Checkpoint inhibition of origin firing prevents inappropriate replication outside of S-phase
Figures
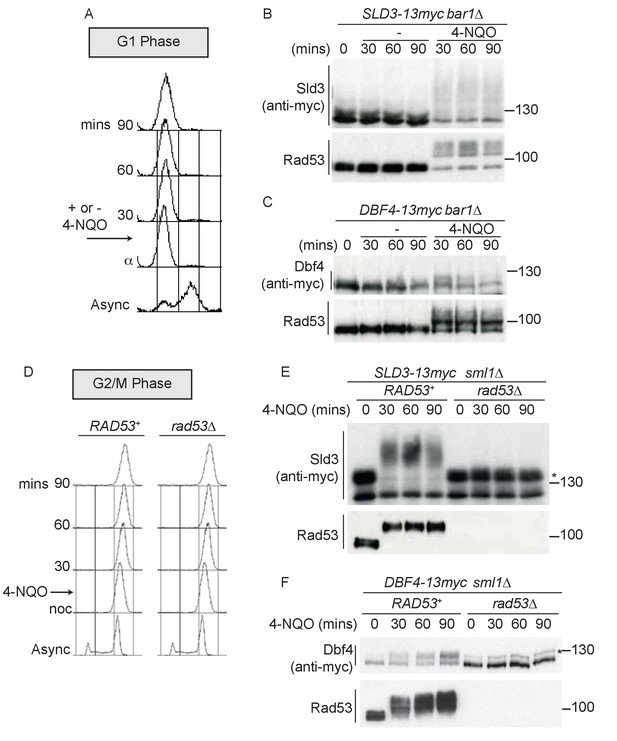
Dbf4 and Sld3 are phosphorylated by Rad53 after DNA damage in G1 and G2 phase.
(A) Flow cytometry of strains arrested in G1 phase with the mating pheromone alpha factor. Strains were held in G1 phase, with or without the addition of 10 μg/ml 4-NQO for the indicated times. All strains are bar1∆ to maintain G1 arrest. (B) Western blot of Sld3 (anti-myc) and Rad53 phosphorylation from the experiment outlined in (A). Sld3 was resolved on a phos-tag sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) gel. (C) As (B), but for Dbf4. Both blots are from SDS–PAGE. (D) As (A), except strains were arrested in G2/M with nocodazole before the addition of 4-NQO. All strains are sml1∆, which is required for viability in cells lacking Rad53. (E) Western blot of Sld3 (anti-myc) and Rad53 phosphorylation as in (B) from the experiment outlined in (D). Sld3 was resolved on a phos-tag SDS–PAGE gel. *Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-phosphorylated Sld3 (see Figure 1—figure supplement 1C). (F) As (E), but for Dbf4. Dbf4 is phosphorylated by other kinases in G2/M, resulting in residual phosphorylated forms remaining in rad53∆ cells *.
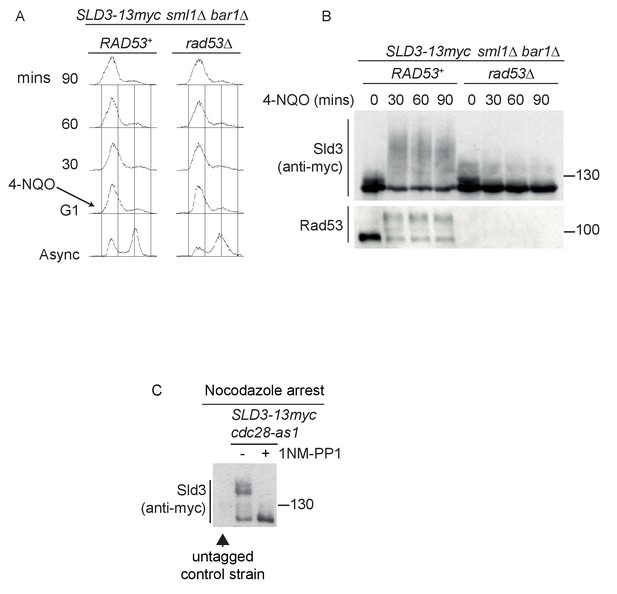
Sld3 phosphorylation in G1 phase after DNA damage is Rad53 dependent.
(A) Flow cytometry of strains arrested in G1 phase with the mating pheromone alpha factor. Strains were held in G1 phase, with the addition of 10 μg/ml 4-NQO for the indicated times. All strains are bar1∆ to maintain G1 arrest and also sml1∆. (B) Western blot of Sld3 and Rad53 phosphorylation from the experiment outlined in (A). Sld3 was resolved on a phos-tag sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel. (C) Western blot of Sld3 from cells arrested in G2/M with nocodazole. These strains contain the cdc28-as1 allele that is inhibited by the addition of the ATP analogue 1-NM-PP1. As Cdc28 is the only catalytic CDK subunit in yeast, the addition of 1-NM-PP1 inhibits CDK activity, revealing that the lower mobility Sld3 band is CDK dependent. The first lane contains untagged Sld3, showing that all bands in this blot correspond to Sld3-13myc.
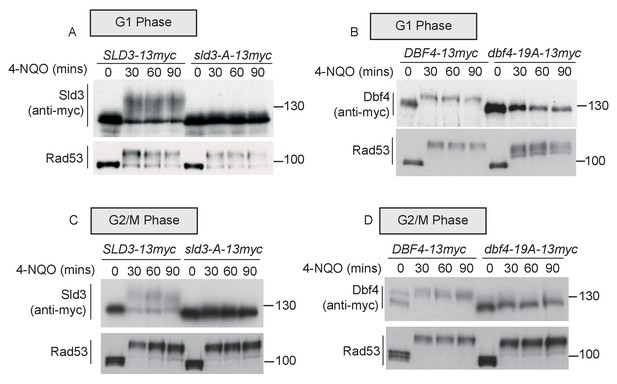
Rad53 phosphorylates Sld3 and Dbf4 in G1 and G2 phases at the same residues as in S-phase (A and B) as Figure 1B,C.
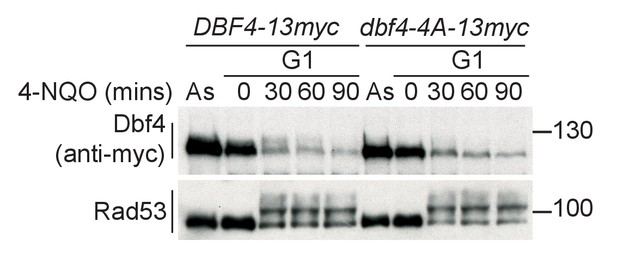
Dbf4-4A is expressed at similar levels to wild type and is also refractory to Rad53 phosphorylation in G1 phase.
Western blot of strains arrested in G1 phase with the mating pheromone alpha factor. Strains were held in G1 phase, with the addition of 10 μg/ml 4-NQO for the indicated times. All strains are bar1∆ to maintain G1 arrest. As is from an asynchronous culture. The dbf4-4A mutant contains four serine/threonine to alanine mutations in the phospho-sites that are critical for Rad53-dependent inhibition of Dbf4. dbf4-4A is referred to as dbf4-A in the rest of this manuscript.
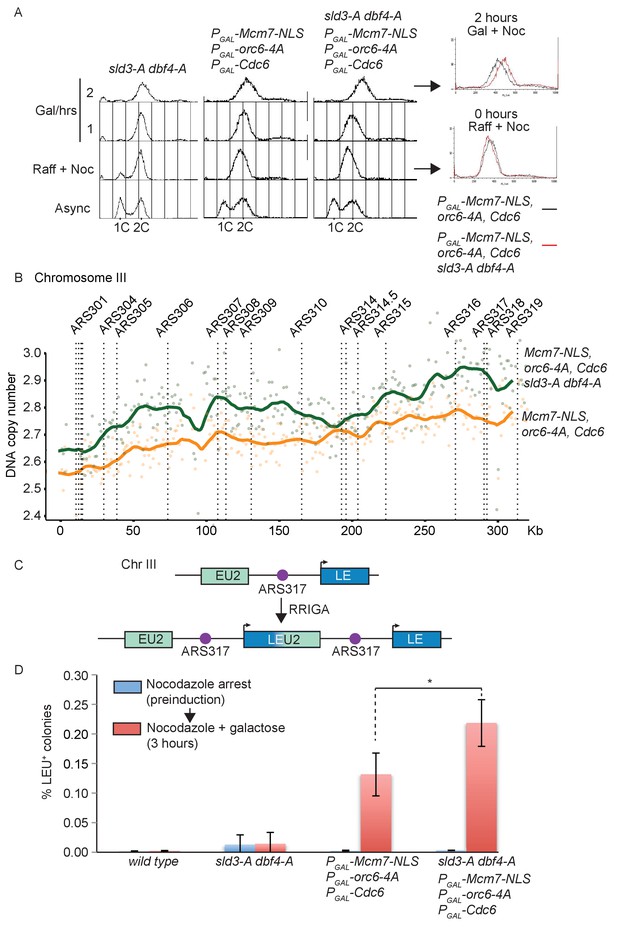
Checkpoint-dependent inhibition of origin firing prevents re-replication in G2 phase.
(A) Flow cytometry of the indicated strains grown overnight in YPraffinose, then arrested in G2/M with nocodazole. After addition of fresh nocodazole, 2% galactose was added for the indicated times to express the licensing mutants. Right, overlay between the 0 and 2 hr time points for the licensing mutant strain with (red) or without (black) the sld3-A/dbf4-A alleles. (B) Copy number analysis of Chromosome III from the experiment in (A), after 4 hr in galactose. As in (A), the strains overexpress wild type Cdc6 and the indicated pre-replicative complex mutants from the galactose inducible promoter. DNA sequencing read depth per 1 kb bin was normalised to the 0 hr time point for each strain. Baseline was set at two as the strains are arrested in G2. The y-axis shows the DNA copy number after these steps. (C) Schematic diagram of re-replication-induced gene amplification (RRIGA) assay for gene amplification events. Re-replication of the split LEU2 gene from origin ARS317 results in tandem head to tail gene duplications, leading to a functional LEU2 gene. (D) RRIGA assay in (C) was performed with the indicated strains. Strains were grown overnight in YPraffinose then arrested in G2/M with nocodazole (pre-induction, blue time point). After addition of fresh nocodazole, 2% galactose was added for 3 hr to express the licensing mutants (red time point). Cells were plated on YPD (viable cell count) and SC-leu plates (Leu+ count) and the % of Leu+ colonies out of the viable cell population was plotted. N = 3, error bars are SD. *The p value was calculated as 0.0481 using an unpaired t-test.
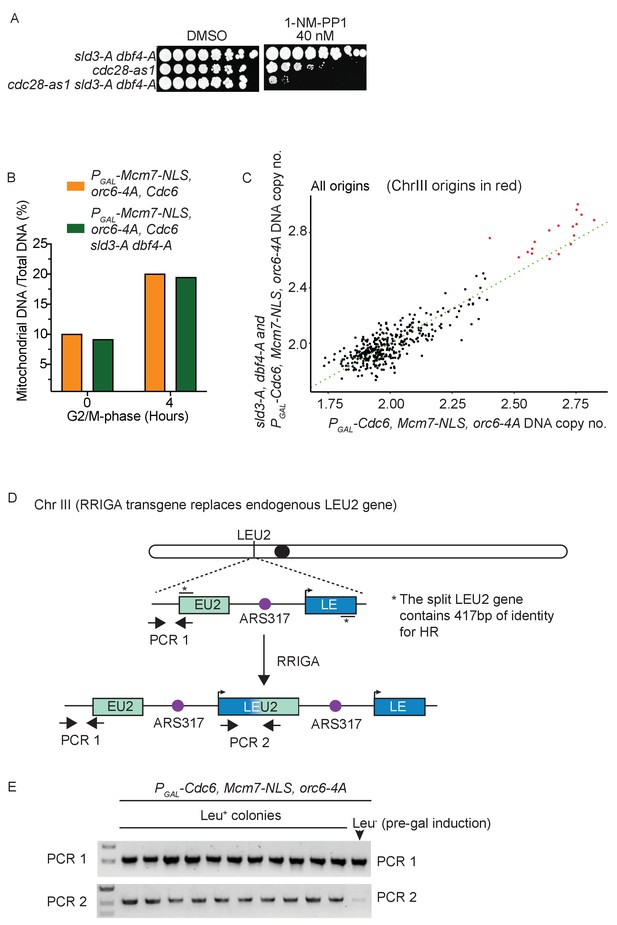
Checkpoint-dependent inhibition of origin firing prevents re-replication in G2 phase.
(A) Growth assay of the indicated strains. (B) Analysis of mitochondrial DNA content by sequencing. (C) Comparison of DNA copy number at all origins between the strain over-expressing the pre-replicative complex mutants (x-axis) vs the same strain also containing the sld3-A/dbf4-A alleles (y-axis). Each dot represents a different origin of replication, and the origins of Chromosome III are red. The green line is the line of equal copy number between the two strains and therefore dots above the line are more re-replicated in the presence of the sld3-A/dbf4-A alleles. Note that the Chr III origins are the most efficiently re-replicated in both strains, with almost all of them showing more replication due to the sld3-A/dbf4-A alleles. (D) Schematic diagram of the RRIGA assay. Endogenous LEU2 was replaced with a split LEU2 marker, separated by the re-replication origin ARS317. The two non-functional halves contain 417 bp of identity*. Re-initiation at ARS317 followed by fork-breakage and strand annealing at the regions of LEU2 homology results in gene amplification and the generation of a functional LEU2 gene. (E) Verification of RRIGA by PCR using the amplicons as depicted in (A). The parental strain (which is Leu–) was induced to re-replicate in the presence of galactose and cells were plated on SC-leu plates. Ten independent Leu+ colonies were assayed for the presence of the duplication and all were positive.
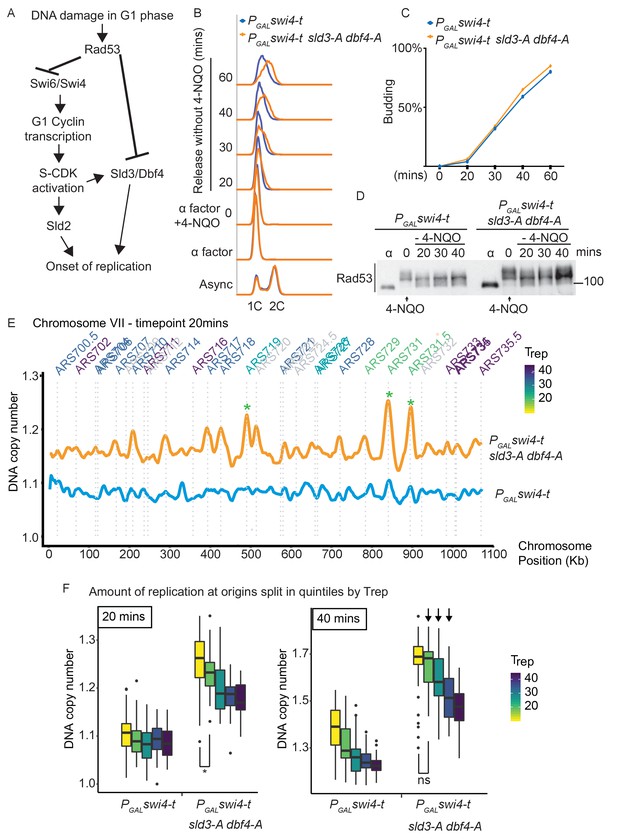
Checkpoint-dependent inhibition of origin firing prevents premature replication initiation at all origins at the G1–S transition.
(A) Activation of Rad53 in G1 phase can delay genome duplication by at least two mechanisms; by inhibition of the transcriptional activator Swi6, which is required for G1- and subsequently S-phase cyclin transcription and by inhibition of the origin firing factors Sld3 and Dbf4. (B) Flow cytometry of the indicated strains grown overnight in YPraffinose, then arrested in G1 phase with alpha factor. Cells were held in fresh alpha factor, while 2% galactose and 0.5 μg/ml 4-NQO was added for 30 min (0 time point) before washing and release from alpha factor arrest into fresh YPgal medium without 4-NQO. Swi4-t is a C-terminally truncated protein that cannot be inhibited by Rad53. (C) Budding index from the experiment in (B). Time point 0 refers to cells held in alpha factor + galactose + 0.5 μg/ml 4-NQO for 30 min. (D) Rad53 western blot from experiment in (B). (E) Copy number analysis of chromosome VII of the indicated strains 20 min after release as in (B–D). The y-axis ratio refers to the amount of DNA at the 20 min time point divided by the DNA copy number in G1 phase. Known origins are annotated above the replication profile and coloured according to their normal median replication time (Trep). (F) Box plots of the amount of replication at all origins, split into equal quintiles depending on their normal median firing time (Trep). Initiation occurs first at early origins in the swi4-t sld3-A dbf4-A strain, for example the yellow and green quintiles are significantly different at 20 min (*p value 0.044), but non-significantly different (ns) at 40 min. Arrows indicate that later firing origins also initiate by 40 min in the swi4-t sld3-A dbf4-A strain. P-values are from t-tests.
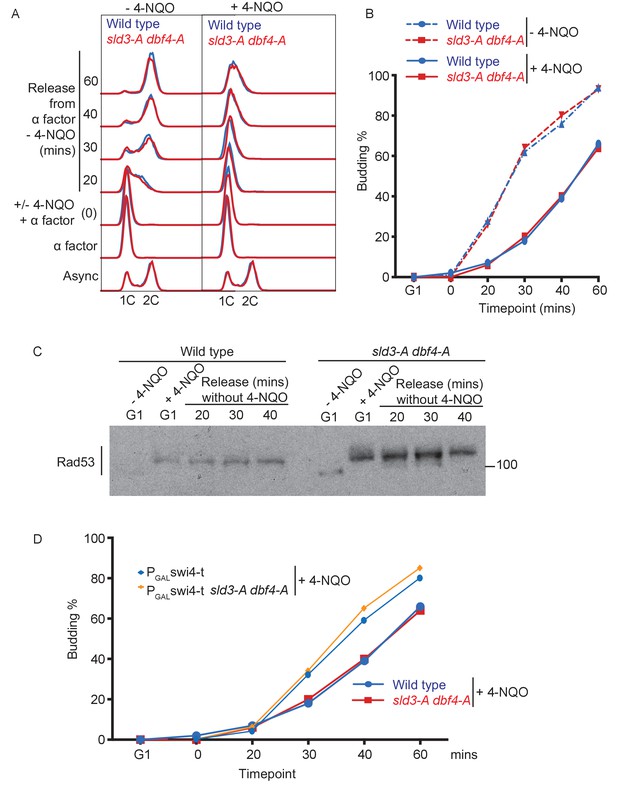
4-NQO addition in G1 phase delays the G1/S transition.
(A) Flow cytometry of the indicated strains, which were grown overnight in YPraffinose and arrested in G1 phase with alpha factor (G1 time point). Strains were then held in G1 phase for an extra 30 min by the addition of fresh alpha factor plus galactose, with or without 0.5 μg/ml 4-NQO. Cells were washed into fresh YPgalactose medium to release into S-phase. Note that YPraffinose and galactose medium was used in this experiment to match the exact conditions that were used in the main Figure 4B with the PGAL-swi4-t strains, allowing a direct comparison, as in (D). (B) Budding index (a G1 cyclin/CDK-mediated event) from experiment in (A). (C) Rad53 western blot from the 4-NQO-treated samples in (A). (D) Overlay of budding profiles (from Figure 4C and this Figure B) between strains expressing or not expressing Swi4-t. Swi4-t, which cannot be inhibited by Rad53, causes earlier activation of G1 cyclin/CDK as shown here by budding.
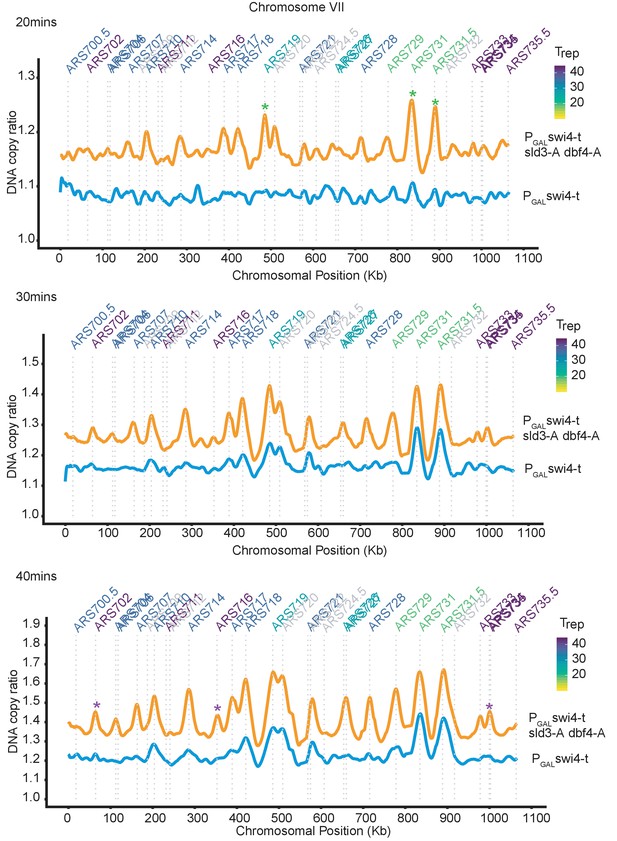
Rad53 activation in G1 phase inhibits all origin firing through phosphorylation of Sld3 and Dbf4.
Replication profile of chromosome VII as an example at 20, 30, and 40 min from the experiment in Figure 4B. Green * are examples of very early firing origins, which initiate at the 20 min time point in the PGAL-swi4-t sld3-A dbf4-A strain. Purple * are examples of late firing origins which do not initiate at the 20 min time point but are clearly firing by the 40 min time point in the PGAL-swi4-t sld3-A dbf4-A strain. This shows that the relative timing of origin firing is not affected in the PGAL-swi4-t sld3-A dbf4-A strain.
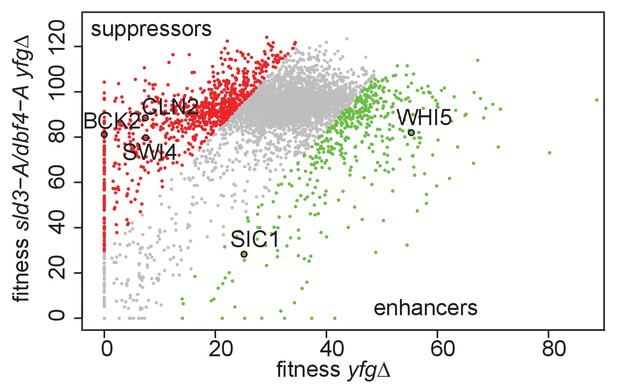
Genetic interactions of the sld3-A dbf4-A alleles with mutants that either accelerate or delay the G1/S transition.
Scatter plot of the fitness of the yeast genome knock out collection grown in 0.5 μg/ml phleomycin with (y-axis) or without (x-axis) the sld3-A dbf4-A alleles. Each dot corresponds to a different gene deletion. The top 25% of gene deletions (yfg, your favourite gene) that significantly enhance (green) or suppress (red) the fitness of sld3-A dbf4-A are indicated. This data was originally published in Morafraile et al., 2019.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-Rad53, rabbit polyclonal | Abcam | (ab104232) | Antibody (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Anti-c-myc, mouse monoclonal | Merck Life Science | (11667149001) | Antibody (1:1000) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Alpha-factor | GenScript | (RP01002) | Peptide |
| Commercial assay or kit | TruSeq Nano DNA Low Throughput Library Prep Kit | Illumina | (20015964) | Commercial assay or kit |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phos-tag Acrylamide AAL-107 | Alpha Laboratories | (304–93521) | Chemical |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nocodazole | Merck Life Science | (M1404) | Chemical |
| Chemical compound, drug | 4-Nitroquinoline N-oxide | Merck Life Science | (N8141) | Chemical |
| Software, algorithm | LocalMapper software | Batrakou et al., 2020 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Repliscope software | Batrakou et al., 2020 |





