TINF2 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor that limits telomere length
Figures
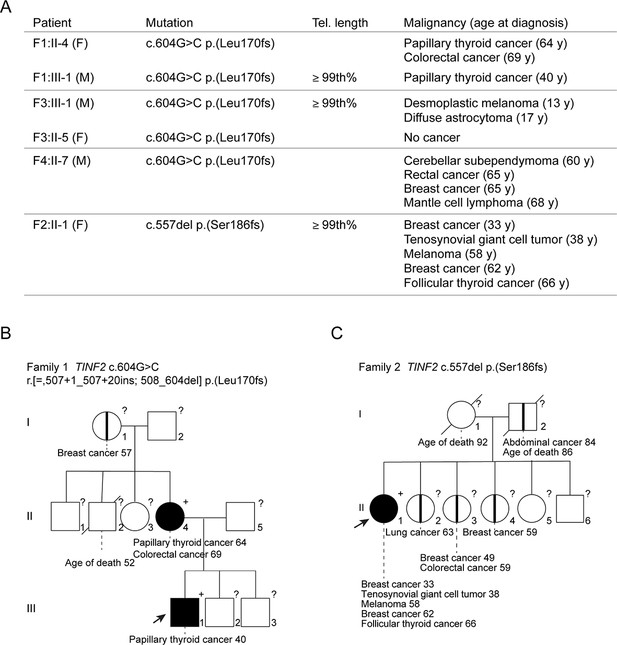
Germline mutations in TINF2 identified in individuals with multiple malignancies.
(A) TINF2 mutations and clinical features of affected individuals in four different families. Telomere length percentile is based on Flow-FISH data (see below Figure 5—figure supplement 1A). (B, C) Pedigrees of one of the c.604G > C families (B) and the c.557del family (C) listed in (A). Probands are highlighted by arrows. Filled symbols indicate patients with confirmed TINF2 mutations and their clinical features are indicated. Symbols with vertical lines denote individuals who have developed cancer but have not been tested for TINF2 mutations. +: TINF2 mutation; -: wild type for TINF2; ?: not tested. See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
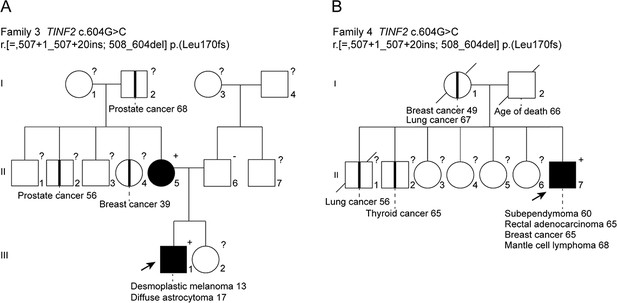
Pedigrees of two c.604G > C TINF2 families.
Pedigrees of two families with heterozygous c.604G > C mutations listed in Figure 1A. Probands are highlighted by arrows. Filled symbols indicate patients with confirmed TINF2 mutations and clinical features are indicated. Symbols with vertical lines stand for individuals who have developed cancer but were not tested for the presence of the TINF2 mutations.
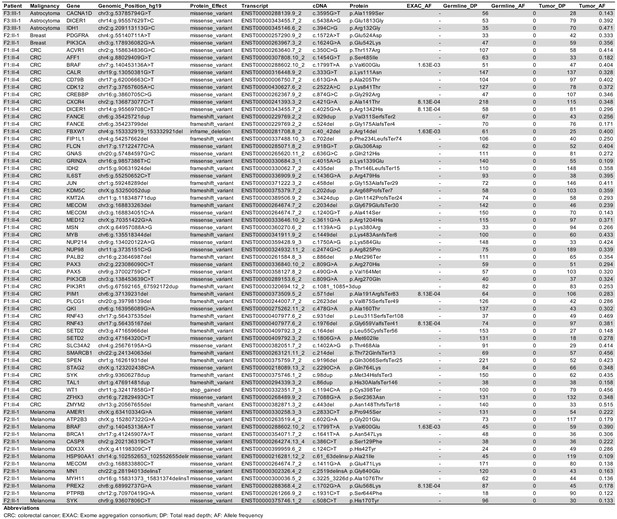
Somatic mutations in the COSMIC cancer gene census identified in malignancies in TINF2 mutation carriers.
Table showing the somatic mutations identified in the tumors of families with TINF2 mutations.
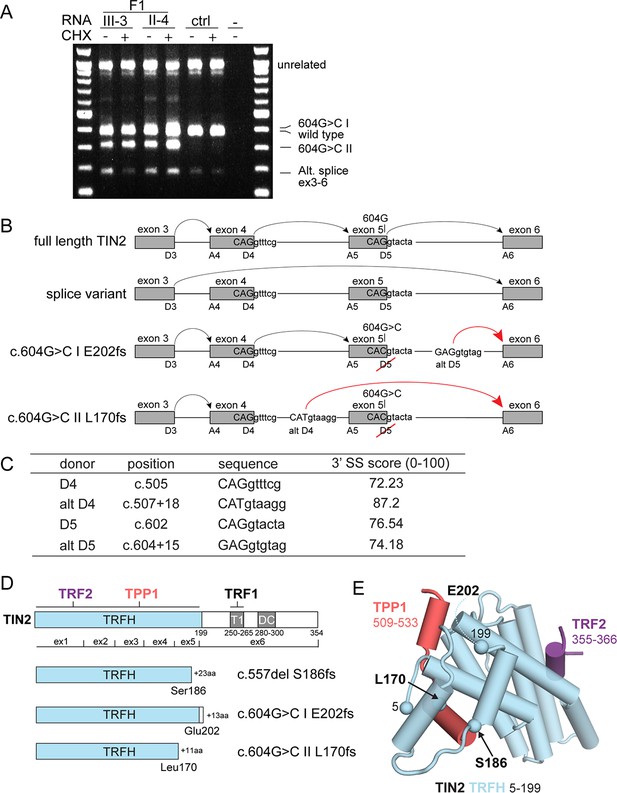
Molecular analysis of transcripts resulting from TINF2 mutations.
(A) Transcript analysis in peripheral blood lymphocytes (with and without cycloheximide treatment, CHX) from patients with the c.604G > C TINF2 mutation (F1:III-3 and F1:II-4; see Figure 1A) and a control individual. RT-PCR products were analyzed by Sanger sequencing. Wild-type full-length TIN2 mRNA, an alternative splice form found in wild-type cells (alt. splice exons 3–6) and mutant allele transcripts (604G > C I and 604G > C II) are indicated. Transcript 604G > C I was identified in heterozygous +/c.604G > C and homozygous c.604G > C RPE1 cells. (B) Schematic showing the splicing of exons 3–6 for full-length wild-type TINF2, the alternative splice variant (exons 3–6), and the aberrant splicing occurring in cells with c.604G > C mutations. Alt D4 and alt D5 indicate alternative splice donor sites. (C) Comparison of the consensus score of alternative splice donor sites alt D4 and alt D5 to splice donors D4 and D5 (as calculated by Human Splicing Finder www.umd.be). (D) Schematic of wild-type TIN2, and the predicted truncations resulting from expression of c.557del p.(S186fs), c.604G > C I p.(E202fs), and c.604G > C II p.(L170fs). Exon boundaries and the regions involved in TIN2 interactions with TRF1, TRF2, and TPP1 and the DC patch are indicated. (E) Structure of the TIN2 TRFH domain (PDB ID: 5xyf; Hu et al., 2017) with the amino acids at the truncation points highlighted. Peptides from TPP1 and TRF2 that interact with the TRFH domain are shown in the structure.
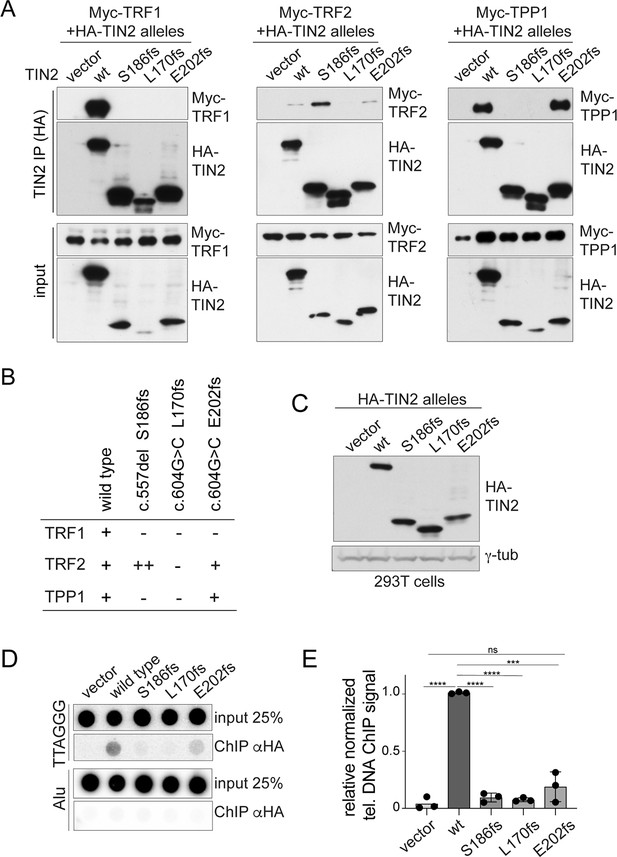
Truncated TIN2 versions show altered binding to shelterin subunits and diminished telomeric localization.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of myc-tagged TRF1 (left panel), TRF2 (middle panel) and TPP1 (right panel) from 293T cells co-transfected with HA-tagged wt TIN2, S186fs, L170fs, E202fs, or the empty vector. Inputs and HA-IPs were probed with HA antibody to detect TIN2 and with myc antibody to detect TRF1, TRF2, and TPP1. To achieve equal expression levels, the ratio of plasmids was: wt 1x, 186fs 2.5x, 202fs 2.5x, and 170fs 5x. This experiment was repeated three times with comparable results. (B) Summary of the interaction of wild type and mutant TIN2 alleles with TRF1, TRF2, or TPP1 as derived from multiple co-IP experiments as in (A). (C) Immunoblot showing expression of HA-tagged wild type and mutant TIN2 versions in 293T cells used for telomeric ChIP. (D) Dot blot assay for telomeric ChIP performed on the indicated 293T cells as shown in (C). (E) Quantification of telomeric DNA recovered with HA Ab (average relative % telomeric DNA recovered in three independent experiments, individual data points and means ± SD are shown). For the quantification, unpaired t-test was used to determine significance, p-values: ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. ns, not significant.
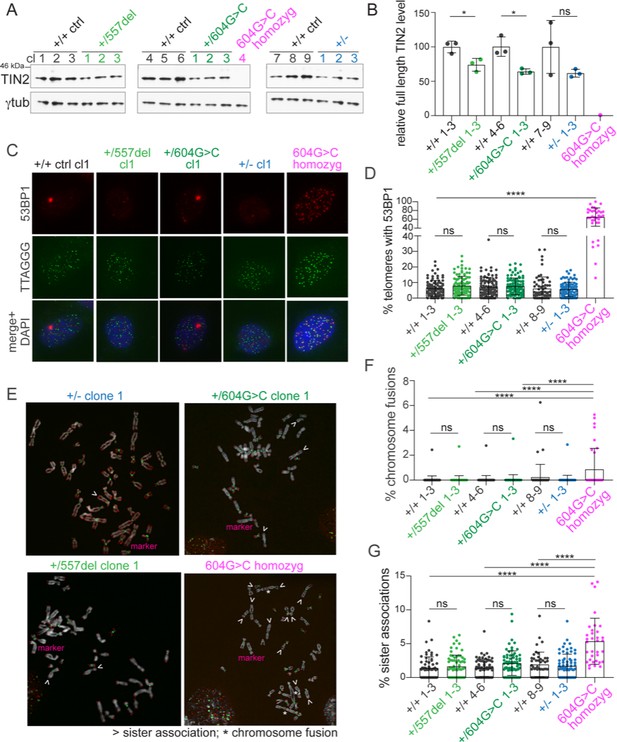
Heterozygous TINF2 mutations do not cause telomere damage or genome instability.
(A) Immunoblot for TIN2 and γtubulin in control cells and the indicated clones with targeted TINF2 alleles. (B) Quantification of the immunoblot shown in A. Unpaired t-test was used to determine significance. Symbols: *p<0.05; ns, not significant (0.16). (C) Representative images of TIF analysis in control and indicated TINF2 mutant cells. IF for 53BP1 (red), telomeric FISH (green) and DNA (DAPI, blue). (D) Quantification of percentage of telomeres colocalizing with 53BP1 foci. Data from ≥50 nuclei per cell line, with three cell lines per genotype (with the exception of the single c.604G > C homozyg clone). (E) Representative metaphase spreads of cells with mutated TINF2 alleles. Sister telomere associations (>), telomere fusions (*), and a marker chromosome found in all clones (marker) are indicated. Telomere FISH (red), centromere FISH (green) and DNA (DAPI, gray). (F) Quantification of telomere fusions ≥20 spreads per cell line, with three cell lines per genotype (except for the single 604G > C homozyg clone). (G) Quantification of the % of telomeres found in sister associations. Data from ≥20 spreads per cell line; three cell lines per condition, except for the single 604G > C homozyg clone. For the quantification in (B), (D), (F), and (G) means ± SD and individual data points are shown. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test was used to determine significance, p-values: ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. ns, not significant. See also Figure 4—figure supplements 1–6.
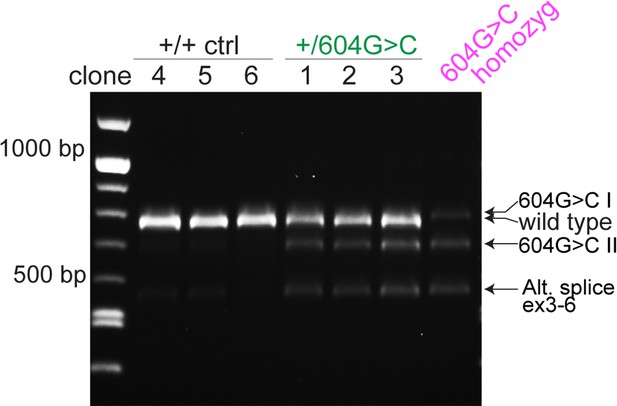
Transcript analysis in 604G > C/+ cells reveals presence of two alternative TINF2 transcripts (604G > C I, 604G > C II).
Transcript analysis in control cells and cells with c.604G > C TINF2 mutations. Wild-type and alternative (604G > C I, 604G > C II, alt. splice exons 3–6) transcripts are indicated. Alt. splice exons 3–6 is present in controls and mutant cells.
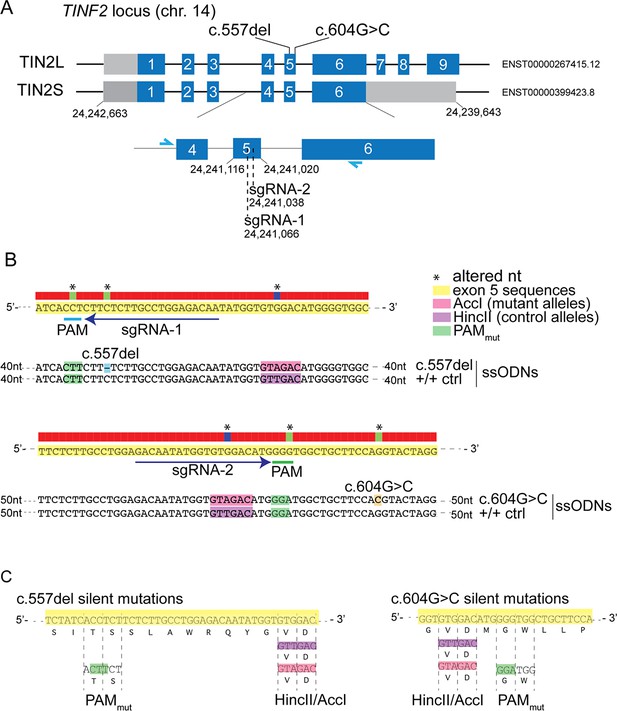
Knock-in strategy for introduction of c.557del and c.604G > C mutations into RPE1 cells.
(A) Schematic of the TINF2 locus showing landmarks relevant to CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-in of TINF2 mutations. The single guide RNA (sgRNA) target regions and the primers used for genotyping (blue arrows) are indicated. (B) Schematic showing the reference sequence (yellow), the PAM (green), sgRNA sequences, and mutant and control (with silent mutations) repair templates that were co-transfected with the sgRNA/Cas9 vector. The upper panel shows the repair template used to introduce c.557del mutations and the lower panel the template used for c.604G > C. Repair templates were designed to introduce the respective mutations, mutate the PAM sequence (green) and introduce restriction sites for screening (pink and purple). (C) Schematic showing that the introduced PAM mutations and added restriction sites do not change the amino acid sequence.
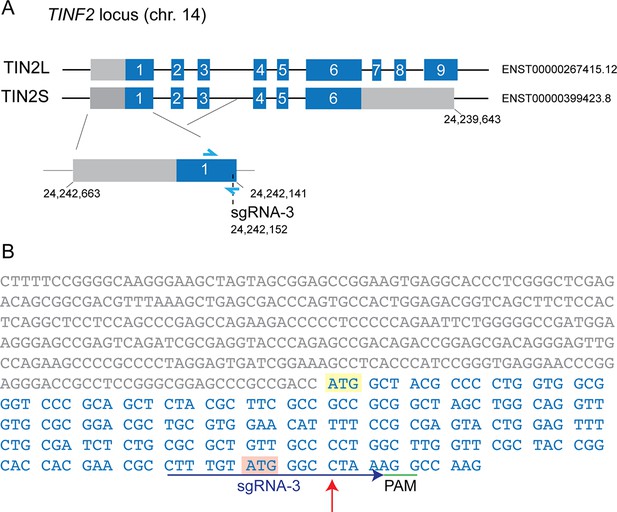
Strategy to generate TIN2+/- RPE1 clones.
(A) Schematic of the TINF2 locus showing landmarks relevant to CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeting of exon1. The single guide RNA (sgRNA) target region and the primers used for genotyping (blue arrows) are indicated. (B) Sequence of TINF2 exon 1 with the 5′ UTR (gray) and coding region (blue). The PAM (green) and sgRNA sequence (blue) is indicated.

Sanger sequencing of CRISPR/Cas9-engineered clones with TINF2 mutations.
(A–C) Reference sequence with sgRNA sequence and PAM and the edited sequences (highlighted) of the obtained cell lines for c.557del (A), c.604G > C (B) and TIN2+/- cells (C) and control cell lines.
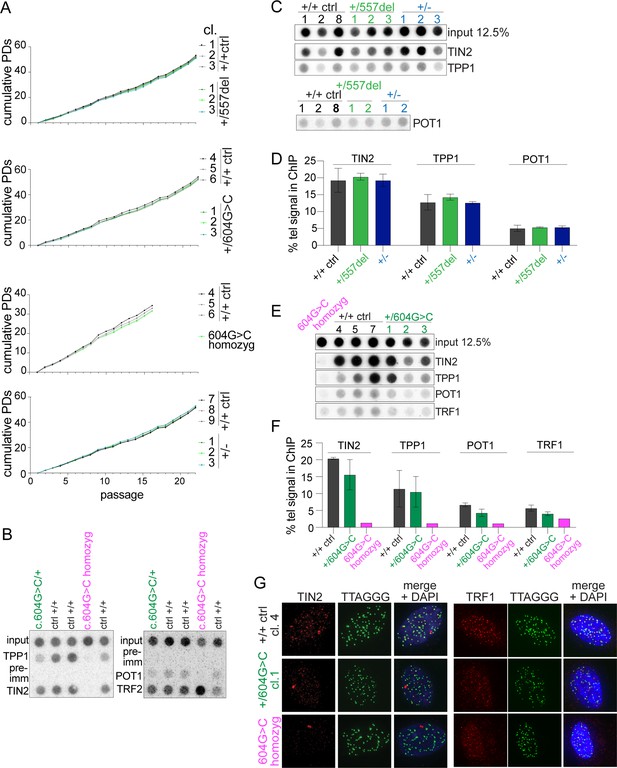
Characterization of cells with targeted TINF2 alleles.
(A) Growth curves of RPE1 control cells and cells with heterozygous c.557del or c.604G > C, homozygous c.604G > C mutations, or TIN2+/- cells. (B) Telomeric ChIP to determine the specificity of Abs for TIN2, TPP1, and POT1 compared to pre-immune serum (pre-imm). Cell lines used are indicated above the rows. (C) Telomeric ChIP analysis with TIN2, TPP1, or POT Ab in control, c.557del mutant and TIN2+/- cells. All samples were processed in parallel. The input shown is the same for the TIN2, TPP1, and POT1. (D) Quantification of telomeric DNA recovered with the respective Abs (mean ± SD, % telomeric DNA recovered in three clones per genotype for TIN2 and TPP1, and two clones for POT1). (E) Telomeric ChIP analysis with TIN2, TPP1, TRF1, and POT1 Ab in control and heterozygous and homozygous c.604G > C clones. (F) Quantification of telomeric DNA recovered with the indicated Abs as in (D) (mean ± SD, % telomeric DNA recovered in three independent clones for control and heterozygous c.604G > C). (G) IF-FISH for TIN2, TRF1, or TRF2 (red) and telomeres (green) in control cells and cells with heterozygous and homozygous c.604G > C mutations.
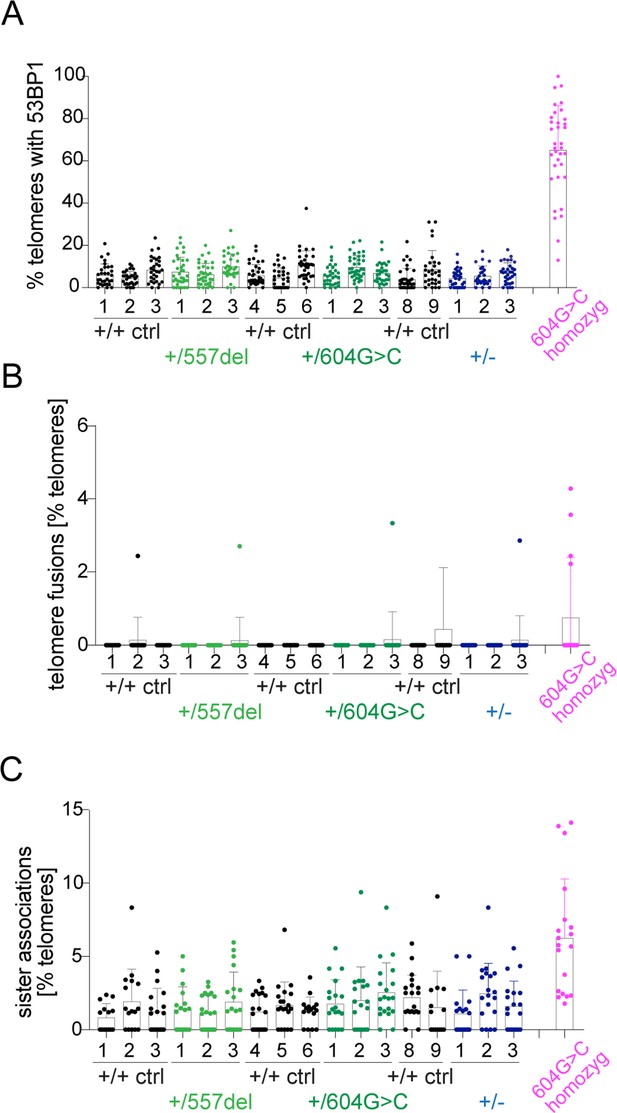
Representation of TIFs, telomere fusions, and sister associations in the individual cell lines.
(A) Quantification of telomeres containing 53BP1 (≥50 nuclei per cell line, with individual cell lines from Figure 4D shown). (B) Quantification of telomere fusions (≥20 spreads per cell line, with individual cell lines from Figure 4F shown). (C) Quantification of sister associations (≥20 spreads per cell line, with individual cell lines from Figure 4G shown).
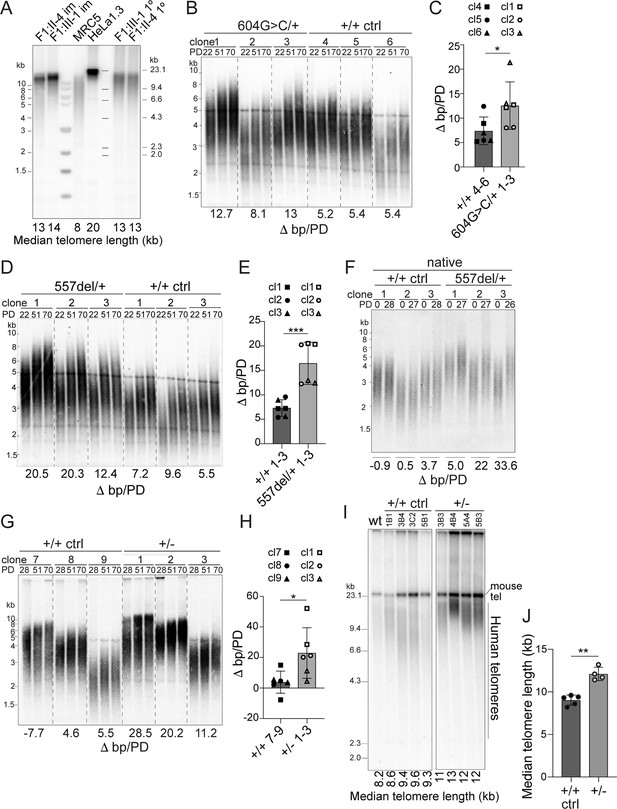
Heterozygous TINF2 mutations induce telomere lengthening.
(A) Telomeric Southern blot of MboI/AluI-digested genomic DNA from immortalized and primary patient cells (lymphocytes), normal lung fibroblasts (MRC5), and HeLa1.3 cells. Median telomere length (MTL) is indicated. (B) Telomeric Southern blot of MboI/AluI-digested genomic DNA from control clones and clones with heterozygous c.604G > C mutations at the indicated PDs. Telomere length changes are indicated and were calculated over 48 PDs. (C) Quantification of median telomere length changes for control cells and cells with heterozygous c.604G > C mutations. Three cell lines per genotype were analyzed in two independent experiments (symbols denote the individual cell lines). (D) Telomeric Southern blot as in (B) for control clones and clones with heterozygous c.557del mutations. (E) Quantification of median telomere length changes for control cells and cells with heterozygous c.557del mutations as in (C). (F) Detection of telomeres in MboI/AluI-digested genomic DNA from control clones and clones with heterozygous c.557del mutation probed under native conditions with a telomeric probe for the 3’ overhang. The change in MTL over 28 PDs is indicated. (G) Telomeric southern blot as in (B) for control cells and TIN2+/- cells. The indicated telomere length changes were calculated over 42 PDs. (H) Quantification of median telomere length changes for control cells and TIN2+/- cells as in C. (I) Telomeric southern blot of MboI/AluI-digested genomic DNA from control and TIN2+/- hESCs. All clones were generated and propagated in parallel and telomere length was determined at 28 days after the CRISPR/Cas9 targeting. (J) Quantification of the median telomere length (as determined by blotting as in (I)) for control and heterozygous hESCs clones (control, n = 5; TIN2+/KO, n = 4). Bar graphs in (C), (E), (H), and (J) show means ± SDs. P-values are based on unpaired t-test. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. ns, not significant. See also Figure 5—figure supplements 1–3.
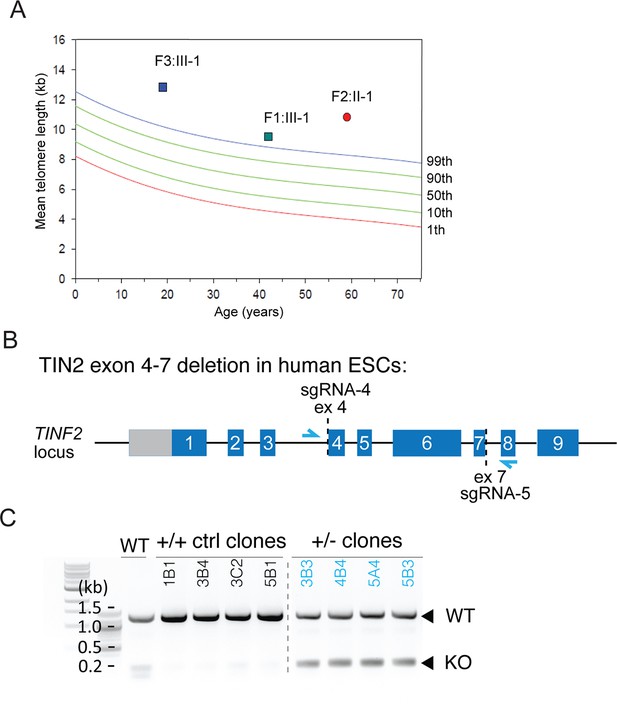
Long telomeres in TINF2 c.604G > C and c.557del patients and hESC CRISPR/Cas9 editing.
(A) Median telomere length (MTL) in individuals with TINF2 truncations as measured by Flow FISH. (B) Schematic of the TINF2 locus showing landmarks relevant to CRISPR/Cas9 mediated targeting of the allele in hESCs. The single guide RNA (sgRNA) target regions and the primers used for genotyping (blue arrows) are indicated. (C) PCR genotyping of hESC clones showing the longer wild-type and shorter edited allele.
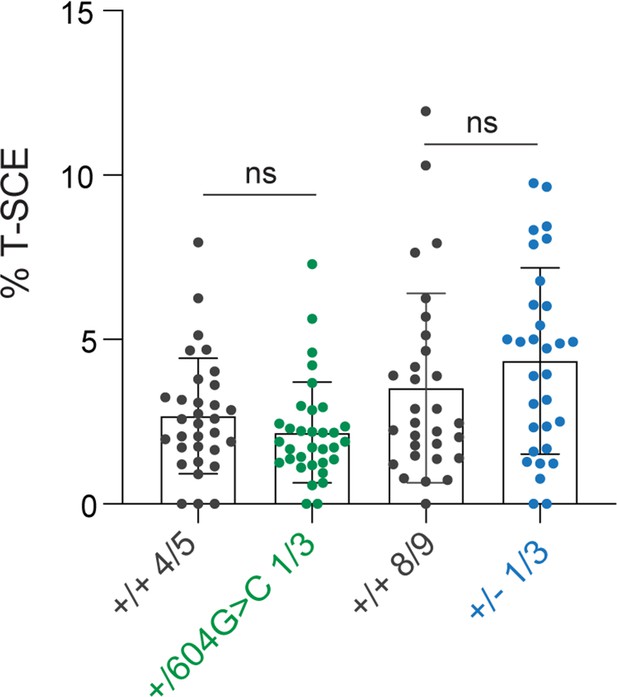
No evidence for increased telomere recombination in c.604G > C mutant and Tin2+/- cells.
Quantification of telomeric sister chromatid exchanges (T-SCE) in RPE1 control cells, cells with heterozygous c.604G > C, or TIN2+/- cells (≥15 spreads per cell line, and two cell lines per condition, means ± SD and individual data points are shown). Unpaired t-test was was used to determine significance, ns, not significant.
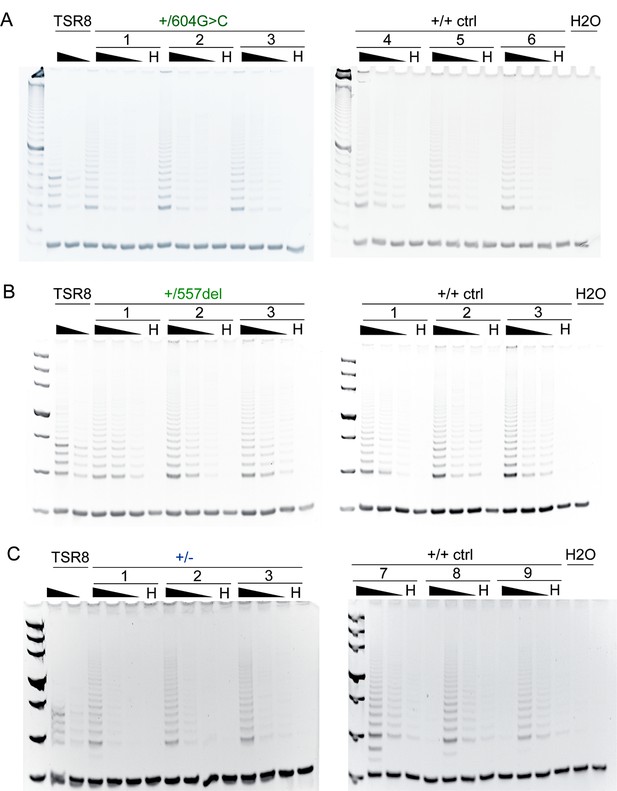
Mutant and control RPE1 clones show similar telomerase activity.
(A–C) TRAP assay using extracts from the indicated c.604G > C (A), control and c.557del (B), or TIN2+/- (C) cells together with the respective control cell lines. Serially diluted extracts (500, 100, 25 cells) were subjected to the TRAP assay. H, heat-treated extract from 500 cells; TSR8, positive control. Mutant and wild-type controls were harvested and analyzed in parallel and the TRAP products were analyzed on two gels (left and right half of each panel).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | 293T | ATCC | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- | Yang et al., 2017 | ||
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/604G > C.1 clone 1–3 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.604G > C | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/604G > C.2 clone 2–23 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.604G > C | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/604G > C.3 clone 1–21 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.604G > C | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl4 clone 1–4 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl5 clone 1–13 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl6 clone 5–8 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/557del.1 clone 1–9 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.557del | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/557del.2 clone 1–14 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.557del | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/557del.3 clone 2–17 m | This paper | Heterozygous forTINF2 c.557del | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl1 clone 2–7 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl2 clone 2–8 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- ctrl3 clone 1–2 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/-.1 clone 1-1het | This paper | Heterozygous for TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/-.2 clone 1-3het | This paper | Heterozygous for TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/-.3 clone 2-4het | This paper | Heterozygous for TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/+ ctrl7 clone 2–9 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/+ ctrl8 clone 3–2 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | hTERT-RPE1 p53-/- Rb-/- +/+ ctrl9 clone 1–4 c | This paper | Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC | Lengner et al., 2010 | NIH stem cell registry number: 0079 | Wild-type |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 1B1 | This paper | +/+ TINF2 Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 3B4 | This paper | +/+ TINF2 Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 3C2 | This paper | +/+ TINF2 Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 5B1 | This paper | +/+ TINF2 Control cell line | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 3B3 | This paper | +/- TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 4B4 | This paper | +/- TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 5A4 | This paper | +/- TINF2 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | WIBR3 hESC 5B3 | This paper | +/- TINF2 | |
| Anti-hTIN2 | Ye and de Lange, 2004 | #864 | ||
| Anti-γTubulin | Sigma | GTU88 | ||
| Anti-Myc | Cell signaling | 9B11 | ||
| Anti-HA | Abcam | Ab9110 | ||
| Anti-53BP1 | Abcam | ab175933 | ||
| Cy3-OO- (TTAGGG)3 | PNA bio | Telomere probe | ||
| FITC-OO-(CCCTAA)3 | PNA bio | Telomere probe | ||
| Alexa Fluor 647-OO-(TTAGGG)3 | PNA bio | Telomere probe | ||
| CENPB-AF488 | PNA bio | F3004 | Centromere probe |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Uncropped images of immunoblots and telomere blots shown in the main figures.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61235/elife-61235-supp1-v1.jpg
-
Supplementary file 2
Uncropped images of immunoblots and telomere blots shown in the main figures.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61235/elife-61235-supp2-v1.jpg
-
Supplementary file 3
Uncropped images of immunoblots and telomere blots shown in the main figures.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61235/elife-61235-supp3-v1.jpg
-
Supplementary file 4
p-Values and summary statistics for key data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61235/elife-61235-supp4-v1.pdf
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61235/elife-61235-transrepform-v1.docx





