Enhanced ER-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase causes embryonic lethality associated with Ubiad1 deficiency
Figures
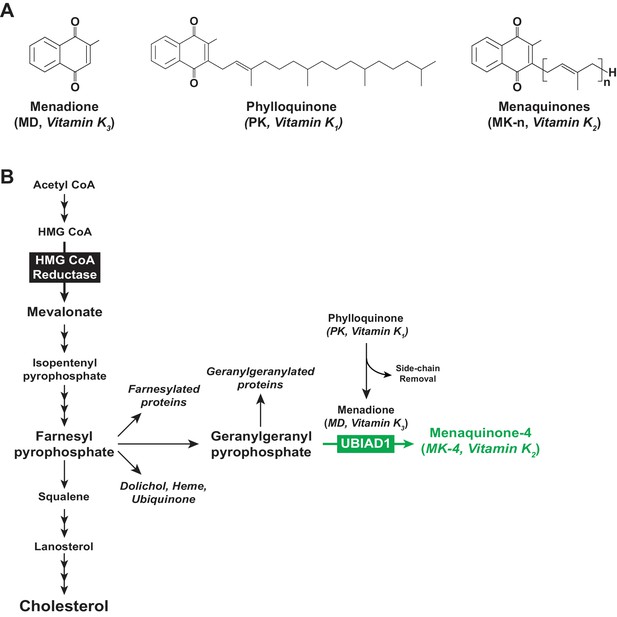
Vitamin K and the mevalonate pathway.
(A) Structures of the main forms of vitamin K. (B) The mevalonate pathway in animal cells.
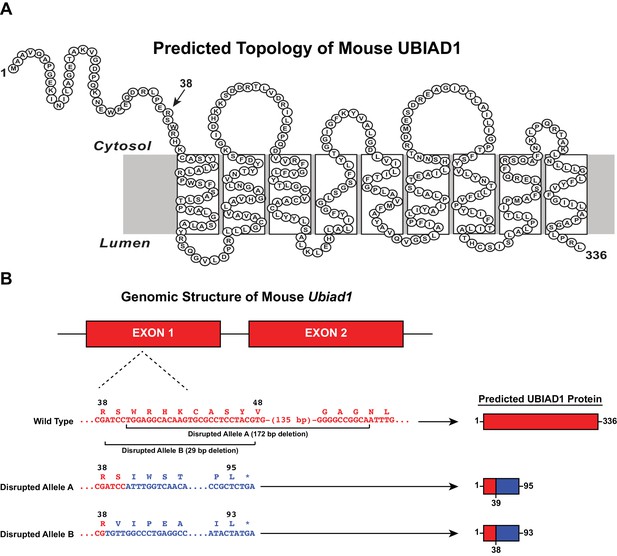
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated disruption of the mouse Ubiad1 gene.
(A) Amino acid sequence and predicted topology of mouse UBIAD1 protein. (B) Genomic structure of mouse Ubiad1 and predicted proteins encoded by CRISPR/Cas9-disrupted Ubiad1 alleles (Disrupted Alleles A and B).
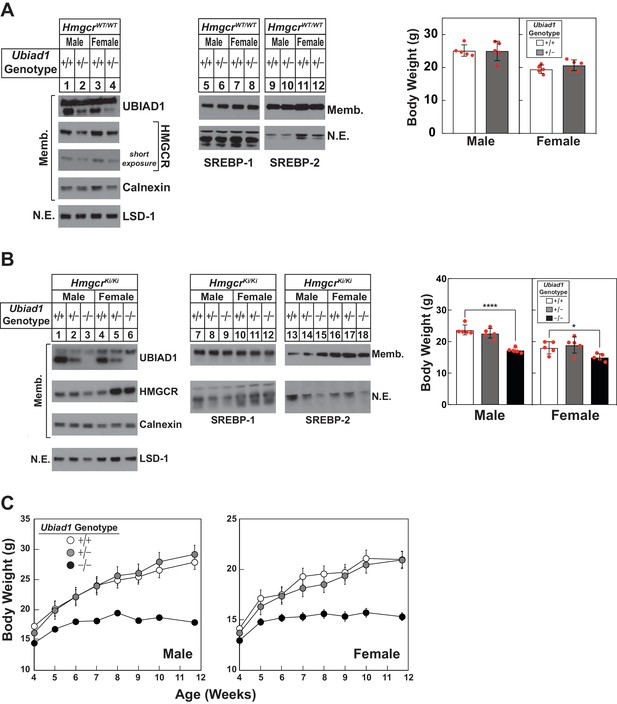
Hepatic immunoblot analysis and body weights of Ubiad1-deficient mice on HmgcrWT/WT and HmgcrKi/Ki backgrounds.
(A and B) Male and female WT and Ubiad1+/- (A) or Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki, Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki, and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki (B) littermates (8 weeks of age, five mice/group) were fed an ad libitum chow diet prior to weighing and sacrifice. Livers were harvested and subjected to subcellular fractionation as described in ‘Materials and methods.’ Aliquots of resulting membrane (Memb.) and nuclear extract (N.E.) fractions (80–160 µg protein/lane) for each group were pooled and subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies against endogenous HMGCR, UBIAD1, SREBP-1, SREBP-2, calnexin, and LSD-1. Although shown in separate panels, LSD-1 is a loading control for nuclear SREBP immunoblots. (C) Male and female Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki, Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki, and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates (eight mice/group) were weaned at 4 weeks of age, fed chow diet ad libitum, and weighed for seven consecutive weeks, after which they were sacrificed. Error bars, S.E. *, p<0.05 and ****, p<0.0001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Body weights of Ubiad1-/-: : HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54841/elife-54841-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
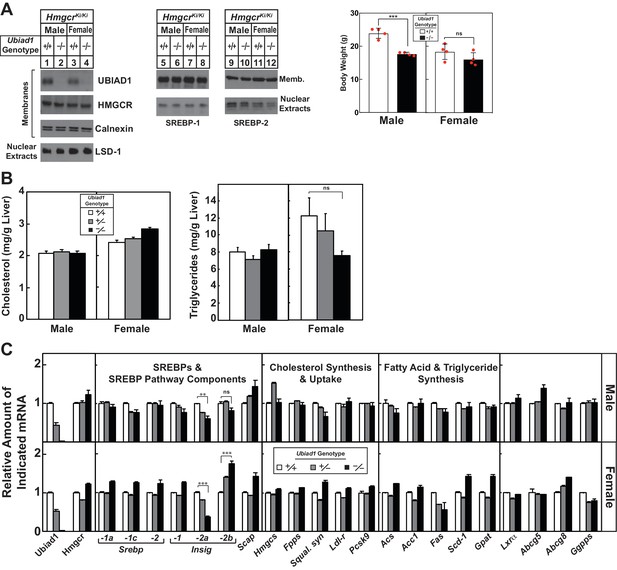
Characterization of Ubiad1-deficient mice.
(A) Male and female Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates (Disrupted Allele B) (8 weeks of age, eight mice/group) were fed an ad libitum chow diet prior to weighing and sacrifice. Livers of the mice were harvested and subjected to subcellular fractionation and immunoblot analysis as described in the legend to Figure 3A and B). (B and C) Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki, Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki, and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates (Disrupted Allele A) were fed an ad libitum chow diet prior to weighing and sacrifice. Livers of the mice were harvested for measurement of cholesterol and triglyceride levels (B) and quantitative real-time PCR analysis using primers against the indicated mRNA and apoB mRNA as an invariant control (C). Each value represents the amount of mRNA relative to that in Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki mice, which was arbitrarily set as 1. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. of data from eight mice. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Body weights and hepatic lipid levels of Ubiad1-/-: : HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54841/elife-54841-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
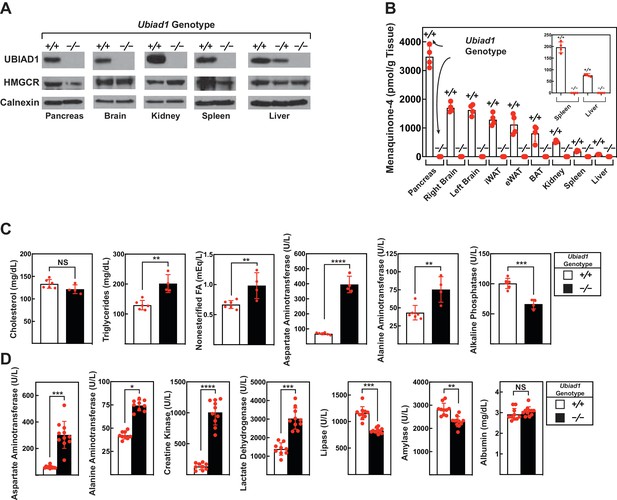
Levels of HMGCR, UBIAD1, and MK-4 in various tissues and blood chemistry analysis of Ubiad1-deficient mice.
Male Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates (12 weeks of age, 4–11 mice/group) were fed an ad libitum chow diet prior to sacrifice. (A and B) Indicated tissues were harvested for subcellular fractionation, after which aliquots of membrane fractions were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against HMGCR, UBIAD1, and calnexin (A). Some of the tissues were subjected to homogenization (B) for subsequent determination of MK-4 levels by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography or liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry as described in ‘Materials and methods.’ (C and D) Blood drawn from mice following sacrifice was subjected to chemical analysis by the Metabolic Phenotyping Core Facility in the Touchstone Diabetes Center (UT Southwestern Medical Center). Bars, mean ± S.E. of data from 4 to 11 mice. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Blood chemistry analysis of male Ubiad1-/-: : HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54841/elife-54841-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
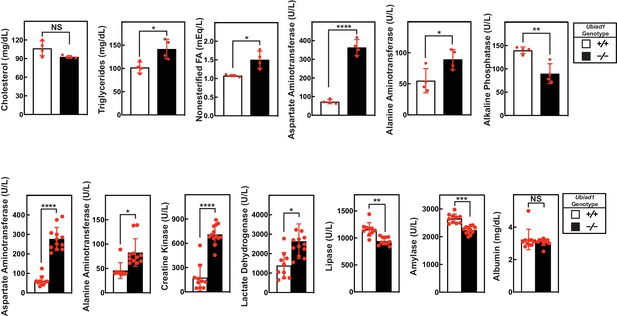
Blood chemistry analysis of female Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
Female Ubiad1+/+::HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates (12 weeks of age, 4–12 mice/group) were fed an ad libitum chow diet prior to sacrifice. Blood drawn from the mice following sacrifice was subjected to chemical analysis by the Metabolic Phenotyping Core Facility in the Touchstone Diabetes Center (University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center). Bars, mean ± S.E. (error bars) of data from 4 to 12 mice. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Blood chemistry analysis of female Ubiad1-/-: : HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/54841/elife-54841-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
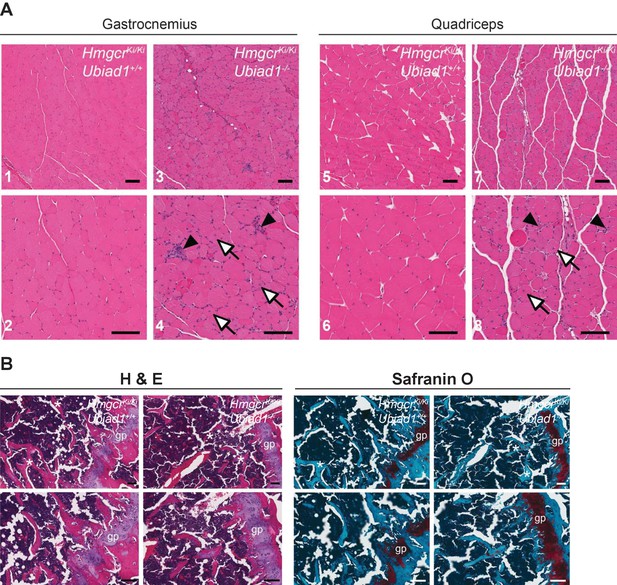
Histological analysis of skeletal muscle and femoral growth plates from Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki mice.
Histological analysis of gastrocnemius and quadriceps muscles (A) and femoral growth plates (B) from male Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates using H and E and Safranin O staining. Myofibers harboring centrally-localized nuclei are indicated by white arrows, and degenerating myofibers with macrophage infiltration are indicted by black arrowheads in (A). Asterisks in (B) indicate boney trabeculae, and red hue in Safranin O-stained sections highlight cartilage. gp, growth plate. Scale bars, 100 µm.
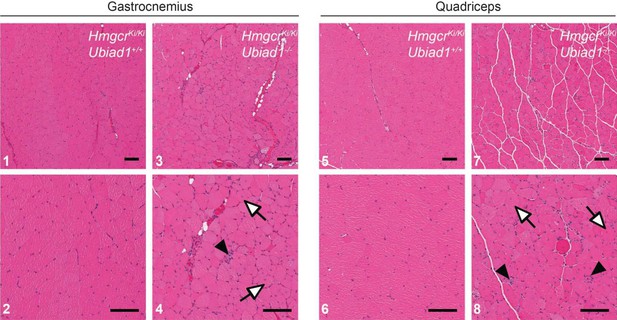
Histological analysis of gastrocnemius and quadriceps muscles from female Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates using H and E staining.
Myofibers harboring centrally-localized nuclei are indicated by white arrows and infiltrating macrophages are indicted by black arrowheads. Scale bars = 100 µm.
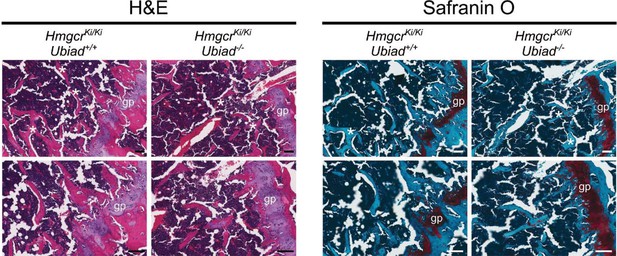
Histological analysis of femoral growth plates from female Ubiad1+/+: :HmgcrKi/Ki and Ubiad1-/-: :HmgcrKi/Ki littermates using H and E and Safranin O staining.
Asterisks denote boney trabeculae, and the red hue in the Safranin O-stained sections highlight cartilage. gp, growth plate. Scale bars = 100 µm.
Tables
Segregation of Disrupted Ubiad1 Alleles in Mice.
| Genotype of breeding pairs | Ubiad1 genotype of offspring | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| +/+ | +/- | -/- | |
| Disrupted Allele A Ubiad1+/-X Ubiad1+/- | 83 | 201 | 0 |
| Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKiKi/Ki X Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKiKi/Ki | 137 | 280 | 114 |
| Disrupted allele B Ubiad1+/-X Ubiad1+/- | 77 | 183 | 0 |
| Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKiKi/Ki X Ubiad1+/-: :HmgcrKiKi/Ki | 23 | 36 | 20 |
-
Genotype was determined by PCR analysis of genomic DNA prepared from tails of mice.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse/Wild Type:C57BL/6J | The Jackson Laboratory | Stock#000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse/HmgcrKi/Ki (HMGCR K89R/K248R):C57BL/6 | PMID: 27129778 | N/A | Knockin mice harboring mutations in the Hmgcr gene that prevent ubiquitination of HMGCR protein |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse/Ubiad1+/∆172:C57BL/6J | This paper | N/A | Mice heterozygous for 172 bp deletion in exon 1 of the Ubiad1 gene |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse/Ubiad1∆172/∆172: : HmgcrKi/Ki (HMGCR K89R/K248R):C57BL/6J | This paper | N/A | HmgcrKi/Ki mice homozygous for 172 bp deletion in exon 1 of the Ubiad1 gene |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse/Ubiad1∆29/∆29: : HmgcrKi/Ki (HMGCR K89R/K248R):C57BL/6J | This paper | N/A | HmgcrKi/Ki mice homozygous for 29 bp deletion in exon 1 of the Ubiad1 gene |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-SREBP-1 | PMID: 28244871 | IgG-20B12 | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-SREBP-2 | PMID: 25896350 | IgG-22D5 | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-UBIAD1 | PMID: 30785396 | IgG-205 | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti- HMGCR | PMID: 27129778 | IgG-839c | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Calnexin | Novus Biologicals | Cat#NB100-1965; RRID: AB_10002123 | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-LSD-1 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2139; RRID: AB_2070135 | used at 1–5 µg/ml for immunoblots |
| Sequence-based reagent | Ubiad1 genotyping primers | Genotyping of mice is described in Materials and methods. | N/A | Forward: TCCCCTTGAGTGGCTCACTTTTA; Reverse: AAATCGAACAACATCCTGGGGCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | HmgcrKi/Ki genotyping primers | PMID: 27129778 | N/A | K89R Forward: GTCCATGAACATGTTCACCG; Reverse: CAGCACGTCCTATTGGCAGA K248R Forward: TCGGTGATGTTCCAGTCTTC; Reverse, GGTGGCAAACACCTTGTATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Guide RNAs (gRNAs) used to target mouse Ubiad1 | Targeting of mouse Ubiad1 gene is described in Materials and methods | N/A | gRNA-A: GGCTTCCCGAACGATCCTGG gRNA-B: CAAGTGCGCCTCCTACGTGT gRNA-C: TGTACACGGGGCCGGCAATT |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for UBIAD1 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for SREBP1a | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for SREBP-1c | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for SREBP-2 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for HMGCR | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for Insig-1 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for Insig-2a | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for Insig-2b | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for SCAP | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for HMGCS | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for FPPS | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for LDLR | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for PCSK9 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for ACS | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for ACC1 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for FAS | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for SCD1 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for GPAT | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for LXRα | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for ABCG5 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for ABCG8 | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for GGPS | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Sequence-based reagent | qRT-PCR Primers for Cyclophilin | PMID: 30785396 | N/A | The sequence of these primers can be found in indicated reference |
| Commercial assay or kit | TaqMan Reverse Transcription | Applied Biosystems | Cat#N8080234 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix | Applied Biosystems | Cat#4367659 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit | Qiagen | Cat#69506 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MEGAshortscript Kit | Ambion | Cat#AM1354 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Surveyor Mutation Detection Kit | Integrated DNA Technologies | Cat#706020 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | FuGENE6 Transfection Reagent | Promega | Cat#1815075 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Menaquinone-4 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#809896 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phylloquinone (Vitamin K1) | Cerilliant | Cat#V-030 |





