A rapid whisker-based decision underlying skilled locomotion in mice
Figures
Head-fixed obstacle avoidance in mice.
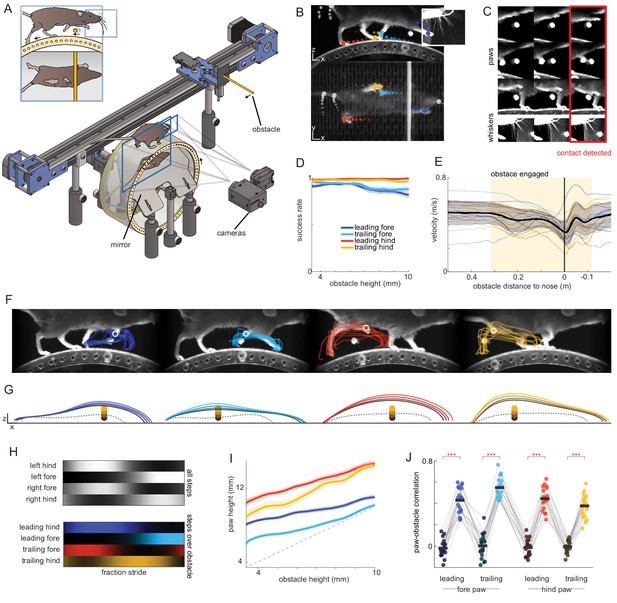
(A) Schematic of the obstacle avoidance setup. A head-fixed mouse runs on top of a wheel with a mirror mounted inside, allowing a single camera to capture two orthogonal views. A second camera focuses on the whiskers. An obstacle is moved toward the mouse along a motorized, belt-driven linear track at a speed matched to that of the wheel. (B) DeepLabCut is used to track the positions of the paws, tail, and nose in both views. Tracking from the two views is combined to reconstruct the three-dimensional pose at 250 Hz. (C) Custom convolutional neural network algorithms were developed to determine when the whiskers (bottom row) and paws (top rows) contact the obstacle. (D-J) Behavioral characterization of head-fixed obstacle clearance for n = 20 mice. (D) Obstacle clearance success rate as a function of obstacle height for each paw (mean with S.E.M. shaded). All paws cleared the obstacle at high rates even for high obstacles. (E) Average running velocity as a function of position relative to the obstacle (standard deviation is shaded; positive numbers mean the obstacle is in front of the mouse). Thin lines are averages for individual mice. Vertical black line shows the position at which the obstacle is beneath the nose of the mouse. (F) Example trial showing (from left to right) the leading forelimb (LF), trailing forelimb (TF), leading hindlimb (LH), and trailing hindlimb (TH) clearing the obstacle. Traces show kinematics from trials selected randomly from a single session. (G) Average kinematics across mice for LF, TF, LH, and TH binned by obstacle height (colored traces). Dashed gray traces are the average of the two steps preceding whisker contact with the obstacle. The obstacle is 3.175 mm in diameter. (H) Hildebrand plots (Hildebrand, 1989) , averaged across mice, reveal trot gaits during normal locomotion and obstacle clearance. Color intensity represents likelihood of stance. The top panel is calculated across all steps, and the bottom panel from steps over the obstacle. (I) Paw height vs. obstacle height averaged across mice (S.E.M. is shaded). Height is measured when the paw is 8 mm in front of the obstacle. The dashed gray line is the unity line. (J) Average correlation between the obstacle height and the height of all paws, measured when the paw is 8 mm in front of the obstacle. Circles represent individual mice. For each paw, the correlation is computed for the step over the obstacle (colored circles), and the preceding control steps (dark circles). See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
Head-fixed obstacle avoidance in mice.
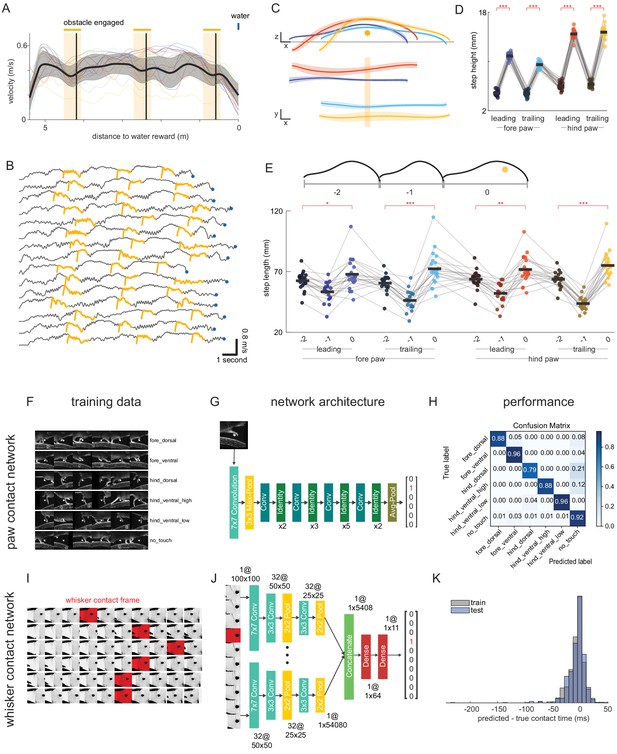
(A) Obstacles are engaged three times per water reward. Average running velocity as a function of position relative to the water reward (n = 20; standard deviation is shaded). Thin lines are averages for individual mice. Vertical black lines show the positions at which the obstacle is beneath the nose of the mouse. (B) The motorized obstacle accurately tracks the velocity of the wheel. Gray traces show the velocity of the wheel for randomly selected trials within a session. The gold traces show the velocity of the obstacle when it becomes engaged. Notice that the obstacle velocity quickly accelerates, then accurately tracks the velocity of the wheel. Blue circles are the times of water reward. (C) Kinematics averaged across mice for leading, trailing, forelimb, and hindlimb steps over the obstacle (n = 20; standard deviation is shaded). Colors are the same as D. (D) Steps over the obstacle are higher than control steps preceding whisker contract with the obstacle (n = 20). Control steps are shown in the dark colored scatter to the left of each paw. Height is measured at the zenith of the trajectory. (E) Steps over the obstacle (0) are lengthened relative to the preceding step (−1) and the step before that (−2) (n = 20). (F-H) A custom neural network algorithm was used to identify contacts of the paw with the obstacle. (F) Five different types of paw contacts were manually identified and used to train the network. (G) Given a sub-frame centered around the obstacle, a convolutional neural network classified the frame as belonging to one of the touch classes, or the no touch class. (H) Confusion matrix depicting the performance of the classifier. (I-K) A custom neural network algorithm was used to identify whisker contacts with the obstacle. (I) Training data consisted of temporally consecutive frames from the whisker camera in which the frame of first contact was manually identified. (J) Features were extracted from each frame using the same convolutional block. These features were concatenated, passed through fully connected layers, and used to classify the frame at which whisker contact first occurred. (K) Histograms showing the difference between the ground truth contact time and that predicted by the network for both training and test sets. Negative numbers correspond to early predictions.
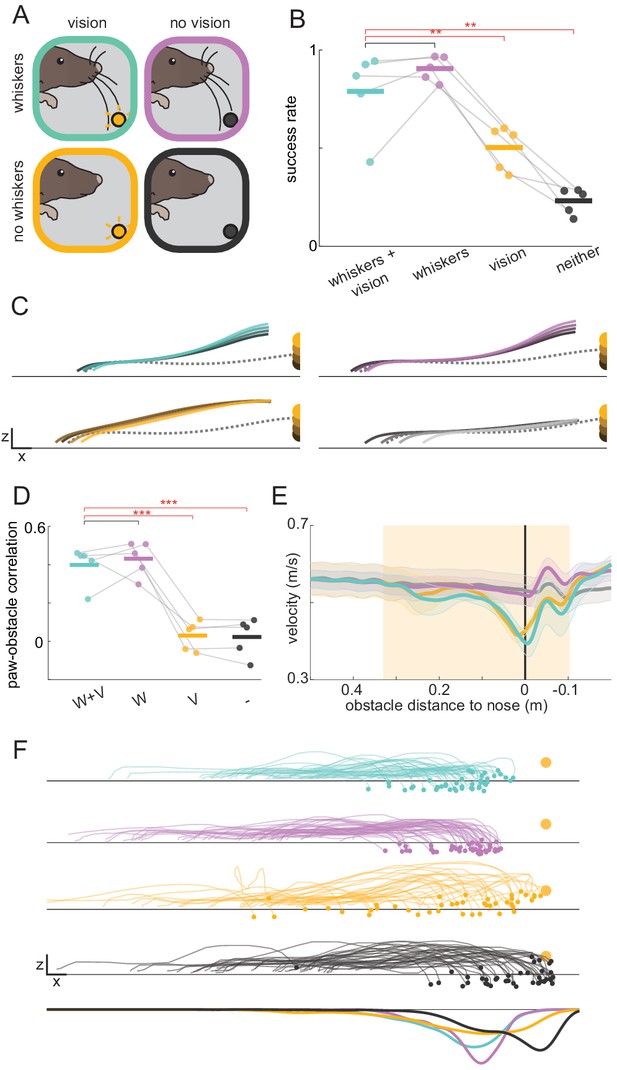
Mice rely on whiskers to clear obstacles.
(A) Schematic of experimental paradigm. Obstacle avoidance was tested with whiskers (top row) and with trimmed whiskers (bottom row) in separate sessions. Within each session, randomly interleaved trials occurred in complete darkness (no vision, right column) or with the obstacle illuminated internally (vision, left column). (B) Obstacle clearance success rates when mice had access to whiskers and vision (W+V), whiskers without vision (W), vision without whiskers (V), or neither vision nor whiskers (-) (n = 5 for this and subsequent panels). (C) Kinematic trajectories of the leading forepaw binned by obstacle height for each sensory condition. Each line is an average across individual mouse averages. The dashed gray line is the average of the two steps preceding whisker contact with the obstacle. Kinematics are truncated 8 mm in front of the obstacle to demonstrate that height shaping emerges before paws can contact the obstacle. Height shaping therefore does not result from paw contacts. (D) Mice adjust the height of their leading forepaw based on the height of the obstacle only when whisker sensory information is available. The correlation between paw and obstacle height is measured when the paw is 8 mm in front of the obstacle. (E) Average wheel velocity binned by the position of the mouse relative to the obstacle (shaded lines are standard error; positive numbers mean the obstacle is in front of the mouse). The shaded box shows when the obstacle is engaged, and the vertical black line is the position at which the obstacle is beneath the nose of the mouse. (F) The landing position of the trailing forepaw is less variable when whisker sensory information is available. The top four rows show the kinematics of the step preceding the step over the obstacle for the lagging forepaw. Each trace is a single trial selected randomly across mice. The bottom row shows the distribution of landing positions pooled across mice. Each mouse was tested for two sessions with and two sessions without whiskers. See also Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
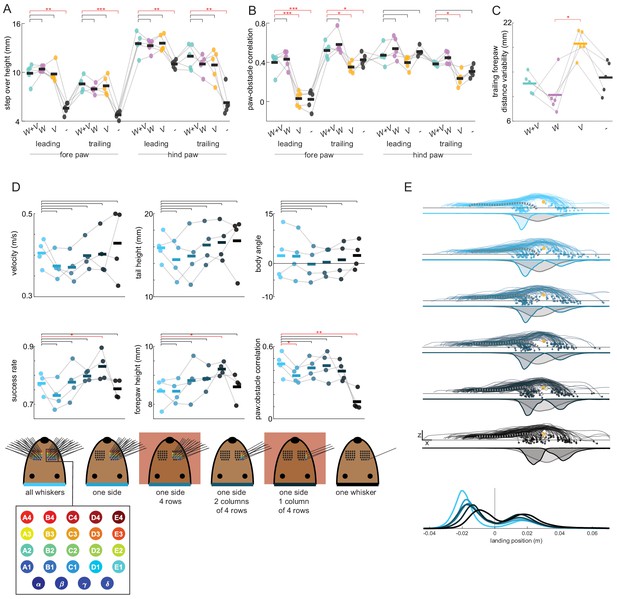
Mice rely on whiskers to clear obstacles.
(A) Height of the step over the obstacle for all paws in each sensory condition when mice had access to vision and whiskers (W+V), whiskers without vision (W), vision without whiskers (V), or neither vision nor whiskers (-). Height was measured when the paw is 8 mm in front of the obstacle. Mice still lift their paws sufficiently with vision and whiskers trimmed, but mice fail to lift high enough with neither whiskers nor vision. (B) Paw-obstacle correlations for all paws in each sensory condition. The paw-obstacle correlation suffers when whiskers are trimmed (with or without vision). (C) Variability of the distance of the trailing forepaw to the obstacle at the end of the penultimate step. This paw lands less consistently in front of the obstacle with only vision. Note that the variability is still low with neither whiskers nor vision because mice collide with the obstacle, and therefore consistently land directly in front of the obstacle (see the landing position distribution in Figure 2F). (D) In a separate experiment (n = 4), we assessed performance as whiskers were gradually trimmed (see schematic on the bottom). Performance was largely intact across all conditions, other than a dramatic decrease in the paw-obstacle correlation when only a single whisker remained. The whisker conditions used in subsequent barrel cortex lesion experiments are boxed in red. (E) Landing position distributions for the paw in swing at whisker contact become less well separated as whiskers are trimmed.
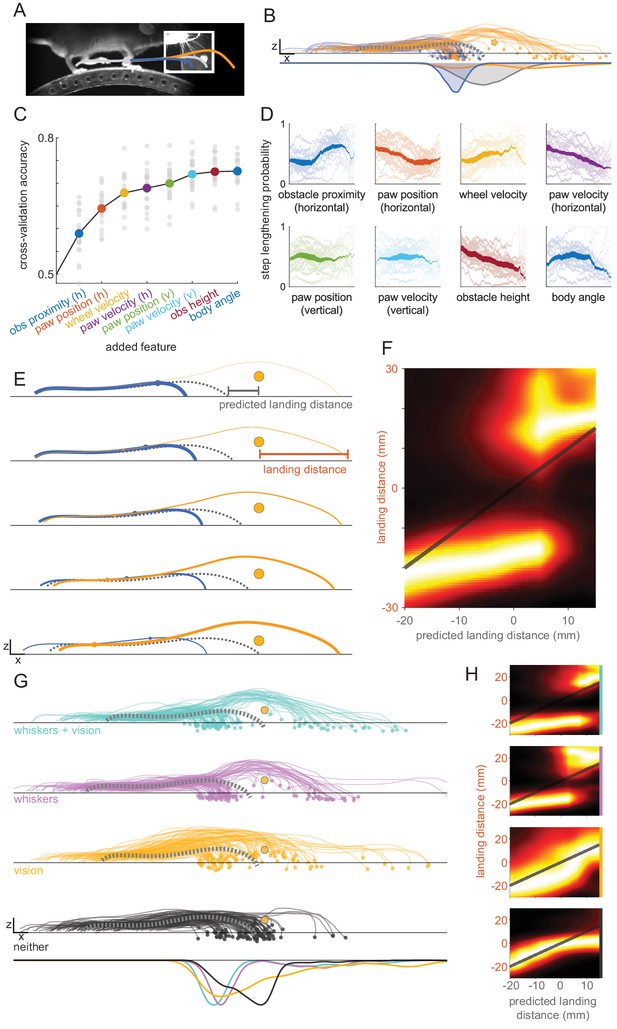
A rapid decision underlies obstacle clearance.
(A). Schematic showing that the paw in swing at whisker contact (gray circle) can be placed in front of the obstacle (blue trace) or extended to clear the obstacle in one step (orange trace). (B) Mice shorten or lengthen their step to avoid the obstacle. Each trace shows the kinematics for the paw in swing at whisker contact for a single trial selected randomly across all mice, colored by whether the step was shortened (blue) or lengthened (orange) relative to control steps. The dashed gray trace shows the average control step. Distributions of landing positions (bottom row) reveal that steps are shortened or lengthened relative to control steps. Trials in which the length of the step is unchanged are not included in this plot. (C) GLMs accurately predict whether steps are lengthened or shortened. Accuracy is plotted as features are added to the model. Models are constructed for each mouse (gray circles) and per-mouse accuracy is the average 15-fold cross-validation accuracy. Features are sequentially added based on their ability to improve the models’ average accuracy across mice. h: horizontal; v: vertical; obs: obstacle. (D) The decision varies systematically with both body state and obstacle position. Each plot shows the probability of step lengthening as a function of one predictor used in the model, sorted by the order in which they are included in the model (colors are the same as C). X axes show the 1st to 99th percentile for each predictor. Transparent lines are averages for individual mice, and opaque lines are the averages across mice. Line thickness represents the probability distribution for the predictor. (E) Mice lengthen or shorten their steps based on where the paw would have landed relative to the obstacle. Each row shows the average kinematics for the paw in swing at contact when that paw is placed in front of the obstacle (blue) or clears the obstacle in one step (orange). The rows are binned by the models’ confidence that the step will be shortened (top row) vs. lengthened (bottom row). Line thickness is proportional to the likelihood of the step landing in front of vs. over the obstacle. Blue and orange dots show the average position within the trajectory at which whisker contact occurs. (F) Distributions of landing distances (columns) conditioned on where the paw would have landed if no modifications were made (‘predicted landing distance’). Predicted landing distance is computed based on running speed and the lift-off position of the paw. (G) Behavioral modifications are more systematic when whiskers are available. Plots are like B, but broken down by sensory condition for the dataset used in Figure 2 (n = 5) and including trials where no modification is made. (H) Like F, but broken down by sensory condition (rows in H correspond to rows in G). Panels B–F use the same dataset from Figure 1 (n = 20). See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
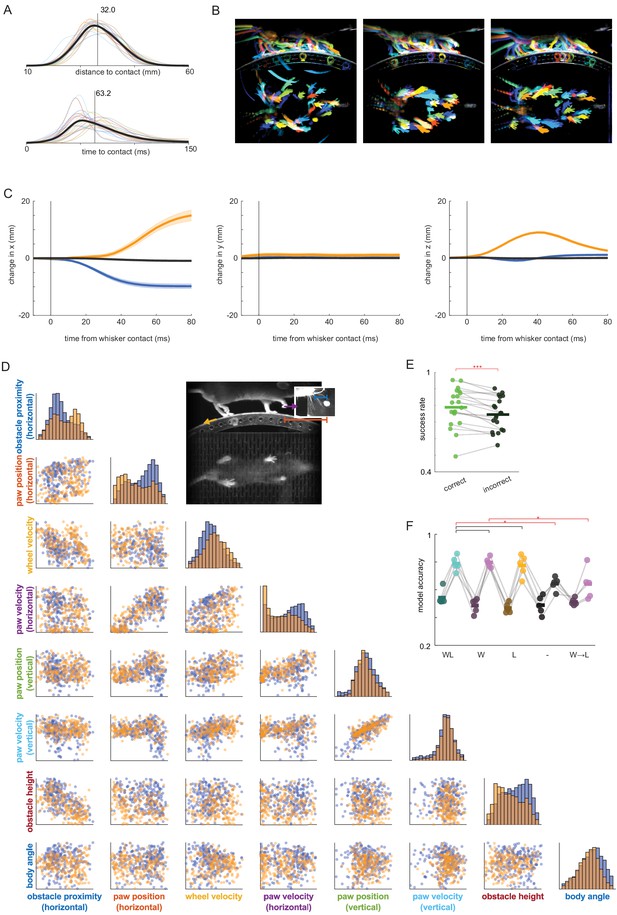
A rapid decision underlies obstacle clearance.
(A) At whisker contact, the foremost paw is very close to the obstacle (~32 mm; top) and will quickly intercept it (in ~63 ms; bottom) if no modifications are made. Thin colored lines show the distance-to-contact (top) and time-to-contact (bottom) distributions for each mouse. Thick black lines are average distributions across mice. (B) The body state is variable at whisker contact. Each panel shows randomly selected, overlaid frames at whisker contact selected within a session. (C) Kinematics diverge from control trajectories rapidly after whisker contact for the forepaw in swing at whisker contact. Orange traces show kinematic change for steps extended over the obstacle. Blue traces show the same for steps landing in front of the obstacle. Black traces show kinematic change for control steps, which are close to zero as expected. The divergence becomes significant ~24 ms after whisker contact (Materials and methods). Error bars show S.E.M. across mice. (D) Joint and marginal distributions for all pairs of predictor variables used in the model pooled across mice, colored by whether steps were shortened (blue) or lengthened (orange). All x axes show the 1st to 99th percentile for each predictor. The marginal distribution histograms along the horizontal show separation between shortened and lengthened steps for many predictors. (E) Mice are less successful on trials where the model is incorrect, suggesting that correct decision-making facilitates obstacle clearance. Correct trials are those in which the model successfully predicts whether the steps were lengthened or shortened. Each dot is the model accuracy for a single mouse. (F) Model accuracy suffers when whiskers are trimmed and lights are off (‘WL’ vs. ‘-‘). Furthermore, models trained on whiskers-only sessions (‘W’) are less accurate when used to predict behavior on trials with light only (‘W → L’), suggesting that the decision-making process is altered when whiskers are not available. The darker bars to the left of each colored bar shows model accuracy trained on shuffled data. These control models have ~50% accuracy, as expected.
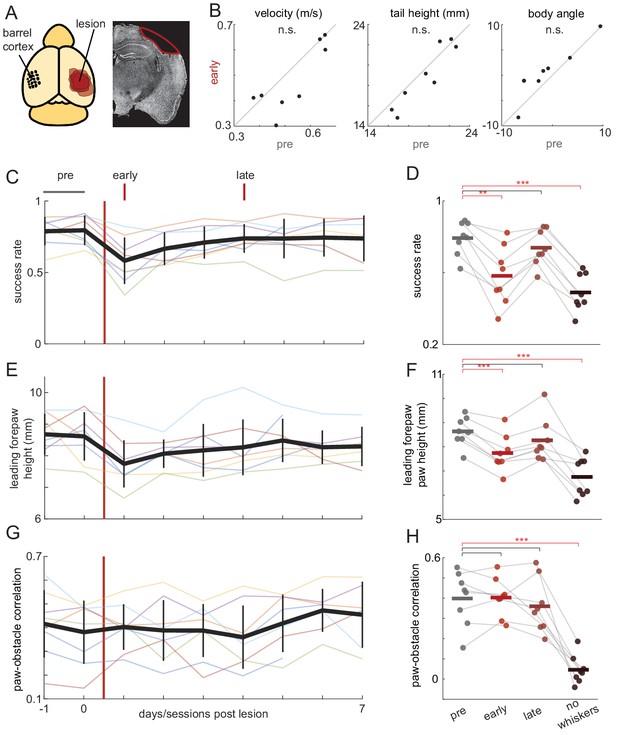
Obstacle clearance minimally affected by barrel cortex lesions.
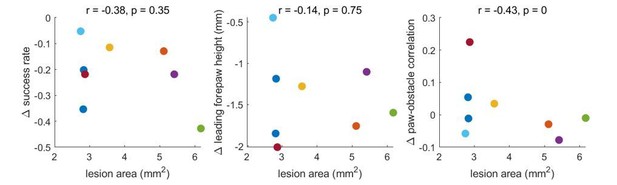
(A) Schematic showing locations and extent of barrel cortex lesions for all mice (n = 8) and an example coronal section for one mouse. (B) Locomotion is unaffected by contralateral barrel cortex lesions. Velocity, tail height, and body angle are similar in the 2 days before the lesion (pre) and the first day post-lesion (early). (C-H) Obstacle clearance is minimally affected by barrel cortex lesions. Left column shows how performance changes across days. Thick black lines show the average across mice, vertical black lines show standard deviation, and thin lines show per-mouse averages. Right column compares performance in the two days before the lesion (‘pre’), the first day post-lesion (‘early’), the fourth day post-lesion (‘late’), and after subsequent whisker trimming (‘no whiskers’). Success rates and forepaw height had small decreases following the lesion that quickly recovered, whereas whisker trimming significantly affected success rates, leading forepaw heights, and paw-obstacle correlations. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
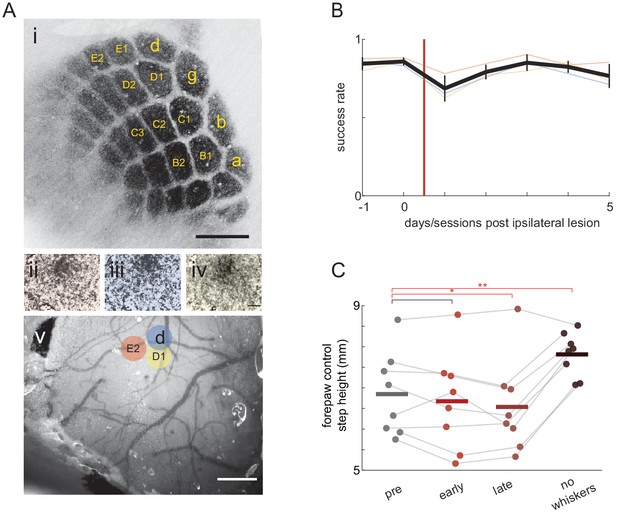
Obstacle clearance minimally affected by barrel cortex lesions.
(A) Barrel cortex lesions were targeted by mapping barrel fields electrophysiologically (not shown) or via intrinsic imaging. (i) shows a map of barrels in S1. L4 cells labeled with GFP to indicate the physical location of each barrel. Intrinsic signal optical imaging reveals barrels while stimulating the E2 (ii), delta (iii), or D1 whisker (iv). (v) shows vasculature through thinned skull surface over S1 with mapped barrels corresponding to those shown in ii-iv. Scale bars: 500 µm. (B) Ipsilateral lesions alone (n = 3) have little effect on success rates. The thick black line shows the average across mice, vertical black lines show standard deviation, and thin lines show per-mouse averages. (C) The impact of whisker trimming on success was not as large in the barrel cortex experiment as in previous experiments (compare Figure 2B and Figure 4D). This appears to be due to a compensatory motor strategy that mice adopted after trimming in barrel cortex experiments. (C) shows that mice lifted their forepaws higher during unobstructed locomotion prior to reaching the obstacle, thus increasing the likelihood of clearing it by chance. We only observed this behavior after trimming all whiskers, meaning it cannot explain the high performance after barrel cortex lesions. Control step height is measured in the two steps before mice reach the obstacle.
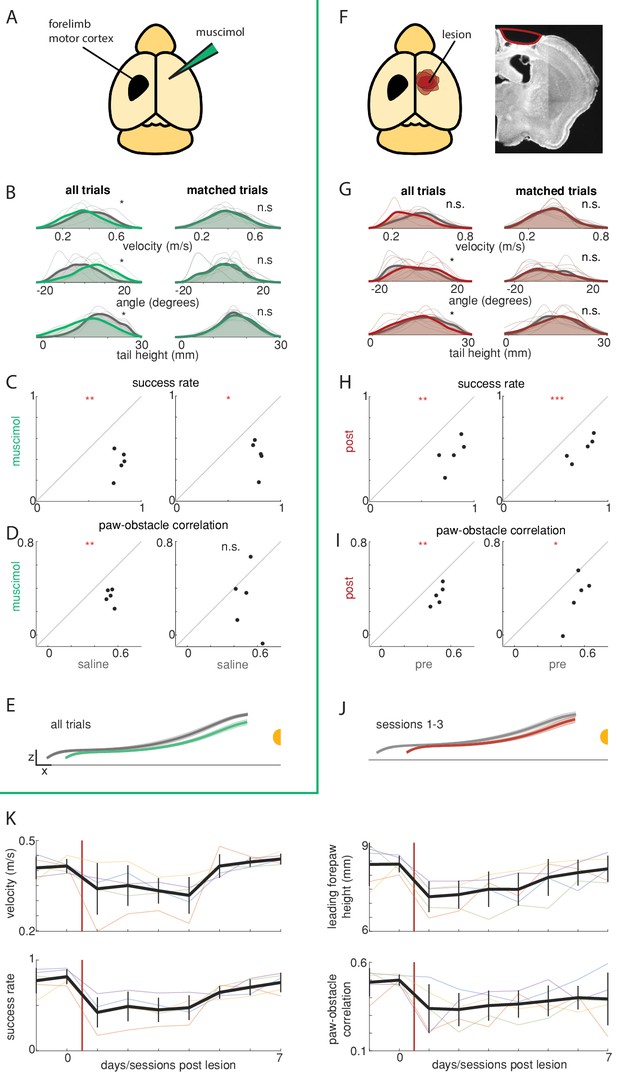
Obstacle avoidance affected by motor cortex manipulations.
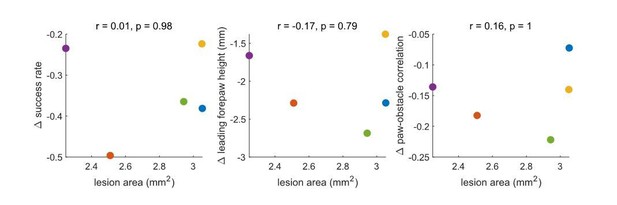
(A–E) Unilateral muscimol injections affect basic characteristics of locomotion as well as obstacle avoidance (n = 5). Left column shows all trials and right column shows 20% of trials selected that are best matched for characteristics of basic locomotion. (B) Distributions for running velocity, body angle, and tail height are matched in the subpopulation of trials. Thin lines show distributions for each mouse in muscimol (green) and saline (gray) conditions. Thick lines show the average distributions across mice, which are very similar following the matching procedure. (C) Mice clear the obstacle at lower rates following muscimol injections (left), even after controlling for changes in locomotion (right). (D) The correlation between the height of the leading forepaw and that of the obstacle decreases following muscimol injection (left), although the difference is no longer significant among matched trials (right). (E) Kinematics of the leading forepaw as it approaches the obstacle for muscimol (green) and saline (gray) sessions. Paw heights were lower following muscimol injections. Shaded area is standard deviation across mice, and thick lines show the average across individual mouse averages. (F) Schematic showing locations of forelimb motor cortex lesions for all mice (n = 5) and an example coronal section for one mouse. (G-J) Like B-E, but comparing performance before and after unilateral motor cortex lesions. ‘Post’ condition shows average performance 1–3 days following the lesion (prior to recovery). Effects on success rates and paw-obstacle correlations persisted in matched trials. (K) Performance recovery over time. Thick black lines show the average across mice, vertical black lines show standard deviation, and thin lines show per-mouse averages. See also Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
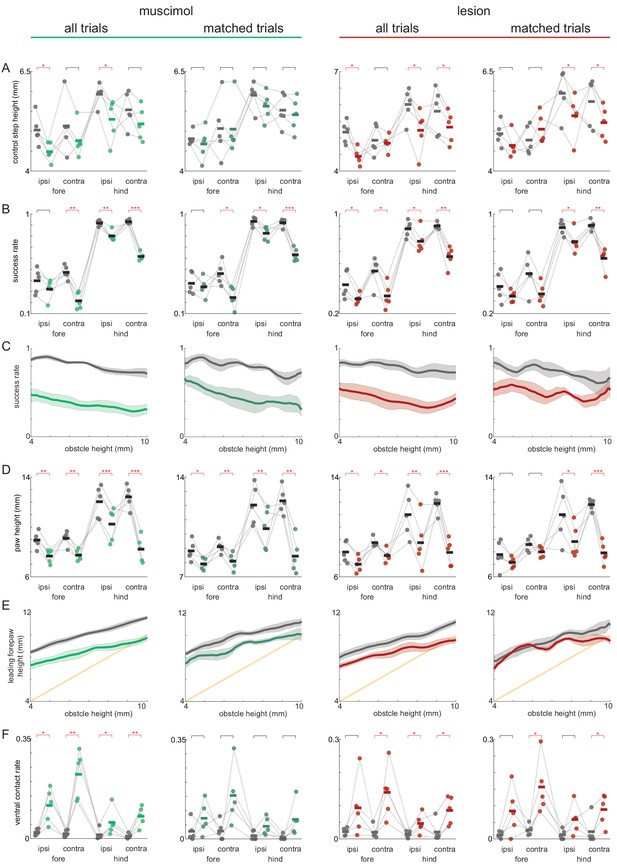
Obstacle avoidance affected by motor cortex manipulations.
Effects of silencing motor cortex (left columns) and lesioning motor cortex (right columns) among all trials (columns 1 and 3) and trials matched for baseline locomotion at whisker contact (columns 2 and 4). Gray lines/dots are saline or pre-lesion conditions, and colored lines/dots are muscimol or post-lesion conditions (1–3 days post-lesion). (A) The height of baseline steps was reduced for some paws. This effect went away among matched trials, except for the hindlimbs in lesion experiments (fourth column). (B) Success rates decreased for most paw even among matched trials. (C) Overall success rates as a function of obstacle height. Success rates decreased similarly regardless of obstacle height. Thick lines are averages across mice, and shaded area show S.E.M. (D) Paw heights for steps over the obstacle are reduced even among matched trials (measured when paws are 8 mm in front of the obstacle) (E) Paw height as a function of obstacle height for the leading forepaw. Decreases in paw heights were similar across obstacle heights. Thick lines are averages across mice and the shaded area shows S.E.M. (F) Manipulations cause mice to grab the obstacle more frequently, as evidenced by increased rates of ventral contacts, especially for the forepaw contralateral to the lesion.
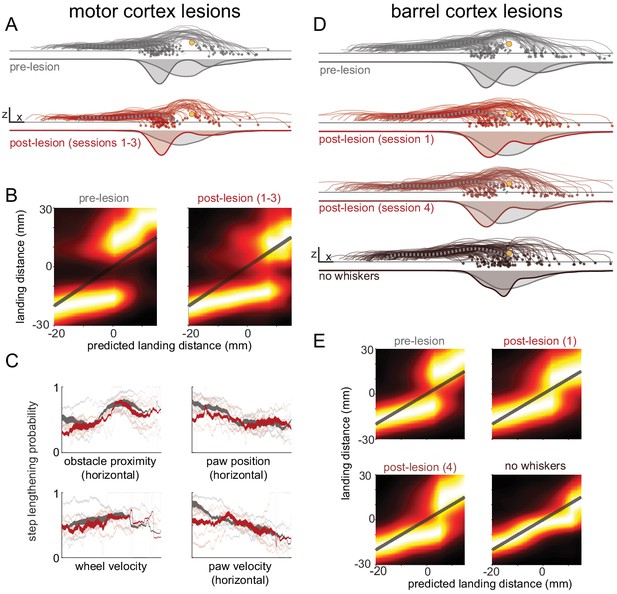
Decision-making is minimally affected by cortical manipulations.
(A) Mice still shorten or lengthen their step to avoid the obstacle following motor cortex lesions. Each trace shows kinematics for the paw in swing at whisker contact for a trial selected randomly across all mice for either pre-lesion (top row) or post-lesion sessions (bottom row). The thick dashed gray traces show the average control step. Distributions of landing positions are shown beneath the kinematics. (B) Distributions of landing distances (columns within each subplot) conditioned on where the paw would have landed if no modifications were made (‘predicted landing distance’). Predicted landing distance is computed based on running speed and the lift-off position of the paw. Mice execute one of two behavioral strategies both before (left) and after (right) lesions. (C) The state of the body and the position of the obstacle are important determinants of whether mice lengthen or shorten their step both before (gray) and after (red) lesions. Each plot shows the probability of step lengthening as a function of one predictor used in the model. X axes show the 1st to 99th percentile for each predictor. Transparent lines are averages for individual mice, and opaque lines are averages across mice. Line thickness represents the probability distribution for the predictor. (D-E) Similar to A-B, but comparing before contralateral barrel cortex lesions, the first day post-lesion, the fourth day post-lesion, and after subsequent whisker trimming. The decision-making process appears to be somewhat affected in the first day post-lesion, but recovers by the fourth day. See also Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
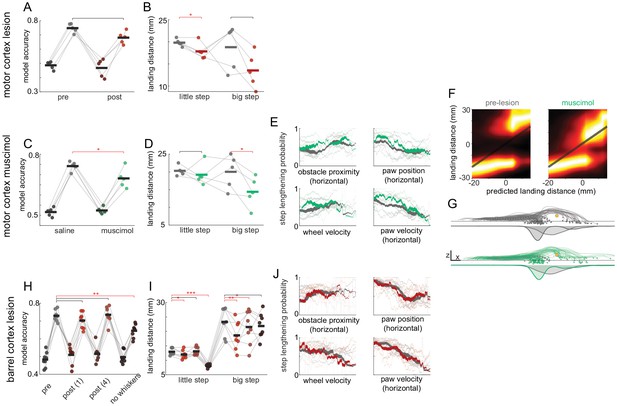
Decision-making is minimally affected by cortical manipulations.
(A,C,H) Cross-validation accuracy for GLMs trained to predict whether mice lengthen or shorten the step of the forepaw in swing at whisker contact. The left-most bar for each condition shows the model evaluated on shuffled data. Motor cortex manipulations cause small (for muscimol experiments, C) or no (for lesion experiments, A) decrease in model accuracy. Barrel cortex lesions did not affect model accuracy (‘pre’ vs. ‘post’, H), whereas whisker trimming did (‘pre’ vs. ‘no whiskers’, H). (B,D,I) Landing distance for the forepaw in swing at whisker contact when it lands in front of the obstacle (‘little step’) or over the obstacle (‘big step’). (E,J) The relationships between the position of the body, the position of the obstacle, and the decision were similar before (gray) and after (colored) cortical manipulations. Each plot shows the probability of step lengthening as a function of one predictor used in the model. X axes show the 1st to 99th percentile for each predictor. Transparent lines are individual mice, and opaque lines are the averages across mice. Line thickness represents the probability distribution for the predictor. (F, G) Mice still lengthen or shorten their step to avoid collision with the obstacle after motor cortex silencing. In F, each plot shows distributions of landing distances (columns within each subplot) conditioned on where the paw would have landed if no modifications were made (‘predicted landing distance’). Predicted landing distance is computed based on running speed and the lift-off position of the paw. In G, each trace shows kinematics for the paw in swing at whisker contact for a trial selected randomly across all mice for either saline (top row) or muscimol sessions (bottom row). The thick dashed gray traces show the average control step. Distributions of landing positions are shown beneath the kinematics.
Videos
Demonstration of the head-fixed obstacle avoidance apparatus, 3D behavioral tracking, and kinematic analysis.
Real-time and slowed-down videos of obstacle avoidance.
Comparison of obstacle avoidance when mice have access to whiskers and vision, whiskers only, vision only, and neither whiskers nor vision.
Demonstration of the two behavioral strategies mice use to clear obstacles.
Videos are paused at whisker contact. The dashed gray traces show the kinematic trajectory expected if no modifications are made.