Transport of DNA within cohesin involves clamping on top of engaged heads by Scc2 and entrapment within the ring by Scc3
Figures
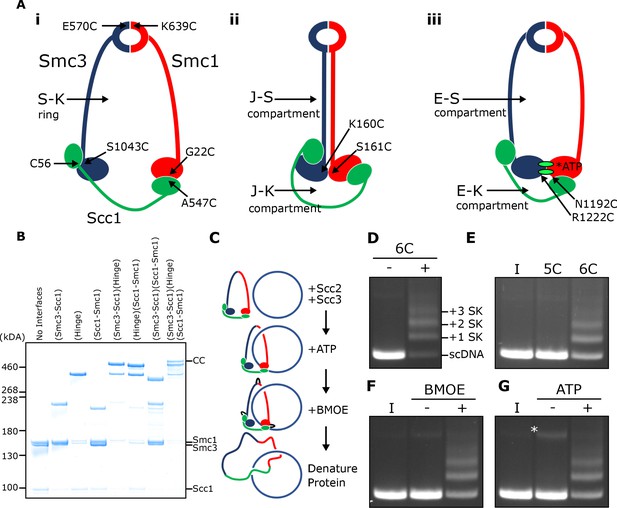
SMC-kleisin (S–K) rings entrap circular DNA in vitro.
(A) Cohesin’s different compartments and the position of cysteine pairs used in our crosslinking studies. (B) BMOE-induced crosslinking of S-K rings with cysteine pairs in the specified interfaces. CC = circular cohesin. (C) The entrapment assay scheme. (D) Entrapment of DNA in S-K rings in the presence or absence of 6C cohesin, or (E) the presence 5C cohesin, lacking Scc1A547C, or 6C cohesin. (F) For DNA in the presence of Scc2, Scc3, and 6C cohesin and the presence or absence of BMOE, or (G) the presence or absence of ATP. Entrapment assays incubated for 40 min (*=damaged open circular DNA; I = input DNA).
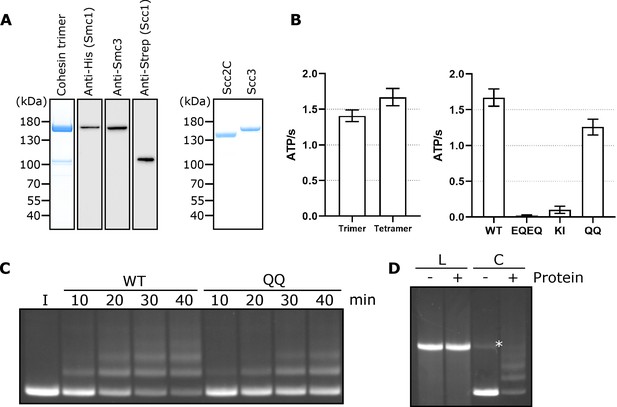
Related to Figure 1.
(A) Left hand panel - Coomassie strain of cohesin trimers. Individual subunits were then probed for by western blotting. Right hand panel – Coomassie stain of Scc2C and Scc3. (B) Left hand panel - ATPase activity for purified cohesin trimers incubated with DNA, Scc2, and ATP in the presence of Scc3 (tetramer) or absence (trimer). Right hand panel – ATPase activity for either WT cohesin tetramer, Smc1E1158Q Smc3E1155Q (EQEQ), Smc3K38I (KI) or Smc3K112Q K113Q (QQ). (C) Entrapment of DNA in S-K rings in the presence of Scc2 and Scc3 comparing WT cohesin to Smc3K112Q K113Q (QQ) (I = input DNA). (D) Entrapment of linear DNA (L) or circular supercoiled DNA (C) in the presence or absence of protein (Trimer, Scc2 and Scc3) (*=damaged open circular DNA).
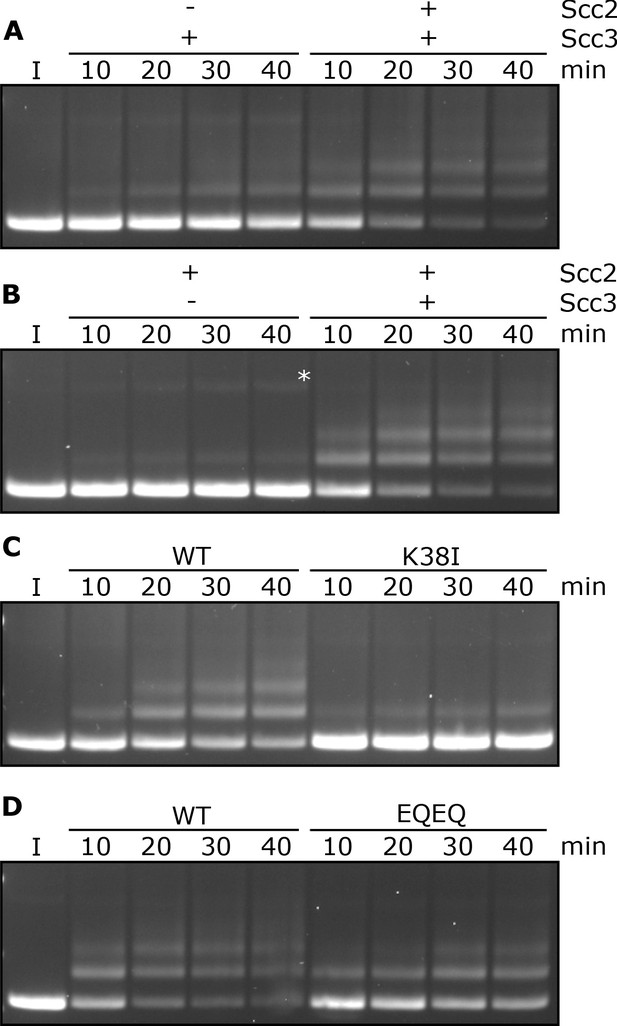
Entrapment within S-K rings requires both Scc2 and Scc3, ATP binding to Smc3, and is stimulated by ATP hydrolysis.
(A) Entrapment of DNA in S-K rings in the presence of Scc3, and the presence or absence of Scc2, or (B) the presence of Scc2, and the presence or absence of Scc3 (*=damaged open circular DNA). (C) DNA entrapment in the presence of Scc2 and Scc3, comparing WT cohesin to Smc3K38I (K38I), or (D) WT cohesin to Smc1E1158Q Smc3E1155Q (EQEQ). Entrapment assays incubated for 40 min with time points taken every 10 min (I = input DNA).
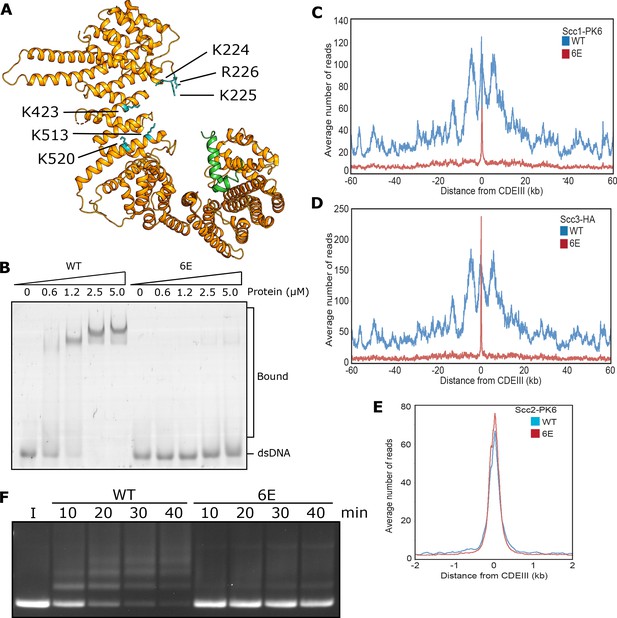
DNA binding to Scc3 is required for its entrapment by S-K rings.
(A) Structure of S. cerevisiae Scc3 (orange) protein in complex with a fragment of Scc1 (green) (PDB 6H8Q). Labelled are the six residues within the DNA binding groove of Scc3 that were mutated to glutamate (Scc3-6E). (B) EMSA comparing the ability of WT Scc3-Scc1269-451 and Scc3-6E-Scc1269-451 complexes to bind dsDNA. (C) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles of Scc1-PK6 60 kb either side of CENs in the presence of ectopic WT Scc3 (KN27821) or Scc3-6E (KN27804). Cells were arrested in G1 with α-factor prior to release into auxin and nocodazole containing media at 25°C to deplete the endogenous Scc3. ChIP-seq samples were taken 60 min after release. (D) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profile of ectopic WT (KN27796) or mutant (KN27802) Scc3-HA performed as in C. (E) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profile of Scc2-PK6 in the presence of ectopic WT Scc3 (KN28075) or Scc3-6E (KN28287). Experiment was performed as in C. (F) Entrapment of DNA within S-K rings in the presence Scc2 and either WT Scc3 or Scc3-6E. Entrapment assay incubated for 40 min with time points taken every 10 min (I = input DNA).
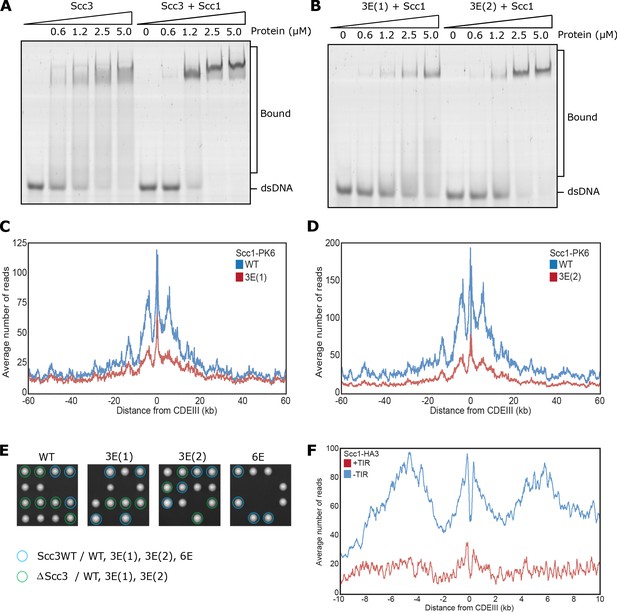
Related to Figure 3.
(A) EMSA comparing the ability of Scc3 to bind dsDNA against Scc3-Scc1269-451 complexes, or (B) of Scc3-3E(1)-Scc1269-451 (Scc3K224E K225E R226E) against Scc3-3E(2)-Scc1269-451 (Scc3K423E K513E K520E) complexes. (C) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles 60 kb either side of CENs of Scc1-PK6 in the presence of WT Scc3 (KN27542) or Scc3-3E(1) (KN27547), taken in cycling cells at 25°C. (D) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles of Scc1-PK6 in the presence of WT Scc3 (KN27542) or Scc3-3E(2) (KN27697), taken in cycling cells at 25°C. (E) Vertical tetrad dissection of spores from diploid cells heterozygous for deletion of the endogenous SCC3 gene, expressing a single copy of either WT Scc3 (KN21273), Scc3-3E(1) (KN27539), Scc3-3E(2) (KN27696), or Scc3-6E (KN27763) from an ectopic locus. WT Scc3, Scc3-3E(1), Scc3-3E(2) are able to support viability but Scc3-6E is not. Further marker selection, protein expression and genotype sequencing confirmed that Scc3-6E causes lethality. (F) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles 10 kb either side of CENs of Scc1-HA3 either expressing TIR necessary for auxin inducible degradation (KN20783) or not (KN20785). Samples were arrested in G1 with α-factor at 25°C prior to release into auxin containing media to deplete endogenous Scc3. ChIP-seq samples were taken 60 min after release.
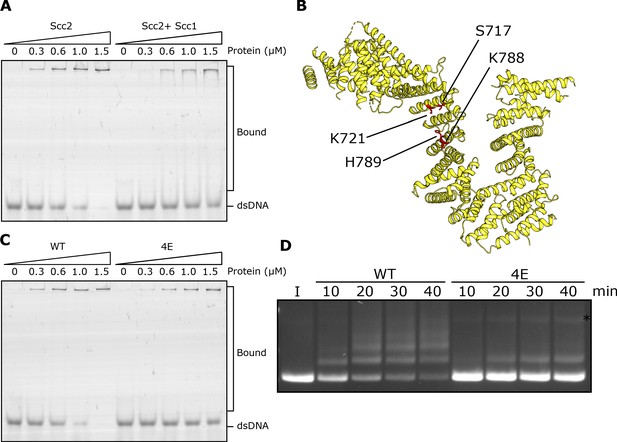
DNA binding to Scc2 facilitates entrapment by S-K rings.
(A) EMSA comparing the ability of Scc2 and Scc2-Scc1150-298 complexes to bind dsDNA. (B) S. cerevisiae Scc2 from the cryo-EM structure (Figure 8) with the four resides within the putative DNA binding surface labelled that were mutated to glutamate (Scc2-4E). (C) EMSA comparing the ability of Scc2 and Scc2-4E complexes to bind dsDNA. (D) Entrapment of DNA in S-K rings in the presence of Scc3 and either Scc2 or Scc2-4E. Entrapment assay incubated for 40 min with time points taken every 10 min (*=damaged open circular DNA; I = input DNA).
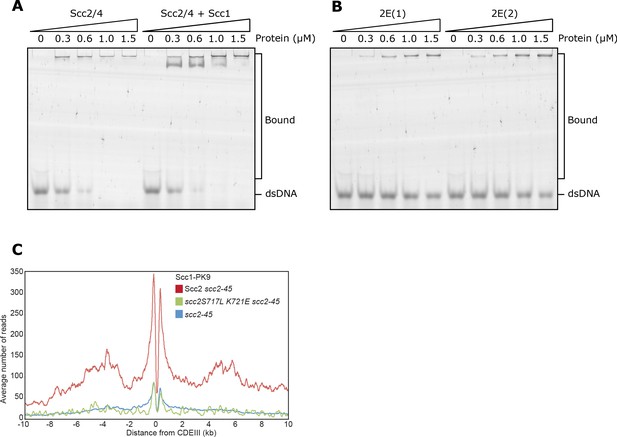
Related to Figure 4.
(A) EMSA comparing the ability of full length Scc2/4 and Scc2/4-Scc1150-298 complexes to bind dsDNA or (B) Comparing Scc2-2E(1) (Scc2S717E K721E) and Scc2-2E(2) (Scc2K788E H789E). (C) Average calibrated ChIP-seq profiles 10 kb either side of CENs of cells expressing WT (KN24185), S717L K721E double mutant (KN27010) or no ectopic copy of SCC2 (KN22390), over endogenous scc2-45. Cells were arrested in G1 with α-factor at 25°C before release into medium containing nocodazole at 37°C. Samples were taken 75 min after release. scc2-45 is a temperature sensitive allele.
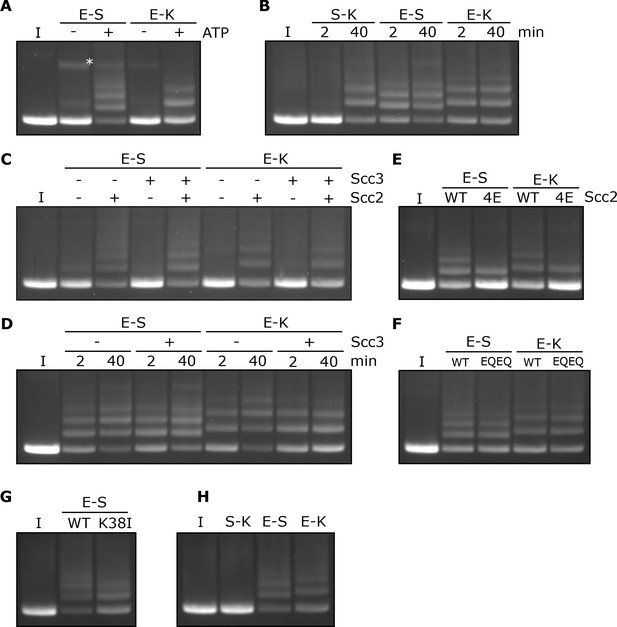
Rapid DNA entrapment in E-S and E-K compartments.
(A) Entrapment of DNA in E-S/E-K compartments in the presence of Scc2 and Scc3, and the presence or absence of ATP, incubated for 40 min (*=damaged open circular DNA). (B) DNA entrapment in S-K rings, or E-S/E-K compartments in the presence of Scc2 and Scc3, incubated for either 2 or 40 min. (C) DNA entrapment in E-S/E-K compartments in the presence of Scc2, Scc3, Scc2 and Scc3, or absence of both, incubated for 2 min. (D) DNA entrapment in E-S/E-K compartments in the presence of Scc2, and either the presence or absence of Scc3, incubated for either 2 min or 40 min. (E) DNA entrapment in E-S/E-K compartments in the presence of either Scc2 or Scc2-4E, or (F) Entrapment in the presence of Scc2 alone, comparing WT and Smc1E1158Q Smc3E1155Q (EQEQ) cohesin, incubated for 2 min. (G) DNA entrapment in E-S compartments in the presence of Scc2 comparing WT and Smc3K38I (K38I) cohesin. (H) Entrapment of DNAs in S-K rings, or E-S/E-K compartments, in the presence of Scc2, incubated for 2 min (I = input DNA).
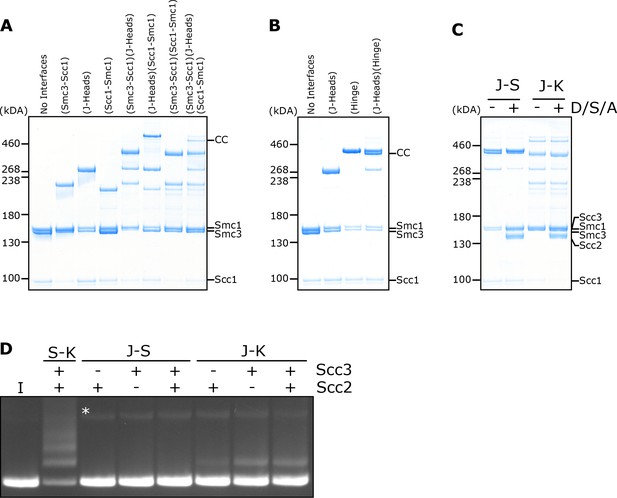
DNA is never entrapped in J-S and only rarely in J-K compartments.
(A) BMOE crosslinking of J-K compartments, or (B) of J-S compartments, with cysteine pairs in the designated interfaces. CC = circular cohesin. (C) Crosslinking of J-S or J-K compartments in the presence of DNA, Scc2, Scc3 and ATP (D/S/A) or absence of all four. (D) Entrapment of DNA in either S-K rings, or J-S/J-K compartments in the presence of Scc2, Scc3, or both Scc2 and Scc3. Incubated for 40 min (*=damaged open circular DNA; I = input DNA).
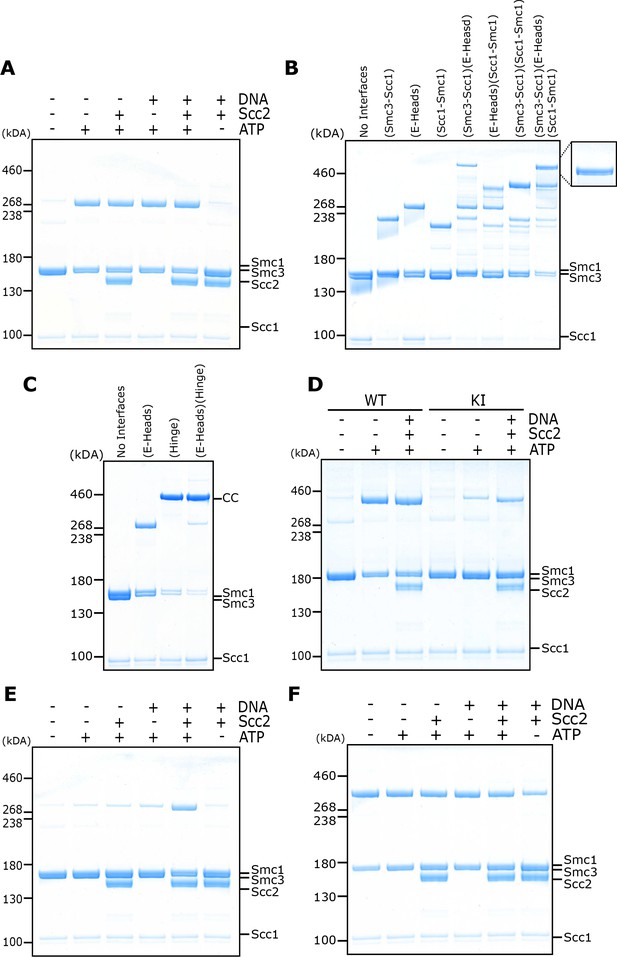
Circularisation of the E-S and E-K compartments and E- and J-state crosslinking under different conditions.
(A) BMOE crosslinking of cohesin containing a cysteine pair for E head association, in the presence of ATP, DNA, or Scc2 in various combinations and in the presence of 1 mM MgCl2. (B) Crosslinking of E-K compartments, or (C) of E-S compartments, with cysteine pairs in the designated interfaces. CC = circular cohesin. (D) Crosslinking of cohesin containing a cysteine pair for E head association, comparing WT cohesin against Smc3K38I (KI) in the presence of ATP, DNA, or Scc2 in various combinations. (E) Crosslinking of cohesin containing a cysteine pair specific for engaged heads, in the presence of ATP, DNA, or Scc2 in various combinations and in the absence of 1 mM MgCl2. (F) BMOE crosslinking of cohesin with a cysteine pair specific for J head association, in the presence of ATP, DNA, or Scc2 in various combinations.
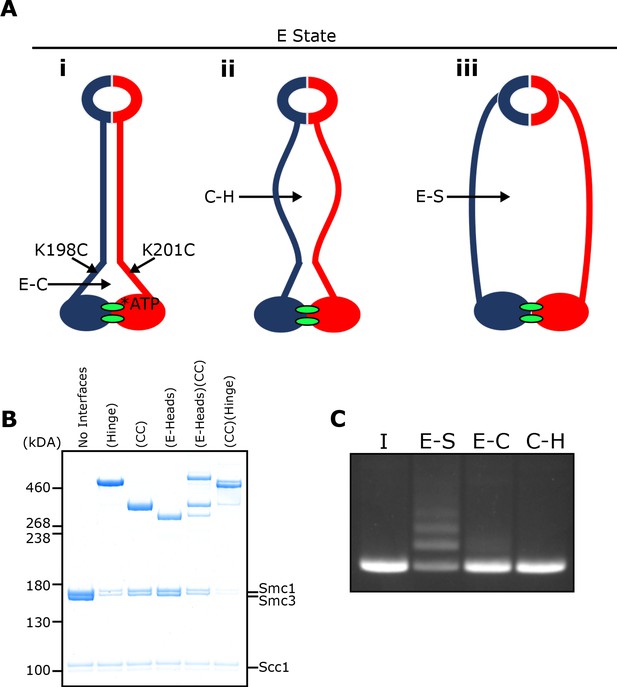
E-S/E-K entrapment leads to dissociation of the coiled coil around the joint.
(A) Scheme showing the location of the joint cysteine pair and how head engagement could lead to different degrees of coiled coil dissociation and sub-compartment formation. (B) BMOE crosslinking of cohesin containing cysteine pairs at the specified interfaces in the presence of ATP. CC = coiled coils. (C) DNA entrapment in E-S compartments, or either E-C or C-H sub-compartments, in the presence of Scc2, incubated for 2 min (I = input DNA).
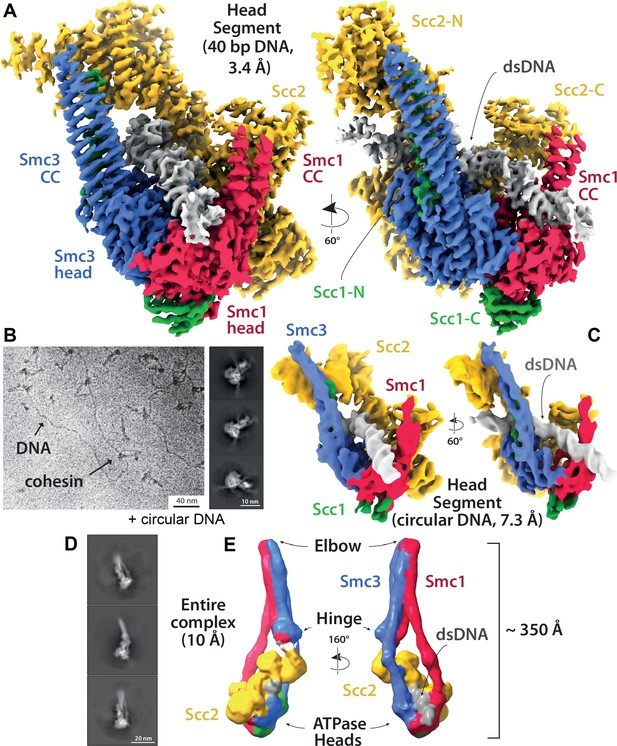
Cryo-EM of cohesin clamping DNA in the E-S/E-K state.
(A) Cryo-EM map of 40 bp DNA clamped by Scc2- and ATP-bound cohesin EQEQ trimer at 3.4 Å resolution. Both front and side views are coloured by subunit. (B) Same complex as shown in A but bound to ~1.8 Kbp relaxed circular DNA as a cryo-EM field view (using Volta phase plate, left) and a selection of 2D class averages (right) clearly showing DNA emanating from cohesin/Scc2 complexes. (C) 7.3 Å resolution cryo-EM map of the complex shown in B, coloured by subunit, demonstrating that the same conformation of the complex has been obtained as with linear DNA (panel A). Same orientations and colours as in A. (D) 2D class averages obtained by reprocessing of the same data set as used for A with an enlarged box size show the position of the coiled coils and the hinge. (E) ~ 10 Å resolution cryo-EM map of the entire tetramer complex as shown in D. Since we used the same complex as used in the in vitro entrapment reactions, we can deduce that the DNA within the clamped structure depicted in A, C and E must be entrapped in both the E-S and E-K compartments.
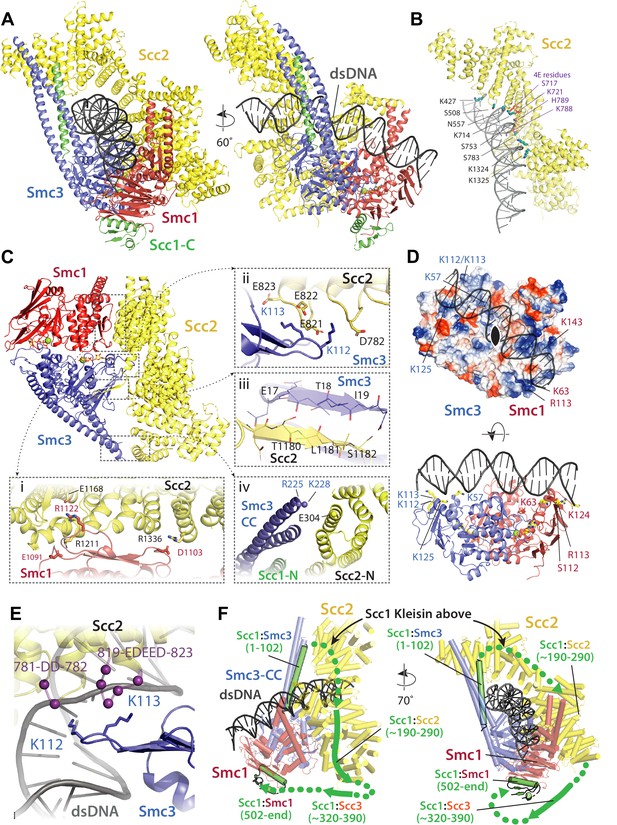
Molecular interactions in the E-S/E-K state.
(A) Cartoon representation of the refined atomic model of cohesin’s clamped (E-S/E-K) state based on the 3.4 Å resolution cryo-EM map (Figure 7A, same orientation and colours, Supplementary file 1). (B) Basic and polar residues of Scc2 involved in the interaction with DNA. Scc2 interacts only with the backbone. Residues in its vicinity are labelled in black while those mutated in Scc2-4E (Figure 4) in purple. (C) Scc2 makes extensive contacts with both Smc1 and Smc3 heads: (i) Scc2 binds Smc1 through its HEAT repeats 18–24 (residues 1127–1493) that dock onto the F-loop on Smc1 (residues 1095–1118) and the emerging coiled coils above it. (ii) Smc3’s K112 K113, whose acetylation reduces loading efficiency, are in the vicinity of a negatively charged patch on Scc2 (819-EDEED-823 and 781-DD-782). (iii) Scc2 binds to Smc3 through a β-strand (part of the otherwise disordered loop 1178–1203) that complements the central β-sheet of Smc3. (iv) The N-terminal section of Scc2 contacts parts of Smc3’s coiled coil arm/neck, close to where the last ordered region of Scc1’s N-terminal domain is bound to the Smc3 coiled coil. (D) DNA binding to the SMC head domains is pseudo-symmetrical. Top: the pseudo two-fold axis of the DNA neatly aligns with that of the head domains underneath. Bottom: The head domains interact with the DNA almost exactly two full DNA turns apart, utilising pseudo symmetry-related surfaces (Smc1: K63, S112, R113, and K124; Smc3: K57, K112, K113, and K125). (E) The two lysines K112 K113 are in contact with a negatively charged patch on Scc2 (see panel C iii), but are also in the vicinity of the DNA backbone. (F) The N-and C-terminal domains of the kleisin Scc1 bind canonically to Smc3 and Smc1, linking the heads and topologically closing the tripartite Smc1/Smc3/Scc1 (S–K) cohesin ring. A tentative path of the disordered regions of Scc1, not visible in our cryo-EM map is shown to demonstrate the topology as deduced from the loading reactions and subsequent crosslinking that show that the DNA must be outside the tripartite S-K ring.
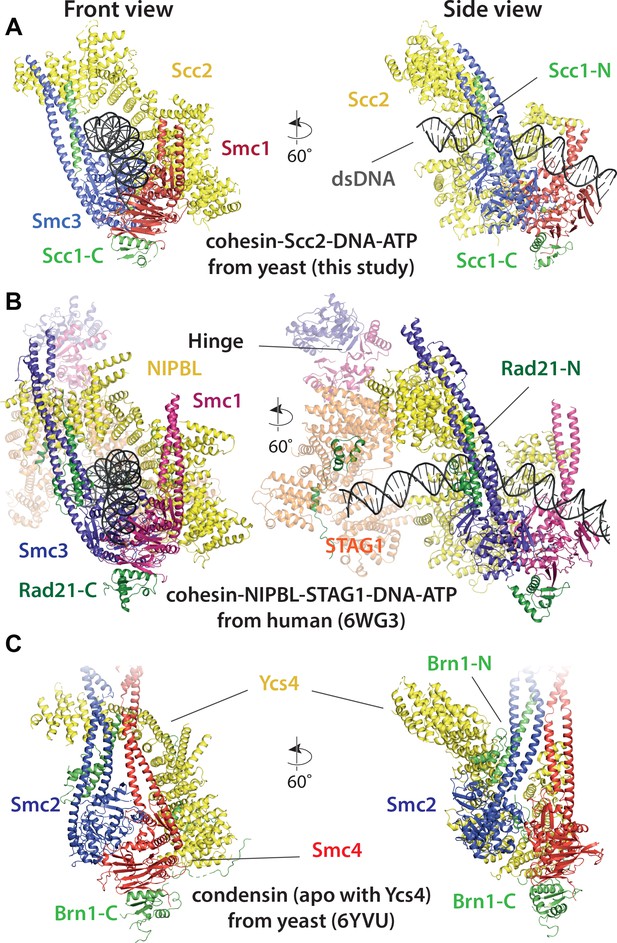
Comparison of cryo-EM structures.
(A) Cohesin tetramer (yeast, this study), (B) pentamer (human, 6WG3) (Shi et al., 2020) and (C) condensin (yeast, 6YVU) (Lee et al., 2020) are shown in two orientations (same or similar to Figures 7A and 8A).
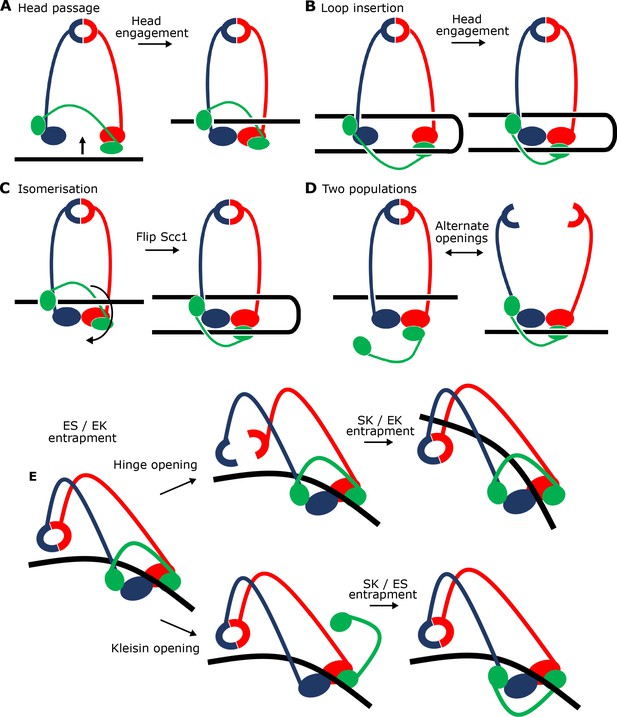
Potential mechanisms for Scc2-driven E-S/E-K entrapment and subsequent S-K ring entrapment.
(A) ES/EK entrapment by DNA passing through open heads, or (B) through a DNA loop being inserted. (C) Topological isomerism between A and B. (D) ES/EK entrapment due to two distinct populations. (E) Models for converting E-S/E-K entrapment to S-K entrapment.
Videos
A model for the formation of the clamped E-S/E-K state of cohesin.
According to this model cohesin transitions from a putative ‘bridged state’ (modelled on the same state of yeast apo condensin as observed by cryo-EM) (Lee et al., 2020) in which Scc2, analogous to Ycs4 in condensin, bridges the Smc1/3 heads. In the bridged state Scc2’s DNA binding surface becomes accessible for DNA to attach without impediment and positions it for the next step, namely clamping. ATP-binding driven head engagement, achieved through a rotation of the Smc3 head relative to the rest of the complex, and with Scc2’s and Smc1’s relative orientations staying the same, results in entrapment in the E-S compartment. Because the disordered kleisin chain has to be pushed upwards during the clamping, the DNA is also in the E-K compartment. The initial binding of DNA to the Scc2 DNA binding site guides the DNA through the large opening of the heads generated by the bridged state and leads to the final clamped state that has been described in this study. The video is a simple morph between a putative bridged state of cohesin modelled on the same state in condensin and the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of the clamped state determined in this study, with a few clashes removed manually because cohesin and condensin subunits, in particular Scc2 and Ycs4, are not completely homologous structurally.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1 promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3 Scc3-PK3-aid::KanMX4 SCC1-HA3::HIS3 | This study | KN20783 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa Scc3-PK3-aid::KanMX4 SCC1-HA3::HIS3 | This study | KN20785 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa/alpha scc3::NatMX4/WT | This study | KN21079 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa/alpha scc3::NatMX4/WT, leu::Scc3-HA3::LEU | This study | KN21273 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa Scc1-PK9::KanMX scc2-45::natMX (L545P D575G) | This study | KN22390 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. glabrata) | MATa, SCC1-PK9::NATMX4 | Petela et al., 2018 | KN23308 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa Scc1-PK9::KanMX scc2-45::natMX (L545P D575G) lys2::Scc2-HyGMX | This study | KN24185 | |
| Strain, strain background (C. glabrata) | MATa, SCC1-HA3::NATMX4 | Petela et al., 2018 | KN25532 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa Scc1-PK9::KanMX scc2-45::natMX (L545P D575G) LYS2::Scc2(S717L,K721E)-HygMX | This study | KN27010 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa/alpha scc3::NatMX4/WT, leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27539 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa scc3::NatMX4, Scc1-PK6::TRP1, leu::Scc3-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27542 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MAT alpha scc3::NatMX4, Scc1-PK6::TRP1, leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27547 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa/alpha scc3::NatMX4/WT, leu::Scc3 (K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27696 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa scc3::NatMX4, Scc1-PK6::TRP1, leu::Scc3 (K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27697 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa/alpha scc3::NatMX4/WT, leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E, K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27763 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-PK3-aid::KanMX4, leu::Scc3-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27796 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1 promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-PK3-aid::KanMX4 leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E, K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27802 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-HA3-aid::KanMX4, Scc1-PK6::TRP1, leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E, K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27804 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-HA3-aid::KanMX4, Scc1-PK6::TRP1, leu::Scc3-HA3::LEU | This study | KN27821 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-HA3-aid::KanMX4, leu::Scc3-HA3::LEU, Scc2-PK9::NatMX | This study | KN28075 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. cerevisiae) | MATa ura::ADH1 promoter-OsTIR1-9myc::URA3, Scc3-HA3-aid::KanMX4, Scc2-PK9::NatMX, leu::Scc3 (K224E, K225E, R226E, K423E, K513E, K520E)-HA3::LEU | This study | KN28287 | |
| Strain, strain background (S. frugiperda) | Sf9 insect cells | ThermoFisher | Cat# 11496015 | |
| Antibody | Anti-His (mouse) | Sigma | Cat# SAB1305538-400UL | 1:2000 |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse HRP | ThermoFisher | Cat# 62–6520 | 1:5000 |
| Antibody | Anti-Smc3 (mouse) | Bethyl Laboratories | Cat# A300-060A | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Strep HRP | iba | Cat# 2-1502-001 | 1:4000 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 SMC1-His | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 SMC3 | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 SMC1-His SMC3 | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 Scc2133-1493-2xStrepII | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 SCC2-2xStrepII | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 2xStrepII-Scc2151-1493 | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pACEbac1 2xStrepII-SCC3 | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIDC SCC1-2xStrepll | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIDC Scc1269-451-2xStrepII | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIDC Scc1150-298-2xStrepII | This Study | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIDC His-SCC4 | This Study | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | ATP Lithium Salt | Sigma | Cat# 11140965001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bismaleimidoethane (BMOE) | ThermoFisher | Cat# 22323 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Complete EDTA free protease inhibitor cocktail | Roche | Cat# 4693132001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cre Recombinase | New England Biolabs | Cat# M0298S | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Desthiobiotin | Fisher Scientific | Cat# 12753064 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EtBr | ThermoFisher | Cat# 15585011 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Fetal Bovine Serum | Sigma | Cat# 12303C | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FuGENE HD Transfection reagent | Promega | Cat# E2311 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Gibson Assembly Mix | New England Biolabs | Cat# E2611L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Immobilon Western ECL | Millipore | Cat# WBLKS0500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NuPAGE 3–8% Tris-Acetate Protein Gels | ThermoFisher | Cat# EA0378BOX | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PMSF | Sigma | Cat# 329-98-6 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Quick Coomassie Stain | Generon | Cat# GEN-QC-STAIN | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RNase A | Roche | Cat# 10109169001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sf900 II SFM | ThermoFisher | Cat# 10902104 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Supernuclease | SinoBiological | Cat# SSNP01 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TCEP | ThermoFisher | Cat# 20490 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4xLDS | ThermoFisher | Cat# NP0007 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 200 | GE Healthcare | Cat# GE28-9893-35 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiSpeed Plasmid Maxi Kit | Qiagen | Cat# 12663 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiTrap Q HP | GE Healthcare | Cat# GE29-0513-25 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | StrepTrap HP | Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11540654 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL | VWR | Cat# 29-0915-96 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | EnzChek phosphate assay kit | Invitrogen | Cat# E6646 | |
| Software, algorithm | RELION 3.1 | doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2012.09.006 | ||
| Software, algorithm | CtfFind4 | doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2015.08.008 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Warp | doi:10.1038/s41592-019-0580-y | ||
| Software, algorithm | CrYOLO 1.5 | doi:10.1038/s42003-019-0437-z | ||
| Software, algorithm | Chimera | https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/ | ||
| Software, algorithm | ChimeraX 1.0 | https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ | ||
| Software, algorithm | COOT | doi:10.1107/S0907444910007493 | ||
| Software, algorithm | MAIN | doi:10.1107/S0907444913008408 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Phenix.real_space_refinement | doi:10.1107/S2059798318006551 | ||
| Software, algorithm | PYMOL 2 | https://pymol.org/2/ | ||
| Software, algorithm | SWISS-MODEL | https://swissmodel.expasy.org | ||
| Other | Quantifoil Au 2/2 holely carbon 200 mesh cryoEM grids | Quantifoil GmbH | ||
| Other | Ultrafoil 2/2 holely gold 200 mesh cryoEM grids | Quantifoil GmbH |





