Three-dimensional growth of breast cancer cells potentiates the anti-tumor effects of unacylated ghrelin and AZP-531
Figures
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits the 3D growth of breast cancer cells.
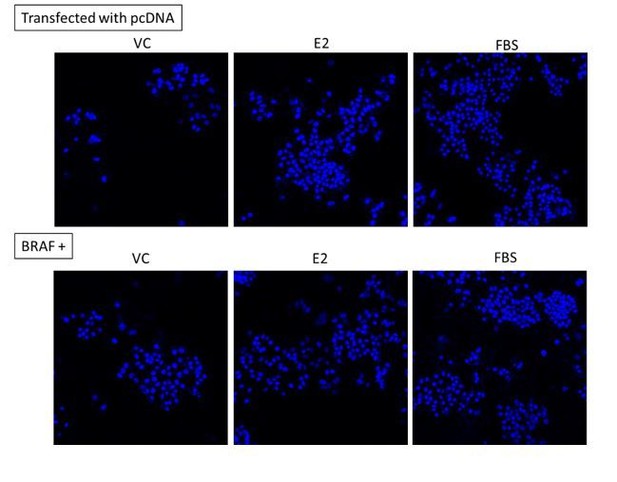
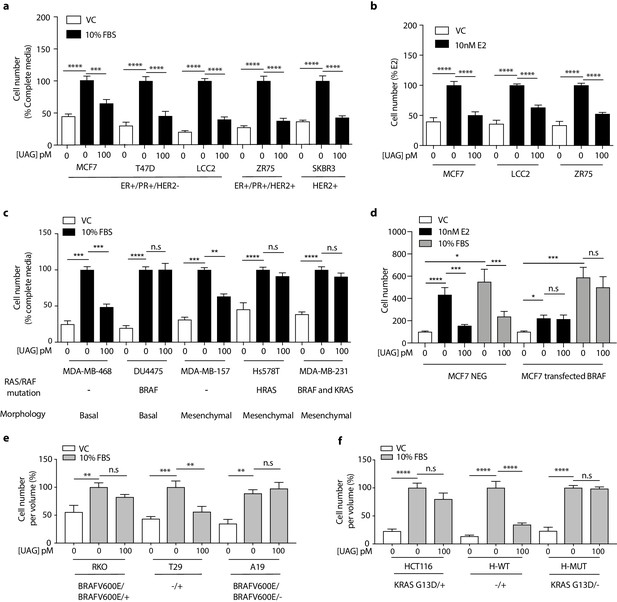
(a, c) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG; 100 pM) inhibits the growth of a panel of breast cancer cell lines under serum-stimulated conditions (six replicates/group) or (b) ER+ breast cancer cell lines in the presence of estradiol (10 nM; six replicates/group). (c) UAG (100 pM) suppresses cell growth of basal-like and mesenchymal-like TNBC breast cancer cell lines that are WT for BRAF and KRAS (6–9 replicates/group). Effects of UAG are abrogated in (d) BRAF-transfected MCF7 cells, and (e) BRAF- and (f) KRAS-mutated colon cancer cells (6–12 replicates/group). Loss of mutated alleles of BRAF or KRAS sensitizes cells to the effect of UAG. Data represent mean ± SEM. Experiments were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control; FBS: fetal bovine serum; E2: estradiol.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits the 3D growth of breast cancer cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells in 3D.
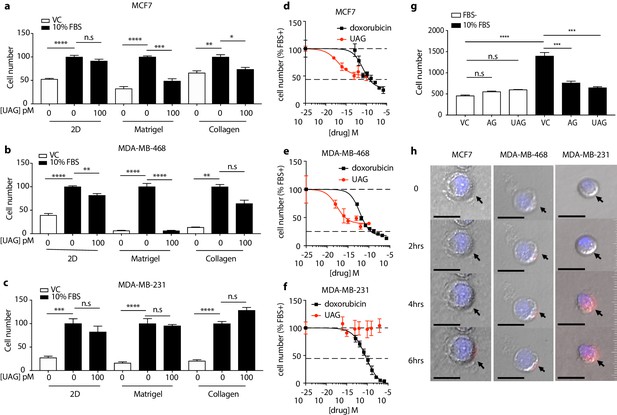
Unacylated ghrelin (UAG; 100pM) inhibits the growth of (a) MCF7 and (b) MDA-MB-468 cells grown in 3D in matrigel or collagen, but not in 2D. (c) UAG had no effect on MDA-MB-231 cell growth in 2D or 3D. Dose-dependent effects of UAG and doxorubicin on (d) MCF7, (e) MDA-MB-468 and (f) MDA-MB-231 cell number in 3D culture. (g) Acyl ghrelin (AG) and UAG (100 pM) inhibit breast cancer cell growth in serum-stimulated conditions. (h) Binding of Cy3-labeled UAG to MCF7, MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 cells over time (representative images). Scale bar represents 20 μm. Data represent mean ± SEM with three replicates/group. Experiments repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; AG: acylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control; FBS: fetal bovine serum.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits the growth of breast cancer cells in 3D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via Gαi-dependent inhibition of cAMP formation.
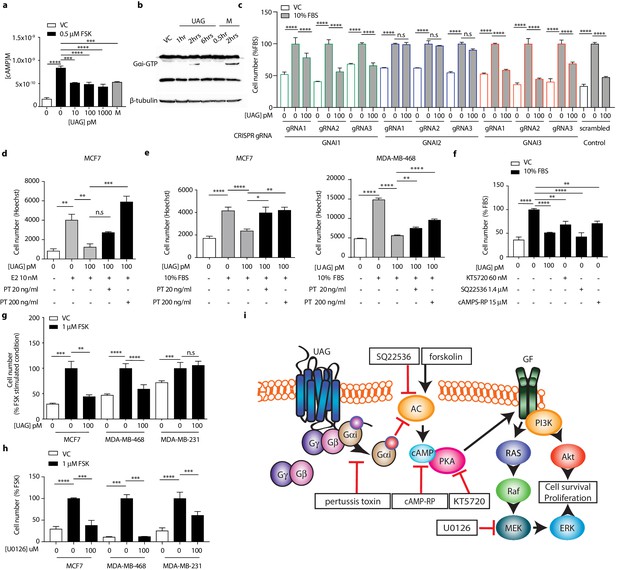
(a) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG; 10–1000 pM) inhibits the forskolin-stimulated production of cAMP in MCF7 cells (3–4 replicates/group). (b) UAG (100 pM) stimulates activation of Gαi (three replicates/group). (c) UAG (100 pM) suppresses the growth of CRISPR GNAI1 and GNAI3 KO cells, but not GNAI2 KO MCF7 cells, suggesting Gαi2-coupled GPCR-mediated effects. Suppression of (d) estradiol- or (e) serum-stimulated breast cancer cell growth with UAG (100 pM) is prevented in the presence of Gαi inhibitor, pertussis toxin (20 ng/ml, 200 ng/ml; three replicates/group). (f) PKA inhibitor (KT5720), adenylyl cyclase inhibitor (SQ22536) or cAMP antagonist (cAMPS-RP) suppress the serum-stimulated growth of MCF7 cells (three replicates/group). (g) UAG (100 pM) inhibits the forskolin-stimulated growth of MCF7 and MDA-MB-468 cells, but not MDA-MB-231 (three replicates/group). (h) U0126 (MEK inhibitor) inhibits the forskolin-stimulated growth of MCF7, MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 cells (three replicates/group). (i) A model summarizing the putative mechanism of action of UAG in breast cancer cells and compounds used to dissect mechanism of action. Data represent mean ± SEM. Experiments were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control; FBS: fetal bovine serum; E2: estradiol; PT: pertussis toxin; M: melatonin; FSK: forskolin.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via Gαi-dependent inhibition of cAMP formation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via Gαi-dependent inhibition of cAMP formation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig2-data2-v1.pdf
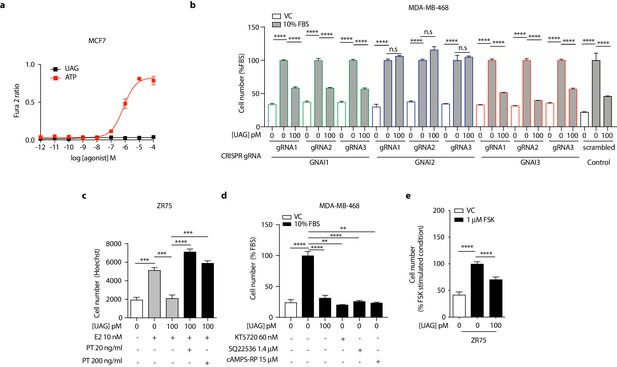
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via Gαi-dependent mechanisms.
(a) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG) has no effect on the release of intracellular Ca2+ in MCF7 cells. (b) Loss of GNAI2 (blue outline) using CRISPR and three validated gRNAs is associated with loss of response to UAG (100 pM), while KO of GNAI1 or GNAI3 had no effect (green and red outline, respectively). (c) Suppression of estradiol-stimulated ZR75 cell growth by UAG (100 pM) is prevented by Gαi inhibitor, pertussis toxin (20 ng/ml, 200 ng/ml). (d) PKA (KT5720) or adenylyl cyclase (SQ22536) inhibitors, or cAMP antagonist (cAMPS-RP) suppress the growth of MDA-MB-468 cells. (e) UAG (100 pM) inhibits the forskolin-stimulated growth of ZR75 cells. Data represent mean ± SEM with three replicates/group. Experiments were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; FBS: fetal bovine serum; E2: estradiol; FSK: forskolin.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via Gαi-dependent mechanisms.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
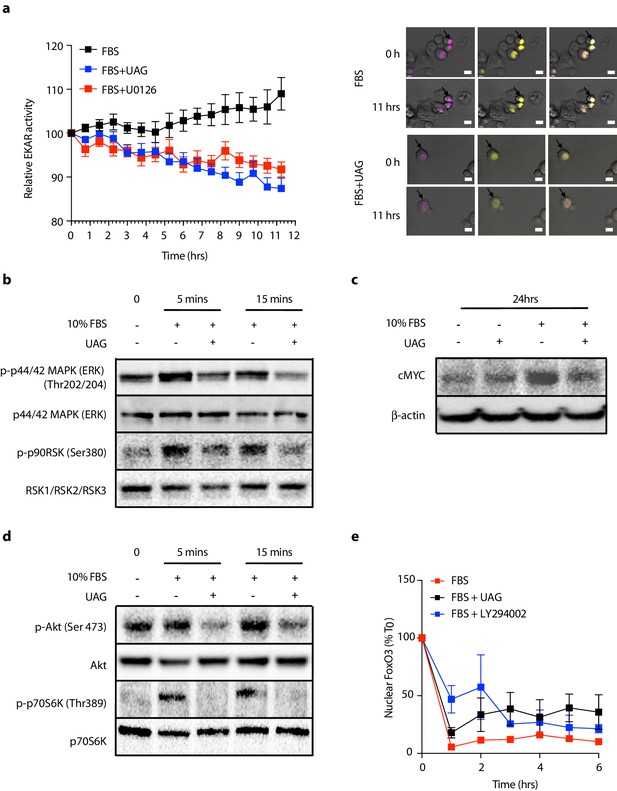
Unacylated ghrelin (UAG) inhibits MAPK and Akt signaling.
(a) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG; 100 pM) inhibits ERK activity (EYFP FRET) in EKAR-transfected MCF7 cells (10 replicates/group). Data were normalized to vector ECFP signal. Scale bar represent 50 μm. Western blotting demonstrates that UAG causes a decrease in the (b) phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and downstream MAPK target p90RSK and (c) expression of cMYC in MCF7 cells. UAG also causes a decrease in (d) the phosphorylation of Akt and its downstream target, p70S6K, as well as (e) FoxO3a nuclear localization FoxO3a-RFP-transfected cells, an effect that is attenuated in cells treated with PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (five replicates/group). Data represent mean ± SEM. Experiment were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; FBS: fetal bovine serum.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin suppresses EKAR and FoxO3 nuclear localization.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits MAPK and Akt signaling.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig3-data2-v1.pdf
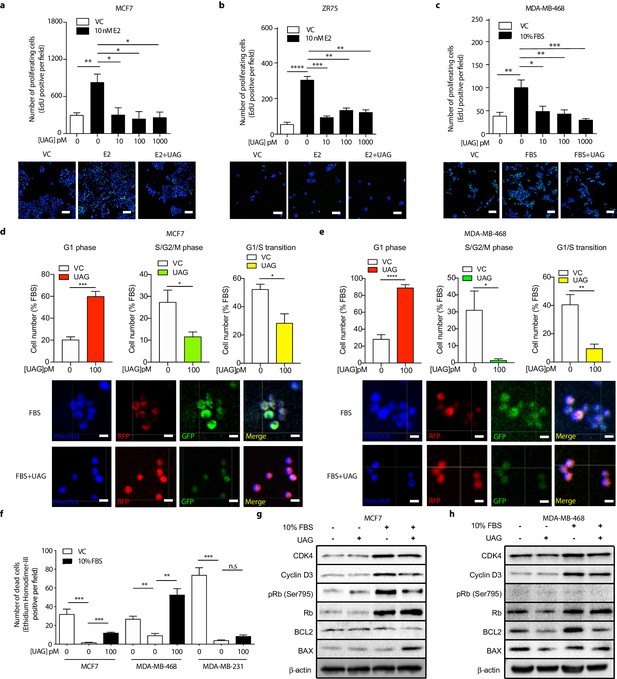
Unacylated ghrelin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Unacylated ghrelin (UAG) significantly inhibits the proliferation of (a) MCF7, (b) ZR75 and (c) MDA-MB-468 in the presence of estradiol (10 nM) or serum (3–6 replicates/group). Representative images showing EdU incorporation (green). Hoechst nuclear stain; blue. Scale bar represent 100 μm. Effects are mediated via induction of G1-phase cell cycle arrest (RFP+) and a reduction in the number of cells in S/G2/M-phase (GFP+) and G1/S transition (YFP+) in (d) MCF7 and (e) MDA-MB-468 cells (four replicates/group). (Hoechst nuclear stain; blue). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (f) UAG stimulates cell death in MCF7 and MDA-MB-468 cells, but not MDA-MB-231 cells (three replicates/group). Western blot results demonstrating that UAG inhibits CDK4/cyclin D3, pRB (Ser 795) and BCL2, and stimulates BAX in (g) MCF7 and (h) MDA-MB-468 cells. Data represent mean ± SEM. Experiments were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control; FBS: fetal bovine serum; E2: estradiol.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Unacylated ghrelin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig4-data2-v1.pdf
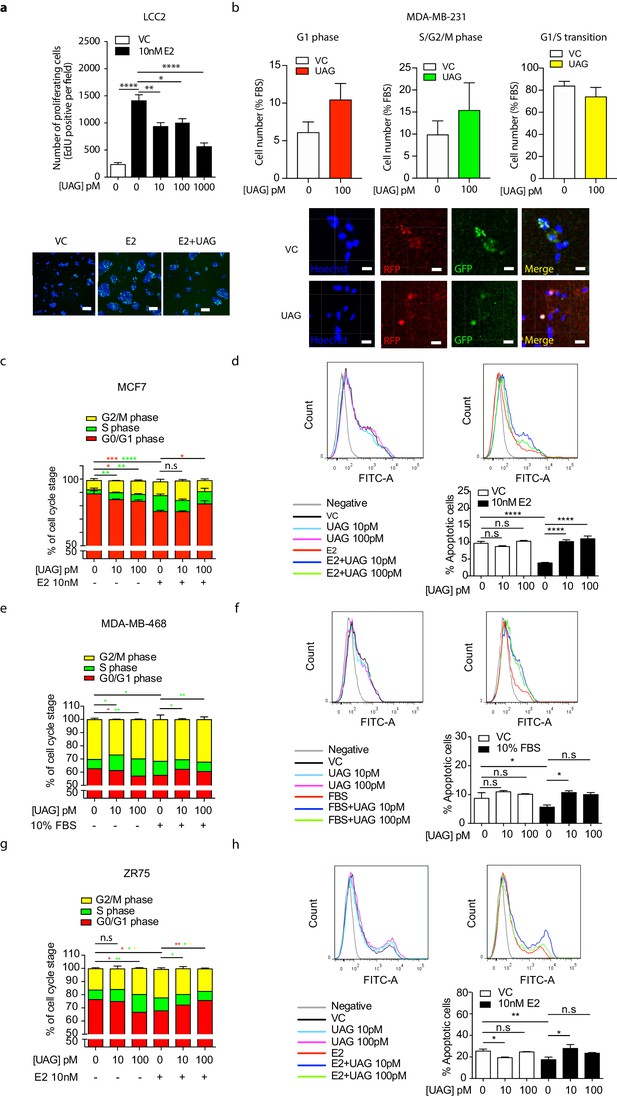
Unacylated ghrelin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
(a) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG) significantly inhibits the proliferation of tamoxifen-resistant LCC2 cells in the presence of estradiol (10 nM). Representative images showing EdU incorporation (green). Hoechst nuclear stain (blue). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (b) No effect of UAG on cell cycle was observed in MDA-MB-231 cell using FUCCI cell cycle system. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrating that UAG induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in (c, d) MCF7, (e, f) MDA-MB-468 and (g, h) ZR75 cells. Data represent mean ± SEM with three replicates/group. Experiments were repeated at least twice. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; FBS: fetal bovine serum; E2: estradiol.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
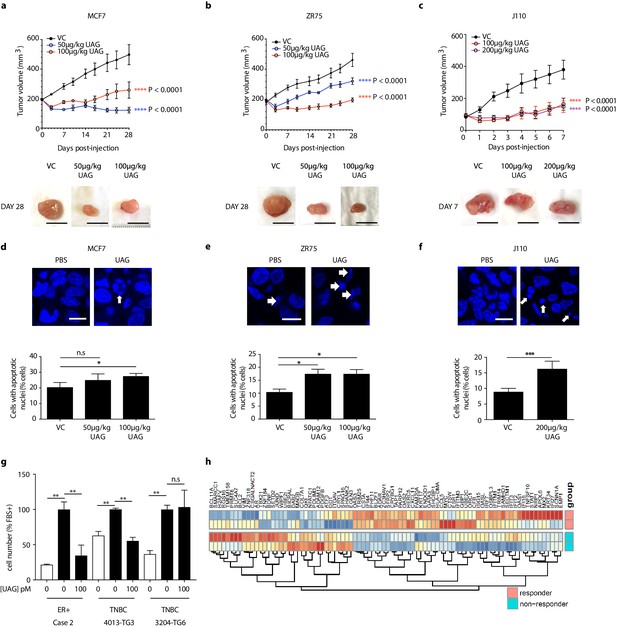
Unacylated ghrelin inhibits tumor growth in xenograft models and patient-derived tumor cells.
Tumor volume in response to treatment with 50 μg/kg (blue), 100 μg/kg (red) or 200 μg/kg (purple) UAG in mice xenografted with (a) MCF7 (six replicates/group), (b) ZR75 (five replicates/group), or allografted with (c) J110 (five replicates/group) cells. Representative tumor (below) with scale bar representing 10 mm. UAG significantly increases the number of cells with apoptotic nuclei in (d) MCF7, (e) ZR75 and (f) J110 xenografts. (g) UAG (100 pM) significantly inhibits the growth of patient-derived ER+ breast cancer cells and 4013-TG3 TNBC cells, but not 3204-TG6 TNBC cells. (h) Heatmap representing baseline differential expression of MAPK-target genes in responsive vs. non-responsive patient-derived cells. Data represent mean ± SEM. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control; FBS: fetal bovine serum.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin and cyclic analog AZP-531 inhibit tumor growth in xenograft models and patient-derived tumor cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
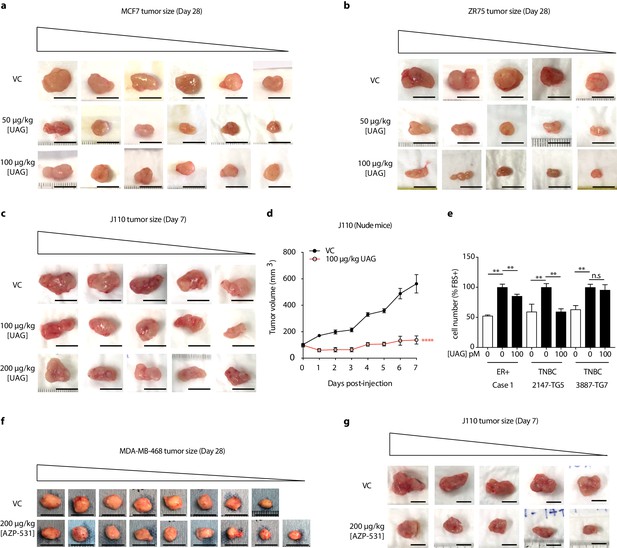
Unacylated ghrelin and cyclic analog AZP-531 inhibit tumor growth in xenograft models and patient-derived tumor cells.
Representative images of tumors in response to treatment with 50 μg/kg or 100 μg/kg unacylated ghrelin (UAG) in nude mice xenografted with (a) MCF7 (six replicates/group) and (b) ZR75 (five replicates/group) cells. Effect of UAG on tumor volume of J110 (five replicates/group) (c) allografts in FVB mice or (d) xenografts in nude mice compared to vehicle control. (e) UAG (100 pM) significantly inhibits the growth of patient-derived ER+ breast cancer, 2147-TG5 TNBC, but has no effect on the growth of 3887-TG7 TNBC. Data represent mean ± SEM. Representative images of tumors in response to treatment with 200 μg/kg AZP-531 in (f) NSG mice xenografted with MDA-MB-468 cells (8–9 replicates/group) or (g) FVB mice allografted with J110 cells (five replicates/group). Scale bars represent 10 mm. UAG: unacylated ghrelin; VC: vehicle control.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin and cyclic analog AZP-531 inhibit tumor growth in xenograft models andpatient-derived tumor cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
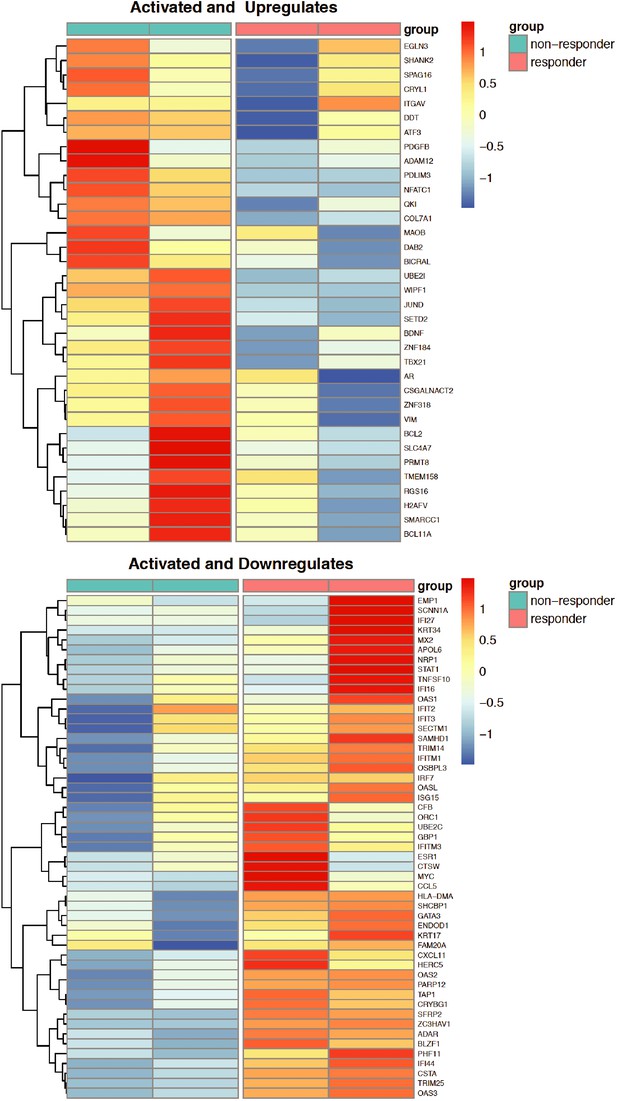
Expression pattern of MAPK-target genes in responder and non-responder TNBC patient-derived breast cancer cases.
Red and blue colors indicate high and low gene expression, respectively.
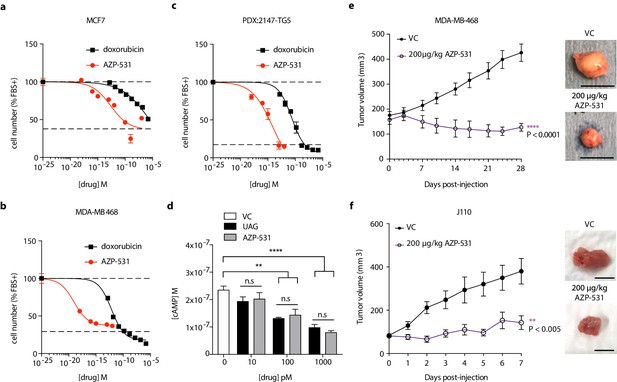
Unacylated ghrelin analog, AZP-531, inhibits breast cancer cell growth in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo.
AZP-531 causes the dose-dependent inhibition of (a) MCF7 and (b) MDA-MB-468 and (c) patient-derived TNBC breast cancer cell growth in 3D, compared with chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin (three replicates/group). (d) Unacylated ghrelin (UAG; 10–1000 pM) and AZP-531 (AZP; 10–1000 pM) inhibits the forskolin-stimulated production of cAMP in MCF7 cells (3–6 replicates/group). Data represent mean ± SEM. Experiments were repeated at least twice. Tumor volume in response to treatment with 200 μg/kg AZP-531 (purple) in mice xenografted with (e) MDA-MB-468 (8–9 replicates/group) or allografted with (f) J110 (five replicates/group) cells. Representative images (below) with scale bars representing 10 mm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Unacylated ghrelin analog, AZP-531, inhibits breast cancer cell growth in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
Characteristics of breast cancer cell lines and patient-derived breast cancer cells, and responsiveness to unacylated ghrelin.
| Breast cancer cell line/Patient sample | Known mutations | Intrinsic subtype | Receptor status | Responsive to Unacylated Ghrelin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line | ||||
| MCF7 | CDKN2A, PIK3CA | Luminal A | ER+/PR+/HER2- | Yes |
| LCC2 | N/A | Luminal A | ER+/PR+/HER2- | Yes |
| T47D | PIK3CA, TP53 | Luminal A | ER+/PR+/HER2- | Yes |
| ZR75 | PTEN | Luminal B | ER+/PR+/HER2+ | Yes |
| SKBR3 | TP53 | HER2+ | HER2+ | Yes |
| MDA-MB-468 | PTEN, RB1, SMAD4, TP53 | Basal-like | TNBC | Yes |
| MDA-MB-157 | NF1, TP53 | Mesenchymal-like | TNBC | Yes |
| MDA-MB-231 | BRAF, KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, NF2 | Mesenchymal-like | TNBC | No |
| HS578T | HRAS, TP53 | Mesenchymal-like | TNBC | No |
| DU4475 | BRAF,APC, MAP2K4, RB1 | Basal-like | TNBC | No |
| Patient samples | ||||
| ER+ Case 1 | N/A | Luminal A | ER+ | Yes |
| ER+ Case 2 | N/A | Luminal A | ER+ | Yes |
| 2147-TG5 | N/A | Basal-like | TNBC | Yes |
| 4013-TG3 | N/A | Basal-like | TNBC | Yes |
| 3887-TG7 | N/A | Mesenchymal-like | TNBC | No |
| 3204-TG6 | N/A | Mesenchymal-like | TNBC | No |
-
Abbreviations: ER, estrogen receptor; PR, progesterone receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; TNBC, triple negative breast cancer; N/A: not available.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | One Shot Stbl3 Chemically Competent E. coli | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# C737303 | |
| Strain, strain background (Mus-musculus) | BALB/c-Foxn1nu/Arc (BALB/c nude) mice | Animal Resources Centre, Australia | Cat# BCNU; RRID:MGI:2161064 | Female, 6 week old |
| Strain, strain background (Mus-musculus) | FVB/NJArc (FVB/N) mice | Animal Resources Centre, Australia | Cat# 001800; RRID:IMSR_JAX:001800 | Female, 6 week old |
| Strain, strain background (Mus-musculus) | NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice | NOD Scid gamma, Jackson laboratory | Cat# 005557; RRID:IMSR_JAX:005557 | Female, 6 week old |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MCF7 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-22; RRID:CVCL_0031 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | T47D | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-133; RRID:CVCL_0553 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | ZR75-1 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# CRL-1500; RRID:CVCL_0588 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MDA-MB-231 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-26; RRID:CVCL_0062 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MDA-MB-468 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-132; RRID:CVCL_0419 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | SKBR3 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-30; RRID:CVCL_0033 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | Hs578T | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-126; RRID:CVCL_0332 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HEK293T | ATCC | ATCC Cat# CRL-1573; RRID:CVCL_0045 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DU4475 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-123; RRID:CVCL_1183 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MDA-MB-157 | ATCC | ATCC Cat# HTB-24; RRID:CVCL_0618 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | LCC2 | obtained from Prof. Robert Clarke | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | RKO | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | RKO-T29 | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | RKO-A19 | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116-HWT | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116-HMUT | Yun et al., 2009 | ||
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | J110 | obtained from Dr. Myles Brown | ||
| Biological sample (human) | Patient-derived breast tumors | obtained from Dr. Giorgio Inghirami | See Materials and methods section | |
| Biological sample (human) | Estrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast tumors | obtained from Dr. Eleni Andreopoulou | See Materials and methods section | |
| Antibody | Goat anti-mouse IgG H and L (HRP) | Abcam | Cat# ab205719; RRID:AB_2755049 | 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG H and L (HRP) | Abcam | Cat# ab7083; RRID:AB_955416 | 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Mouse Monoclonal anti-Tubulin, beta, (KMX-1) | MilliporeSigma | Cat# MAB3408; RRID:AB_94650 | 1:10000 |
| Antibody | Mouse Monoclonal anti-β-Actin−Peroxidase | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#A3854; RRID:AB_262011 | 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-CDK4 (D9G3E) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 12790; RRID:AB_2631166 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse Monoclonal anti-Cyclin D3 (DCS22) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 2936; RRID:AB_2070801 | 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Polyclonal anti-phospho-Rb (Ser795) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9301; RRID:AB_330013) | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Mouse Monoclonal anti-Rb (4H1) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9309; RRID:AB_823629 | 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-Bcl-2 (D55G8) (Human Specific) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 4223; RRID:AB_1903909 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-Bax | Cell Signaling | Cat# 2772; RRID:AB_10695870 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Polyclonal anti-phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9101; RRID:AB_331646 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) (137F5) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 4695; RRID:AB_390779 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-phospho-p90RSK (Ser380) (D3H11) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 11989; RRID:AB_2687613 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-RSK1/RSK2/RSK3 (32D7) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9355; RRID:AB_659900 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-c-Myc (D84C12) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 5605; RRID:AB_1903938 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Polyclonal anti-phospho-Akt (Ser473) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9271; RRID:AB_329825 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Polyclonal anti-Akt | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9272; RRID:AB_329827 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-phospho-p70 S6 Kinase (Thr389) (108D2) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9234; RRID:AB_2269803 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Rabbit Monoclonal anti-p70 S6 Kinase (49D7) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 2708; RRID:AB_390722 | 1:1000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPBJ—puro-FRET3-EKAR-nls | obtained from Dr. John Albeck | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCMV-hyPBase transposase vector | obtained from Dr. John Albeck | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMSCV-puro-Foxo3a-H212R-N400-mCherry | obtained from Dr. John Albeck | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | lentiCRISPR v2 | Sanjana et al., 2014 | Addgene Cat# 52961; RRID:Addgene_52961 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | BRAFV600E plasmid | obtained from Dr. Dan Gough | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | psPAX2 | This paper | Addgene Cat# 12260; RRID:Addgene_12260 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | VSV-G | Reya et al., 2003 | Addgene Cat# 14888; RRID:Addgene_14888 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | See Supplementary file 1 for GNAI sequence guide strands used in this study | |||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Rat des-octanoyl ghrelin | China Peptides | Cat# Rat des-octanoyl ghrelin | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | [Des-octanoyl]-Ghrelin (rat) | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 2951 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Ghrelin (rat) | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1465 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | AZP531 | MedChem Express | Cat# HY-P0231 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Cy3-tagged UAG | Pepmic Co, LtD | Cat# Cy3-GR-28 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | EarlyTox Live/Dead Assay Kit | Molecular Devices | Cat# P/N R8340 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Click-iT Plus EdU Alexa Fluor 488 Imaging Kit | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# C10637 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cell Line NucleofectorKit V | Lonza | Cat# VCA-1003 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lance Ultra cAMP Detection Kit | Perkin Elmer | Cat# TRF0262 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Gαi Activation Assay Kit | New East Biosciences | Cat# 80301 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Premo FUCCI Cell Cycle Sensor (BacMam 2.0) | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# P36237 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PureYield Plasmid Miniprep System | Promega | Cat# A1223 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PureYield Plasmid Maxiprep System | Promega | Cat# A2392 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Pertussis Toxin from B. pertussis, Lyophilized (Salt-Free) | List Biological Laboratories | Cat# 181 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | U0126 | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9903S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | LY294002 | Cell Signaling | Cat# 9901 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | KT 5720 | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1288 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SQ 22536 | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1435 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | cAMPS-Rp, triethylammonium salt | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 1337 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Melatonin | Tocris Bioscience | Cat# 3550 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Doxorubicin hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D1515 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Forskolin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F3917 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | β-Estradiol | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# E8875-1G | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_005375 | http://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
| Software, algorithm | Imaris | Bitplane | RRID:SCR_007370 | https://imaris.oxinst.com/ |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji | ImageJ | RRID:SCR_002285 | https://imagej.net/Fiji |
| Software, algorithm | Image Lab | BIO-RAD | RRID:SCR_014210 | http://www.biorad.com/en-us/product/image-lab-software?ID=KRE6P5E8Z; |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN software | ZEISS | RRID:SCR_013672 | https://www.zeiss.com/ microscopy/ us/products/microscope-software/zen-lite.html |
| Software, algorithm | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis | Qiagen | RRID:SCR_008653 | https://www.qiagenbioinformatics. com/products/ingenuity-pathway-analysis |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo software | FlowJo | RRID:SCR_008520 | https://www.flowjo.com/solutions/flowjo |
| Other | Hoechst 33342, Trihydrochloride, Trihydrate | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# H3570 | |
| Other | FITC Annexin V | BD Pharmingen | Cat# 556420 | |
| Other | Propidium Iodine | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# P1304MP | |
| Other | Fura-2, AM, cell permeant | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# F1221 | |
| Other | Probenecid, Water Soluble | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# P36400 | |
| Other | Pluronic F-127 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# P6867 | |
| Other | BsmBI | New England BioLabs | Cat# R0580S | |
| Other | Polyethylenimine, linear (PEI) | Polysciences, Inc | Cat# 23966–1 | |
| Other | Polybrene | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-134220 | |
| Other | Puromycin Dihydrochloride | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# A1113803 | |
| Other | Blasticidin S HCl (10 mg/mL) | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat# A1113903 | |
| Other | Corning Matrigel Growth Factor Reduced (GFR) Basement Membrane Matrix, Phenol Red-free, *LDEV-free, | Corning | Cat# 356231 | |
| Other | Collagen | Obtained from Dr. Jason Spector | ||
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Oligonucleotide Sequences.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/56913/elife-56913-transrepform-v1.docx