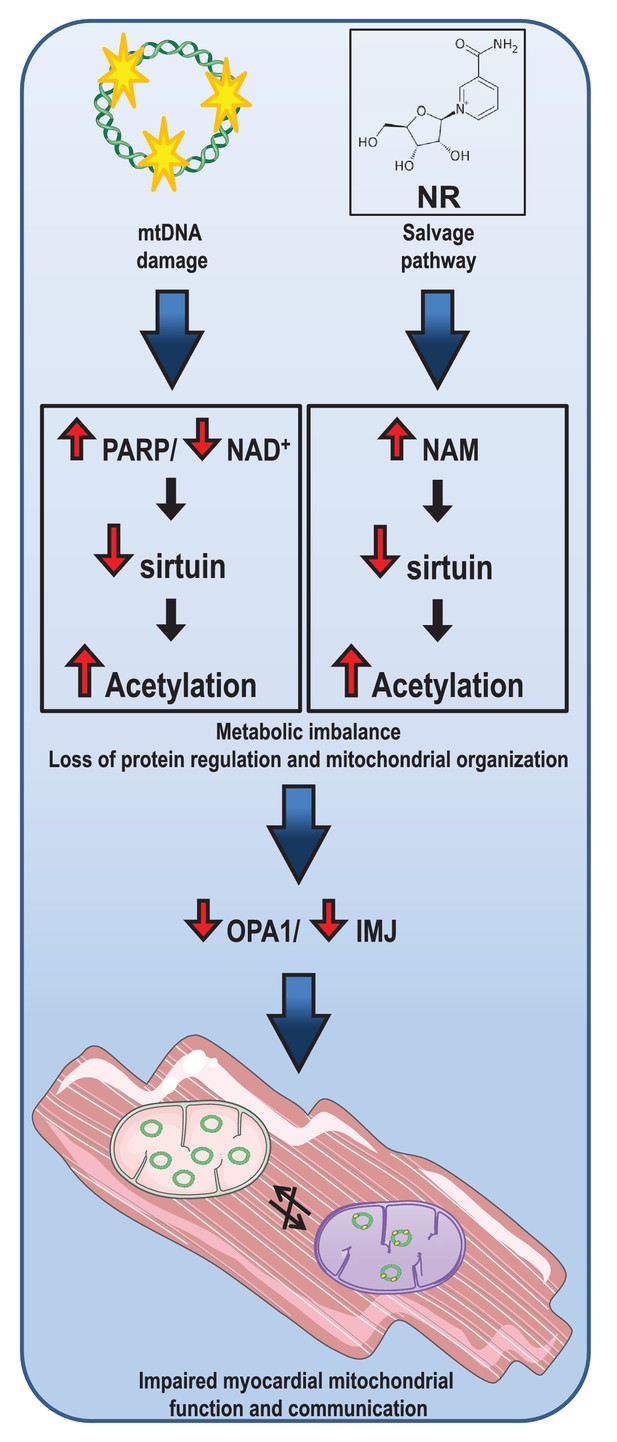
Instability in NAD+ metabolism leads to impaired cardiac mitochondrial function and communication
Figures
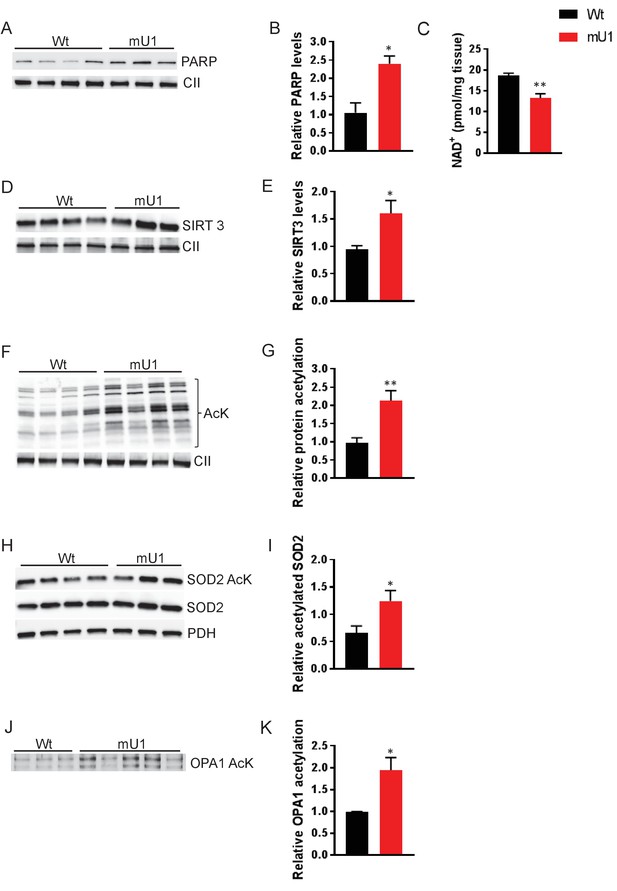
Elevated PARP activity depletes cardiac NAD+ levels and reduces mitochondrial protein deactylation.
(A) Western blot showing PARP levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates. (B) Quantification of PARP levels in western blot. (C) NAD+ levels from heart tissue from wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice measured with HPLC. (D) Western blot of SIRT3 levels in extract of mitochondria isolated from cardiac tissue from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates. (E) Quantification of SIRT3 levels in western blot. (F) Western blot of protein acetylation levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates. (G) Quantification of protein acetylation levels in western blot. (H) Western blot of SOD2 and acetylated SOD2 levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates. (I) Quantification of relative acetylated SOD2 protein levels in western blot. (J) Western blot acetylated protein levels of samples of immunoprecipitated OPA1 from total extract (200 µg protein) of cardiac tissue from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates. (K) Quantification of relative acetylated OPA1 protein levels in western blot. Data is presented as mean ± SE. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Wt chow. Abbreviations: Wt = Wild-type mice, mU1 = mutUNG1-expressing mice, PARP = poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, CII = mitochondrial complex II, SIRT3 = sirtuin 3, AcK = acetylated lysine, SOD2 = superoxide dismutase 2, PDH = pyruvate dehydrogenase, OPA1 = optic atrophy 1, and NAD+ = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Raw data are presented in Source data 1.
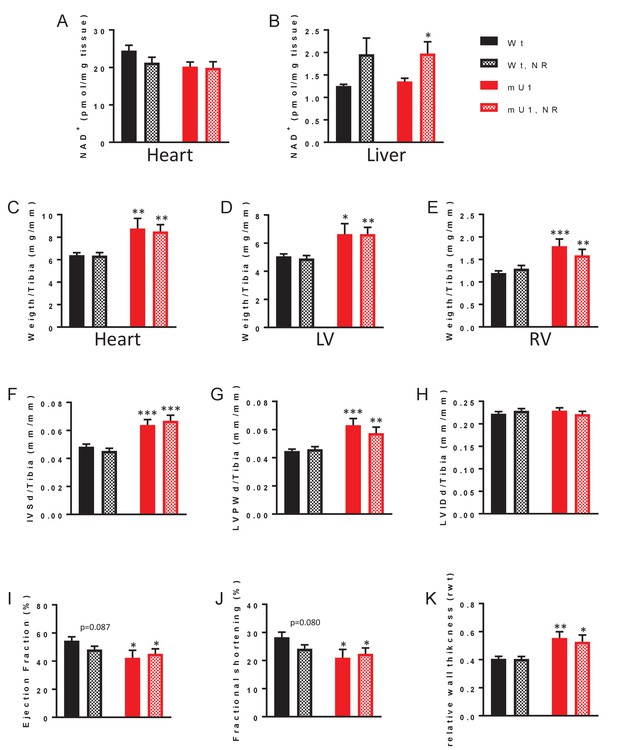
Elevation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels through nicotinamide riboside (NR) treatment does not mitigate cardiac hypertrophy in mutUNG1-expressing mice.
NAD+ levels in heart tissue (A) and liver tissue (B) from wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with or without NR, measured by HPLC. Weight of (C) heart, (D) left ventricle, and (E) right ventricle of wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with or without NR. Echocardiographic measurement of (F) interventricular septum thickness at end-diastole, (G) left ventricular posterior wall thickness, (H) left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole, (I) ejection fraction, (J) fractional shortening, and (J) relative wall thickness at end-diastole in wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with or without NR. (C-H) Normalized against tibia length. Data is presented as mean ± SE. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. Wt chow (for C-J, N = Wt; 15, Wt-NR; 17, mU1; 8, mU1-NR; 11). Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
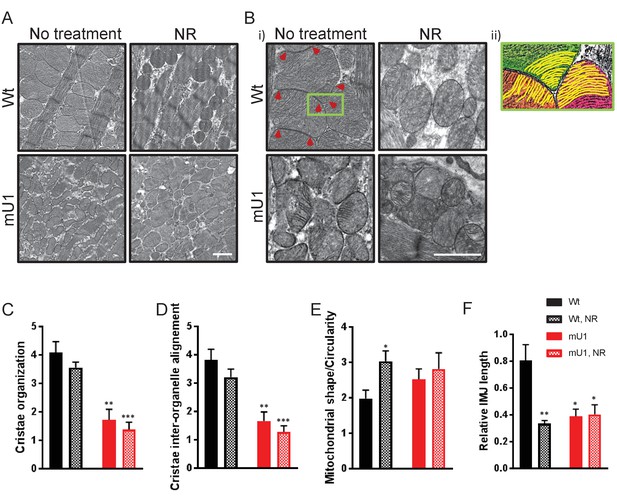
Nicotinamde riboside (NR) treatment does not alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction in mutUNG1-expressing mice, but does alter mitochondrial morphology in wild-type mitochondria.
(A and B) Electron microscope images of wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with and without NR. (B, ii) Detail of panel from (B) with an Illustration of aligned cristae (yellow) in three neighboring mitochondria (orange, green, and pink) in wild-type cardiac tissue. Electron-dense inter-mitochondrial junctions (IMJs) labeled with red arrowheads. The images are representative of five mice of each genotype and treatment. Scalebar = 1 µM. Analysis by scoring of (C) cristae organization, (D) cristae inter-organelle alignment, and (E) mitochondrial shape/circularity. (F) Quantification of relative IMJ length. Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
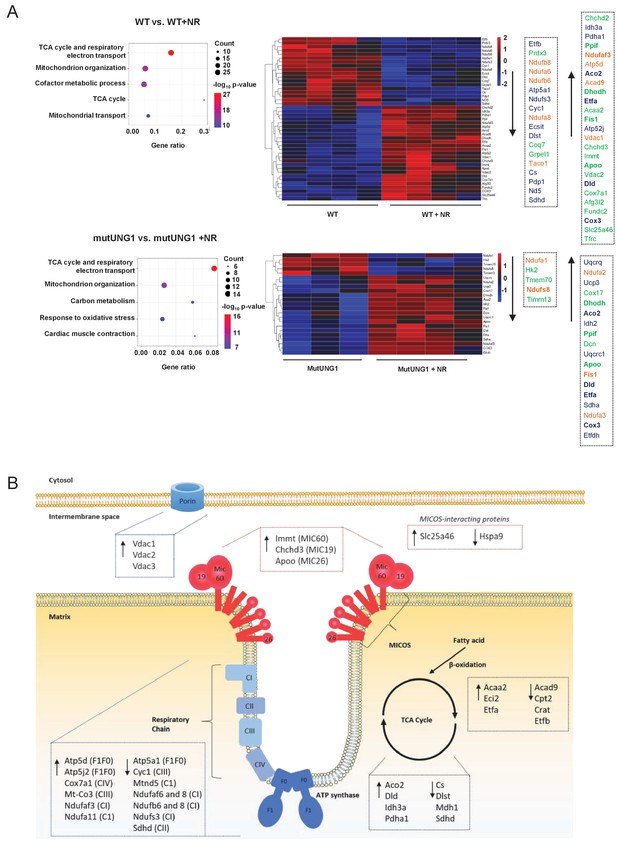
Proteom analyses support structural effects of nicotinamde riboside (NR) treatment on mitochondria.
(A) Proteomic analysis of cardiac mitochondrial extract evaluating the effect of NR supplement in Wt and mutUNG1 mice. Shown are top five members by gene enrichment analysis. The differently regulated proteins (DEPs) included in the gene ontology terms the citric acid (TCA) cycle and respiratory electron transport (blue) and mitochondrial organization (green) are shown in the heatmap. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) included in both pathways are marked in orange. (B) A simplified illustration modified from Pfanner et al., 2019 including important regulators of the cristae structure. The selection of DEPs is based on the gene enrichment analysis. Analysis is based on data presented in Source data 1.
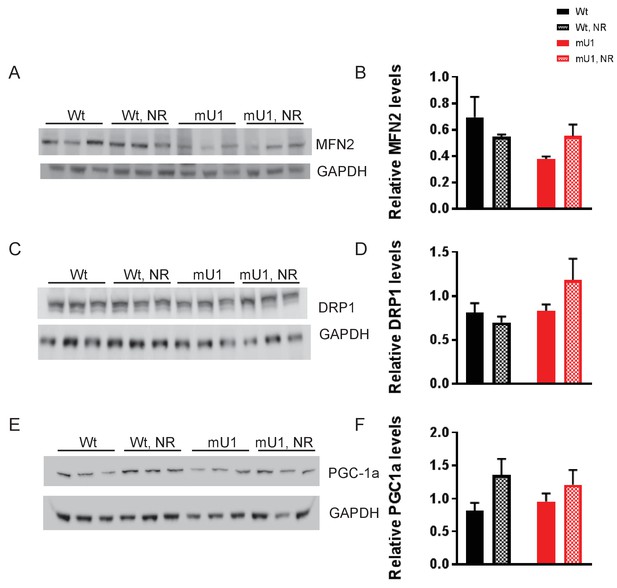
Protein levels of mitofusin 2 (MFN2), dynamin-related protein (DRP1), and peroxisome proliferator-activator receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1a) in mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates.
(A) Western blot showing MFN2 levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without nicotinamde riboside (NR). (B) Quantification of MFN2 levels in western blot. (C) Western blot showing DRP1 levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without NR. (D) Quantification of DRP1 levels in western blot. (E) Western blot showing PGC-1a levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without NR. (F) Quantification of PGC-1a levels in western blot. Raw data are presented in Source data 3.
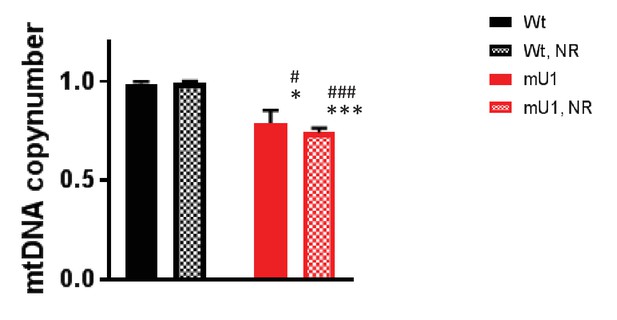
mtDNA copy numbers.
Rt-PCR analysis of total DNA shows a decrease in mtDNA copy number in mutUNG1-expressing mice compared with wild-type littermates fed chow with or without nicotinamde riboside (NR) (*p=0.048, ***p=0.001, #p=0.45, and ###p=0.00095). Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
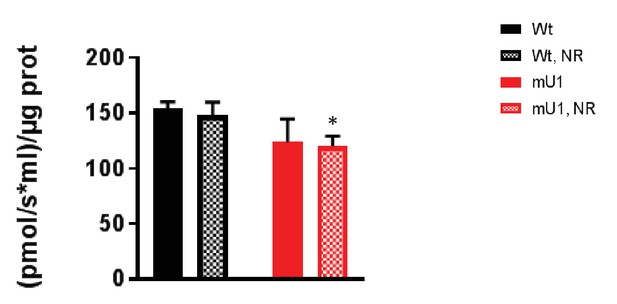
Mitochondrial respiration.
Mitochondrial complex II-driven respiratory capacity in heart homogenates from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without nicotinamde riboside (NR). Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
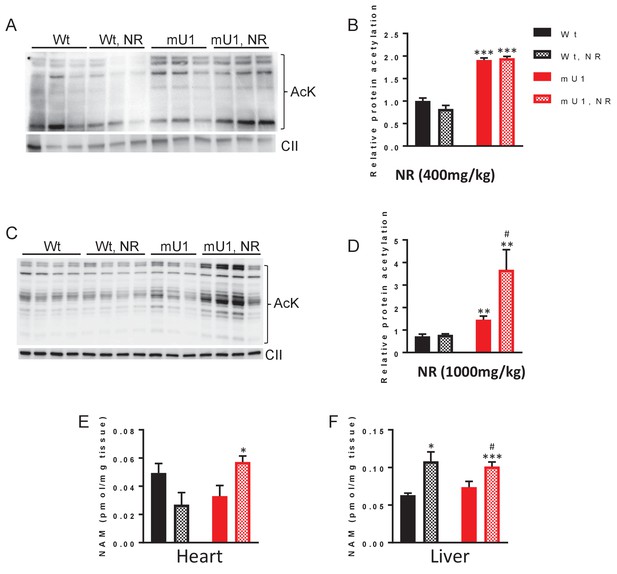
Nicotinamde riboside (NR) treatment does not counteract mitochondrial protein acetylation in cardiomyocytes but causes accumulation of nicotinamide.
(A) Western blot of protein acetylation levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without medium dose of NR. (B) Quantification of protein acetylation levels in western blot. (C) Western blot of protein acetylation levels in cardiac mitochondrial extract from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without high dose of NR. (D) Quantification of protein acetylation levels in western blot. Nicotinamide (NAM) levels in heart tissue (E) and liver tissue (F) from wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with or without NR, measured with HPLC. Data is presented as mean ± SE. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Wt chow. #p<0.05 vs. mutUNG1 chow. Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
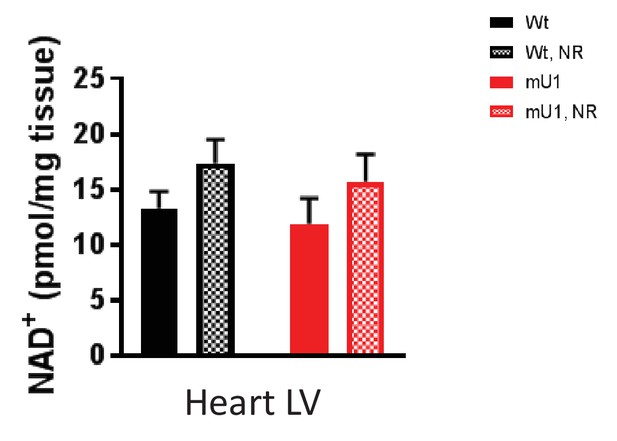
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels.
NAD+ levels in liver tissue from wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed chow with or without high-dose nicotinamde riboside (NR), measured by HPLC. Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
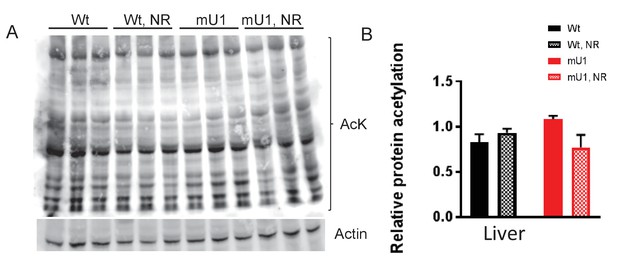
Protein acetylation levels.
(A) Western blot of protein acetylation levels in liver homogenate from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without high dose of nicotinamde riboside (NR). (B) Quantification of protein acetylation levels in western blot. Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
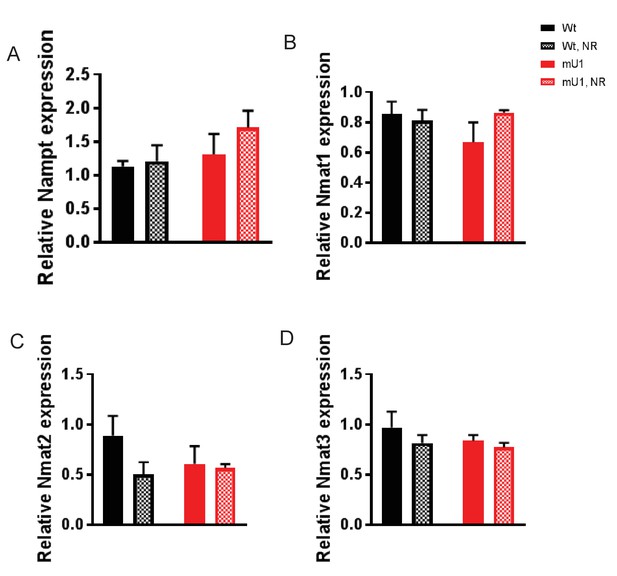
Gene expression levels Nampt and Nmat 1–3.
qPCR data from cardiac tissue from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without nicotinamde riboside (NR). Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
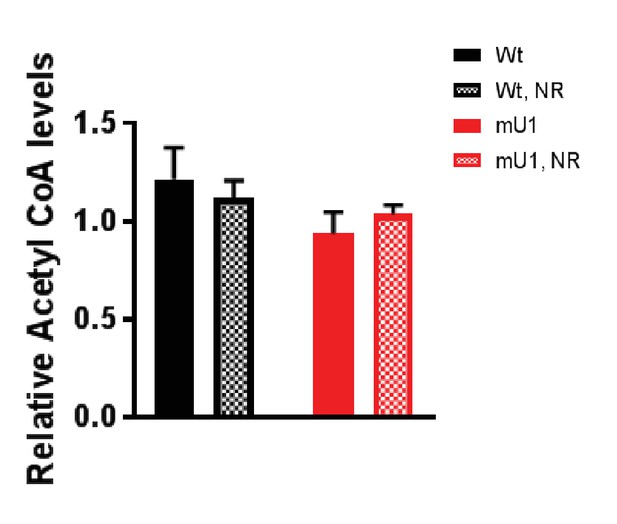
Acetyl CoA levels.
Acetyl CoA levels in cardiac tissue from mutUNG1-expressing mice and wild-type littermates fed chow with or without nicotinamde riboside (NR). Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
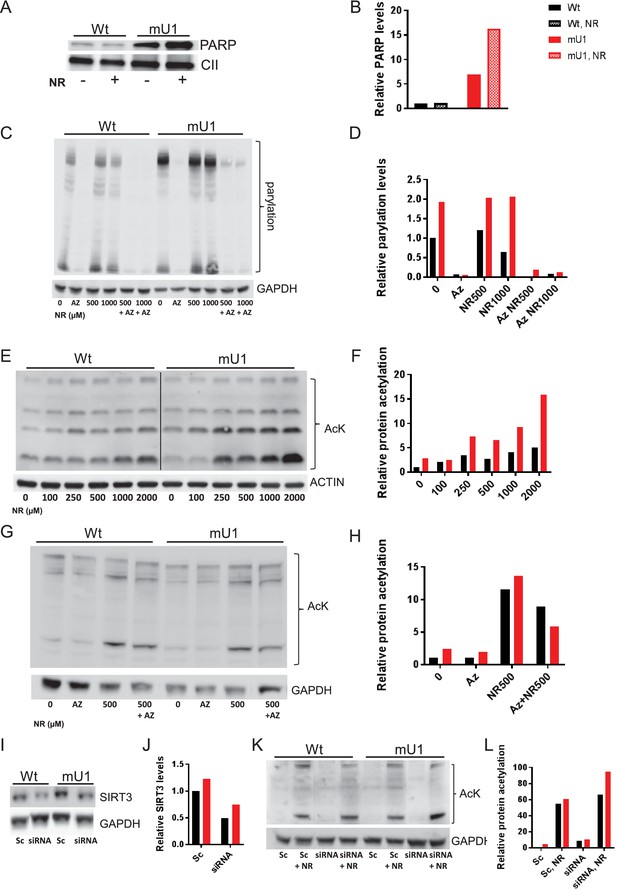
Increasing doses of nicotinamde riboside (NR) progressively inhibit deacetylation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage.
(A) Western blot of PARP levels in extract from cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1 grown in vitro with or without NR. (B) Quantification of PARP levels in western blot. (C) Western blot of poly:mono-ADP ribose/PARylation levels in cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1, treated with PARP inhibitor and/or NR. (D) Quantification of PARylation in western blot. (E) Western blot of protein acetylation levels in total extract in cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1, and increasing concentrations of NR. (F) Quantification of protein acetylation levels in western blot. (G) Western blot of acetylation levels in cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1, treated with PARP inhibitor and/or NR. (H) Quantification of acetylation in western blot. (I) Western blot of SIRT3 levels in cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1, transfected with SIRT3 silencing RNA (siRNA) and scrambled control. (J) Quantification of SIRT3 levels in western blot. (K) Western blot of acetylation levels in cells with (mU1) and without (wt) expression of mutUNG1, transfected with SIRT3 siRNA and scrambled control and NR treatment. (L) Quantification of acetylation in Western blot. Abbreviations: Az=AZD2461/Olaparib, Sc = Scrambled. Raw data are presented in Source data 2.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | mutUNG1 | PMID:26055793 | Dr Knut H Lauritzen (Oslo University Hospital) | |
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HeLA/ mutUNG1 | PMID:20065039 | Cat:631183 RRID:CVCL_V353 | Stable transfected; HeLa Tet-On 3 G Cell Line |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nicotinamide Riboside Chloride (Nigagen) | ChromaDex | Cat:ASB-00014315–15 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | AZD2461/ Olaparib | Merck | Cat:SML1858 | 25 µM |
| Transfected construct (human) | siRNA to SIRT3 (ID:S23766) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:4392420 | Transfected construct (human) |
| Transfected construct (human) | siRNA, Negative control | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:AM4635 | |
| Antibody | PARP (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:9542 RRID:AB_2160739 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | SIRT3 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:5490 RRID:AB_10828246 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | SDHA (CII) (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat:ab14715 RRID:AB_301433 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Acetylated-Lysine (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:9441 RRID:AB_331805 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | SOD2 (acetyl K68) (Rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat:ab137037 RRID:AB_2784527 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | SOD2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:13194 RRID:AB_2750869 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Poly/Mono-ADP Ribose (E6F6A) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:83732 RRID:AB_2749858 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | PHD (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:2784 RRID:AB_2162928 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | OPA1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:80471 RRID:AB_2734117 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | beta-Actin (Mouse monoclonal) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat:A5441 RRID:AB_476744 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | MFN2 (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat:ab56889 RRID:AB_2142629 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | DRP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat:8570 RRID:AB_10950498 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | PGC-1a (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat:ab54481 RRID:AB_881987 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling | Cat: 7074 RRID:AB_2099233 | WB: (1:20000) |
| Antibody | Ant-Mouse IgG | Cell Signaling | Cat:7076 RRID:AB_330924 | WB: (1:20000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | NAMPT_f | Merck | PCR primers | ATCCAGGAGGCCAAAGAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NAMPT_r | Merck | PCR primers | ATCGGGAGATGACCATCGTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT1_f | Merck | PCR primers | TGCATGCTACAGGAAAATAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT1_r | Merck | PCR primers | AAGTTCTGCCATGATGATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT2_f | Merck | PCR primers | GGCAGATATGGAAGTGATTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT2_r | Merck | PCR primers | GGAGTATGGAGGAGTGATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT3_f | Merck | PCR primers | CAGCATGAAGAACCGAATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NMNT3_r | Merck | PCR primers | TGGTACCTTCCTGTTTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | 18 s_f | Merck | PCR primers | CGCGGTTCTATTTTGTTGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | 18 s_r | Merck | PCR primers | AGTCGGCATCGTTTATGGTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | mtDNA_f | Merck | PCR primers | CCCAGCTACTACCATCATTCAAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | mtDNA_r | Merck | PCR primers | GATGGTTTGGGAGATTGGTTGATGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | OGG1_f | Merck | PCR primers | ATGAGGACCAAGCTAGGTGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OGG1_r | Merck | PCR primers | GCCTCACAATCAACTTATCCC |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:23228 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | Cat:74106 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Acetyl-Coenzyme A Assay kit | Merck | Cat:MAK039 | |
| Other | RM1+ 6000 ppm | Special Diets Services | Custom Dox diet | |
| Other | TRI Reagent | Merck | Cat:9424 | |
| Other | qScript cDNA Supermix | Quantbio | Cat:95048 | |
| Other | PerfeCTa SYBR Green Supermix | Quantbio | Cat: 95054 | |
| Other | Sodium succinate dibasic hexahydrate | Merck | Cat:S2378 | 10 mM |
| Other | Cytochrome c | Merck | Cat:C7752 | 10 µM |
| Other | Halt Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:1861284 | |
| Other | M-PER Mammalian protein extraction reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:78505 | |
| Other | Dynabeads Protein G | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:10003D | |
| Other | Oligofectamine Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat:12252–011 |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Rawdata; protemics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Source data 2
Rawdata; all quantifications.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-data2-v1.xlsx
-
Source data 3
Rawdata; all supplementary quantifications.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-data3-v1.xlsx
-
Source data 4
Raw data; original western blots.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-data4-v1.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
Table of gene ontology (GO) terms from proteomic analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/59828/elife-59828-transrepform-v1.docx