm. (C) IP-WB detection of mZCWPW1 from 10 weeks old B6 mouse testis. Left panel: Lane 1, 100 µg protein extract; Lanes 2–3, IP from 2.6 mg protein extract using ZCWPW1 antiserum (lane 2) or the pre-immune serum (lane 3). The ZCWPW1 antibody detects a unique protein band within the expected MW range (predicted at 70.5 KDa) both by direct WB (lane 1) and IP-WB (lane 2). No signal is detected by the pre-immune serum (lane 3). Right panel: the testis protein extract was resolved on a higher (4–20%) SDS-PAGE gel; no detection of ZCWPW2 is observed by WB at the 38KDa MW range predicted for mouse ZCWPW2, only a single band is present within the expected MW range for ZCWPW1. The images in (B–C) are representative of the results obtained in two mice. (D) Specific IP-WB and WB detection of FLAG-tagged mZCWPW1 over ZCWPW2 from transfected HEK293T cells. Lanes 1,3: protein extracts from untransfected cells; Lanes 2,4: protein extracts from cells transfected with mZCWPW1-FLAG (lane 2) or mZCWPW2-FLAG (lane 4). Lanes 1–2, 5 µg extracts; lanes 3–4: 50 µg extracts. The ZCWPW1 antiserum detects the same protein band as the anti-FLAG antibody in the expected MW range (74 KDa) both by direct WB and by IP-WB, but does not show any reactivity against mZCWPW2-FLAG. The preimmune serum does not detect the mZCWPW1-FLAG protein band. Detection of beta-actin serves as a loading control. The asterisk indicates degradation fragments typically observed, as in (A). (E) Specific IF detection of FLAG-tagged mZCWPW1 over ZCWPW2 from transfected HEK293T cells. Cells were co-immunostained with ZCWPW1 antiserum or the pre-immune serum (green), and a FLAG antibody (red). The ZCWPW1 antiserum detects mZCWPW1-FLAG (precisely overlapping the signal detected by the FLAG antibody results in yellow fluorescence in the merged image), but not mZCWPW2-FLAG protein. No signal is detected with the pre-immune serum.
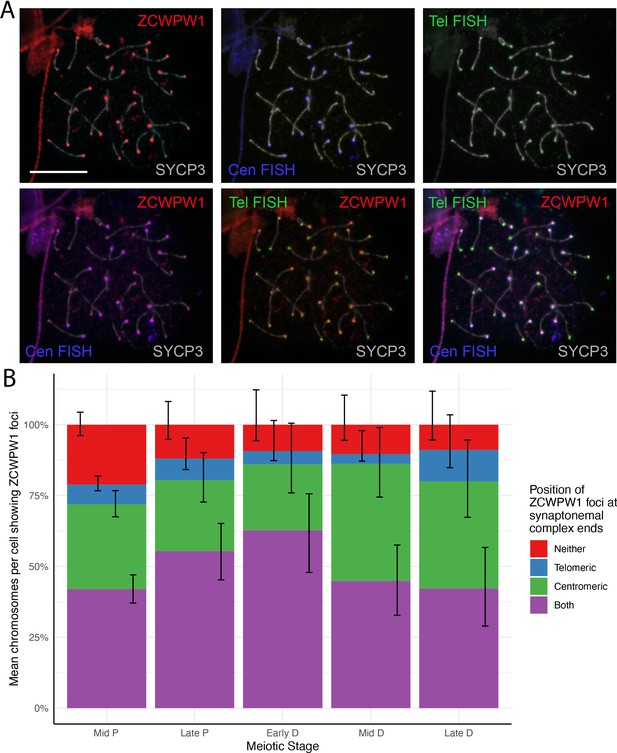
ZCWPW1 localises to both subtelomeric and subcentromeric regions of chromosomes in pachytene cells.
(A) Testis chromosome spreads from 10-week-old WT mice were immunostained for SYCP3 and ZCWPW1, and hybridised by FISH with distal telomeric (Tel) and proximal centromeric (Cen) probes. To aid the visualisation of each signal, the bottom right merged image was decomposed into multiple combinations of two to three individual channels, as indicated. Note that the ZCWPW1 foci do not exactly co-localize with the FISH signals, and generally lie more internally (subtelomerically and subcentromerically) on the chromosome axis. These images are representative of the results obtained for three mice. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) The localisation of ZCWPW1 foci to either Tel or Cen end, or both ends, of the synaptonemal complex was quantified in mid-Pachytene to late-Diplotene cells. Chromosomes that did not show any ZCWPW1 foci were recorded as ‘not labeled’. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals using the Wilson method. n = 3–25 cells of each stage from one mouse. Raw data in Figure 2—source data 1.
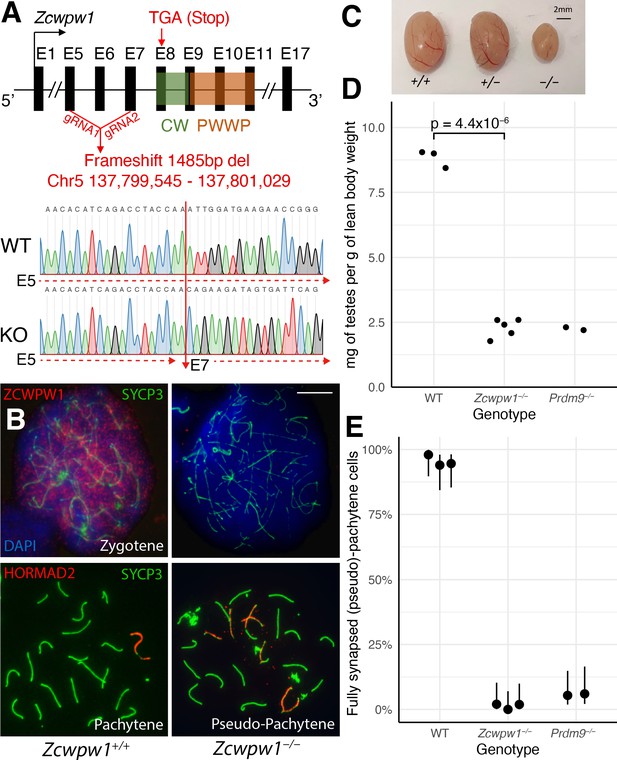
Zcwpw1−/ male mice show reduced testis size and asynapsis, similar to the Prdm9−/− mutant.
(A) Schematic of the Zcwpw1 knockout (KO) mouse line. E: Exon. gRNA: guideRNA. Sanger sequencing DNA chromatograms of wild-type (WT) and KO mice encompassing the deletion are shown. The intron-exon organisation is not to scale. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of testis nuclear spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice for ZCWPW1 or HORMAD2 (red) which marks asynapsed chromosomes, and the synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3 (green) which labels the chromosome axis. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to visualise nuclei (top images). These images are representative of the data obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Representative testes from 9- to 10-week-old WT (+/+), Het (+/−) and Hom (−/−) Zcwpw1 KO mice are shown. (D) Paired testes weight was normalised to lean body weight. Each datapoint represents one mouse. The p-value is from Welch’s two sided, two sample t-test. Raw data in Figure 3—source data 1. (E) Synapsis quantification in testis chromosome spreads immunostained with HORMAD2, as in (B). The percentage of mid-Pachytene (WT) or pseudo-Pachytene (Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/−) cells with all autosomes fully synapsed is plotted by genotype; each datapoint represents one mouse, each with n≥ 49 cells analysed. Vertical lines are 95% Wilson binomial confidence intervals. Raw data in Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Fertility measures in WT (+/+), Zcwpw1-/- and Prdm9-/- males.
Fertility was assessed in mice ranging from 8 to 12 weeks of age through measurement of paired testes weight and sperm count. Mouse ID is consistent across Figure 3—source data 2 and Figure 4—source data 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Breeding performance of Zcwpw1-/- females.
All females were crossed with a WT male. N/A, not applicable; TLL, total litter loss; *assigned a value of 0 as the number of pups born in the total counts.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
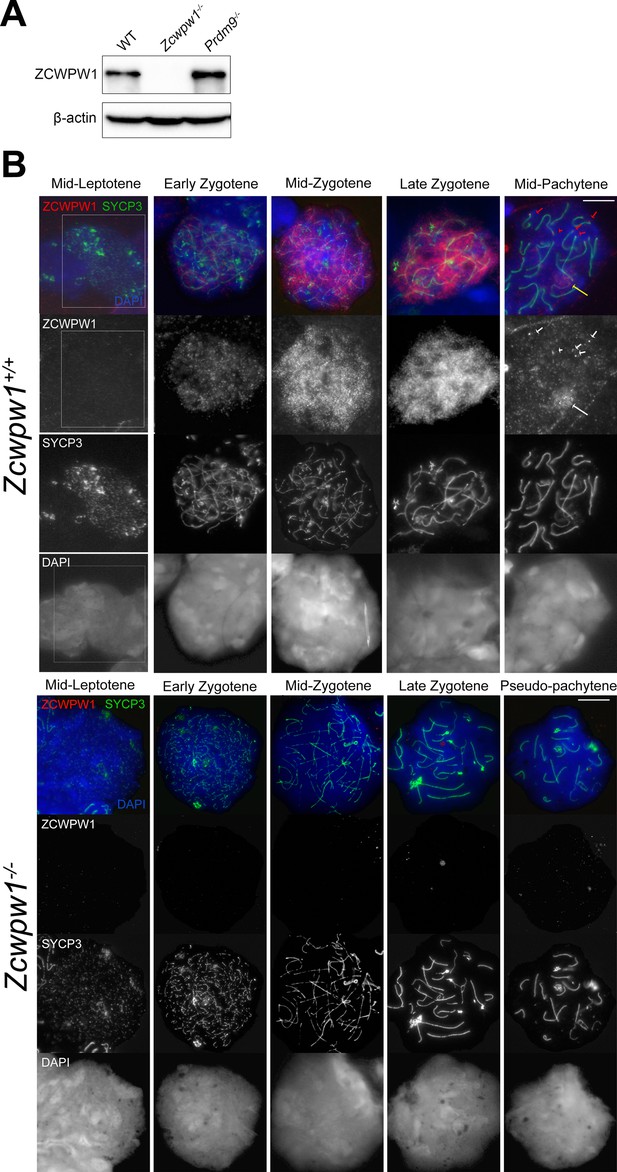
Loss of ZCWPW1 expression in Zcwpw1−/− mouse testis.
(A) Testis protein extracts from adult (10–12 weeks old) B6 wild-type (WT), Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/− were immunoprecipitated with an anti-ZCWPW1 antibody (2.7mg/IP), followed by western blot detection with the same antibody. Detection of beta-actin from protein extracts (100µg) shows equal input for IP. (B) Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice were immunostained with antibodies against the synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3, and ZCWPW1, and counterstained with DAPI to visualise nuclei. Developmental stages are indicated at the top. The top row of panels shows merged signals, and the bottom rows individual signals. For ease of comparison, the boundaries of the mid-Leptotene cell in the Zcwpw1+/+ sample are marked by a rectangle. Red arrows point to ZCWPW1 foci at the ends of the synaptonemal complex (white arrows in the single-channel image). The yellow arrow points to the XY body. These images are representative of the results obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm.
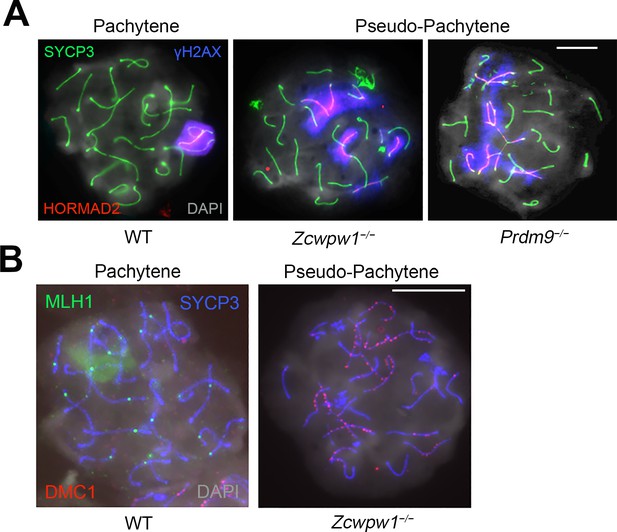
Asynapsis, and lack of XY body formation and crossover sites in Zcwpw1−/− mouse testis.
Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 12-week-old WT, Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/− mice were immunostained with antibodies against SYCP3 (A–B), γ-H2AX (phosphorylated form) and HORMAD2 (A), or MLH1 and DMC1 (B), and counterstained with DAPI (A–B). WT Pachytene cells show full synapsis of all autosomes, an XY body strongly labeled by γ-H2AX and at least one (obligate) crossover site per chromosome labeled by MLH1. In contrast, many chromosomes are asynapsed and the XY body is absent in pseudopachytene cells from Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/− mice; in the Zcwpw1−/− mutant, no MLH1 foci are observed either, and many DMC1 foci persist on asynapsed chromosomes. In the Prdm9−/− mutant, mispairing of homologues is evident by the formation of branched structures referred to as ‘tangled’ chromosomes in the text and Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1. These images are representative of the results obtained for two (Prdm9−/−) to three mice (WT and Zcwpw1−/−) per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Impaired synapsis in Zcwpw1-/- males.
The number of normal pachytene cells showing full synapsis of all autosomes and sex chromosomes (expressed as ‘% synapsis’ of all cells analysed) was determined by immunostaining of testis chromosome spreads against SYCP3, HORMAD2 and γ-H2AX (see images in Figure 3—figure supplement 2). The nature of the defects observed in cells with asynapsis was recorded as either ‘tangled’ (when chromosomes pair with the wrong partner, forming branched tangled structures); ‘multibodies’ strongly positive for HORMAD2 (when asynapsed chromosomes form multiple XY-like bodies which end up merging with each other, and with the XY body); or ‘split XY’ (when the X and Y sex chromosomes are found away from each other in different areas of the cell nucleus). Mouse ID is consistent across Figure 3—source data 1 and 2 and Figure 4—source data 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
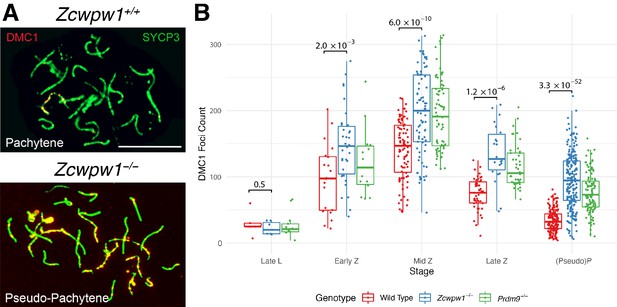
Similar DMC1 count elevation in Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/− mice, compared to wild-type.
(A) Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice were immunostained for DMC1 and SYCP3. Late (pseudo)-Pachytene cells are shown. These images are representative of the data obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) The number of DMC1 foci in cells from the indicated stages of prophase I were counted; see Figure 4—source data 1 for number of cells per stage per mouse. p-values are from Welch’s two sided, two sample t-test. L: Leptotene, Z: Zygotene, P: Pachytene. n = 3 mice for Zcwpw1−/− and wild-type, n = 2 for Prdm9−/−. Raw data in Figure 4—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data for DMC1, RAD51 and RPA2 foci counts.
Stages: L, Leptotene; Z, Zygotene; P, Pachytene. WT: wild-type. Mouse ID is consistent across Figure 3—source data 1 and 2 and Figure 4—source data 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
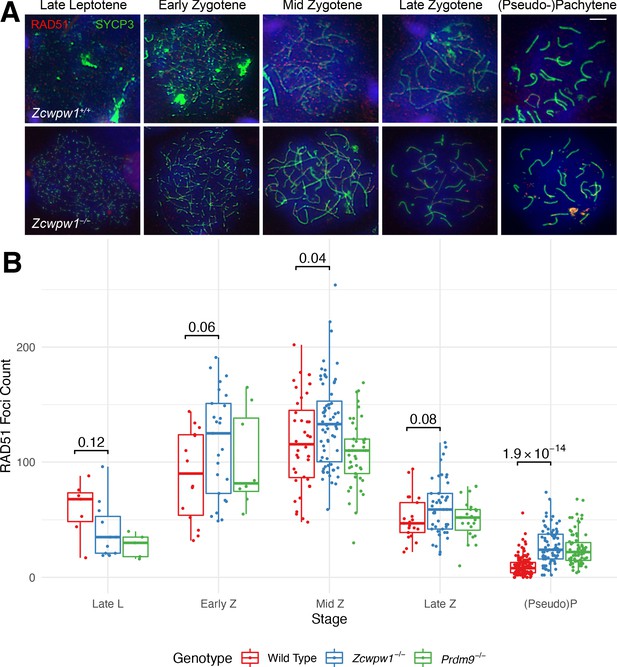
Similar RAD51 count elevation in Zcwpw1−/− and Prdm9−/− mice, compared to wild-type.
(A) Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice were immunostained with antibodies against the synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3 and the recombinase RAD51, and counterstained with DAPI to visualise nuclei. Developmental stages are indicated at the top. These images are representative of the results obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) The number of RAD51 foci in cells from the indicated stages of prophase I were counted; see Figure 4—source data 1 for the number of cells per stage per mouse. p-values are from Welch’s two sided, two sample t-test. L: Leptotene, Z: Zygotene, P: Pachytene. n = 2 mice per genotype (Zcwpw1−/− and WT), n = 1 for Prdm9−/− (Raw data in Figure 4—source data 1).
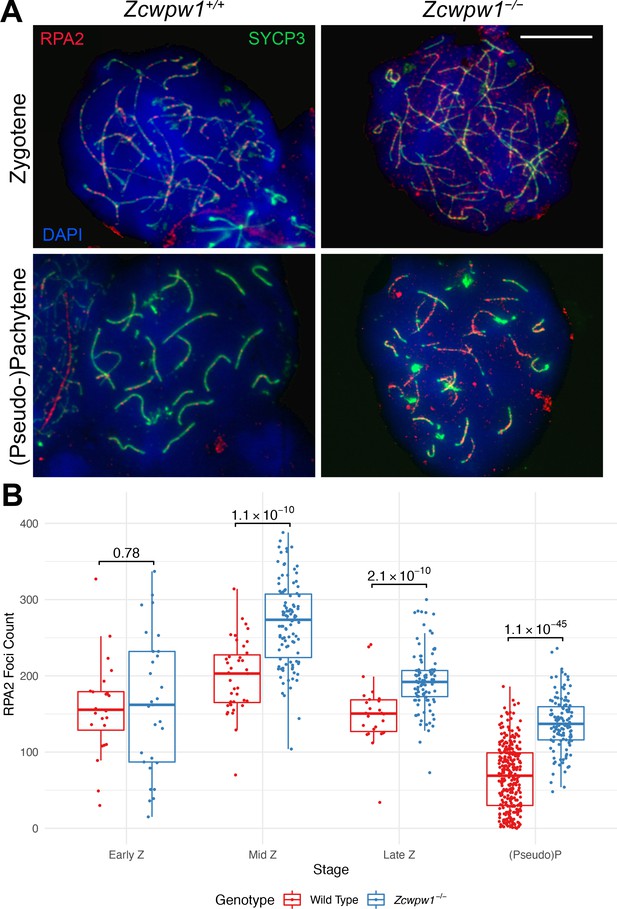
RPA2 count elevation in the Zcwpw1−/− mouse.
(A) Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice were immunostained with antibodies against SYCP3 and RPA2, and counterstained with DAPI to visualise nuclei. Developmental stages are indicated on the side. These images are representative of the results obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) The number of RPA2 foci in cells from the indicated stages of prophase I were counted; see Figure 4—source data 1 for the number of cells per stage per mouse. p-values are from Welch’s two sided, two sample t-test. Z: Zygotene, P: Pachytene. n = 3 mice per genotype (Raw data in Figure 4—source data 1).
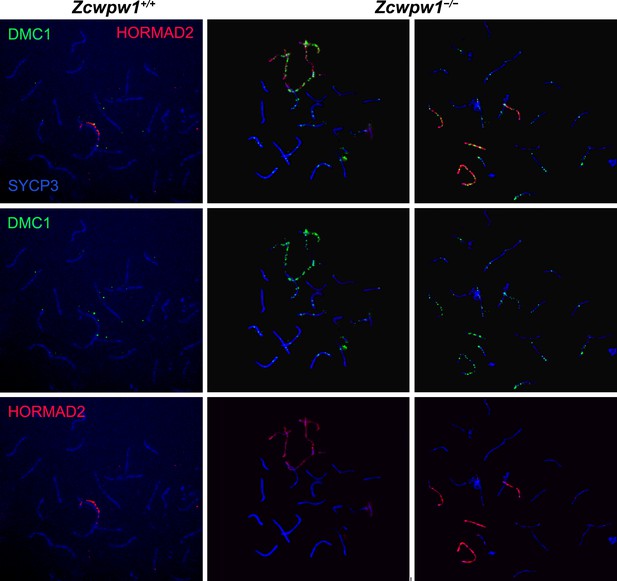
DSB repair is delayed with accumulation of DMC1 on asynapsed chromosomes in the Zcwpw1−/− mouse.
Testis chromosome spreads from 9- to 10-week-old Zcwpw1+/+ and Zcwpw1−/− mice were immunostained for DMC1, HORMAD2, and SYCP3. Representative images of two mutant pseudo-pachytene cells show accumulation of DMC1 foci on HORMAD2-positive asynapsed chromosomes. In contrast wild-type pachytene cells only show residual DMC1 foci on partially synapsed XY sex chromosomes. Note that in mutant cells, even synapsed chromosomes abnormally retain some level of DMC1. These images are representative of the results obtained for three mice per genotype. Scale bar: 10 μm.
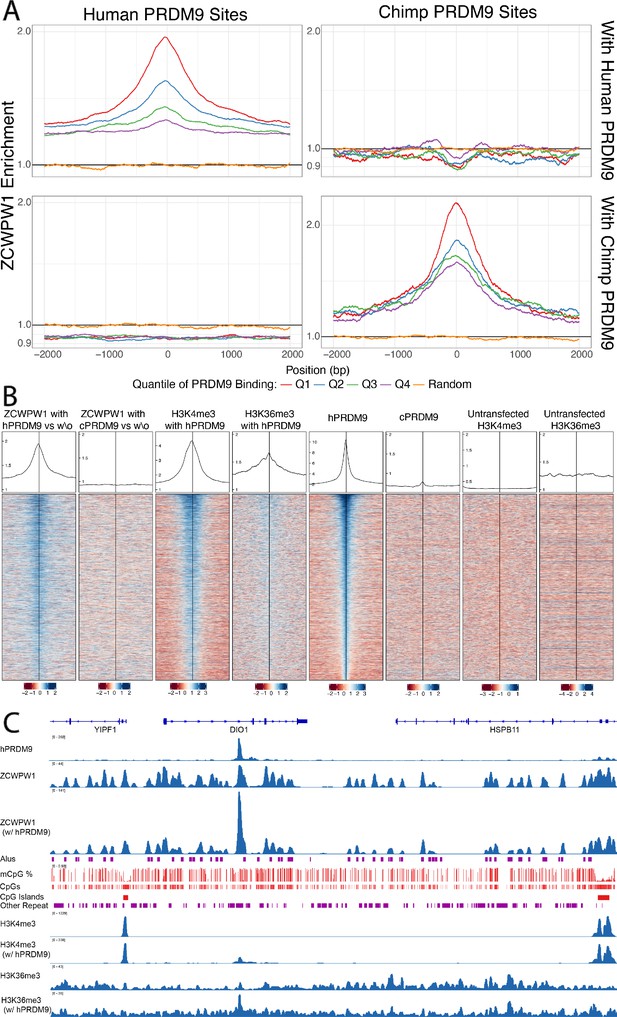
Enrichment and binding profiles of ZCWPW1 and other factors.
(A) Enrichment of ZCWPW1 (with vs without PRDM9) at PRDM9-binding sites when co-transfected with PRDM9 with either Human or Chimp Zinc Finger (Materials and methods section ‘Enrichment Profiles’). Q = quartile. Human PRDM9 sites are centered and stranded by the motif. Y-axis is log10 scale (y-axis labels remaining in linear space). (B) Profiles and heatmaps of reads from cells co-transfected with human (h) or chimp (c) PRDM9 around the top 25% of individual human PRDM9-binding sites (rows). Heatmaps: log-fold change of target (indicated in column titles, Materials and methods) vs input, for various labelled target proteins, ordered by human PRDM9. ZCWPW1, H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 each become enriched at human PRDM9 sites, following (co-)transfection with human PRDM9. Profiles: Sum of all target coverage divided by sum of all input coverage for all regions shown in the heatmap, shown on a linear scale. w\o, without. (C) ChIP-seq data and annotation in a genome plot illustrate the behaviour of ZCWPW1 and other factors. ChIP-seq tracks show fragment coverage. Tracks where PRDM9 is present are labeled ‘w/PRDM9’, and below, corresponding tracks without PRDM9. ZCWPW1 binds to Alus, CpG islands and other CpG-rich sequences even in the absence of PRDM9. On addition of PRDM9, ZCWPW1 becomes strongly enriched at PRDM9 binding locations (center left peak within DIO1). mCpG, methylated CpG.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
RT-PCR analysis of PRDM9, ZCWPW1 and ZCWPW2 transcript expression in HEK293T cells.
Cells were transfected with the indicated constructs (one biological replicate per sample). Each PCR reaction was carried out in triplicate (three technical replicates per sample), and the mean Ct value was used to calculate the relative expression of each gene relative to the basal expression in untransfected cells, normalised to endogenous GAPDH levels (ΔΔCt method). Formula: 2^(Ct gene in untransfected cells - Ct gene in transfected cells)/2^(Ct GAPDH in untransfected cells - Ct GAPDH in transfected cells). Expression of ZCWPW2 was only detected in cells transfected with a construct encoding hZCWPW2-HA. Stdev, standard deviation. *For calculation purposes, Cts were assigned the maximum value of 40 cycles of amplification in all samples not transfected with hZCWPW2-HA (no detectable amplification). **Gene expression was normalised to GAPDH and expressed relative to the expression in untransfected cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/53392/elife-53392-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
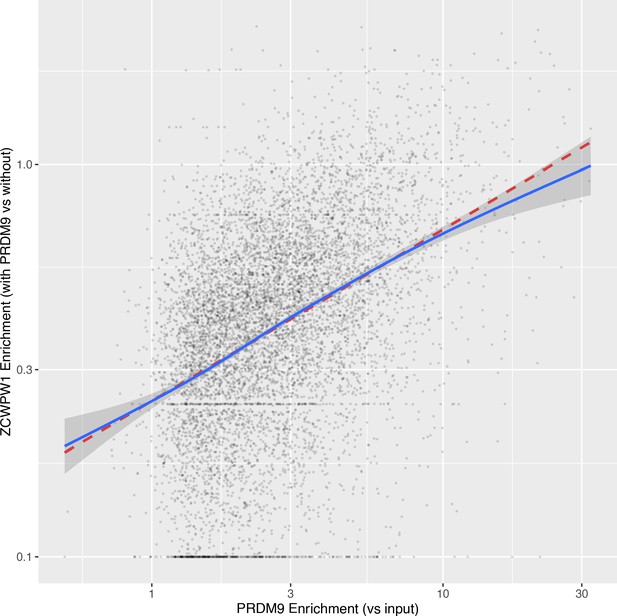
Correlation between PRDM9 enrichment and ZCWPW1 enrichment at sites of PRDM9 binding.
ZCWPW1 binding with vs without PRDM9 was force called at sites with PRDM9 peaks (Materials and methods). Peaks were excluded if PRDM9 input coverage was ≤10 or ZCWPW1 input coverage was ≤3. Additionally, the top 10 peaks (out of 8,373) by enrichment for each of PRDM9 and ZCWPW1 were excluded to remove outliers. The red dashed line shows the fit of a linear model (log(ZCWPW1+0.1)~a + b*log(PRDM9+0.1)) and the blue line and grey error shows a Generalised Additive Model smooth. For plotting, each axis is displayed with a log10 scale (with break values shown in linear space) and 0.1 was added to all values (x and y) to avoid infinite values.
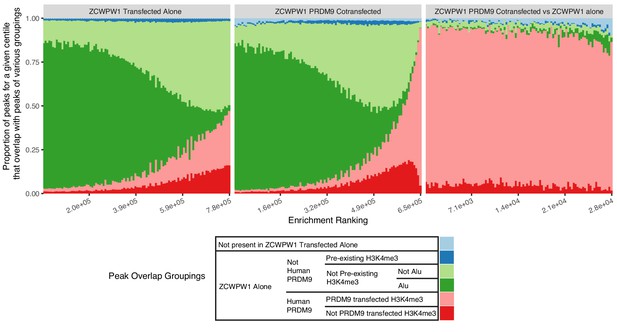
Proportion of ZCWPW1 peaks, ordered by enrichment of ZCWPW1 binding over input, overlapping various other marks.
For example dark green peaks are those which overlap with ZCWPW1 peaks when transfected alone, but not overlapping Human PRDM9 peaks, and not overlapping pre-existing H3K4me3 peaks but do overlap with Alu repeats. Pre-existing H3K4me3 refers to H3K4me3 peaks found without PRDM9 or ZCWPW1 transfection. The three plots show results for peaks in HEK293T cells with ZCWPW1 transfected alone (Left), PRDM9+ZCWPW1 co-transfection (Middle), and peaks whose ZCWPW1 occupancy increases in PRDM9+ZCWPW1 vs ZCWPW1 transfected alone (Right, Materials and methods). In cells expressing ZCWPW1 in the presence (middle plot) but not in the absence (left plot) of PRDM9, the strongest peaks are dominated by PRDM9-bound sites marked by H3K4me3 (pink), while ZCWPW1 occupancy increases occur nearly exclusively at these sites, following co-transfection with PRDM9 (right plot).
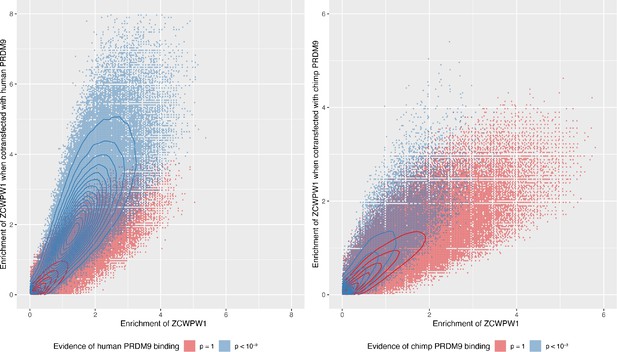
Enrichment of ZCWPW1 when co-transfected with human or chimp PRDM9 is dependent on the ability of ZCWPW1 to bind, more weakly, in the absence of PRDM9 (there are no peaks with high co-transfected enrichment [y-axis] when the untransfected enrichment [x-axis] is close to 0) and co-transfecting with PRDM9 increases the enrichment.
Enrichment was force called in 100bp windows across all autosomes. Data is conditioned on having input coverage of >5 and enrichment >0.01 for both axes. Hexagons are coloured if at least three data points are present. Solid lines show density contours estimated by MASS::kde2d() in R.
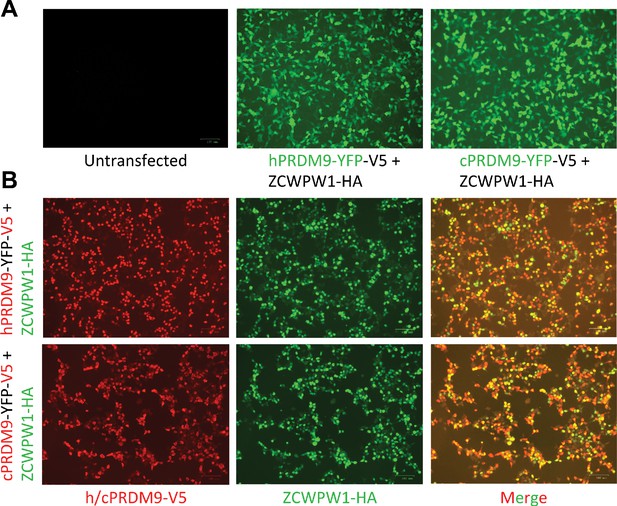
Co-expression of ZCWPW1 and PRDM9 in HEK293T cells.
Cells were co-transfected with human (h) or chimp (c) PRDM9-YFP-V5 (hPRDM9-YFP-V5 or cPRDM9-YFP-V5, respectively) and ZCWPW1-HA, or mock transfected (untransfected). (A) Direct microscopic observation of transfected cells shows high and comparable levels of YFP fluorescence emitted from hPRDM9-YFP-V5 and cPRDM9-YFP-V5. (B) Immunofluorescence staining against the protein tags (HA and V5) shows high and comparable expression levels of each protein across transfected samples, and a reasonable proportion of co-expressing cells with merged overlapping signals (ranging from light green to yellow and light red depending on the expression ratio of the two proteins).
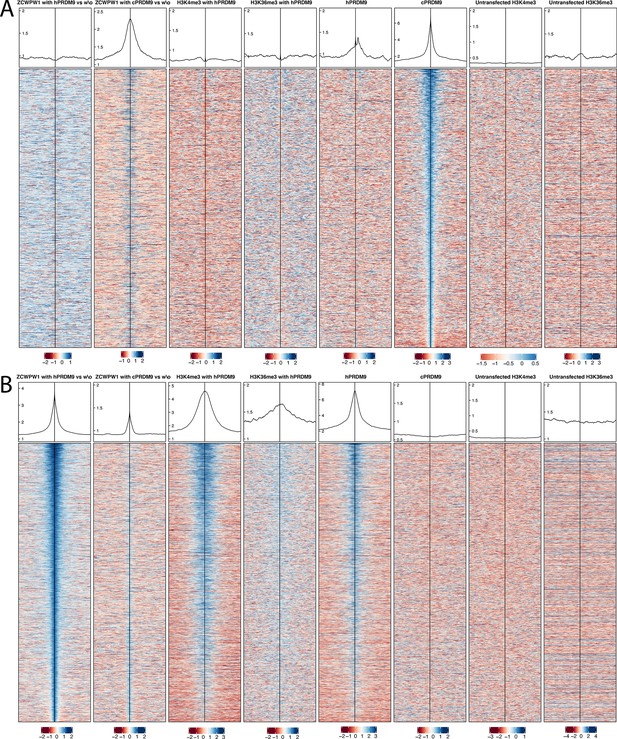
Profiles and heatmaps of reads at locations of either chimp PRDM9 binding or ZCWPW1 binding when co-transfected with human PRDM9.
(A) Profiles and heatmaps of reads at locations of chimp PRDM9 (cPRDM9) binding. Heatmaps show log fold change of sample (as indicated in the title of each column, Materials and methods) vs input, for the top ¼ of cPRDM9 peaks, for various samples, ordered by cPRDM9. ZCWPW1 is found at sites of cPRDM9 peaks, when co-transfected with cPRDM9, but not at human PRDM9 (hPRDM9) peaks. w\o, without. (B) Profiles and heatmaps of reads at locations of ZCWPW1 binding co-transfected with human PRDM9 (hPRDM9). Heatmaps show log fold change of sample (as indicated in the title of each column, Materials and methods) vs input, for the top ¼ of ZCWPW1 peaks when co-transfected with PRDM9, for various samples, ordered by first column. Note that H3K4me3, H3K36me3 and hPRDM9 are found at ZCWPW1 peaks when co-transfected with hPRDM9.
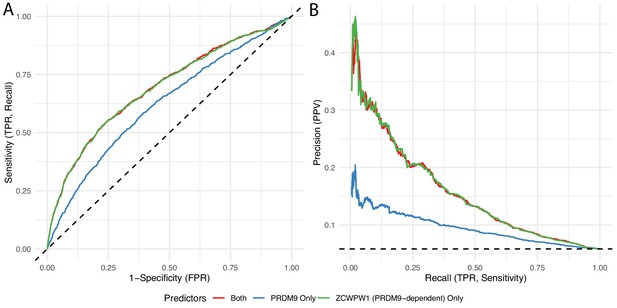
Among human PRDM9 binding sites, we identified those at which male recombination hotspots occur, defined by the presence/absence of an overlapping human DMC1 peak, and fitted a linear model to predict this hotspot status based on PRDM9 binding strength (PRDM9 Only), ZCWPW1 enrichment (with human PRDM9 vs without, referring to enrichment of ZCWPW1 co-transfected with PRDM9 relative to ZCWPW1 transfected alone), or both (see Materials and methods ‘DMC1 prediction’). We fitted a logistic regression model, and present the results in the form of standard Receiver Operating Characteristic curves (A) and Precision Recall Curves (B).
Lines with greater area under the curve (those higher up) represent greater predictive ability (models better able to classify/separate PRDM9 sites into those with DMC1 binding and those without). Black dotted lines show a baseline of random prediction. TPR: True positive rate, FPR: False positive rate. PPV: positive predictive value (proportion of predicted positives that are true positives). Estimated PRDM9-dependent ZCWPW1 enrichment (green) provides a better predictor than does PRDM9 binding strength (blue).
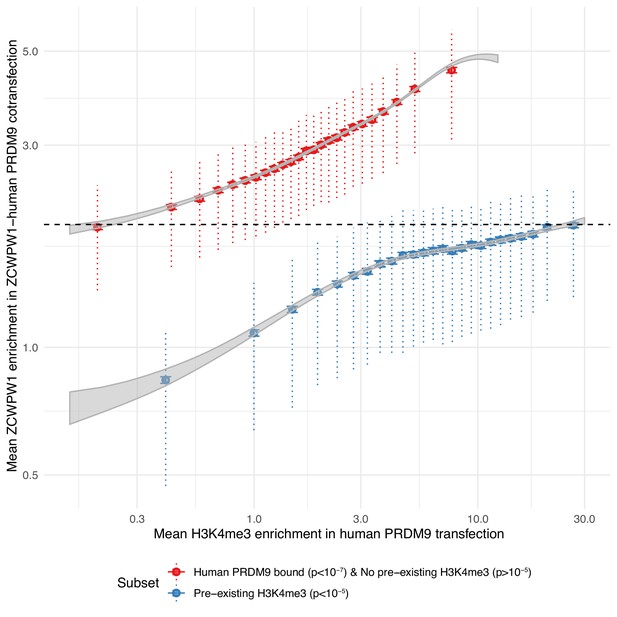
PRDM9-bound regions (H3K4me3 and H3K36me3) are a stronger recruiter of ZCWPW1 than promoters (H3K4me3 only).
For any given level of H3K4me3 (x-axis), ZCWPW1 enrichment (y-axis) is higher at PRDM9-bound regions (red) than regions with pre-existing H3K4me3 (promoters, blue). H3K4me3 and ZCWPW1 were force called in 100bp windows across all autosomes. These windows were split into two sets defined as indicated in the legend (where ‘p’ is the p-value from peak-calling required for a window to be included in the subset) with the additional constraint of requiring input fragment coverage >5 for ZCWPW1 and >15 for H3K4me3. p: p-value for non-zero level of input corrected coverage in that bin. ‘pre-existing H3K4me3’ refers to H3K4me3 that is present without transfection (of either PRDM9 or ZCWPW1), which is mainly found at promoter regions. For each subset, H3K4me3 was split into 25 bins with equal number of data points. Horizontal bars: two standard errors of the mean. Vertical dotted bars: upper and lower quartiles. Grey ribbons show two standard errors for a Generalized additive model on log(mean H3K4me3 enrichment + 0.1). Dashed black horizontal line highlights that the mean enrichment of the highest bin for promoters is similar to that of the lowest bin for PRDM9-bound sites.
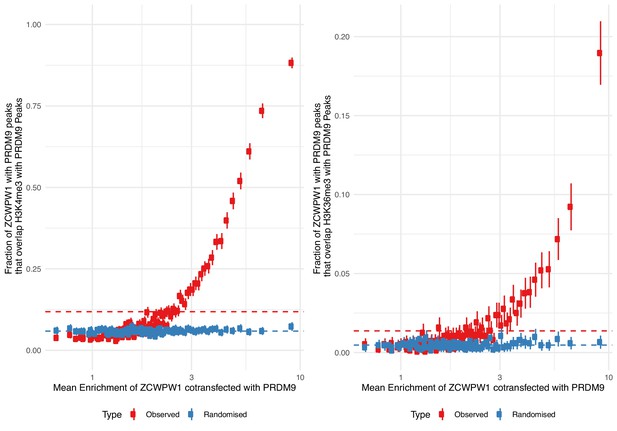
ZCWPW1 binding is positively associated with levels of both H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 marks.
Fraction of ZCWPW1 peaks (co-transfected with PRDM9 with input coverage of at least 5) that overlap either (A) H3K4me3 or (B) H3K36me3 peaks, for different bins of ZCWPW1 enrichment (100 equal sample size bins of increasing ZCWPW1 enrichment). Error bars show ±2 s.e. of the proportion. ‘Randomised’ shows expected proportions when x-axis regions are randomly shifted within a range of 100 million bases (or the chromosome size if lower). Dotted lines show overall means for each colour.
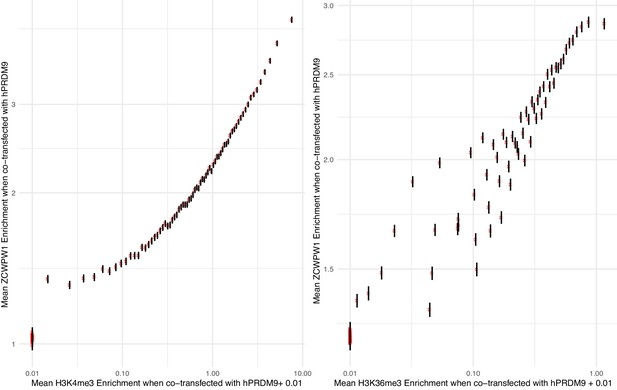
Enrichment from 100-bp non-overlapping windows, genome-wide, is binned into 100 equal sample size bins by either.
(A) H3K4me3 or (B) H3K36me3 levels, and mean enrichment of ZCWPW1 co-transfected with PRDM9 is plotted for each bin (error bars show ±2 s.e. of the mean). This is in some sense opposite (but complementary) to Figure 6—figure supplement 1 in which the subject of the axis is reversed. Windows with evidence of PRDM9-independent H3K4me3 have been removed from the H3K4me3 plot. Additionally, x-axis regions were removed if input reads were <15 and y-axis regions if <5. 0.01 has been added to the x-axis values in order to display enrichment estimates of zero on the log scale.
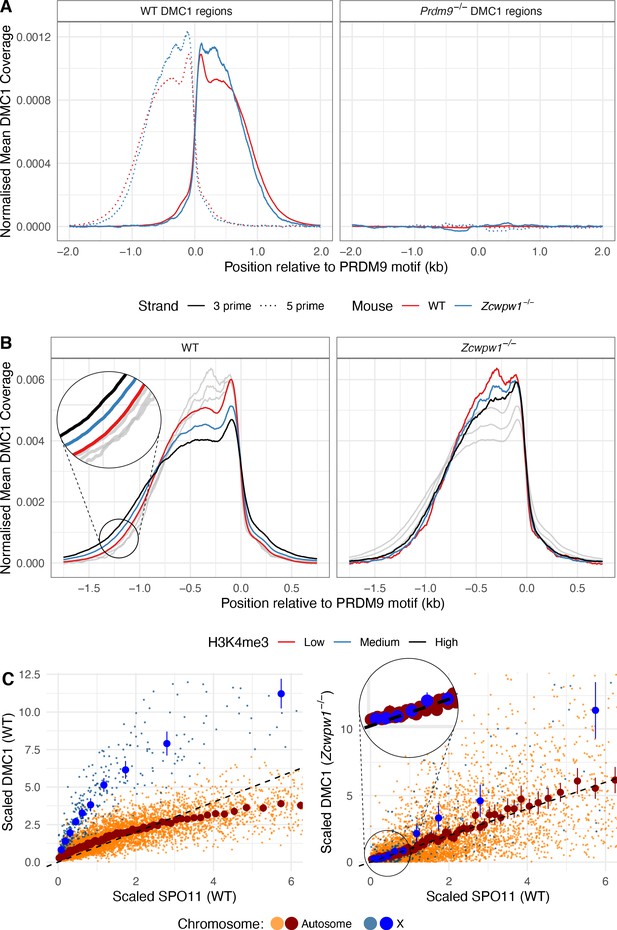
DMC1 levels in the Zcwpw1−/− mouse compared to DMC1 and SPO11 levels in WT.
(A) DSBs occur at normal hotspot locations in the Zcwpw1−/− male mouse. Average coverage of reads from DMC1 SSDS ChIP-seq in a 10-week-old mouse at previously mapped regions (Materials and methods) in B6 WT (left) and Prdm9−/− (right) mice is shown, centered at the PRDM9 motif (left). DMC1 profiles from a WT mouse are shown in red, data from Brick et al., 2012. (B) Normalised DMC1 profile (both strands combined) is plotted for WT and Zcwpw1−/−, stratified by H3K4me3 (a proxy for PRDM9 binding). Low: <50th percentile cumulative enrichment, High: >75th percentile cumulative enrichment, with Medium being the remaining data. Greyed out lines show the alternative genotype for comparison. (C) Relationship between WT SPO11-oligos (measuring the number of DSBs) vs DMC1 (a measure of the number and persistence of DSBs) at each B6 hotspot for WT and Zcwpw1−/−. Unlike WT mice, DMC1 signals in Zcwpw1−/− mice are approximately linearly associated with WT SPO11. The DMC1 enrichment was force called at the positions of B6 WT hotspots. Black dashed line is y = x for reference. SPO11 and DMC1 enrichment have been scaled by dividing by the mean autosomal enrichment. Large dark blue and dark red points show mean DMC1 signal, binned into groups containing equal numbers of hotspots by WT SPO11 signal (vertical lines: corresponding 95% CIs), for X (10 bins) and autosomal data (100 bins) respectively (smaller lighter dots represent individual hotspots).
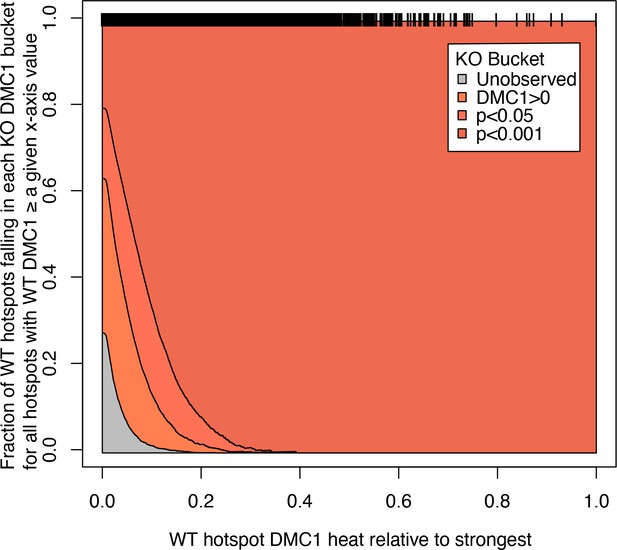
Fraction of wild-type (WT) hotspot locations seen in Zcwpw1−/− DMC1 ChIP-seq at different p-values.
Black bars along the top of the plot show the heat of individual hotspots relative to the hottest, according to the DMC1 data, in the WT male mouse. Y-axis values at x = 0 show the fraction of all hotspots falling into the buckets shown in the inset colour legend. As the x-axis increases the y-axis values show the same thing, but only for those hotspots with a heat greater than or equal to the x-axis value, that is those black bars further to the right. Therefore, almost all WT hotspots with activity >20% of the hottest hotspot are observed, and non-observed hotspots show only weak activity in WT, and so our power to detect them is expected to be reduced. ‘DMC1>0’ refers to the hotspot locations at which DMC1 signal is observed in Zcwpw1−/− DMC1 ChIP-seq, but with significance level (p-value) greater than or equal to 0.05, ‘p<0.05’ refers to the locations at which this significance level is less than 0.05 but greater or equal to 0.001, and ‘p<0.001’ refers to locations at which the p-value is less than 0.001.
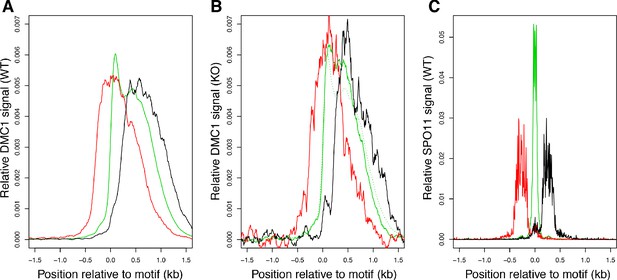
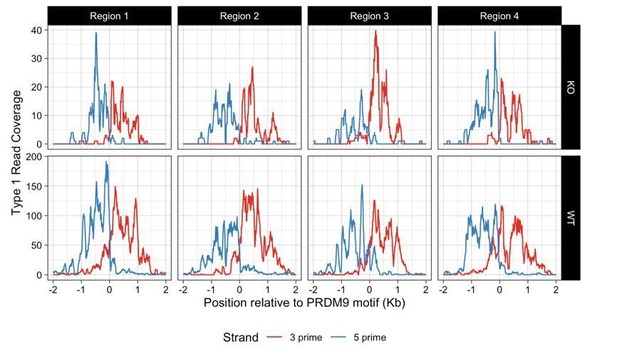
DSBs in Zcwpw1−/− are positioned at WT locations within hotspots.
Hotspots relative to PRDM9 binding motif: upstream (red), downstream (black), central (green). For DMC1 hotspots with an identified PRDM9-binding motif (Materials and methods), we measured positions relative to this motif and identified hotspots in three groups according to SPO11 signal: Green: active hotspots (top 30%) with >90% of the SPO11 signal in the central 300bp region. Red: >90% upstream of the PRDM9 binding motif (position <0) and <50% central. Black: >90% downstream of the PRDM9 binding motif and <50% central. We then plotted the average profiles of DMC1 in wild-type (WT) (left), DMC1 in Zcwpw1−/− (KO) mice (middle) and SPO11 (right), normalised to have unit area. Hotspots with more upstream/downstream DSB sites (SPO11) also show more upstream/downstream DMC1 signals, in both WT and KO mice.
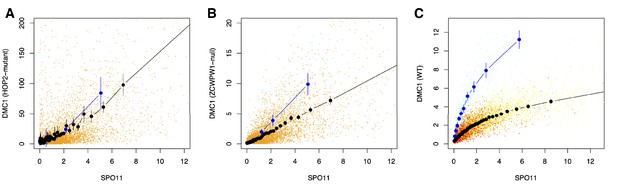
Relationship between WT SPO11-oligos (measuring the number of DSBs) vs DMC1 (a measure of the number and persistence of DSBs) at each B6 hotspot for Hop2−/− male mice (A) Zcwpw1−/− (B) and WT (C) as in Figure 7C are replotted, for comparison.
Similarly to Figure 7C, the DMC1 enrichment was force called at the positions of B6 WT hotspots, in the Hop2−/− data from GSM851661 (Khil et al., 2012). SPO11 and DMC1 enrichment have been scaled by dividing by the mean autosomal enrichment. Blue points are X chromosome data, orange points are autosomal. Large blue and black points show mean DMC1 signal binned into groups containing equal numbers of hotspots by WT SPO11 signal (vertical lines: corresponding 95% CIs), for X and autosomal data, respectively. Other details as for Figure 7C. Hop2−/− (A) and Zcwpw1−/− (B) mouse KO mutants show a similar linear relationship of DMC1 ChIP-seq vs SPO11.
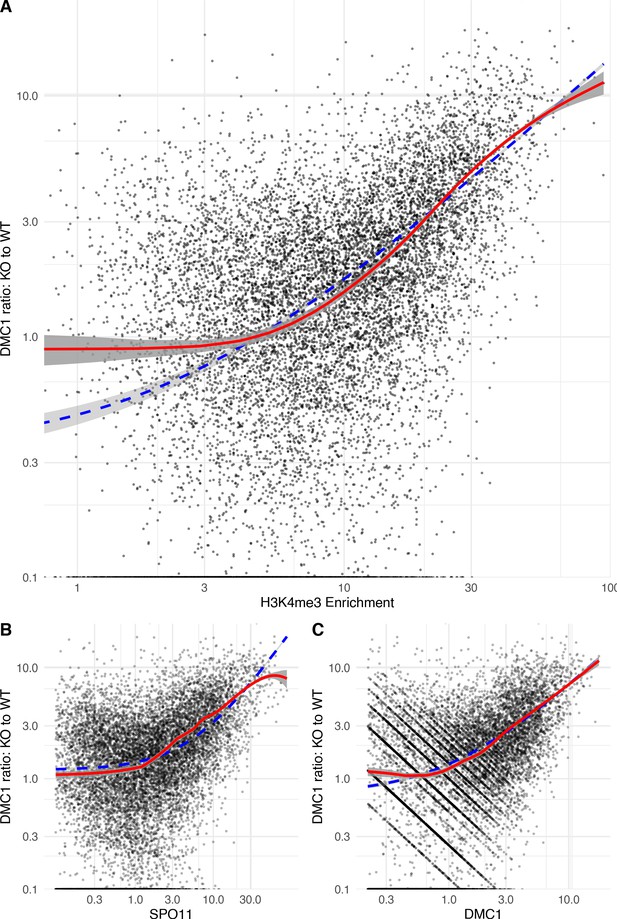
Regression of the ratio of DMC1 signal in the Zcwpw1−/− (KO) vs wild-type (WT) male mice against H3K4me3 [a proxy of PRDM9 binding] (A), SPO11 (B), and DMC1 (C) in WT.
The DMC1 signal in the KO relative to the WT increases as H3K4me3 (~PRDM9) increases. We calculated the ratio of KO to WT DMC1 force-called enrichment at each autosomal B6 mouse hotspot not overlapping pre-existing H3K4me3. We excluded weak hotspots whose estimated SPO11 or DMC1 WT heats were in the bottom 10% (because accurate ratio estimation is not possible for these hotspots). Dots: the force-called signal strength (of either H3K4me3, SPO11 or WT DCM1), vs the ratio, for each of the resulting hotspots. Blue dashed line, linear regression line of best fit (fit in linear space, displayed in log space). Red line: Generalised Additive model (able to fit non-linear effects if present, again fit in linear space).
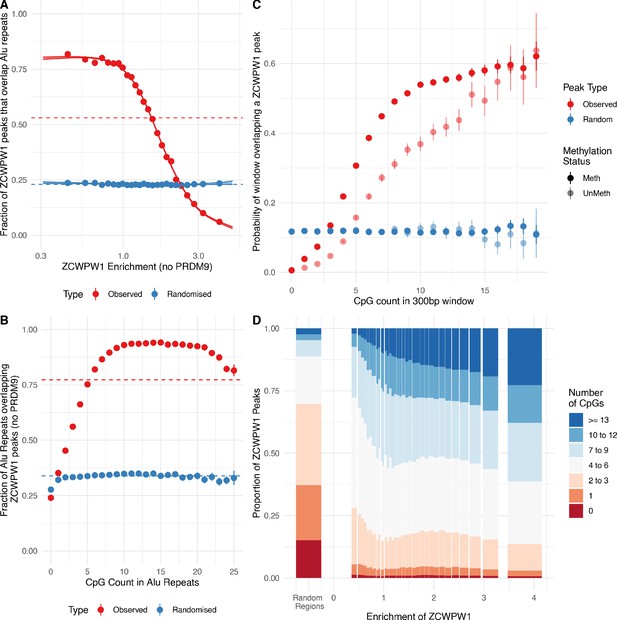
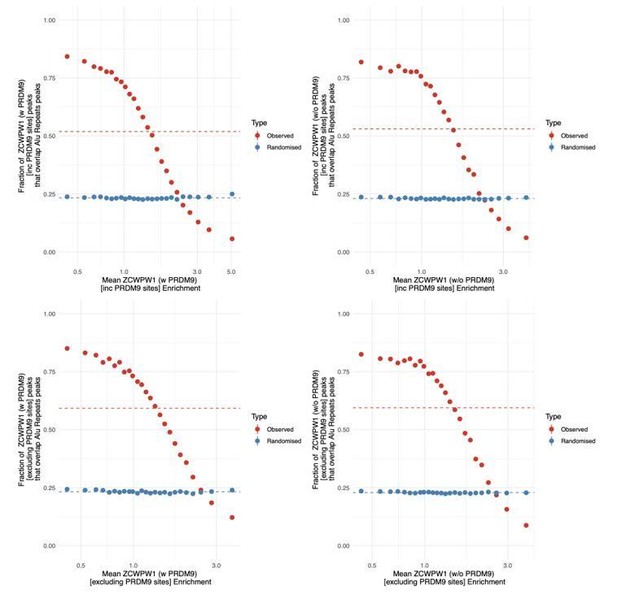
ZCWPW1 binds CpG-rich sequences such as Alu repeats.
(A) Fraction of overlap of ZCWPW1 binding peaks, , with Alusin HEK293T cells transfected with ZCWPW1 alone, ordered by enrichment in ZCWPW1 binding. ZCWPW1 peaks are binned into 25 bins with equal number of data points, and means of both enrichment and overlap are plotted. Solid ribbons: prediction from GAM logistic regression. Dotted lines: overall means. Red points show actual observed peaks, blue points the same number of peaks placed at random genomic positions. (B) Rate of overlap of Alu repeats with ZCWPW1 peaks, for Alus with different numbers of CpG dinucleotides. Other details as A. (C) The probability of a 300bp window on an autosome overlapping a ZCWPW1 peak increases with increasing CpG count in that window. Windows overlapping (by 10bp or more) Alus, other repeats, or CpG islands have been excluded. Methylated CpG regions (full colour) are those with a methylated to unmethylated reads ratio of >0.75, and unmethylated <0.25 (semi-transparent, Materials and methods). (D) Relative proportion of peaks with given numbers of CpGs (stacked bars) +/− 150bp from peak center, within peaks binned by ZCWPW1 enrichment (x-axis). ZCWPW1 peaks are enriched in CpGs compared to random peak locations (leftmost bar). ‘Meth’, methylated; ‘UnMeth’, unmethylated.
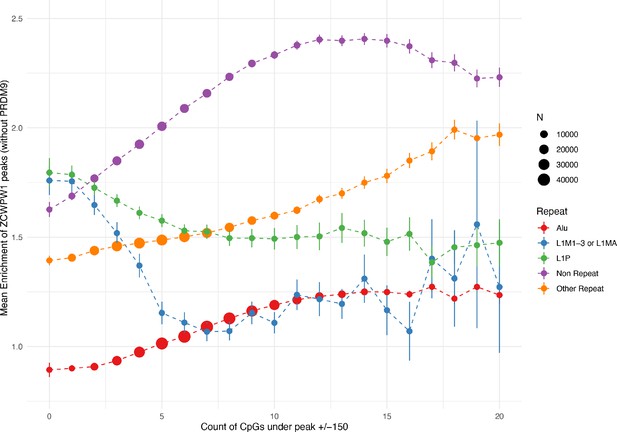
CpG count around ZCWPW1 peaks (+/− 150bp, for those peaks with input coverage >5) is positively associated with ZCWPW1 enrichment score (measuring the level of ZCWPW1 recruitment) in both peaks overlapping Alus and peaks not overlapping Alus, but not at L1M1-3, L1MA or L1P repeats.
Error bars show ±2 s.e. of the mean.
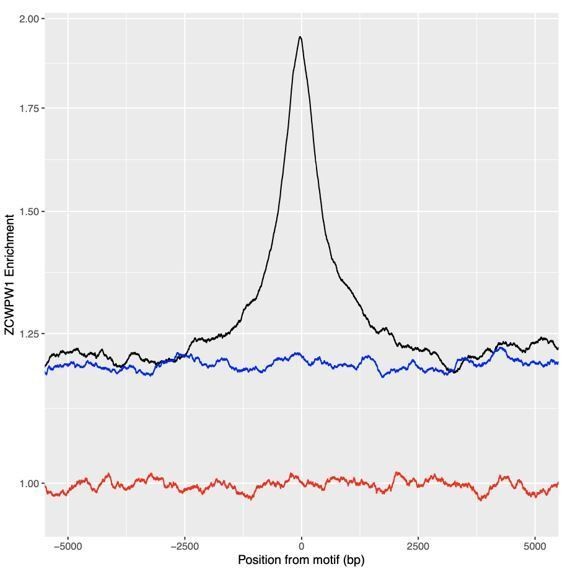
Black: Profile of peaks.
Blue: profile of locations 15 to 10kb downstream. Red: profile of globally (whole genome) random locations.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (167 species) | ZCWPW1 | This paper using BlastP and tBLASTn (www.blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and Ensembl (www.ens.embl.org) | Details in Materials and methods | Also see Figure 1—source data 1 |
| Gene (225 species) | PRDM9 | Baker et al., 2017 (doi: 10.7554/eLife.24133) | Also see Figure 1—source data 2 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Zcwpw1-/- | Toronto Centre for Phenogeno-mics (Canada) | RRID:IMSR_CMMR:ADVN; Strain name C57BL/6N-Zcwpw1em1(IMPC)Tcp | Constitutive knock out for Zcwpw1 carrying a 1485bp CRISPR/Cas9-induced deletion (chr5:137799545–13780101029) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Prdm9-/- | RIKEN BioResource Research Center (Japan) | RRID:MGI:3624989; Strain name B6.129P2-Prdm9 < tm1Ymat>, strain number RBRC05145 | Originating article Hayashi et al., 2005. |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | Embryonic Epithelial Kidney | ATCC | Cat. CRL-3216 | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | hPRDM9-V5-YFP | Altemose et al., 2017 (doi: 10.7554/eLife.28383) | Human PRDM9 B allele cloned into pLENTI CMV/TO Puro DEST vector (Addgene plasmid #17293; Campeau et al., 2009) in frame with a Twin-strep tag, a V5 tag, and a self-cleaving YFP tag due to the presence of an upstream P2A sequence | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens/Pan troglodyte hybrid) | cPRDM9-V5-YFP | Altemose et al., 2017 (doi: 10.7554/eLife.28383) | hPRDM9-V5-YFP construct where Exon 10 encoding the human zinc finger array was replaced with the equivalent sequence from the chimpPRDM9 w11a allele | |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | hZCWPW1-HA | GenScript | Clone ID OHu16813 | ZCWPW1, transcript variant 1, mRNA (NM_017984.5) cloned into pCDNA3.1+/C-HA |
| Transfected construct (Homo sapiens) | hZCWPW2-HA | GenScript | Clone ID OHu31001C | ZCWPW2, transcript variant 1, mRNA (NM_001040132.3) cloned into pCDNA3.1+/C-HA |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | mZCWPW1-FLAG | OriGene | Clone ID MR209594 | Zcwpw1, Transcript variant 2 mRNA (NM_001005426) cloned with a C-terminal Myc-DDK(FLAG) tag |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | mZCWPW2-FLAG | This paper | pCMV6-Entry (OriGene, Cat. PS100001) | Generated by cloning custom-synthesised mZCWPW2 into pCMV6-Entry |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | mZCWPW1-His | This paper | pET22b(+) Novagen (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. 69744) | Generated by sub-cloning mZCWPW1 from clone ID MR209594 (OriGene) into pET22b(+) in frame with a C-terminal 6-histidines tag |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | mZCWPW2 | Origene | Mouse Zcwpw2-206; Transcript ID ENSMUST00000238919.1 | Custom synthesis of full-length cDNA sequence |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | BL21(DE3) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. C600003 | Chemically competent cells |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | mZCWPW1-His | This paper | Used to produce a rabbit polyclonal antibody against mouse ZCWPW1 by immunisation (Eurogentec) | |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse ZCWPW1 antiserum, and pre-immune serum (rabbit polyclonal) | This paper | Custom generation (Eurogentec) | IF (1:100), WB (1:1000), IP (5 μl on transfected cells, 10 μl on mouse testis) |
| Antibody | Anti-Human ZCWPW1 (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. SAB1409478 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-SYCP3 (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat. sc-74569, RRID:AB_2197353 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-SYCP3 (biotinylated, rabbit polyclonal) | Novus | Cat. NB300-232, RRID:AB_2087193 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-DMC1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat. sc-22768, RRID:AB_2277191, Discontinued | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-DMC1 2H12/4 (mouse monoclonal) | Novus | Cat. NB100-2617, RRID:AB_2245859 | ChIP (5 μg) |
| Antibody | Anti-HORMAD2 (rabbit polyclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat. sc-282192, RRID:AB_2121124 | IF (1:300) |
| Antibody | Anti-RAD51 (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat. ab88572, RRID:AB_2042762 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-RPA2 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat. ab10359, RRID:AB_297095 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-H2AX (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat 05–636, RRID:AB_309864 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho γ-H2AX (chicken polyclonal) | Biorbyt | Cat. orb195374 Discontinued | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 488 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-11008, RRID:AB_143165 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-11001, RRID:AB_2534069 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 594 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-11012, RRID:AB_141359 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 594 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-11005, RRID:AB_141372 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 647 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-21235, RRID:AB_2535804 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-chicken IgY Alexa Fluor 647 secondary (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. A-21449, RRID:AB_2535866 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor 647 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. S32357 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-poly-His (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. H1029, RRID:AB_260015 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-HA (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat. ab9110, RRID:AB_307019 | IF (1:100), WB (1:1000), IP (2 μg), ChIP (5 μg) |
| Antibody | Anti-HA (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. H3663, RRID:AB_262051 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-V5 (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat. ab9116, RRID:AB_307024 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-FLAG M2 (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. F3165, RRID:AB_259529 | IF (1:500), WB (1:2000), IP (3 μg) |
| Antibody | Anti-β-Actin (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. A1978, RRID:AB_476692 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | ECL Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (donkey polyclonal) | GE Healthcare | Cat. NA934, RRID:AB_772206 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | ECL Mouse IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab (sheep polyclonal) | GE Healthcare | Cat. NA931, RRID:AB_772210 | WB (1:10000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | pIRESMinor | Chan et al., 2017 | biotin labelled minor satellite probe | |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_F (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_002046 | GCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCGGCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_R (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_002046 | ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | PRDM9_F (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_020227 | ACGAAGAGGCAGCCAACAATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | PRDM9_R (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_020227 | GCCACCAGGTTCTGCTCTTCAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | ZCWPW1_F (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_017984 | GATGGCTCAAGAGGCAGAACAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ZCWPW1_R (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_017984 | TGGGCTGTTCAAACCAGAGAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | ZCWPW2_F (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_001040432 | AAGAGCTGGAGCAAATGCTGCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ZCWPW2_R (Human) | OriGene | PCR primers, transcript detection, NM_001040432 | CAGGAGCTTCTGGGCTGCATTT |
| Commercial assay or kit | Telomere PNA FISH Kit/Cy3 | Agilent | Cat. K5326 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce BCA protein assay kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. 23227 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ECL Prime Western Blotting Detection Reagent | GE Healthcare | Cat. 10308449 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Minelute Reaction Cleanup Kit | QIAGEN | Cat. 28204 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Qubit dsDNA HS Assay kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. Q32851 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | IPTG | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. I5502 | 0.5 mM final |
| Other | Fast SYBR Green Master Mix | Applied Biosystems | Cat. 4385610 | RNA extraction and RT-qPCR |
| Other | Dynabeads M-280 Sheep anti-Rabbit IgG | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. 11203D, RRID:AB_2783009 | IP and ChIP experiments; IP (25–75 ul), ChIP (65 ul) |
| Other | Dynabeads M-280 Sheep anti-Mouse IgG | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. 11202D, RRID:AB_2783640 | IP and ChIP experiments; IP (25 ul), ChIP (65 ul) |
| Other | TALON Metal Affinity Resin | Takara | Cat. 635502 | Expression and purification of ZCWPW1 recombinant protein; 2 ml per L of IPTG-induced bacterial culture |
| Other | TRI Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. T9424 | RNA extraction and RT-qPCR |
| Other | Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. P8340 | IP and WB detection; 1:100 dilution |
| Other | Complete Mini Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat. 11697498001 | ChIP; 1 tablet in 10 ml volume |
| Other | Novex WedgeWell 4%to 20%, Tris-Glycine, Protein Gel | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. XP04200BOX | IP and WB detection |
| Other | Novex WedgeWell 8%, Tris-Glycine, Protein Gel | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat. XP00080BOX | IP and WB detection |
| Software, Algorithm | MAPeakCaller | Altemose et al., 2017 (doi: 10.7554/eLife.28383) | https://github.com/MyersGroup/PeakCaller/ (archived at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3783600) | |
| Software, Algorithm | BWA MEM | Li, 2013 (arXiv:1303.3997) | bwa mem (version 0.7.17-r1188) | |
| Software, Algorithm | bwtool | Pohl and Beato, 2014 (doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu056) | RRID:SCR_003035; v1.0 | https://github.com/CRG-Barcelona/bwtool |
| Software, Algorithm | Picard | ‘Picard Toolkit.’ 2019. Broad Institute, GitHub Repository. http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/; Broad Institute | RRID:SCR_006525; version 2.20.4-SNAPSHOT | |
| Software, Algorithm | SAMtools | PMID:19505943 | RRID:SCR_002105; v1.9 | https://www.htslib.org/download/ |
| Software, Algorithm | BEDtools | Quinlan and Hall, 2010 (doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033) | RRID:SCR_006646; v2.28.0 | bedtools.readthedocs.io |
| Software, Algorithm | SEQkit | Shen et al., 2016 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163962) | ||
| Software, Algorithm | IGV | Thorvaldsdóttir et al., 2013 (doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs017) |