LRRC8A is essential for hypotonicity-, but not for DAMP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Figures
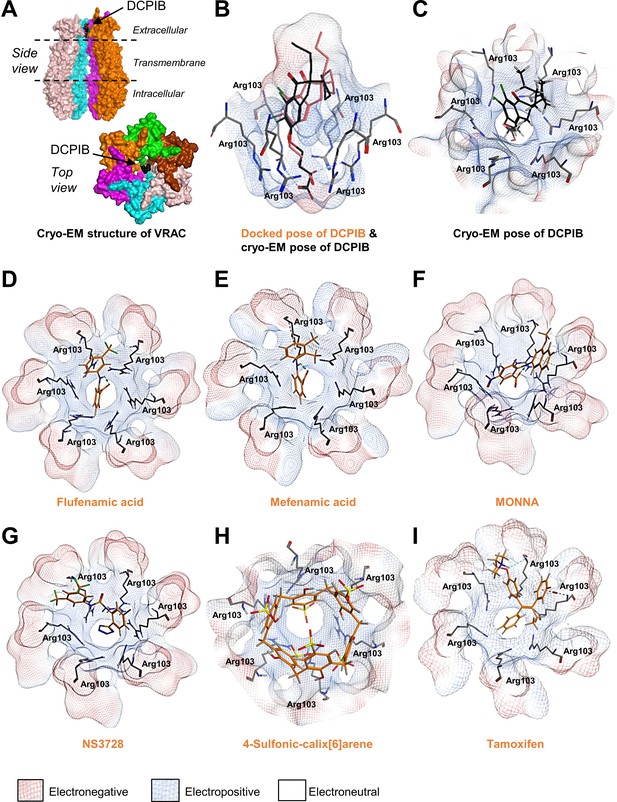
Modelling of proposed VRAC inhibitors on the Cryo-EM structure of LRRC8 channels.
(A) Two orthogonal views: a side view with two chains removed from the hexameric LRRC8A protein with bound DCPIB and a top view for the hexameric VRAC channel (PDB:6NZW). (B, D–I) Docked VRAC inhibitors (orange) in the VRAC Arg103 extracellular selectivity filter. Protein surface coloured according to electrostatics: electronegative (red), electropositive (blue), and electroneutral (white). (B) MM/GBVI binding energies of docked DCPIB (orange) in VRAC (−5.2 kcal mol−1) in a side view superimposed on the cryo-EM DCPIB pose (black). (C) Top-view of cryo-EM pose of DCPIB (black) in VRAC. (D) Flufenamic acid (−5.1 kcal mol−1) (E) Mefenamic acid (−5.2 kcal mol−1) (F) MONNA (−5.8 kcal mol−1) (G) NS3728 (−6.4 kcal mol−1) (H) 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene (−9.9 kcal mol−1) (I) Tamoxifen (−6.5 kcal mol−1).
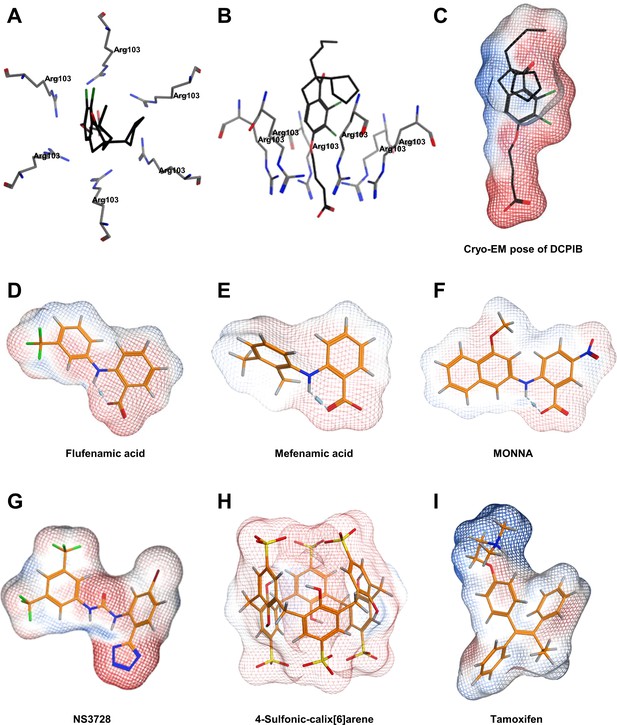
Further modelling of VRAC inhibitors.
(A) Top view and (B) side view of the cryo-EM structure of DCPIB in the arginine pore of VRAC (C–I). Molecular surfaces coloured by electrostatic potential for the docked poses of VRAC inhibitors, indicating regions of negative (red) and positive (blue) potential. (C) Cryo-EM pose of DCPIB. Docked poses of (D) Flufenamic acid (E) Mefenamic acid (F) MONNA (G) NS3728 (H) 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene and (I) tamoxifen.
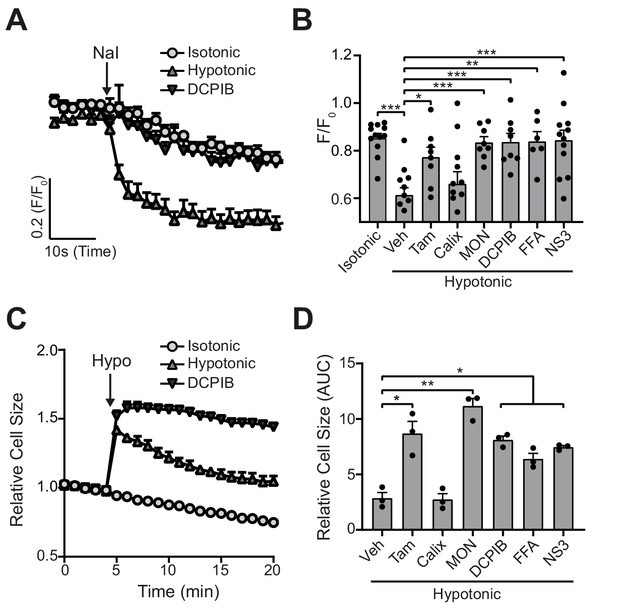
VRAC inhibitors block hypotonicity-induced Cl- channel opening and regulatory volume decrease (RVD).
(A) Cl- channel opening measured in HeLa cells transiently expressing the halide-sensitive EYFP (H148Q/I152L). HeLa cells were pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO) or DCPIB (10 µM) and incubated in an isotonic (310 mOsm kg−1) or hypotonic (215 mOsm kg−1) solution for 5 min before quenching by addition of NaI (40 mM). (B) Normalised EYFP (H148Q/I152L) fluorescence values from HeLa cells pre-treated with either a vehicle control (DMSO), tamoxifen (Tam, 10 µM), 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene (Calix, 100 µM), MONNA (MON, 50 µM), DCPIB (10 µM), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM) or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM). Cells were incubated an isotonic (310 mOsm kg−1) or hypotonic (215 mOsm kg−1) solution for 5 min before quenching by addition of NaI. Fluorescent measurement was taken 30 s after NaI addition (n = 6–12). (C) Relative cell size of murine bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) incubated in isotonic (340 mOsm kg−1) or hypotonic (117 mOsm kg−1) solution, pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO) or DCPIB (10 µM). BMDMs were labelled with the fluorescent dye calcein and area of fluorescence was measured over time. (D) Area under the curve of BMDMs incubated in a hypotonic solution (117 mOsm kg−1) in the presence of either a vehicle control (DMSO), tamoxifen (Tam, 10 µM), 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene (Calix, 100 µM), MONNA (MON, 50 µM), DCPIB (10 µM), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM) or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) (n = 3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.01 determined by a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (vs vehicle control) post hoc analysis. Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59704/elife-59704-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
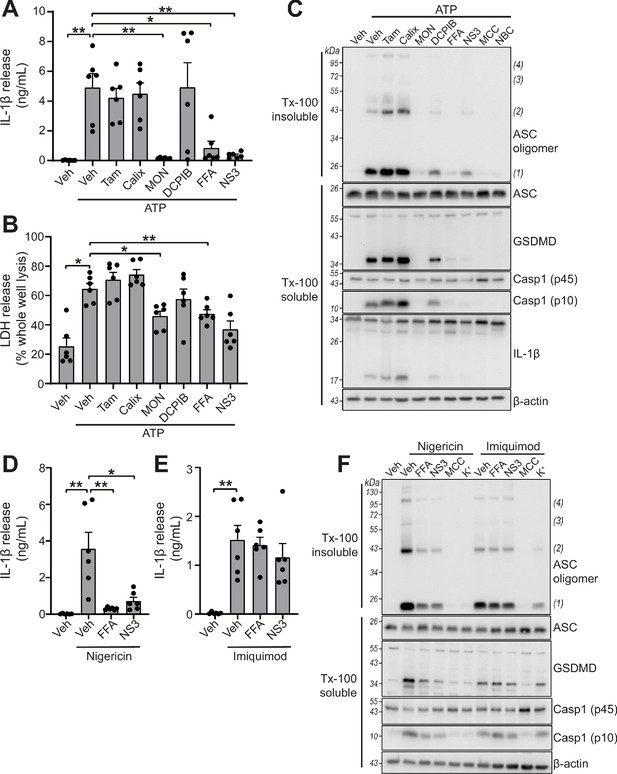
VRAC inhibitors differentially regulate NLRP3.
(A) IL-1β release was determined by ELISA on supernatants from murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs). LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs were pre-treated with either a vehicle control (DMSO), tamoxifen (Tam, 10 µM), 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene (Calix, 100 µM), MONNA (MON, 50 µM), DCPIB (10 µM), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM), or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) before stimulation with ATP (5 mM, 2 hr) (n = 6). (B) Cell death determined by an LDH assay of cells treated in (A). (C) Western blot of Triton x-100 insoluble crosslinked ASC oligomers and soluble total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for ASC, GSDMD, caspase-1 and IL-1β. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs were pre-treated with either a vehicle control (DMSO), tamoxifen (Tam, 10 µM), 4-sulfonic calix[6]arene (Calix, 100 µM), MONNA (MON, 50 µM), DCPIB (10 µM), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM), NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) or the NLRP3 inhibitors MCC950 (MCC, 10 µM) and NBC19 (NBC, 10 µM) before stimulation with ATP (5 mM, 2 hr) (n = 3). (D) IL-1β release from LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM), or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) before stimulation with nigericin (10 µM, 2 hr) (n = 6). (E) IL-1β release from LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM) or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) before stimulation with imiquimod (75 µM, 2 hr) (n = 6). (F) Western blot of Triton x-100 insoluble crosslinked ASC oligomers and soluble total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for ASC, GSDMD, and caspase-1. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs were pre-treated with either a vehicle control (DMSO), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM), NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM), the NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 (MCC, 10 µM) or KCl (K+, 25 mM) before stimulation with nigericin (10 µM, 2 hr) or imiquimod (75 µM, 2 hr) (n = 3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, determined by a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (vs vehicle control) post hoc analysis. Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
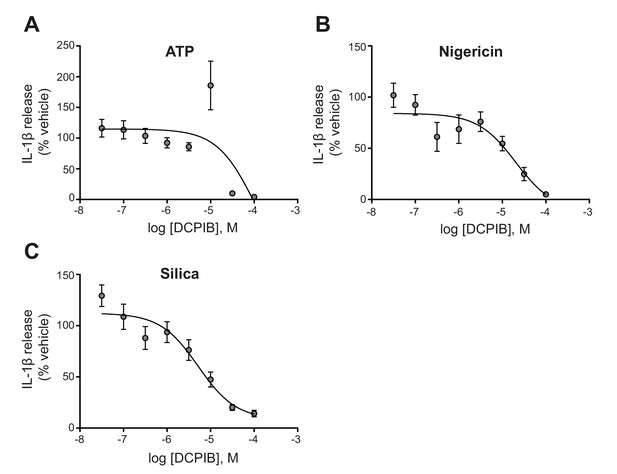
Dose-response curve for DCPIB.
IL-1β release detected by ELISA on supernatants from LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) pre-treated with the indicated dose of DCPIB (0.03–100 µM, 15 min) before stimulation with ATP (5 mM), nigericin (10 µM), or silica (300 µg mL−1) for 2 hr (n = 6). Experiments with different stimuli were performed in parallel. IL-1β release was normalised to that of vehicle (DMSO)-treated BMDMs. Dose-response curves were fitted using a three parameter logistical (3PL) model. Values shown are mean ± the SEM.
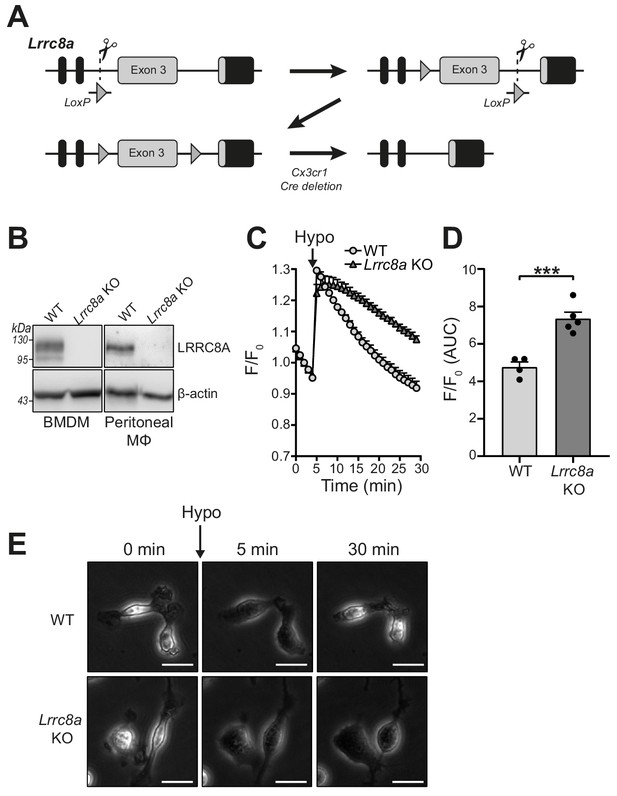
Lrrc8a KO macrophages are unable to undergo hypotonicity-induced regulatory volume decrease (RVD).
(A) Generation of LRRC8A conditional allele. LRRC8A is found on mouse chromosome two and consists of four exons. Untranslated sequences are represented by black boxes, and coding sequences by grey boxes. Exon three contains the vast majority of coding sequence and was flanked by loxP sites in two sequential steps, first integrating the 5’ LoxP by CRISPR-Cas9 (scissors) mediated double strand break and the supply of a homology flanked ssODN repair template containing the loxP site (grey triangle). This 5’ fl background was then bred to establish a colony and the process repeated to integrate the second 3’ loxP on this background. At each step, integration of loxP was confirmed by PCR and Sanger sequencing. Finally crossing with a Cre driver knocked into the Cx3cr1 locus results in recombinase mediated excision of Exon 3. (B) Western blot of LRRC8A from wild-type (WT) or Lrrc8a knockout (KO) bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and peritoneal macrophages (Mϕ) (n = 3). (C) Regulatory volume decrease measured by calcein fluorescence in WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs incubated in a hypotonic buffer (117 mOsm kg−1) (n = 4–5). (D) Area under the curve (AUC) analysis of (C) (n = 4–5). (E) Representative phase contrast images of WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs incubated in a hypotonic buffer (117 mOsm kg−1) at indicated time points (n = 3, Scale = 20 µm). ***p<0.001 determined by an unpaired t-test. Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
source data for data shown in Figure 4C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59704/elife-59704-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
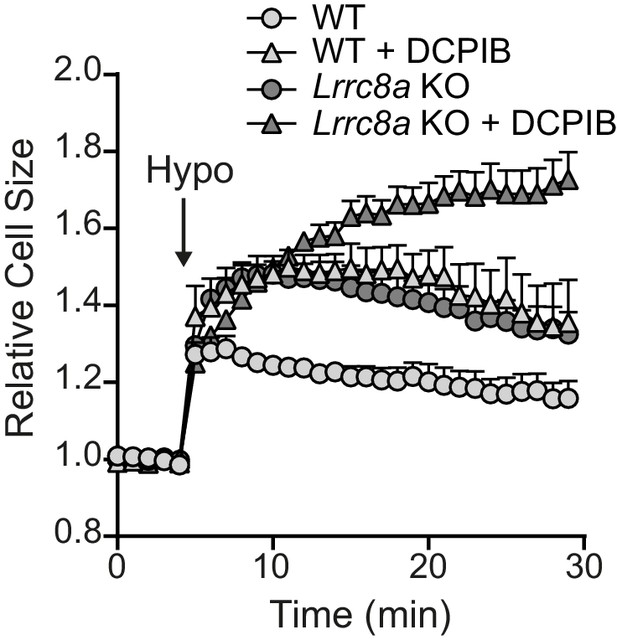
Effect of VRAC inhibitors on the RVD response of WT and Lrrc8a KO BMDMs.
Relative cell size of wild-type (WT) or Lrrc8a knockout (KO) murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) incubated in isotonic (340 mOsm kg−1) or hypotonic (117 mOsm kg−1) solution, pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO) or DCPIB (10 µM) (n = 5). BMDMs were labelled with the fluorescent dye calcein and area of fluorescence was measured over time. These data were generated from the same experiment shown for the Figure 4C–D (vehicle traces). Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
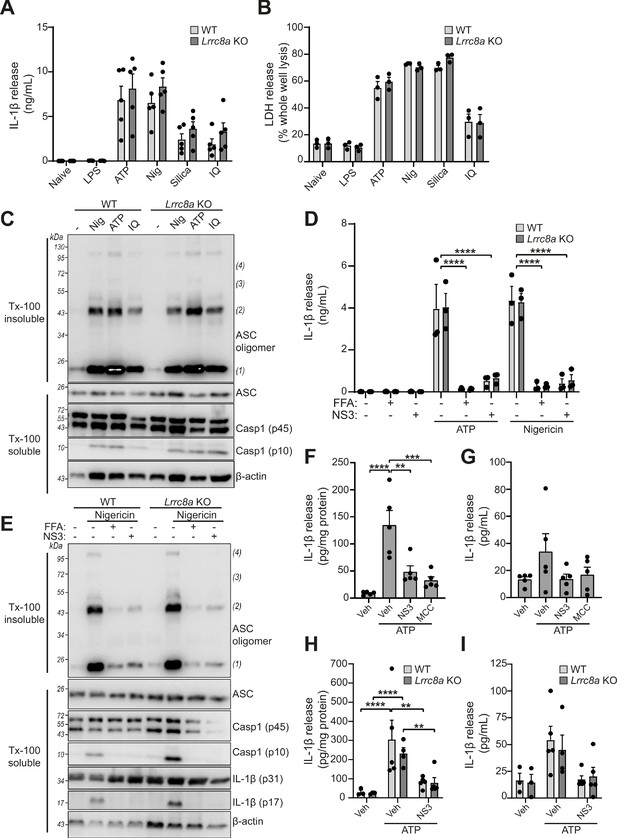
LRRC8A is dispensable for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
(A) IL-1β release was determined by ELISA on supernatants from wild-type (WT) or Lrrc8a knockout (KO) bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Naïve or LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) BMDMs were stimulated with either vehicle, ATP (5 mM), nigericin (Nig, 10 µM), silica (300 µg mL−1) or imiquimod (IQ, 75 µM) for 2 hr (n = 5). (B) Cell death determined by an LDH assay of cells treated in (A) (n = 3). (C) Western blot of Triton x-100 insoluble crosslinked ASC oligomers and soluble total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for ASC and caspase-1. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs were stimulated with either nigericin (Nig, 10 µM), ATP (5 mM) or imiquimod (IQ, 75 µM) for 2 hr (n = 3). (D) IL-1β release from LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs pre-treated with a vehicle control (DMSO), flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM) or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) and then stimulated with ATP (5 mM) or nigericin (10 µM) for 2 hr (n = 3). (E) Western blot of Triton x-100 insoluble crosslinked ASC oligomers and soluble total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for ASC, caspase-1 and IL-1β. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs were pre-treated with a vehicle control, flufenamic acid (FFA, 100 µM) or NS3728 (NS3, 10 µM) and stimulated with nigericin (10 µM, 2 hr) (n = 5). (F–G) IL-1β detected by ELISA in the peritoneal lavage (F) or plasma (G) from WT mice. Mice were pre-treated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with a vehicle control, NS3728 (NS3, 50 mg kg−1) or MCC950 (MCC, 50 mg kg−1) and LPS (1 µg). 4 hr after injection with LPS, mice were anaesthetised and injected with additional vehicle control, NS3728 (NS3, 50 mg kg−1) or MCC950 (MCC, 50 mg kg−1) before i.p. injection of ATP (100 mM, 500 µL, 15 min) (n = 5). (H–I) IL-1β detected by ELISA in the peritoneal lavage (H) or plasma (I) from Lrrc8a KO and WT littermates as treated in (F) (n = 3–5). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 determined by a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (vs vehicle control) post hoc analysis (F,G) or a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis (A,B,D,H,I). Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
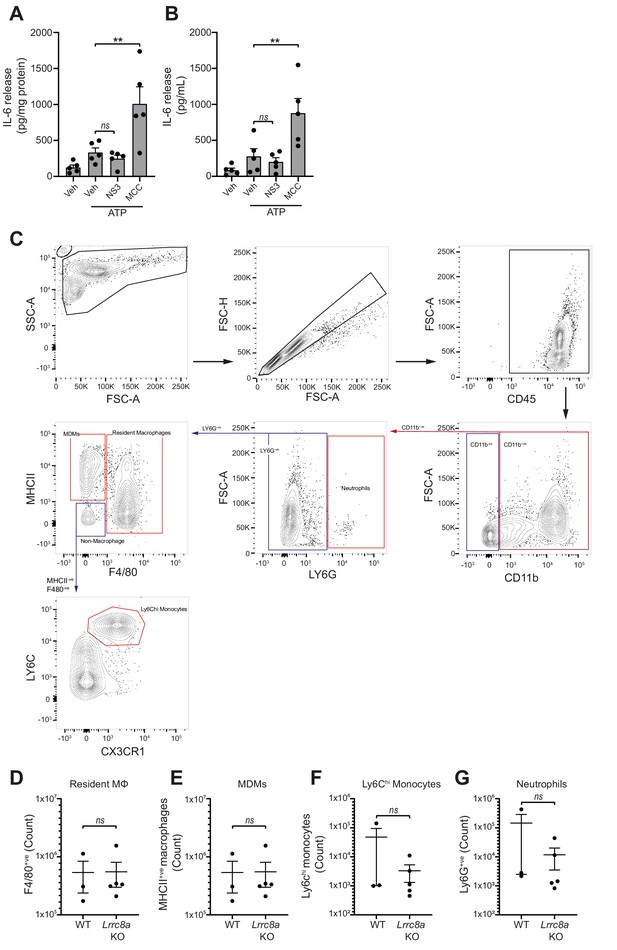
Loss of LRRC8a does not affect myeloid populations in the peritoneum.
(A–B) IL-6 detected by ELISA in the peritoneal lavage (A) or plasma (B) from wild-type mice. Mice were pre-treated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with a vehicle control, NS3728 (NS3, 50 mg kg−1) or MCC950 (MCC, 50 mg kg−1) and LPS (1 µg). 4 hr after injection with LPS, mice were anaesthetised and injected with additional vehicle control, NS3728 (NS3, 50 mg kg−1) or MCC950 (MCC, 50 mg kg−1) before i.p. injection of ATP (100 mM, 500 µL, 15 min) (n = 5). NS3728 treatment did not significantly alter IL-6 levels. Injection of MCC950 significantly enhanced IL-6 release in the peritoneum and plasma compared to vehicle. (C–G) Flow cytometry of immune cells in naïve peritoneal lavage from WT or Lrrc8a KO mice (n = 3–5). Representative gating strategy (C) and quantification of immune cells (D–G). Immune cells were initially gated on CD45+ve/CD11b+ve cells and cell populations were identified as follows: neutrophils (LY6Ghi), monocyte-derived-macrophages (MDMs) (LY6G-ve/MHCIIhi/F4/80-ve), resident macrophages (Mϕ) (LY6G-ve/F4/80hi), and Ly6Chi monocytes (LY6G-ve/MHCII-ve/F4/80-ve/CX3CR1hi/Ly6Chi). ns not significant, **p<0.01 determined by a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (vs vehicle control) post hoc analysis (A,B) or an unpaired t-test (D–G). Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
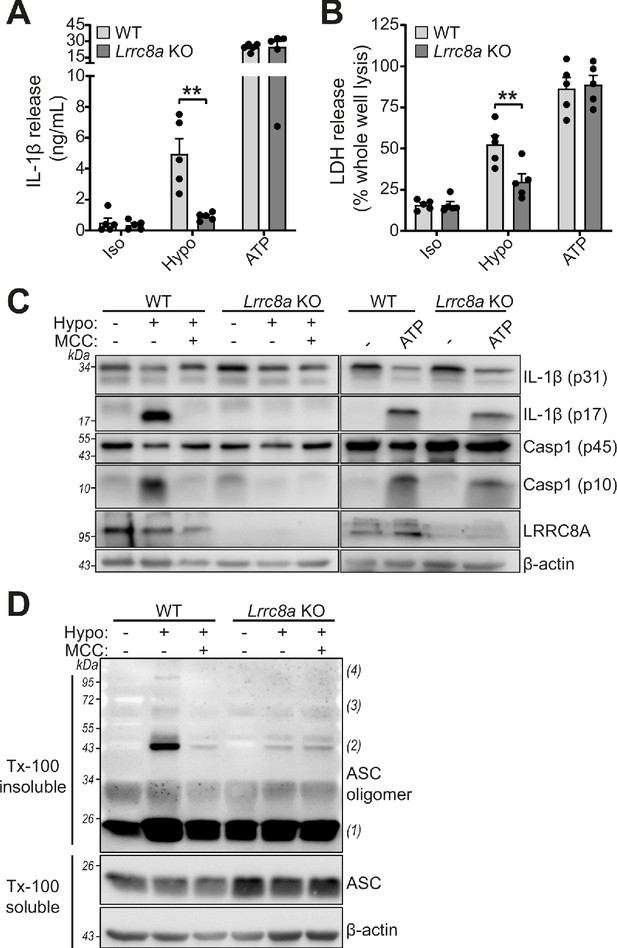
LRRC8A is an essential component of hypotonicity-induced NLRP3 activation.
(A) IL-1β release was determined by ELISA on supernatants from wild-type (WT) or Lrrc8a knockout (KO) bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs). LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) wild-type (WT) or Lrrc8a knockout (KO) BMDMs were incubated in either an isotonic buffer (340 mOsm kg−1), hypotonic buffer (117 mOsm kg−1) or isotonic buffer with ATP (5 mM) for 4 hr (n = 5). (B) Cell death determined by an LDH assay of cells treated in (A). (C) Western blot of total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for IL-1β, caspase-1 and LRRC8A. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs were pre-treated with a vehicle control or a NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 (MCC, 10 µM) before incubation in either an isotonic buffer (340 mOsm kg−1), hypotonic buffer (117 mOsm kg−1) or isotonic buffer with ATP (5 mM) for 4 hr. (D) Western blot of Triton x-100 insoluble crosslinked ASC oligomers and soluble total BMDM cell lysates (cell lysate + supernatant) probed for ASC. LPS-primed (1 µg mL−1, 4 hr) WT or Lrrc8a KO BMDMs were pre-treated with a vehicle control or MCC950 (MCC, 10 µM) and incubated in either an isotonic buffer (340 mOsm kg−1), hypotonic buffer (117 mOsm kg−1) for 4 hr (n = 3). **p<0.01 determined by a two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values shown are mean plus the SEM.
Videos
Phase contrast time-lapse of the regulatory volume decrease of wild-type (WT) littermate bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).
WT BMDMs were incubated in an isotonic buffer (340 mOsm kg−1) for 5 min before dilution to a hypotonic solution (117 mOsm kg−1) for the duration of the recording. Images were captured every minute (n = 3, Scale = 20 µm).
Phase contrast time-lapse of the regulatory volume decrease of Lrrc8a knockout (KO) bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).
Lrrc8a KO BMDMs were incubated in an isotonic buffer (340 mOsm kg−1) for 5 min before dilution to a hypotonic solution (117 mOsm kg−1) for the duration of the recording. Images were captured every minute (n = 3, Scale = 20 µm).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6J | Charles River | C57BL/6NCrl | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | C57BL/6J.LRRC8AEm1Uman (Lrrc8afl/fl) | This paper | Line maintained by David Brough lab, University of Manchester | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | B6J.B6N(Cg)-Cx3cr1tm1.1(cre)Jung/J | Jackson lab | Stock No: 025524 RRID:IMSR_JAX:025524 | Obtained from breeding colony managed by John Grainger lab (University of Manchester) |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | Bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) | In house | Generated from bone marrow from above mouse lines | |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | Peritoneal macrophages | In house | Generated by peritoneal lavage from above mouse lines | |
| Cell line (Homo Sapien) | HeLa | ATCC | HeLa (ATCC CCL-2) RRID:CVCL_0030 | |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IL-1β (goat polyclonal) | R and D Systems | AF-401-NA RRID:AB_416684 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-Caspase1 + p10 + p12 (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab179515 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti- mouse GSDMD (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab209845 RRID:AB_2783550 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse ASC/TMS1 (D2W8U) (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 67824 RRID:AB_2799736 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | LRRC8A (8H9) (mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-517113 | (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-β-Actin−Peroxidase (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma | A3854 RRID:AB_262011 | (1:20000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit Immunoglobulins HRP (goat polyclonal) | Agilent | P044801-2 RRID:AB_2617138 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse Immunoglobulins HRP (rabbit polyclonal) | Agilent | P026002-2 RRID:AB_2636929 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Goat Immunoglobulins HRP (rabbit polyclonal) | Agilent | P044901-2 | (1:1000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA3.1 Hygro EYFP H148Q/I152L | Addgene | 25874 RRID:Addgene_25874 | A gift from Peter Haggie |
| Commercial assay or kit | CytoTox 96 Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity (LDH) Assay | Promega | G1780 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Mouse IL-1β/IL-1F2 DuoSet ELISA | R and D systems | DY401 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli O26:B6 | Sigma | L2654 | For in vitro experiments |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli O127:B8 (in vivo) | Sigma | L3880 | For in vivo experiments |
| Chemical compound, drug | Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) | Sigma | A2383 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nigericin sodium salt | Sigma | N7143 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Silica | U.S. Silica | MIN-U-SIL 15 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Imiquimod | InvivoGen | R837 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen | Sigma | T5648 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4-Sulfonic calix[6]arene Hydrate | Thermo Fisher | 10494735 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4-[(2-Butyl-6,7-dichloro-2-cyclopentyl-2,3-dihydro-1-oxo-1H-inden-5-yl)oxy]butanoic acid (DCPIB) | Tocris | 1540 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Flufenamic acid (FFA) | Sigma | F9005 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NS3728 | David Brough Lab, University of Manchester | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | CP-456773 sodium salt (MCC950) | Sigma | PZ0280 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NBC19 | David Brough Lab, University of Manchester | PMID:28943355 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Calcein, AM, cell-permeant dye | Thermo Fisher | C1430 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Disuccinimidyl suberate (DSS) | Thermo Fisher | 21555 |





