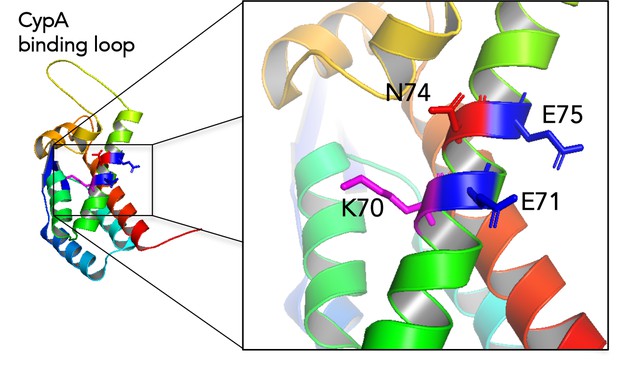
MxB sensitivity of HIV-1 is determined by a highly variable and dynamic capsid surface
Figures
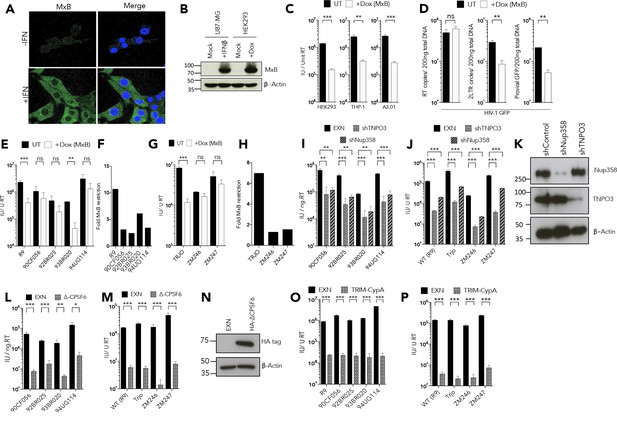
MxB restriction is independent of the viral nuclear import pathway.
(a) Immunofluorescence staining MxB (green) in U87-MG cells 24 hr post-treatment with IFN (1000 U/ml). Counterstaining for DAPI (blue). (b) Immunoblot detecting MxB in U87-MG or HEK293 cell lysates after treatment with IFN or doxycycline as shown. Actin detected as a loading control. (c) HIV-1 GFP vector titre in HEK293-iMxB, THP-1-iMxB or A3.01-iMxB untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (d) HIV-1 GFP RT products, 2LTR circles and proviral DNA of HIV-1 GFP vector in HEK293 untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (e, g) Titre and (f, h) fold MxB restriction, of HIV-1 GFP vectors, containing gag-pro from. (e, f) founder isolates or. (g, h) other M-group clones, in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). Titre of HIV-1 GFP vectors, containing gag-pro sequences from the stated isolates, in. (i, j) HeLa cells stably expressing control, TNPO3 or Nup358 specific short hairpin RNA. (k) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (i,j) detecting Nup358 or TNPO3. Actin detected as loading control. (l, m) HeLa cells stably expressing either control or deltaCPSF6. (n) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (l,m) detecting HA epitope. Actin detected as loading control. (o, p) CRFK cells stably expressing either empty control vector or Trim-CypA. + / - SEM n = 3. (***) p<0.01 (**) p<0.05 (*) p<0.1 (ns) not significant p>0.1.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Data presented in Figure 4C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56910/elife-56910-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
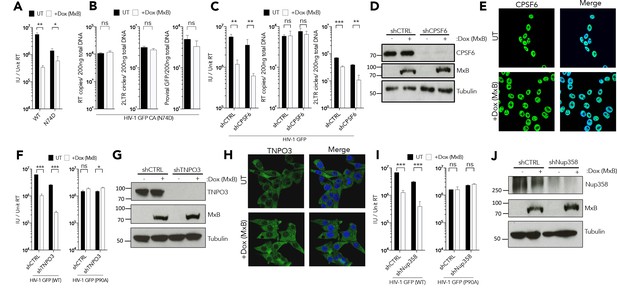
MxB restriction is independent of cofactor usage.
(a) HIV-1 GFP WT or N74D vector titre on HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (a) HIV-1 GFP WT or N74D vector titre on HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (b) HIV-1 N74D RT products, 2LTR circles and proviral DNA in HEK293 untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (c) HIV-1 GFP vector titre, RT products, 2LTR circles in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) and depleted of CPSF6 by shRNA transduction. (d) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (c) detecting MxB or CPSF6. Tubulin detected as loading control. (e) Immunofluorescence of CPSF6 (yellow) in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). Counterstaining with DAPI (blue). (f) HIV-1 GFP WT (left) or P90A (right) vector titre on HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) and depleted of TNPO3 by shRNA transduction. (g) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (f) detecting MxB or TNPO3. Tubulin detected as loading control. (h) Immunofluorescence of TNPO3 (green) in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). Counterstaining with DAPI (blue). (i) HIV-1 GFP WT (left) or P90A (right) vector titre on HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) and depleted of Nup358 by shRNA transduction. (j) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (i) detecting MxB or Nup358. Tubulin detected as loading control. + / - SEM n = 3. (***) p<0.01 (**) p<0.05 (*) p<0.1 (ns) not significant p>0.1.
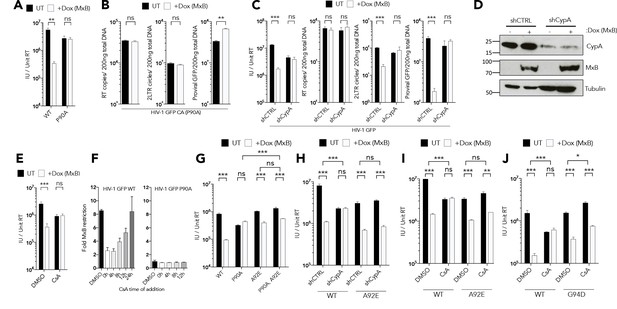
CypA is required for MxB restriction.
(a) HIV-1 GFP WT or P90A vector titre in HEK293 untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (b) HIV-1 GFP P90A RT products, 2LTR circles and proviral DNA in HEK293 untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)). (c) HIV-1 GFP vector titre, RT products, 2LTR circles in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) and depleted of CypA by shRNA transduction. (d) Matched representative immunoblot analysis from (c) detecting MxB or CypA. Tubulin detected as loading control. (e) HIV-1 GFP vector titre on HEK293 untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) after treatment with CsA at the point of infection. (f) HIV-1 GFP WT (left) or P90A (right) vector titre on HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) after CsA was added at the stated times after infection. Titre of HIV-1 GFP vector containing the stated CA mutants in. (g) HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)),. (h) HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) and depleted of CypA by shRNA transduction or. (i, j) HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) after treatment with CsA at the point of infection. + / - SEM n = 3. (***) p<0.01 (**) p<0.05 (*) p<0.1 (ns) not significant p>0.1.
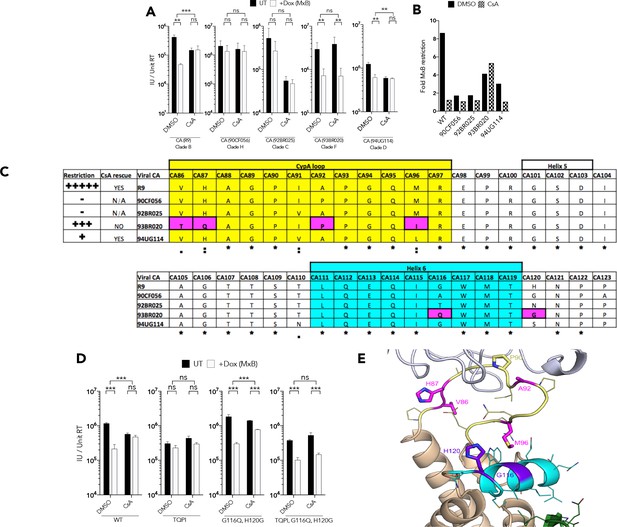
CypA induced HIV-1 capsid conformational change is required for MxB restriction.
(a) Titre and (b) fold MxB restriction of HIV-1 GFP vector, containing gag-pro sequences from the stated isolates, in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) after CsA was added at the point of infection. (c) Summary of virus phenotypes, amino acid sequence, and conservation around the CypA binding loop of the stated isolates. (d) Titre of HIV-1-GFP wild type or indicated mutant in HEK293 cells untreated (UT) or treated with Dox to induce MxB expression (+Dox (MxB)) after CsA was added at the point of infection. (e) Structure of HIV-1 CA protein (PDB: 6ES8) indicating interaction of residues M96, G116 and H120. + / - SEM n = 3. (***) p<0.01 (**) p<0.05 (*) p<0.1 (ns) not significant p>0.1.
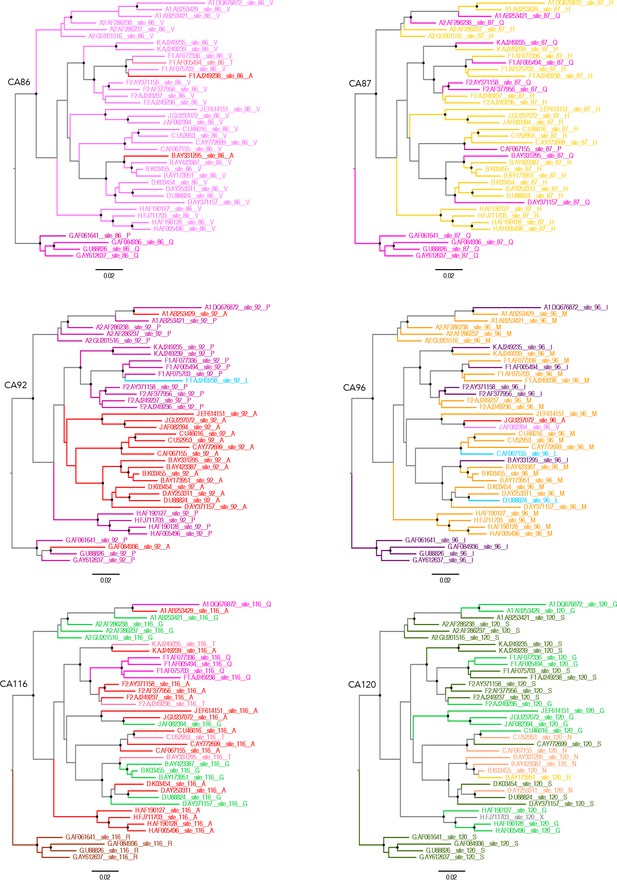
Capsid residues important for MxB restriction are variable.
Phylogenetic trees of a set of HIV-1 M group subtype reference genome sequences for residues CA86, CA87, CA92, CA96, CA116 and CA120 using ChromaClade.
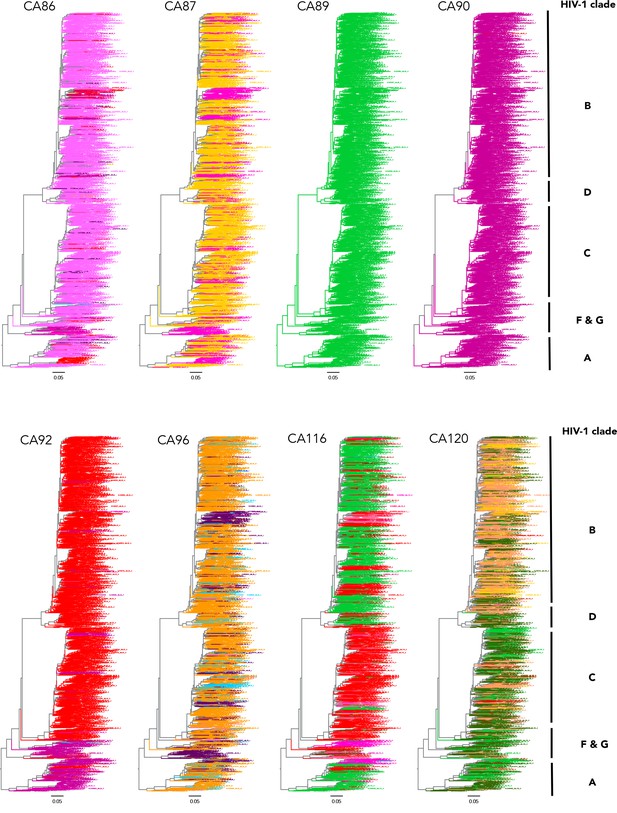
Phylogenetic trees of conserved and variable CA residues in HIV-1 M group viruses.
Phylogenetic trees of a larger complied dataset of approximately 1300 HIV-1 M genome sequences for residues CA86, 87, 89, 90, 92, 96, 116 and 120.
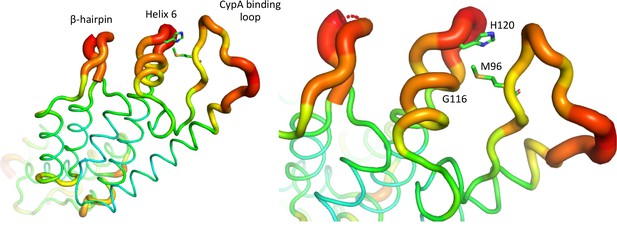
HIV-1 capsid is dynamic and variable.
B factor putty representation of HIV-1 CA protein (PDB: 4XFX) indicating location of mutated residues, CypA binding loop and β-hairpin.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Sequence alignment of HIV-1 isolates between aa207-210 of capsid protein.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56910/elife-56910-supp1-v1.pptx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56910/elife-56910-transrepform-v1.docx