Modular metabolite assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans depends on carboxylesterases and formation of lysosome-related organelles
Figures
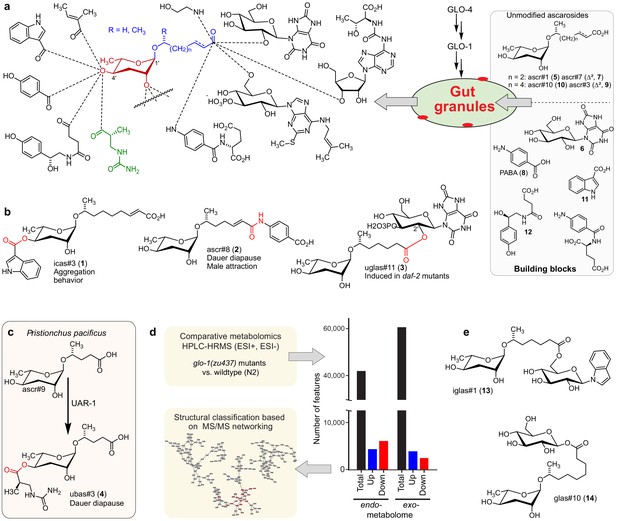
Modular ascarosides in nematodes and proposed role of the Rab-GTPase GLO-1.
(a) Modular ascarosides are assembled from simple ascarosides, e.g. ascr#1 (5) or ascr#3 (9), and building blocks from other metabolic pathways, e.g. glucosyl uric acid (6), p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA, 8) indole-3-carboxylic acid (11), or succinyl octopamine (12). We hypothesize that glo-1-dependent gut granules play a central role in their biosynthesis. (b) Examples for modular ascarosides and their biological context. (c) UAR-1 in P. pacificus converts simple ascarosides into the 4′-ureidoisobutyric-acid-bearing ascarosides, for example ubas#3 (4). (d) Strategy for comparative metabolomic analysis of LRO-deficient glo-1 mutants. (e) Example for modular ascarosides whose production is increased in glo-1 mutants.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1d.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
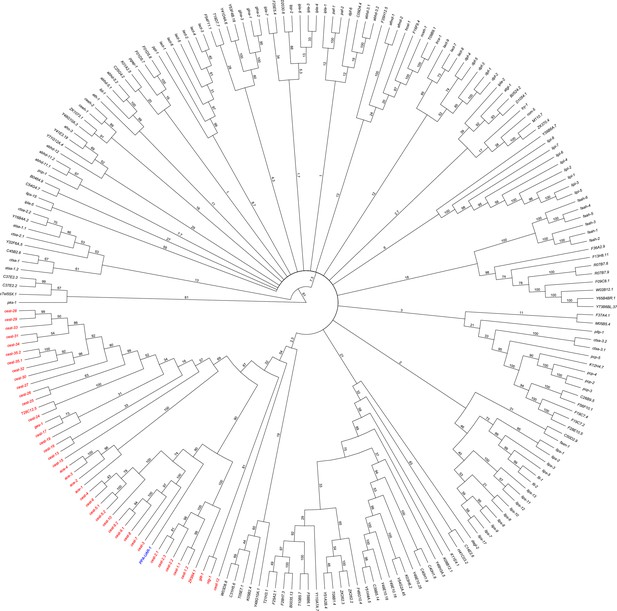
Dendrogram of serine hydrolase annotated in C. elegans and Ppa-uar-1 (marked blue).
cest genes (direct homologs of Ppa-uar-1) are colored in red.
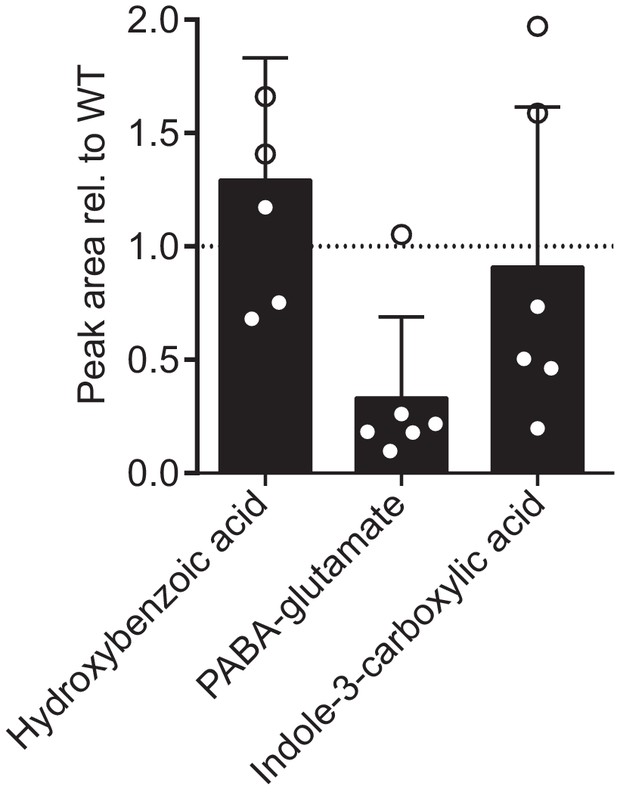
MS peak areas relative to wildtype (N2) of several building blocks of modular ascarosides.
Bars represent the mean of six replicates and error bars standard deviation.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 1—figure supplement 2.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
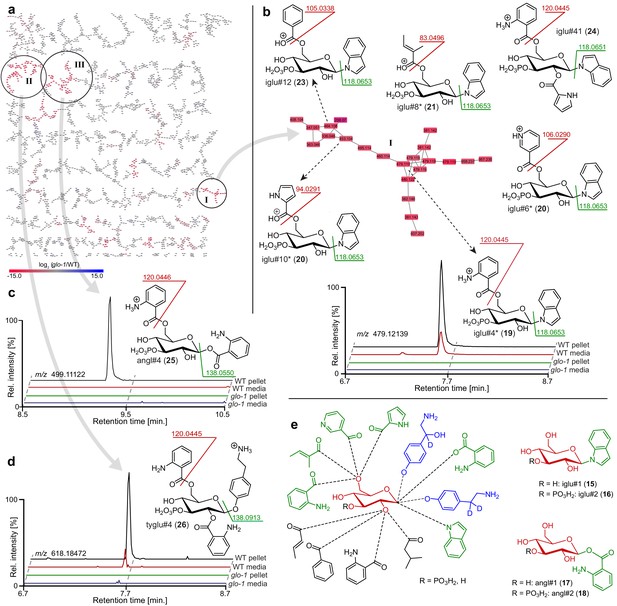
Comparative metabolomic analysis ofglo-1mutants.
(a) Partial MS2 network (positive ion mode) for C. elegans endo-metabolome highlighting three clusters of modular glucosides that are down regulated in the glo-1 mutants (also see Figure 2—figure supplements 1–4). Red represents downregulated and blue upregulated features compared to wildtype C. elegans. (b) Cluster I feature several modular indole glucoside derivatives. Structures were proposed based on MS2 fragmentation patterns, also see Appendix 1—table 1. Compounds whose non-phosphorylated analogs were synthesized are marked (*). Shown ion chromatograms demonstrate loss of iglu#4 in glo-1 mutants. (c,d) Examples for modular glucosides detected as part of clusters II and III. Ion chromatograms show abolishment of angl#4 (25) (c) and tyglu#4 (26) (d) production in glo-1 mutants. (e) Modular glucosides are derived from combinatorial assembly of a wide range of building blocks. Incorporation of moieties was confirmed via total synthesis of example compounds (green) or stable isotope labeling (blue). For all compounds, 3-phosphorylation was proposed based on the established structures of iglu#2 (16), angl#2 (18), and uglas#11 (3).
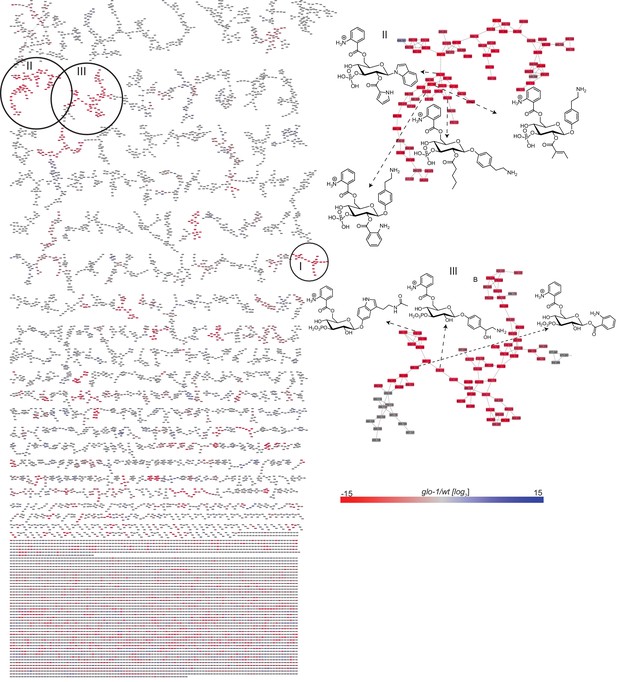
Full MS2 molecular network of endo-metabolome acquired in positive ion mode (left).
Red and blue represent features that are down- and up-regulated in glo-1 mutant worms, respectively. Clusters II and III with representative modular glucoside structures that are glo-1 dependent (right).
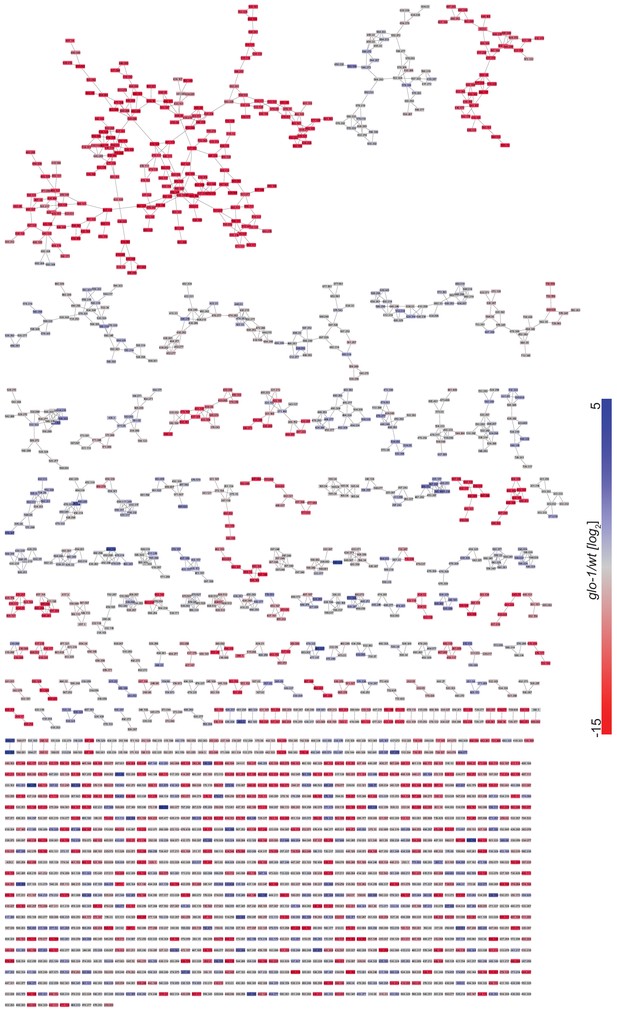
Full MS2 molecular network of endo-metabolome acquired in negative ion mode.
Red and blue represent features that are down- and up-regulated in glo-1 mutant worms, respectively.
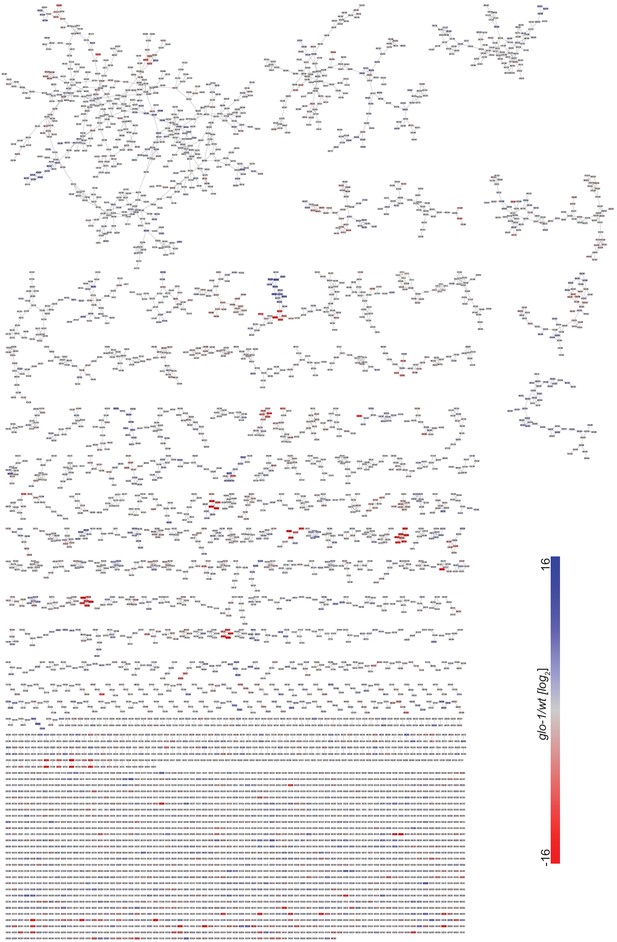
Full MS2 molecular network of exo-metabolome acquired in positive ion mode.
Red and blue represent features that are down- and upregulated in glo-1 mutant worms, respectively.
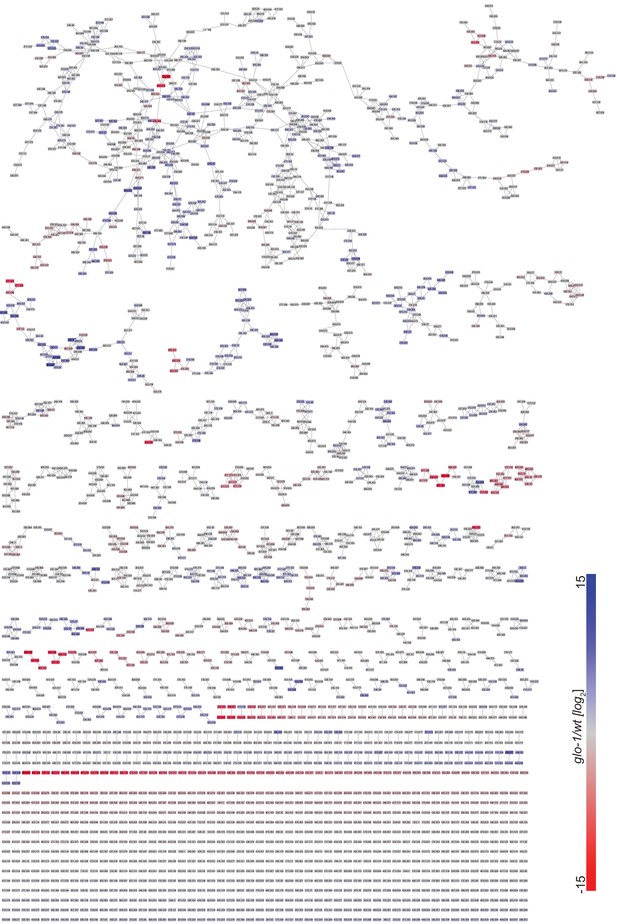
Full MS2 molecular network of exo-metabolome acquired in negative ion mode.
Red and blue represent features that are down- and upregulated in glo-1 mutant worms, respectively.
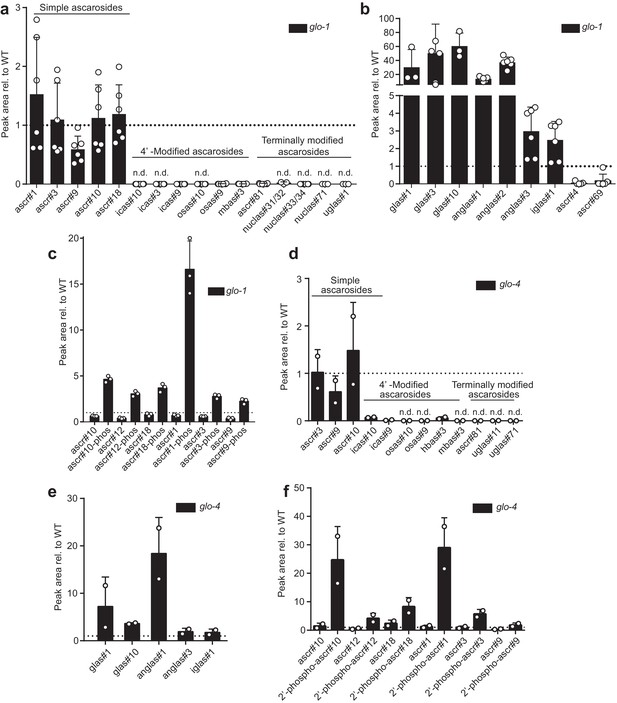
MS peak areas relative to wildtype (N2) of simple and modular ascarosides, glucosylated ascarosides, and phosphorylated ascarosides in glo-1 (a, b, c) and glo-4 (d, e, f) mutant worms.
Bars represent the mean of 6 (glo-1) and 2 (glo-4) biological replicates and error bars standard deviation. (c) Peak area relative to wildtype of simple and modular ascarosides in glo-4 mutant worms. Bars represent the mean of two replicates. n.d., not detected.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 5a–f.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig2-figsupp5-data1-v2.xlsx
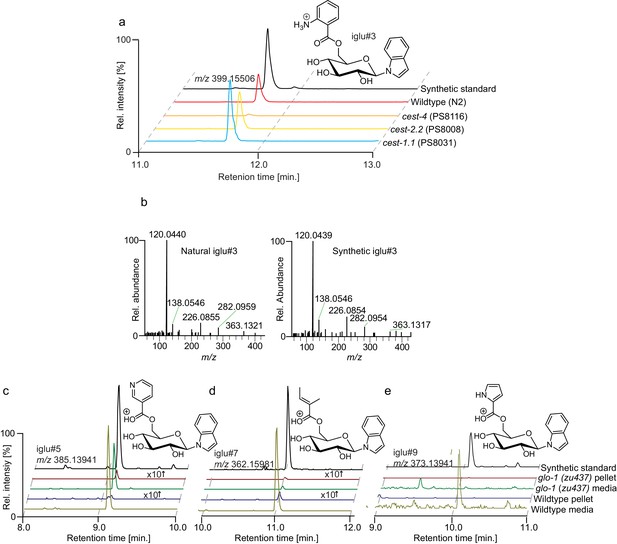
Identification of iglu metabolites.
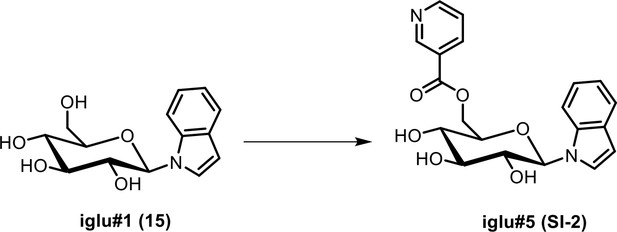
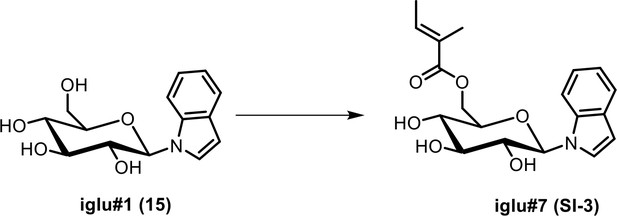
(a) Ion chromatograms of synthetic iglu#4 (19), and the levels of iglu#3 (34) in wildtype (N2), cest-4, cest-2.2 and cest-1.1. (b) MS2 spectra of synthetic iglu#3 (34) and the natural compound. Ion chromatograms of other indole containing glucosides in C. elegans and corresponding synthetic samples (black traces), including iglu#5 (SI-2), whose production is reduced but not abolished in glo-1 mutants, as well as largely glo-1 dependent iglu#7 (SI-3) and, iglu#9 (SI-4).
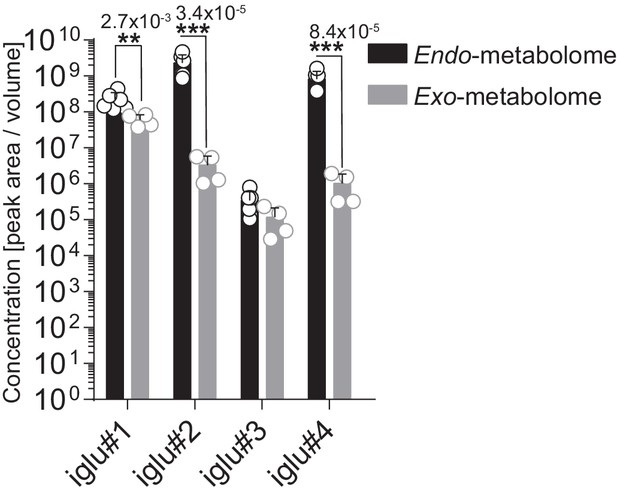
Concentration of simple and modular glucosides in the endo- or exo-metabolomes wild-type C. elegans.
Concentrations were calculated with respect to the volume pre-extraction, that is, the aggregate volume of the worm bodies and the volume of the media. Bars represent mean of six replicates. Error bars are standard deviation of the mean, and p-values are depicted in the Figure.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 7—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 7.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig2-figsupp7-data1-v2.xlsx
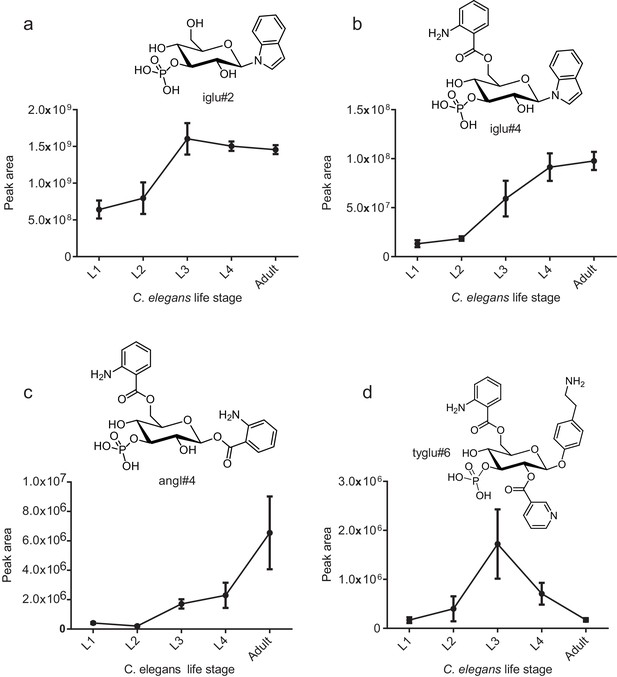
Production of modular glucosides is life-stage-dependent.
Levels of (a) iglu#2 (16), (b) iglu#4 (19), (c) angl#4 (25), and (d) tyglu#6 (proposed structure, SI-6) at different stages of development of C. elegans.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 8—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 8a–d.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig2-figsupp8-data1-v2.xlsx
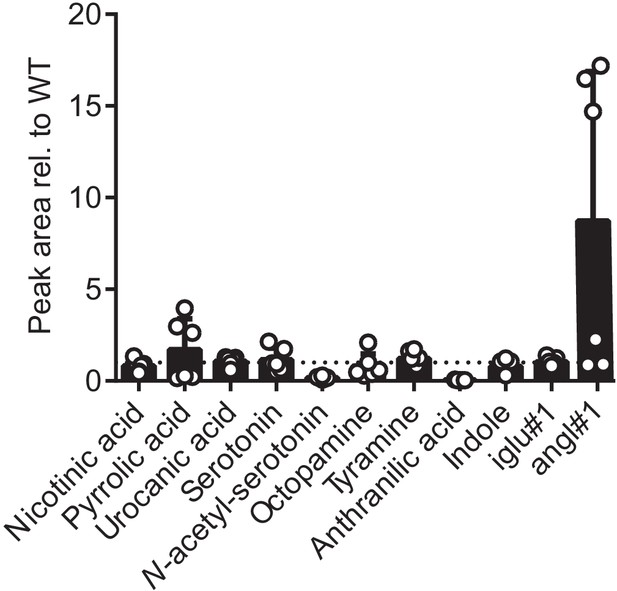
Peak area relative to wildtype (N2) of building blocks of modular glucosides in glo-1 mutant worms.
Bars represent mean of 6 replicates, with error bar representing standard deviation.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 9—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 9.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig2-figsupp9-data1-v2.xlsx
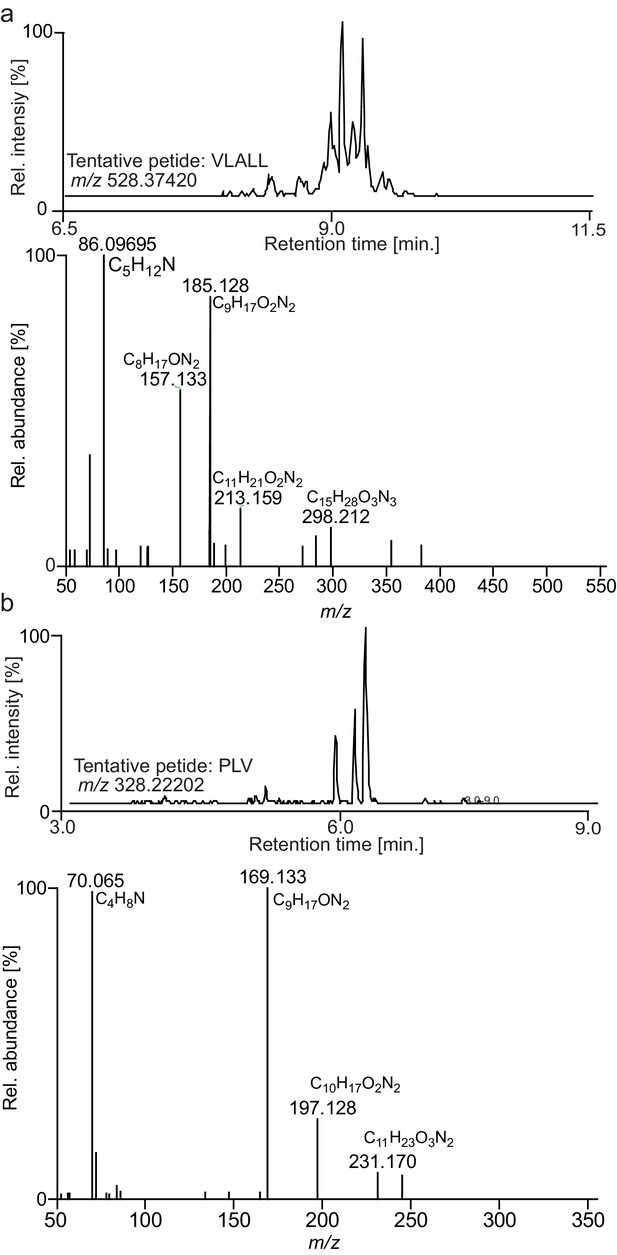
Representative ion chromatograms and MS2 spectra of upregulated leucine- and proline-containing peptides.
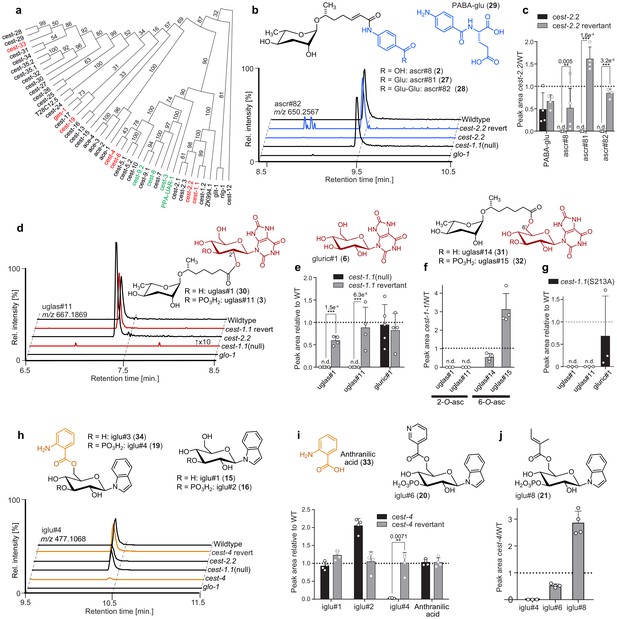
Carboxylesterases are required for modular assembly.
(a) Serine hydrolase dendrogram relating P. pacificus uar-1 to homologous predicted genes in C. elegans. Ppa-uar-1, cest-3, cest-8, cest-9.2 (green) mediate ester formation at the 4′-position of ascarosides in P. pacificus and C. elegans. Genes shown in red color were selected for the current study. (b,c) Production of ascr#8 (2), ascr#81 (27), and ascr#82 (28) is abolished in cest-2.2 mutants Isogenic revertant strains of the cest-2.2 null mutants in which the STOP-IN cassette was precisely excised, demonstrate wild-type-like recovery of the associated metabolite. (d,e) Production of uglas#1 and uglas#11 is abolished in cest-1.1(null) mutants and recovered in genetic revertants. (f) Biosynthesis of positional isomers uglas#14 (31) and uglas#15 (32) is unaltered or increased in cest-1.1 mutants (f). (g) Production of uglas#1 and uglas#11, but not gluric#1, is abolished in cest-1.1(S213) mutants. (h,i) Production of the anthranilic-acid-modified glucoside iglu#4 is largely abolished in cest-4 mutants and fully recovered in genetic revertants. (j) Production of iglu#6 (36) and iglu#8 (37), whose structures are closely related to that of iglu#4, is not abolished in cest-4 mutants. Ion chromatograms in panels b, d, and g further demonstrate abolishment in glo-1 mutants. n.d., not detected. Error bars are standard deviation of the mean, and p-values are depicted in the Figure.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3c,e,f,g,I,j.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
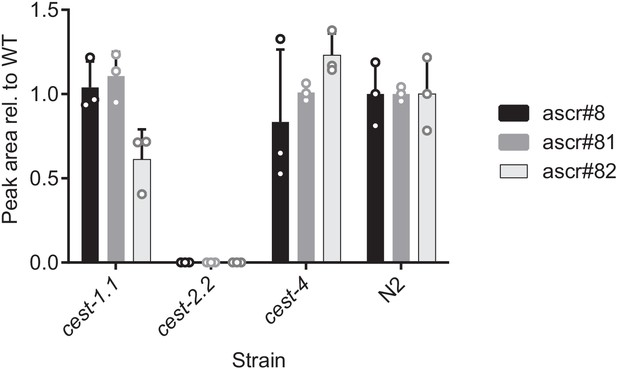
Relative abundances of ascr#8 (2) and related metabolites in cest-1.1, cest-2.2, cest-4 mutants, and wild type (N2).
Values were normalized relative to ascr#82 (28). Bars represent the mean of 3 replicates, and error bars are standard deviation.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
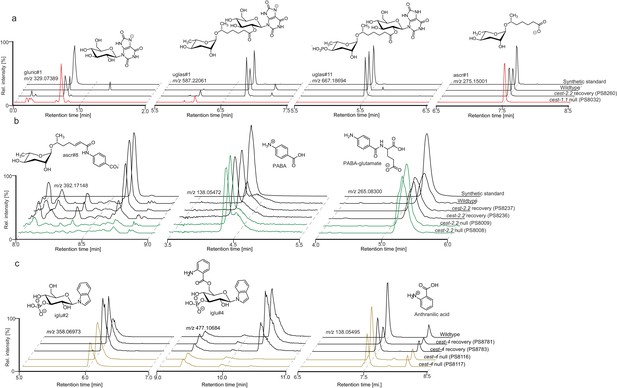
Ion chromatograms demonstrating that abundances of potential precursors of (a) cest-1.1-dependent, (b) cest-2.2-dependent, and (c) cest-4-dependent metabolites is large unchanged in the corresponding mutants.
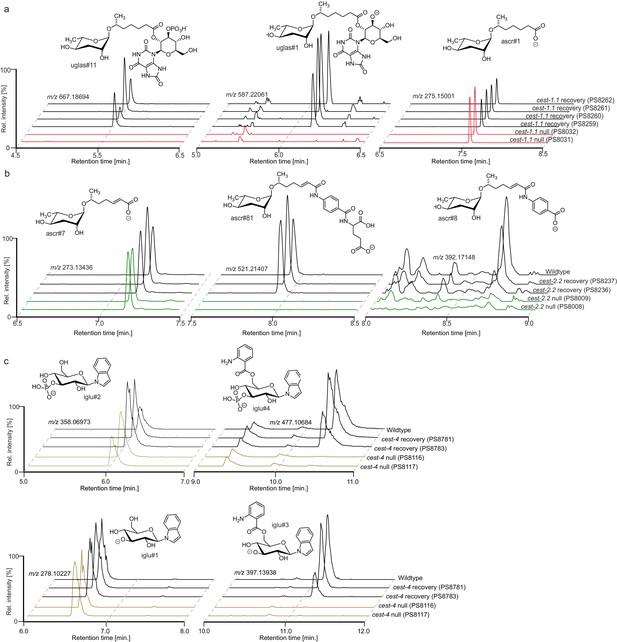
Ion chromatograms demonstrating recovery of (a) cest-1.1-dependent, (b) cest-8-dependent, (c) cest-2.2-dependent, (d) cest-4-dependent metabolites from CRISPR/Cas9 reversions of the corresponding null mutants.
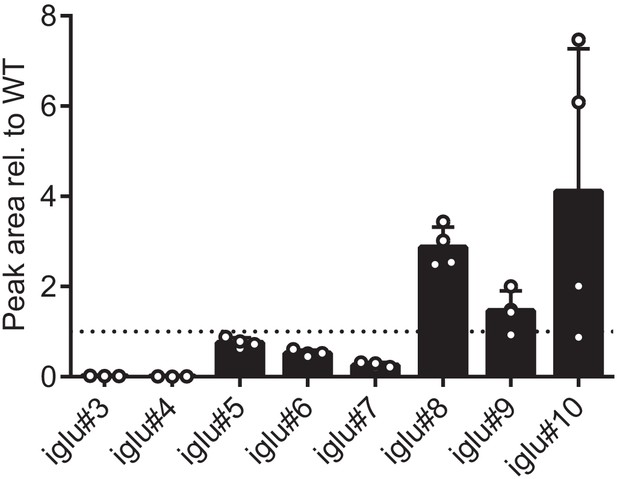
Relative abundance of other indole containing glucosides in cest-4 mutants, demonstrating that cest-4 is specifically required for the production of iglu#3 (34) and #4 (19).
Bars represent the mean of three replicates, and error bars are standard deviation.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3—figure supplement 4.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig3-figsupp4-data1-v2.xlsx
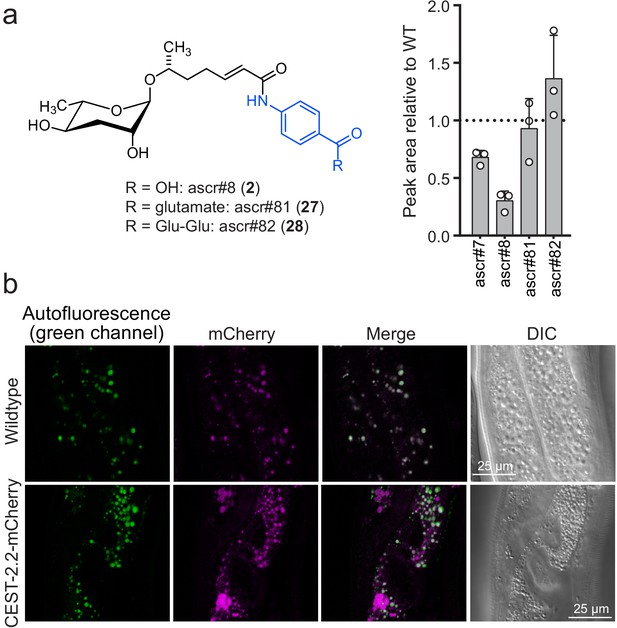
CEST-2.2 localizes to intestinal granules.
(a) Relative amounts of cest-2.2-dependent metabolites in worms expressing C-terminally mCherry-tagged CEST-2.2. (b) Red fluorescence in intestinal granules in wild-type and cest-2.2-mCherry gravid adults. Top, wild-type (N2) control; bottom, cest-2.2-mCherry worms.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4a.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx

Amino acid sequence alignments of human acetyl cholinesterase (hAChE), P. pacificus UAR-1, and C. elegans CEST-1.1, CEST-2.2, and CEST-4.
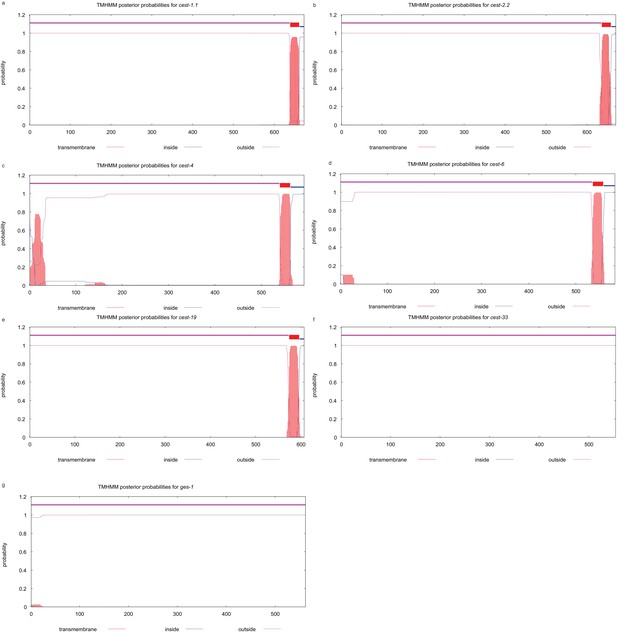
Transmembrane domain prediction for CEST proteins in this study (cest-1.1, cest-2.2, cest-4, cest-6, cest-19, cest-33, ges-1).
Predictions were performed by the TMHMM, as described previously.
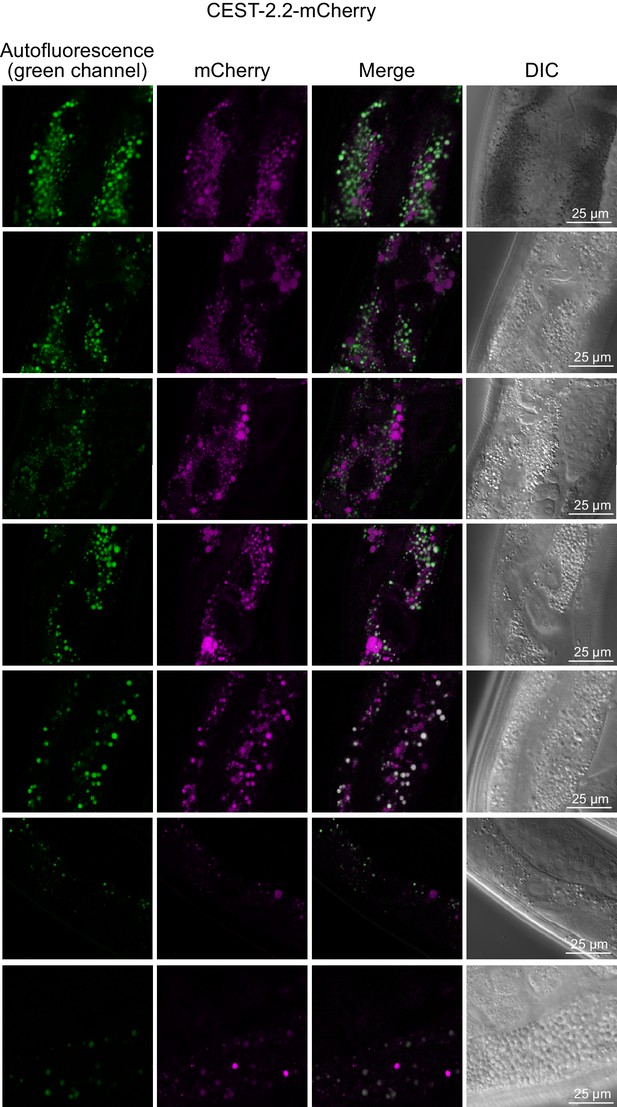
Red fluorescence in intestinal granules in gravid adults, expressing C-terminally mCherry-tagged CEST-2.2.
Images in the two bottom rows are from younger worms closer to young adult stage.
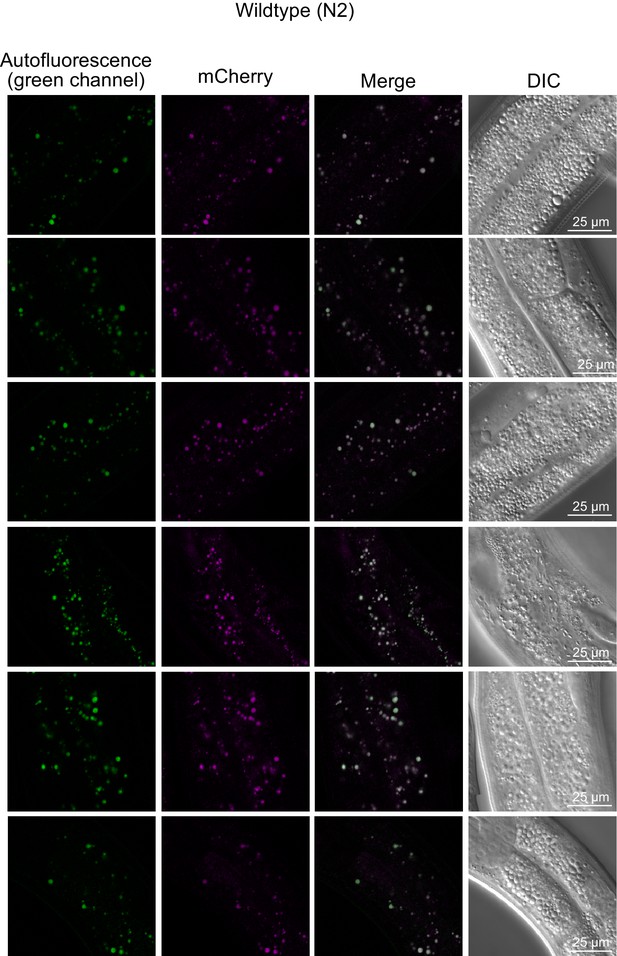
Co-localization of green and red autofluorescence in wild-type (N2) gravid adults.
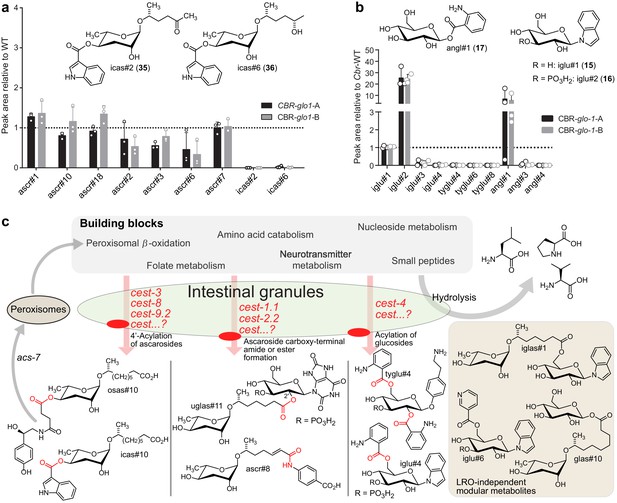
Relative abundance of (a) simple and modular ascarosides and (b) simple and modular glucosides in the endo-metabolome of Cbr-glo-1 mutants relative to wild-type C. briggsae.
n.d., not detected. (c) Model for modular metabolite assembly. CEST proteins (membrane-bound in the LROs, red) mediate attachment of building blocks from diverse metabolic pathways to glucose scaffolds and peroxisomal β-oxidation-derived ascarosides via ester and amide bonds. Some of the resulting modular ascarosides may undergo additional peroxisomal β-oxidation following activation by acs-7 (Dolke et al., 2019).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5a–b.
Attached as a separate file.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
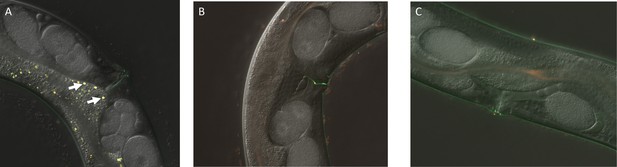
Gut granules in C. briggsae.
(a) C. briggsae WT AF16 has gut granules similar to C. elegans which are also both birefringent and easily tagged by Lysotracker Red (see arrows). Gut granule loss is evident in both (b) Cbr-glo-1(sy1382) and (c) Cbr-glo-1(sy1383).
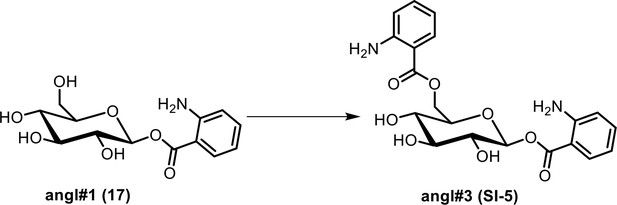
Synthesis of an HPLC standard of ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)−6-((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)−3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 2-aminobenzoate (angl#3, SI-5).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | N2 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | Wild type | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | GH10 | David Gems | glo-1(zu437) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | RB811 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | glo-4(ok623) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | RB2053 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | ges-1(ok2716) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8031 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1180) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8032 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1181) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | DP683 | This work | cest-1.1(dp683) (S213A) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8259 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1180 sy1250) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8260 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1180 sy1251) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8261 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1181 sy1252) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8262 | This work | cest-1.1(sy1181 sy1253) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8008 | This work | cest-2.2(sy1170) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8009 | This work | cest-2.2 (sy1171) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8236 | This work | cest-2.2(sy1170 sy1236) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8238 | This work | cest-2.2(sy1171 sy1238) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | FCS02 | SunyBiotech | cest-2.2-mCherry | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8116 | This work | cest-4(sy1192) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8117 | This work | cest-4(sy1193) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8781 | This work | cest-4(sy1192) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8782 | This work | cest-4(sy1193) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8783 | This work | cest-4(sy1194) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8784 | This work | cest-4(sy1195) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | RB1804 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC) | cest-6(ok2338) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8029 | This work | cest-19(sy1178) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8030 | This work | cest-19(sy1179) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8033 | This work | cest-33(sy1182) | |
| Strain, strain background Caenorhabditis elegans | PS8034 | This work | cest-33(sy1183) | |
| Strain (Caenorhabditis briggsae) | PS8515 | This work | CBR-glo-1(sy1382) | |
| Strain (Caenorhabditis briggsae) | PS8516 | This work | CBR-glo-1(sy1383) | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Proteinase K | New England Biolabs | New England Biolabs: P8107S | |
| Software, algorithm | Metaboseek | Metaboseek (metaboseek.com) | Version 0.9.6 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Prism (graphpad.com) | Version 8.4.3 |
MS2 data of glo-1-dependent features presented in this manuscript.
| Representative MS/MS spectra of modular glucosides. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | RT [min.] | Compound number | SMID | m/z (M+H) | m/z (M-H) | ms/ms fragments, positive ionization mode | ms/ms fragments, negative ionization mode | Substituents on glucose | Stable isotope labeling |
| C26H26N3O12P | 9.30 | angl#10 | 604.13381 | 602.11813 | 105.03366 (C7 H5 O+) 120.04469 (C7 H6 O N+) | 96.96870 (H2 O4 P-) 121.02911 (C7 H5 O2-) 136.03983 (C7 H6 O2 N-) | anthranilic acid, nicotinic acid | ||
| C20H22N2O7 | 8.67 | SI-5 | angl#3 | 403.14998 | 401.13542 | 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05496 (C7 H8 O2 N+) | anthranilic acid, anthranilic acid | ||
| C20H23N2O11P | 9.26 | 25 | angl#4 | 499.11235 | 497.09667 | 120.04463 (C7H6ON+) | 96.96868 (H2 O4 P-) 78.95800 (O3 P-) 136.03999 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 223.00078 (C6 H8 O7 P-) | anthranilic acid, anthranilic acid | |
| C19H21N2O9P | 9.59 | 22 | iglu#10 | 453.10574 | 451.09119 | 94.02916 (C5 H4 O N+) 118.06535 (C8 H8 N+) C14 H12 O2 N (C14 H12 O2 N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96867 (H2 O4 P-) 110.02444 (C5 H4 O2 N-) 116.05042 (C8 H6 N-) | indole, nicotinic acid | |
| C21H22NO9P | 10.79 | 23 | iglu#12 | 464.11049 | 462.09594 | 105.03382 (C7 H5 O+) 118.06538 (C8 H8 N+) 226.08620 (C14 H12 O2 N+) 348.12271 (C21 H18 O4 N+) | 78.95801 (O3 P-) 96.96865 (H2 O4 P-) | indole, benzoic acid | |
| C14H18NO8P | 6.05 | 16 | iglu#2 | 360.08541 | 358.06973 | 98.98453 (H4 O4 P+) 118.06536 (C8 H8 N+) 244.09660 (C14 H14 O3 N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96869 (H2 O4 P-) | indole | |
| C21H22N2O6 | 10.69 | 34 | iglu#3 | 399.15506 | 397.13938 | 116.05032 (C8 H6 N-) 136.04002 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 215.09431 (C13 H13 O2 N-) | indole, anthranilic acid | ||
| C21H23N2O9P | 10.29 | 19 | iglu#4 | 479.12252 | 477.10684 | 118.06536 (C8 H8 N+) 120.04456 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05490 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 226.08612 (C14 H12 O2 N+) | 78.95801 (O3 P-) 96.96867 (H2 O4 P-) 116.05042 (C8 H6 N-) 136.03970 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 358.06805 (C14 H17 O8 N P-) | indole, anthranilic acid | |
| C27H26N3O10P | 10.49 | 41 | iglu#41 | 584.14398 | 582.1283 | 96.04494 (C5 H6 O N+) 120.04456 (C7 H6 O N+) 124.03937 (C6 H6 O2 N+) 166.04985 (C8 H8 O3 N+) 228.06477 (C13 H10 O3 N+) 330.03705 (C12 H13 O8 N P+) | 78.95801 (O3 P-) 96.96867 (H2 O4 P-) 122.02431 (C6 H4 O2 N-) 136.04013 (C7 H6 O2 N-) | indole, anthranilic acid, nicotinic acid | |
| C26H29N2O10P | 10.48 | 20 | iglu#42 | 561.16439 | 559.14871 | 83.04974 (C5 H7 O+) 118.06553 (C8 H8 N+) 120.04465 (C7 H6 O N+) 202.08635 (C12 H12 O2 N+) | 78.95805 (O3 P-) 96.96868 (H2 O4 P-)136.03995 (C7 H6 O2 N-) | indole, antranilic acid, tiglic acid | |
| C20H20N2O6 | 8.93 | SI-2 | iglu#5 | 385.13941 | 383.12373 | 106.02911 (C6 H4 O N+) 118.06535 (C8 H8 N+) 124.03936 (C6 H6 O2 N+) 268.08124 (C12 H14 O6 N+) | indole, nicotinic acid | ||
| C20H21N2O9P | 8.29 | 20 | iglu#6 | 465.10687 | 463.09119 | 106.02907 (C6 H4 O N+) 118.06532 (C8 H8 N+) 124.03942 (C6 H6 O2 N+) 226.08630 (C14 H12 O2 N+) 250.07079 (C12 H12 O5 N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96868 (H2 O4 P-) 122.02421 (C6 H4 O2 N-) 340.05878 (C14 H15 O7 N P-) | indole, nicotinic acid | |
| C19H23NO6 | 11.24 | SI-3 | iglu#7 | 362.15981 | 360.14413 | 83.04967 (C5 H7 O+) 101.06001 (C5 H9 O2+) 118.06536 (C8 H8 N+) 198.09097 (C13 H12 O N+) 226.08626 (C14 H12 O2 N+) | indole, tiglic acid | ||
| C19H24NO9P | 10.48 | 21 | iglu#8 | 442.12727 | 440.11159 | 83.04967 (C5 H7 O+) 101.06020 (C5 H9 O2+) 118.06538 (C8 H8 N+) 226.08621 (C14 H12 O2 N+) | 78.95798 (O3 P-) 96.96864 (H2 O4 P-) 116.05011 (C8 H6 N-) | indole, tiglic acid | |
| C19H20N2O6 | 6.33 | SI-4 | iglu#9 | 373.13941 | 371.12486 | 110.02437 (C5 H4 O2 N-) 116.05027 (C8 H6 N-) | indole, nicotinic acid | ||
| C21H27N2O11P | 4.31 | oglu#4 | 515.14365 | 513.12797 | 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 136.07550 (C8 H10 O N+) 138.05511 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 216.06795 (C12 H10 O3 N+) | 78.95781 (O3 P-) 96.96854 (H2 O4 P-) 136.03995 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 223.00067 (C6 H8 O7 P-) 376.07953 (C14 H19 O9 N P-) | octopamine, anthranilic acid | d1 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
| C18H24N2O7 | 4.79 | sgnl#1 | 381.16563 | 379.14995 | 217.09767 (C12 H13 O2 N2-) | n-acetylserotonin | |||
| C25H29N3O8 | 7.34 | sgnl#3 | 500.20274 | 498.18706 | 120.04427 (C7H6NO+) 160.07555 (C10H10NO+) | n-acetylserotonin, anthranilic acid | |||
| C25H30N3O11P | 7.89 | sgnl#4 | 580.1702 | 578.15452 | 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05498 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 160.07590 (C10 H10 O N+) 219.11266 (C12 H15 O2 N2+) | (O3 P-) 96.96865 (H2 O4 P-) 136.04048 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 223.00072 (C6 H8 O7 P-) | n-acetylserotonin, anthranilic acid | ||
| C29H33N2O11P | 8.22 | tyglu#12 | 617.1906 | 615.17492 | 120.04458 (C7 H6 O N+) 238.08728 (C15 H12 O2 N+) | 78.95803 (O3 P-) 96.96867 (H2 O4 P-) 136.04008 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 135.04503 (C8 H7 O2-) 360.08469 (C14 H19 O8 N P-) 478.12738 (C29 H20 O6 N-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid, phenylacetic acid | d2 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
| C26H35N2O11P | 7.92 | tyglu#14 | 583.20625 | 581.19057 | 109.02870 (C6 H5 O2+) 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05489 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 204.10226 (C12 H14 O2 N+) 257.12808 (C15 H17 O2 N2+) 348.14429 (C18 H22 O6 N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96866 (H2 O4 P-) 101.05991 (C5 H9 O2-) 136.04047 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 444.14252 (C19 H27 O9 N P-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid, (iso)valeric acid | ||
| C28H31N2O11P | 7.97 | tyglu#16 | 603.17495 | 601.15927 | 105.03380 (C7 H5 O+) 120.04455 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05487 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 224.07047 (C14 H10 O2 N+) 257.12775 (C15 H17 O2 N2+) 368.11160 (C20 H18 O6 N+) | 78.95805 (O3 P-)96.96869 (H2 O4 P-) 121.02914 (C7 H5 O2-) 136.03978 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 464.11099 (C21 H23 O9 N P-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid, carboxy-benzyl | d2 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
| C21H27N2O10P | 5.40 | tyglu#2 | 499.14874 | 497.13306 | 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05487 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 138.09137 (C8 H12 O N+) 257.12814 (C15 H17 O2 N2+) 264.08633 (C13 H14 O5 N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96870 (H2 O4 P-) 136.04005 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 223.00053 (C6 H8 O7 P-) 360.08472 (C14 H19 O8 N P-) | tyramine,anthranilic acid | d2 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
| C28H32N3O11P | 7.65 | 26 | tyglu#4 | 618.18585 | 616.17017 | 120.04459 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.09137 (C8 H12 O N+) | 78.95802 (O3 P-) 96.96867 (H2 O4 P-) 136.03989 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 479.12198 (C21 H24 O9 N2 P-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid (x2) | |
| C27H30N3O11P | 6.55 | tyglu#6 | 604.1702 | 602.15452 | 106.02901 (C6 H4 O N+) 120.04460 (C7 H6 O N+) 124.03939 (C6 H6 O2 N+) 138.05513 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 166.04988 (C8 H8 O3 N+) 257.12781 (C15 H17 O2 N2+) | 78.95781 (O3 P-) 96.96851 (H2 O4 P-) 223.00017 (C6 H8 O7 P-) 381.09375 (C16 H17 O9 N2-) 534.17279 (C22 H33 O12 N P-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid, nicotinic acid | d2 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
| C26H33N2O11P | 7.67 | tyglu#8 | 581.1906 | 579.17492 | 83.04968 (C5 H7 O+) 120.04460 (C7 H6 O N+) 138.05479 (C7 H8 O2 N+) 257.12848 (C15 H17 O2 N2+) | 78.95779 (O3 P-) 96.96852 (H2 O4 P-) 99.04408 (C5 H7 O2-) 136.03972 (C7 H6 O2 N-) 442.12637 (C19 H25 O9 N P-) | tyramine, anthranilic acid, tiglic acid | d2 from d2-L-Tyrosine | |
BLASTp results from the WormBase BLAST engine when searching against the amino acid sequence of UAR-1 and CRISPR/Cas9 targets for this study (red).
| Sequence | Score | E-value |
|---|---|---|
| C01B10.10 | 280 | 2e-75 |
| C01B10.4a | 260 | 2e-69 |
| T22D1.11 | 248 | 7e-66 |
| C42D4.2 | 233 | 4e-61 |
| 231 | 1e-60 | |
| C23H4.4a | 225 | 8e-59 |
| C23H4.7 | 199 | 6e-51 |
| C23H4.3 | 194 | 1e-49 |
| E01G6.3 | 193 | 3e-49 |
| C23H4.2 | 168 | 1e-41 |
| 157 | 2e-38 | |
| F15A8.6a | 154 | 1e-37 |
| F15A8.6b | 154 | 1e-37 |
| ZC376.3 | 153 | 3e-37 |
| T02B5.3 | 150 | 2e-36 |
| 148 | 1e-35 | |
| 147 | 2e-35 | |
| F56C11.6b | 141 | 1e-33 |
| F56C11.6a | 137 | 2e-32 |
| Y71H2AM.13 | 136 | 5e-32 |
| ZC376.1 | 135 | 1e-31 |
| R173.3 r | 129 | 6e-30 |
| T07H6.1a | 127 | 2e-29 |
| T28C12.4a | 124 | 1e-28 |
| T28C12.4b | 124 | 2e-28 |
| K07C11.4 | 119 | 6e-27 |
| 118 | 1e-26 | |
| K11G9.2 | 116 | 4e-26 |
| 02B12.4 | 115 | 8e-26 |
| Y75B8A.3 | 114 | 3e-25 |
| Y48B6A.8 | 113 | 4e-25 |
| F13H6.3 | 111 | 2e-24 |
| Y48B6A.7 | 109 | 5e-24 |
| 09B12.1 | 108 | 9e-24 |
| K11G9.1 | 108 | 2e-23 |
| ZC376.2c | 105 | 7e-23 |
| F07C4.12b | 105 | 7e-23 |
| C52A10.1 | 101 | 1e-21 |
| Y44E3A.2 | 101 | 2e-21 |
| K11G9.3 | 99 | 1e-20 |
| C52A10.2 | 97 | 3e-20 |
| C40C9.5d | 96 | 6e-20 |
| C40C9.5b | 96 | 6e-20 |
| C40C9.5a | 96 | 6e-20 |
| F55D10.3 | 96 | 1e-19 |
| C40C9.5f | 94 | 2e-19 |
| C01B10.4b | 94 | 2e-19 |
| C40C9.5g | 94 | 2e-19 |
| C40C9.5c | 94 | 3e-19 |
| C40C9.5e | 94 | 3e-19 |
| B0238.7 | 93 | 4e-19 |
| B0238.1 | 92 | 1e-18 |
| F55F3.2b | 83 | 6e-16 |
| F55F3.2a | 83 | 7e-16 |
| C23H4.4b | 50 | 5e-06 |
| Y43F8A.3a | 42 | 0.002 |
| Y43F8A.3b | 35 | 0.18 |
List of C. elegans strains used in this study.
| Strain name | Identifier | Description | Associated metabolites |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS8031 | cest-1.1(sy1180) | cest-1.1 null | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8032 | cest-1.1(sy1181) | cest-1.1 null | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8259 | cest-1.1(sy1180 sy1250) | cest-1.1 null reverted to WT sequence | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8260 | cest-1.1(sy1180 sy1251) | cest-1.1 null reverted to WT sequence | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8261 | cest-1.1(sy1181 sy1252) | cest-1.1 null reverted to WT sequence | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8262 | cest-1.1(sy1181 sy1253) | cest-1.1 null reverted to WT sequence | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| PS8008 | cest-2.2(sy1170) | cest-2.2 null | ascr#8, ascr#81, ascr#82 |
| PS8009 | cest-2.2(sy1171) | cest-2.2 null | ascr#8, ascr#81, ascr#82 |
| PS8236 | cest-2.2(sy1170 sy1236) | cest-2.2 null reverted to WT sequence | ascr#8, ascr#81, ascr#82 |
| PS8238 | cest-2.2(sy1171 sy1238) | cest-2.2 null reverted to WT sequence | ascr#8, ascr#81, ascr#82 |
| PS8116 | cest-4(sy1192) | cest-4 null | iglu class modular glucosides |
| PS8117 | cest-4(sy1193) | cest-4 null | iglu class modular glucosides |
| JJ1271 | glo-1(zu437) | glo-1 null | Most known modular ascarosides/glucosides |
| PS8781 | cest-4(sy1192) | cest-4 null reverted to WT sequence | iglu class modular glucosides |
| PS8782 | cest-4(sy1193) | cest-4 null reverted to WT sequence | iglu class modular glucosides |
| PS8783 | cest-4(sy1194) | cest-4 null reverted to WT sequence | iglu class modular glucosides |
| PS8784 | cest-4(sy1195) | cest-4 null reverted to WT sequence | iglu class modular glucosides |
| PS8515 | CBR-glo-1-A (sy1382) | C. briggsae glo-1 null | Most known modular ascarosides/glucosides |
| PS8516 | CBR-glo-1-B (sy1383) | C. briggsae glo-1 null | Most known modular ascarosides/glucosides |
| PS8029 | cest-19(sy1178) | cest-19 null | Undetermined |
| PS8030 | cest-19(sy1179) | cest-19 null | Undetermined |
| PS8033 | cest-33(sy1182) | cest-33 null | Undetermined |
| PS8034 | cest-33(sy1183) | cest-33 null | Undetermined |
| RB2053 | ges-1 (ok2716) | ges-1 null | Undetermined |
| RB1804 | cest-6(ok2338) | cest-6 null | Undetermined |
| DP683 | cest-1.1(dp683) | cest-1.1 (S213A) point mutant | uglas#1 uglas#11 |
| FCS02 | cest-2.2-mCherry | cest-2.2 C-terminal mCherry | ascr#8, ascr#81, ascr#82 |
NMR spectroscopic data for iglu#3 (34).
1H (600 MHz), HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectroscopic data were acquired in methanol-d4. Chemical shifts were referenced to δ(CHD2OD)=3.31 ppm and δ(13CHD2OD)=49.00 ppm.
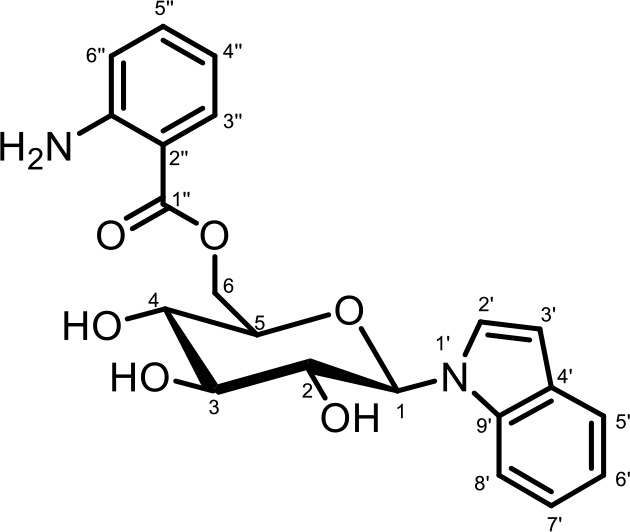 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δ 13C [ppm] | δ 1H ([ppm] JHH[Hz]) | HMBC |
| 1 | 86.9 | 5.51 (J1,2 = 9.3) | C-2, C-3, C-5, C-2’, C-9’ |
| 2 | 73.0 | 3.99 (J2,3 = 9.0) | C-1, C-3 |
| 3 | 78.7 | 3.65 (J3,4 = 9.0) | C-4 |
| 4 | 71.3 | 3.64 (J4,5 = 9.1) | C-3 |
| 5 | 77.5 | 3.91 (J5,6a = 5.5) | C-4 |
| 6a | 64.1 | 4.43 (J6a,6b = 12.1) | C-5, C-1′′ |
| 6b | 4.67 (J5,6b = 2.2) | C-4, C-1′′ | |
| 2′ | 126.3 | 7.37 (J2’,3’=3.3) | C-1 (weak), C-3', C-4’, C-8’ (weak), C-9’ |
| 3′ | 102.9 | 6.48 | |
| 4′ | 130.4 | ||
| 5′ | 121.4 | 7.52 (J5’,6’=8.0) | C-3’, C-7’, C-9’ |
| 6′ | 120.8 | 7.03 (J6’,7’=7.4, J3’,6’=1.1) | C-4’, C-8’ |
| 7′ | 122.4 | 7.06 | C-5’, C-9’ |
| 8′ | 111.5 | 7.53 | C-4’, C-6’ |
| 9′ | 137.5 | ||
| 1′′ | 168.6 | ||
| 2′′ | 112.8 | ||
| 3′′ | 132.1 | 7.90 (J3’’,4’’=8.2, J3’’,5’’=1.4) | C-1’’, C-5’’, C-7’’ |
| 4′′ | 118.2 | 6.73 (J4’’,5’’=7.6) | C-2’’, C-6’’ |
| 5′′ | 135.0 | 7.32 (J5’’,6’’=7.8) | C-3’’, C-7’’ |
| 6′′ | 118.6 | 6.84 | C-2’’, C-4’’ |
| 7′′ | 149.9 | ||
NMR spectroscopic data for iglu#5 (SI-2).
1H (600 MHz), HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectroscopic data were acquired in methanol-d4. Chemical shifts were referenced to δ(CHD2OD)=3.31 ppm and δ(13CHD2OD)=49.00 ppm.
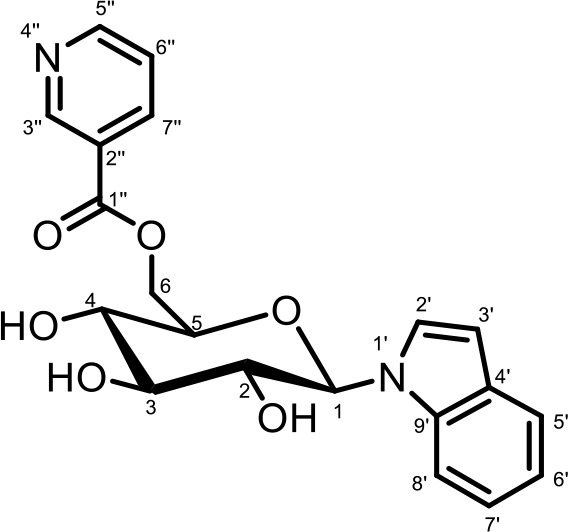 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δ 13C [ppm] | δ 1H ([ppm] JHH[Hz]) | HMBC |
| 1 | 86.9 | 5.51 (J1,2 = 9.2) | C-2, C-3, C-5, C-2’, C-9’ |
| 2 | 73.0 | 4.00 (J2,3 = 9.0) | C-1, C-3 |
| 3 | 78.7 | 3.65 (J3,4 = 9.0) | C-4 |
| 4 | 71.4 | 3.63 (J4,5 = 8.9) | C-3 |
| 5 | 77.4 | 3.95 (J5,6a = 5.8) | C-4 |
| 6a | 65.3 | 4.51 (J6a,6b = 12.1) | C-4, C-5, C-1′′ |
| 6b | 4.75 (J5,6b = 2.3) | C-4, C-5, C-1′′ | |
| 2′ | 126.4 | 7.37 (J2’,3’=3.5) | C-3', C-4’, C-9’ |
| 3′ | 103.1 | 6.47 | C-2', C-4’, C-9’ |
| 4′ | 130.5 | ||
| 5′ | 121.4 | 7.51 (J5’,6’=7.9) | C-4’, C-6’, C-9’ |
| 6′ | 120.8 | 7.01 (J6’,7’=7.5, J3’,6’=1.2) | C-4’, C-8’ |
| 7′ | 122.5 | 7.05 | C-4’, C-5’, C-8’, C-9’ |
| 8′ | 111.4 | 7.49 | C-4’, C-6’ |
| 9′ | 137.6 | ||
| 1′′ | 165.8 | ||
| 2′′ | 127.7 | ||
| 3′′ | 150.8 | 9.12 (J3’’,6’’=0.5, J3’’,7’’=2.0) | C-2’’, C-5’’, C-7’’ |
| 5′′ | 153.7 | 8.74 (J5’’,6’’=4.9, J5’’’,7’’=1.7) | C-3’’, C-6’’, C-7’’ |
| 6′′ | 125.1 | 7.54 (J6’’’,7’’=8.0) | C-2’’, C-5’’ |
| 7′′ | 138.9 | 8.37 | C-1’’, C-2’’, C-5’’ |
NMR spectroscopic data for iglu#7 (SI-3).
1H (600 MHz), HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectroscopic data were acquired in methanol-d4. Chemical shifts were referenced to δ(CHD2OD)=3.31 ppm and δ(13CHD2OD)=49.00 ppm.
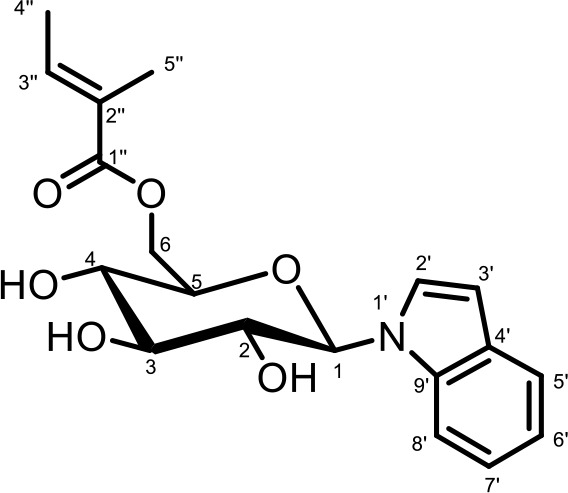 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δ 13C [ppm] | δ 1H ([ppm] JHH[Hz]) | HMBC |
| 1 | 86.9 | 5.46 (J1,2 = 9.1) | C-2, C-3, C-5, C-2’, C-9’ |
| 2 | 73.2 | 3.96 (J2,3 = 9.0) | C-1, C-3 |
| 3 | 78.9 | 3.61 (J3,4 = 9.0) | C-2, C-4 |
| 4 | 71.4 | 3.55 (J4,5 = 9.6) | C-3, C-5, C-6 |
| 5 | 77.6 | 3.81 (J5,6a = 5.6) | C-1 (weak), C-3, C-4 |
| 6a | 64.5 | 4.27 (J6a,6b = 11.9) | C-4, C-5, C-1′′ |
| 6b | 4.49 (J5,6b = 2.2) | C-4, C-5, C-1′′ | |
| 2′ | 126.6 | 7.35 (J2’,3’=3.5) | C-1 (weak), C-3', C-4’, C-5’ (weak), C-8’ (weak), C-9’ |
| 3′ | 103.2 | 6.48 | |
| 4′ | 130.6 | ||
| 5′ | 121.6 | 7.53 (J5’,6’=7.9) | C-3’, C-7’, C-9’ |
| 6′ | 120.9 | 7.05 (J6’,7’=7.5, J3’,6’=1.1) | C-4’, C-8’, C-9’ (weak) |
| 7′ | 122.5 | 7.11 | C-5’, C-8’ (weak), C-9’ |
| 8′ | 111.7 | 7.50 | C-4’, C-6’ |
| 9′ | 137.6 | ||
| 1′′ | 169.2 | ||
| 2′′ | 129.3 | ||
| 3′′ | 138.9 | 6.87 (J3’’,4’’=6.8) | C-1’’, C-4’’, C-5’’ |
| 4′′ | 14.2 | 1.79 | C-2’’, C-3’’ |
| 5′′ | 11.9 | 1.81 | C-1’’, C-2’’, C-3’’ |
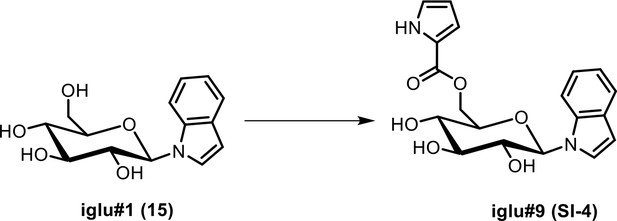
NMR spectroscopic data for iglu#9 (SI-4).
1H (600 MHz), HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectroscopic data were acquired in methanol-d4. Chemical shifts were referenced to δ(CHD2OD)=3.31 ppm and δ(13CHD2OD)=49.00 ppm.
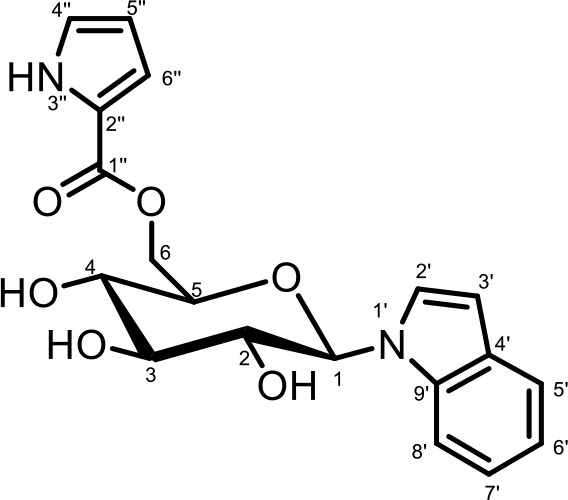 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δ 13C [ppm] | δ 1H ([ppm] JHH[Hz]) | HMBC |
| 1 | 86.9 | 5.47 (J1,2 = 9.1) | C-2, C-3, C-5, C-2’, C-9’ |
| 2 | 73.2 | 3.96 (J2,3 = 9.0) | C-1, C-3 |
| 3 | 78.7 | 3.62 (J3,4 = 9.8) | C-4 |
| 4 | 71.3 | 3.61 (J4,5 = 9.7) | C-3 |
| 5 | 77.9 | 3.86 (J5,6a = 5.7) | |
| 6a | 63.9 | 4.38 (J6a,6b = 11.9) | C-5, C-1′′ |
| 6b | 4.68 (J5,6b = 2.1) | C-4, C-1′′ | |
| 2′ | 126.6 | 7.36 (J2’,3’=3.4) | C-3', C-4’, C-9’ |
| 3′ | 103.1 | 6.47 | C-2', C-4’, C-9’ |
| 4′ | 130.6 | ||
| 5′ | 121.4 | 7.52 (J5’,6’=7.8) | C-7’, C-9’ |
| 6′ | 120.8 | 7.02 (J6’,7’=7.3, J3’,6’=1.2) | C-4’, C-8’ |
| 7′ | 122.4 | 7.05 | C-5’, C-9’ |
| 8′ | 111.6 | 7.50 | C-4’, C-6’ |
| 9′ | 137.4 | ||
| 1′′ | 162.4 | ||
| 2′′ | 123.0 | ||
| 4′′ | 124.7 | 6.96 (J4’’,5’’=2.5, J4’’,6’’=1.4) | C-2’’, C-5’’, C-6’’ |
| 5′′ | 110.6 | 6.20 (J5’’,6’’=3.8) | C-2’’(weak), C-4’’(weak) |
| 6′′ | 116.8 | 6.90 | C-2’’, C-4’’, C-5’’ |
DNA oligonucleotides used for this study.
| Target gene | Sequence name | Strain | Allelle | Guide sequence | ssDNA repair oligonucleotide sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cest-1.1 | T02B5.1 | PS8031, PS8032 | sy1180, sy1181 | ACTCCTTCCCATGATTTCGG | TATTCATTTGTTACCAAAACTCCTTCCCATGATTTG CTAGCTTATCACTTAGTCACCTCTGCTCTGGACAAA CTTCCCCGGTGGACGGGGTTTTCGATATCGAAGGTCTCCAATTG |
| cest-2.2 | ZC376.2 | PS8008, PS8009 | sy1170, sy1171 | GGAGGCGAAGGAGTATAAAG | CCCTGGGACGGAGTTTTGGAGGCGAAGGAGTATA GGGAAGTTTGTCCAGAGCAGAGGTGACTAAGTGATAA GCTAGCAAGCGGCTTGTATGAGTGATCAGAAGTAAGAGATA |
| cest-4 | C17H12.4 | PS8116, PS8117 | sy1192, sy1193 | ACTCCGGTCCATTTCTCAGG | CATACCTTTTGCATTTCTCACTCCGGTCCATTTCTCGCTAGC TTATCACTTAGTCACCTCTGCTCTGGACAAACTTCCCAGGCGG TTCTGGTTTTTGAAATCTTAATTTTCCAATTG |
List of all modular metabolites referred to in the text and Figures.
| Compound number | SMID ID | IUPAC Name | Evidence | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | icas#3 | (R)−8-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−5-((1H-indole-3-carbonyl)oxy)−3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)nonanoic acid | Previously identified via synthesis (Srinivasan et al., 2012) | 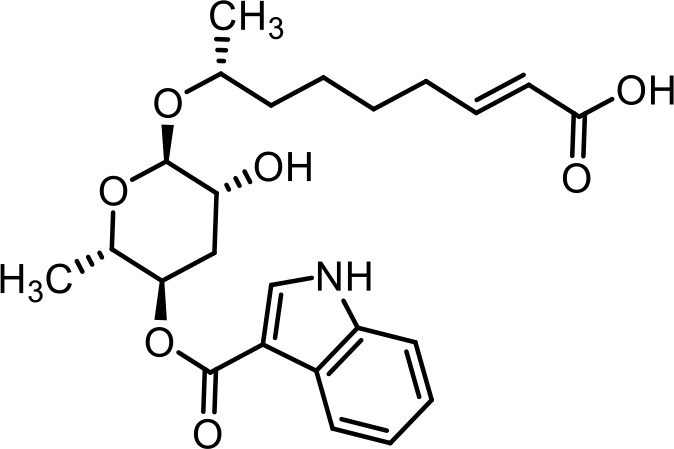 |
| 2 | ascr#8 | 4-((R,E)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)hept-2-enamido)benzoic acid | Previously identified via synthesis (Pungaliya et al., 2009) | 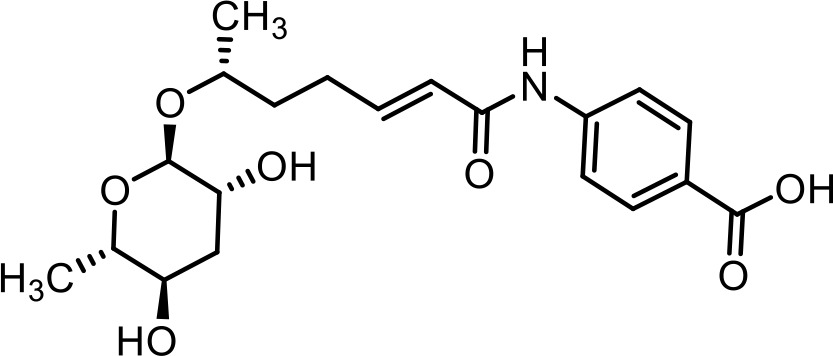 |
| 3 | uglas#11 | (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)−4-(phosphonooxy)−2-(2,6,8-trioxo-1,2,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-3H-purin-3-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoate | Previously identified via synthesis (Curtis et al., 2020) | 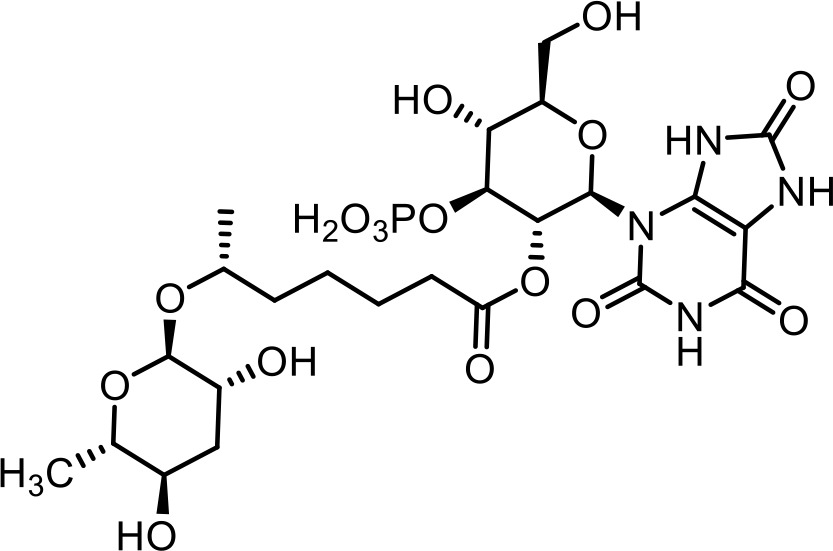 |
| 4 | ubas#3 | (R)−4-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3-hydroxy-6-methyl-5-(((R)−2-methyl-3-ureidopropanoyl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)pentanoic acid | Previously inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (Falcke et al., 2018) | 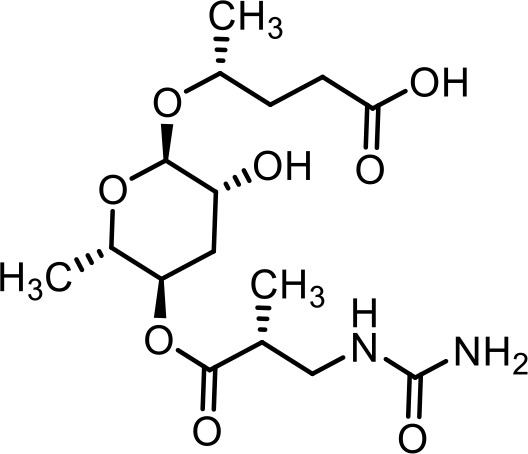 |
| 5 | ascr#1 | (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoic acid | Previously identified via NMR and synthesis (Jeong et al., 2005) | 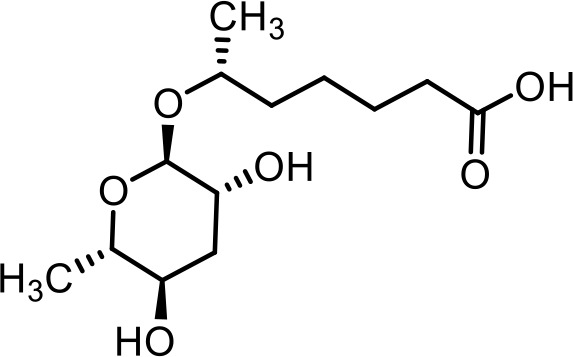 |
| 6 | gluric#1 | 3-((2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)−7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8 (3H)-trione | Previously identified via synthesis (Curtis et al., 2020) | 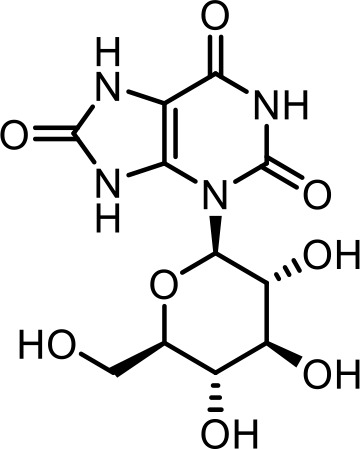 |
| 7 | ascr#7 | (R,E)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)hept-2-enoic acid | Previously identified via synthesis (Pungaliya et al., 2009) | 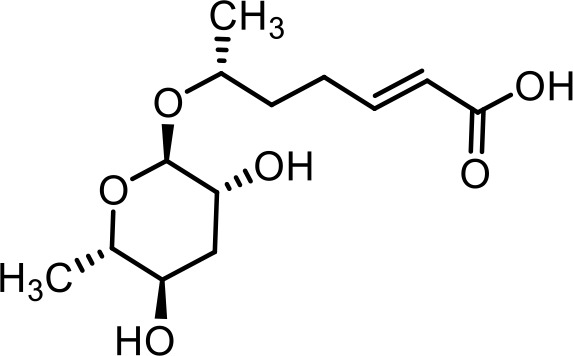 |
| 8 | PABA | 4-Aminobenzoic acid | Commercial product (Sigma-Aldrich) | 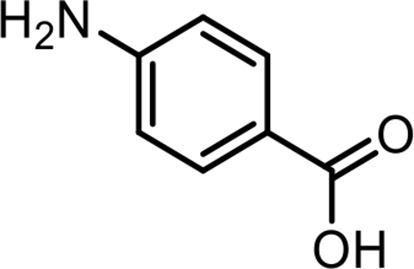 |
| 9 | ascr#3 | (R,E)−8-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)non-2-enoic acid | Previously identified via synthesis (Butcher et al., 2007) | 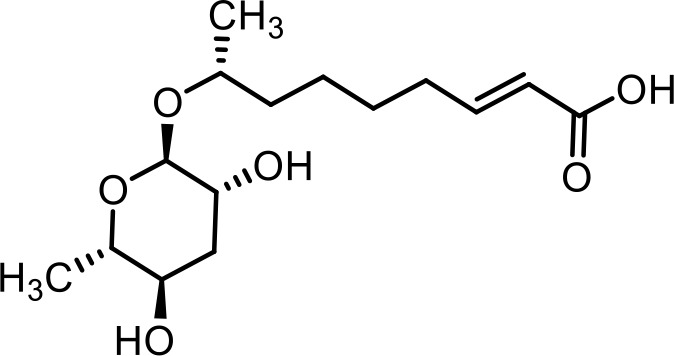 |
| 10 | ascr#10 | (R)−8-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)nonanoic acid | Previously identified via synthesis (Srinivasan et al., 2012) | 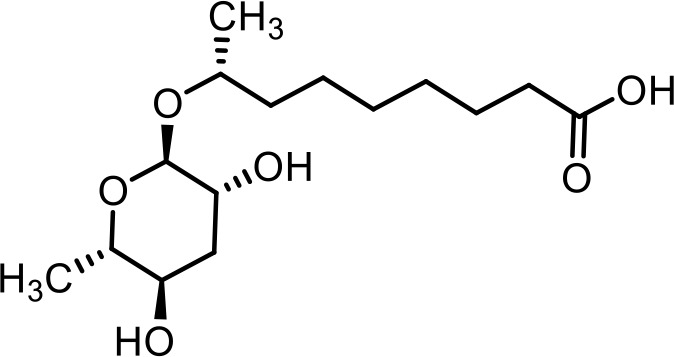 |
| 11 | 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid | Commercial product (Sigma-Aldrich) | 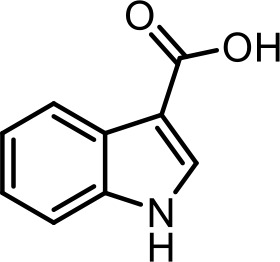 | |
| 12 | (R)−4-((2-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl)amino)−4-oxobutanoic acid | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 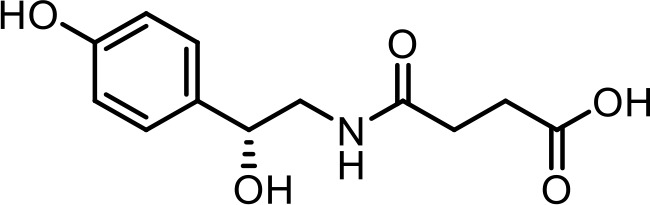 | |
| 13 | iglas#1 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoate | Previously identified via synthesis (Artyukhin et al., 2018) | 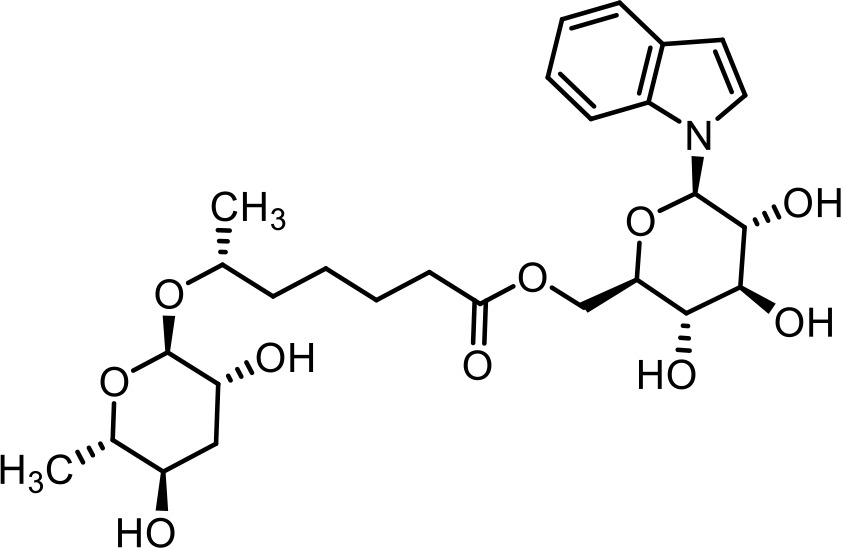 |
| 14 | glas#10 | (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl (R)−8-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)nonanoate | Previously identified via NMR and synthesis (Coburn et al., 2013) | 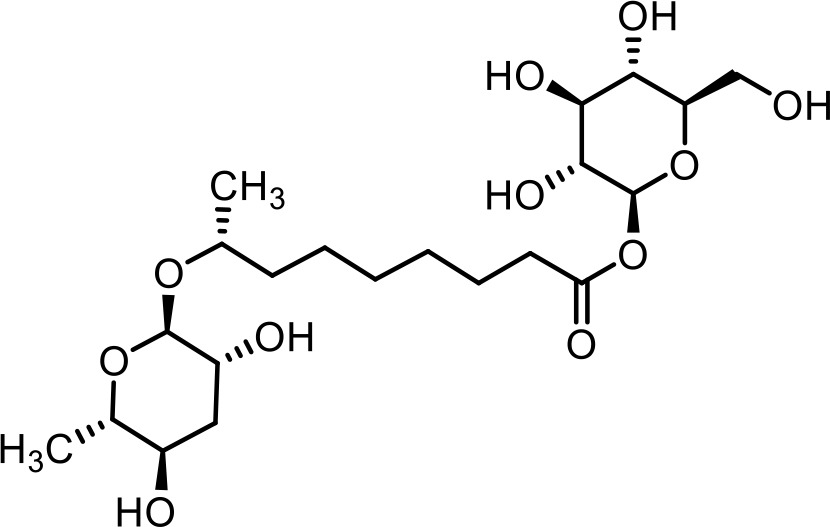 |
| 15 | iglu#1 | (2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−2-(hydroxymethyl)−6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol | Previously identified via NMR and synthesis (Coburn et al., 2013) | 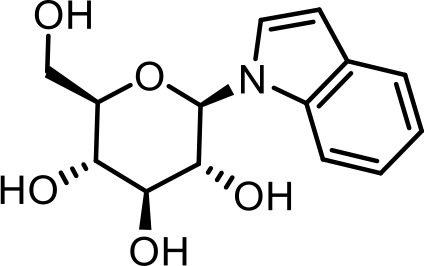 |
| 16 | iglu#2 | (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)−6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl dihydrogen phosphate | Previously identified via NMR (Coburn et al., 2013) | 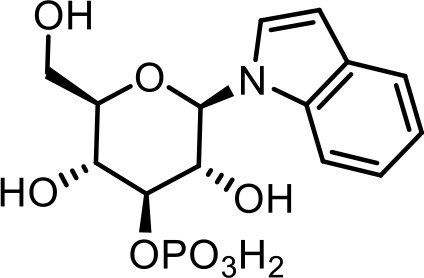 |
| 17 | angl#1 | (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl 2-aminobenzoate | Previously identified via NMR and synthesis (Coburn et al., 2013) | 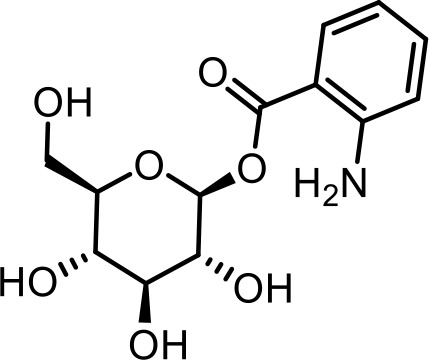 |
| 18 | angl#2 | (2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl 2-aminobenzoate | Previously identified via NMR (Coburn et al., 2013) | 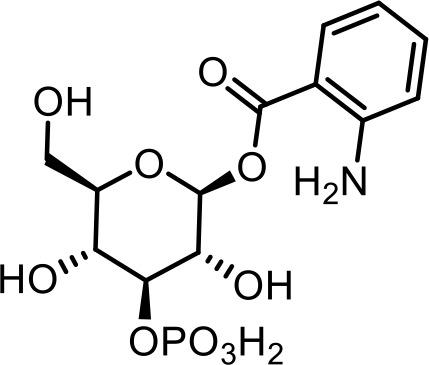 |
| 19 | iglu#4 | (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-(pyran-2-yl)methyl 2-aminobenzoate | Proposed structure, based on identification of non-phosphorylated derivative (34) via synthesis (This manuscript) | 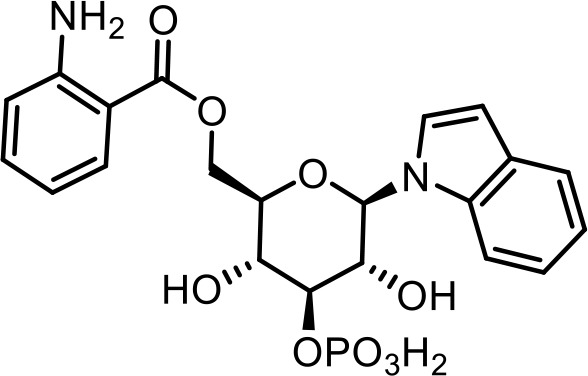 |
| 20 | iglu#6 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl nicotinate | Proposed structure, based on identification of non-phosphorylated derivative (SI-2) via synthesis (This manuscript) | 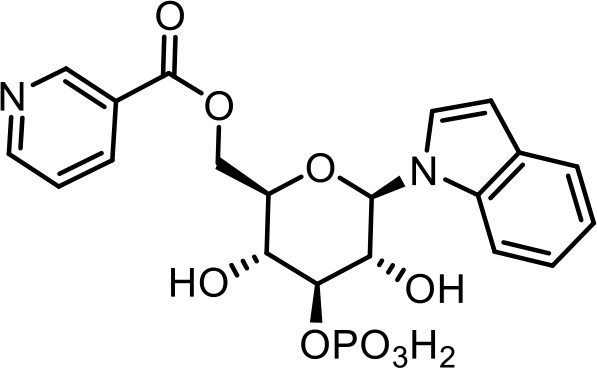 |
| 21 | iglu#8 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (E)−2-methylbut-2-enoate | Proposed structure, based on identification of non-phosphorylated derivative (SI-3) via synthesis (This manuscript) | 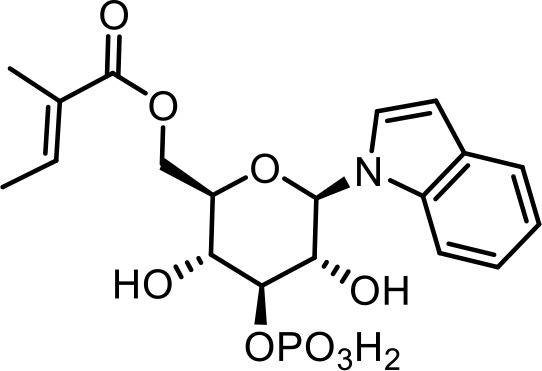 |
| 22 | iglu#10 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate | Proposed structure, based on identification of non-phosphorylated derivative (SI-4) via synthesis (This manuscript) | 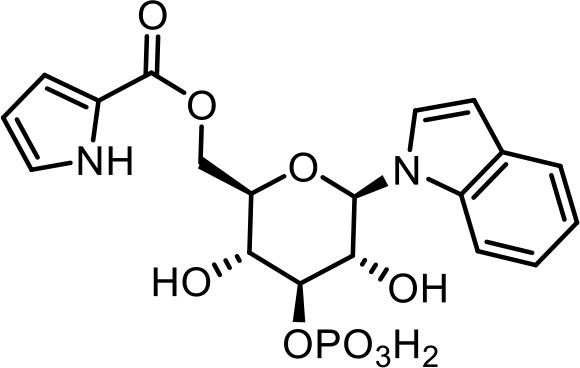 |
| 23 | iglu#12 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl benzoate | Proposed structure. Inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (This manuscript) | 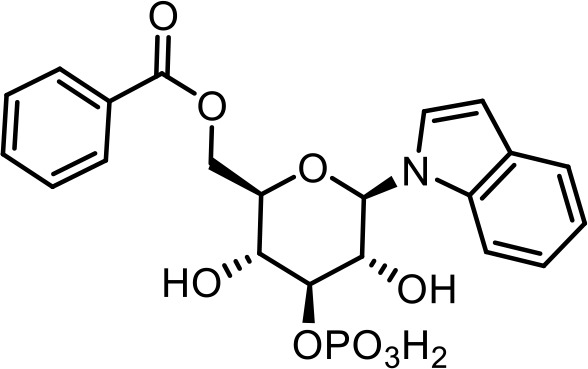 |
| 24 | iglu#41 | (2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−6-(((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)methyl)−5-hydroxy-2-(1H-indol-1-yl)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate | Proposed structure. Inferred from iglu#3 (34) via tandem mass spectrometry (This manuscript) | 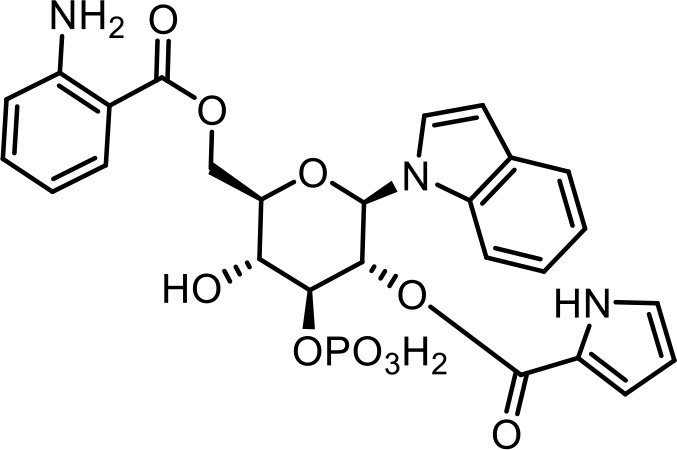 |
| 25 | angl#4 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6S)−6-((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)−3,5-dihydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 2-aminobenzoate | Proposed structure. Inferred from angl#3 (SI 5) via tandem mass spectrometry (This manuscript) | 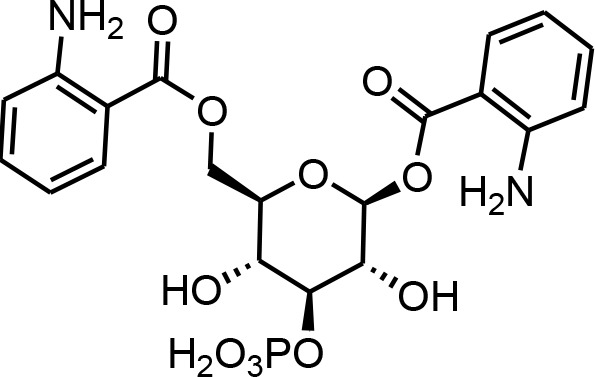 |
| 26 | tyglu#4 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−5-((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)−3-hydroxy-6-((4-(2-aminoethyl)phenoxy)−4-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl))methyl 2-aminobenzoate | Proposed structure. Initially described (O'Donnell et al., 2020) and further inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (This manuscript) | 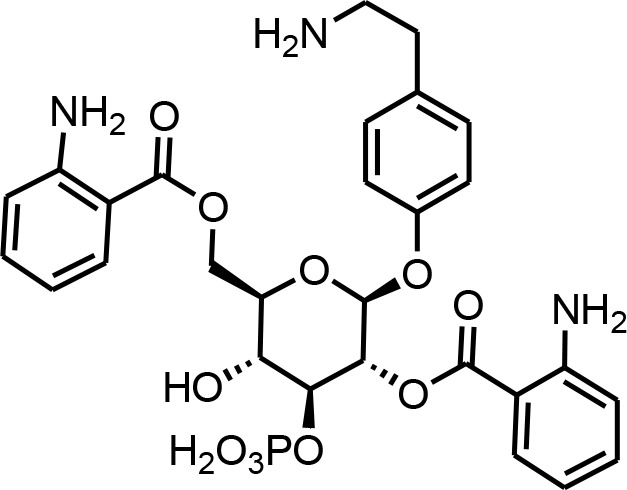 |
| 27 | ascr#81 | (4-((R,E)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)hept-2-enamido)benzoyl)-L-glutamic acid | Identified via synthesis (Artyukhin et al., 2018) | 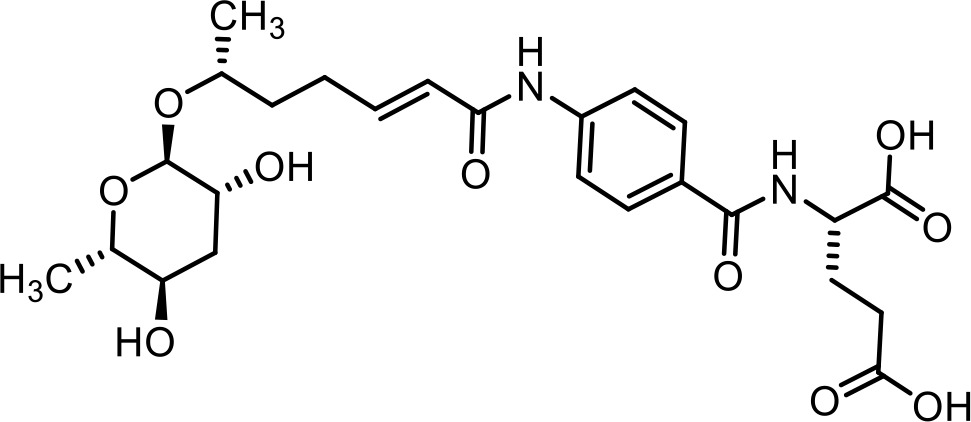 |
| 28 | ascr#82 | ((S)−4-carboxy-4-(4-((R,E)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)hept-2-enamido)benzamido)butanoyl)-L-glutamic acid | Previously inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (Artyukhin et al., 2018) | 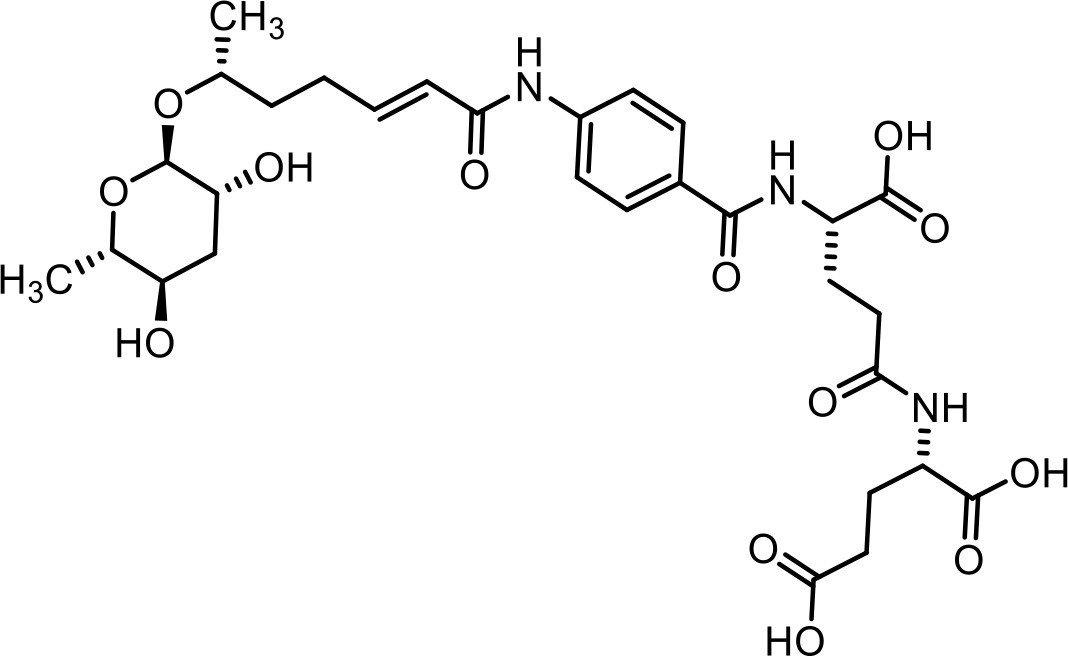 |
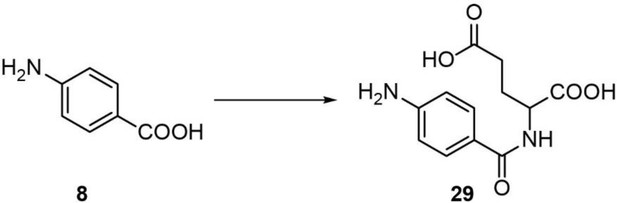
| 29 | PABA-glu | (4-aminobenzoyl)-L-glutamic acid | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 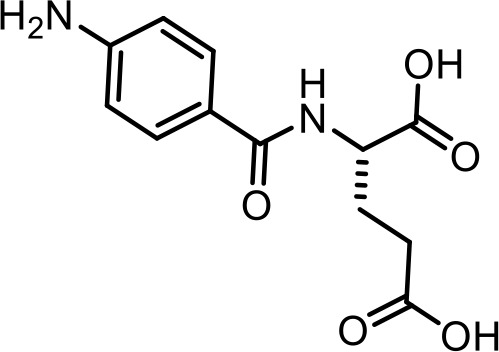 |
| 30 | uglas#1 | (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)−4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)−2-(2,6,8-trioxo-1,2,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-3H-purin-3-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoate | Identified via synthesis (Curtis et al., 2020) | 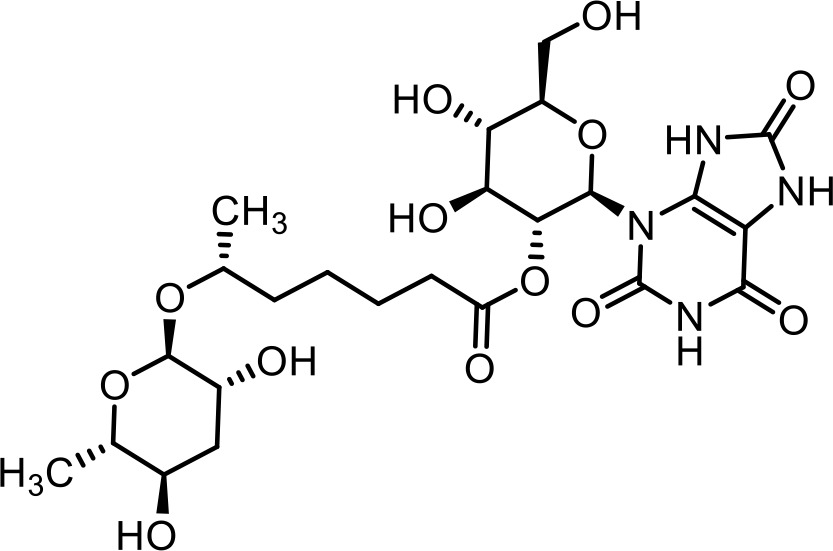 |
| 31 | uglas#14 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(2,6,8-trioxo-1,2,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-3H-purin-3-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoate | Identified via synthesis (Curtis et al., 2020) | 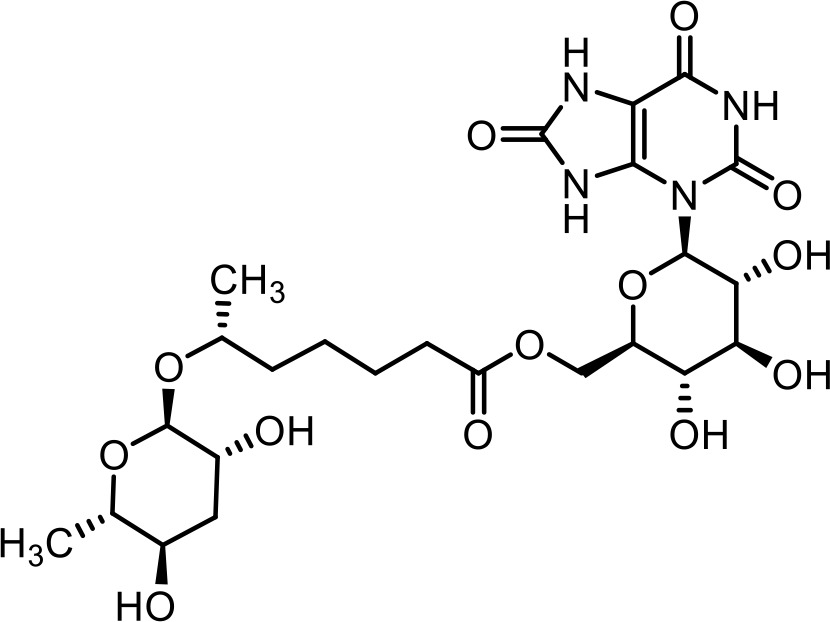 |
| 32 | uglas#15 | ((2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)−3,5-dihydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)−6-(2,6,8-trioxo-1,2,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-3H-purin-3-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (R)−6-(((2R,3R,5R,6S)−3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)heptanoate | Previously inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (Artyukhin et al., 2018; Curtis et al., 2020) | 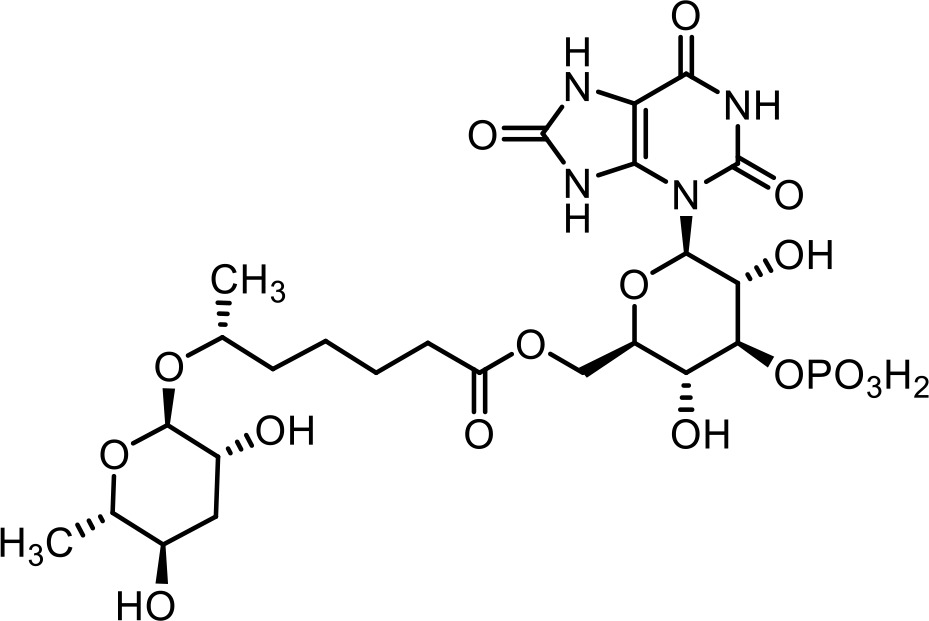 |
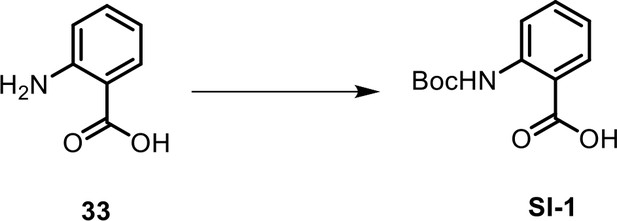
| 33 | 2-Aminobenzoic acid | Commercial product (Sigma-Aldrich) | 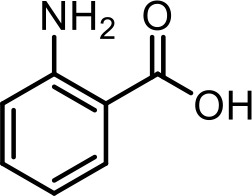 | |
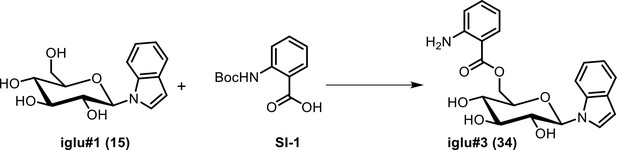
| 34 | iglu#3 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 2-aminobenzoate | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 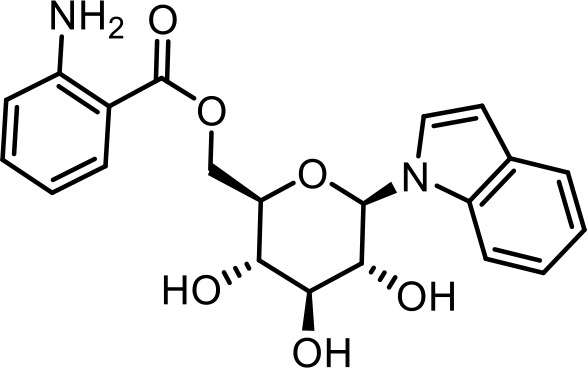 |
| 35 | icas#2 | (2S,3R,5R,6R)−5-hydroxy-2-methyl-6-(((R)−5-oxohexan-2-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 1H-indole-3-carboxylate | Identified via synthesis (Dong et al., 2016) | 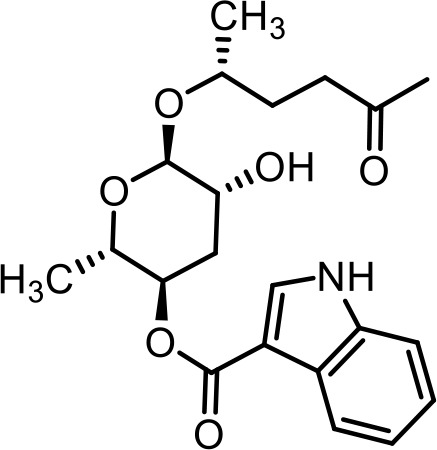 |
| 36 | icas#6.2 | (2S,3R,5R,6R)−5-hydroxy-6-(((2R,5S)−5-hydroxyhexan-2-yl)oxy)−2-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl 1H-indole-3-carboxylate | Identified via synthesis (Dong et al., 2016) | 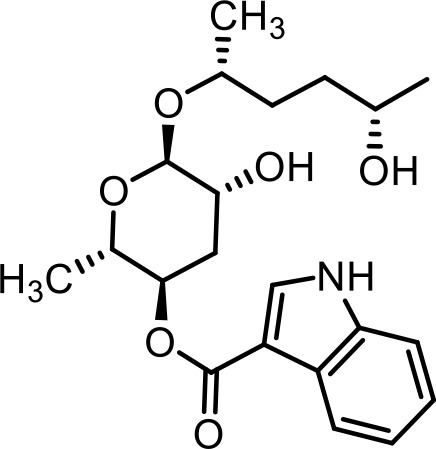 |
| SI 1 | 2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)-amino)benzoic acid | Characterized via synthesis (This manuscript) | 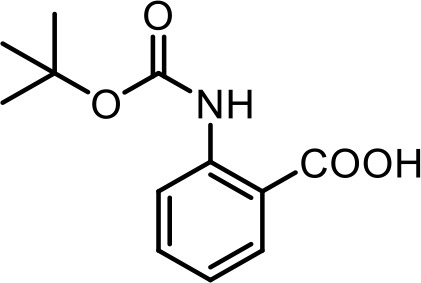 | |
| SI 2 | iglu#5 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl nicotinate | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 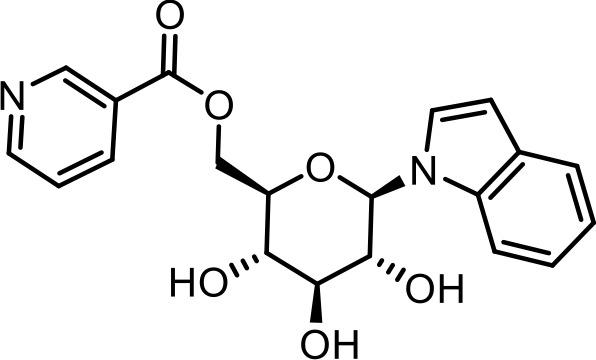 |
| SI 3 | iglu#7 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl (E)−2-methylbut-2-enoate | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 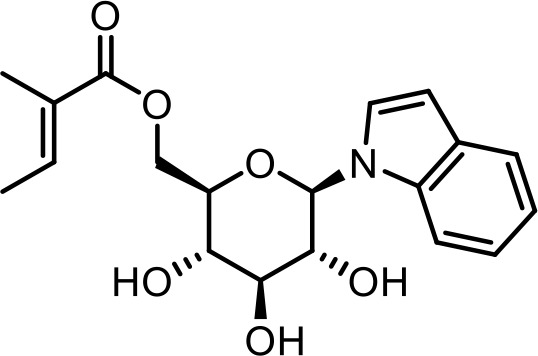 |
| SI 4 | iglu#9 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)−3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(1H-indol-1-yl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate | Identified via synthesis (This manuscript) | 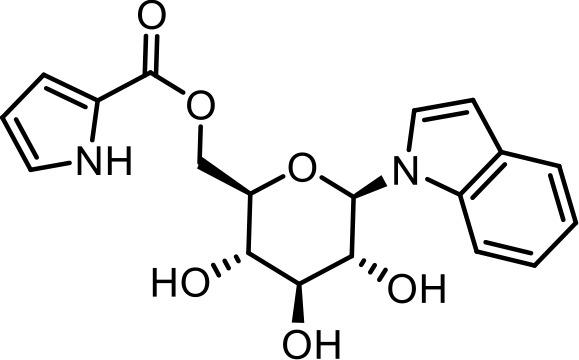 |
| SI 5 | angl#3 | ((2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)−6-((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)−3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 2-aminobenzoate | Proposed structure based on synthesis of a reference sample for MS (This manuscript) | 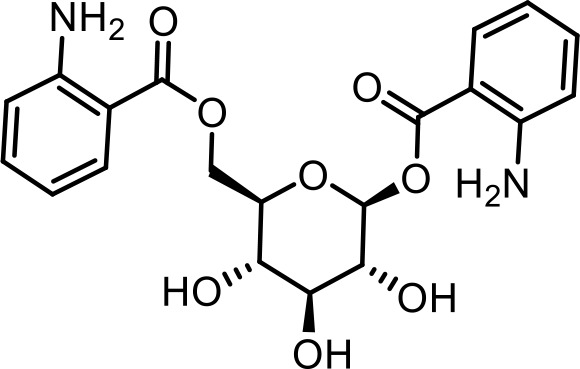 |
| SI 6 | tyglu#6 | (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)−6-(((2-aminobenzoyl)oxy)methyl)−2-((4-(2-aminoethyl)-phenoxy))−5-hydroxy-4-(phosphonooxy)-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl nicotinate | Proposed structure. Initially described (O'Donnell et al., 2020) and further inferred via tandem mass spectrometry (This manuscript) | 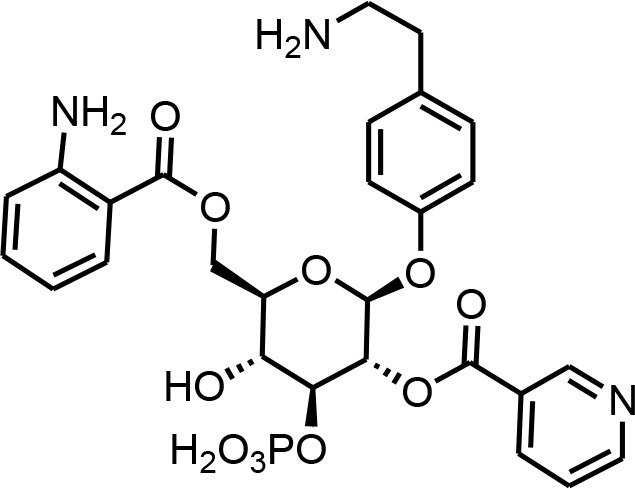 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
NMR spectra appendix.
NMR spectra of synthetic intermediates and newly identified metabolites.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-supp1-v2.pdf
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/61886/elife-61886-transrepform-v2.docx