Control of brown adipose tissue adaptation to nutrient stress by the activin receptor ALK7
Figures
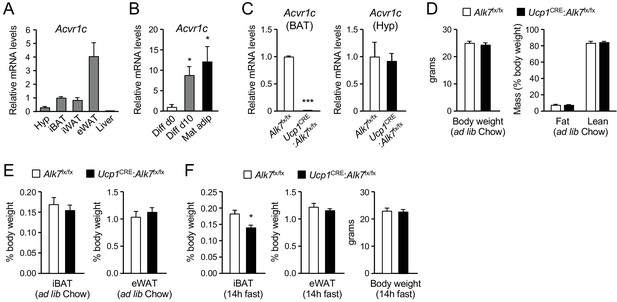
Reduced iBAT mass in Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx conditional mutant mice after fasting.
(A) Q-PCR determination of Acvr1c mRNA expression in hypothalamus (Hyp), interscapular BAT (iBAT), inguinal WAT (iWAT), epididymal WAT (eWAT) and liver of wild type mice. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in iBAT and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 or 6 (iWAT) mice per group. (B) Q-PCR determination of Acvr1c mRNA expression in iBAT stromal vascular fraction (Diff d0), adipocytes differentiated in vitro (Diff d10), and freshly isolated mature adipocytes (Mat adip). The values were normalized to mRNA levels in the Diff d0 sample, and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 independent experiments. *, p<0.05; two-tailed Mann Whitney test. (C) Q-PCR determination of Acvr1c mRNA expression in iBAT (left) and hypothalamus (right) from conditional mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) and control (Alk7fx/fx) mice using primers flanking the kinase domain. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in control mice and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per group. ***, p<0.001; two-tailed Mann Whitney test. (D) Body weight (left) at 2 months (ad libitum Chow diet) and fat and lean mass (expressed as percentage of body weight) assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (right). Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per group. (E) Relative iBAT and eWAT mass expressed as percentage of body weight at 2 months (ad libitum Chow diet) in conditional mutant and control mice. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. (F) Relative iBAT mass, eWAT mass, and body weight at 2 months (ad libitum Chow diet) following 14 hr fasting in conditional mutant and control mice. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. *, p<0.05; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
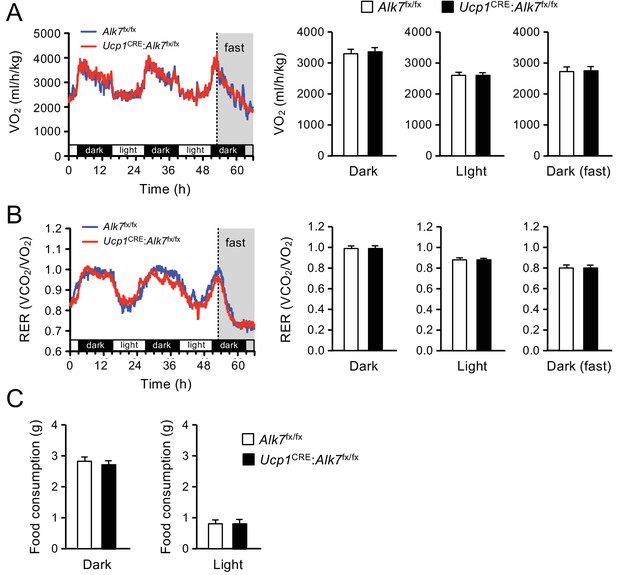
Normal energy consumption and food intake in mutant mice lacking ALK7 in BAT.
(A, B) VO2 and RER measured by indirect calorimetry at room temperature in 2 month old mice. RER values close to unit indicate carbohydrate usage, while values around 0.7 indicate fat consumption. Animals were fasted during the last 14 hr of the experiment (N = 10–12 mice per group). (C) Food consumption in 12 hr dark or light cycle at room temperature N = 14–16 mice per group.
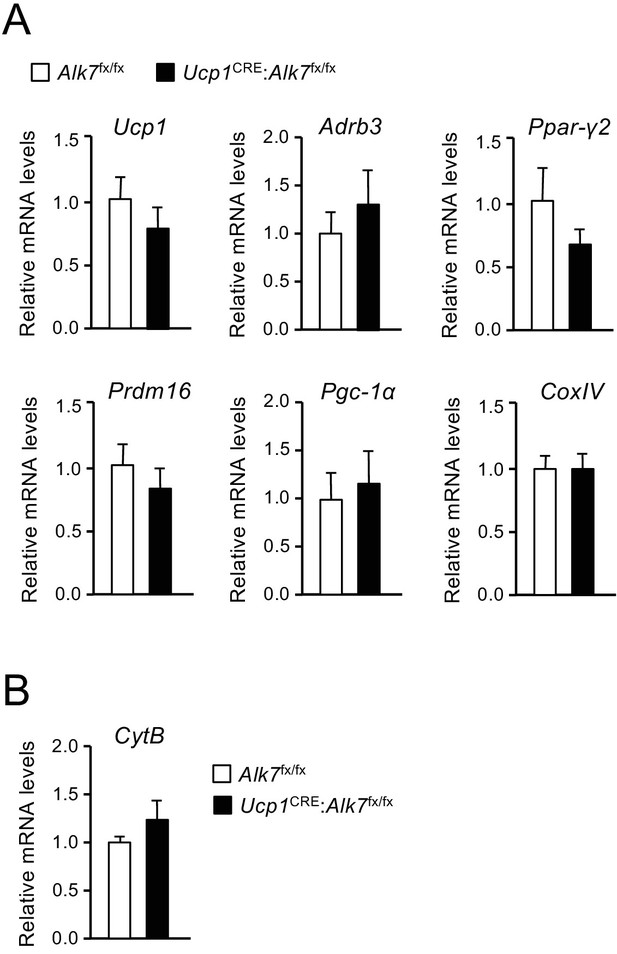
Normal BAT differentiation in mice lacking ALK7 in brown adipocytes.
(A) mRNA expression of differentiation and maturation markers in BAT of 2 month old control (Alk7fx/fx) and mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) mice assessed by Q-PCR. Values are expressed relative to levels in control mice. Ucp1, Uncoupling protein-1; Adrb3, Adrenergic receptor beta 3; Ppar-γ2, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 2; Prdm16, PR/SET Domain 16; Pgc-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator one alpha; CoxIV, Cytochrome C oxidase subunit 4. N = 4–5 mice per group. (B) Mitochondrial DNA content was determined by quantitative PCR using primers specific for the mitochondrial gene CytB, Cytochrome B. N = 5 mice per group.
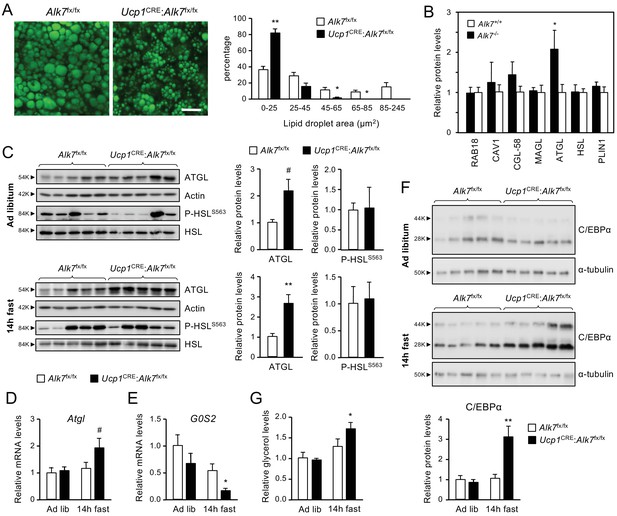
Fasting induces abnormally increased fat catabolism in BAT of Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx conditional mutant mice.
(A) Representative BODIPY 493/503 staining of iBAT sections of conditional mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) and control (Alk7fx/fx) mice. Scale bar, 20 µm. Histograms to the right show quantitative analysis of lipid droplet size. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per group. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; vs. control, respectively; unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) Proteomic analysis of BAT lipid droplet fractions in global Alk7-/- knock-out mice and wild type controls. PLIN1, Perilipin 1; HSL, Hormone-sensitive lipase; ATGL, Adipose triglyceride lipase; MAGL, Monoacylglycerol lipase; CGL-58, Comparative Gene Identification-58; CAV1, caveolin-1. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per genotype. *, p<0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test. (C) Western blot analysis of ATGL and phosphorylated HSL (P-HSLS563) in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum (D) or after 14 hr fasting (E). Histograms to the right show quantitative analyses of protein levels normalized to actin (for ATGL) or total HSL (for P-HSLS563) signals from re-probed blots, relative to those in control Alk7fx/fx mice. N = 5 mice per genotype. #, p=0.077; *, p<0.05; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (D, E) Q-PCR determination of Atgl (D) and G0S2 (E) mRNA expression in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in control mice fed ad libitum and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per group. #, p=0.078 vs. control; *, p<0.05 vs. control; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (F) Western blot analysis of C/EBPα in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum (D) or after 14 hr fasting (E). Histogram below show quantitative analyses of protein levels normalized to α-tubulin signals from re-probed blots, relative to those in control Alk7fx/fx mice. C/EBPα runs as two bands of 28 and 44 kDa, respectively. N = 5 mice per genotype. **, p<0.01; two-way ANOVA. (G) Basal lipolysis measured as glycerol release ex vivo from iBAT explants from conditional mutant and control mice fed ad libitum or after 6 hr fasting. Values were normalized to ad libitum levels in control mice and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 6 (ad lib) and 5 (fast) mice per group. *, p<0.05 vs. control; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
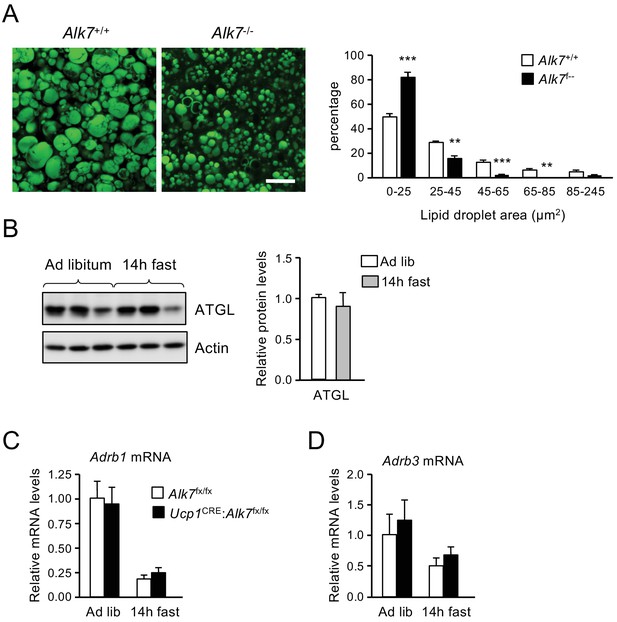
Reduced lipid droplets in iBAT from Alk7 knock-out mice, unchanged levels of ATGL protein in fasted wild type mice, and normal Adrb1 and Adrb3 mRNA levels in iBAT lacking ALK7.
(A) Representative BODIPY 493/503 staining of iBAT sections of global Alk7-/- knock out mice and wild type controls. Scale bar, 20 µm. Histogram to the right show quantitative analysis of lipid droplet size. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 4 mice per group. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; vs. control, respectively; unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) ATGL in BAT of wild type mice fed on Chow ad libitum or fasted for 14 hr, assessed by western blotting of BAT lysates. Histograms show ATGL normalized to actin relative to ad libitum. N = 3 mice per group. (C and D) Levels of Adrb1 (C) and Adrb3 (D) mRNAs in iBAT assessed by Q-PCR. Shown are averages relative to control levels ± SEM. Values were normalized to control mice Ad lib. N = 4 mice per group.
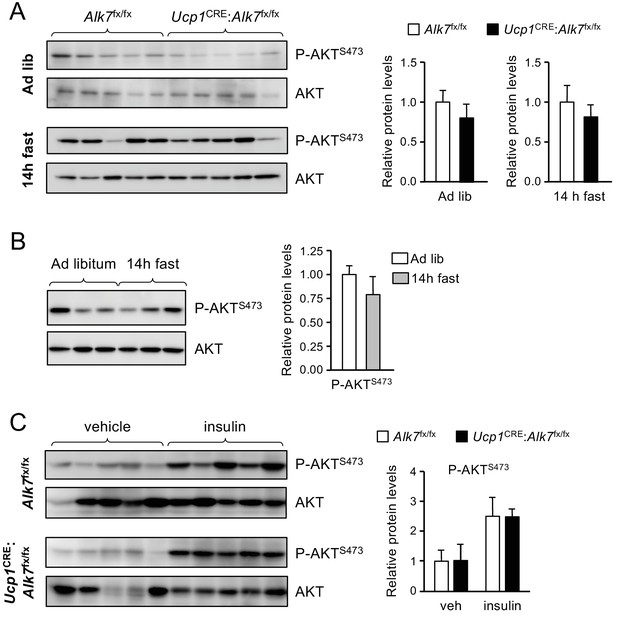
Normal P-AKT levels and insulin sensitivity in iBAT lacking ALK7.
(A) Phospho-AKTS473 in BAT of control (Alk7fx/fx) and mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) 2 month old mice fed on Chow ad libitum (Ad lib) or fasted for 14 hr, assessed by western blotting of BAT lysates. Histograms show P-AKTS473 levels normalized to total AKT relative to control. N = 5 mice per group. (B) Phospho-AKTS473 in BAT of wild type mice fed on Chow ad libitum or fasted for 14 hr, assessed by western blotting of BAT lysates. Histogram shows P-AKTS473 normalized to total AKT relative to ad libitum. N = 3 mice per group. (C) Phospho-AKTS473 in BAT of control (Alk7fx/fx) and mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) 2 month old mice following injection with insulin or vehicle assessed by western blotting of BAT lysates. Histograms show P-AKTS473 levels normalized to total AKT relative to control. N = 5 mice per group.
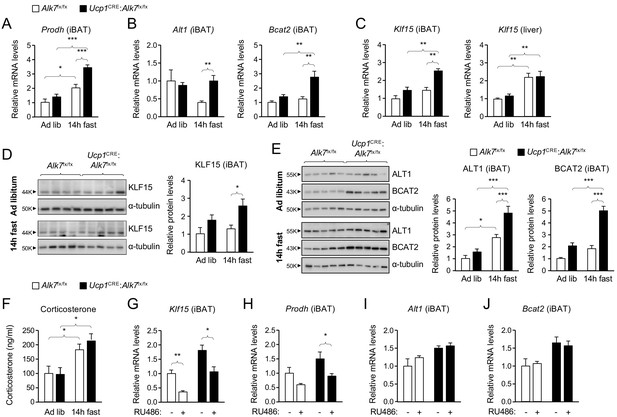
Abnormally enhanced amino acid catabolism upon nutrient stress in iBAT lacking ALK7.
(A, B) Q-PCR determination of Prodh (A) and Alt1 and Bcat2 (B) mRNA expression in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in control mice fed ad libitum and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 9 (A) or 5 (B) mice per group. *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001; vs. control, respectively; unpaired Student’s t-test. (C) Q-PCR determination of Klf15 mRNA expression in iBAT (left) and liver (right) of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in control mice fed ad libitum and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. **, p<0.01; vs. control, respectively; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. (D, E) Western blot analysis of KLF15, (D) ALT1, and BCAT2 (E) in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting, as indicated. Histograms show quantitative analyses of protein levels normalized to α-tubulin signals from re-probed blots, relative to control Alk7fx/fx mice fed ad libitum. N = 3 experiments each in triplicate (mean ± SEM). *, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. (F) Serum corticosterone levels (ng/ml) in 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 9 mice per group. *, p<0.05 vs. control; unpaired Student’s t-test. (G–J) Q-PCR determination of Klf15 (G), Prodh (H), Alt1 (I) and Bcat2 (J) mRNA expression in iBAT of 14h-fasted conditional mutant and control mice 4 hr after injection with RU486 or vehicle, as indicated. The values were normalized to mRNA levels in control mice injected with vehicle, and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; vs. control, respectively; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test.
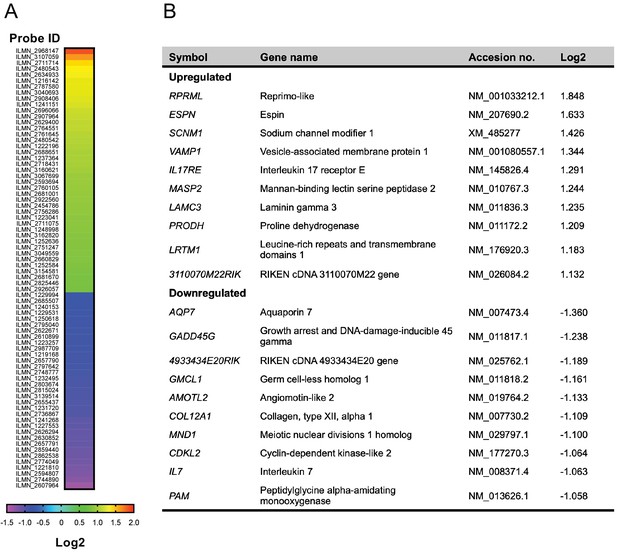
Microarray analysis of genes differentially expressed in iBAT of Alk7-/- global knock-out mice compared to wild type.
(A) Heat map showing relative expression of mRNAs differentially expressed (p<0.05) in iBAT of Alk7-/- global knock-out mice relative to wild type controls. The animals (N = 4 per group) were kept at 30°C prior to iBAT extraction. Illumina microarray Probe IDs are indicated. Values are expressed as Log2 of knock-out to wild type expression ratio. (B) Top 10 up- and down-regulated genes in iBAT of Alk7-/- mice compared to wild type.
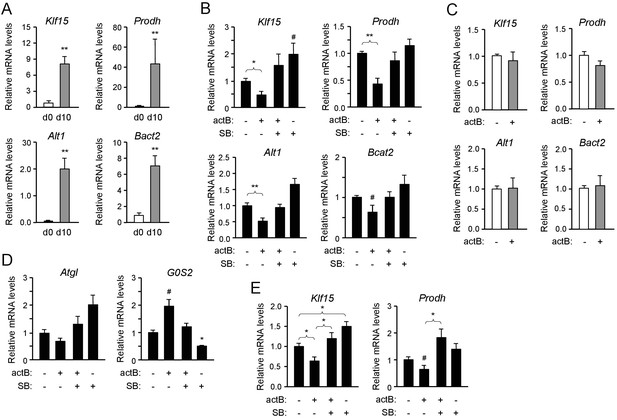
Activin B suppresses expression of mRNAs encoding KLF15 and amino acid degrading enzymes in isolated mouse and human brown adipocytes.
(A) Q-PCR determination of Klf15, Prodh, Alt1 and Bcat2 mRNA expression in primary cultures of differentiated (d10) compared to non-differentiated (d0) brown adipocytes isolated from iBAT of wild type mice. The values were normalized to mRNA levels at d0 and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. **, p<0.01 vs. d0; unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) Q-PCR determination of Klf15, Prodh, Alt1 and Bcat2 mRNA expression in primary cultures of differentiated brown adipocytes isolated from iBAT of wild type mice treated with activin B (actB) or SB-431542 (SB) for 24 hr as indicated. The values were normalized to levels in untreated cultures and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. #, p=0.088; *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 vs. untreated; two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. (C) Q-PCR determination of Klf15, Prodh, Alt1 and Bcat2 mRNA expression in primary cultures of differentiated brown adipocytes isolated from iBAT of Alk7-/- knock-out mice treated with activin B (actB) for 24 hr as indicated. The values were normalized to levels in untreated cultures and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 3 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. (D) Q-PCR determination of Atgl and G0S2 mRNA expression in primary cultures of differentiated brown adipocytes isolated from iBAT of wild type mice treated with activin B (actB) or SB-431542 (SB) for 24 hr as indicated. The values were normalized to levels in untreated cultures and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. #, p=0.05; *, p<0.05 vs. untreated; two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. (E) Q-PCR determination of Klf15 and Prodh mRNA expression in primary cultures of differentiated human brown adipocytes isolated treated with activin B (actB) or SB-431542 (SB) for 24 hr as indicated. The values were normalized to levels in untreated cultures and are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 independent experiments each performed in duplicate. *, p<0.05; vs. untreated; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
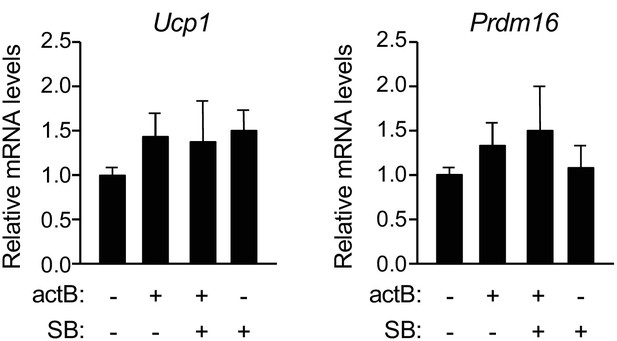
Effect of activin B on mRNA expression of BAT markers Ucp1 and Prdm16 assessed in cultured brown adipocytes.
Relative levels of Ucp1 and Prdm16 mRNAs were assessed by Q-PCR after 24hstimulation with activin B in the presence or absence of SB431542 inhibitor as indicated. Values were normalized to control untreated cultures. Shown are average ± SEM of N = 5 independent experiments each performed in duplicate.
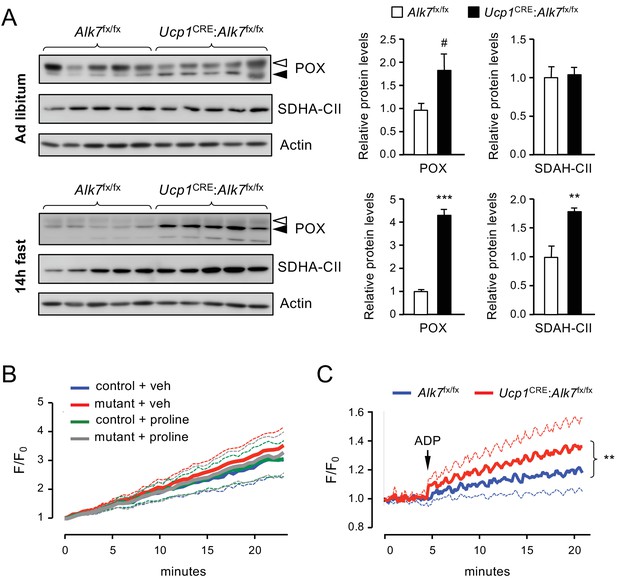
Increased proline-dependent ATP generation in mitochondria from iBAT lacking ALK7.
(A) Western blot analysis of proline dehydrogenase (POX) and succinate dehydrogenase CII subunit (SDHA-CII) in iBAT of 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice fed Chow ad libitum (top) or after 14 hr fasting (bottom). Solid arrowheads point to POX band, open arrowheads denote unspecific band. Histograms to the right show quantitative analyses of protein levels normalized to actin signals from re-probed blots, relative to those in control Alk7fx/fx mice. N = 5 mice (mean ± SEM). #, p=0.069; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) Traces of ROS production in mitochondria isolated from iBAT of 14h-fasted conditional mutant (red and grey) and control (blue and green) mice after vehicle (blue and red) or proline stimulation (green and grey). Dotted lines represent standard error. N = 3 independent experiments. (C) Traces of proline-induced ATP production in mitochondria isolated from iBAT of 14h-fasted conditional mutant (red) and control (blue) mice. Dotted lines represent standard error. N = 3 independent experiments. **, p<0.01; two-way ANOVA.
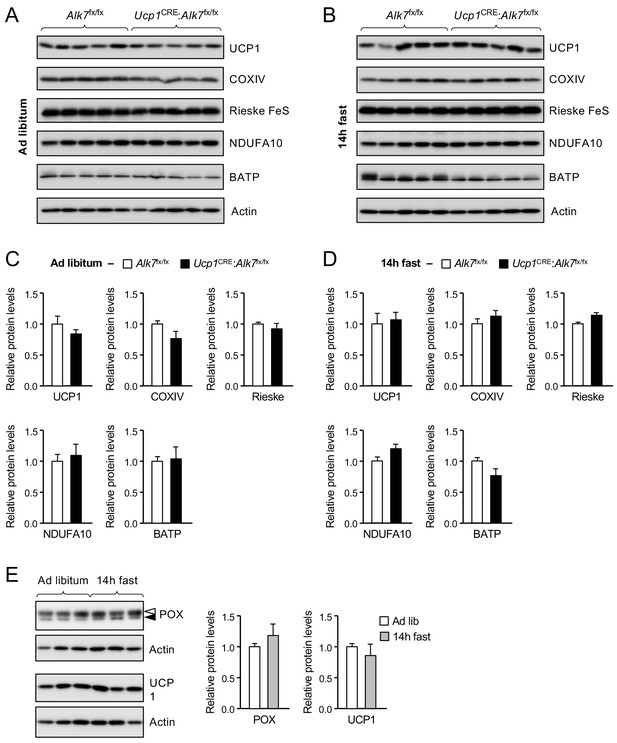
Expression of mitochondrial proteins in BAT of control and conditional mutant mice fed ad libitum or after 14 hr fasting.
(A, B) Expression of UCP1, COXIV, Rieske FeS, NDUFA10 and beta F1 ATPase (BATP) in BAT of control (Alk7fx/fx) and mutant (Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx) 2 month old mice fed on Chow ad libitum (Ad lib) (A) or after 14 hr fasting (B) assessed by western blotting of BAT lysates. (C, D) Histograms showing levels of the indicated proteins normalized to actin relative to control in Alk7fx/fx (white bars) and mutant (black bars) mice fasted for 14 hr. N = 5 mice per group. (E) POX and UCP1 protein in BAT of wild type mice fed on Chow ad libitum or fasted for 14 hr, assessed by western blotting. Solid arrowheads point to POX band, open arrowheads denote unspecific band. Histogram shows POX normalized to actin relative to ad libitum. N = 3 mice per group.
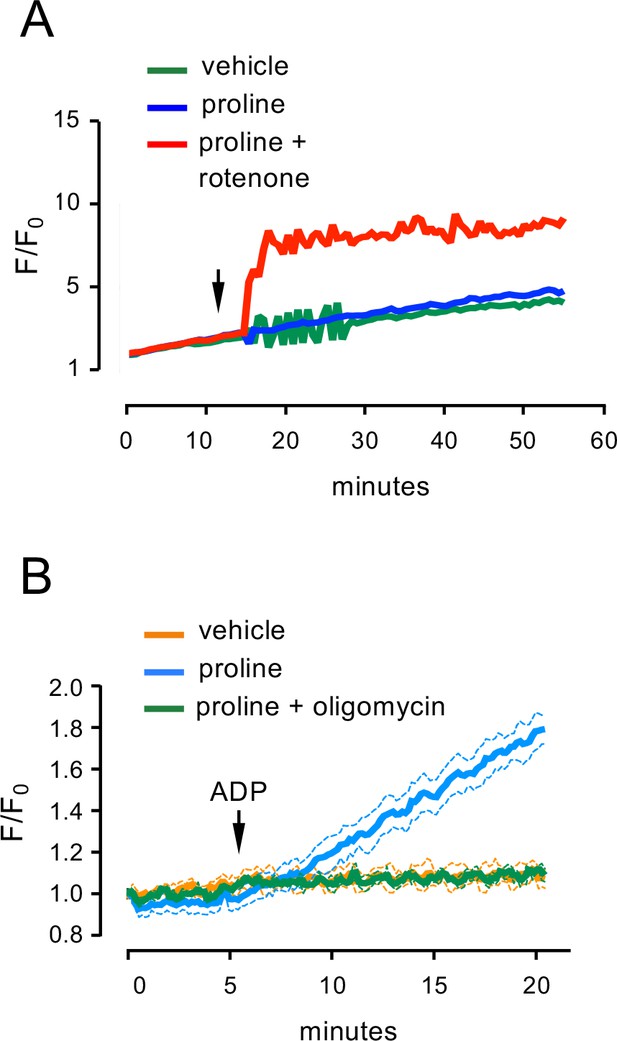
Control experiments for measurements of ROS and ATP production.
(A) ROS production in BAT mitochondria from wild type mice induced by rotenone and proline (arrow). N=3 independent mitochondrial preparations. (B) ATP generation in liver mitochondria from fasted wild type mice was robustly induced by ADP (arrow) in the presence of proline (blue) and was blocked by addition of the ATP synthase inhibitor oligomycin (green). N=3 independent mitochondrial preparations.
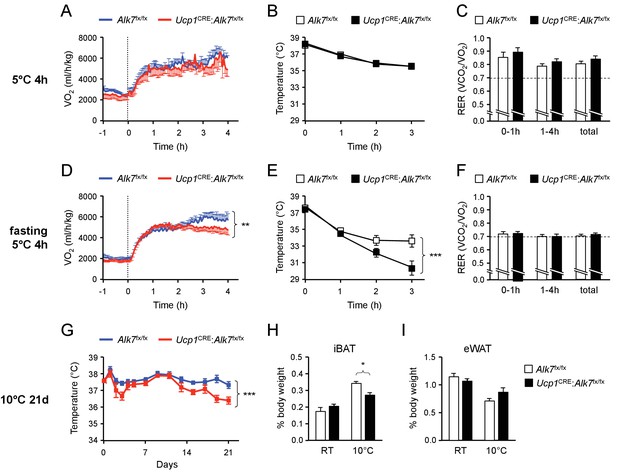
Fasting-induced hypothermia in mice lacking ALK7 in brown adipocytes.
(A, D) VO2 measured by indirect calorimetry in ad libitum fed (A) or 14h-fasted (D) 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice during exposure to 5°C in metabolic cages. N = 5 (A) and 10–12 (D) mice per group. **, p<0.01; two-way ANOVA (B, E) Rectal temperature in ad libitum fed (B) or 14h-fasted (D) 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice during exposure to 5°C. N = 8 (B) and 10 (E) mice per group. ***, p<0.001; two-way ANOVA. (C, F) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) measured by indirect calorimetry in ad libitum fed (C) or 14h-fasted (F) 2 month old conditional mutant and control mice during exposure to 5°C in metabolic cages. N = 5 (C) and 10–12 (F) mice per group. (G) Rectal temperature in conditional mutant and control mice during chronic exposure to 10°C for 21 days (preceded by 14d acclimatization at 18°C). Temperature was measured every 2 days during the light phase of the day cycle. N = 5 mice per group. ***, p<0.001; two-way ANOVA. (H, I) Relative iBAT and eWAT mass expressed as percentage of body weight in conditional mutant and control mice after 21d chronic cold exposure at 10°C. Values are presented as average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. *, p<0.05; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post test.
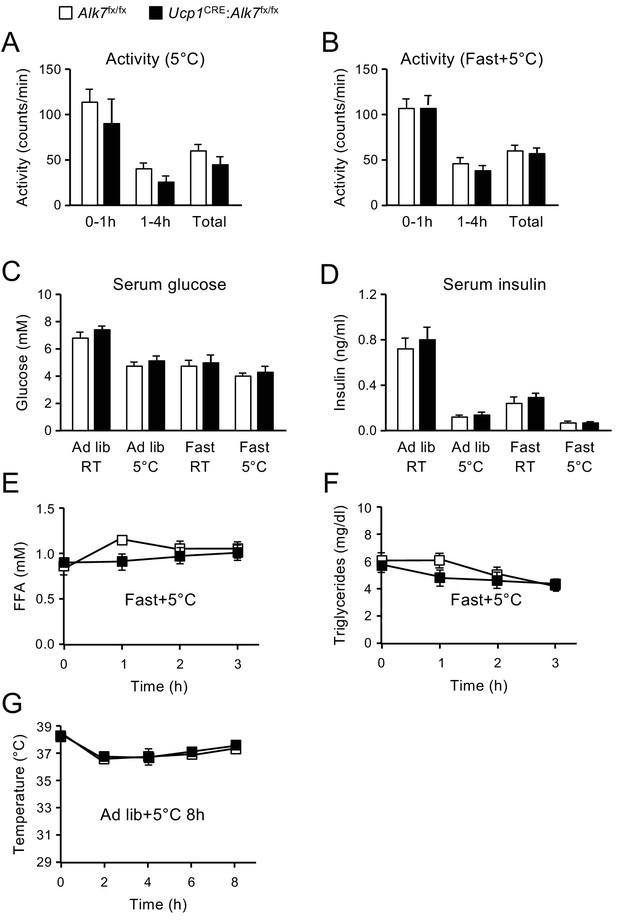
Influence of fasting and cold exposure on levels of glucose, insulin, activity, free-fatty acids, triglycerides and body temperature.
(A, B) Activity in metabolic chambers of mice during exposure at 5°C preceded by ad libitum feeding (panel A, N = 5 mice per genotype) or after 14 hr fasting (panel B, N = 10 mice per genotype). (C) Serum glucose levels under different feeding and temperature conditions. Fasting was 14 hr and cold exposure was 4 hr. Values show averages ± SEM. N = 15, (ad lib RT); 5, ad lib 5°C; 10, fast RT; 10, fast 5°C. (D) Serum insulin levels under different feeding and temperature conditions. Fasting was 14 hr and cold exposure was 4 hr. Values show averages ± SEM. N numbers as above. (E, F) Serum free fatty acids (FFA, panel E) and triglycerides (F) in control and conditional mutant mice exposed to 5°C for 3 hr after 14 hr fasting. Shown are averages ± SEM. N = 6 mice per group. (G) Rectal temperature in control and conditional mutant mice during 8 hr exposure at 5°C fed ad libitum both before and during cold exposure. Shown are averages ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group.
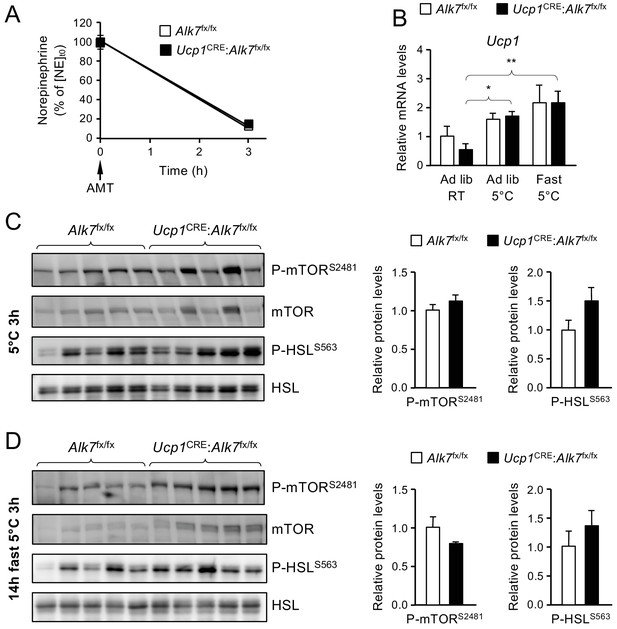
Unchanged norepinephrine signaling in iBAT of Ucp1CRE:Alk7fx/fx mutant mice after fasting and acute cold exposure.
(A) Norepinephrine (NE) turnover in iBAT. After 14 hr fasting (t = 0), mice were injected with α-Methyl-DL-tyrosine methyl ester hydrochloride (AMT) and placed at 5° for 3 hr, after which NE was measured in iBAT. NE levels before AMT injection and cold exposure was normalized to 100%. Shown are averages ± SEM. N = 6 mice per group. (B) Relative levels of Ucp1 mRNA in iBAT of mutant and control mice assessed by Q-PCR. Values are presented relative to levels in control mice kept ad libitum at RT. Ad lib, mice fed ad libitum at room temperature (RT) or 3 hr at 5°C. The third group was fasted for 14 hr prior to 3 hr exposure at 5°C. Values are average ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. (C, D) Levels of mTORC2 phosphorylated at Ser2481 and HSL phosphorylated at Ser563 assessed by western blotting of iBAT lysates from control and mutant mice exposed to 5°C for 3 hr after ad libitum feeding (C) or after 14 hr fasting (D). Histograms show averages ± SEM of optical densities normalized to levels in control mice. N = 5 mice per group.
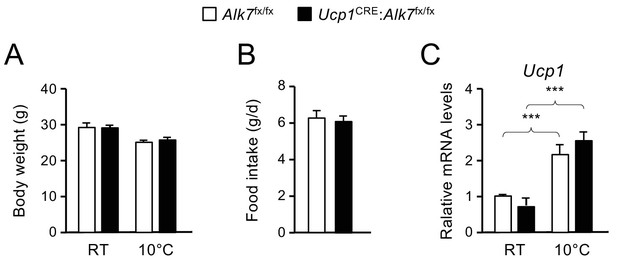
Body weight, food intake and Ucp1 mRNA levels after chronic cold exposure (21 d at 10°C) in control and mutant mice.
(A) Body weight. RT, room temperature. Shown are averages ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. (B) Daily food intake. Shown are averages ± SEM. N = 5 mice per group. (C) Levels of Ucp1 mRNA in iBAT assessed by Q-PCR. Shown are averages relative to control levels ± SEM. Values were normalized to control mice at RT. N = 5 mice per group. ***, p<0.001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post test.
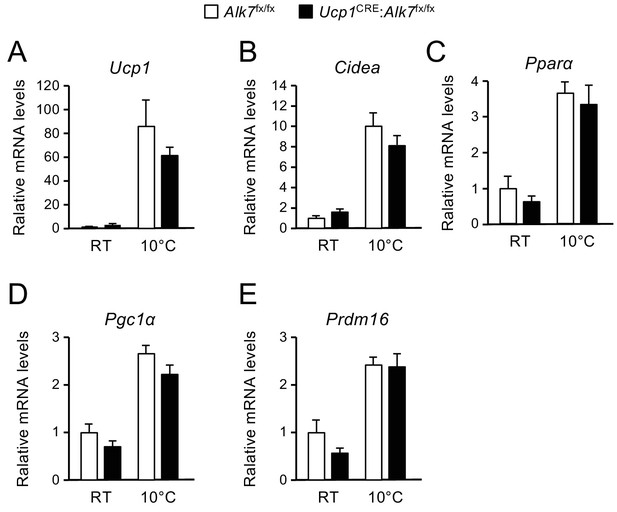
Expression of mRNA levels encoding thermogenic markers in inguinal WAT after chronic cold exposure (21 d at 10°C) in control and conditional mutant mice.
(A to E) Levels of Ucp1, Cidea, Pparα, Pgc1α and Prdm16 mRNAs in inguinal WAT assessed by Q-PCR in mice kept at room temperature and after chronic cold exposure. Shown are averages relative to control levels ± SEM. Values were normalized to control mice at RT. N = 5 mice per group. ***, p<0.001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post test.
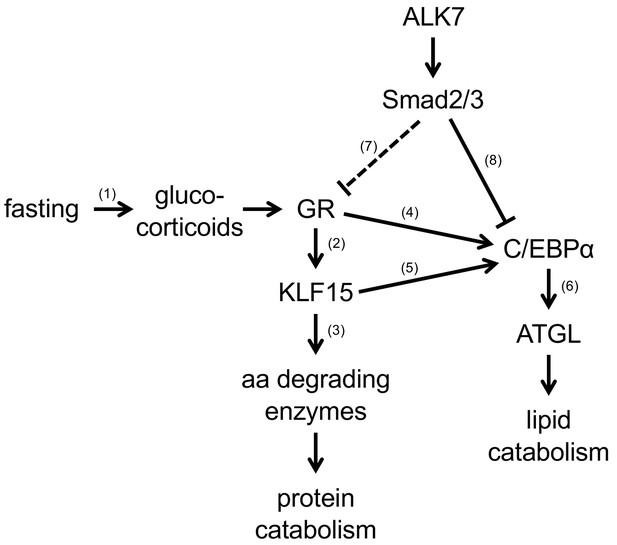
Schematic model for possible signaling pathway related to the role of ALK7 in mediating BAT responses to nutrient stress.
(1) Dallman et al., 1993 (2) Gray et al., 2007; Sasse et al., 2013 (3) Gray et al., 2007; Shimizu et al., 2011; Sasse et al., 2013 (4) Cram et al., 1998; Rüdiger et al., 2002; Muratcioglu et al., 2015 (5) Asada et al., 2011 (6) Yogosawa et al., 2013; Hasan et al., 2018 (7) Implied by this work (molecular mechanism unknown) (8) Choy and Derynck, 2003.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
PCR primers.
The PCR primers used in this study are listed here.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54721/elife-54721-supp1-v3.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Antibodies.
The primary antibodies used in this study are listed here.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54721/elife-54721-supp2-v3.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54721/elife-54721-transrepform-v3.docx





