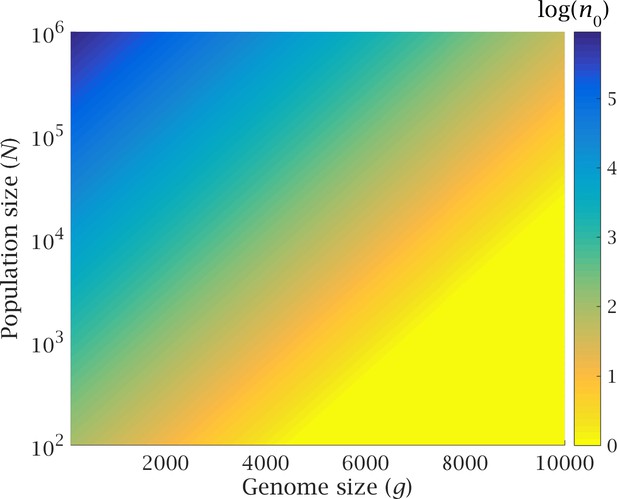
Genome expansion in early eukaryotes drove the transition from lateral gene transfer to meiotic sex
Figures
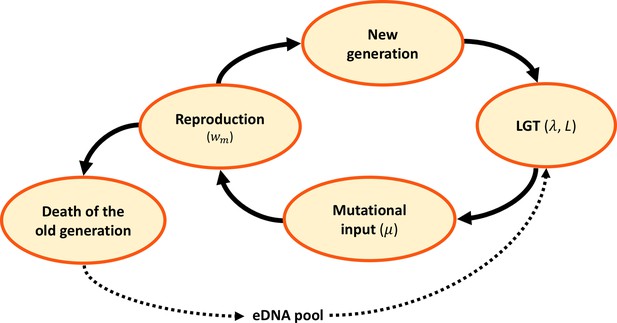
Model dynamics.
After the birth of a new generation, eDNA is acquired from the environment and randomly recombined with recombination length , at a rate per genome. Following LGT, mutations are randomly introduced at a rate per locus. A new generation is then sampled at random, in proportion to reproductive fitness . The old generation dies and its DNA is released, constituting the eDNA pool for the new generation.
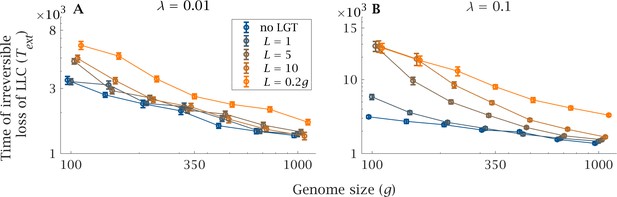
Impact of LGT and genome size on the ratchet.
The mean extinction time (generations) of the Least-Loaded Class () is shown as a function of genome size () for various recombination lengths (), in the presence of (A) low () and (B) high () LGT rates. The blue lines show the extinction time when there is no LGT, and is the same in (A) and (B). Parameters: , , , . Error bars show the standard deviation over 50 independent iterations.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Time of extinction of least loaded class.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58873/elife-58873-fig2-data1-v1.mat.zip
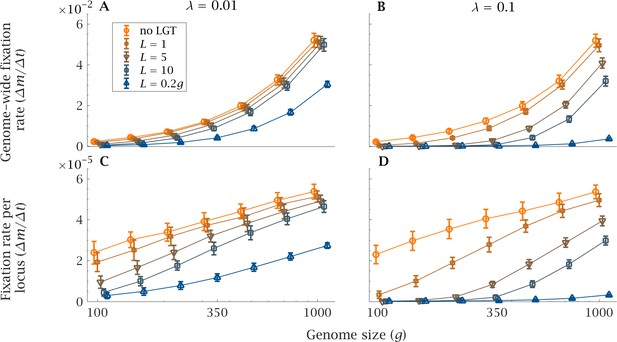
Impact of LGT and genome size on the rate of accumulation of mutation.
The mean genome-wide rate of fixation of deleterious mutations per generation, calculated over a time interval generations, as a function of genome size () for various recombination lengths (). This is shown for (A) low () and (B) high () LGT rates. Similarly, the rate of fixation of deleterious mutation per locus per generation is shown, again for (C) low () and (D) high () LGT rates. As genome size increases, LGT becomes less effective in reducing the mutational burden of a population. An increase in recombination length improves the efficiency of LGT in preventing the accumulation of mutations, but this beneficial effect declines rapidly with genome size. Only if recombination length is of the same order of magnitude as genome size () and the rate of LGT is high () can large genomes be maintained in a mutation-free state. Parameters: , , , . Error bars show the standard deviation over 50 independent iterations.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Rate of accumulation of mutations with variable genome-wide mutation rate.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58873/elife-58873-fig3-data1-v1.mat.zip
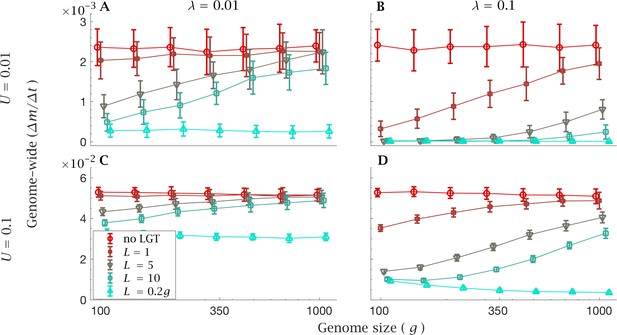
Rate of fixation of mutations with constant genome-wide mutation rate.
The mean genome-wide rate of fixation of deleterious mutations per generation. This is shown for a low rate genome-wide mutation rate for (A) low () and (B) high () LGT rates, and a high genome-wide mutation rate for (C) low () and (D) high () LGT rates, across a range of recombination lengths (). The fixation rate was calculated over a time interval of generations, as a function of genome size. LGT is not able to prevent the accumulation of mutation in large genomes, except for a recombination length on the order of the whole genome (). Parameters: , . Error bars show the standard deviation over 50 independent iterations. The different data points have been slightly off-set in order to prevent overlap between errorbars.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Rate of fixation of mutations with constant genome-wide mutation rate.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/58873/elife-58873-fig4-data1-v1.mat.zip
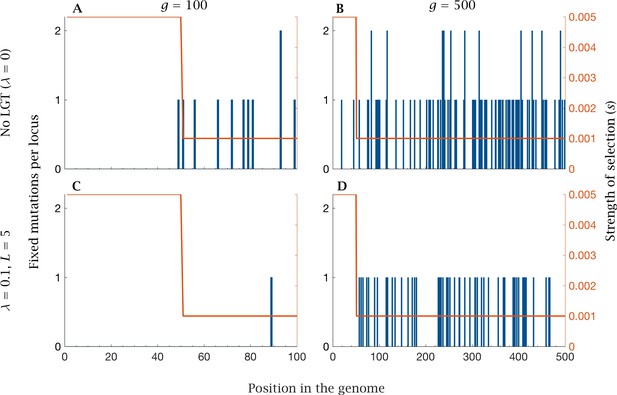
| Fixation of mutations in the core and accessory genome.
Fixed mutations in the core and accessory genome after generations for no LGT with (A) small () and (B) large () genome size, and for LGT (, ) with (C) small () and (D) large () genome size. Mutations preferentially accumulate in the accessory genome under weaker selection (), while the strongly selected core genome () accumulates few or no mutations. The rate of fixation increases with genome size, while the benefits of LGT decline with genome size. Parameters: , ,.
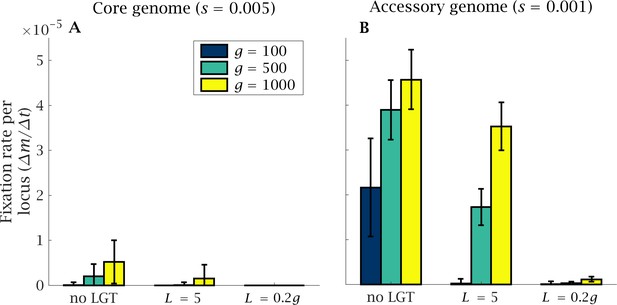
Rate of fixation of mutations in the core and accessory genome.
The fixation of mutants in (A) the core and (B) the accessory genome is shown after generations, normalised by genome size. A higher number of mutations accumulate in the accessory genome that is under weaker selection. Genome size expansion increases the severity of the ratchet and the number of fixed mutations in the core and accessory genome. The introduction of LGT considerably reduces the mutational burden. Parameters: , , and .
Tables
Parameters and variables.
| population size | |
| mutation rate per locus per generation | |
| genome size (number of loci) | |
| genome-wide mutation rate | |
| strength of selection against deleterious mutations | |
| LGT rate | |
| recombination length (number of loci) |