Tetramerisation of the CRISPR ring nuclease Crn3/Csx3 facilitates cyclic oligoadenylate cleavage
Figures
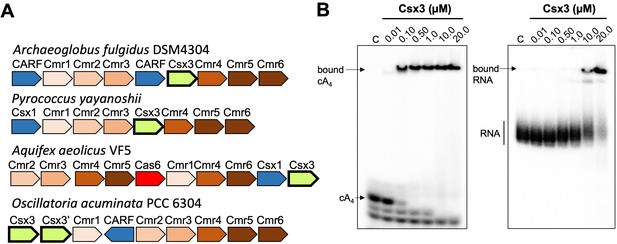
Csx3 is a type III CRISPR accessory protein that binds cA4.
(A) Genome context of selected Csx3 orthologues. Csx3 is found next to type III-B CRISPR operons and adjacent to Csx1 and other uncharacterised CARF family proteins. Csx3’ is a longer version of Csx3, common in cyanobacteria, consisting of an N-terminal Csx3 domain fused to a C-terminal kinase/transferase domain of unknown function. (B) Phosphor images of native gel electrophoresis visualising cA4 (20 nM) or RNA oligonucleotide 49-9A (50 nM) binding by A. fulgidus Csx3. Csx3 binds to cA4 with high affinity (apparent KD <100 nM) and binds the RNA 49-9A with significantly lower affinity (apparent KD ~10 µM). Images are representative of three technical replicates.

Multiple sequence alignment of Csx3 proteins showing conserved residues.
Csx3 proteins are shown from Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Methanosarcinia mazei; Candidatus Bathyarchaeota; Thermococcus celericrescens; Methylacidiphilum fumariolicum; Aquifex aeolicus; Dictyoglomus turgidum; Spirulina major; Oscillatoria nigro-viridis. Absolutely conserved residues are shaded. Conserved residues H60 and D69 (Afu numbering) are indicated by asterisks.
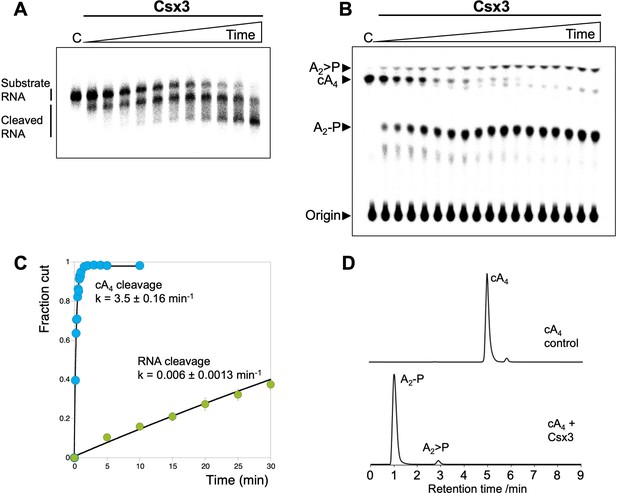
Csx3 is a potent ring nuclease.
(A) Denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis visualising cleavage of 5’-end radiolabelled RNA 49-9A (50 nM) by Csx3 (8 µM dimer) at 50°C (time points every 5 min from 5 to 40 min, then 50, 60 and 90 min, n = 3 technical replicates). (B) TLC analysis of the reaction products of radiolabelled cA4 (200 nM) incubated with A. fulgidus Csx3 (8 µM dimer) in reaction buffer at 50°C (time points every 5 s from 10 to 60 s then 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 10 min, n = 6 technical replicates). The cA4 was rapidly converted into A2-P, with a small amount of A2 >P (linear A2 with a cyclic 2’,3’ terminal phosphate). (C) Plot comparing single-turnover kinetics of cA4 (blue) and RNA 49-9A (green) cleavage by AfCsx3 at 50°C. Data points are the average of three technical replicates and error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. (D) Liquid-chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis of reaction products when cA4 (100 µM, top) was incubated with AfCsx3 (10 µM) for 10 min at 50°C (bottom). cA4 was fully degraded to form A2-P (di-adenylate containing a 3’ phosphate) with a minor amount of A2 >P (di-adenylate containing a 2’,3’ cyclic phosphate).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Excel spreadsheet with raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Excel spreadsheet with raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-fig2-data2-v2.xlsx
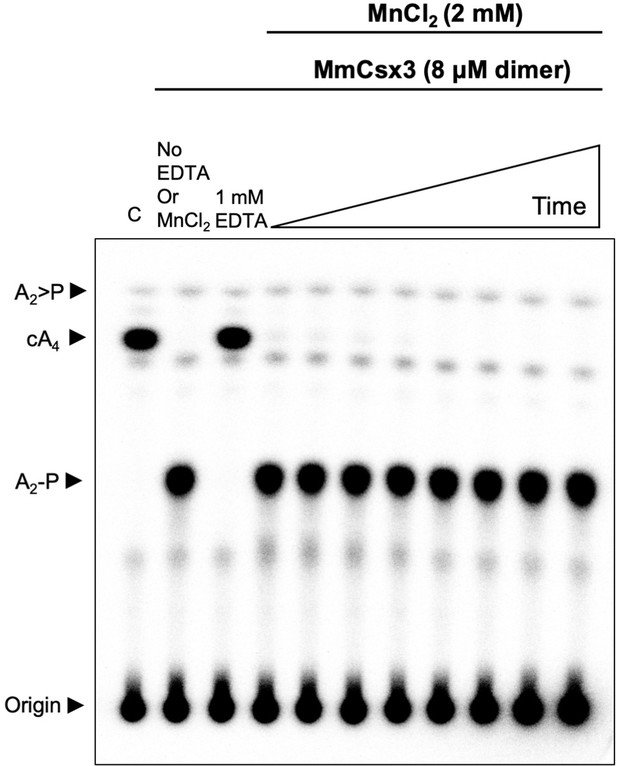
Csx3 from M. mazei is a ring nuclease.
TLC analysis of cleavage products obtained after incubating radiolabelled cA4 (~200 nM) with MmCsx3 (8 µM dimer) in reaction buffer at 50°C (time points are 10 s, 20 s, 30 s, 1 min, 5 min, 15 min, 30 min and 60 min, n = 3 technical replicates). The cA4 was rapidly converted into A2-P, which remained unchanged thereafter. C is a negative control showing cA4 incubated in buffer in the absence of protein.
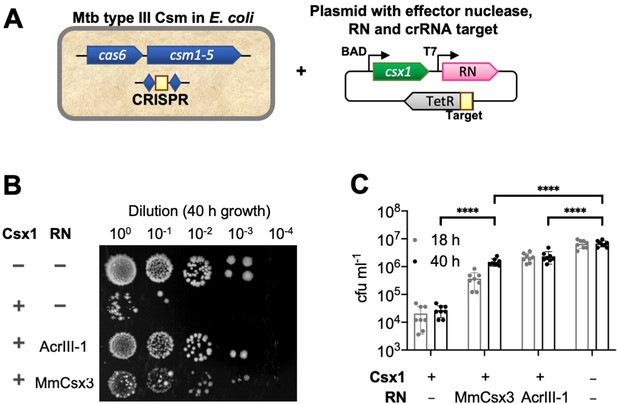
Csx3 functions as a ring nuclease in vivo.
(A) Schematic of plasmid transformation assay. A plasmid containing the effector nuclease Csx1, a ring nuclease (RN) and a target sequence that is complementary to the crRNA is transformed into E. coli expressing the M. tuberculosis (Mtb) Csm complex charged with crRNA. (B) The effector ribonuclease Csx1 prevents an incoming plasmid carrying a CRISPR-target sequence from being established, resulting in a reduction of number of transformants by almost 3 orders of magnitude under selective conditions. Both AcrIII-1 from phage THSA-485 and M. mazei (Mm)Csx3 provide a level of protection against Csx1-mediated plasmid immunity, with MmCsx3 requiring an extended incubation period to achieve a similar effect as its viral counterpart. (C) Number of transformants of Csx1-mediated plasmid immunity in the absence and presence of cA4-degrading ring nucleases. AcrIII-1 almost completely prevented Csx1-mediated cell death or growth arrest, whereas MmCsx3 yielded partial but still significant relief from immunity. Transformants were counted after 18 and 40 hr of growth. Data are representative of two biological replicates and four technical replicates each, N = 8; individual data points are shown and error bars represent the standard deviation. Significance threshold was set at p<0.05, ****: p<0.00001 (unpaired, two-tailed Welch t test). Key: RN – ring nuclease; MmCsx3 – M. mazei Csx3.
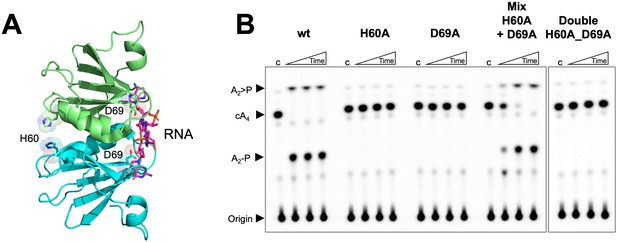
Both faces of the Csx3 dimer are required for ring nuclease activity.
(A) Structure of the Csx3 dimer (monomers in cyan and green) bound to an RNA tetraloop (magenta) (PDB 3WZI), with residues D69 and H60 indicated. (B) Phosphorimage of TLC visualising cA4 (~200 nM) cleavage by A. fulgidus Csx3 (8 µM protein dimer) wild-type and variants at 70°C. While neither the H60A nor the D69A variant of Csx3 had detectable ring nuclease activity, a mixture of the two inactive variants restored activity. The double mutant was inactive. Control lane c – cA4 in absence of protein. Time points were 10, 60 and 600 s. This phosphorimage is representative of 3 technical replicates.
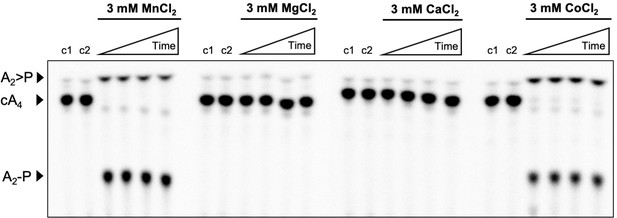
Metal dependence of Csx3.
Phosphor image of TLC visualising cA4 (~200 nM) cleavage by Csx3 (8 µM protein dimer) at 70°C when supplemented with 3 mM MnCl2, MgCl2, CaCl2 or CoCl2. Csx3 ring nuclease activity requires the presence of Mn2+ or Co2+ ions and cannot be substituted with Ca2+ or Mg2+. Control lane c1 is cA4 in absence of protein and the lane c2 is protein incubated in assay buffer containing 1 mM EDTA before adding cA4 (no metal control). Time points were 10 s, 20 s, 60 s and 10 min. This phosphorimage is representative of 3 technical replicates.
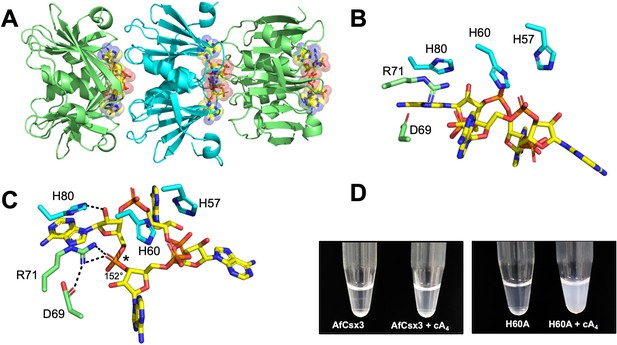
Structure of the H60A variant of Csx3 in complex with cA4.
(A) Crystal structure of H60A Csx3 in complex with cA4. The crystal lattice reveals an extended filament with dimers of Csx3 sandwiching cA4. Three dimers are shown (green and cyan), with the cA4 in yellow sticks. (B and C) Two views of the Csx3 H60A variant in complex with cA4 showing the conserved residues implicated in binding and catalysis (colouring as in panel A). Whilst H60 was not present in our structure (as an alanine variant was crystallised), the position has been inferred by superposition with PDB 3WZI. In panel C, hydrogen bonds are indicated as black dashed lines. The geometry of the phosphodiester bond is labelled (*), which is likely positioned by a bidentate hydrogen bond with R71, meaning it is suitable for in-line nucleophilic attack by the adjacent 2’-OH moiety. (D) Photograph comparing wild-type and H60A Csx3 (80 µM dimer) in the absence and presence of equimolar cA4. The inactive variant forms a milky, colloidal liquid when incubated with cA4, consistent with the formation of extended fibres.
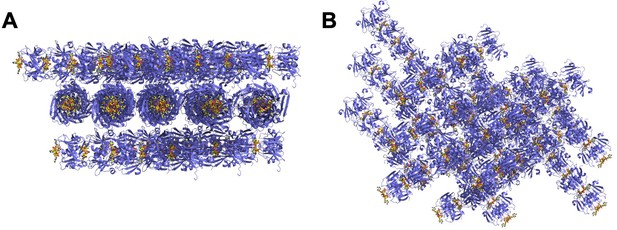
The crystal lattice of the Csx3:cA4 complex.
(A and B) Different views of the crystal lattice of Csx3 (mauve) in complex with cA4 (yellow). The asymmetric unit contains 5 dimers of Csx3, which with the crystallographic symmetry forms longer filaments.
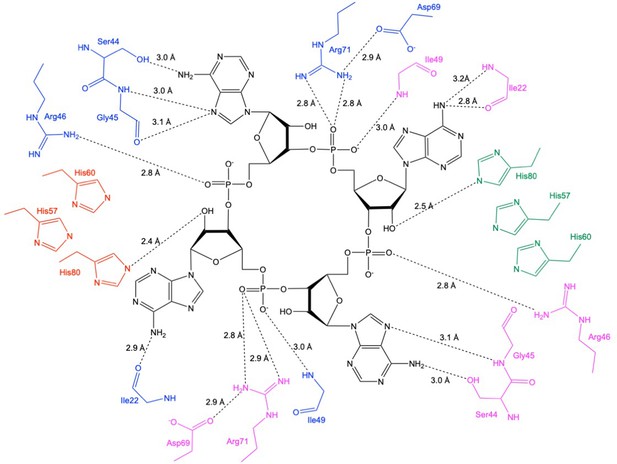
Schematic showing interactions between Csx3 and cA4.
The residues in blue and pink represent the two monomers in the dimer constituting the ‘D69 face’, and the residues in green and red represent the two monomers in the dimer constituting the ‘H60’ face. Whilst H60 was not present in our structure, the position has been inferred by superposition with PDB 3WZI.
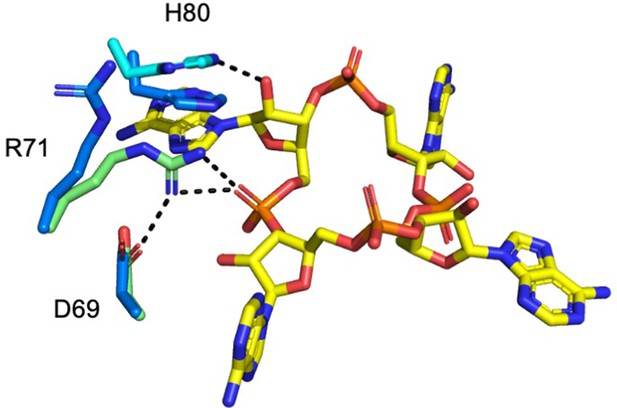
Superimposition of Csx3 in complex with cA4 and apo Csx3.
The active site of Csx3 (cyan and green, with the different colours representing different monomers in the dimer) in complex with cA4 (yellow) is superimposed with apo Csx3 (blue) (PDB: 3WZG). The hydrogen bonds (dotted black lines) are formed upon movement of R71 and H80 in the complex with cA4, both by 3.3 Å.
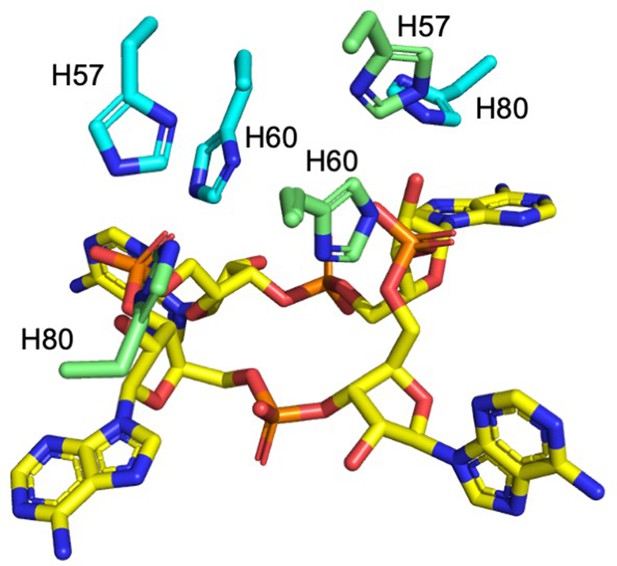
Histidine residues in the active site of Csx3.
H57, H60 (H60 was not present in our structure, the position has been inferred by superposition with PDB 3WZI; both the alanine from our structure and superimposed histidine are shown for clarity), and H80 from both monomers (coloured cyan and green) in a dimer are shown in complex with cA4 (yellow sticks).
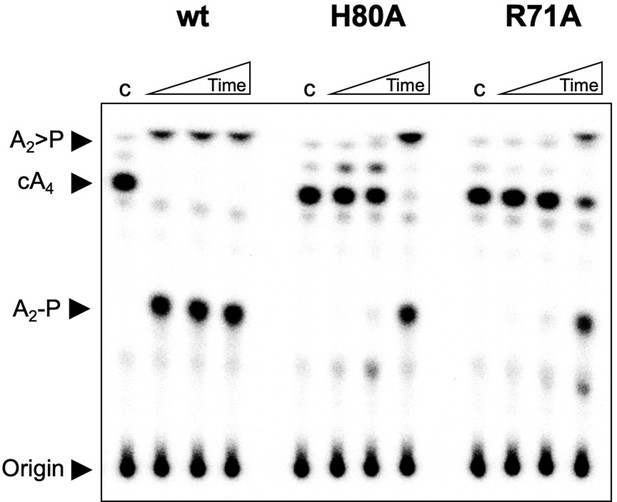
Investigation of H80A and R71A variants of Csx3.
TLC comparing ring nuclease activity of wild-type, H80A and R71A variants of Csx3 at 70°C. Both variants had severely reduced activity. Time points were 10, 60 and 600 s. Control c is reaction in absence of Csx3. This result is representative of 3 technical replicates.

Sigmoidal response of ring nuclease activity as a function of Csx3 concentration.
Plot visualising initial reaction rates of cA4 cleavage across increasing Csx3 concentrations. The cA4 concentration was 129 µM (25-fold greater than the highest concentration of protein assayed) for all experiments. Instead of a linear relationship between enzyme concentration and activity, a pronounced sigmoidal shape was observed. This could be fitted to a Hill equation to give a good fit with a Hill coefficient of 1.8, consistent with a requirement for two Csx3 dimers to associate with one cA4 substrate molecule to effect catalysis. The maximum multiple turnover rate constant observed was 0.075 min−1 at 70°C. Each datapoint is the average of three technical replicates and error bars show the standard deviation of the mean.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Excel spreadsheet with raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
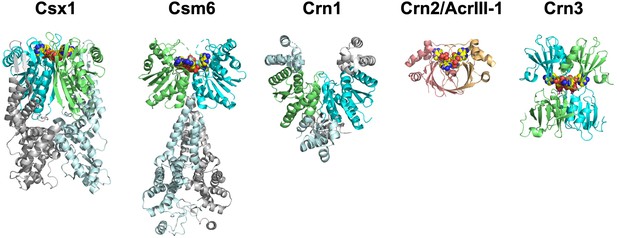
The ring nucleases.
The Crn1 family (represented here by Sso1393, PDB code 3QYF) is restricted to the crenarchaea (Athukoralage et al., 2018). The Csx1 family (represented here by PDB code 6O6Y) is self-limiting cA4-dependent ribonucleases (Athukoralage et al., 2019; Jia et al., 2019). One Csm6 enzyme (PDB code 6TUG) has been shown to degrade cA6 (Garcia-Doval et al., 2020). The Crn3 family is present in type III CRISPR systems in euryarchaeal and cyanobacteria. In contrast, the DUF1874 (Crn2/AcrIII-1) family uses a different protein fold to bind cA4. The Crn2 family of ring nucleases is quite widespread in bacterial type III CRISPR systems (Samolygo et al., 2020). The same fold is used by the anti-CRISPR AcrIII-1 in archaeal viruses and bacteriophage (Athukoralage et al., 2020a). CARF domains in each ring nuclease (where present) are coloured green and cyan; cOA is shown as yellow spheres.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Sulfolobus solfataricus) | SsoCsm complex (eight subunits) | PMID:24119402 | virus expression construct | |
| Gene (Archaeoglobus fulgidus) | Csx3/Crn3 | PMID:26106927 | UniProtKB – O28415 | plasmid expression construct |
| Gene (Methanosarcina mazei) | MmCsx3 | This paper | UniProtKB - A0A0F8HGG9 | plasmid expression construct |
| Gene (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) | MtbCsm complex (five subunits) | PMID:31392987 | plasmid expression construct | |
| Gene (Thioalkalivibrio sulfidiphilus) | TsuCsx1 | PMID:31392987 | UniProtKB – B8GSI1 | plasmid expression construct |
| Gene (Thermoanaerobacterium phage THSA-485A) | AcrIII-1 | PMID:31942067 | UniProtKB - I3VYU1 | plasmid expression construct |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Data collection and refinement statistics for H60A mutant of Csx3 in complex with cA4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Dynamic light scattering studies with AfCsx3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-supp2-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/57627/elife-57627-transrepform-v2.docx





