The kinase PDK1 is critical for promoting T follicular helper cell differentiation
Figures
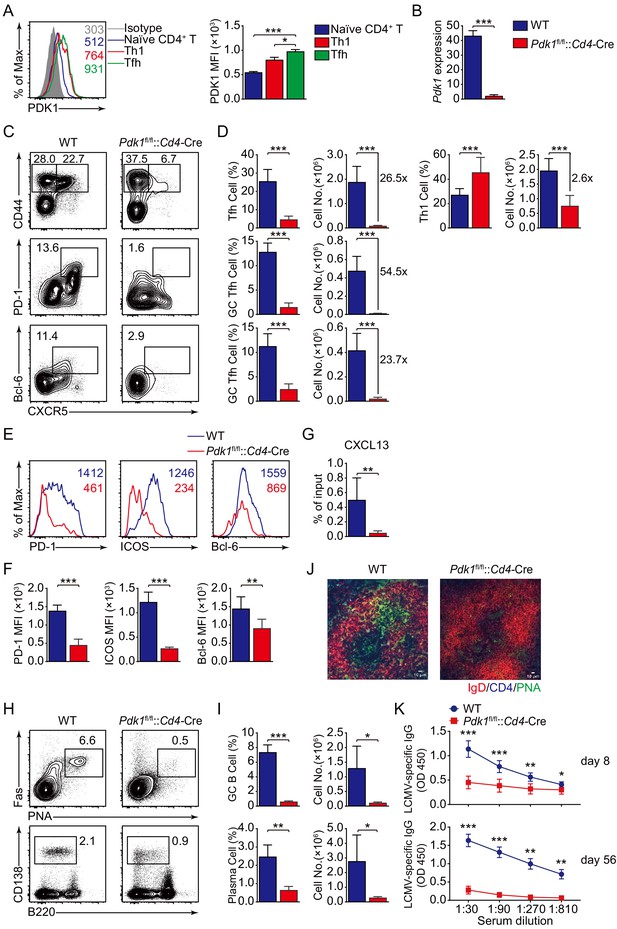
PDK1 supports Tfh cell differentiation and effector functions.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of PDK1 expression in naïve CD4+ T (CD62LhiCD44lo), Th1, and Tfh cells from C57BL/6J mice on 8 dpi. Quantification of PDK1 MFI is shown on the right (n = 8). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Pdk1 abundance in naïve CD4+ T cells, from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice (n = 3). (C, D) Flow cytometry analysis of CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cells and CD44+CXCR5- Th1 cells gated on total CD4+ T cells (top panel), or PD-1hiCXCR5+ GC Tfh cells (middle panel) and Bcl-6hiCXCR5+ GC Tfh cells (bottom panel) gated on CD44+CD62L-CD4+ T cells from spleens of WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on 8 dpi with representative contour plots and cumulative data in (C) and (D), respectively (n ≥ 6). (E, F) Expression of PD-1, ICOS, and Bcl-6 on Tfh cells (CD4+CD44+CXCR5+) was analyzed by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data in (E) and (F), respectively (n = 6). (G) Chemotaxis transwell assay for Tfh cells. Splenocytes from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on 8 dpi were added to a transwell plate and migration in the presence of CXCL13 was assessed (n ≥ 5). (H, I) Flow cytometry analysis of splenic PNA+Fas+ GC B cells (top panel) and B220−CD138+ plasma cells (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on 8 dpi with representative contour plots and cumulative data in (H) and (I), respectively (n = 4). (J) Confocal microscopy analysis of GC histology in spleen sections from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on 8 dpi. Green: PNA, red: IgD, blue: CD4; scale bar: 10 μm. (K) LCMV-specific IgG concentration of sera from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on day 8 (top panel) and 56 (bottom panel) post-infection was measured by ELISA (n ≥ 7). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments (A, B, E–G, H–I, K) or pooled from three independent experiments (C, D). Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
PDK1 supports Tfh cell differentiation and effector functions.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
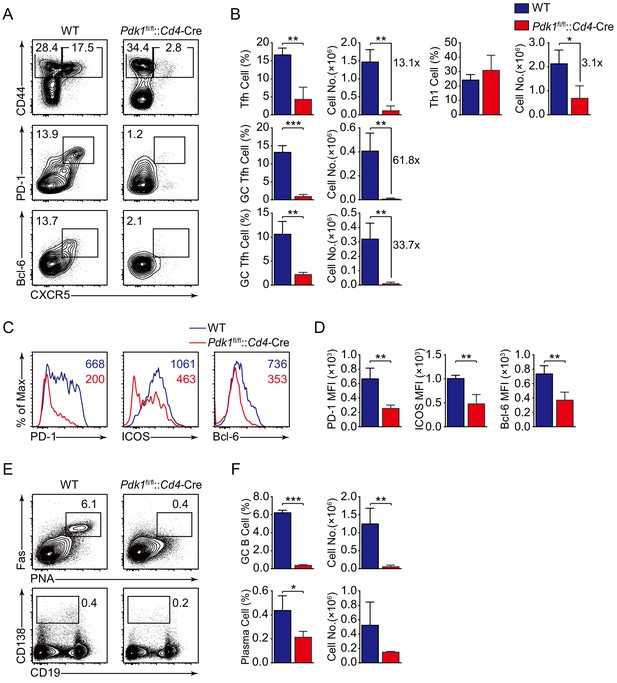
PDK1 is essential for Tfh cell differentiation upon protein immunization.
(A, B) Flow cytometry analysis of CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cells and CD44+CXCR5− Th1 cells gated on splenic CD4+ T cells (top panel) or PD-1hiCXCR5+ GC Tfh cells (middle panel) and Bcl-6hiCXCR5+ GC Tfh cells (bottom panel) gated on splenic CD44+CD62L-CD4+ T cells from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on day 8 post-KLH immunization with representative contour plots and cumulative data in (A) and (B), respectively (n = 3). (C, D) Expression of PD-1, ICOS, and Bcl-6 on Tfh cells (CD4+CD44+CXCR5+) was analyzed by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data in (C) and (D), respectively (n = 3). (E, F) Flow cytometry analysis of splenic PNA+Fas+ GC B cells (top panel) and B220-CD138+ plasma cells (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on day 8 post-KLH immunization with representative contour plots and cumulative data in (E) and (F), respectively (n = 3). Data are representative of two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
PDK1 is essential for Tfh cell differentiation and GC responses upon KLH immunization.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
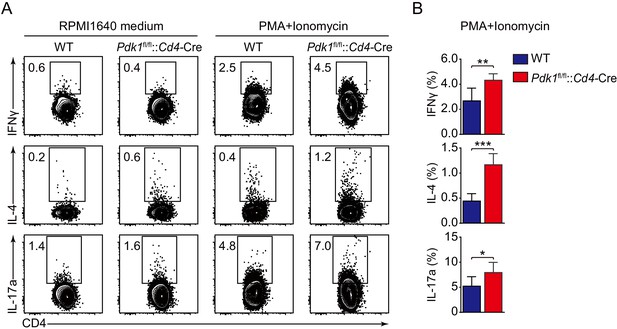
Analysis of T helper cells upon KLH immunization.
(A) Splenocytes from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice on day 8 post-KLH immunization were restimulated with PMA and Ionomycin at 37℃ for 5 hr. Then the cells were surface stained, followed by intracellular staining of IFNγ, IL-4, and IL-17a (n = 6). (B) Cumulative data on frequency of IFNγ+, IL-4+, and IL-17a+ cells gated on splenic CD4+CD44+CD62L− T cells from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice (n = 6). Data are pooled from two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Analysis of distinct T helper subsets upon KLH immunization.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
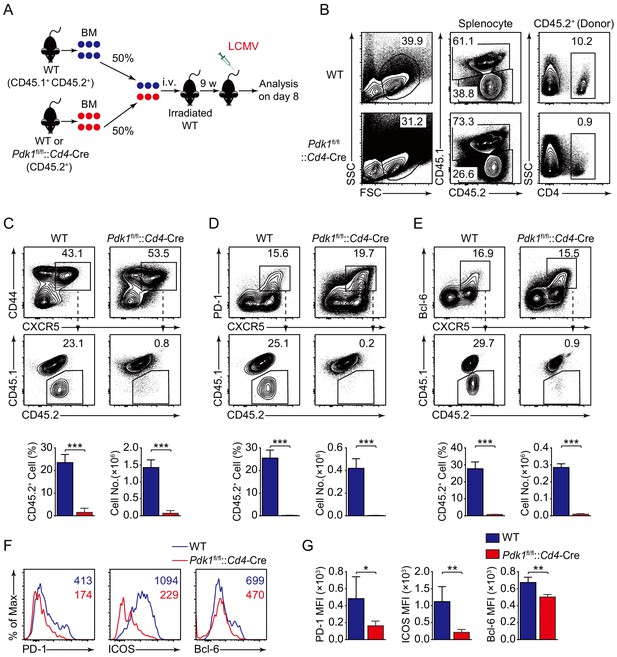
PDK1 intrinsically regulates Tfh cell differentiation.
(A) Generation of bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice. BM cells from WT or Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre mice (CD45.2+) were mixed with WT (CD45.1+CD45.2+) competitor cells at a 1:1 ratio, and transferred to lethally irradiated WT recipients (CD45.1+CD45.2+). After 9 weeks reconstitution, the recipients were infected with LCMV and analyzed 8 days later. (B) Analysis of chimerism by flow cytometry. WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre cells (CD45.2+) in CD4+ T cells of chimera mice were determined. (C–E) Flow cytometry analysis of competitive contributions by CD45.2+ cells to the total CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh (C), PD-1hiCXCR5+ GC Tfh (D), and Bcl-6hiCXCR5+ Tfh (E) cell population from recipients with representative contour plots and cumulative data (n = 4). (F, G) Detection of PD-1, ICOS, and Bcl-6 expression on CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cells from recipients by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data in (F) and (G), respectively (n = 4). Data are representative of two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
PDK1 intrinsically programs Tfh cell differentiation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
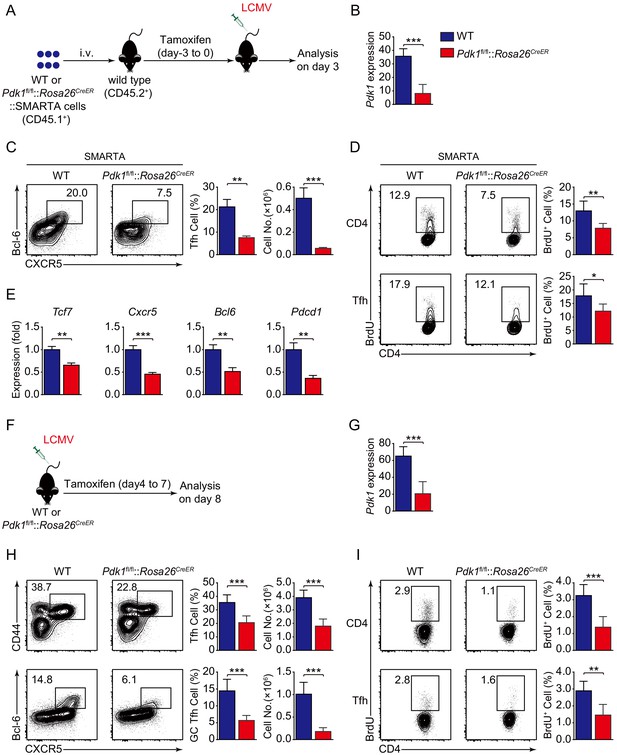
PDK1 is required for both early differentiation and late maintenance of Tfh cells.
(A) Schematic of the SMARTA cell transfer system used for characterization of early Tfh cell commitment. SMARTA CD4+ T cells from Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER::SMARTA mice were transferred into C57BL/6J (CD45.2+) host mice, followed by Tamoxifen treatment for four consecutive days, LCMV infection, and analyzed on 3 dpi. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Pdk1 abundance in donor-derived CXCR5+ Tfh cells from recipients on 3 dpi as in (A) (n = 6). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of Bcl-6+CXCR5+ Tfh cells gated on SMARTA CD4+ T cells from recipients on 3 dpi with representative contour plots and cumulative data (n = 3). (D) Contour plots represents BrdU+ cells gated on donor-derived activated CD4+ T cells (top panel) and CXCR5+ Tfh cells (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER::SMARTA mice on 3 dpi. Cumulative data on frequency of BrdU+ cells are shown on the right (n = 6). (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of selected genes in donor-derived CXCR5+ Tfh cells from recipients as in (A) (n = 3). (F) Schematic of the Tamoxifen-induced deletion system used for characterization of late Tfh cell differentiation. WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER mice were treated with Tamoxifen from day 4 to day 7 post-LCMV infection and analyzed on 8 dpi. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Pdk1 abundance in Tfh cells from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER mice on 8 dpi as in (F) (n ≥ 5). (H) Flow cytometry analysis of CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cells (top panel) gated on CD4+ T cells and Bcl-6+CXCR5+ GC Tfh cells (bottom panel) gated on CD44+CD62L-CD4+ T cells on 8 dpi with representative contour plots and cumulative data (n ≥ 5). (I) Contour plots represents BrdU+ cells gated on activated CD4+CD44+ T cells (top panel) and CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cells (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER mice on 8 dpi. Cumulative data on frequency of BrdU+ cells are shown on the right (n ≥ 5). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (B–C, E, G–H) or pooled from two independent experiments (D). Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
PDK1 is essential for Tfh cell differentiation at both early and late stages.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
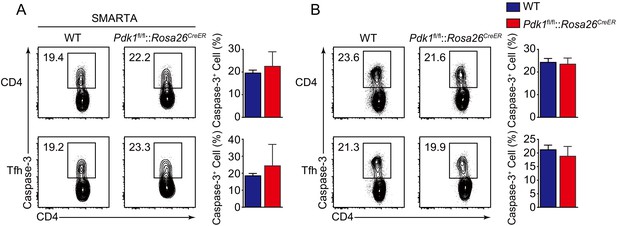
Detection of apoptosis of activated CD4+ T cells and Tfh cells.
(A) Contour plots represents Caspase-3+ cells gated on donor-derived activated CD4+ T cells (top panel) and CXCR5+ Tfh cells (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER::SMARTA mice on 3 dpi. Cumulative data on frequency of Caspase-3+ cells are shown on the right (n = 6). (B) Contour plots represents Caspase-3+ cells gated on activated CD4+CD44+ T cells (top panel) and CD44+CXCR5+ Tfh cell (bottom panel) from WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Rosa26CreER mice on 8 dpi. Cumulative data on frequency of Caspase-3+ cells are shown on the right (n ≥ 5). Data are pooled from two independent experiments (A) or representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Analysis of apoptosis of CD4 T and Tfh cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
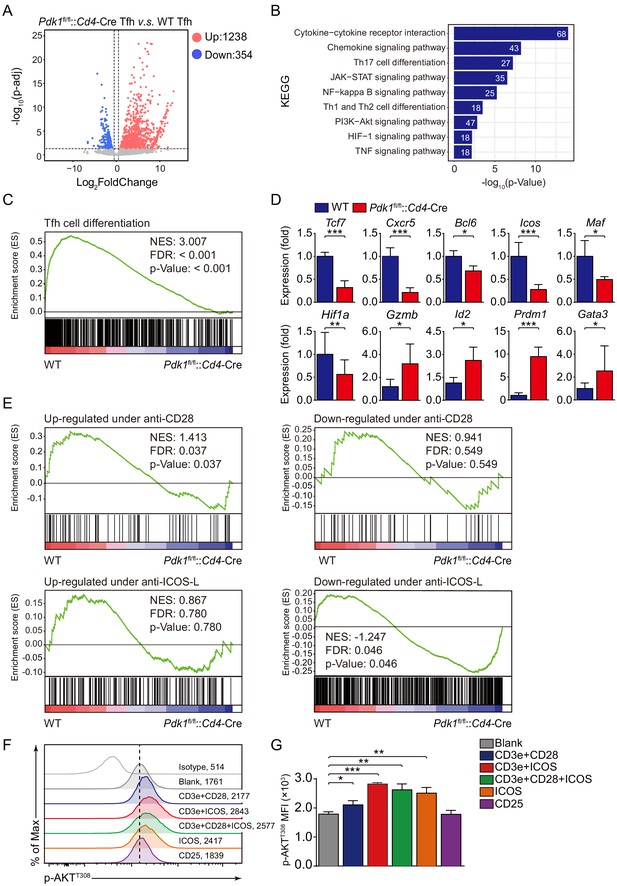
ICOS-dependent PDK1 promotes transcriptional program for Tfh cells.
(A) RNA-seq analysis of Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre or WT Tfh cells sort-purified on 8 dpi. Volcano plot shows genes upregulated (red) or downregulated (blue) in Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre Tfh cells compared with WT cells. (B) KEGG pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes in Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre Tfh cells relative to their expression in WT Tfh cells. (C) GSEA of the Tfh cell gene signature in Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre Tfh cells relative to their expression in WT Tfh cells. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of selected genes in Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre and WT Tfh cells. Relative expression was normalized to WT cells (n ≥ 4). (E) GSEA of ‘Up-regulated under anti-CD28’, ‘Down-regulated under anti-CD28’, ‘Up-regulated under anti-ICOS-L’, and ‘Down-regulated under anti-ICOS-L’ gene sets in WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre Tfh cells. (F, G) Flow cytometry analysis of p-AKTT308 level on CD4+ T cells from WT SMARTA cells, cultured in medium without any stimulus (blank), or stimulated with anti-CD3e + anti-CD28, anti-CD3e + anti-ICOS, anti-CD3e + anti-CD28 + anti-ICOS, anti-ICOS, and anti-CD25. Representative histogram plot and cumulative data are shown in (F) and (G), respectively (n = 3). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments (D, F, G). Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
ICOS-dependent PDK1 activity regulates Tfh cell transcriptional files.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
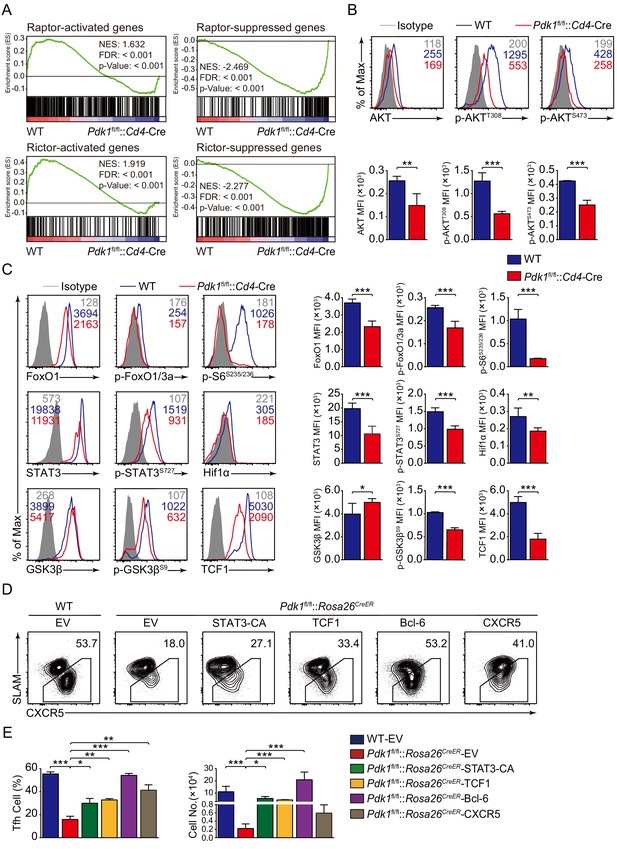
PDK1 deficiency impaired Tfh cell differentiation via mTORC1 and mTORC2 signal-dependent TCF1 expression.
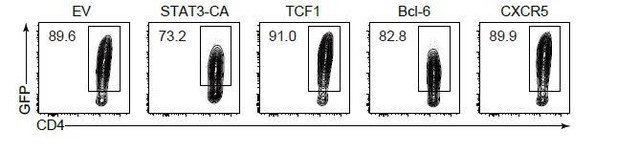
(A) GSEA of ‘Raptor-activated genes’, ‘Raptor-suppressed genes’, ‘Rictor-activated genes’, and ‘Rictor-suppressed genes’ gene sets in WT and Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre Tfh cells. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of AKT, p-AKTT308, and p-AKTS473 levels on Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre and WT Tfh cells on 8 dpi by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data (n = 4). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of FoxO1, p-FoxO1/3a, STAT3, p-STAT3S727, Hif1α, p-S6, GSK3β, p-GSK3βS9, and TCF1 levels on Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre and WT Tfh cells on 8 dpi by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data (n ≥ 4). (D, E) Flow cytometry analysis of Tfh populations from recipients adoptively transferred with STAT3-CA, TCF1, Bcl-6, or CXCR5 retrovirus-infected SMARTA cells on 8 dpi by flow cytometry with representative contour plots and cumulative data in (D) and (E), respectively (n ≥ 3). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
PDK1 regulates Tfh cell differentiation via mTORC1 and mTORC2 signal-dependent TCF1 expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
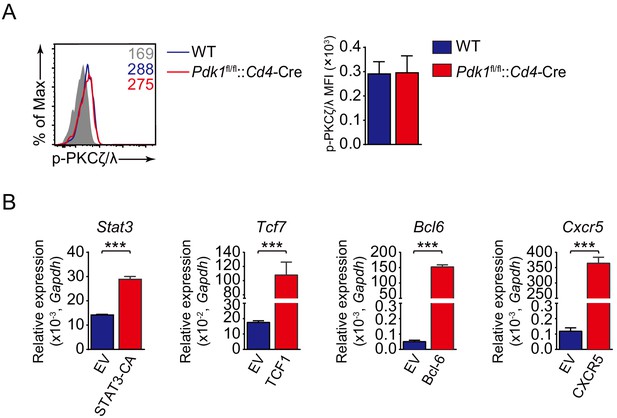
Analysis of p-PKCζ/λ level in Tfh cells and detection of overexpression level of relative genes in primed CD4+ cells via retrovirus transduction.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of p-PKCζ/λ level on Pdk1fl/fl::Cd4-Cre and WT Tfh cells on 8 dpi by flow cytometry with representative histograms and quantification data (n = 3). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Tcf7, Stat3, Bcl6, or Cxcr5 in GFP+ cells transduced with indicated retrovirus (n = 3). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Error bars represent SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 (Student’s t-test).
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Analysis of p-PKCζ/λ level and validation of overexpression efficiency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61406/elife-61406-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
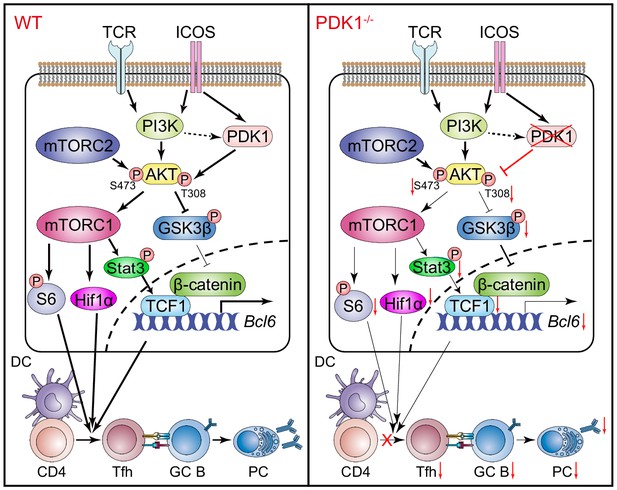
Working model of PDK1 in regulating Tfh cell differentiation.
Left panel: In PDK1-sufficient cells, AKT gets activated by phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473. p-AKT activates mTORC1, and mTORC1 further phosphorylates S6 and supports Hif1α expression, promoting protein synthesis, proliferation, and metabolization. mTORC1 also phosphorates STAT3 to induce TCF1 expression. In addition, p-AKT also guards TCF1 activity through the inactivation of GSK3β, an inhibitor of TCF1 and β-catenin. Enhanced TCF1 contributes to Tfh cell differentiation, GC responses, and humoral immunity. Right panel: In PDK1-deficient cells, AKT remains inactivated by loss of phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473, which contributes to impaired mTORC1 activity and activities of downstream molecules, inducing p-STAT3-dependent TCF1 expression. In addition, inactivation of p-AKT leads to compromised p-GSK3β, resulting in increased GSK3β activity and subsequently inhibition on TCF1 level. Decreased TCF1 leads to impaired Tfh cell differentiation, GC responses, and humoral immunity.
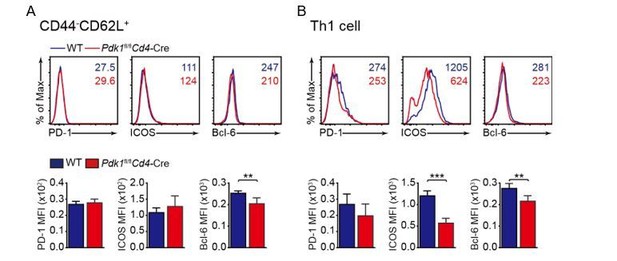
Analysis of PD-1, ICOS, and Bcl-6 expression in naive (A), and Th1 (B) cells.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse: C57BL/6J (CD45.2 and CD45.1) | Jackson Laboratory | RRID: IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse: B6. Cg-Tg(Cd4-cre)1Cwi/BfluJ (Cd4-Cre) | Jackson Laboratory | RRID: IMSR_JAX:022071 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse: B6. Cg-Ndor1Tg(UBC-cre/ERT2)1Ejb/2J (Rosa26CreER) | Jackson Laboratory | RRID: IMSR_JAX:008085 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse: B6. SMARTA | R. Ahmed | Emory University | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Mouse: B6. Pdk1fl/fl | W. Yuan | Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HEK293T (human embryonic kidney cells) | ATCC | Cat # CRL-3216, RRID: CVCL_0063 | |
| Biological sample (M. musculus) | Primary mouse splenocytes | China Agricultural University | Freshly isolated from mice | |
| Biological sample (M. musculus) | Primary mouse bone marrow cells | China Agricultural University | Freshly isolated from mice | |
| Biological sample (M. musculus) | Primary mouse serum | China Agricultural University | Freshly isolated from mice | |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD19-PE/Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 25-0193-82, RRID: AB_657663 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD25-PE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 12-0251-83; RRID: AB_465608 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD4-PE/Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 25-0041-82; RRID: AB_469576 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD4-APC/eFluor 780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 47-0041-82; RRID: AB_11218896 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD4-BV510 | BD Biosciences | Cat # 563106; RRID: AB_2687550 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human CD44-FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 11-0441-82; RRID: AB_465045 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human CD44-APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-0441-83; RRID: AB_469391 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD45.1-APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-0453-82; RRID: AB_469398 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse CD45.1- Percp/Cy5.5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 45-0453-82; RRID: AB_1107003 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse CD45.2- APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-0454-82; RRID: AB_469400 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse CD45.2- eFluor 506 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 69-0454-82 RRID: AB_2637105 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD62L- BV510 | BioLegend | Cat # 104441; RRID: AB_2561537 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD62L- APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-0621-83; RRID: AB_469411 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human CD45R-FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 11-0452-86; RRID: AB_465056 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD45R- PerCP/Cy5.5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 45-0451-82; RRID: AB_1107002 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human CD45R- Biotin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 13-0452-86; RRID: AB_466451 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse IgD- APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-5993-82; RRID: AB_10598660 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human GL7- eFluor 450 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 48-5902-82; RRID: AB_10870775 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-mouse PD-1- PE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 12-9985-82; RRID: AB_466295 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse TCR Vα2-PE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 12-5812-82; RRID: AB_465949 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/rat Foxp3-PerCP/Cy5.5 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 45-5773-82 ; RRID: AB_914351 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/rat Foxp3-APC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 17-5773-82 ; RRID: AB_469457 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD138-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat # 553714; RRID: AB_395000 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse CD138-BV421 | BD Biosciences | Cat # 562610; RRID: AB_11153126 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-mouse Fas-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat # 561985; RRID: AB_10895586 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-mouse/human Bcl6-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat # 561522; RRID: AB_10717126 | FACS (1:40) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse SLAM-PE | BioLegend | Cat # 115904; RRID: AB_10895586 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse SLAM-APC | BioLegend | Cat # 115910; RRID: AB_493460 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse/human ICOS-PE/Cy7 | BioLegend | Cat # 313520; RRID: AB_10643411 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse IFN-γ-FITC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 11-7311-82; RRID: AB_465412 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse IL-17a-PE | BD Biosciences | Cat # 559502; RRID: AB_397256 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-mouse IL-4-PE/Cy7 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 25-7041-80; RRID: AB_2573519 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/human TCF1 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 2203; RRID: AB_2199302 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human PDK1 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 3062; RRID: AB_2236832 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/human Hif1a | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 36169; RRID: AB_2799095 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human FoxO1 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 2880; RRID: AB_2106495 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human p-AKTT308 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 13038; RRID: AB_2629447 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human p-AKTS473 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 4060; RRID: AB_2315049 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human p-S6S235/236 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 4858; RRID: AB_916156 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclone anti-mouse/rat/human p-FoxO1/3a | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 9464; RRID: AB_329842 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclone anti-mouse/rat/human p-PKCζ/λ | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 9378; RRID: AB_2168217 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclone anti-mouse/rat/human AKT | Beyotime Biotechnology | Cat # AA326 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/human GSK3β | Beyotime Biotechnology | Cat # AF1543 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human p-GSK3βS9 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 5558 RRID: AB_10013750 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclone anti-mouse/rat/human p-STAT3S727 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 9134 RRID: AB_331589 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Rabbit monoclonal anti-mouse/rat/human STAT3 | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat # 4904 RRID: AB_331269 | FACS (1:100) |
| Antibody | Donkey polyclonal anti-rabbit IgG (minimal x-reactivity)-FITC | BioLegend | Cat # 406403; RRID: AB_893531 | FACS (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Donkey polyclonal anti-rabbit IgG (minimal x-reactivity)-AF647 | BioLegend | Cat # 406414; RRID: AB_2563202 | FACS (1:1000) |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | MIGR1 (MSCV-IRES-GFP) (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Retrovirus construct to transfect |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | MIGR1-Tcf7 overexpressing (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Retrovirus construct to transfect |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | MIGR1-Bcl6 overexpressing (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Retrovirus construct to transfect |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | MIGR1-STAT3-CA (constitutive-active) (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Retrovirus construct to transfect |
| Transfected construct (M. musculus) | MIGR1-Cxcr5 overexpressing (plasmid) | This paper | N/A | Retrovirus construct to transfect |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tcf7_F | This paper | PCR primers | CCCTTCCTGCGGATATAGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tcf7_R | This paper | PCR primers | GGTACACCAGATCCCAGCAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Cxcr5_F | This paper | PCR primers | CATGGGCTCCATCACATACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Cxcr5_R | This paper | PCR primers | GGCATGAATACCGCCTTAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Bcl6_F | This paper | PCR primers | AGACGCACAGTGACAAACCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Bcl6_R | This paper | PCR primers | AGTGTGGGTCTTCAGGTTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Icos_F | This paper | PCR primers | TGCCGTGTCTTTGTCTTCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Icos_R | This paper | PCR primers | CTTCCCTTGGTCTTGGTGAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Pdcd1_F | This paper | PCR primers | CTGGTCATTCACTTGGGCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Pdcd1_R | This paper | PCR primers | AAACCATTACAGAAGGCGGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Maf_F | This paper | PCR primers | AGCAGTTGGTGACCATGTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Maf_R | This paper | PCR primers | TGGAGATCTCCTGCTTGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Hif1a_F | This paper | PCR primers | CCTTAACCTGTCTGCCACTTTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Hif1a_R | This paper | PCR primers | TCAGCTGTGGTAATCCACTCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gzmb_F | This paper | PCR primers | CAAAGACCAAACGTGCTTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gzmb_R | This paper | PCR primers | CTCAGCTCTAGGGACGATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Id2_F | This paper | PCR primers | GTCCTTGCAGGCATCTGAAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Id2_R | This paper | PCR primers | TTCAACGTGTTCTCCTGGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Prdm1_F | This paper | PCR primers | ACAGAGGCCGAGTTTGAAGAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Prdm1_R | This paper | PCR primers | AAGGATGCCTCGGCTTGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gata3_F | This paper | PCR primers | CTTATCAAGCCCAAGCGAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gata3_R | This paper | PCR primers | CATTAGCGTTCCTCCTCCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Stat3_F | This paper | PCR primers | CAATACCATTGACCTGCCGAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Stat3_R | This paper | PCR primers | GAGCGACTCAAACTGCCCT |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | KLH | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat# H7017 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | GP61-80 (GLNGPDIYKGVYQFKSVEFD) | Synthesized by ChinaPeptides | N/A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | recombinant murine IL-2 | R and D | Cat # 212–12 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | recombinant murine IL-7 | R and D | Cat # 217–17 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Phosflow Lyse/Fix buffer, 5X | BD Biosciences | Cat # 558049; RRID: AB_2869117 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Phosflow Perm buffer I | BD Biosciences | Cat # 557885 RRID: AB_2869104 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Caspase-3 Staining Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 88-7004-42; RRID: AB_2574939 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Fixation/Permeabilization Solution Kit | BD Biosciences | Cat # 554714 RRID: AB_2869008 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Dynabeads M-280 Streptavidin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 60210 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lipofectamine 2000 Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 11668019 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | Cat # 74106 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | FastQuant RT Kit | Tiangen | Cat # KR106-02 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SuperReal PreMix Plus SYBR Green | Tiangen | Cat # FP205-02 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Freund’s Adjuvant, Complete | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # F5881 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tamoxifen | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # T5648 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Corn Oil | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # C8267 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | PMA | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # P8139 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ionomycin | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # I0634 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polybrene | Sigma–Aldrich | Cat # H9268 | |
| Software, algorithm | Flowjo v10.5 | Treestar | RRID: SCR_008520 | |
| Software, algorithm | Graphpad Prism 8 | Graphpad | RRID: SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | Adobe Illustrator | Adobe | RRID: SCR_010279 | |
| Software, algorithm | GSEA | http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsea/ | RRID: SCR_003199 | |
| Other | 7-AAD | BD Biosciences | Cat # 559925 RRID: AB_2869266 | |
| Other | PNA-FITC | Vector Laboratories | Cat # FL-1071; RRID: AB_2315097 | FACS (1:500) |
| Other | PNA-Biotin | Vector Laboratories | Cat# BA-0074; RRID: AB_2336190 | IF (1:50) |
| Other | Streptavidin-APC/eFluor 780 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 47-4317-82; RRID: AB_10366688 | FACS (1:500) |
| Other | Streptavidin-eFluor 450 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat # 48-4317-82; RRID: AB_10359737 | FACS (1:500) |